Polymorphism of BoLA-DRB3 in Semen and Its Influence on Progeny Derived from Semen with Resistance and Susceptibility to Bovine Leukemia Virus Proviral Load
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and Plasma Isolation
2.2. Ethics Approval
2.3. Detection of Anti-BLV gp51 Antibodies
2.4. Determination of the BLV PVL Using BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR-2
2.5. BoLA-DRB3 Genotyping
2.6. Classification of BoLA-DRB3 Alleles and Genotype Grouping
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of BoLA-DRB3 Alleles in Widely Used Commercial Frozen Semen
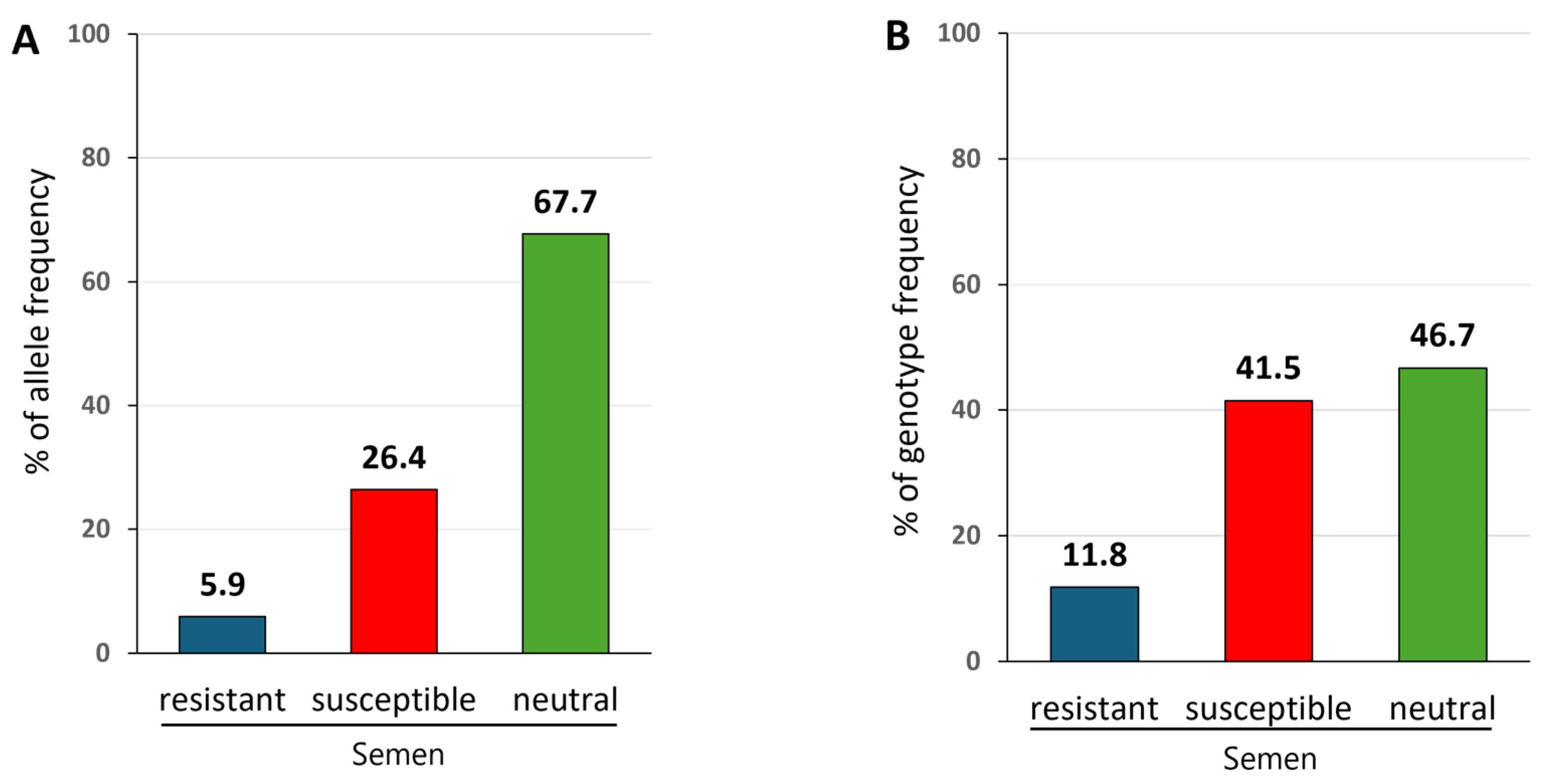
3.2. Distribution of Susceptible, Resistant, and Neutral BoLA-DRB3 Alleles in Widely Used Commercial Frozen Semen
3.3. Distribution of Susceptible, Resistant, and Neutral BoLA-DRB3 Genotypes in Widely Used Commercial Frozen Semen
3.4. Selection of Semen and Progeny for BLV Susceptibility Evaluation
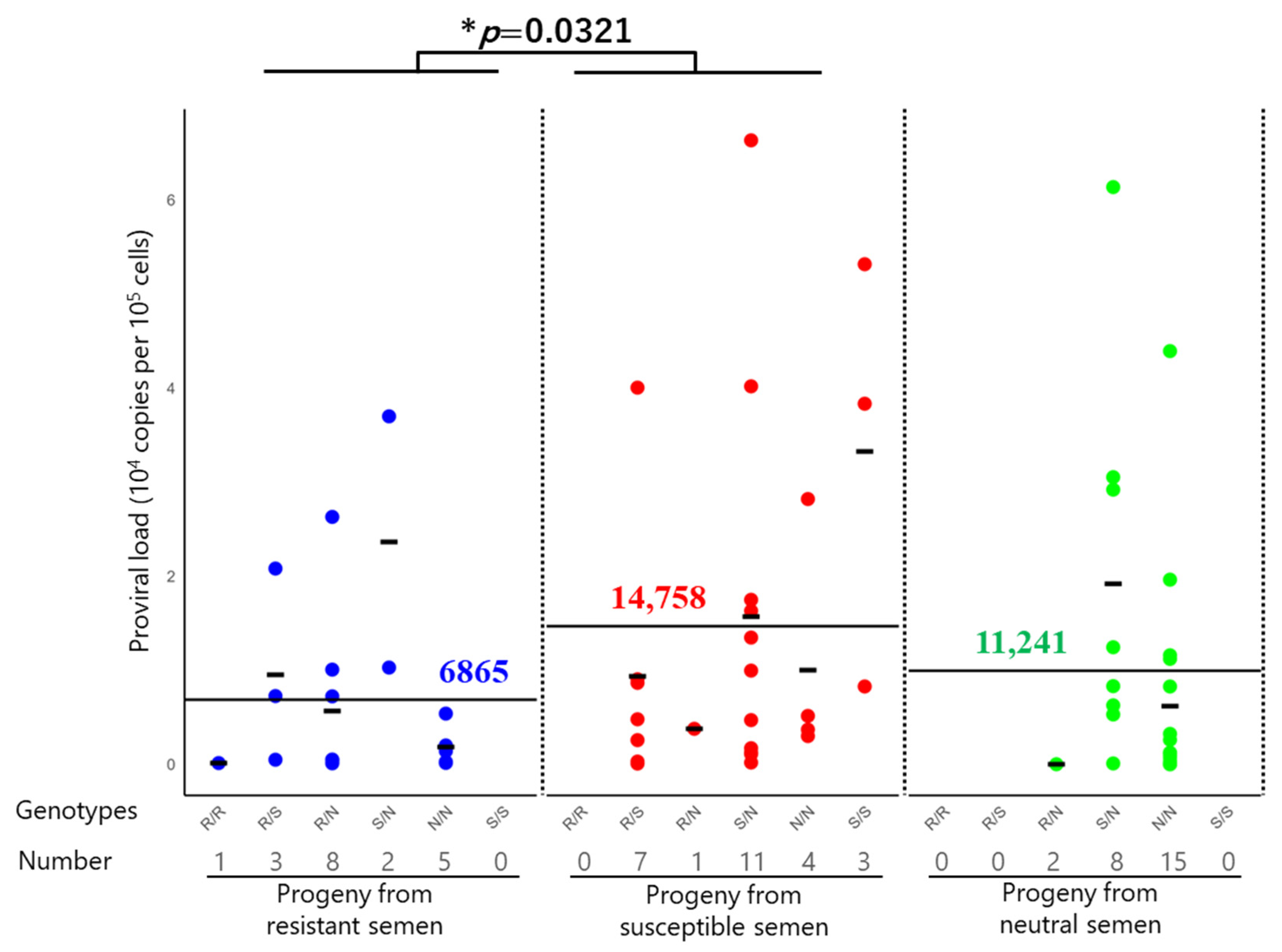
3.5. BLV Infection and PVL in Progeny Derived from Different Sire Genotypes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aida, Y.; Murakami, H.; Takahashi, M.; Takeshima, S.N. Mechanisms of pathogenesis induced by bovine leukemia virus as a model for human T-cell leukemia virus. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech-Nielsen, S.; Piper, C.E.; Ferrer, J.F. Natural mode of transmission of the bovine leukemia virus: Role of bloodsucking insects. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1978, 39, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panei, C.J.; Larsen, A.E.; Fuentealba, N.A.; Metz, G.E.; Echeverría, M.G.; Galosi, C.M.; Valera, A.R. Study of horn flies as vectors of bovine leukemia virus. Open Vet. J. 2019, 9, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGiacomo, R.F.; Hopkins, S.G.; Darlington, R.L.; Evermann, J.F. Control of bovine leukosis virus in a dairy herd by a change in dehorning. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1987, 51, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kohara, J.; Konnai, S.; Onuma, M. Experimental transmission of Bovine leukemia virus in cattle via rectal palpation. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 54, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, J.F.; Piper, C.E. Role of colostrum and milk in the natural transmission of the bovine leukemia virus. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 4906–4909. [Google Scholar]
- Meas, S.; Usui, T.; Ohashi, K.; Sugimoto, C.; Onuma, M. Vertical transmission of bovine leukemia virus and bovine immunodeficiency virus in dairy cattle herds. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 84, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanuki, S.; Takeshima, S.N.; Borjigin, L.; Sato, H.; Bai, L.; Murakami, H.; Sato, R.; Ishizaki, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Aida, Y. Visualizing bovine leukemia virus (BLV)-infected cells and measuring BLV proviral loads in the milk of BLV seropositive dams. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjigin, L.; Lo, C.-W.; Bai, L.; Hamada, R.; Sato, H.; Yoneyama, S.; Yasui, A.; Yasuda, S.; Yamanaka, R.; Mimura, M.; et al. Risk Assessment of Bovine Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II DRB3 Alleles for Perinatal Transmission of Bovine Leukemia Virus. Pathogens 2021, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, O.C.; Weiland, F.; Frenzel, B. Results of hematological and serological research on natural and artificial transmission of bovine and leukosis. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1974, 81, 581–583. [Google Scholar]
- Kuckleburg, C.J.; Chase, C.C.; Nelson, E.A.; Marras, S.A.; Dammen, M.A.; Christopher-Hennings, J. Detection of bovine leukemia virus in blood and milk by nested and real-time polymerase chain reactions. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2003, 15, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworski, J.P.; Porta, N.G.; Gutierrez, G.; Politzki, R.P.; Alvarez, I.; Galarza, R.; Abdala, A.; Calvinho, L.; Trono, K.G. Relationship between the level of bovine leukemia virus antibody and provirus in blood and milk of cows from a naturally infected herd. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5629–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, G.; Lomonaco, M.; Alvarez, I.; Fernandez, F.; Trono, K. Characterization of colostrum from dams of BLV endemic dairy herds. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadpour, R.; Jafari, R. Detection of bovine leukosis provirus in blood and semen samples of bulls. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 21, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dus Santos, M.J.; Trono, K.; Lager, I.; Wigdorovitz, A. Development of a PCR to diagnose BLV genome in frozen semen samples. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 119, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, O.J.; Roberts, J.N.; Norby, B.; Bartlett, P.C.; Takeshima, S.N.; Watanuki, S.; Aida, Y.; Grooms, D.L. Breeding bulls as a potential source of bovine leukemia virus transmission in beef herds. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2019, 254, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaja, R.W.; Olson, C. Non-infectivity of semen from bulls infected with bovine leukosis virus. Theriogenology 1982, 18, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Van der Maaten, M.J. Infectivity tests of secretions and excretions from cattle infected with bovine leukemia virus. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1979, 62, 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Monke, D.R. Noninfectivity of semen from bulls infected with bovine leukosis virus. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1986, 188, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, A.; Watanuki, S.; Matsuura, R.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Kawata, R.; Aida, Y. No evidence of bovine leukemia virus proviral DNA in a widely used commercially frozen semen in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 87, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acaite, J.; Tamosiunas, V.; Lukauskas, K.; Milius, J.; Pieskus, J. The eradication experience of enzootic bovine leukosis from Lithuania. Prev. Vet. Med. 2007, 82, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuotio, L.; Rusanen, H.; Sihvonen, L.; Neuvonen, E. Eradication of enzootic bovine leukosis from Finland. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 59, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettmann, R.; Burny, A.; Callebaut, I.; Droogmans, L.; Mammerickx, M.; Willems, L. Bovine leukemia virus. Retroviridae 1994, 3, 39–81. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, A.; Jaworski, J.P.; Droscha, C.; VanderWeele, S.; Taxis, T.M.; Valas, S.; Brnić, D.; Jungić, A.; Ruano, M.J.; Sánchez, A.; et al. Inter-laboratory comparison of eleven quantitative or digital PCR assays for detection of proviral bovine leukemia virus in blood samples. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczewski, A.; Orsel, K.; Barkema, H.W.; Kelton, D.F.; Hutchins, W.A.; van der Meer, F.J.U. Short communication: Evaluation of 5 different ELISA for the detection of bovine leukemia virus antibodies. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2433–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Wang, J.; Lian, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, R. The global epidemiology of bovine leukemia virus: Current trends and future implications. Animals 2024, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, S.N.; Kitamura-Muramatsu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Polat, M.; Saito, S.; Aida, Y. BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR-2: Improvements to the BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR assay for bovine leukemia virus by reducing primer degeneracy and constructing an optimal standard curve. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, J.P.; Pluta, A.; Rola-Łuszczak, M.; McGowan, S.L.; Finnegan, C.; Heenemann, K.; Carignano, H.A.; Alvarez, I.; Murakami, K.; Willems, L.; et al. Interlaboratory Comparison of Six Real-Time PCR Assays for Detection of Bovine Leukemia Virus Proviral DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00304-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, V.J.; Bartlett, P.C. Control of Bovine Leukemia Virus in Three US Dairy Herds by Culling ELISA-Positive Cows. Vet. Med. Int. 2019, 2019, 3202184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaDronka, R.M.; Ainsworth, S.; Wilkins, M.J.; Norby, B.; Byrem, T.M.; Bartlett, P.C. Prevalence of bovine leukemia virus antibodies in US dairy cattle. Vet. Med. Int. 2018, 2018, 5831278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, R.; Rochus, C.M.; Houlahan, K.; Lynch, C.; Oliveira, G.A., Jr.; Rojas de Oliveira, H.; van Staaveren, N.; Kelton, D.F.; Miglior, F.; Schenkel, F.S.; et al. Estimation of genetic parameters and genome-wide association study for enzootic bovine leukosis resistance in Canadian Holstein cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinecke, N.; Tórtora, J.; Martínez, H.A.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, V.D.; Ramírez, H. Detection and genotyping of bovine leukemia virus in Mexican cattle. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Gong, Q.; Sheng, C.; Liu, Y.; Ge, G.; Li, D.; Diao, N.; Shi, K.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; et al. Prevalence of bovine leukemia in 1983–2019 in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.O.; Meas, S.; Park, N.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Lim, Y.K.; Endoh, D.; Lee, S.I.; Pjasjo, K.; Sugimoto, C.; Onuma, M. Seroprevalence of bovine immunodeficiency virus in dairy and beef cattle herds in Korea. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1999, 61, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Murakami, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Konishi, M.; Kameyama, K.; Tsutsui, T. Nationwide survey of bovine leukemia virus infection among dairy and beef breeding cattle in Japan from 2009–2011. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Kim, E.J.; Ratthanophart, J.; Vitoonpong, R.; Kim, B.H.; Cho, I.S.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, K.K.; Shin, Y.K. Molecular epidemiological and serological studies of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) infection in Thailand cattle. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 41, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, M.; Ohno, A.; Takeshima, S.N.; Kim, J.; Kikuya, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Mingala, C.N.; Onuma, M.; Aida, Y. Detection and molecular characterization of bovine leukemia virus in Philippine cattle. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, K.K.; Polat, M.; Borjigin, L.; Matsuura, R.; Hein, S.T.; Moe, H.H.; Aida, Y. New evidence of bovine leukemia virus circulating in Myanmar cattle through epidemiological and molecular characterization. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochirkhuu, N.; Konnai, S.; Odbileg, R.; Nishimori, A.; Okagawa, T.; Murata, S.; Ohashi, K. Detection of bovine leukemia virus and identification of its genotype in Mongolian cattle. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, R.; Fereig, R.M.; Metwally, S. The Influence of Risk Factors on Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection and Proviral Load in Egyptian Cattle. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, N.; Florins, A.; Boxus, M.; Burteau, C.; Nigro, A.; Vandermeers, F.; Balon, H.; Bouzar, A.B.; Defoiche, J.; Burny, A. Mechanisms of leukemogenesis induced by bovine leukemia virus: Prospects for novel anti-retroviral therapies in human. Retrovirology 2007, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, S.; Johnson, R.; Wells, S.J. Association between bovine-leukosis virus seroprevalence and herd-level productivity on US dairy farms. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 61, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erskine, R.J.; Bartlett, P.C.; Byrem, T.M.; Render, C.L.; Febvay, C.; Houseman, J.T. Association between bovine leukemia virus, production, and population age in Michigan dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekouei, O.; VanLeeuwen, J.; Stryhn, H.; Kelton, D.; Keefe, G. Lifetime effects of infection with bovine leukemia virus on longevity and milk production of dairy cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.K.; Pelzer, K.D.; Johnson, Y.J. Economic implications of bovine leukemia virus infection in mid-Atlantic dairy herds. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.L.; Moore, D.A. Reasons for whole carcass condemnations of cattle in the United States and implications for producer education and veterinary intervention. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 235, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, P.C.; Sordillo, L.M.; Byrem, T.M.; Norby, B.; Grooms, D.L.; Swenson, C.L.; Zalucha, J.; Erskine, R.J. Options for the control of bovine leukemia virus in dairy cattle. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 244, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norby, B.; Bartlett, P.C.; Byrem, T.M.; Erskine, R.J. Effect of infection with bovine leukemia virus on milk production in Michigan dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez, O.J.; LaDronka, R.M.; Norby, B.; Grooms, D.L.; Bartlett, P.C. The effect of bovine leukemia virus on dairy cow longevity. JDS Commun. 2022, 3, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frie, M.C.; Coussens, P.M. Bovine leukemia virus: A major silent threat to proper immune responses in cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 163, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konnai, S.; Murata, S.; Ohashi, K. Immune exhaustion during chronic infections in cattle. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA. Bovine Leukosis Virus (BLV) on U.S. Dairy Operations. 2007. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/animal_health/nahms/dairy/downloads/dairy07/Dairy07_is_BLV.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Burny, A.; Bex, F.; Chantrenne, H.; Cleuter, Y.; Dekegel, D.; Ghysdael, J.; Kettmann, R.; Leclercq, M.; Leunen, J.; Mammerickx, M.; et al. Bovine leukemia virus involvement in enzootic bovine leukosis. Adv. Cancer Res. 1978, 28, 251–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marawan, M.A.; Alouffi, A.; El Tokhy, S.; Badawy, S.; Shirani, I.; Dawood, A.; Guo, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Alshammari, F.A.; Selim, A. Bovine leukaemia virus: Current epidemiological circumstance and future prospective. Viruses 2021, 13, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, V.J.; Norby, B.; Benitez, O.J.; Hutchinson, H.; Sporer, K.; Droscha, C.; Swenson, C.L.; Bartlett, P.C. Controlling bovine leukemia virus in dairy herds by identifying and removing cows with the highest proviral load and lymphocyte counts. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9165–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, P.C.; Norby, B.; Byrem, T.M.; Parmelee, A.; Ledergerber, J.T.; Erskine, R.J. Bovine leukemia virus and cow longevity in Michigan dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczewski, A.; Hogeveen, H.; Orsel, K.; Wolf, R.; Thompson, J.; Spackman, E.; van der Meer, F. Economic evaluation of 4 bovine leukemia virus control strategies for Alberta dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 2578–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kohara, J.; Adachi, Y.; Makita, K. Estimation of economic loss by carcass weight reduction of Japanese dairy cows due to infection with bovine leukemia virus. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 198, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neefjes, J.; Jongsma, M.L.; Paul, P.; Bakke, O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, S.; Aida, Y. Structure, function and disease susceptibility of the bovine major histocompatibility complex. Anim. Sci. J. 2006, 77, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loat, S.; Kumari, N.; Saini, S.; Dige, M.S.; Kumar, A.; Dhilor, N.; Dang, A.K.; Lathwal, S.S.; Sodhi, M.; Kataria, R.S. Allelic diversity at BoLA DRB3 locus and association with predisposition to clinical mastitis in indicus and crossbred cattle. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 34, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Furuta, H.; Kondo, Y.; Mukoyama, H. Association of BoLA-DRB3 alleles with mastitis resistance and susceptibility in Japanese Holstein cows. Anim. Sci. J. 2012, 83, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangjinda, M.; Jindatajak, Y.; Tipvong, W.; Sriwarothai, J.; Pattarajinda, V.; Katawatin, S.; Boonkum, W. Association of BoLA-DRB3 alleles with tick-borne disease tolerance in dairy cattle in a tropical environment. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, O.E.; Khodary, M.G.; El-Deeb, A.H.; Hussein, H.A. Five BoLA-DRB3 genotypes detected in Egyptian buffalo infected with Foot and Mouth disease virus serotype O. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.P.A.; López-Herrera, A.; Zuluaga, J.E. Association of BoLA DRB3 gene polymorphisms with BoHV-1 infection and zootechnical traits. Open Vet. J. 2020, 10, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.W.; Borjigin, L.; Saito, S.; Fukunaga, K.; Saitou, E.; Okazaki, K.; Mizutani, T.; Wada, S.; Takeshima, S.N.; Aida, Y. BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphism is Associated with Differential Susceptibility to Bovine Leukemia Virus-Induced Lymphoma and Proviral Load. Viruses 2020, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.W.; Takeshima, S.N.; Okada, K.; Saitou, E.; Fujita, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Wada, S.; Inoko, H.; Aida, Y. Association of Bovine Leukemia Virus-Induced Lymphoma with BoLA-DRB3 polymorphisms at DNA, amino acid, and binding pocket property levels. Pathogens 2021, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, T.; Takeshima, S.N.; Jimba, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Matsuhashi, T.; Sentsui, H.; Aida, Y. Identification of bovine leukocyte antigen class II haplotypes associated with variations in bovine leukemia virus proviral load in Japanese Black cattle. Tissue Antigens 2013, 81, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuchi, A.; Watanuki, S.; Borjigin, L.; Sato, H.; Bai, L.; Matsuura, R.; Kuroda, M.; Murakami, H.; Sato, R.; Asaji, S.; et al. BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphism Controls Proviral Load and Infectivity of Bovine Leukemia Virus (BLV) in Milk. Pathogens 2022, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, S.N.; Ohno, A.; Aida, Y. Bovine leukemia virus proviral load is more strongly associated with bovine major histocompatibility complex class II DRB3 polymorphism than with DQA1 polymorphism in Holstein cow in Japan. Retrovirology 2019, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezawa, M.; Fujii, Y.; Akagami, M.; Kawakami, J.; Inokuma, H. BoLA-DRB3*15:01 allele is associated with susceptibility to early enzootic bovine leukosis onset in Holstein-Friesian and Japanese Black cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 284, 109829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbakht Brujeni, G.; Ghorbanpour, R.; Esmailnejad, A. Association of BoLA-DRB3.2 Alleles with BLV Infection Profiles (Persistent Lymphocytosis/Lymphosarcoma) and Lymphocyte Subsets in Iranian Holstein Cattle. Biochem. Genet. 