Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Urine of Individuals Vaccinated with Janssen AD26.COV2.S COVID-19 Vaccine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.2.1. Vaccinated Individuals
2.2.2. Unvaccinated Individuals
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. ELISA
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
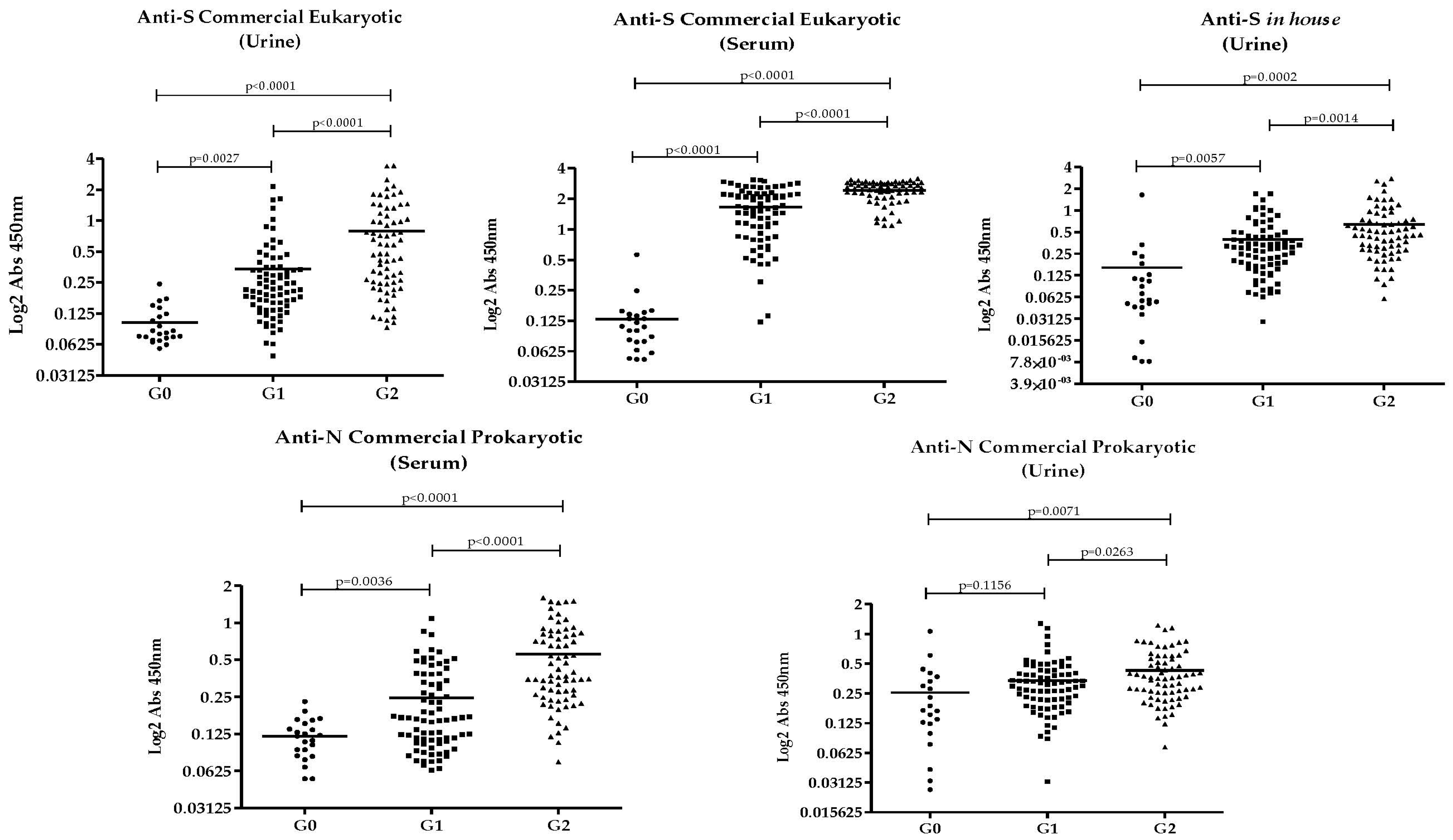
3.2. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Results in Urine and Serum
3.3. Influence of Age, Sex, and Urine Retention Time on Antibody Levels
3.4. Correlation Between Antibody Responses to Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Proteins
3.5. Accuracy of Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Proteins
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Itoh, M.; Weerasooriya, M.V.; Qiu, G.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Anantaphruti, M.T.; Tesana, S.; Rattanaxay, P.; Fujimaki, Y.; Kimura, E. Sensitive and specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of Wuchereria bancrofti infection in urine samples. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 65, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.S.; Chitambar, S.D.; Arankalle, V.A.; Chadha, M.S. Evaluation of Urine as a Clinical Specimen for Diagnosis of Hepatitis A. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2002, 9, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, M.; Ohta, N.; Kanazawa, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Sho, M.; Minai, M.; Daren, Z.; Chen, Y.; He, H.; He, Y.-K.; et al. Sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with urine samples: A tool for surveillance of schistosomiasis japonica. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2003, 34, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, S.; Cabezas, S.; Pérez, A.B.; Pupo, M.; Ruiz, D.; Calzada, N.; Bernardo, L.; Castro, O.; González, D.; Serrano, T.; et al. Kinetics of antibodies in sera, saliva, and urine samples from adult patients with primary or secondary dengue 3 virus infections. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamudomkarn, C.; Sithithaworn, P.; Kamamia, C.; Yakovleva, A.; Sithithaworn, J.; Kaewkes, S.; Techasen, A.; Loilome, W.; Yongvanit, P.; Wangboon, C.; et al. Diagnostic performance of urinary IgG antibody detection: A novel approach for population screening of strongyloidiasis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y. Accuracy of testing for anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG in urine for H. pylori infection diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e013248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejazi, S.A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Bakhteyar, A.K.; Mumtaz, A.A.; Pandey, K.; Das, V.N.R.; Das, P.; Rahaman, M.; Goswami, R.P.; Ali, N.; et al. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis: Development and Evaluation of Two Urine-Based Immunoassays for Detection of Leishmania donovani Infection in India. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, S.; Hosseini Teshnizi, S.; Fakhar, M.; Banimostafavi, E.S.; Soosaraei, M. Is urine a reliable clinical sample for the diagnosis of human visceral leishmaniasis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, F.; Yamazaki, T.