Abstract
Innate immunity is an important component of the immune system and serves as the first line of defense for the host against the invasion of foreign pathogens. Viperin (RSAD2), a core member of the interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) family, plays a key role in innate immunity through direct inhibition of viral replication and modulation of the host immune–metabolic network. The intracellular expression of Viperin rises markedly after viral infection or interferon-induced induction, showing a wide range of antiviral activities. In recent years, the versatility of Viperin in viral infections, autoimmune diseases, and tumor immune metabolism has been gradually revealed. Here, we summarize and discuss the gene regulatory network, molecular functions, and multi-dimensional roles of Viperin in diseases to provide a theoretical basis for the development of broad-spectrum antiviral strategies and immunometabolic therapies based on Viperin.
1. Introduction
Viral infections are one of the major threats to global public health, with pathogens such as influenza virus, HIV, HCV, and novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) causing millions of infections and deaths each year [1]. The innate immune system is the host’s first line of defense against viral invasion, and its core mechanism relies on the interferon (IFN) system. IFN, as a functional protein in the host, plays an important antiviral role in intrinsic and adaptive immunity. However, it is not the IFN itself that exerts antiviral function, but rather the downstream effectors (interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs)) that are produced by IFN recognition and binding to cognate receptors, thereby activating cellular signaling [2,3,4,5]. IFN induces the expression of hundreds of ISGs by activating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, resulting in a broad spectrum of antiviral effects [3]. ISGs play a key role by directly inhibiting viral replication or modulating host immune signaling pathways, for example, by inhibiting viral RNA polymerase activity or interfering with viral particle assembly [5]. However, viruses escape the surveillance of the interferon system through evolutionary mechanisms, such as blocking IFN signaling or degrading ISG products, creating a dynamic balance between host and pathogen [6]. This mechanism is particularly prominent in emerging infectious diseases such as COVID-19, where functional deficits in the IFN system correlate strongly with disease severity [7,8,9]. In recent years, high-throughput screening techniques have disclosed the functional diversity of ISGs. For example, Schoggins et al. identified through systematic screening that hundreds of ISGs possess specificity for targeting different viruses. Among them, Viperin (RSAD2) has drawn considerable attention because of its unique enzymatic activity and metabolic regulatory functions. It inhibits the replication of a broad spectrum of viruses, including dsDNA viruses, positive and negative single-stranded RNA viruses, and retroviruses in humans and other species. Examples include ZIKV, West Nile virus (WNV), Influenza A Virus (IAV), Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 (HIV-1), and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) [10,11,12,13,14]. Its encoded protein catalyzes the synthesis of ddhCTP through NADPH-dependent reductase activity and directly inhibits RNA virus genome replication [15]. This versatility makes it a key molecule in linking innate immunity to metabolic regulation.
Although important advances have been made in the antiviral mechanism of Viperin, its specific effects against different viruses, manifestations in diseases, and clinical translational potential still need to be systematically summarized. This review aims to integrate recent studies and analyze the gene regulation, molecular function, and role of Viperin in diseases to provide a theoretical basis for the development of Viperin-based antiviral strategies. For example, the broad-spectrum antiviral potential of ddhCTP, a product of Viperin’s enzymatic activity, its novel function in tumor immunity, and the association of its overactivation with autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus [15,16], suggest that it holds great promise as a therapeutic target. By combing the multidimensional regulatory mechanisms of Viperin, this review will provide new ideas for antiviral drug design and immunotherapy optimization.
