Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of aEPEC/STEC Escherichia coli Pathotypes with Serotype Links to Shigella boydii 16 Isolated from Irrigation Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Isolation and Biochemical Characterization of E. coli
2.3. Genomic DNA Extraction
2.4. Molecular Identification of E. coli
2.5. Determination of Diarrheagenic Pathotypes
2.6. Adherence Assay
2.7. Serotyping
2.8. Phylogenetic Group Determination
2.9. Virulence-Associated Genes
2.10. Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus-Polymerase Chain Reaction (ERIC-PCR)
2.11. Antibiotic Susceptibility
2.12. Molecular Identification of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamases (ESBLs) and Non-ESBL Genes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Diarrheagenic Pathotypes
3.2. Serotyping
3.3. Phylogenetic Group Determination
3.4. Virulence-Associated Genes and ERIC-PCR
3.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamases Genes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banach, J.L.; Van Der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Microbiological reduction strategies of irrigation water for fresh produce. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; He, Z.; Geng, X.; Tang, M.; Hao, R.; Wang, S.; Shang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Pu, W. The emergence of multi-drug resistant and virulence gene carrying Escherichia coli strains in the dairy environment: A rising threat to the environment, animal, and public health. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1197579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Tang, M.; Aqib, A.I.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, J.; Hao, R.; Wang, S.; et al. Dairy farm waste: A potential reservoir of diverse antibiotic resistance and virulence genes in aminoglycoside- and beta-lactam-resistant Escherichia coli in Gansu Province, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, A.M.; Yang, Z. Detection and occurrence of indicator organisms and pathogens. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, T.H.; Michalski, J.; Luo, Q.; Shetty, A.C.; Daugherty, S.C.; Fleckenstein, J.M.; Rasko, D.A. Comparative genomics and transcriptomics of Escherichia coli isolates carrying virulence factors of both enteropathogenic and enterotoxigenic E. coli. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulu, B.M.; Belete, M.A.; Demlie, T.B.; Tassew, H.; Sisay Tessema, T. Characteristics of Pathogenic Escherichia coli associated with diarrhea in children under five years in Northwestern Ethiopia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; Hilbert, F.; Lindqvist, R.; et al. Pathogenicity assessment of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and the public health risk posed by contamination of food with STEC. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e05967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana de Mello Santos, C.; Santos, F.F.; Silva, R.M.; Gomes, T.A.T. Diversity of hybrid- and hetero-pathogenic Escherichia coli and their potential implication in more severe diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabulsi, L.R.; Keller, R.; Gomes, T.A.T. Typical and Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Angeles, M.G. Principales características y diagnóstico de los grupos patógenos de Escherichia coli. Salud Public. Mex. 2002, 44, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Eslava, C.; Perea, L.M.; Inzunza, A.; Delgado, G.; Morales-Espinosa, R.; Cheasty, T.; Cravioto, A. New enterovirulent Escherichia coli serogroup 64474 showing antigenic and genotypic relationships to Shigella boydii 16. