Microbial Load and Diversity of Bacteria in Wild Animal Carcasses Sold as Bushmeat in Ghana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Approval and Permission
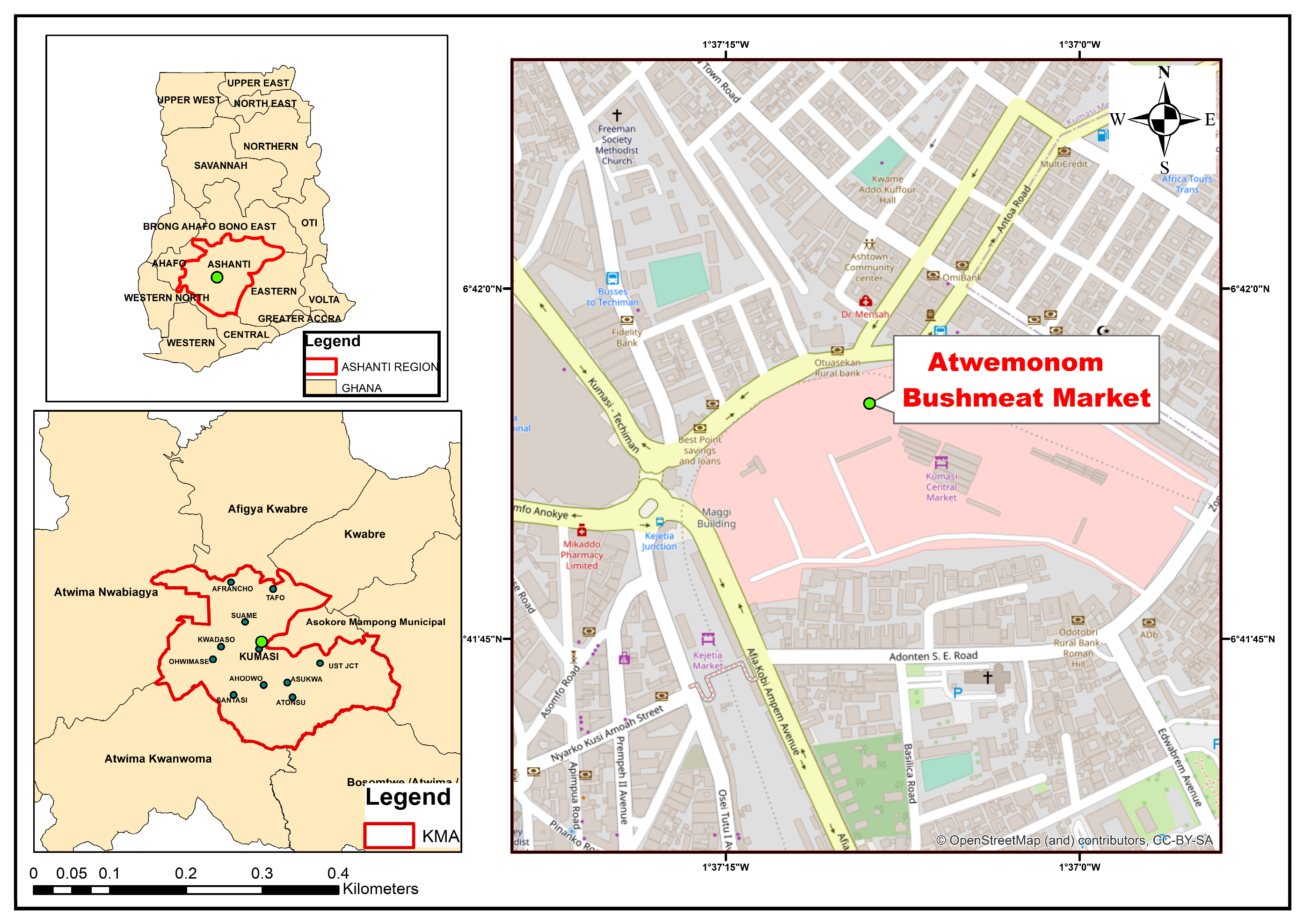
2.2. Study Area and Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Microbiological Analysis
2.4.1. Enumeration of Total Aerobic Bacteria, Enterobacteriaceae, and Fungi in Wild Animal Carcasses and Intestinal Content
2.4.2. Culture and Identification of Bacteria
2.4.3. Identification of Bacteria Species Using MALDITOF Mass Spectrometry
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Microbial Load of Meat and Intestines of Wild Animal Carcasses
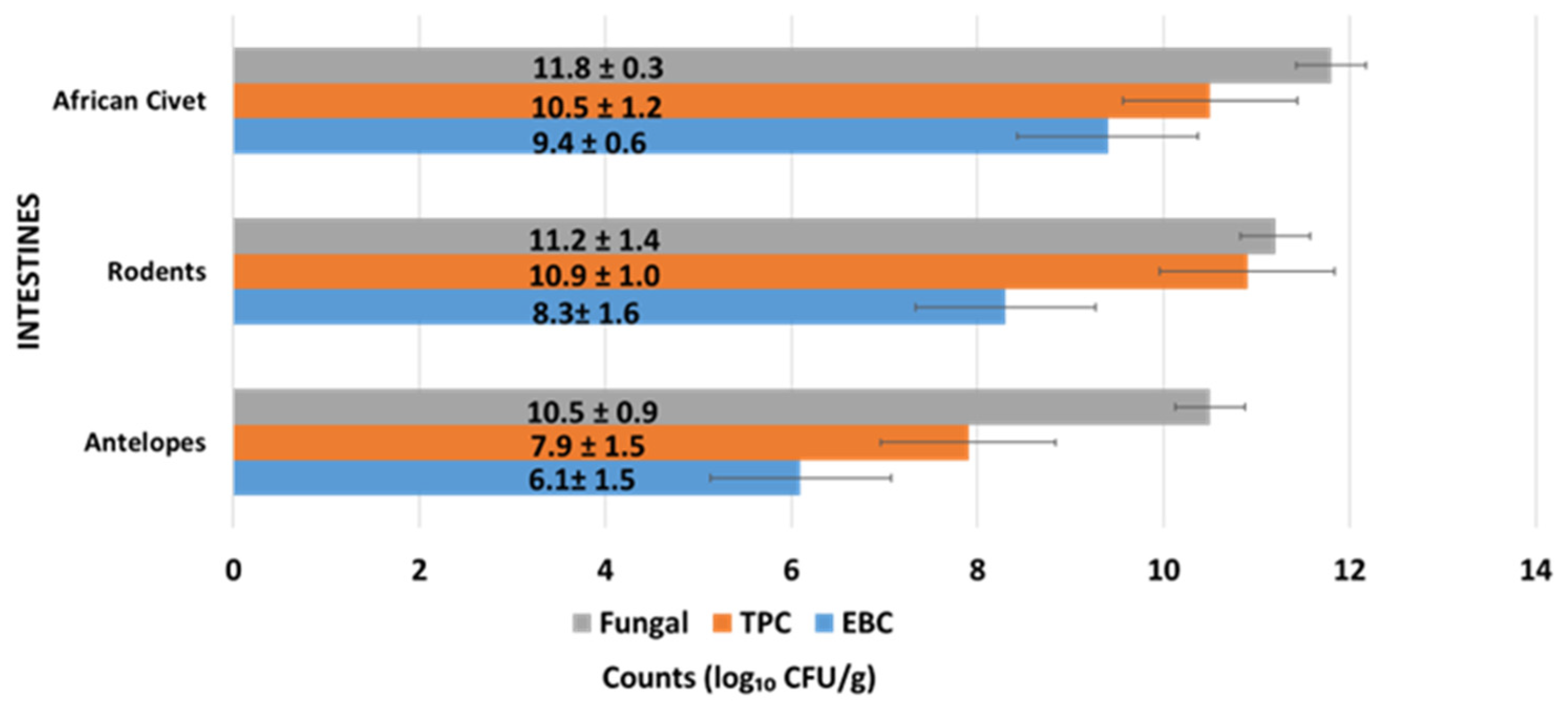
3.1.1. Microbial Load of Intestines of Wild Animal Carcasses (Bushmeat)
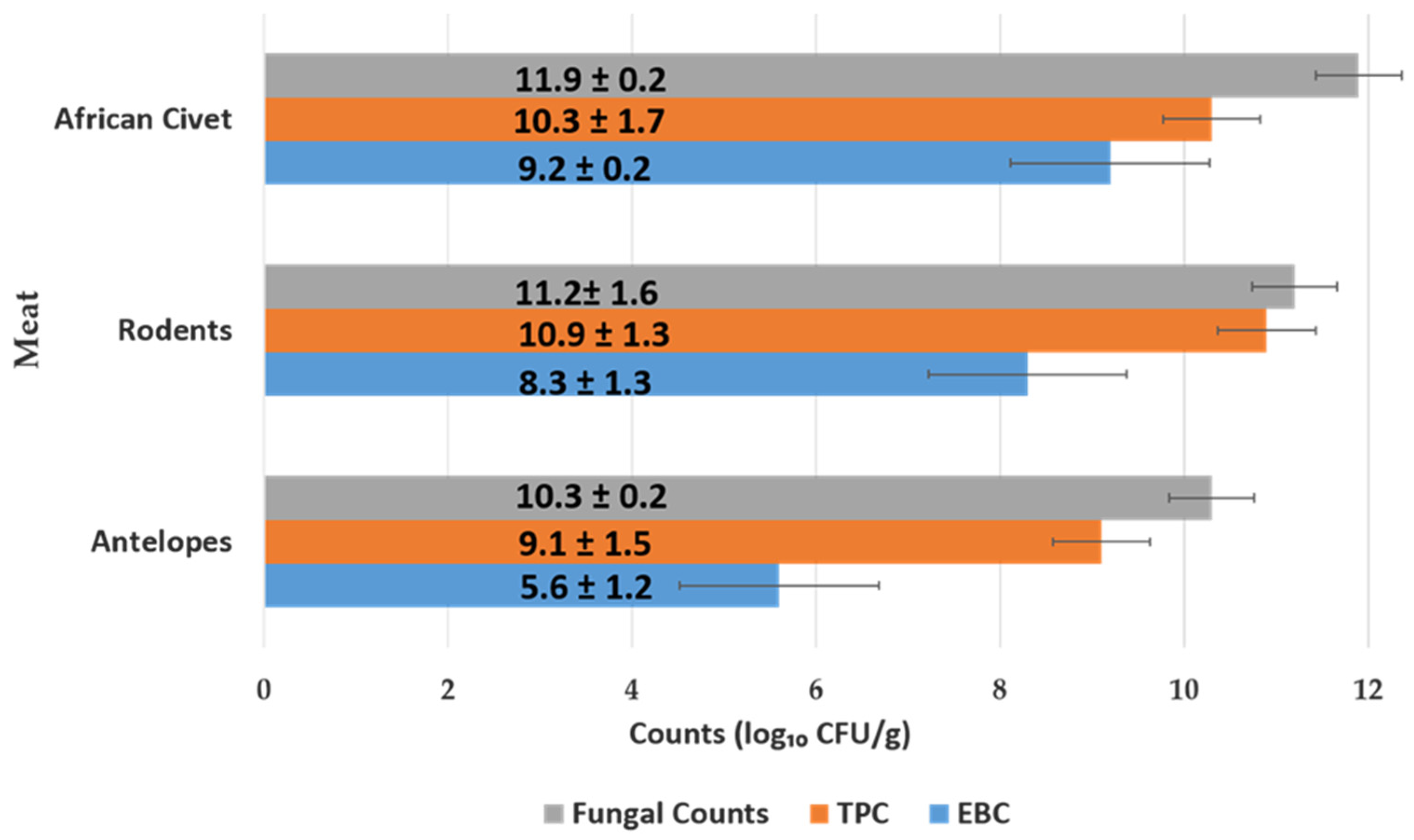
3.1.2. Microbial Load of Meat of Wild Animal Carcasses (Bushmeat)
3.2. Prevalence and Diversity of Bacteria Isolated from Wild Animal Carcasses
3.3. Bacteria Prevalence in Animal Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurpiers, L.A.; Schulte-Herbrüggen, B.; Ejotre, I.; Reeder, D.M. Bushmeat and Emerging Infectious Diseases: Lessons from Africa, in Problematic Wildlife; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 507–551. [Google Scholar]
- Wajah, A.; Emikpe, B.; Asare, D.; Asenso, T.; Essel-Cobbinah, D. Preference for grasscutter offal by some consumers in the Greater Accra and Ashanti regions of Ghana. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 20, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboagye, I.F.; Nkansa-Gyamfi, N.A.; Obimpeh, M.A.; Ansa-Tuah, A.K.; Owusu, E.H. Wildlife Species as Potential Sources of Human Exposure to Parasitic Pathogens in Accra, Ghana. West Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 27, 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Delahay, R.J.; de la Fuente, J.; Smith, G.C.; Sharun, K.; Snary, E.L.; Girón, L.F.; Nziza, J.; Fooks, A.R.; Brookes, S.M.; Lean, F.Z.X.; et al. Assessing the risks of SARS-CoV-2 in wildlife. One Health Outlook 2021, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarshie, J.T.; Cofie, J.K.; Dewornu, F.S.; Quaye, O.; Aikins, A.R. Risk of Heavy Metal Poisoning From Consuming Grasscutter Digesta in Ghana. Environ. Health Insights 2023, 17, 11786302231175339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emelue; Idaewor, J. Assessment Of Microbial Count Loads Of Bush Meats Sold At Different Markets In Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 3, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeh, M.; Anele, B.C.; Ogbodo, U.A. Assessment of Microbiological Quality Associated with Ready-to-Eat Bush Meat Sold at Rumuokoro Market in Rivers State. Asian J. Res. Zool. 2021, 4, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amponsah, A.S.; Ankar-Brewoo, G.M.; Lutterodt, H.E.; Ofosu, I.W. Assessing the microbial diversity and proximate composition of smoked-fermented bushmeat from four different bushmeat samples. BioTechnologia 2024, 105, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, Z.T.; Mhlongo, L.C.; Hugo, A. Microbial profiles of meat at different stages of the distribution chain from the abattoir to retail outlets. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2022–2025; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025; Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/nutrition-and-food-safety/monitoring-nutritional-status-and-food-safety-and-events/foodborne-disease-estimates/2nd-edition-%282025%29?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Bachand, N.; Ravel, A.; Onanga, R.; Arsenault, J.; Gonzalez, J.-P. Public health significance of zoonotic bacterial pathogens from bushmeat sold in urban markets of Gabon, Central Africa. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesilay, G.; Dos Santos, O.A.L.; Hazeem, L.J.; Backx, B.P.; Kamel, A.H.; Bououdina, M. Impact of pathogenic bacterial communities present in wastewater on aquatic organisms: Application of nanomaterials for the removal of these pathogens. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 261, 106620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintsis, T. Foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, J. The Dynamics of a Bushmeat Hunting System Under Social, Economic and Environmental Change; Imperial College London: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Adjei, V.Y.; Mensah, G.I.; Kunadu, A.P.-H.; Tano-Debrah, K.; Ayi, I.; Addo, K.K. Microbial Safety of Beef Along Beef Value Chains in the Ashaiman Municipality of Ghana. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 813422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonga, C.H.; Zacharia, I.; Mkupasi, E.; Ngowi, H. Assessment of Bacterial contamination and associated risk factors in pork slaughtered and marketed in urban Tanzania. Tanzan. J. Health Res. 2023, 24, 460–470. [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher, F.S.; Clark, D.S.; Silliker, J.H.; Elliott, R.P.; Baird-Parker, A.C. Microorganisms in Foods; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1968; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Alcalá, L.; Marín, M.; Ruiz, A.; Quiroga, L.; Zamora-Cintas, M.; Fernández-Chico, M.A.; Muñoz, P.