2. Structure and Expression Regulation of Viperin
Viperin (RSAD2) is a broad-spectrum antiviral protein induced by interferon [10,17] and is a member of the Radical S-adenosylmethionine (Radical SAM) superfamily, which are conserved proteins with a predicted molecular weight of 42 kDa [18]. It is approximately 361 amino acids in length and contains three major structural domains: a variable amino-terminal domain with an amphiphilic α-helix and a leucine zip domain, a conserved central domain containing a free-radical S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) domain, and a highly conserved C-terminal domain [18,19] (Figure 1). The N-terminal transmembrane domain consists of an amphipathic α-helix, which is responsible for anchoring Viperin to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and lipid droplets (LDs), a position that is essential for its antiviral function [20,21]. It has been found that the N-terminal domain of Viperin is crucial for the association between the endoplasmic reticulum and lipid droplets [20,22], and the amphiphilic helix at the N-terminus of Viperin is required for its antiviral activity against the release of chikungunya virus (CHIKV) and Equine Infectious Anemia Virus (EIAV) [21,23]. The SAM domain is central to the catalytic activity of Viperin and is involved in the regulation of lipid metabolism and viral suppression functions [24,25] and contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster responsible for the production of catalytically essential 5′-deoxyadenosine radicals from SAM. Mutations in the binding motif of the [4Fe-4S] cluster reduced the antiviral activity of Viperin against West Nile virus (WNV), Dengue virus (DENV), tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), and Bunyamwera virus (BUNV), suggesting that free radical SAM activity is critical for limiting viral replication [11,26,27,28,29,30]. In addition, the active center of Viperin contains several positively charged conserved residues, such as Arg193 and Arg211, which promote its catalytic activity by interacting with the phosphate group of the substrate CTP [31]. In recent years, it has been found that the C-terminal structural domain of Viperin also activates TRAF6-dependent ubiquitination signaling and enhances the type I interferon response [32]. The C-terminus of Viperin drives the accumulation of molecules that specifically antagonize viral polymerases and force strand termination during RNA viral replication [33]. These findings reveal the complexity and functional diversity of the Viperin gene structure [24,34].
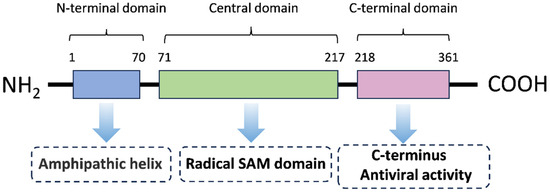
Figure 1.
The primary structure of Viperin. The Viperin protein is composed of 361 amino acids and has three distinct regions in its primary structure: an N-terminus (which varies in length and sequence with species), a central conserved region, and a highly conserved C-terminus. The tertiary structure of Viperin is a bilayer structure containing both α-helices and β-sheets. The C-terminal region of Viperin is also highly conserved and has been demonstrated to be critical for its ability to limit the replication of a number of viruses.
The expression of Viperin is mainly regulated by type I (IFN-α/β) and type II (IFN-γ) interferons through the classical JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Through the binding of interferon receptors to the cell surface, JAK kinases are activated and contribute to the formation of STAT1/STAT2 heterodimers, which further bind to IFN regulatory factors (IRFs) to initiate the expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) such as Viperin [3,35]. It is known that the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) is an enhancer that regulates gene expression, and the promoter of Viperin contains two ISRE binding sites, and ISGF3 can directly bind to the ISRE to promote Viperin transcription [36] (Figure 2). Studies have shown that in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) significantly upregulate Viperin expression through IFN-α/β autocrine signaling, which in turn inhibits viral replication [37]. STAT1 and IRF3 are key transcription factors in this pathway, which are phosphorylated and bind to the ISRE in the Viperin promoter region to drive gene expression [38]. In addition, pro-inflammatory factors such as LPS and IFN-γ synergistically enhance Viperin expression through STAT1-dependent signaling in an atherosclerosis model, suggesting its dual role in inflammatory diseases [38,39].
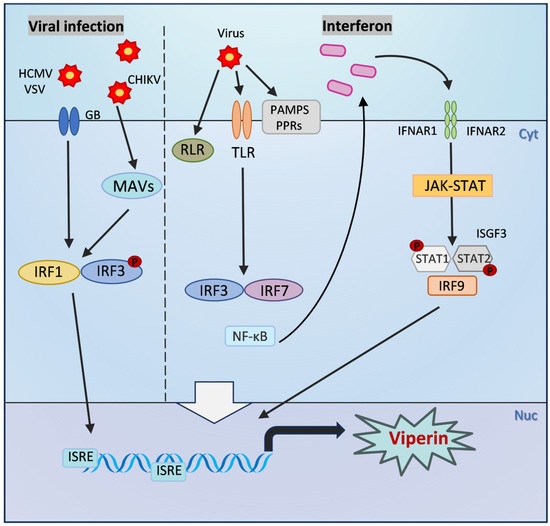
Figure 2.