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shoaib, M.; Tang, M.; Awan, F.; Aqib, A.I.; Hao, R.; Ahmad, S.; Wang, S.; Shang, R.; Pu, W. Genomic characterization of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing E. coli harboring blaOXA−1-catB3-arr-3 genes isolated from dairy farm environment in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 3526395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Gul, S.; Majeed, S.; He, Z.; Hao, B.; Tang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Pu, W. Pathogenomic characterization of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli strains carrying wide efflux-associated and virulence genes from the dairy farm environment in Xinjiang, China. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciso-Martínez, Y.; Barrios-Villa, E.; Sepúlveda-Moreno, C.O.; Ballesteros-Monrreal, M.G.; Valencia-Rivera, D.E.; González-Aguilar, G.A.; Martínez-Téllez, M.A.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F. Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant E. coli strains in a local farm and packing facilities of Honeydew melon in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Moreno, E.; Caporal-Hernandez, L.; Mendez-Pfeiffer, P.A.; Enciso-Martinez, Y.; De la Rosa López, R.; Valencia, D.; Arenas-Hernández, M.M.P.; Ballesteros-Monrreal, M.G.; Barrios-Villa, E. Characterization of diarreaghenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy donors, including a triple hybrid strain. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning a Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Pr: Long Island, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Carreón León, E.A. Estudio Molecular de la Resistencia y Virulencia de Cepas de Escherichia coli Productoras de β-lactamasas de Espectro Extendido Aisladas de Vegetales Crudo; Benemérita Universidad Autonóma de Puebla: Puebla, Mexico, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.I.; McQuillan, J.; Taiwo, M.; Parks, R.; Stenton, C.A.; Morgan, H.; Mowlem, M.C.; Lees, D.N. A highly specific Escherichia coli qPCR and its comparison with existing methods for environmental waters. Water Res. 2017, 126, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros-Monrreal, M.G.; Arenas-Hernández, M.M.P.; Barrios-Villa, E.; Juarez, J.; Álvarez-Ainza, M.L.; Taboada, P.; De la Rosa-López, R.; Bolado-Martínez, E.; Valencia, D. Bacterial morphotypes as important trait for uropathogenic E. coli diagnostic; a virulence-phenotype-phylogeny study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orskov, F.; Orskov, I. Serotyping of Escherichia coli; Bergan, T., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix Murray, K.R. Caracterización Genotípica, Mediante ERIC-PCR, de Aislamientos Clínicos de Escherichia coli y Klebsiella Pneumoniae Productoras de Beta-lactamasas de Espectro Extendido; Universidad de Sonora: Hermosillo, México, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Bethlehem, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alfinete, N.W.; Bolukaoto, J.Y.; Heine, L.; Potgieter, N.; Barnard, T.G. Virulence and phylogenetic analysis of enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from children with diarrhoea in South Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 114, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Ambikan, A.; Jernberg, C.; Ehricht, R.; Scheutz, F.; Xiong, Y.; Matussek, A. Molecular characterization and comparative genomics of clinical hybrid Shiga toxin-producing and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC/ETEC) strains in Sweden. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolukaoto, J.Y.; Singh, A.; Alfinete, N.; Barnard, T.G. Occurrence of hybrid diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli associated with multidrug resistance in environmental water, Johannesburg, South Africa. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Meniño, I.; García, V.; Alonso, M.P.; Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, J.; Mora, A. Clones of enterotoxigenic and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli implicated in swine enteric colibacillosis in Spain and rates of antibiotic resistance. