Global Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Metallo-β-Lactamase (MBL)-Producing Acinetobacter Clinical Isolates: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Objectives
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
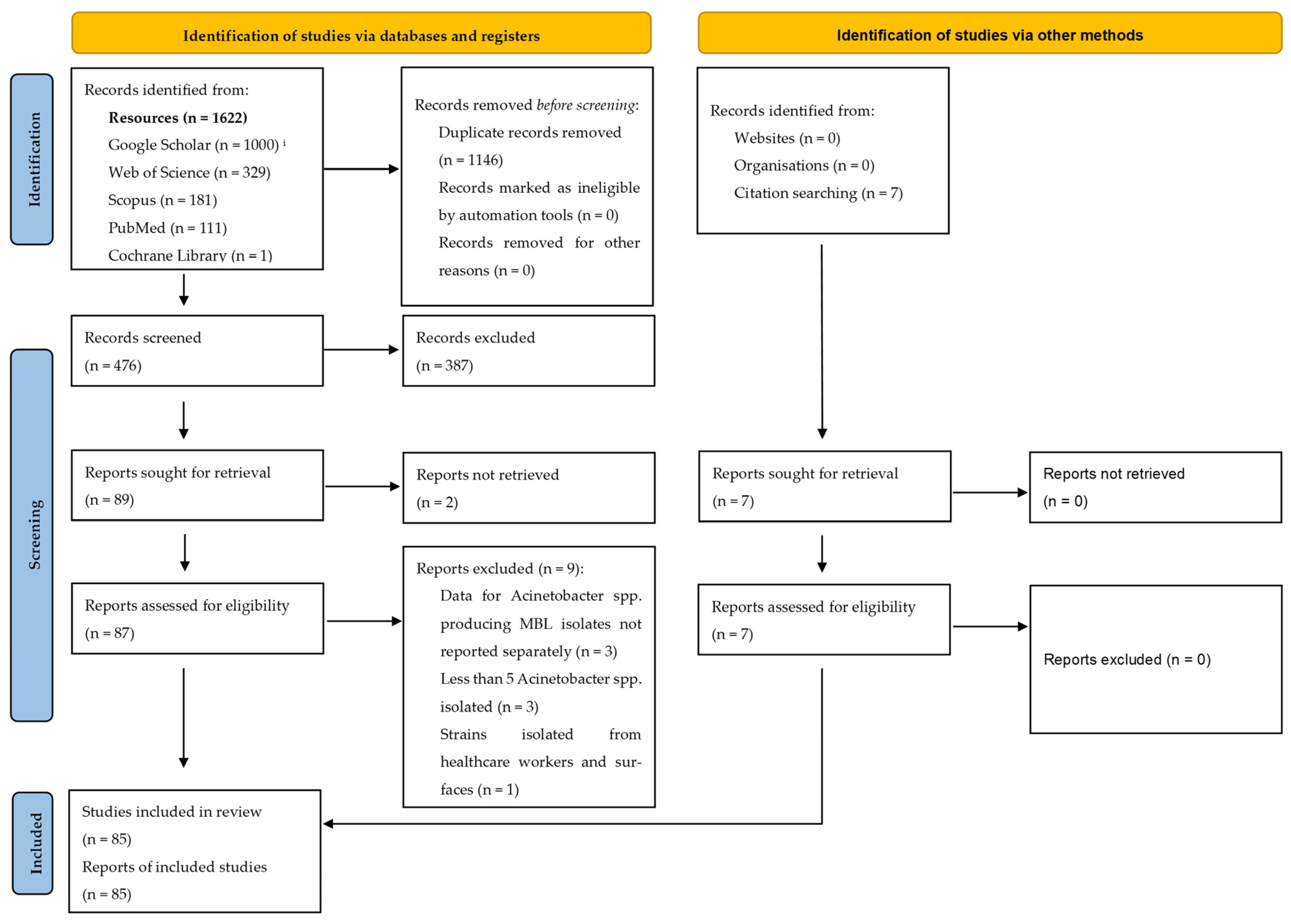
2.4. Selection of Articles
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Adherence to the PRISMA Guidelines
3. Results
Identification of Relevant Articles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| CDT | Combined disk test |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| DDST | Double-disk synergy test |
| EDTA | Ethylene-diamine-tetra-acetic acid |
| EUCAST | European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| MBL | Metallo-β-lactamase |
| MDR | Multidrug resistant |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PDR | Pandrug resistant |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| XDR | Extensively drug resistant |
References
- Oliveira, M.; Antunes, W.; Mota, S.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Dias da Silva, D. An Overview of the Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Karveli, E.A.; Kelesidis, I.; Kelesidis, T. Community-acquired Acinetobacter infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 26, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Rafailidis, P.I. Attributable mortality of Acinetobacter baumannii: No longer a controversial issue. Crit. Care Lond. Engl. 2007, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, E.V.; de la Hoz, F.P.; Einarson, T.R.; McGhan, W.F.; Quevedo, E.; Castañeda, C.; Kawai, K. Carbapenem resistance and mortality in patients with Acinetobacter baumannii infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance, to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/376776 (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Wong, D.; Nielsen, T.B.; Bonomo, R.A.; Pantapalangkoor, P.; Luna, B.; Spellberg, B. Clinical and Pathophysiological Overview of Acinetobacter Infections: A Century of Challenges. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 409–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambler, R.P.; Baddiley, J.; Abraham, E.P. The structure of β-lactamases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 289, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K. Past and Present Perspectives on β-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01076-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagshetty, K.; Shilpa, B.M.; Patil, S.A.; Shivannavar, C.T.; Manjula, N.G. An Overview of Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamases and Metallo Beta Lactamases. Adv. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 37–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaha-Kfoury, J.N.; Araj, G.F. Recent developments in β lactamases and extended spectrum β lactamases. BMJ 2003, 327, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, C.; Liolios, L.; Peleg, A.Y. Phenotypic Detection of Carbapenem-Susceptible Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Gram-Negative Bacilli in the Clinical Laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3139–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebrone, C. Metallo-beta-lactamases (classification, activity, genetic organization, structure, zinc coordination) and their superfamily. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1686–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palzkill, T. Metallo-β-lactamase structure and function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1277, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ezpeleta-Lobato, G.; Han, X.; Carmona-Cartaya, Y.; Quiñones-Pérez, D. Carbapenamase-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii in China, Latin America and the Caribbean. MEDICC Rev. 2022, 24, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindu, M.; Derseh, L.; Gelaw, B.; Moges, F. Carbapenemase-Producing Non-Glucose-Fermenting Gram-Negative Bacilli in Africa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 9461901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-Y.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Khan, E.; Suwantarat, N.; Ghafur, A.; Tambyah, P.A. Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Enterobacteriaceae in South and Southeast Asia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djahmi, N.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Pantel, A.; Dekhil, M.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P. Epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and Acinetobacter baumannii in Mediterranean countries. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 305784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajikhani, B.; Sameni, F.; Ghazanfari, K.; Abdolali, B.; Yazdanparast, A.; Asarehzadegan Dezfuli, A.; Nasiri, M.J.; Goudarzi, M.; Dadashi, M. Prevalence of blaNDM-producing Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from clinical samples around the world; a systematic review. Gene Rep. 2023, 30, 101728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardakas, K.Z.; Mavroudis, A.D.; Georgiou, M.; Falagas, M.E. Intravenous colistin combination antimicrobial treatment vs. monotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwa, A.L.; Falagas, M.E.; Michalopoulos, A.; Tam, V.H. Benefits of aerosolized colistin for ventilator-associated pneumonia: Absence of proof versus proof of absence? Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2011, 52, 1278–1279; author reply 1279–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kyriakidou, M.; Voulgaris, G.L.; Vokos, F.; Politi, S.; Kechagias, K.S. Clinical use of intravenous polymyxin B for the treatment of patients with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections: An evaluation of the current evidence. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 24, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Vardakas, K.Z.; Tsiveriotis, K.P.; Triarides, N.A.; Tansarli, G.S. Effectiveness and safety of high-dose tigecycline-containing regimens for the treatment of severe bacterial infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarou, A.; Stathopoulos, P.; Tzvetanova, I.D.; Asimotou, C.-M.; Falagas, M.E. β-Lactam/β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combination Antibiotics Under Development. Pathogens 2025, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, D.; Lee, K.; Yum, J.H.; Shin, H.B.; Rossolini, G.M.; Chong, Y. Imipenem-EDTA Disk Method for Differentiation of Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas spp. and Acinetobacter spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3798–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Chong, Y.; Shin, H.B.; Kim, Y.A.; Yong, D.; Yum, J.H. Modified Hodge and EDTA-disk synergy tests to screen metallo-β-lactamase-producing strains of Pseudomonas and Acinetobactet species. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2001, 7, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, A.; Antony, B.; Shenoy, P. Comparative Evaluation of Four Phenotypic Tests for Detection of Metallo-β-Lactamase and Carbapenemase Production in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2014, 8, DC05–DC08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Mathur, P.; Das, A.; Kapil, A.; Sharma, V. An evaluation of four different phenotypic techniques for detection of metallo-beta-lactamase producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 26, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhi, N.N.; Alam, A.S.M.R.U.; Sultana, M.; Rahaman, M.M.; Hossain, M.A. Diversity of carbapenemases in clinical isolates: The emergence of blaVIM-5 in Bangladesh. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Pan, C.Z.; Zhao, Z.W.; Zhao, Z.X.; Chen, H.L.; Lu, W.B. Effects of a combination of amlodipine and imipenem on 42 clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii obtained from a teaching hospital in Guangzhou, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahir, H.R.; Patel, P.H.; Berry, R.A.; Parmar, R.; Soni, S.T.; Shah, P.K.; Vegad, M.M.; Patil, S. Prevalence of metallo-β-lactamases producing Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter species in tertiary care teaching hospital, Gujarat. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 4, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana Rao, K.; Aradita, C.; Lakshminarayana, S. Detection of metallo-beta-lactamase (MBL) producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter spp. from a Tertiary Care Hospital. J. Res. Appl. Basic Med Sci. 2024, 10, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee Molay, C.B.L. Prevalence of ESBL and MBL in Acinetobacter Species Isolated from Clinical Samples in Tertiary Care Hospital. Int. J. Sci. Res. IJSR 2015, 4, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Binnani, A.; Bishnoi, B.R.; Meena, S.; Singh, D. Study of Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Matello-Beta-Lactamase Producing Acinetobacter spp. Isolated at a Tertiary Care Institute in North West Region of Rajasthan. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2521–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.S.; Kumar, S.H.; Baveja, S.M. Prevalence of metallo-β-lactamase producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter species in intensive care areas in a tertiary care hospital. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. Peer-Rev. Off. Publ. Indian Soc. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 14, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.; Dolma, K.G.; Khandelwal, B.; Goyal, R.K.; Mitsuwan, W.; Pereira, M.d.L.G.; Klangbud, W.K.; Gupta, M.; Wilairatana, P.; Siyadatpanah, A.; et al. Acinetobacter baumannii in suspected bacterial infections: Association between multidrug resistance, virulence genes, & biofilm production. Indian J. Med. Res. 2023, 158, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girija, S.A.; Jayaseelan, V.P.; Arumugam, P. Prevalence of VIM- and GIM-producing Acinetobacter baumannii from patients with severe urinary tract infection. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2018, 65, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, N.; Punia, P.; Chaudhary, U. Prevalence of ESBL, MBL and Amp C producing XDR Acinetobacter isolates from lower respiratory tract specimens. Int. J. Contemp. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 2091–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Hodiwala, A.; Dhoke, R.; Urhekar, A. Incidence of metallo-betalactamase producing pseudomonas, acinetobacter & enterobacterial isolates in hospitalised patients. Int. J. Pharamcy Biol. Sci. 2013, 3, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Jena, J.; Sahoo, R.K.; Subudhi, E.; Debata, N. Prevalence of ESBL, MBL and Ampc-b-lactamases producing multidrug resistance gram negative bacteria in a tertiary care hospital. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 8, 4099–4105. [Google Scholar]
- Jethwa, D.K.; Vegad, M. Phenotypic Detection & Prevalence of Metallo-β-lactamases in Acinetobacter spp. in Clinical Isolates at Tertiary Care Hospital. Med. Sci. 2013, 2, 270–271. [Google Scholar]
- John, S.; Balagurunathan, R. Metallo beta lactamase producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 29, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Gupta, V.; Chhina, D. Prevalence of metalo- β-lactamase-producing (MBL) Acinetobacter species in a tertiary care hospital. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2014, 6, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, S. Prevalence of Extended Spectrum Betalactamase (ESBL) and Metallobetalactamase (MBL) Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Various Clinical Samples. J. Pathog. 2018, 2018, 6845985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, E.; Usha, K.; Ramana, B.; Chaudhury, A.; GOPAL, D. Prevalence of various β-lactamase (ESBL, AmpC and MBL) producing multidrug-resistant clinical isolates of Acinetobacter spp. in a tertiary care hospital. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pandya, Y.; Singh, S.; Badodariya, D.; Shethwala, N. Metallo-β-Lactamase Producing Clinical Isolates Of Acinetobacter Baumannii And Pseudomonas Aeruginosa In A Teaching Hospital Of Rural Gujarat-India.: Metallo-β-Lactamase Producing Clinical Isolates Of Acinetobacter Baumannii And Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Natl. J. Integr. Res. Med. 2016, 7, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, H.V.; Mohite, S.T.; Patil, V.C. Metallo-beta-lactamase-producing multidrug-resistant acinetobacter isolates in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2021, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynga, D.; Shariff, M.; Deb, M. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from Delhi, India. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2015, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, S.; Gogoi, I.; Oloo, A.; Sharma, M.; Puzari, M.; Chetia, P. Co-production of metallo-β-lactamase and OXA-type β-lactamases in carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in North East India. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, P.; Sikka, R.; Deep, A.; Chaudhary, U. Phenotypic detection and prevalence of metallo β-lactamases (MBLs) in carbapenem resistant isolates of acinetobacter species at a tertiary care hospital in north India. Int. J. Pharm. Med. Bio Sci. 2013, 2, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, N.; Agarwal, J.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, M. Analysis of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter from a tertiary care setting in North India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 31, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugumaran, S.; Devi, S.U. Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Producers among Non-Fermenting Gram Negative Bacilli. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2019, 18, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakar, V.H.; Chakraborthy, A.; Modak, M.; Krunal, L. Detection of Metallo-β-lactamase production amongst Acinetobacter species from a tertiary care hospital. J. Acad. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Gajbhiye, S. Prevalence of multidrug resistance, ESBL and MBL production in Acinetobacter spp. Int. J. Recent. Trends Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Uma Karthika, R.; Srinivasa Rao, R.; Sahoo, S.; Shashikala, P.; Kanungo, R.; Jayachandran, S.; Prashanth, K. Phenotypic and genotypic assays for detecting the prevalence of metallo-beta-lactamases in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii from a South Indian tertiary care hospital. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamsi, K.S.; Moorthy, S.R.; Murali, T.; Hemiliamma, M.; Reddy, Y.; Reddy, B.; Kumar, J.S. Phenotypic Methods for the Detection of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Production by Gram-negative Bacterial Isolates from Hospitalized Patients in A Tertiary Care Hospital in India. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamiri, S.; Amirmozafari, N.; Fallah Mehrabadi, J.; Fouladtan, B.; Hanafi Abdar, M. Antibiotic resistance patterns and a survey of metallo-β-lactamase genes including bla-IMP and bla-VIM types in Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from hospital patients in Tehran. Chemotherapy 2016, 61, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahantigh, M.; Javadi, R.; Bameri, Z.; Dehvari, A. Evaluation of Antibiotic Susceptibility, Carbapenemase and Metallobetalactamase-producing Strains of Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Hospitalized Patients in Zahedan During 2019–2022. Int. J. Infect. 2024, 10, e143968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledi, M.; Shahini Shams Abadi, M.; Validi, M.; Zamanzad, B.; Vafapour, R.; Gholipour, A. Phenotypic and genotypic detection of metallo-β-lactamases in A. baumanii isolates obtained from clinical samples in Shahrekord, southwest Iran. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maspi, H.; Mahmoodzadeh Hosseini, H.; Amin, M.; Imani Fooladi, A.A. High prevalence of extensively drug-resistant and metallo beta-lactamase-producing clinical Acinetobacter baumannii in Iran. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 98, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.; Motamedifar, M.; Sarvari, J.; Ebrahim-Saraie, H.S.; Same, M.M.; Moghadam, F. Emergence of multidrug resistance and metallo-beta-lactamase producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from patients in Shiraz, Iran. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2016, 6, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moulana, Z.; Babazadeh, A.; Eslamdost, Z.; Shokri, M.; Ebrahimpour, S. Phenotypic and genotypic detection of metallo-beta-lactamases in Carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 11, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, M.; Karimi, A.; Fallah, F.; Hashemi, A.; Alimehr, S.; Goudarzi, H.; Aghamohammad, S. High Prevalence of Metallo-beta-lactamase Producing Acinetobacter. Arch. Pediatr. 2014, 2, e15439. [Google Scholar]
