Epidemiologic Characteristics of Chronic Hepatitis B and Coinfections with Hepatitis C Virus or Human Immunodeficiency Virus in South Korea: A Nationwide Claims-Based Study Using the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
2.2. Study Population and Clinical Variables
2.3. Statistical Analyses
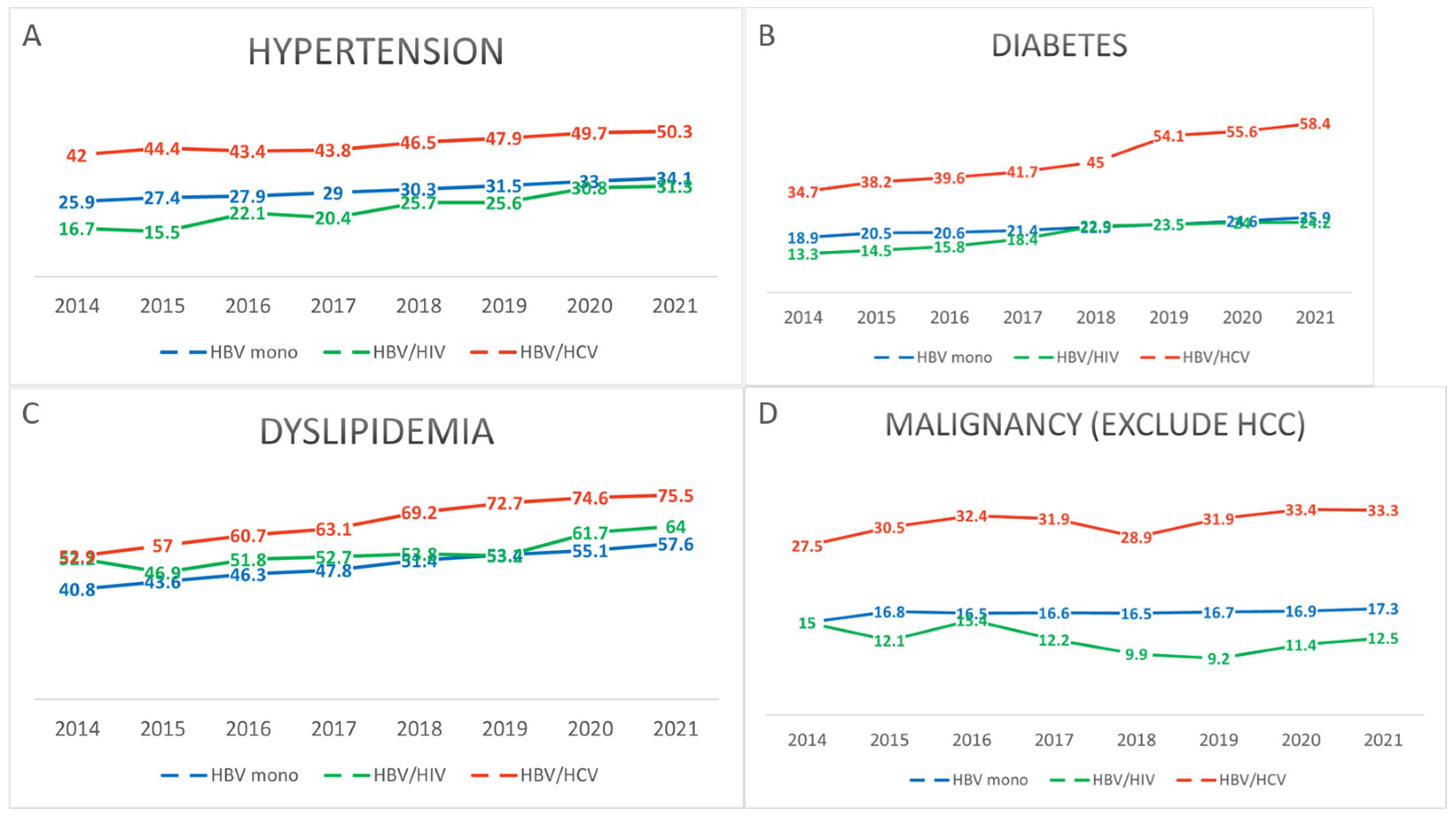
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of Study Population
3.2. Major Adverse Liver Outcomes of Study Population
3.3. Proportion of Antiviral Prescriptions, Including Nucleos(t)ide Analogues, in Study Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CHB | Chronic hepatitis B |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HIVs | Human immunodeficiency viruses |
| ART | Antiretroviral therapy |
| DAA | Direct-acting antivirals |
| NAs | nucle-os(t)ide analogues |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HIRA | Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service |
| NHI | National Health Insurance |
| ICD-10 | International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| DLD | Dyslipidemia |
| CCI | Charlson Comorbidity Index |
| MALOs | Major adverse liver outcomes |
References
- WHO. Hepatitis B. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Leoni, M.C.; Ustianowski, A.; Farooq, H.; Arends, J.E. HIV, HCV and HBV: A Review of Parallels and Differences. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2018, 7, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavilia, M.G.; Wu, G.Y. HBV-HCV Coinfection: Viral Interactions, Management, and Viral Reactivation. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi Gharaei, H.; Fararouei, M.; Mirzazadeh, A.; Sharifnia, G.; Rohani-Rasaf, M.; Bastam, D.; Rahimi, J.; Kouhestani, M.; Rezaian, S.; Dianatinasab, M. The global and regional prevalence of hepatitis C and B co-infections among prisoners living with HIV: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2021, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagnaw, M.; Muche, A.A.; Geremew, B.M.; Gezie, L.D. Prevalence and burden of HBV-HIV co-morbidity: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1565621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awadh, A.A.; Alharthi, A.A.; Alghamdi, B.A.; Alghamdi, S.T.; Baqays, M.K.; Binrabaa, I.S.; Malli, I.A. Coinfection of Hepatitis B and C Viruses and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2024, 16, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhu, L.; Liu, S.; Xie, W.F. A meta-analysis of case-control studies on the combined effect of hepatitis B and C virus infections in causing hepatocellular carcinoma in China. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Health Sector Strategies on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections 2022–2030. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240053779 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, K.T.; Chang, H.H.; Jun, Y.; Sohn, J.W.; Park, D.W.; Song, J.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Significance of Decreasing Rate of HIV and HBV Co-infection in a Nationwide Korean HIV/AIDS Cohort. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakenhoff, S.M.; de Man, R.A.; de Knegt, R.J.; Bindels, P.J.E.; de Schepper, E.I.T. Epidemiology and management of hepatitis B and C in primary care in the Netherlands: Data from the Rijnmond Primary Care database. Fam. Pract. 2023, 40, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Bello, K.E.; Radwan, Z.; Hassouneh, A.K.; Alrasheed, H.A.; Alotaibi, J.; Basrana, B.; Zaidan, A.A.; Garout, M.A.; Zaidan, T.I.; et al. The Dual Burden of Hepatitis B and C Among Drug Users in Asia: The First Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, N.; Hill, A. Combined “Test and Treat” Campaigns for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C: A Systematic Review to Provide Evidence to Support World Health Organization Treatment Guidelines. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofad666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocroft, A.; Geressu, A.; Beguelin, C.; Llibre, J.M.; Lazarus, J.V.; Tomazic, J.; Smidt, J.; Parczewski, M.; Brännström, J.; Sedlacek, D.; et al. The role of HIV/hepatitis B virus/hepatitis C virus RNA+ triple infection in end-stage liver disease and all-cause mortality in Europe. AIDS 2023, 37, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramier, C.; Boyd, A.; Smit, C.; van Zoest, R.; Claassen, M.A.A.; Pogány, K.; Posthouwer, D.; de Vries-Sluijs, T.; Carrieri, P.; Van der Valk, M. Impact of Socio-Economic, Behavioural and Clinical Factors on Liver Disease Progression in Individuals With HIV and Hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e70191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, D.W.; Yoon, Y.K.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, B.Y.; et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hepatitis Virus Coinfection among HIV-Infected Korean Patients: The Korea HIV/AIDS Cohort Study. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 49, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Yim, H.J.; Kim, B.H.; Lee, C.K.; Park, C.K.; Park, S.H. Clinical features and treatment efficacy of peginterferon alfa plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients coinfected with hepatitis B virus. Korean J. Hepatol. 2011, 17, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyoung, D.S.; Kim, H.S. Understanding and Utilizing Claim Data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and Health Insurance Review & Assessment (HIRA) Database for Research. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2022, 11, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.A.; Yoon, S.; Kim, L.Y.; Kim, D.S. Towards Actualizing the Value Potential of Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) Data as a Resource for Health Research: Strengths, Limitations, Applications, and Strategies for Optimal Use of HIRA Data. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, V.W.; Chan, S.L.; Wong, V.W.; Liang, L.Y.; Yip, T.C.; Lai, J.C.; Yuen, B.W.; Luk, H.W.; Tse, Y.K.; Lee, H.W.; et al. Increasing antiviral treatment uptake improves survival in patients with HBV-related HCC. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornberg, M.; Sandmann, L.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kennedy, P.; Lampertico, P.; Lemoine, M.; Lens, S.; Testoni, B.; Lai-Hung Wong, G.; Russo, F.P. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2025, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, I.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Kim, B.O.; Jung, S.; Nguyen, M.H. Increasing comorbidities in a South Korea insured population-based cohort of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.; Lee, H.; Park, H. Surveillance System for Infectious Disease Prevention and Management: Direction of Korea’s Infectious Disease Surveillance System. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2025, 40, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, T.; Chang, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Yoo, J.-J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.U.; Jang, J.Y. Adverse impact of metabolic dysfunction on fibrosis regression following direct-acting antiviral therapy: A multicenter study for chronic hepatitis C. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, A.; Ramirez, S.; Bukh, J. Lipid Droplets Accumulation during Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Cell-Culture Varies among Genotype 1-3 Strains and Does Not Correlate with Virus Replication. Viruses 2021, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, S.; Haour, G.; Fontaine, H.; Dorival, C.; Petrov-Sanchez, V.; Bourliere, M.; Capeau, J.; Carrieri, P.; Larrey, D.; Larsen, C.; et al. The negative impact of HBV/HCV coinfection on cirrhosis and its consequences. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.T.; Wu, L.W.; Tseng, T.C.; Chen, C.L.; Yang, H.C.; Su, T.H.; Wang, C.C.; Kuo, S.F.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, P.J.; et al. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Loss and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Patients With Dual Hepatitis B and C Infection. Medicine 2016, 95, e2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, F.; Yu, X.; Xiong, Y. The sex differences in diseases progression and prognosis among persons with HIV and HBV coinfection. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihealsick, E.; Word, A.; Scully, E.P. The impact of sex on HIV immunopathogenesis and therapeutic interventions. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e180075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, D.K.; Vorla, M.; Michos, E.D.; Agarwala, A.; Virani, S.; Duell, P.B.; Raal, F.J. Dyslipidemia in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Warner, C.; Duan, X.; Cheng, Z.; Jeyarajan, A.J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Shao, T.; Salloum, S.; Chen, P.J.; et al. HIV coinfection exacerbates HBV-induced liver fibrogenesis through a HIF-1α- and TGF-β1-dependent pathway. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trickey, A.; McGinnis, K.; Gill, M.J.; Abgrall, S.; Berenguer, J.; Wyen, C.; Hessamfar, M.; Reiss, P.; Kusejko, K.; Silverberg, M.J.; et al. Longitudinal trends in causes of death among adults with HIV on antiretroviral therapy in Europe and North America from 1996 to 2020: A collaboration of cohort studies. Lancet HIV 2024, 11, e176–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavascki, A.P.; Fuchs, S.C. The need for reappraisal of AIDS score weight of Charlson comorbidity index. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2007, 60, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, L.-G.; Das, M.; Karim, Q.A.; Ahmed, K.; Batting, J.; Brumskine, W.; Gill, K.; Harkoo, I.; Jaggernath, M.; Kigozi, G.; et al. Twice-Yearly Lenacapavir or Daily F/TAF for HIV Prevention in Cisgender Women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.S.; Nguyen, M.H.; Hernaez, R.; Huang, D.Q.; Wilder, J.; Piscoya, A.; Simon, T.G.; Falck-Ytter, Y. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Prevention and Treatment of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in At-Risk Individuals. Gastroenterology 2025, 168, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Variable | HBV Monoinfection (n = 469,834) | HBV/HIV Coinfection (n = 297) | HBV/HCV Coinfection (n = 3672) | HBV/HCV/HIV Coinfection (n = 8) | p for Trend * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (%) | 267,688 (57.0) | 269 (90.6) | 2018 (55.0) | 6 (75.0) | <0.001 |
| Age group, n (%) | |||||
| 20–39 | 50,999 (10.9) | 48 (16.2) | 248 (6.8) | 1 (12.5) | <0.001 |
| 40–49 | 111,242 (23.7) | 79 (26.6) | 450 (12.3) | 4 (50.0) | |
| 50–59 | 142,101 (30.2) | 90 (30.3) | 986 (26.9) | 1 (12.5) | |
| 60–69 | 117,735 (25.1) | 58 (19.5) | 1162 (31.6) | 1 (12.5) | |
| 70- | 47,757 (10.2) | 22 (7.4) | 826 (22.5) | 1 (12.5) | |
| HTN (%) | 160,321 (34.1) | 93 (31.3) | 1847 (50.3) | 2 (25.0) | <0.001 |
| DM (%) | 121,845 (25.9) | 72 (24.2) | 2143 (58.4) | 2 (25.0) | <0.001 |
| DLD (%) | 270,583 (57.6) | 190 (64.0) | 2772 (75.5) | 3 (37.5) | <0.001 |
| Other malignancy (%) | 81,055 (17.3) | 37 (12.5) | 1223 (33.3) | 3 (37.5) | <0.001 |
| CCI without HIV (%) | |||||
| 1 | 191,964 (40.9) | 139 (46.8) | 559 (15.2) | 3 (37.5) | <0.001 |