2016, 54, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somura, Y.; Sugiyama, E.; Fujikawa, H.; Murakami, K. Comparison of the copy numbers of bovine leukemia virus in the lymph nodes of cattle with enzootic bovine leukosis and cattle with latent infection. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2693–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliarena, M.A.; Barrios, C.N.; Ceriani, M.C.; Esteban, E.N. Hot topic: Bovine leukemia virus (BLV)-infected cows with low proviral load are not a source of infection for BLV-free cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4586–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Inagaki, Y.; Ohnuki, N.; Sato, R.; Murakami, S.; Imakawa, K. Increasing Bovine leukemia virus (BLV) proviral load is a risk factor for progression of Enzootic bovine leucosis: A prospective study in Japan. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 178, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, A.; Takeshima, S.N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Aida, Y. Risk factors associated with increased bovine leukemia virus proviral load in infected cattle in Japan from 2012 to 2014. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohara, J.; Bai, L.; Takeshima, S.N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Hirai, T.; Aida, Y. Correlation between the Biodistribution of Bovine Leukemia Virus in the Organs and the Proviral Load in the Peripheral Blood during Early Stages of Experimentally Infected Cattle. Pathogens 2023, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Kitamura-Muramatsu, Y.; Saito, S.; Ishizaki, H.; Nakano, M.; Haga, S.; Matoba, K.; Ohno, A.; Murakami, H.; Takeshima, S.N.; et al. Detection of the BLV provirus from nasal secretion and saliva samples using BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR-2: Comparison with blood samples from the same cattle. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekata, H.; Sekiguchi, S.; Konnai, S.; Kirino, Y.; Horii, Y.; Norimine, J. Horizontal transmission and phylogenetic analysis of bovine leukemia virus in two districts of Miyazaki, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliarena, M.A.; Poli, M.; Sala, L.; Ceriani, C.; Gutierrez, S.; Dolcini, G.; Rodriguez, E.M.; Marino, B.; Rodriguez-Dubra, C.; Esteban, E.N. Association of BLV infection profiles with alleles of the BoLA-DRB3.2 gene. Anim. Genet. 2008, 39, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daous, H.E.; Mitoma, S.; Elhanafy, E.; Thi Nguyen, H.; Thi Mai, N.; Notsu, K.; Kaneko, C.; Norimine, J.; Sekiguchi, S. Relationship between Allelic Heterozygosity in BoLA-DRB3 and Proviral Loads in Bovine Leukemia Virus-Infected Cattle. Animals 2021, 11, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borjigin, L.; Watanuki, S.; Hamada, R.; Bai, L.; Hirose, T.; Sato, H.; Yoneyama, S.; Yasui, A.; Yasuda, S.; Yamanaka, R.; et al. Effectiveness of integrated bovine leukemia virus eradication strategies utilizing cattle carrying resistant and susceptible histocompatibility complex class II DRB3 alleles. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 9393–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Borjigin, L.; Sato, H.; Takeshima, S.; Asaji, S.; Ishizaki, H.; Kawashima, K.; Obuchi, Y.; Sunaga, S.; Ando, A.; et al. Kinetic Study of BLV Infectivity in BLV Susceptible and Resistant Cattle in Japan from 2017 to 2019. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.W.; Aida, Y. Association of BoLA-DRB3 with bovine leukemia virus. Major Histocompat. Complex 2022, 29, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, T.; Hoque, M.A.; Hitomi, T.; Uchida, H.; Namikawa, K. Genetic parameters for traits in performance and progeny tests and their genetic relationships in Japanese black cattle. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 19, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.W.; Weitzner, G.; Rozen, R.; Scriver, C.R. A rapid procedure for extracting genomic DNA from leukocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimba, M.; Takeshima, S.N.; Murakami, H.; Kohara, J.; Kobayashi, N.; Matsuhashi, T.; Ohmori, T.; Nunoya, T.; Aida, Y. BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR: A useful tool for evaluating bovine leukemia virus infection status. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rola-Łuszczak, M.; Finnegan, C.; Olech, M.; Choudhury, B.; Kuźmak, J. Development of an improved real-time PCR for the detection of bovine leukaemia provirus nucleic acid and its use in the clarification of inconclusive serological test results. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 189, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanuki, S.; Bao, A.; Saitou, E.; Shoji, K.; Izawa, M.; Okami, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Aida, Y. BLV-CoCoMo dual qPCR assay targeting LTR region for quantifying bovine leukemia virus: Comparison with multiplex real-time qPCR assay targeting pol region. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Miyasaka, T.; Saito, H.; Onuma, M.; Aida, Y. A new method for typing bovine major histocompatibility complex class II DRB3 alleles by combining two established PCR sequence-based techniques. Tissue Antigens 2011, 78, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, H.A.; Schmitt, K.; Hubert, R.; van Eijk, M.J.T.; Arnheim, N. Close linkage between bovine prolactin and BoLA-DRB3 genes: Genetic mapping in cattle by single sperm typing. Genomics 1992, 13, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, T.; Takeshima, S.N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Matsuhashi, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Tanabe, Y.; Ishibashi, K.; Sentsui, H.; Aida, Y. The diversity of bovine MHC class II DRB3 and DQA1 alleles in different herds of Japanese Black and Holstein cattle in Japan. Gene 2011, 472, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, S.; Ando, T.; Sekiguchi, S.; Notsu, K.; Ishida, S.; Daidoji, T.; Hagiwara, K. Investigating BoLA Class II DRB3*009:02 carrying cattle in Japan. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2025, 27, 100425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Mekata, H.; Sekiguchi, S.; Kirino, Y.; Mitoma, S.; Honkawa, K.; Horii, Y.; Norimine, J. Cattle with the BoLA class II DRB3* 0902 allele have significantly lower bovine leukemia proviral loads. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1552–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunari, K.; Chiba, Y. Status of Bovine Leukemia Virus-Resistant Gene Carriers among Cattle in Iwate Prefecture. Iwate Vet. 2022, 48, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Victoria, M.; Farias, N.; Caffaro, M.E.; Lendez, P.A.; Passucci, J.; Poli, M.; Ceriani, M.C.; Dolcini, G. A novel association of BoLA DRB3 alleles in BLV infected cattle with different proviral loads. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2017, 54, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, R.; Hernandez, A.; Mallard, B.A. Association of bovine leukocyte antigen (BoLA) DRB3.2 with immune response, mastitis, and production and type traits in Canadian Holsteins. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashmi, M.; Qanbari, S.; Ghorashi, S.A.; Sharifi, A.R.; Simianer, H. Analysis of relationship between bovine lymphocyte antigen DRB3.2 alleles, somatic cell count and milk traits in Iranian Holstein population. J. Anim. Breed Genet. 2009, 126, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, S.; Mallard, B.A.; Wilkie, B.N.; Sargeant, J.M.; Scott, H.M.; Dekkers, J.C.; Leslie, K.E. Associations of the bovine major histocompatibility complex DRB3 (BoLA-DRB3) alleles with occurrence of disease and milk somatic cell score in Canadian dairy cattle. Anim. Genet. 1998, 29, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.X.; Yang, Z.P.; Wang, X.L.; Mao, Y.J.; Li, S.C.; Shi, X.K.; Chen, Y. Restriction fragment length polymorphism in the exon 2 of the BoLA-DRB3 gene in Chinese Holstein of the south China. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zanotti, M.; Strillacci, M.G.; Taboni, I.; Samorè, A.B.; Longeri, M. Histocompatibility genes and somatic cell count (SCC) in Italia Holstein Friesian. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 2, 85–87. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Vernau, W.; Jacobs, R.M.; Valli, V.E.; Heeney, J.L. The immunophenotypic characterization of bovine lymphomas. Vet. Pathol. 1997, 34, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, W.; Hirose, T.; Wada, S.; Matsuura, R.; Takeshima, S.N.; Aida, Y. PRMT5 Is Required for Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection in Vivo and Regulates BLV Gene Expression, Syncytium Formation, and Glycosylation in Vitro. Viruses 2020, 12, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Hirose, T.; Assi, W.; Wada, S.; Takeshima, S.-N.; Aida, Y. Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection Affects Host Gene Expression Associated with DNA Mismatch Repair. Pathogens 2020, 9, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Kuroiwa, T.; Suzuki, K.; Miura, Y.; Sentsui, H. Analysis of Syk expression in bovine lymphoma and persistent lymphocytosis induced by bovine leukemia virus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konnai, S.; Usui, T.; Ikeda, M.; Kohara, J.; Hirata, T.; Okada, K.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha genetic polymorphism may contribute to progression of bovine leukemia virus-infection. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnuki, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Matsuo, M.; Nishikaku, K.; Kusama, K.; Torii, Y.; Inagaki, Y.; Hori, M.; Imakawa, K.; Satou, Y. A target enrichment high throughput sequencing system for characterization of BLV whole genome sequence, integration sites, clonality and host SNP. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Todaka, H.; Uchiyama, J.; Sato, R.; Sogawa, K.; Sakaguchi, M.; Tsukamoto, K. A point mutation to the long terminal repeat of bovine leukemia virus related to viral productivity and transmissibility. Virology. 2019, 537, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, H.; Uchiyama, J.; Nikaido, S.; Sato, R.; Sakaguchi, M.; Tsukamoto, K. Inefficient viral replication of bovine leukemia virus induced by spontaneous deletion mutation in the G4 gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2753–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Hidano, A.; Tsutsui, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Hayama, Y.; Nishida, T.; Muroga, N.; Konishi, M.; Kameyama, K.; Murakami, K. Analysis of risk factors associated with bovine leukemia virus seropositivity within dairy and beef breeding farms in Japan: A nationwide survey. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 96, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| BoLA-DRB3 Allele | Allele Frequency | Susceptibility of Alleles b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n a | % | ||
| *001:01 | 7 | (2.0) | N |
| *002:01 | 29 | (8.1) | N |
| *005:02 | 22 | (6.2) | N |
| *005:03 | 25 | (7.0) | N |
| *005:08 | 2 | (0.6) | N |
| *006:01 | 1 | (0.3) | N |
| *007:01 | 19 | (5.3) | N |
| *008:01 | 6 | (1.7) | N |
| *009:02 | 2 | (0.6) | R |
| *010:01 | 37 | (10.4) | N |
| *011:01 | 19 | (5.3) | R |
| *012:01 | 18 | (5.1) | N |
| *013:02 | 13 | (3.7) | N |
| *014:01:01 | 8 | (2.2) | N |
| *015:01 | 47 | (13.2) | N |
| *016:01 | 94 | (26.4) | S |
| *020:01:02 | 1 | (0.3) | N |
| *027:03 | 4 | (1.1) | N |
| *034:01 | 1 | (0.3) | N |
| *040:02 | 1 | (0.3) | N |
| Semen | Progeny from Selected Semen | Semen | Progeny from Selected Semen | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BoLA-DRB3 Genotype | Frequency | Selected Semen | n | BoLA-DRB3 Genotype | Frequency | Selected Semen | n | ||
| n a | % | n | % | ||||||
| Resistant | *010:01/*013:02 | 3 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| *011:01/*015:01 | 4 | 2.2 | 0 | 0 | *002:01/*002:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| *011:01/*002:01 | 3 | 1.7 | 1 | 12 | *002:01/*005:02 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| *011:01/*016:01 | 3 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | *002:01/*010:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| *011:01/*013:02 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | *002:01/*012:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| *009:02/*012:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *005:03/*005:03 | 2 | 1.1 | 1 | 14 |
| *009:02/*016:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *005:03/*010:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| *011:01/*001:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 16 | *007:01/*007:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| *011:01/*005:02 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 13 | *007:01/*015:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 2 | 12 |
| *011:01/*006:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *008:01/*008:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| *011:01/*007:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *010:01/*010:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| *011:01/*010:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *012:01/*012:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 1 | 1 |
| *011:01/*012:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *012:01/*015:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 1 | 1 |
| *011:01/*014:01:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *013:02/*015:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 21 | 11.8 | 3 | 41 | *015:01/*027:03 | 2 | 1.1 | 1 | 2 |
| Susceptible | *001:01/*005:02 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| *016:01/*016:01 | 16 | 9.0 | 7 | 51 | *001:01/*007:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*010:01 | 12 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | *001:01/*010:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*015:01 | 11 | 6.2 | 1 | 1 | *001:01/*012:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*005:03 | 7 | 3.9 | 2 | 30 | *001:01/*015:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*007:01 | 7 | 3.9 | 2 | 4 | *002:01/*005:03 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 4 |