- Owlia, P.; Azimi, L.; Gholami, A.; Asghari, B.; Lari, A.R. ESBL- and MBL-mediated resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: A global threat to burn patients. Infez. Med. 2012, 20, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peymani, A.; Nahaei, M.-R.; Farajnia, S.; Hasani, A.; Mirsalehian, A.; Sohrabi, N.; Abbasi, L. High prevalence of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing acinetobacter baumannii in a teaching hospital in Tabriz, Iran. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 64, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Farahani, A. Study of genetic diversity, biofilm formation, and detection of Carbapenemase, MBL, ESBL, and tetracycline resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from burn wound infections in Iran. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Fazeli, H.; Halaji, M.; Moghadampour, M.; Faghri, J. Prevalence of metallo-beta-lactamase producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from intensive care unit in tertiary care hospitals. Ann. Ig. Med. Prev. E Comunita 2018, 30, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.; Saidijam, M.; Bahador, A.; Jafari, R.; Alikhani, M.Y. High prevalence of multidrug resistance and metallo-beta-lactamase (MbetaL) producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from patients in ICU wards, Hamadan, Iran. J. Res. Health Sci. 2013, 3, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani, B.; Heidari, H.; Ebrahim-Saraie, H.S.; Hadi, N.; Mardaneh, J.; Motamedifar, M. Molecular characteristics of multiple and extensive drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates obtained from hospitalized patients in Southwestern Iran. Infez. Med. Riv. Period. Eziologia Epidemiol. Diagn. Clin. E Ter. Patol. Infett. 2018, 26, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Vala, M.H.; Hallajzadeh, M.; Hashemi, A.; Goudarzi, H.; Tarhani, M.; Tabrizi, M.S.; Bazmi, F. Detection of Ambler class A, B and D ß-lactamases among Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from burn patients. Ann. Burns Fire Disasters 2014, 27, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Al Marjani, M.; Al-Ammar, M.; Kadhem, E. Occurrence of ESBL and MBL genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from Baghdad, Iraq. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2013, 5, 2482–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Anoar, K.A.; Ali, F.A.; Omer, S.A. Detection of metallo beta-lactamase enzyme in some gram negative bacteria isolated from burn patients in sulaimani city, Iraq. Eur. Sci. J. 2014, 10, 485–496. [Google Scholar]
- Numan, S.; Al-Saedi, F.; Burhan, I. Prevalence of Extended Spectrum Betalactamase and Metallobetalactamase Producing Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Different Infections in Baghdad City of Iraq. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2022, 12, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhi, S.H.; Al-Charrakh, A.H. Occurrence of MBLs and Carbapenemases among MDR and XDR Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Hospitals in Iraq. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smail, S.B.; Al-Otrachi, K.I. Phenotypic Characterization of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases and Metallo-Beta-Lactamase of Multi Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Causing Nosocomial Infections in Erbil City. Al-Mustansiriyah J. Sci. 2019, 30, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishii, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Yoshida, A.; Okuzumi, K.; Uetera, Y.; Yasuhara, H.; Moriya, K. Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of Acinetobacter species isolated from blood cultures in two Japanese university hospitals. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Nagao, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Hotta, G.; Matsushima, A.; Ito, Y.; Takakura, S.; Ichiyama, S. Regional dissemination of Acinetobacter species harbouring metallo-β-lactamase genes in Japan. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajjar Soudeiha, M.; Dahdouh, E.; Daoud, Z.; Sarkis, D.K. Phenotypic and genotypic detection of β-lactamases in Acinetobacter spp. isolates recovered from Lebanese patients over a 1-year period. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 12, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziz, M.N.H.; Chakravarthi, S. ESBL and MBL detection in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter species. MAHSA Int. J. Health Med. 2021, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Koirala, A.; Agrahari, G.; Dahal, N.; Ghimire, P. ESBL and MBL mediated resistance in clinical isolates of nonfermentating Gram negative bacilli (NFGNB) in Nepal. J. Microb. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 3, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, M.; Bhattarai, N.R.; Rai, K.; Pandit, T.K.; Khanal, B. Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter: Detection of ESBL, MBL, blaNDM-1 Genotype, and Biofilm Formation at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Eastern Nepal. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 8168000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.K.; Acharya, J.; Kattel, H.P.; Koirala, J.; Rijal, B.P.; Pokhrel, B.M. Metallo-beta-lactamase producing gram-negative bacterial isolates. J. Nepal Health Res. Counc. 2012, 10, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.; Mishra, S.K.; Shrestha, A. Characterisation of ESKAPE Pathogens with Special Reference to Multidrug Resistance and Biofilm Production in a Nepalese Hospital. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Jaishi, N.; Yadav, B.K.; Shah, P.K. Prevalence of extended spectrum beta lactamases (ESBL) and metallo beta lactamases (MBL) mediated resistance in gram negative bacterial pathogens. Tribhuvan Univ. J. Microbiol. 2017, 4, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, M.; Tohya, M.; Hishinuma, T.; Sherchand, J.B.; Kirikae, T.; Tada, T. Molecular epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a hospital in Nepal. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 38, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Tada, T.; Shrestha, B.; Ohara, H.; Kirikae, T.; Rijal, B.; Pokhrel, B.; Sherchand, J. Phenotypic characterization of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii with special reference to metallo-β-lactamase production from the hospitalized patients in a tertiary care hospital in Nepal. J. Inst. Med. Nepal 2015, 37, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, P.; Bhandari, D.; Shrestha, D.; Parajuli, H.; Chaudhary, P.; Amatya, J.; Amatya, R. A hospital based surveillance of metallo-beta-lactamase producing gram negative bacteria in Nepal by imipenem-EDTA disk method. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Bhujel, R.; Hamal, P.; Mishra, S.K.; Sharma, S.; Sherchand, J.B. Burden of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infection in Hospitalized Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Nepal. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Ejaz, H.; Zafar, A.; Hamid, H. Phenotypic Detection of Metallo-Beta-Lactamases in Carbapenem Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Pediatric Patients in Pakistan. J. Pathog. 2016, 2016, 8603964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, B.; Perveen, K.; Olsen, B.; Zahra, R. Emergence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in hospitals in Pakistan. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, S.; Zafar, A.; Guhar, D.; Ahsan, T.; Hasan, R. Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Clinical Isolates Of Acinetobacter Species And Pseudomonas Aeruginosa From Intensive Care Unit Patients Of A Tertiary Care Hospital. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 26, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, F.; Masood, R.; Faiz, M. Prevalence of New Delhi metallo beta-lactamase (NDM) producing Gram-negative bacteria from different tertiary care hospitals in Lahore, Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2020, 52, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Malik, M.; Javed, I.; Mushtaq, S.; Imran, F.; Jameel, R. Detection of metallo beta lactamase production in imipenem resistant gram negative bacilli non fermenters isolated in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Prof. Med. J. 2019, 26, 2080–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.W.; Yasir, M.; Farman, M.; Jiman-Fatani, A.A.; Almasaudi, S.B.; Alawi, M.; El-Hossary, D.; Azhar, E.I. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Molecular Characterization of Clinical Strains of Acinetobacter baumannii in Western Saudi Arabia. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.Y.; Koo, S.H.; Kim, S.; Kwon, G.C. Emergence of Acinetobacter pittii harboring New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase genes in Daejeon, Korea. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-F.; Peng, C.-F.; Hsu, H.-J.; Chen, Y.-H. Molecular characterisation of the metallo-β-lactamase genes in imipenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria from a university hospital in southern Taiwan. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesli, E.; Berrazeg, M.; Drissi, M.; Bekkhoucha, S.N.; Rolain, J.-M. Prevalence of carbapenemase-encoding genes including New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase in Acinetobacter species, Algeria. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e739–e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Glil, R. New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase 1 (NDM-1) producing Acinetobacter baumannii in Egyptian hospitals. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 3, 470–478. [Google Scholar]