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 252, 108924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Del Valle, M.D.; De la Garza-García, J.A.; Díaz-Aparicio, E.; Valdivia-Flores, A.G.; Cisneros-Guzmán, L.F.; Rosario, C.; Manjarrez-Hernández, Á.H.; Navarro, A.; Xicohtencatl-Cortes, J.; Maravilla, P.; et al. Characterization of Escherichia coli strains from red deer (Cervus elaphus) faeces in a Mexican protected natural area. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2016, 62, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Manure-borne pathogens as an important source of water contamination: An update on the dynamics of pathogen survival/transport as well as practical risk mitigation strategies. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 227, 113524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandie, C.E.; Ogunniyi, A.D.; Ferro, S.; Hall, B.; Drigo, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Venter, H.; Myers, B.; Deo, P.; Donner, E.; et al. Disinfection options for irrigation water: Reducing the risk of fresh produce contamination with human pathogens. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2144–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwknegt, M.; Verhaelen, K.; Rzeżutka, A.; Kozyra, I.; Maunula, L.; von Bonsdorff, C.-H.; Vantarakis, A.; Kokkinos, P.; Petrovic, T.; Lazic, S.; et al. Quantitative farm-to-fork risk assessment model for norovirus and hepatitis A virus in European leafy green vegetable and berry fruit supply chains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 198, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.I.; Selma, M.V.; Suslow, T.; Jacxsens, L.; Uyttendaele, M.; Allende, A. Pre- and postharvest preventive measures and intervention strategies to control microbial food safety hazards of fresh leafy vegetables. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, A.; Lan, R.; Reeves, P.R. Evolutionary changes of the flhDC flagellar master operon in Shigella strains. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4295–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Yao, T.; Yang, W.; Yang, Q.; Yan, J.; Yang, B. Regulation of flagellar motility and biosynthesis in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chart, H.; Daniel, R.M.A.; Cheasty, T. The expression of lipopolysaccharide by strains of Shigella dysenteriae, Shigella flexneri and Shigella boydii and their cross-reacting strains of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 292, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowrouzian, F.L.; Adlerberth, I.; Wold, A.E. Enhanced persistence in the colonic microbiota of Escherichia coli strains belonging to phylogenetic group B2: Role of virulence factors and adherence to colonic cells. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clermont, O.; Gordon, D.; Denamur, E. Guide to the various phylogenetic classification schemes for Escherichia coli and the correspondence among schemes. Microbiology 2015, 161, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corzo-Ariyama, H.A.; García-Heredia, A.; Heredia, N.; García, S.; León, J.; Jaykus, L.A.; Solís-Soto, L. Phylogroups, pathotypes, biofilm formation and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolates in farms and packing facilities of tomato, jalapeño pepper and cantaloupe from Northern Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Johnston, B.D.; Delavari, P.; Thuras, P.; Clabots, C.; Sadowsky, M.J. Phylogenetic backgrounds and virulence-associated traits of Escherichia coli Isolates from surface waters and diverse animals in Minnesota and Wisconsin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01329-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Dai, S.; Gu, H.; Hao, L.; Ye, H.; Wang, Z. Advances in aptasensors for the detection of food contaminants. Analyst 2016, 141, 3942–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.C.; Penha Filho, R.A.C.; Kuaye, A.P.Y.; Andrade, L.N.; Chang, Y.