| *016:01/*002:01 | 4 | 2.2 | 0 | 0 | *002:01/*013:02 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*005:02 | 4 | 2.2 | 2 | 5 | *002:01/*014:01:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*013:02 | 3 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | *005:02/*005:02 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*014:01:01 | 3 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | *005:02/*007:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 7 |
| *016:01/*008:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 1 | 2 | *005:02/*014:01:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*012:01 | 2 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | *005:02/*015:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*001:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *005:03/*005:08 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 3 |
| *016:01/*020:01:02 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *005:03/*007:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *016:01/*034:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | *005:03/*012:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 74 | 41.6 | 15 | 93 | *005:08/*007:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 2 |
| Neutral | *007:01/*027:03 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| *002:01/*015:01 | 8 | 4.5 | 0 | 0 | *010:01/*014:01:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 1 |
| *010:01/*015:01 | 6 | 3.4 | 1 | 1 | *010:01/*040:02 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *005:03/*015:01 | 5 | 2.8 | 2 | 13 | *012:01/*013:02 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *005:02/*005:03 | 4 | 2.2 | 2 | 3 | *012:01/*027:03 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *005:02/*010:01 | 4 | 2.2 | 1 | 1 | *014:01:01/*015:01 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| *005:02/*012:01 | 3 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | Total | 83 | 46.6 | 18 | 66 |
| Susceptibility of Semen | BoLA-DRB3 Genotype | Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n d | (%) | ||
| Resistant a | *009:02/*009:02 | 0 | (0.0) |
| *009:02/*016:01 | 1 | (0.6) | |
| *009:02/neutral | 1 | (0.6) | |
| *011:01/*011:01 | 0 | (0.0) | |
| *011:01/*016:01 | 3 | (1.7) | |
| *011:01/neutral | 16 | (8.9) | |
| *009:02/*011:01 | 0 | (0.0) | |
| Total | 21 | (11.8) | |
| Susceptible b | *016:01/*016:01 | 16 | (8.9) |
| *016:01/neutral | 58 | (32.6) | |
| Total | 74 | (41.5) | |
| Neutral c | neutral/neutral | 83 | (46.7) |
| Total | 83 | (46.7) | |
| Total | 178 | (100.0) | |
| Susceptibility of Selected Semen (Heads) | Progeny | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | BLV-Infected Rate | Average PVL e | PVL Range | |||
| BLV-Positive n d | Tested n (%) | |||||
| Resistant (3) | R/R a | 1/2 | (50.0) | 124 | 124–124 | |
| R/S b | 3/5 | (60.0) | 9515 | 480–20,813 | ||
| R/N c | 8/16 | (50.0) | 5663 | 97–26,305 | ||
| S/N | 2/6 | (33.3) | 23,643 | 10,284–37,002 | ||
| N/N | 5/12 | (41.7) | 1835 | 140–5384 | ||
| Total | 19/41 | (46.3) | 6865 | |||
| Susceptible (15) | S/S | 3/13 | (23.1) | 33,725 | 8272–53,180 | |
| S/N | 11/55 | (20.0) | 15,745 | 1274–66,356 | ||
| R/S | 7/9 | (77.8) | 9362 | 72–40,052 | ||
| R/N | 1/1 | (100.0) | 3770 | 3770–3770 | ||
| N/N | 4/15 | (26.7) | 10,007 | 3000–28,205 | ||
| Total | 26/93 | (28.0) | 14,758 | |||
| Neutral (18) | S/N | 8/22 | (36.4) | 19,188 | 83–61,382 | |
| R/N | 0/2 | (0.0) | ND f | ND | ||
| N/N | 15/42 | (35.7) | 6179 | 26–43,941 | ||
| Total | 23/66 | (34.8) | 11,241 | |||
| Total | 68/200 | (34.0) | 11,363 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, A.; Watanuki, S.; Matsuura, R.; Matsumoto, Y.; Wang, J.; Shimizu, H.; Niwano, A.; Kawata, R.; Aida, Y. Polymorphism of BoLA-DRB3 in Semen and Its Influence on Progeny Derived from Semen with Resistance and Susceptibility to Bovine Leukemia Virus Proviral Load. Pathogens 2025, 14, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090837
Bao A, Watanuki S, Matsuura R, Matsumoto Y, Wang J, Shimizu H, Niwano A, Kawata R, Aida Y. Polymorphism of BoLA-DRB3 in Semen and Its Influence on Progeny Derived from Semen with Resistance and Susceptibility to Bovine Leukemia Virus Proviral Load. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090837
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Aronggaowa, Sonoko Watanuki, Ryosuke Matsuura, Yasunobu Matsumoto, Jinliang Wang, Hiroyuki Shimizu, Ayuha Niwano, Ryusaku Kawata, and Yoko Aida. 2025. "Polymorphism of BoLA-DRB3 in Semen and Its Influence on Progeny Derived from Semen with Resistance and Susceptibility to Bovine Leukemia Virus Proviral Load" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090837
APA StyleBao, A., Watanuki, S., Matsuura, R., Matsumoto, Y., Wang, J., Shimizu, H., Niwano, A., Kawata, R., & Aida, Y. (2025). Polymorphism of BoLA-DRB3 in Semen and Its Influence on Progeny Derived from Semen with Resistance and Susceptibility to Bovine Leukemia Virus Proviral Load. Pathogens, 14(9), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090837