- Elbrolosy, A.M.; Labeeb, A.Z.; Hassan, D.M. New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-producing Acinetobacter isolates among late-onset VAP patients: Multidrug-resistant pathogen and poor outcome. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Din, R.A.A.; El-Bassat, H.; El-Bedewy, M.; El-Mohamady, H. Prevalence of metallo-β-lactamases producers among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from diabetic foot ulcers. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattouh, M.; El-Din, A. Emergence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in the intensive care unit in Sohag University Hospital, Egypt. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 732–744. [Google Scholar]
- Fouad, M.; Attia, A.S.; Tawakkol, W.M.; Hashem, A.M. Emergence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii harboring the OXA-23 carbapenemase in intensive care units of Egyptian hospitals. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e1252–e1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.M.; Salem, S.T.; Hassan, S.I.M.; Hegab, A.S.; Elkholy, Y.S. Molecular characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Egyptian patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasfi, R.; Rasslan, F.; Hassan, S.S.; Ashour, H.M.; Abd El-Rahman, O.A. Co-Existence of carbapenemase-encoding genes in Acinetobacter baumannii from cancer patients. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olu-Taiwo, M.A.; Opintan, J.A.; Codjoe, F.S.; Obeng Forson, A. Metallo-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Acinetobacter spp. from Clinical Isolates at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Ghana. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3852419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathlouthi, N.; El Salabi, A.A.; Ben Jomàa-Jemili, M.; Bakour, S.; Al-Bayssari, C.; Zorgani, A.A.; Kraiema, A.; Elahmer, O.; Okdah, L.; Rolain, J.-M.; et al. Early detection of metallo-β-lactamase NDM-1- and OXA-23 carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii in Libyan hospitals. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbaj, H.; Seffar, M.; Belefquih, B.; Akka, D.; Handor, N.; Amor, M.; Alaoui, A.E. Prevalence of metallo-β-Lactamases Producing Acinetobacter baumannii in a Moroccan Hospital. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 154921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nogbou, N.-D.; Phofa, D.T.; Nchabeleng, M.; Musyoki, A.M. Investigating multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates at a tertiary hospital in Pretoria, South Africa. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 39, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawi, H.S.; Elhag, K.M.; Mahgoub, E.; Altayb, H.N.; Ntoumi, F.; Elton, L.; McHugh, T.D.; Tembo, J.; Ippolito, G.; Osman, A.Y.; et al. Detection and characterization of carbapenem resistant Gram-negative bacilli isolates recovered from hospitalized patients at Soba University Hospital, Sudan. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateete, D.P.; Nakanjako, R.; Namugenyi, J.; Erume, J.; Joloba, M.L.; Najjuka, C.F. Carbapenem resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii at Mulago Hospital in Kampala, Uganda (2007–2009). SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemura, M.; Wise, M.G.; Hackel, M.A.; Sahm, D.F.; Yamano, Y. In vitro activity of cefiderocol against MBL-producing Gram-negative bacteria collected in North America and Europe in five consecutive annual multinational SIDERO-WT surveillance studies (2014–2019). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Gómez, C.; Blanco, V.M.; Motoa, G.; Correa, A.; Maya, J.J.; de la Cadena Vivas, E.; Perenguez, M.; Rojas, L.; Hernández, A.; Vallejo, M.; et al. Evolución de la resistencia antimicrobiana de bacilos Gram negativos en unidades de cuidados intensivos en Colombia. Bioméd. Rev. Inst. Nac. Salud 2014, 34, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mereuţă, A.I.; Bădescu, A.C.; Dorneanu, O.S.; Iancu, L.S.; Tuchiluş, C.G. Spread of VIM-2 metallo-beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Iaşi, Romania. Rev. Romana Med. Lab. 2013, 21, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, M.; Verma, S.; Venkatesh, V.; Gupta, P.; Tripathi, P.; Agarwal, A.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Arshad, Z.; Prakash, V. Emergence of blaNDM-1 and blaVIM producing Gram-negative bacilli in ventilator-associated pneumonia at AMR Surveillance Regional Reference Laboratory in India. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuschek, E.; Ahman, J.; Webster, C.; Kahlmeter, G. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of colistin—Evaluation of seven commercial MIC products against standard broth microdilution for Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter spp. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galani, I.; Rekatsina, P.D.; Hatzaki, D.; Plachouras, D.; Souli, M.; Giamarellou, H. Evaluation of different laboratory tests for the detection of metallo-β-lactamase production in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daef, E.A.; Mohamed, I.S.; Ahmed, A.S.; Elsherbiny, N.M.; Sayed, I.M. Evaluation of different phenotypic assays for the detection of metallo-β-lactamase production in carbapenem susceptible and resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. J. Am. Sci. 2012, 8, 292–299. [Google Scholar]
- Pandya, N.P.; Nirav, P.; Pandya, S.B.P. Evaluation of various methods for detection of metallo-β-lactamase (mbl) production in gram negative bacilli. Int. J. Biol. Med. Res. 2011, 2, 775–777. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Bliziotis, I.A.; Siempos, I.I. Attributable mortality of Acinetobacter baumannii infections in critically ill patients: A systematic review of matched cohort and case-control studies. Crit. Care Lond. Engl. 2006, 10, R48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kopterides, P. Risk factors for the isolation of multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A systematic review of the literature. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 64, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Bonnin, R.A.; Nordmann, P. Genetic basis of antibiotic resistance in pathogenic Acinetobacter species. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Danziger, L.H. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter infections: An emerging challenge to clinicians. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karageorgopoulos, D.E.; Kelesidis, T.; Kelesidis, I.; Falagas, M.E. Tigecycline for the treatment of multidrug-resistant (including carbapenem-resistant) Acinetobacter infections: A review of the scientific evidence. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulikakos, P.; Tansarli, G.S.; Falagas, M.E. Combination antibiotic treatment versus monotherapy for multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter infections: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Skalidis, T.; Vardakas, K.Z.; Legakis, N.J.; Hellenic Cefiderocol Study Group. Activity of cefiderocol (S-649266) against carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria collected from inpatients in Greek hospitals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Liguori, L.; Covino, S.; Petrucci, F.; Cogliati-Dezza, F.; Curtolo, A.; Savelloni, G.; Comi, M.; Sacco, F.; Ceccarelli, G.; et al. Clinical effectiveness of cefiderocol for the treatment of bloodstream infections due to carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii during the COVID-19 era: A single center, observational study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 43, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, F.; Onorato, L.; De Luca, I.; Macera, M.; Monari, C.