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Itoh, M. Detection of Urinary Antibodies and Its Application in Epidemiological Studies for Parasitic Diseases. Vaccines 2021, 9, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuragi, K.; Noda, A.; Tachikawa, T.; Azuma, A.; Mukai, F.; Murakami, K.; Fujioka, T.; Kato, M.; Asaka, M. Highly sensitive urine-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 1998, 3, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shao, C.; Li, M.; Sun, W.; Gao, Y. A comprehensive analysis and annotation of human normal urinary proteome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludolf, F.; Ramos, F.F.; Bagno, F.F.; Oliveira-Da-Silva, J.A.; Reis, T.A.R.; Christodoulides, M.; Vassallo, P.F.; Ravetti, C.G.; Nobre, V.; da Fonseca, F.G.; et al. Detecting anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in urine samples: A noninvasive and sensitive way to assay COVID-19 immune conversion. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.F.; Bagno, F.F.; Vassallo, P.F.; Oliveira-da-Silva, J.A.; Reis, T.A.R.; Bandeira, R.S.; Machado, A.S.; Lage, D.P.; Martins, V.T.; Fernandes, A.P.; et al. A urine-based ELISA with recombinant non-glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for detecting anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike antibodies. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.F.; Pereira, I.A.G.; Cardoso, M.M.; Bandeira, R.S.; Lage, D.P.; Scussel, R.; Anastacio, R.S.; Freire, V.G.; Melo, M.F.N.; Oliveira-Da-Silva, J.A.; et al. B-Cell Epitopes-Based Chimeric Protein from SARS-CoV-2 N and S Proteins Is Recognized by Specific Antibodies in Serum and Urine Samples from Patients. Viruses 2023, 15, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, H.D. Urine Test Detects SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. JAMA 2022, 327, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagno, F.F.; Sérgio, S.A.R.; Figueiredo, M.M.; Godoi, L.C.; Andrade, L.A.F.; Salazar, N.C.; Soares, C.P.; Aguiar, A.; Almeida, F.J.; Silva, E.D.; et al. Development and validation of an enzyme-linked immunoassay kit for diagnosis and surveillance of COVID-19. J. Clin. Virol. Plus 2022, 2, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K. Kinetics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection antibody responses. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 864278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sadoff, J.; Gray, G.; Vandebosch, A.; Cárdenas, V.; Shukarev, G.; Grinsztejn, B.; Goepfert, P.A.; Truyers, C.; Fennema, H.; Spiessens, B.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Single-Dose Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine against COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2187–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez Bernal, J.; Andrews, N.; Gower, C.; Gallagher, E.; Simmons, R.; Thelwall, S.; Stowe, J.; Tessier, E.; Groves, N.; Dabrera, G.; et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, Y.; McDermott, A.B.; Benkeser, D.; Roels, S.; Stieh, D.J.; Vandebosch, A.; Le Gars, M.; Van Roey, G.A.; Houchens, C.R.; Martins, K.; et al. Immune correlates analysis of the ENSEMBLE single Ad26.COV2.S dose vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1996–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Wong, M.C.; Chong, K.C.; He, D.; Li, J. Ratio of asymptomatic COVID-19 cases among ascertained SARS-CoV-2 infections in different regions and population groups in 2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis including 130 123 infections from 241 studies. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e049752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mvula, M.; Mtonga, F.; Mandolo, J.; Jowati, C.; Kalirani, A.; Chigamba, P.; Lisimba, E.; Mitole, N.; Chibwana, M.G.; Jambo, K.C. Longevity of hybrid immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in adults vaccinated with an adenovirus-based COVID-19 vaccine. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tummala, M.K.; Taub, D.D.; Ershler, W.B. Clinical Immunology: Immune Senescence and the Acquired Immune Deficiency of Aging. In Brocklehurst’s Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Klein, S.; Flanagan, K. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sensibility | Specificity | AUC | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-N Commercial Prokaryotic | serum | G0 × G2 | 91.55 | 91.3 | 0.9547 | <0.0001 |
| serum | G0 × G1 | 61.54 | 60.87 | 0.7018 | 0.0034 | |
| serum | G2 × G1 | 73.24 | 69.23 | 0.7879 | <0.0001 | |
| urine | G0 × G2 | 77.46 | 61.9 | 0.7428 | 0.00076 | |
| urine | G0 × G1 | 67.95 | 61.9 | 0.6716 | 0.016 | |
| urine | G2 × G1 | 60.56 | 50 | 0.603 | 0.03 | |
| Anti-S Commercial Eukaryotic | serum | G0 × G2 | 98.59 | 100 | 0.9988 | <0.0001 |
| serum | G0 × G1 | 97.44 | 95.65 | 0.9875 | <0.0001 | |
| serum | G2 × G1 | 77.14 | 70.51 | 0.7866 | <0.0001 | |
| urine | G0 × G2 | 88.73 | 91.3 | 0.9602 | <0.0001 | |
| urine | G0 × G1 | 83.33 | 78.26 | 0.8824 | <0.0001 | |
| urine | G2 × G1 | 69.01 | 62.82 | 0.7294 | <0.0001 | |
| Anti-S in-house Prokaryotic | urine | G0 × G2 | 90 | 82.61 | 0.9155 | <0.0001 |
| urine | G0 × G1 | 83.33 | 78.26 | 0.8478 | <0.0001 | |
| urine | G2 × G1 | 65.71 | 60.26 | 0.6737 | 0.00027 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melo, M.F.N.; Lira, R.C.D.; Câmara, R.S.B.; Pereira, I.A.G.; Ramos, F.F.; Costa, C.S.F.; Amorim, L.F.; Teixeira, Q.D.; da Fonseca, F.G.; Nobre, V.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Urine of Individuals Vaccinated with Janssen AD26.COV2.S COVID-19 Vaccine. Pathogens 2025, 14, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080827
Melo MFN, Lira RCD, Câmara RSB, Pereira IAG, Ramos FF, Costa CSF, Amorim LF, Teixeira QD, da Fonseca FG, Nobre V, et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Urine of Individuals Vaccinated with Janssen AD26.COV2.S COVID-19 Vaccine. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080827
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelo, Marina F. N., Rômulo C. D. Lira, Raquel S. B. Câmara, Isabela A. G. Pereira, Fernanda F. Ramos, Carolina S. F. Costa, Laura F. Amorim, Quezia D. Teixeira, Flávio G. da Fonseca, Vandack Nobre, and et al. 2025. "Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Urine of Individuals Vaccinated with Janssen AD26.COV2.S COVID-19 Vaccine" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080827
APA StyleMelo, M. F. N., Lira, R. C. D., Câmara, R. S. B., Pereira, I. A. G., Ramos, F. F., Costa, C. S. F., Amorim, L. F., Teixeira, Q. D., da Fonseca, F. G., Nobre, V., Ferreira, F. G. F., Pinto, J., Coelho, E. A. F., Ludolf, F., & Caporali, J. F. M. (2025). Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Urine of Individuals Vaccinated with Janssen AD26.COV2.S COVID-19 Vaccine. Pathogens, 14(8), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080827







