Mytilus galloprovincialis as a Natural Reservoir of Vibrio harveyi: Insights from GFP-Tagged Strain Tracking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vibrio harveyi Strain and Inoculum Preparation
2.2. Water and Mussels
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Microbiological Determinations
2.5. Histological Determinations
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results
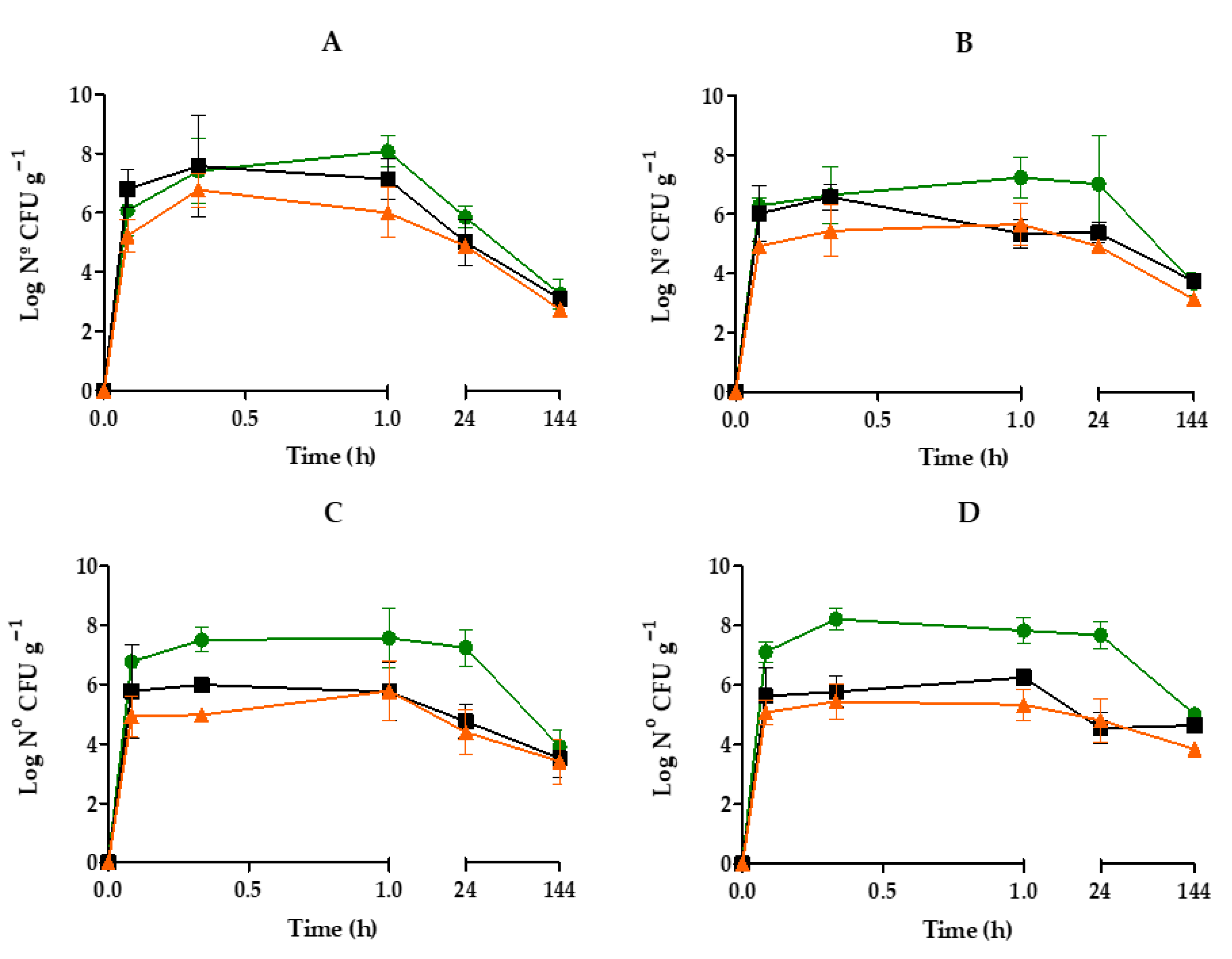
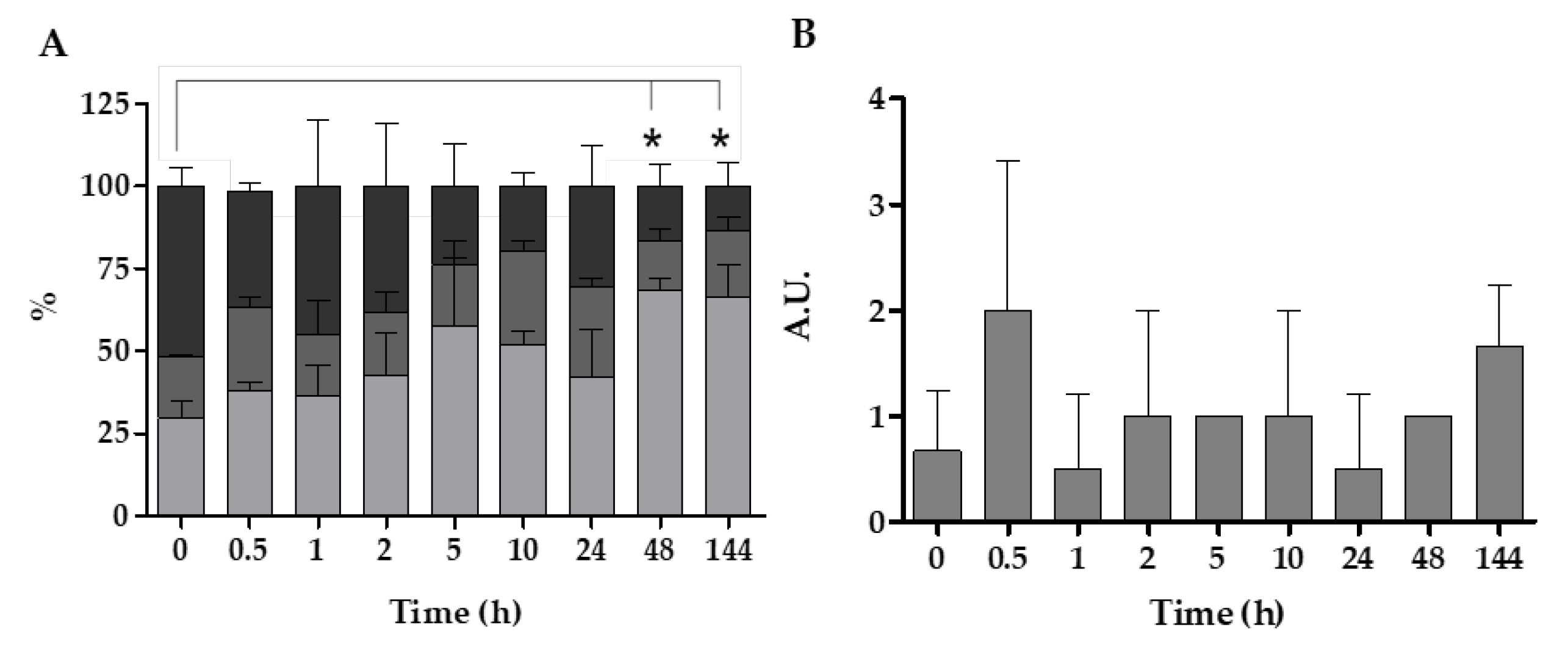
3.1. Accumulation and Distribution of V. harveyi in Mussel Organs
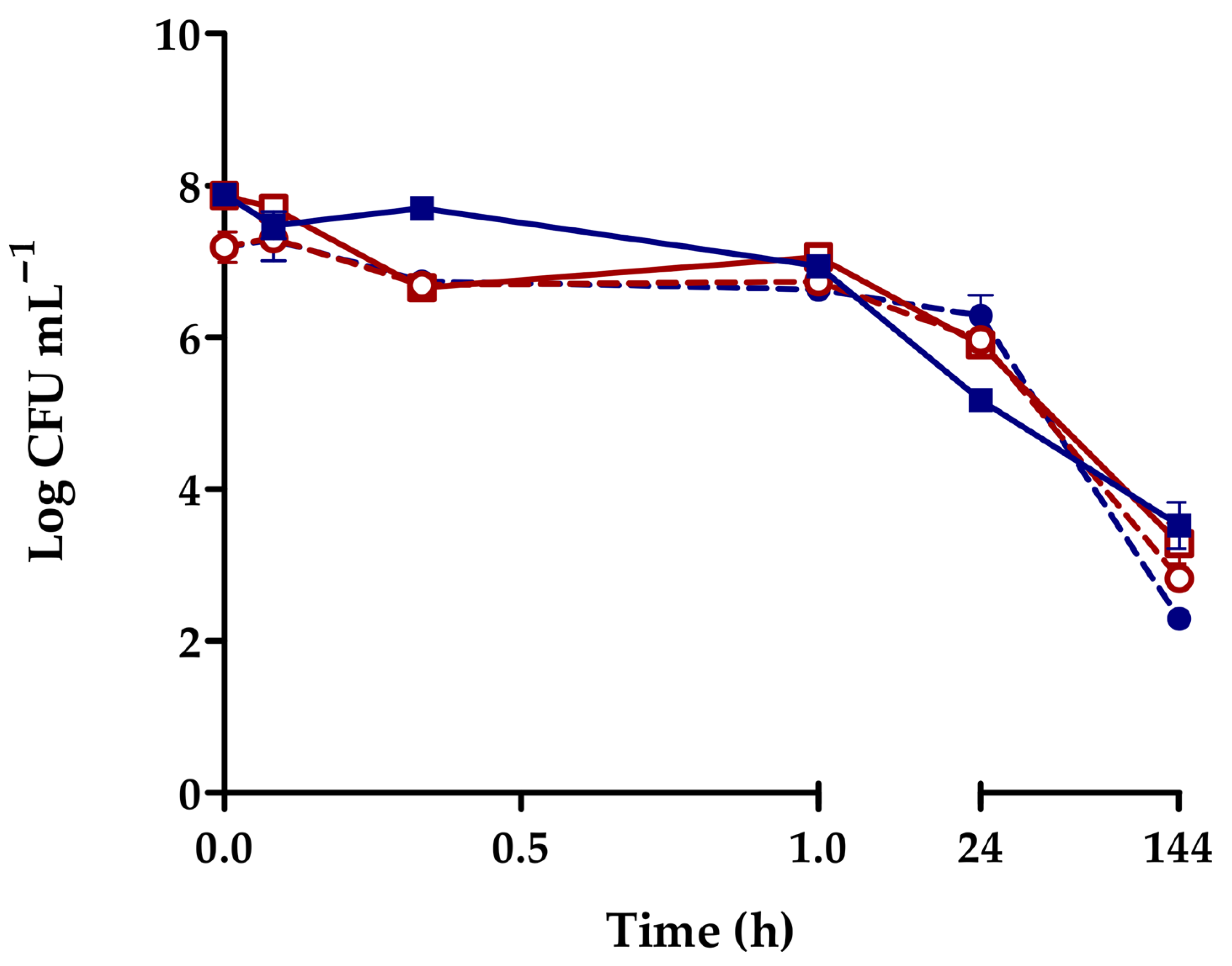
3.2. Bacterial Removal and Accumulation in Biodeposits
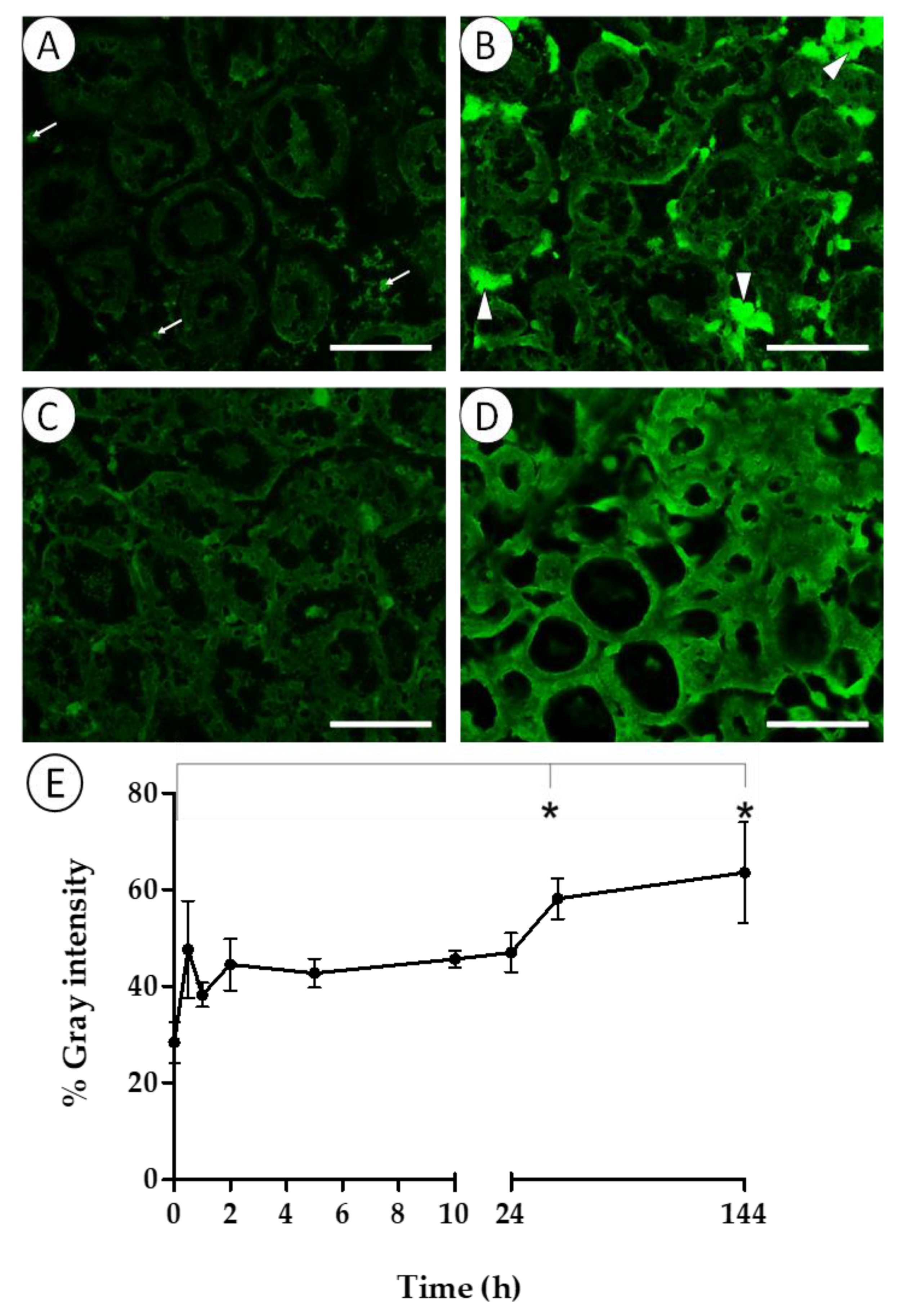
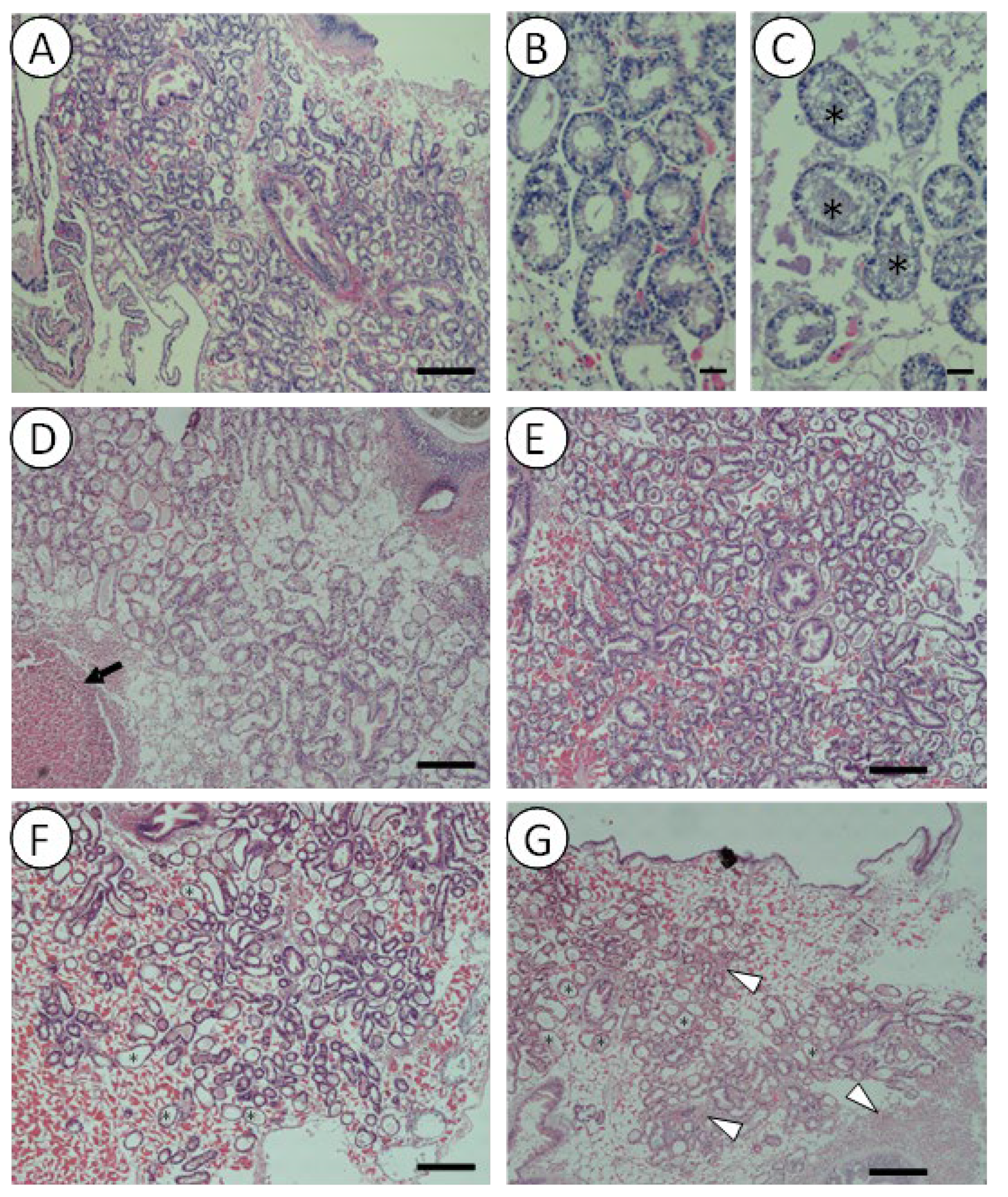
3.3. Histopathology and Immune Response of Mussels Exposed to V. harveyi
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Thompson, F.L.; Iida, T.; Swings, J. Biodiversity of vibrios. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 403–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erken, M.; Lutz, C.; McDougald, D. Interactions of Vibrio spp. with zooplankton. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, A.; Costa, M.M.; Forn-Cuni, G.; Balseiro, P.; Chamorro, R.; Dios, S.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Occurrence, seasonality and infectivity of Vibrio strains in natural populations of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 108, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuixech-Martí, S.; Culloty, S.C.; Lynch, S.A. Co-occurrence of pathogen assemblages in a keystone species the common cockle Cerastoderma edule on the Irish coast. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, C.M.; Saul-McBeth, J.; Matson, J.S. Vibrio responses to extracytoplasmic stress. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 10, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orruño, M.; Parada, C.; Ogayar, E.; Kaberdin, V.R.; Arana, I. Effects of abiotic and biotic factors on Vibrio harveyi ATCC 14126T survival dynamics in seawater microcosms. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 83, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-H.; He, X.; Austin, B. Vibrio harveyi: A serious pathogen of fish and invertebrates in mariculture. Mar. Life Sci. Tech. 2020, 2, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Amal, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Saad, M.Z.; Nasruddin, N.S.; Al-saari, N.; Sawabe, T. Vibriosis in cultured marine fishes: A review. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.J.; Fisher, S.W.; Landrum, P.F. Clearance and processing of algal particles by zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha). J. Great Lakes Res. 1996, 22, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo-da-Cunha, A. Structure and function of the digestive system in molluscs. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 377, 475–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkbeck, T.H.; McHenery, J.G. Degradation of bacteria by Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 1982, 72, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrak, M.R.; Molloy, S.D.; Bouchard, D.A.; Singer, J.T.; Bricknell, I. Potential role of Mytilus edulis in modulating the infectious pressure of Vibrio anguillarum 02β on an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture farm. Aquaculture 2012, 326–329, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masanja, F.; Yang, K.; Xu, Y.; He, G.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Jiang, X.; Luo, X.; Mkuye, R.; Deng, Y.; et al. Bivalves and microbes: A mini-review of their relationship and potential implications for human health in a rapidly warming ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1182438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matozzo, V.; Ercolini, C.; Serracca, L.; Battistini, R.; Rossini, I.; Granato, G.; Quaglieri, E.; Perolo, A.; Finos, L.; Arcangeli, G.; et al. Assessing the health status of farmed mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) through histological, microbiological and biomarker analyses. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 153, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Pruzzo, C. Specificity of innate immunity in bivalves: A lesson from bacteria. In Lessons in Immunity; Ballarin, L., Cammarata, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Chapter 6; pp. 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviani, E. Immunocyte: The invertebrate counterpart of the vertebrate macrophage. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2011, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, G.C.; da Silva, P.M.; Barracco, M.A.; Hering, A.F.; Albuquerque, M.C.P.; Coelho, J.D.R.; Schmidt, É.C.; Bouzon, Z.; Rosa, R.D.; Perazzolo, L.M. Morphological and functional characterization of the hemocytes from the pearl oyster Pteria hirundo and their immune responses against Vibrio infections. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 70, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Sardo, A.; Mangoni, O.; Di Cioccio, D.; Urciuolo, G.; De Vico, G.; Zingone, A. Quantitative histopathology of the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis L.) exposed to the harmful dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 127, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijangos, L.; Ziarrusta, H.; Ros, O.; Kortazar, L.; Fernández, L.A.; Olivares, M.; Zuloaga, O.; Prieto, A.; Etxebarria, N. Occurrence of emerging pollutants in estuaries of the Basque Country: Analysis of sources and distribution, and assessment of the environmental risk. Water Res. 2018, 147, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- URA (Uraren Euskal Agentzia/Agencia Vasca del Agua). Available online: https://www.uragentzia.euskadi.eus/contenidos/documentacion/red_costa_2022/es_def/adjuntos/RSEETyC_2022_MEMORIA.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Baña, Z.; Abad, N.; Uranga, A.; Azúa, I.; Artolozaga, I.; Unanue, M.; Iriberri, J.; Arrieta, J.M.; Ayo, B. Recurrent seasonal changes in bacterial growth efficiency, metabolism and community composition in coastal waters. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Layton, C. The hematoxylins and eosin. In Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 8th ed.; Suvarna, S.K., Layton, C., Bancroft, J.D., Eds.; Elsevier Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Chapter 10; pp. 126–138. [Google Scholar]
- Villalba, A.; Mourelle, S.G.; López, M.C.; Carballal, M.J.; Azevedo, C. Marteiliasis affecting cultured mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis of Galicia (NW Spain). I. Etiology, phases of the infection, and temporal and spatial variability in prevalence. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1993, 16, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, R.W. Synchrony in the digestive diverticula of Mytillus edulis L. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1975, 55, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, M.G.; Langellotti, A.L.; Russo, V.; Martello, A.; Monin, M.; Di Bartolo, I.; Ianiro, G.; Di Concilio, D.; Galiero, G.; Fusco, G. Accumulation and depuration kinetics of rotavirus in mussels experimentally contaminated. Food Environ. Virol. 2019, 12, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosteo, R.; Goñi, P.; Miguel, N.; Abadías, J.; Valero, P.; Ormad, M.P. Bioaccumulation of pathogenic bacteria and amoeba by zebra mussels and their presence in watercourses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, K.; Silver, M.; Byrne, B.A.; Berardi, T.; Aguilar, B.; Melli, A.; Smith, W.A. Fecal indicator bacteria and zoonotic pathogens in marine snow and California mussels (Mytilus californianus). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Lombardo, L.; Fiorentino, C.; Orlandella, B.; Monticelli, L.; Nostro, A.; Alonzo, V. Uptake of Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae non-O1 and Enterococcus durans by, and depuration of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 99, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrfurth, D.; Oeleker, K.; Pund, R.