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, B. Identifying anaerobic bacteria using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: A four-year experience. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 521014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarżyńska, M.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Wasyl, D.; Karunasagar, I. A metagenomic glimpse into the gut of wild and domestic animals: Quantification of antimicrobial resistance and more. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfoh, D.A.; Kwarteng, E.; Asante, J. Mycological contamination in dried bushmeat sold in Ghanaian markets. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 16, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Roque, K.; Lim, G.-D.; Jo, J.-H.; Shin, K.-M.; Song, E.-S.; Gautam, R.; Kim, C.-Y.; Lee, K.; Shin, S.; Yoo, H.-S.; et al. Epizootiological characteristics of viable bacteria and fungi in indoor air from porcine, chicken, or bovine husbandry confinement buildings. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 17, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahouanse, G.G.A.; Issa-Zacharia, A.; Majaliwa, N. Bushmeat Consumption in Africa: A Microbiological Safety Challenge? Asian Food Sci. J. 2023, 22, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anachinaba, I.A.; Adzitey, F.; Teye, G.A. Assessment of the microbial quality of locally produced meat (beef and pork) in Bolgatanga Municipal of Ghana. Internet J. Food Saf. 2015, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Katani, R.; Schilling, M.A.; Lyimo, B.; Tonui, T.; Cattadori, I.M.; Eblate, E.; Martin, A.; Estes, A.B.; Buza, T.; Rentsch, D.; et al. Microbial diversity in bushmeat samples recovered from the Serengeti ecosystem in Tanzania. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonardi, S.; Tansini, C.; Cacchioli, A.; Soliani, L.; Poli, L.; Lamperti, L.; Corradi, M.; Gilioli, S. Enterobacteriaceae and Salmonella contamination of wild boar (Sus scrofa) carcasses: Comparison between different sampling strategies. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2021, 67, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, S.M.; Castellsagués, L.; Ballén, V.; Gabasa, Y.; Mayor, P.; Brull, G.R.; Funk, S.M.; Fa, J.E. Prevalence of bacterial contamination on wild meat processing and cooking surfaces in rural Cameroon. One Health 2025, 20, 101028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fey, P.D.; Wickert, R.S.; Rupp, M.E.; Safranek, T.J.; Hinrichs, S.H. The prevalence of non-O157: H7 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) in Namibian game meat. Vet. Ital. 2018, 54, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Dela, H.; Egyir, B.; Behene, E.; Sulemana, H.; Tagoe, R.; Bentil, R.; Bongo, R.N.; Bonfoh, B.; Zinsstag, J.; Bimi, L.; et al. Microbiological quality and antimicrobial resistance of Bacteria species recovered from ready-to-eat food, water samples, and palm swabs of food vendors in Accra, Ghana. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 396, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalage, D.; Sontakke, T.; Biradar, A.; Jogdand, V.; Kale, R.; Harke, S.; Kale, R.; Dixit, P. The impact of environmental toxins on the animal gut microbiome and their potential to contribute to disease. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderaro, A.; Chezzi, C. MALDI-TOF MS: A reliable tool in the real life of the clinical microbiology laboratory. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altakhis, M.; Pillidge, C.J.; Osborn, A.M.; Torley, P.J.; Kaur, M. Assessment of the potential use of MALDI-TOF MS for the identification of bacteria associated with chilled vacuum-packaged lamb meat. Meat Sci. 2021, 177, 108508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Animal Group | N | Animal Sub-Group | N | Anal Swabs | Oral Swabs | Intestines | Meat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rodents | 44 | Grasscutters (Thryonomys swinderianus) | 44 | 43 | 44 | 42 | 42 |
| Antelopes | 14 | Bushbuck (Tragelaphus scriptus) | 7 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 |
| Maxwell’s Duiker (Philantomba maxwellii) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Red flank Duiker (Cephalophus rufilatus) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | ||
| African Civets | 3 | African Civet (Civettictis civetta) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Total Number | 61 | 61 | 59 | 61 | 57 | 55 |
| Bacteria Species | Rodents (n = 44) | Antelopes (n = 14) | African Civet (n = 3) | Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anal | Oral | Intestinal | Meat | Anal | Oral | Intestinal | Meat | Anal | Oral | Intestinal | Meat | ||
| Escherichia coli | 13 | 6 | 18 | 27 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 95 (18.1%) |