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Massa, A.; Gentile, I.; Di Caprio, G.; Pagliano, P.; et al. Outcome of patients with carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections treated with cefiderocol: A multicenter observational study. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Echols, R.; Matsunaga, Y.; Ariyasu, M.; Doi, Y.; Ferrer, R.; Lodise, T.P.; Naas, T.; Niki, Y.; Paterson, D.L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of cefiderocol or best available therapy for the treatment of serious infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria (CREDIBLE-CR): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, pathogen-focused, descriptive, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargianou, M.; Stathopoulos, P.; Vrysis, C.; Tzvetanova, I.D.; Falagas, M.E. New β-Lactam/β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combination Antibiotics. Pathogens 2025, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, K.S.; Shorr, A.F.; Wunderink, R.G.; Du, B.; Poirier, G.E.; Rana, K.; Miller, A.; Lewis, D.; O’Donnell, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sulbactam-durlobactam versus colistin for the treatment of patients with serious infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex: A multicentre, randomised, active-controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority clinical trial (ATTACK). Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafailidis, P.I.; Ioannidou, E.N.; Falagas, M.E. Ampicillin/sulbactam: Current status in severe bacterial infections. Drugs 2007, 67, 1829–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year | Continent | Country | Population, Department, Hospital | Isolate Sources [n/N (%)] | Isolates (n) | Genes (n) | Genotypic Detection; Genes, n/N (%) | Phenotypic Detection; n/N (%), Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesli, 2013 [99] | Africa | Algeria | Three different hospitals in western Algeria, hospital environment and patients admitted to ICU, hematology, surgery, and neurosurgery wards | Tracheal aspirate, urine, rectal swab, wound | A. baumannii (106) A. radioresistens (1) A. nosocomialis (2) A. pittii (4) | blaNDM-1 | 5/113 (4.4) | 5/113 (4.4), DDST |
| Abd El-Glil, 2015 [100] | Africa | Egypt | ICU patients, Benha University, and Benha Teaching hospitals | Sputum [11/40 (17.5)], exudates [9/10 (22.5)], BAL [7/40 (17.5)], blood [6/40 (15)], urine [3/40 (7.5)] | A. baumannii (40) | blaNDM-1 | 5/40 (12.5) | 26/40 (65), E-test 25/40 (62.5), CDT 22/40 (55.0), DDST |
| Elbrolosy, 2019 [101] | Africa | Egypt | Patients with VAP in different ICUs in Menoufia and Kasr Al Ainy University Hospitals | Tracheal aspirate [64/64 (100)] | A. baumannii (37) A. calcoaceticus (15) A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (12) | blaNDM-1 | 42/64 (65.6) | 22/64 (34.4), CDT |
| El-Din, 2014 [102] | Africa | Egypt | Hospitalized patients, Tanta University Hospital | Diabetic ulcers [26/26 (100)] | A. baumannii (26) | blaVIM blaIMP | Total 6/26 (23.1) blaVIM 4/26 (15.4) blaIMP 2/26 (7.7) | 9/26 (34.6), CDT |
| Fattouh, 2014 [103] | Africa | Egypt | ICU patients, Microbiology Department, Sohag University | Endotracheal secretion [7/21 (33.3)], urine [6/21 (28.6)], blood [4/21 (19)], pus [4/21 (19)] | A. baumannii (21) | blaIMP-1 blaVIM-1 | 0/21 (0) | 13/21 (61.9), CDT |
| Fouad, 2013 [104] | Africa | Egypt | ICU patients, three hospitals (6th October hospital, MUST hospital, National Cancer Institute) | Respiratory tract [24/53 (45.3)], wound [22/53 (41.5)], urine [6/53 (11.3)], blood [1/53 (1.9)] | A. baumannii (53) | blaVIM | 1/53 (1.9) | NR |
| Hassan, 2021 [105] | Africa | Egypt | Hospitalized and ICU patients, Kasr Al-Aini hospital | Wound [77/206 (37.4)], respiratory secretions [56/206 (27.2), blood [37/206 (18)], urine [27/206 (13.1)], body fluid and drains [9/206 (4.4)] | A. baumannii (206) | blaVIM blaIMP blaGIM blaSPM blaSIM-1 blaNDM-1 | Total 39/206 (18.9) blaNDM-1 24/106 (11.7) blaSPM 13/206 (6.3) blaVIM 1/206 (0.5) blaSIM-1 1/206 (0.5) | NR |
| Wasfi, 2021 [106] | Africa | Egypt | Cancer patients at the National Cancer Institute, Giza, Egypt, | Blood [48/48 (100)] | A. baumannii (48) | blaNDM blaGIM blaSPM blaSIM blaIMP | 31/48 (63.6) | NR |
| Olu-Taiwo, 2020 [107] | Africa | Ghana | Clinical isolates, patients over 50 years old, Korle-Bu Teaching Hospital | Wound [(45/87 (51.7)], urine [25/87 (28.7)], ear swabs [8/87 (9.2)], eye swabs [6/48 (6.9)] aspirates [3/48 (3.5)] | Acinetobacter spp. (87) | blaNDM | 7/87 (8) | 23/87 (26.4), CDT |
| Mathlouthi, 2016 [108] | Africa | Libya | Clinical isolates, Tripoli Medical Center and Burn and Plastic Surgery Hospital in Tripoli | Wound [15/36 (41.6)], catheter [3/36 (8.3)], septum [3/36 (8.3)], swab [3/36 (8.3)], urine [3/36 (8.3)], blood [2/36 (5.6)], CSF [2/36 (5.6)], chest tube [1/36 (2.8)], endotracheal tube [1/36 (2.8)], GT tube [1/36 (2.8)], mouth [1/36 (2.8)], throat [1/36 (2.8)] | A. baumannii (36) | blaNDM-1 | 7/36 (22.2) | NR |
| Kabbaj, 2013 [109] | Africa | Morocco | Hospitalized patients, ICU, neurosurgery ward, neurology ward, Rabat Specialty Hospital | Respiratory tract (69), urine (22), surgical site infection (5), CSF (4) | A. baumannii (47) | NR | NR | 20/47 (24.6) i |
| Nogbou, 2021 [110] | Africa | South Africa | Clinical isolates, teaching hospital in Pretoria | NR ii | A. baumannii (70) | blaVIM blaIMP-5 blaNDM blaSIM-1 | blaVIM 60/70 (85.7) blaNDM 41/70 (58.6) blaIMP-5 5/70 (7.1) blaSIM-1 2/70 (2.9) | NR |
| Elbadawi, 2021 [111] | Africa | Sudan | Children and adults, neonatal ICU, medicine, pediatric, and surgery wards, ICU, renal unit, Soba University Hospital | Blood (36), wound (24), urine (21), body fluids (7), catheter tips (6), sputum (6) | A. baumannii (36) | blaNDM | 17/36 (47.2) | 19/36 (52.8), E-test |
| Kateete, 2016 [112] | Africa | Uganda | Hospitalized patients, hospital environment, Mulago Hospital in Kampala | Hospital environment [11/40 (27.5)], tracheal aspirate [9/40 (22.5)], ear swabs [8/40 (20)], pus [4/40 (10)], blood [4/40 (10)], sputum [2/40 (5)], body fluids [1/40 (2.5)] | A. baumannii (40) | blaVIM-1 | 2/15 (40) | 3/40 (7.5), DDST |
| Rakhi, 2019 [31] | Asia | Bangladesh | Clinical isolates, Dhaka Medical College Hospital | Blood, pleural fluid, pus, tracheal aspirate, urine, vaginal swab, wound | A. baumannii (4) | blaNDM | blaNDM + blaOXA-48 1/4 (25) | 1/4 (25), CDT |
| Li, 2013 [32] | Asia | China | Medical and surgical wards, ICU, burn department, teaching hospital in Guangzhou | Respiratory tract [35/42 (83.3)], blood [3/42 (7.1)], wound [2/42 (4.8)], urine [1/42 (2.4)], CSF [1/42 (2.4)] | A. baumannii (42) | NR | NR | 1/42 (2.4), E-test |
| Ahir, 2012 [33] | Asia | India | Hospitalized patients, tertiary care teaching hospital, Gujarat | Swab [40/78 (51.3)], urine [8/78 (10.3)], sputum [7/78 (9)], pleural fluid [7/78 (9)], pus [5/78 (6.4)], blood [67.7)], other body fluid [5/78 (6.4)] iii | A. baumannii (40) A. lwoffii (20) A. hemolyticus (10) A. calcoaceticus (8) | NR | NR | 78/750 (10.4), CDT and DDST |
| Archana Rao, 2024 [34] | Asia | India | Pediatrics, medical, surgery, ENT, and gynecology wards, Raja Rajeswari Medical College tertiary care hospital | Sputum [14/25 (56)], pus [4/25 (16)], urine [3/25 (12)], ear discharge [2/25 (8)], blood [2/25 (8)] | Acinetobacter spp. (25) | NR | NR | 5/25 (20), CDT |
| Banerjee, 2015 [35] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences and Hospital, Barabanki | Endotracheal tube [17/67 (25.4)], sputum [16/67 (23.9)], pus [13/67 (19.4)], blood [9/67 (13.4)], urine [7/67 (10.4)], ascitic fluid [5/67 (7.5)] | Acinetobacter spp. (67) | NR | NR | 16/67 (23.9), CDT |
| Binnani, 2018 [36] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, Tertiary Care Institute in the North West Region of Rajasthan, India | Urine [6/21 (28.6)], sputum and respiratory tract specimens [8/21 (38.1)], blood [5/21 (23.8)], pus and other wound discharges [2/21 (9.5)] | Acinetobacter spp. (21) | NR | NR | 8/21 (38.1), CDT |
| De, 2010 [37] | Asia | India | Adults, children, intensive care areas in Lokmanya Tilak Municipal Medical College and Hospital | Blood, endotracheal secretions | Acinetobacter spp. (25) | ΝR | NR | 9/25 (36), DDST |