| ≥2 | 277,870 (59.1) | 158 (53.2) | 3113 (84.8) | 5 (62.5) | |
| Precise_CCI (%) † | |||||
| 1 | 191,964 (40.9) | 139 (46.8) | 559 (15.2) | 3 (37.5) | <0.001 |
| 2 | 107,423 (22.9) | 66 (22.2) | 506 (13.8) | 0 (0.0) | |
| 3 | 44,205 (9.4) | 24 (8.1) | 380 (10.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| 4 | 47,193 (10.0) | 19 (6.4) | 457 (12.4) | 3 (37.5) | |
| 5 | 29,957 (6.4) | 17 (5.7) | 467 (12.7) | 1 (12.5) | |
| 6 | 49,092 (10.4) | 32 (10.8) | 1303 (35.5) | 1 (12.5) |
| Variable | HBV Monoinfection (n = 469,834) | HBV/HIV Coinfection (n = 297) | HBV/HCV Coinfection (n = 3672) | HBV/HCV/HIV Coinfection (n = 8) | p for Trend * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC (%) | 29,410 (6.3) | 15 (5.1) | 388 (10.6) | 1 (12.5) | <0.001 |
| Liver transplantation (%) | 5658 (1.2) | 4 (1.3) | 77 (2.1) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Varices (%) | 35,989 (7.7) | 25 (8.4) | 461 (12.6) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Variceal_hemorrhage (%) | 432 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.089 |
| Ascites (%) | 21,748 (4.6) | 16 (5.4) | 354 (9.6) | 1 (12.5) | <0.001 |
| Hepatic_encephalopathy (%) | 5961 (3.4) | 12 (4.0) | 219 (6.0) | 1 (12.5) | <0.001 |
| Hepatorenal_syndrome (%) | 170 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0.930 |
| Spontaneous_bacterial_peritonitis (%) | 173 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0.554 |
| Variable | HBV Monoinfection (n = 469,834) | HBV/HIV Coinfection (n = 297) | HBV/HCV Coinfection (n = 3672) | HBV/HCV/HIV Coinfection (n = 8) | p for Trend * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBV_IFN (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA |
| HBV_NAs (%) | 234,685 (50.0) | 287 (96.6) | 945 (25.7) | 7 (87.5) | <0.001 |
| HIV_ART (%) | 0 (0.0) | 293 (98.7) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (87.5) | <0.001 |
| HCV_IFN (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA |
| HCV_DAA (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 164 (4.5) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, H.; Sohn, W.; Choi, N.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.; Nam, S.W.; Jeong, J.Y. Epidemiologic Characteristics of Chronic Hepatitis B and Coinfections with Hepatitis C Virus or Human Immunodeficiency Virus in South Korea: A Nationwide Claims-Based Study Using the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database. Pathogens 2025, 14, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070715
Oh H, Sohn W, Choi NR, Lee HY, Kim Y, Nam SW, Jeong JY. Epidemiologic Characteristics of Chronic Hepatitis B and Coinfections with Hepatitis C Virus or Human Immunodeficiency Virus in South Korea: A Nationwide Claims-Based Study Using the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database. Pathogens. 2025; 14(7):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070715
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Hyunwoo, Won Sohn, Na Ryung Choi, Hyo Young Lee, Yeonjae Kim, Seung Woo Nam, and Jae Yoon Jeong. 2025. "Epidemiologic Characteristics of Chronic Hepatitis B and Coinfections with Hepatitis C Virus or Human Immunodeficiency Virus in South Korea: A Nationwide Claims-Based Study Using the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database" Pathogens 14, no. 7: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070715
APA StyleOh, H., Sohn, W., Choi, N. R., Lee, H. Y., Kim, Y., Nam, S. W., & Jeong, J. Y. (2025). Epidemiologic Characteristics of Chronic Hepatitis B and Coinfections with Hepatitis C Virus or Human Immunodeficiency Virus in South Korea: A Nationwide Claims-Based Study Using the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Database. Pathogens, 14(7), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070715