| Klebsiella sp. | 22 | 10 | 22 | 20 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 81 (15.5%) |
| Hafnia alevi | 9 | 20 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 52 (9.9%) |
| Serratia sp. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 19 | 13 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 41 (7.8%) |
| Aeromonas sp. | 15 | 14 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 37 (7.1%) |
| Yersinia ruckeri | 21 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32 (6.1%) |
| Pseudomonas sp. | 9 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 32 (6.1%) |
| Enterococcus sp. | 11 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 (5.9%) |
| Enterobacter sp. | 0 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 26 (4.9%) |
| Macrococcus caseolyticus | 0 | 5 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 (4.8%) |
| Moelleralla wisconsensis | 3 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 (2.9%) |
| Acinetobacter sp. | 1 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 (2.7%) |
| Ralstonia mannitolityca | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 (2.3) |
| Staphylococcus sp. | 0 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 (2.1%) |
| Proteus mirabilis | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 (1.3%) |
| Pontoea agglomerans | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (1.0%) |
| Psychrobacter sanguinis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (0.6%) |
| Buttiauxella gaviniae | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (0.4%) |
| Citrobacter sp. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (0.4%) |
| Bacillus cereus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.2%) |
| Total | 107 | 79 | 80 | 90 | 39 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 524 (100%) |
| Bacteria Species | A. Rodents (n = 44) | B. Antelope (n = 14) | C. African Civet (n = 3) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence | 95% CI | Prevalence | 95% CI | Prevalence | 95% CI | ||
| Escherichia coli | 72.7 | 58.2–83.7 | 50 | 26.8–73.2 | 66.7 | 58.3–98.3 | 0.03 |
| Klebsiella sp. | 65.9 | 51.1–78.1 | 35.7 | 16.3–61.2 | 33.3 | 1.71–88.2 | |
| Hafnia alevi | 47.7 | 33.8–62.1 | 64.3 | 38.8–83.7 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Yersinia ruckeri | 47.7 | 33.8–62.1 | 26.3 | 11.8–48.8 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Pseudomonas sp. | 43.2 | 29.7–57.8 | 42.9 | 21.4–77.4 | 66.7 | 11.8–98.3 | |