| Gautam, 2023 [38] | Asia | India | Hospitalized and outpatients, children and adults, Central Referral Hospital located in Gangtok, Sikkim | Endotracheal tube, sputum, pus, urine, blood, catheter tips, urogenital swabs | A. baumannii (307) | blaIMP-1 blaVIM-1 | blaIMP-1 4/100 (4) blaVIM-1 8/100 (8) | NR |
| Girija, 2018 [39] | Asia | India | Patients with severe urinary tract infections | Urine [73/73 (100)] | A. baumannii (73) | blaVIM blaGIM | Total 37/73 (50.7) blaVIM 25/73 (34.2) blaGIM 12/73 (16.4) | 31/73 (42.5), DDST |
| Goel, 2017 [40] | Asia | India | ICU patients, teaching tertiary care hospital | Transtracheal or bronchoscopic aspirates [88/88 (100)] | A. baumannii (88) | NR | NR | 28/37 (75.7), DDST iv |
| Hodiwala, 2013 [41] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates | Blood, catheter tips, CSF, endotracheal secretions, pus, sputum, urine, various body fluids (synovial, ascitic, pleural) | A. baumannii (68) | NR | NR | 9/68 (13.2), CDT and DDST |
| Jena, 2014 [42] | Asia | India | Outpatients, ICU, neonatal ICU, IMS and SUM Hospital in Bhubaneswar | Blood, urine, stool, pus, sputum, wound, tracheal aspiration, CSF, high vaginal swab | Acinetobacter spp. (66) | NR | NR | 23/66 (34.8), DDST |
| Jethwa, 2013 [43] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, tertiary care hospital | Swab [334/854 (39.1)], blood [278/854 (32.6)], body fluids [94/854 (11)], sputum [65/854 (7.6)], pus [39/854 (4.6)], urine [35/854 (4.1)], other [9/854 (1.1)] | Acinetobacter spp. (854) | NR | NR | 68/854 (8), CDT |
| John, 2011 [44] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, ICU patients | Urine, blood, sputum, pus, endotracheal aspirates, bronchial secretions, wound swabs, vaginal swabs | A. baumannii (242) | NR | NR | 36/242 (14.8), DDST |
| Kaur, 2014 [45] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, microbiology department | Respiratory samples, pus, blood, others, urine | A. baumannii (389) | NR | NR | 313/389 (80.5), CDT |
| Kaur, 2018 [46] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, ICU and medical wards, Microbiology Department, Adesh Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Bathinda | Endotracheal tube secretions [34/116 (29.3)], tracheal aspirate [28/116 (24.1)], pus [29/116 (25)], urine [9/116 (7.8)], sputum [7/116 (6)], blood [6/116 (5.2)], various body fluids [3/116 (2.6)] | A. baumannii (116) | NR | NR | 52/116 (44.8), CDT |
| Kumar, 2013 [47] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, tertiary care hospital | NR ii | Acinetobacter spp. (180) | NR | NR | 43/180 (29.3), DDST |
| Pandya, 2016 [48] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, medical wards including ICU, Teaching Hospital in rural Gujarat | Endotracheal secretions [26/81 (32.1)], pus [16/81 (19.8)], tracheostomy secretions [12/81 (14.8)], blood [6/81 (7.4)], sputum [6/81 (7.4)], urine [6/81 (7.4)], broncho-alveolar lavage [3/81 (3.7)], central venous catheter tip [2/81 (2.5)], ascitic fluid [1/81 (1.2)], catheter tip [1/81 (1.2)], drain [1/81 (1.2)], pleural fluid [1/81 (1.2)] | A. baumannii (81) | NR | NR | 24/81 (29.6), CDT |
| Patil, 2021 [49] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, patients with VAP, ICU, tertiary care hospital | Respiratory tract [246/246 (100)] | Total (188) A. baumannii (156) A. lwoffii (15) A. calcoaceticus (9) A. hemotyticus (5) A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (3) | NR | NR | 146/188 (77.7), CDT 141/188 (75), DDST 152/188 (80.9), E-test |
| Rynga, 2015 [50] | Asia | India | ICU (28%), burns (15%), respiratory (15%), surgery (14%), burns ICU (10%), gynecology (9%), orthopedic (5%) wards, respiratory medicine outpatient department (2%) | Endotracheal aspirate [31/100 (31)], pus [28/100 (28)], wound [25/100 (25)], sputum [14/100 (14)], drain fluid [1/100 (1)], high vaginal swab [1/100 (1)] | A. baumannii (100) | blaVIM blaGIM blaSIM blaIMP | Total 18/100 (18) blaVIM 9/100 (9) blaGIM 6/100 (6) blaSIM 2/100 (2) blaIMP 1/100 (1) | 25/100 (25), CDT |
| Saikia, 2023 [51] | Asia | India | Hospitalized patients, ICU, internal medicine wards, Dibrugarh University | NR ii | A. baumannii (172) | blaNDM blaIMP blaVIM | Total 139/172 (80.8) blaNDM 121/172 (70.3) blaIMP 88/172 (51.2) blaVIM 42/172 (24.4) | 144/172 (83.7), CDT 117/172 (68), E-test |
| Singla, 2013 [52] | Asia | India | Outpatients, hospitalized patients, adults and children, tertiary care hospital | Blood, BAL, CSF, endotracheal aspirates, high vaginal swabs, pus, sputum, throat swabs, urine, wound, other body fluids | Total (70) A. baumannii (66) A. lwoffii (4) | NR | NR | A. baumannii 38/66 (57.6) A. lwoffii 1/4 (25), modified CDT method v |
| Sinha, 2013 [53] | Asia | India | Hospitalized patients, tertiary care center | Pus [52/140 (37.1)], blood [32/140 (22.6)], urine [19/140 (13.6)] | Total (140) A. baumannii (129) A. lwoffii (9) A. hemolyticus (2) | blaIMP-1 blaVIM-1 blaVIM-2 | 10/140 (7.1) | 16/140 (11.4), DDST |
| Sugumaran, 2019 [54] | Asia | India | Hospitalized patients (81.2%), outpatients (18.8%), Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, Puducherry | Aspirates, central line catheter tip, ear swab, endotracheal tube, groin swab, pus, sputum, synovial fluid, tissue, urine, wound | A. baumannii (19) | NR | NR | 10/19 (90.9), imipenem CDT 10/19 (90.9), imipenem DDST 13/19 (68.9), ceftazidime CDT 13/19 (68.9), ceftazidime DDST |
| Thakar, 2021 [55] | Asia | India | Hospitalized patients, outpatients, tertiary care hospital | Pus [30/72 (41.7)], respiratory tract [16/72 (22.2)], urine [16/72 (22.2)], blood [6/72 (8.3)], others [4/72 (5.6)] | Acinetobacter spp. (72) | blaVIM | 15/15 (100) | 32/72 (44.4), CDT |
| Tripathi, 2013 [56] | Asia | India | Clinical isolates, microbiology department | NR ii | Acinetobacter spp. (46) | NR | NR | 40/46 (87), CDT |
| Uma Karthika, 2009 [57] | Asia | India | ICU, acute medical care units, Pondicherry Institute of Medical Sciences tertiary care hospital | Blood, CSF, endotracheal tube, urine, wound | A. baumannii (36) | blaIMP-1 blaVIM-2 | Total 23/54 (42.6) blaIMP-1 23/54 (42.6) blaVIM-2 0/54 (0) | 39/54 (72.2), DDST |
| Vamsi, 2021 [58] | Asia | India | Hospitalized patients, SVS Medical College, Hospital in Mahabubnagar | Endotracheal tube [12/17 (70.6)], pus [2/17 (11.8)], blood [1/17 (5.9)], CSF [1/17 (5.9)], urine [1/17 (5.9)] | Acinetobacter spp. (23) | NR | NR | 17/23 (73.9) vi |
| Aghamiri, 2016 [59] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, 11 hospitals in Tehran | Wound [59/176 (33.5)], tracheal aspirate [34/176 (19.3)], urine [24/176 (13.6)], body fluids [20/176 (11.4)], sputum [11/176 (6.3)], catheter [10/176 (5.7)], blood [18/176 (1)] | A. baumannii (176) | blaIMP blaVIM | 123/176 (69.9) | 165/169 (97.6), DDST |
| Jahantigh, 2023 [60] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, Ali Ebne Abitaleb Hospital in Zahedan, Iran | Blood (39.5), endotracheal tube (34.4), wound (20.7) | A. baumannii (372) | NR | NR | 352/372 (94.6), CDT |
| Khaledi, 2019 [61] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, Kashani and Hajar Hospitals in Shahrekord | Blood, CSF, pleural effusion, trachea, urine, wound | A. baumannii (100) | blaVIM-1 blaIMP-1 | Total 26/100 (26) blaVIM-1 23/100 (23) blaIMP-1 3/100 (3) | 65/100 (65), E-test 59/100 (59), CDT |
| Maspi, 2016 [62] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, Baqiyatallah hospitals | Wound, pleural effusion, urine, blood, tracheal aspirate, BAL, sputum, ascites, abscess | A. baumannii (86) | blaIMP blaSPM blaVIM blaGIM blaSIM | Total 23/86 (26.7) blaIMP 13/86 (15.1) blaSPM 4/86 (4.7) blaVIM 2/86 (2.3) blaGIM 2/86 (2.3) blaSIM 2/86 (2.3) | 44/86 (51.2), CDT |
| Moghadam, 2016 [63] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, Nemazee and Faghihi hospitals | Sputum [35/98 (35.7)], wound (15/98 (15.3)], body fluids [13/98 (13.3)], blood [9/98 (9.2)], urine [9/98 (9.2)], endotracheal tube [8/98 (8.2)], CSF [5/98 (5.1)], BAL [2/98 (2)], axillary swab [1/98 (1)], eye swab [1/98 (1)] | A. baumannii (96) | blaIMP blaVIM blaSPM | Total 37/96 (38.5) blaIMP 23/96 (24) blaVIM 14/96 (14.6) blaSPM 0/96 (0) | 43/96 (44.8), E-test |
| Moulana, 2020 [64] | Asia | Iran | Clinical isolates, units at Babol University of Medical Sciences affiliated hospitals | Endotracheal aspirates, sputum [30/50 (60)], ulcers [12/50 (24)], urinary specimens [6/50 (12)], blood [2/50 (4)] | A. baumannii (50) | blaVIM | 13/50 (26) | 15/50 (30), DDST |
| Noori, 2014 [65] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, Loghman Hakim and Milad hospitals | Tracheal tube [57/108 (52.8)], urine [29/108 (26.9)], blood [8/108 (7.4)], pleural fluid [8/108 (7.4)], wound [4/108 (3.7)], other [2/108 (1.9)] | A. baumannii (108) | blaIMP blaSPM | Total 3/108 (2.8) blaIMP 3/108 (2.8) blaSPM 0/108 (0) | 86/108 (88.9), CDT |