-P.; Strauch, E.; Scheartz, K.; Leer, J.; Gölz, G.; Alter, T.; Huehn, S. Uptake and localization of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) of the Baltic Sea. J. Shellfish Res. 2013, 32, 855–859. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Joven, C.; de Blas, I.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Furones, M.D.; Roque, A. Experimental uptake and retention of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in two species of clams: Ruditapes decussatus and Ruditapes philippinarum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras, A.; Moreira, R.; Sendra, M.; Novoa, B. Genomics and immunity of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in a changing environment. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Barmo, C.; Fabbri, R.; Ciacci, C.; Vergani, L.; Roch, P.; Gallo, G. Effects of Vibrio challenge on digestive gland biomarkers and antioxidant gene expression in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, N.; Zorita, I.; Costa, P.M.; Franco, J.; Larreta, J. Development of histopathological indices in the digestive gland and gonad of mussels: Integration with contamination levels and effects of confounding factors. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 162, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, D.; Shi, X. Enumeration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oyster tissues following artificial contamination and depuration. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saco, A.; Rey-Campos, M.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A. Transcriptomic response of mussel gills after a Vibrio splendidus infection demonstrates their role in the immune response. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 615580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, H.R.; Macey, B.M.; Burnett, L.E.; Burnett, K.G. Differential localization and bacteriostasis of Vibrio campbellii among tissues of the Eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehr, S.; Diehle, N.; Kaegi, R.; Schlechtriem, C. Ingestion of bivalve droppings by benthic invertebrates may lead to the transfer of nanomaterials in the aquatic food chain. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, L.H.; Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.A.; Dark, E.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Wayles, J.; Sacks, P.E.; Walters, L.J. Oyster reefs are reservoirs for potential pathogens in a highly disturbed subtropical estuary. Environments 2023, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacci, C.; Manti, A.; Canonico, B.; Campana, R.; Camisassi, G.; Baffone, W.; Canesi, L. Responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis hemocytes to environmental strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio vulnificus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 65, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbi, S.; Avio, G.C.; Benedetti, M.; Totti, C.; Accoroni, S.; Pichierri, S.; Bacchiocchi, S.; Orletti, R.; Graziosi, T.; Regoli, F. Effects of harmful dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata exposure on immunological, histological and oxidative responses of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vico, G.; Carella, F. Morphological features of the inflammatory response in molluscs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olalemi, A.; Baker-Austin, C.; Ebdon, J.; Taylor, H. Bioaccumulation and persistence of faecal bacterial and viral indicators in Mytilus edulis and Crassostrea gigas. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pourmozaffar, S.; Tamadoni Jahromi, S.; Rameshi, H.; Sadeghi, A.; Bagheri, T.; Behzadi, S.; Gozari, M.; Zahedi, M.R.; Abrari Lazarjani, S. The role of salinity in physiological responses of bivalves. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1548–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreyeva, A.; Gostyukhina, O.; Gavruseva, T.; Sigacheva, T.; Tkachuk, A.; Podolskaya, M.; Chelebieva, E.; Kladchenko, E. Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) under salinity stress: Effects on antioxidant capacity and gill structure. J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2025, 343, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, B.L.; Somero, G.N. Transcriptomic responses to salinity stress in invasive and native blue mussels (genus Mytilus). Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, M.J.; Cheney, D.; Su, Y.-C. Temperature effects on the depuration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus from the American Oyster (Crassostrea virginica). J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, M62-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroda, A.V.; Kipryushina, Y.O.; Odintsova, N.A. The effects of cold stress on Mytilus species in the natural environment. Cell Stress Chaperones 2020, 25, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almaraz, A.; Uriarte, F.O.; González-Rivacoba, M.; Arana, I.; Arranz-Veiga, I.; Zaldibar, B.; Orruño, M. Mytilus galloprovincialis as a Natural Reservoir of Vibrio harveyi: Insights from GFP-Tagged Strain Tracking. Pathogens 2025, 14, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070687
Almaraz A, Uriarte FO, González-Rivacoba M, Arana I, Arranz-Veiga I, Zaldibar B, Orruño M. Mytilus galloprovincialis as a Natural Reservoir of Vibrio harveyi: Insights from GFP-Tagged Strain Tracking. Pathogens. 2025; 14(7):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070687
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmaraz, Arkaitz, Flor O. Uriarte, María González-Rivacoba, Inés Arana, Itziar Arranz-Veiga, Beñat Zaldibar, and Maite Orruño. 2025. "Mytilus galloprovincialis as a Natural Reservoir of Vibrio harveyi: Insights from GFP-Tagged Strain Tracking" Pathogens 14, no. 7: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070687
APA StyleAlmaraz, A., Uriarte, F. O., González-Rivacoba, M., Arana, I., Arranz-Veiga, I., Zaldibar, B., & Orruño, M. (2025). Mytilus galloprovincialis as a Natural Reservoir of Vibrio harveyi: Insights from GFP-Tagged Strain Tracking. Pathogens, 14(7), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14070687