| Aeromonas sp. | 31.8 | 20.0–46.6 | 35.7 | 16.3–61.2 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Enterococcus sp. | 25 | 14.6–39.4 | 21.4 | 7.6–47.6 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Enterobacter sp. | 20.5 | 11.2–34.5 | 42.9 | 21.4–67.4 | 66.7 | 11.8–98.2 | |
| Acinetobacter sp. | 18.5 | 10.4–30.8 | 14.3 | 2.5–39.9 | 0 | 0–56.3 | |
| Macrococcus caseolyticus | 18.2 | 9.5–32.0 | 35.7 | 16.3–61.2 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Serratia sp. | 18.2 | 9.5–32.0 | 73.3 | 48.1–89.1 | 66.7 | 11.8–98.2 | |
| Staphylococcus sp. | 15.9 | 7.9–29.4 | 7.1 | 0.4–31.5 | 0 | 0–56.4 | |
| Moelleralla wisconsensis | 15.9 | 7.9–29.4 | 14.3 | 2.5–39.9 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Ralstonia mannitolityca | 13.6 | 6.4–26.7 | 50.0 | 26.8–73.2 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Proteus mirabilis | 6.8 | 2.3–18.2 | 7.1 | 0.4–31.5 | 100 | 43.9–100 | |
| Psychrobacter sanguinis | 2.3 | 0.1–11.8 | 0 | 0–21.5 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Buttiauxella gaviniae | 0 | 0–8.0 | 12.5 | 2.2–36.0 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Bacillus cereus | 0 | 0–8.0 | 7.1 | 0.4–31.4 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
| Citrobacter sp. | 0 | 0–8.0 | 6.7 | 0.3–29.8 | 0 | 0–56.2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oduro, D.; Offih-Kyei, W.; Yeboah, J.A.; Yeboah, R.; Danso-Coffie, C.; Boafo, E.; Adjei, V.Y.; Aboagye, I.F.; Mensah, G.I. Microbial Load and Diversity of Bacteria in Wild Animal Carcasses Sold as Bushmeat in Ghana. Pathogens 2025, 14, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080754
Oduro D, Offih-Kyei W, Yeboah JA, Yeboah R, Danso-Coffie C, Boafo E, Adjei VY, Aboagye IF, Mensah GI. Microbial Load and Diversity of Bacteria in Wild Animal Carcasses Sold as Bushmeat in Ghana. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080754
Chicago/Turabian StyleOduro, Daniel, Winnifred Offih-Kyei, Joanita Asirifi Yeboah, Rhoda Yeboah, Caleb Danso-Coffie, Emmanuel Boafo, Vida Yirenkyiwaa Adjei, Isaac Frimpong Aboagye, and Gloria Ivy Mensah. 2025. "Microbial Load and Diversity of Bacteria in Wild Animal Carcasses Sold as Bushmeat in Ghana" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080754
APA StyleOduro, D., Offih-Kyei, W., Yeboah, J. A., Yeboah, R., Danso-Coffie, C., Boafo, E., Adjei, V. Y., Aboagye, I. F., & Mensah, G. I. (2025). Microbial Load and Diversity of Bacteria in Wild Animal Carcasses Sold as Bushmeat in Ghana. Pathogens, 14(8), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080754