| Owlia, 2012 [66] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, burn unit in Motahari Hospital, Tehran | Burns [126/126 (100)] | A. baumannii (126) | NR | NR | 42/126 (33.3), DDST |
| Peymani, 2011 [67] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, tertiary care teaching hospital | Tracheal aspirate [37/100 (37)], urine [21/100 (21)], sputum [9/100 (9)], blood [7/100 (7)], catheter [6/100 (6)], bronchial washings [6/100 (6)], wound [5/100 (5)], abscess [3/100 (3)], CSF [2/100 (2)], ascites [2/100 (2)], pleural effusion [2/100 (2)] | A. baumannii (100) | blaIMP blaVIM | Total 28/100 (28) blaIMP 19/100 (19) blaVIM 9/100 (9) | 31/100 (31), E-test |
| Ranjbar, 2019 [68] | Asia | Iran | Patients with burns, three major hospital centers | Burns [163/163 (100)] | A. baumannii (163) | blaIMP blaVIM | 111/163 (68.1) | 147/163 (90.2), E-test |
| Rezaei, 2018 [69] | Asia | Iran | ICU patients, three teaching hospitals located in Isfahan | Tracheal aspirate (68/100 (68)], CSF [10/100 (10)], wound [9/100 (9)], sputum [3/100 (3)], blood [3/100 (3)], catheters [2/100 (2)], other samples [5/100 (5)] | A. baumannii (100) | blaIMP-1 blaVIM-1 blaVIM-2 blaIMP-2 | Total 38/100 (38) blaIMP-1 21/100 (21) blaVIM-1 7/100 (7) blaVIM-2 6/100 (6) blaIMP-2 4/100 (4) | 36/100 (36), CDT 21/100 (21), DDST |
| Safari, 2013 [70] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, ICU, three educational hospitals in Hamadan city | Tracheal aspirate [74/100 (74)], blood [16/100 (16)], urine [5/100 (5)], sputum [4/100 (4)], wound [1/100 (1)] | A. baumannii (100) | NR | NR | 99/100 (99), E-test |
| Soltani, 2018 [71] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, Nemazee tertiary care hospital | Respiratory tract [61/92 (66.3)], blood [11/92 (12)], skin [8/92 (8.7)], urine [5/92 (5.4)], body fluids [5/92 (5.4)], eyes [2/92 (2.2)] | A. baumannii (92) | blaVIM blaIMP blaSPM | 76/92 (82.6) | NR |
| Vala, 2014 [72] | Asia | Iran | Hospitalized patients, burn unit at Shahid Motahari Hospital | Wound [28/28 (100)] | A. baumannii (28) | blaSPM blaIMP blaVIM blaDIM blaNDM blaGIM | blaSPM 1/28 (3.6) | 12/28 (42.9), CDT |
| Al Marjani, 2013 [73] | Asia | Iraq | Clinical isolates, medical centers in Baghdad | NR ii | A. baumannii (17) | blaIMP-1 | 3/17 (42.8) | 7/17 (41.1), CDT |
| Anoar, 2014 [74] | Asia | Iraq | Clinical isolate, Burn and Plastic Surgery Hospital in Sulaimani city | Wound [44/44 (100)] | Acinetobacter spp. (44) | blaIMP blaVIM | blaIMP 19/44 (43.2) blaVIM 5/44 (11.4) | NR |
| Numan, 2022 [75] | Asia | Iraq | Hospitalized patients, four hospitals in Baghdad | Sputum [35/69 (50.7)], blood [21/69 (30.4)], urine [9/69 (13)], CSF [2/69 (2.9)], wound [2/69 (2.9)] | A. baumannii (69) | NR | NR | 51/69 (74), CDT |
| Radhi, 2019 [76] | Asia | Iraq | Outpatients, Hillah Teaching Hospital and Babylon Teaching Hospital for Maternity and Pediatrics | Burns [24/30 (80)], blood [4/30 (13.3)], urine [1/30 (3.3)], wound [1/30 (3.3)] | A. baumannii (30) | NR | NR | 22/30 (73.3), E-test |
| Smail, 2019 [77] | Asia | Iraq | Hospitalized patients, ICU, three educational hospitals in Hamadan city | Blood, CSF, pleural fluid, pus, sputum, urine, wound | A. baumannii (112) | NR | NR | 112/112 (100) vii |
| Kishii, 2014 [78] | Asia | Japan | Clinical isolates, two university hospitals | Blood [123/123 (100)] | Acinetobacter spp. (123) | blaIMP | 3/123 (2.4) | NR |
| Yamamoto, 2013 [79] | Asia | Japan | Clinical isolates, three university hospitals, two city hospitals in Kyoto and Shiga Prefecture | NR ii | Acinetobacter spp. (82) | blaIMP blaVIM blaNDM-1 | 48/54 (88.9) | 44/82 (53.7) viii |
| Soudeiha, 2018 [80] | Asia | Lebanon | Hospitalized patients, Saint George Hospital University Medical Center | Respiratory tract [62/100 (62)], wound [21/100 (21)], urine [10/100 (10)], blood [4/100 (4)], catheters [3/100 (3)] | Total (100) A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (95) A. hemolyticus (3) A. radioresistens (1) A. junii (1) | blaVIM blaIMP blaNDM | 0/100 (0) | Total 4/100 (4) ix |
| Maziz, 2021 [81] | Asia | Malaysia | Clinical isolates, Selayang Hospital, Kuala Lumpur | Urine [16/50 (38)], blood [14/50 (26)], pus [7/50 (14)], skin [5/50 (10)], respiratory secretions [3/50 (6)] and sputum [3/50 (6)] | Acinetobacter spp. (50) | NR | NR | 0/50 (0), DDST and E-test |
| Koirala, 2017 [82] | Asia | Nepal | Clinical isolates, B&B Hospital Kathmandu | Pus [36/109 (33)], suction tip [23/109 (21.1)], sputum [19/109 (17.4)], tracheostomy [16/109 (14.7)], catheter tip [7/109 (6.4)], central venous catheter [6/109 (5.5)], body fluids [1/109 (0.9)], urine [1/109 (0.9)] | Acinetobacter spp. (109) | NR | NR | 48/109 (44), CDT |
| Kumari, 2021 [117] | Asia | Nepal | Clinical isolates, Koirala Institute of Health Sciences | Blood, pus, urine, sputum, endotracheal aspirate, exudate body fluid, central venous catheter, CSF, high vaginal swab, nasal swab, tissue, semen | Total (324) A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (167) A. lwoffii (83) A. hemolyticus (38) A. radioresistens (30) A. junii (6) | blaNDM-1 | Total 33/324 (10.2) A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex 28/167 (16.8) A. junii 1/6 (16.7) A. hemolyticus 2/38 (5.2) A. lwoffii 2/83 (2.4) | Total 70/324 (21.6) A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex 56/167 (33.5) A. lwoffii 3/83 (3.6) A. hemolyticus 7/38 (18.4) A. radioresistens 3/30 (10.0) A. junii 1/6 (16.7), EDTA-modified carbapenem inactivation method |
| Mishra, 2012 [84] | Asia | Nepal | Clinical isolates, bacteriology laboratory at Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital | Lower respiratory tract [60/60 (100)] | Total (62) A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (60) A. lwoffii (2) | NR | NR | 3/62 (4.8), CDT and DDST |
| Pandey, 2021 [85] | Asia | Nepal | Clinical isolates, 100-bed hospital in the capital city of Nepal | Sputum [25/39 (64.1)], urine [9/39 (23.1)], pus [2/39 (5.1)], catheters and tubes [2/39 (5.1)], blood [1/39 (2.6)] | A. baumannii (39) | NR | NR | 4/39 (10.3), CDT and E-test |
| Pathak, 2017 [86] | Asia | Nepal | Clinical isolates, Shahid Gangalal National Heart Centre, Kathmandu, Nepal | Urine [5/11 (45.5)], endotracheal tube [2/11 (18.2)], suction tip [2/11 (18.2)], central venous catheter tip [1/11 (9.1)], pericardial fluid [1/11 (9.1)] | Acinetobacter spp. (11) | NR | NR | 1/11 (9.1), CDT |
| Sakuma, 2024 [87] | Asia | Nepal | Clinical isolates, university hospital in Nepal | Respiratory tract [28/66 (42.4)], pus [16/66 (24.2)], blood [9/66 (13.6)], wound [7/66 (10.6)], urine [3/66 (4.5)], body fluids [3/66 (4.5)] | A. baumannii (66) | blaNDM-1 | 26/66 (39.4) | NR |
| Shrestha, 2015 [88] | Asia | Nepal | Hospitalized patients, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital | Respiratory tract [60/122 (49.2)], pus [31/122 (25.4)], urine [13/122 (10.7)] | A. baumannii (122) | NR | NR | 50/122 (41), CDT |
| Thapa, 2017 [89] | Asia | Nepal | Hospitalized and outpatients, Nepal Medical College, Kathmandu | Pus [21/58 (36.2)], urine [21/58 (36.2], sputum [10/58 17.2)], body fluids [6/58 (10.3)] | A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (58) | NR | NR | 18/58 (31), CDT |
| Yadav, 2020 [90] | Asia | Nepal | Hospitalized patients, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital | Respiratory tract [76/161 (47.2)], pus [44/161 (27.3)], CSF [18/161 (11.1)], urine [11/161 (6.8)], blood [10/161 (6.2)], catheters [2/161 (1.2)] | A. baumannii (161) | ΝR | NR | 109/161 (67.7), CDT |
| Anwar, 2016 [91] | Asia | Pakistan | Clinical isolates, children, Children’s Hospital and Institute of Child Health Lahore | Blood, body fluids, pus, sputum, tracheal secretions, urine | A. baumannii (66) | NR | NR | 63/66 (95.5), CDT 51/66 (72.3), DDST |
| Hasan, 2014 [92] | Asia | Pakistan | Clinical isolates, patients with secondary or nosocomial infections from different hospitals in Pakistan | Catheters and tubes [5/19 (26.3)], tracheal aspirate [4/19 (21.1)], blood [4/19 (21.1)], pus [2/19 (10.5)], wound [2/19 (10.5)], body fluids [1/19 (5.3)] | A. baumannii (90) | blaNDM-1 | 1/90 (1.1) | NR |
| Irfan, 2008 [93] | Asia | Pakistan | Clinical isolates, Aga Khan University Hospital | Blood, respiratory secretions, urine, wound | Acinetobacter spp. (90) | NR | NR | 83/90 (92.2), CDT |
| Rashid, 2020 [94] | Asia | Pakistan | Clinical isolates, tertiary care referral hospitals | Blood, CSF, pus, sputum, urine, vaginal swab | A. baumannii (12) | blaNDM-1 | 2/12 (16.7) | (5), DDST |