-F.; Darini, A.L.C. Virulence potential of commensal multidrug resistant Escherichia coli isolated from poultry in Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servin, A.L. Pathogenesis of Afa/Dr diffusely adhering Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 264–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanli, L.; Dagi, H.T.; Arslan, U. Investigation of Antibiotic susceptibility and virulence genes in Escherichia coli strains isolated from blood and urine samples. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2022, 17, 098–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailovskaya, V.S.; Remezovskaya, N.B.; Zhdanova, I.N.; Starčič Erjavec, M.; Kuznetsova, M.V. Virulence potential of faecal Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy cows and calves on farms in Perm Krai. Vavilov J. Genet. Breed. 2022, 26, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, T.; Han, D.; Jang, J.; Widmer, K.; Ko, G.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Hur, H.-G. Genotypic and phenotypic trends in antibiotic resistant pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from humans and farm animals in South Korea. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.-Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.-K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, N.G.; Diez-Santos, I.; Abbott, L.R.; Maxwell, A. Quinolones: Mechanism, lethality and their contributions to antibiotic resistance. Molecules 2020, 25, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avalos, E.; Catanzaro, D.; Catanzaro, A.; Ganiats, T.; Brodine, S.; Alcaraz, J.; Rodwell, T. Frequency and geographic distribution of gyrA and gyrB mutations associated with fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates: A Systematic review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Mechanisms of drug resistance: Quinolone resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1354, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, M.; Bee, G. Invited review: Tannins as a potential alternative to antibiotics to prevent coliform diarrhea in weaned pigs. Animal 2020, 14, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. El Plan De Acción de la FAO Sobre La Resistencia a los Antimicrobianos 2016–2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, F.; Eloe-Fadrosh, E.A.; Bowers, R.M.; Jarett, J.; Nielsen, T.; Ivanova, N.N.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Woyke, T. Towards a balanced view of the bacterial tree of life. Microbiome 2017, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekenidis, M.-T.; Qi, W.; Hummerjohann, J.; Zbinden, R.; Walsh, F.; Drissner, D. Antibiotic-resistant indicator bacteria in irrigation water: High prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, L.; Irazabal, J.; Cardenas, P.; Graham, J.P.; Trueba, G. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producing-Escherichia coli isolated from irrigation waters and produce in Ecuador. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 709418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Dasí, D.; González, A.; Ferrús, M.A.; Castillo, M.Á. Occurrence of antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes in agricultural irrigation waters from Valencia city (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizalez-Roman, A.; Velazquez-Roman, J.; Valdez-Flores, M.A.; Flores-Villaseñor, H.; Vidal, J.E.; Muro-Amador, S.; Guadrón-Llanos, A.M.; Gonzalez-Nuñez, E.; Medina-Serrano, J.; Tapia-Pastrana, G.; et al. Detection of antimicrobial-resistance diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains in surface water used to irrigate food products in the northwest of Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 304, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwu, C.D.; Kayode, A.J.; Igere, B.E.; Okoh, A.I. High Levels of multi drug resistant Escherichia coli pathovars in preharvest environmental samples: A ticking time bomb for fresh produce related disease outbreak. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 858964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livermore, D.M.; Canton, R.; Gniadkowski, M.; Nordmann, P.; Rossolini, G.M.; Arlet, G.; Ayala, J.; Coque, T.M.; Kern, I.; Luzzaro, F.; et al. CTX-M: Changing the face of ESBLs in Europe. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 59, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, K.R.S.; Fabbricotti, S.H.; Fagundes-Neto, U.; Scaletsky, I.C.A. Single multiplex assay to identify simultaneously enteropathogenic, enteroaggregative, enterotoxigenic, enteroinvasive and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains in Brazilian children. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 267, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratamico, P.M.; Sackitey, S.K.; Wiedmann, M.; Deng, M.Y. Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2188–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, G.; Giron, J.A.; Valmassoi, J.; Schoolnik, G.K. Multi-gene amplification: Simultaneous detection of three virulence genes in diarrhoeal stool. Mol. Microbiol. 1989, 3, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, K.R.S.; Fagundes-Neto, U.; Scaletsky, I.C.A. Evaluation of multiplex PCRs for diagnosis of infection with diarrheagenic Escherichia coli and Shigella spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5849–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansan-Almeida, R.; Pereira, A.L.; Giugliano, L.G. Diffusely adherent Escherichia coli strains isolated from children and adults constitute two different populations. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clermont, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bingen, E. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4555–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Monrreal, M.G.; Arenas-Hernández, M.M.P.; Enciso-Martínez, Y.; Martinez de la Peña, C.F.; Rocha-Gracia, R.; Lozano-Zarain, P.; Navarro-Ocaña, A.; Martínez-Laguna, Y.; de la Rosa-López, R. Virulence and resistance determinants of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from pregnant and non-pregnant women from two states in Mexico. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Siek, K.E.; Johnson, S.J.; Nolan, L.K. DNA Sequence of a ColV plasmid and prevalence of selected plasmid-encoded virulence genes among avian Escherichia coli strains. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, M.; Alonso, M.P.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; Dahbi, G.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.E.; López, C.; Cortés, P.; Llagostera, M.; Leflon-Guibout, V.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Escherichia coli producing extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Lugo (Spain): Dissemination of clone O25b:H4-ST131 producing CTX-M-15. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.R.; Stell, A.L. Extended virulence genotypes of Escherichia coli strains from patients with urosepsis in relation to phylogeny and host compromise. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiba, M.R.; Yano, T.; da Silva Leite, D. Genotypic characterization of virulence factors in Escherichia coli strains from patients with cystitis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2008, 50, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza-Ramos, U.; Davila, G.; Gonzalez, V.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.; López-Collada, V.R.; Alcantar-Curiel, D.; Newton, O.; Silva-Sanchez, J. The blaSHV-5 gene is encoded in a compound transposon duplicated in tandem in Enterobacter cloacae. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Gracia, R.; Ruiz, E.; Romero-Romero, S.; Lozano-Zarain, P.; Somalo, S.; Palacios-Hernández, J.M.; Caballero-Torres, P.; Torres, C. Detection of the plasmid-borne quinolone resistance determinant qepA1 in a CTX-M-15-producing Escherichia coli strain from Mexico. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamane, K.; Wachino, J.; Suzuki, S.; Arakawa, Y. Plasmid-mediated qepa gene among Escherichia coli clinical isolates from Japan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1564–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhar, F.; Seyedpour, S. Prevalence of qnr and aac(6’)-Ib-cr genes in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae from Imam Hussein hospital in Tehran. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 40, 515–521. [Google Scholar]

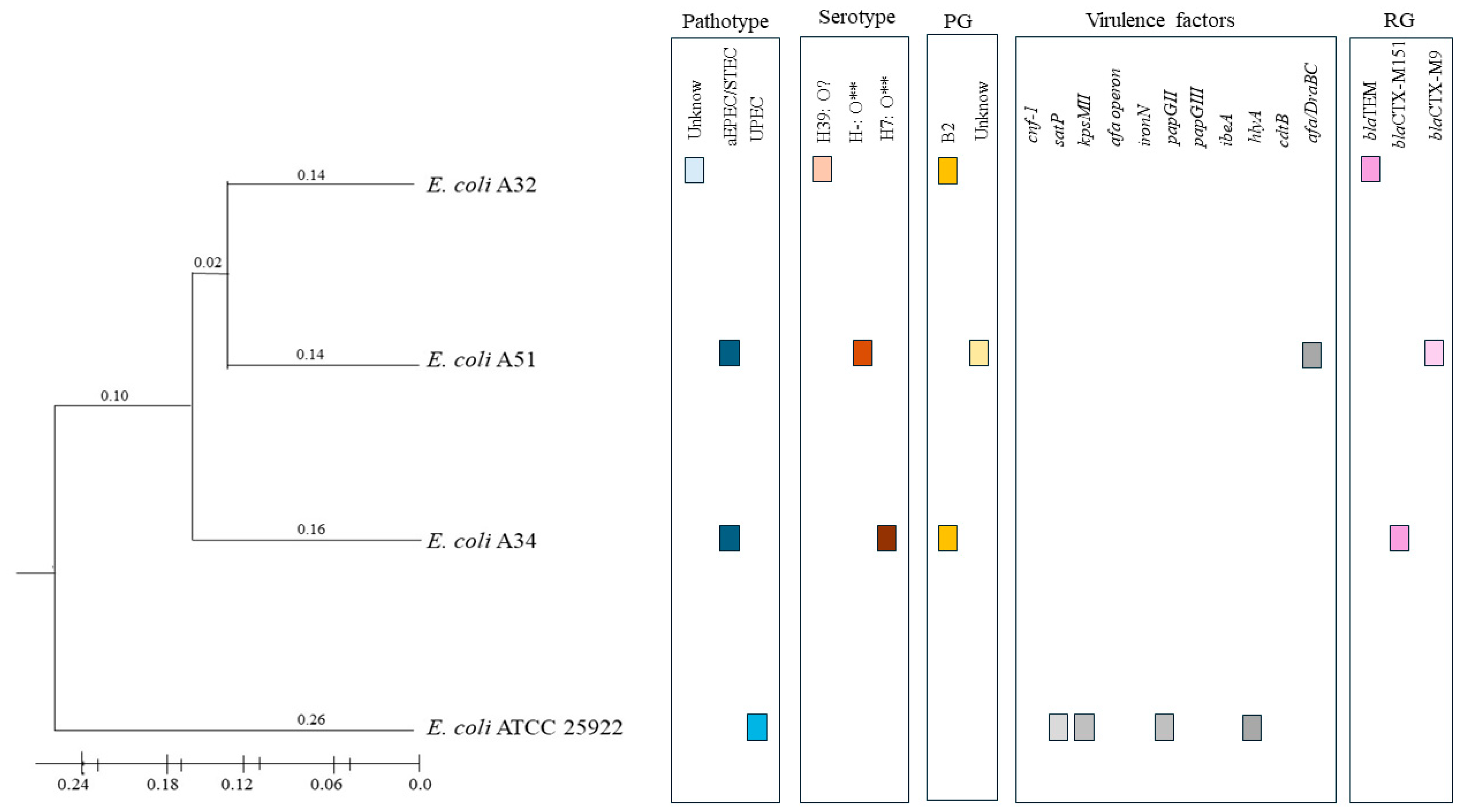
| Strain | Source | Pathotype | Serotyping | Phylogenetic Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A34 | Irrigation water | aEPEC/STEC | H7: O** | B2 |
| A51 | Irrigation water | aEPEC/STEC | H-: O** | Unknown |
| Antigen | Titers of Unabsorbed Sera | Titers of Sera Absorbed with Boiled Cultures | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli 64474 absorbed with: | S. boydii 16 absorbed with: | |||||||||
| E. coli 64474 | E. coli 0179 | E. coli 0188 | S. boydii 16 | E. coli 0179 | E. coli 188 | S. boydii 16 | E. coli 64474 | E. coli 0179 | E. coli 0188 | |
| E. coli A34 | 1:100 | - | - | 1:800 | - | - | - | - | 1:800 | 1:1600 |
| E. coli A51 | 1:100 | - | - | 1:800 | - | - | - | - | 1:800 | 1:1600 |
| Strain | cnf-1 | satP | kpsMII | afa operon | iroN | afa/draBC | papGII | papGIII | ibeA | hlyA | cdtB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A34 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| A51 | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Strain | Resistotype | ESBL Genes | ESBL Non-Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| A34 | CTX, CXM, CRO, FEP, MEM, ETP, AMC, AMP, CIP, STX | blaCTX-M-151 | -- |
| A51 | CTX, CXM, CRO, FEP, MEM, ETP, AMC, AMP, CIP, SXT | blaCTX-M-9 | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enciso-Martínez, Y.; Barrios-Villa, E.; Ballesteros-Monrreal, M.G.; Navarro-Ocaña, A.; Valencia, D.; González-Aguilar, G.A.; Martínez-Téllez, M.A.; Palomares-Navarro, J.J.; Ayala-Zavala, F. Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of aEPEC/STEC Escherichia coli Pathotypes with Serotype Links to Shigella boydii 16 Isolated from Irrigation Water. Pathogens 2025, 14, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060549
Enciso-Martínez Y, Barrios-Villa E, Ballesteros-Monrreal MG, Navarro-Ocaña A, Valencia D, González-Aguilar GA, Martínez-Téllez MA, Palomares-Navarro JJ, Ayala-Zavala F. Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of aEPEC/STEC Escherichia coli Pathotypes with Serotype Links to Shigella boydii 16 Isolated from Irrigation Water. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060549
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnciso-Martínez, Yessica, Edwin Barrios-Villa, Manuel G. Ballesteros-Monrreal, Armando Navarro-Ocaña, Dora Valencia, Gustavo A. González-Aguilar, Miguel A. Martínez-Téllez, Julián Javier Palomares-Navarro, and Fernando Ayala-Zavala. 2025. "Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of aEPEC/STEC Escherichia coli Pathotypes with Serotype Links to Shigella boydii 16 Isolated from Irrigation Water" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060549
APA StyleEnciso-Martínez, Y., Barrios-Villa, E., Ballesteros-Monrreal, M. G., Navarro-Ocaña, A., Valencia, D., González-Aguilar, G. A., Martínez-Téllez, M. A., Palomares-Navarro, J. J., & Ayala-Zavala, F. (2025). Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of aEPEC/STEC Escherichia coli Pathotypes with Serotype Links to Shigella boydii 16 Isolated from Irrigation Water. Pathogens, 14(6), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060549