The inducible expression pathway of Viperin. After viral infection: PAMPs, PPRs, and RLR are activated, which in turn activates the phosphorylation of transcription factors NF-κB and interferon regulatory factors IRF3 and IRF7, and induces the production of type I interferons. Interferons can bind to type I interferon receptors on the cell surface in a paracrine and autocrine manner. The dimerization of IFNAR subunits activates the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, ultimately inducing the formation of ISGF3. ISGF3 can directly bind to the ISRE and promote the transcription of Viperin. Viperin is also produced independently of the interferon pathway and is directly regulated by IRF1 or IRF3. The membrane glycoprotein glycoprotein B (GB) of HCMV can induce the phosphorylation of IRF3 and bind to the ISRE upstream of the Viperin promoter, thereby directly initiating its transcription. VSV infection stimulates IRF1 to bind to the two proximal ISREs of the Viperin promoter, activating its transcription. CHIKV infection also directly induces Viperin expression by activating MAVS and downstream IRF3.
In addition to gene transcriptional regulation, post-translational modifications (PTMs) are another central mechanism for regulating the protein stability and antiviral activity of Viperin. Our team systematically investigated the PTM network of Viperin and revealed its dynamic regulation under viral infection and host metabolic stress. Specifically, viral or IFN stimulation catalyzes an acetylation modification of the lysine (Lys) 197 position of the Viperin protein by inducing the expression of the acetyltransferase HAT1. This modification leads to rapid degradation of Viperin protein in epithelial cells by enhancing the interaction of the ubiquitin ligase UBE4A with Viperin, prompting UBE4A to further catalyze K6-linked polyubiquitination at Lys206 of Viperin. Experiments showed that UBE4A knockdown completely restored the protein level of Viperin in epithelial cells, confirming that UBE4A is a key factor in regulating its stability [40]. Notably, the ubiquitination modification of Viperin is closely related to the dynamic balance of deubiquitination: our study demonstrated that high-salt environments weakened the host antiviral response by inhibiting the expression of the deubiquitinating enzyme USP33, leading to elevated levels of ubiquitination and reduced stability of Viperin, whereas low-salt diets significantly enhanced Viperin accumulation and antiviral function by inhibiting p97 acetylation to upregulate USP33 expression [41]. Our recent study found that when coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) infected cardiomyocytes, the viral 3C protease blocked its ubiquitination function by cleaving UBE4A, which contributed to the abnormal accumulation of Viperin in cardiomyocytes. Excess Viperin activates the SGK1-KCNQ1 signaling axis by degrading STAT1, triggering electrophysiological disturbances in cardiomyocytes, ultimately leading to acute heart failure (AHF) [42]. This finding reveals the dual role of post-translational modifications of Viperin in viral pathogenicity—both as an antiviral effector molecule and potentially exacerbating tissue damage due to regulatory imbalance.
In addition to the classical JAK/STAT signaling pathway, the transcriptional regulation of Viperin is also regulated by other non-classical pathways, and the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway also plays a key role in Viperin expression. For example, TLR4 activates Viperin expression through its downstream NF-κB and IRF3 pathways, a mechanism that is critical in the response to various bacterial and viral infections [43]. In addition, Viperin is also produced independently of the interferon pathway and is directly regulated by IRF1 or IRF3 [44,45]. The membrane glycoprotein of HCMV, glycoprotein B (GB), induces the phosphorylation of IRF3 and binds to the ISRE upstream of the Viperin promoter, which in turn directly initiates its transcription [46]. VSV infection stimulates IRF1 to bind to the two proximal ISREs of the Viperin promoter, which in turn activates its transcription [47]. Viperin transcription is also affected by regulatory factors such as microRNAs (miRNAs). miR-23a was found to be able to promote HSV-1 replication by downregulating the expression of IRF1, which in turn affects Viperin expression [48]. Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) and peroxisomal signaling are also involved in regulation, and Viperin expression can also be directly induced by activation of MAVS and downstream IRF3 after chikungunya virus (CHIKV) infection [49]. Viperin was found to interact with PEX19 to mediate peroxisomal enhancement of the innate antiviral response [50]. In a recent study, Viperin was also found to inhibit viral translation by inducing ribosome collisions that activate the integrative stress response (ISR) pathway [34]. Together, these pathways constitute a complex regulatory network of Viperin in host defense and provide clues to further understand the molecular mechanisms of its antiviral action (Figure 2).