| Sajjad, 2019 [95] | Asia | Pakistan | Clinical isolates, Lahore General Hospital | NR ii | A. baumannii (13) A. junii (1) | NR | NR | A. baumannii 11/13 (84.6), DDST A. junii 0/1 (0), DDST |
| Shah, 2019 [96] | Asia | Saudi Arabia | Clinical isolates, King Abdulaziz University Hospital, an 845-bed major territory care hospital in Jeddah | Tracheal aspirate [29/135 (21.5)], blood [28/135 (20.7)], wound [19/135 (14.1), urine [19/135 (14.1)], body fluids [7/135 (5.2)], catheters and tubes [9/135 (6.7)], skin [5/135 (3.7)], others [19/135 (14.1)] | A. baumannii (135) | blaIMP blaVIM blaNDM | blaIMP 113/135 (83.7) blaVIM 25/135 (18.5) blaNDM 2/135 (1.5) | NR |
| Sung, 2015 [97] | Asia | South Korea | Clinical isolates, university hospital in Daejeon | Urine [18/21 (85.7)], sputum [2/21 (9.5)], wound [1/21 (4.8)] | A. pittii (21) | blaIMP-1 blaNDM-1 | blaIMP-1 19/21 (90.5) blaNDM-1 2/21 (9.5) | NR |
| Lee, 2008 [98] | Asia | Taiwan | Clinical isolates, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital | NR ii | Total (185) A. baumannii (184) A. hemolyticus (1) | blaVIM-2 blaVIM-3 blaVIM-11 blaIMP-8 | Total 79/185 (42.7) A. hemolyticus 1/1 (100) A. baumannii 78/184 (42.3) | Total 80/185 (43.2), E-test A. baumannii 79/184 (42.9) A. hemolyticus 1/1 (100) |
| Mereuţă, 2013 [115] | Europe | Romania | Clinical isolates, five university hospitals in Iasi | Urine [5/16 (31.3)], pus [5/16 (31.3)], sputum [3/16 (18.8)], tracheal aspirate [1/16 (6.3)], blood [1/16 (6.3)], CSF [1/16 (6.3)] | A. baumannii (16) | blaVIM | 2/16 (12.5) | 3/16 (18.8), E-test |
| Takemura, 2023 [113] | North America | Canada | Clinical specimens | NR ii | A. baumannii (20) | blaIMP blaVIM blaNDM blaGIM | blaNDM 1/20 (5) | NR |
| Takemura, 2023 [113] | North America | USA | Clinical isolates, SIDERO-WT surveillance studies | NR ii | A. baumannii (20) | blaIMP blaVIM blaNDM blaGIM | blaNDM 2/20 (10) | NR |
| Hernández-Gómez, 2014 [114] | South America | Colombia | Adult, pediatric, and neonatal ICU patients, 23 clinics and hospitals | Blood, urine, respiratory tract, other | A. baumannii (241) | blaVIM | 0/241 (0) | NR |
| Author, Year | Continent | Country | Isolates (n) | Resistance n/N (%) to Antimicrobial Agent(s) i |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abd El-Glil, 2015 [100] | Africa | Egypt | A. baumannii (40) | 5/5 (100) imipenem, meropenem, piperacillin, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, cefepime, aztreonam, ciprofloxacin 4/5 (80) amikacin 3/5 (60) gentamicin |
| Elbrolosy, 2019 [101] | Africa | Egypt | A. baumannii (37), A. calcoaceticus (15), A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (12) | 42/42 (100) imipenem, meropenem, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefepime, cotrimoxazole, piperacillin–tazobactam, tetracycline, aztreonam, ciprofloxacin, amikacin 6/42 (14.3) colistin |
| Olu-Taiwo, 2020 [107] | Africa | Ghana | Acinetobacter spp. (87) | 23/23 (100) ampicillin, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, cefuroxime, meropenem 22/23 (95.7) amoxicillin–clavulanate, levofloxacin 21/23 (91.3) gentamicin 20/23 (87) ciprofloxacin 17/23 (73.9) cotrimoxazole 14/23 (60.9) nitrofurantoin 8/23 (34.8) amikacin |
| Kateete, 2016 [112] | Africa | Uganda | A. baumannii (40) | 3/3 (100) ciprofloxacin, imipenem, meropenem, piperacillin–tazobactam 2/3 (66.7) gentamicin, ceftazidime, aztreonam, amikacin |
| Archana Rao, 2024 [34] | Asia | India | Acinetobacter spp. (25) | 0/5 (0) colistin, tigecycline 5/5 imipenem and/or meropenem |
| Binnani, 2018 [36] | Asia | India | Acinetobacter spp. (21) | 8/8 (100) ceftazidime, doxycycline, imipenem, meropenem, nitrofurantoin 7/8 (87.5) ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin 5/8 (62.5) amikacin 0/8 (0) colistin, polymyxin B |
| De, 2010 [37] | Asia | India | Acinetobacter spp. (25) | 9/9 (100) imipenem, gentamicin, amikacin, netilmicin, amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefepime, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, piperacillin, piperacillin–tazobactam |
| John, 2011 [44] | Asia | India | A. baumannii (242) | 36/36 (100) ciprofloxacin, piperacillin, gentamicin, ceftazidime 0/36 (0) tigecycline |
| Kaur, 2014 [45] | Asia | India | Total (1017), A. baumannii (964), A. lwoffii (48), A. hemolyticus (5) | A. baumannii: ii 313/313 (100) imipenem 309/313 (98.7) ceftazidime 307/313 (98.1) ciprofloxacin 305/313 (97.4) cotrimoxazole 304/313 (97.1) cefepime 295/313 (94.2) gentamicin 285/313 (91.1) piperacillin 273/313 (87.2) amikacin 209/313 (66.8) netilmicin 179/313 (57.2) piperacillin–tazobactam |
| Pandya, 2016 [48] | Asia | India | A. baumannii (81) | 24/24 (100) ampicillin–sulbactam, ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, ticarcillin–clavulanic acid, ceftriaxone, piperacillin |
| Patil, 2021 [49] | Asia | India | Total (188), A. baumannii (156), A. lwoffii (15), A. calcoaceticus (9), A. hemotyticus (5), A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (3) | 164/164 (100) piperacillin, piperacillin–tazobactam, ciprofloxacin, ceftazidime, cefepime, imipenem, meropenem 162/164 (98.8) ceftriaxone 152/164 (92.7) tetracycline 147/164 (89.6) doxycycline 143/164 (87.2) gentamicin 137/164 (83.5) amikacin 131/164 (79.9) cotrimoxazole |
| Singla, 2013 [52] | Asia | India | Total (70), A. baumannii (66), A. lwoffii (4) | 39/39 (100) cefepime, ceftriaxone, imipenem 38/39 (97.4) amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, ticarcillin–clavulanic acid 37/39 (94.8) cefotaxime, ceftazidime 35/39 (89.7) cotrimoxazole 34/39 (87.1) gentamicin 33/39 (84.6) doxycycline 30/39 (76.9) amikacin, ciprofloxacin 27/39 (69.2) netilmicin 25/39 (64.1) piperacillin–tazobactam |
| Thakar, 2021 [55] | Asia | India | Acinetobacter spp. (72) | 32/32 (100) ampicillin–sulbactam, carbapenem, third and fourth generation cephalosporins 29/32 (90.6) fluoroquinolones 28/32 (87.5) amikacin 0/32 (0) colistin |
| Khaledi, 2019 [61] | Asia | Iran | A. baumannii (100) | 65/65 (100) imipenem, meropenem |
| Owlia, 2012 [66] | Asia | Iran | A. baumannii (126) | 42/42 (100) cefotaxime, ceftazidime, piperacillin–tazobactam, aztreonam, ciprofloxacin, amikacin, imipenem, piperacillin, ticarcillin, ticarcillin–clavulanic acid, kanamycin 12/42 (28.6) tobramycin, gentamicin 0/42 (0) colistin |
| Soltani, 2018 [71] | Asia | Iran | A. baumannii (92) | 76/76 (100) cotrimoxazole, ciprofloxacin, imipenem, meropenem, ticarcillin–clavulanic acid, levofloxacin 0/76 (0) colistin, polymyxin B |
| Al-Marjani, 2013 [73] | Asia | Iraq | A. baumannii (17) | 7/7 (100) cefoxitin, ceftriaxone, amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, cefepime, aztreonam |
| Kishii, 2014 [78] | Asia | Japan | Acinetobacter spp. (123) | 3/3 (100) imipenem, meropenem 2/3 (66.7) levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin 1/3 (33.3) amikacin |
| Mishra, 2012 [84] | Asia | Nepal | A. baumannii–calcoaceticus complex (60) | 2/3 (66.7) imipenem, meropenem 0/3 (0) colistin, polymyxin B |
| Pandey, 2021 [85] | Asia | Nepal | A. baumannii (39) | 4/4 (100) imipenem 0/4 (0) polymyxin B |
| Sakuma, 2024 [87] | Asia | Nepal | A. baumannii (66) | 26/26 (100) imipenem, meropenem, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, amikacin, ciprofloxacin 0/26 (0) tigecycline |
| Irfan, 2008 [93] | Asia | Pakistan | Acinetobacter spp. (90) | 83/83 (100) imipenem |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falagas, M.E.; Kontogiannis, D.S.; Zidrou, M.; Filippou, C.; Tansarli, G.S. Global Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Metallo-β-Lactamase (MBL)-Producing Acinetobacter Clinical Isolates: A Systematic Review. Pathogens 2025, 14, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060557
Falagas ME, Kontogiannis DS, Zidrou M, Filippou C, Tansarli GS. Global Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Metallo-β-Lactamase (MBL)-Producing Acinetobacter Clinical Isolates: A Systematic Review. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060557
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalagas, Matthew E., Dimitrios S. Kontogiannis, Maria Zidrou, Charalampos Filippou, and Giannoula S. Tansarli. 2025. "Global Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Metallo-β-Lactamase (MBL)-Producing Acinetobacter Clinical Isolates: A Systematic Review" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060557
APA StyleFalagas, M. E., Kontogiannis, D. S., Zidrou, M., Filippou, C., & Tansarli, G. S. (2025). Global Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Metallo-β-Lactamase (MBL)-Producing Acinetobacter Clinical Isolates: A Systematic Review. Pathogens, 14(6), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060557