4. Role of Viperin in Disease
4.1. Viperin in Diseases Associated with Viral Infections
Viperin plays an important role in a variety of diseases associated with viral infections. In viral hepatitis, for example, it has been shown that Viperin plays a key role in the process of HCV infection [72]. The anti-HCV activity of Viperin is located at its C-terminus and interferes with its interaction with HCV NS5A by competitively interacting with the C-terminal structural domain of the host protein hVAP-33 [62]. In addition, Viperin competitively inhibits influenza virus RNA polymerase (IAV) through SAM-dependent enzymatic activity catalyzing the generation of ddhCTP, thereby limiting viral replication [15]. Studies have shown that IAV replication was significantly enhanced in MDCK cells knocked down for Viperin, while RSAD2 overexpression inhibited viral proliferation, suggesting its potential application in influenza vaccine production [73]. Viperin also inhibited NF-κB- and MAPK-mediated inflammatory responses and attenuated lung injury by activating the AMPKα signaling pathway in an influenza infection model [71]. Furthermore, in the context of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection, Viperin expression may lead to enhanced infectivity, which may be achieved by altering cellular metabolism and disrupting the actin cytoskeleton [74].
The role of Viperin in COVID-19 has received much attention in recent years. Single-cell transcriptome analyses have shown abnormally high expression of Viperin in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of COVID-19 critically ill patients, which correlates with type I interferon signaling storms and may exacerbate immunopathological damage [75]. In addition, Viperin interacts with the 3′-5′ exonuclease (ExoN) of SARS-CoV-2 to block viral RNA synthesis by catalyzing ddhCTP, and mutations in ExoN attenuate this inhibitory effect [76]. Clinical cohort studies have demonstrated a positive correlation between Viperin expression levels and the rate of viral clearance in COVID-19 patients, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target [77,78]. These studies have shown that Viperin plays a role in inhibiting viral replication and influencing the disease process in different viral infection-associated diseases through a variety of mechanisms, which is important for the occurrence, development, and prognosis of viral infectious diseases [34,77,79].
4.2. Potential Function of Viperin in Autoimmune Diseases
Notably, Viperin not only plays an important role in antiviral immunity but also exhibits potential functions in autoimmune diseases. Several studies have shown that the expression level of Viperin is significantly altered in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and that it exhibits bi-directional immunoregulation in autoimmune diseases, where it may influence the progression of the disease by modulating the immune response [80,81]. SLE is an autoimmune disease characterized by excessive production of IFN-I, especially IFN-α [82]. Recent studies have found that serum type I IFN levels in SLE patients are positively correlated with disease activity and that IFN-induced genes are strongly associated with the incidence of SLE [83]. In particular, the type I IFN pathway can induce autoimmunity by regulating a series of downstream genes. Therefore, it is important to study the relationship between type I IFN-induced genes and SLE [84,85,86]. Viperin has been found to be highly expressed in synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and promotes disease progression by modulating the inflammatory response [87] and has been used clinically as a predictor of RA progression [88,89]. Furthermore, RSAD2 is significantly upregulated in atherosclerosis, and its expression is regulated by pro-inflammatory agents (i.e., lipopolysaccharides, cytomegalovirus, and IFN-γ) but not by tumor necrosis factor α or IL-1β [39].
The expression level of Viperin is also significantly increased in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and correlated with the severity of the disease. RSAD2 is considered to be a key diagnostic ISG for SLE and may be useful for personalized targeted therapy for this disease [90]. A meta-analysis showed that RSAD2 had an important regulatory role in SLE patients and was significantly higher in SLE patients than in normal controls [91]. Meanwhile, some studies using gene microarrays to screen differentially expressed genes found that RSAD2 was significantly upregulated in SLE patients compared with normal controls, suggesting that the increased expression of RSAD2 may be related to the mechanism of the development of SLE and may reflect the activity of the disease to some extent [92]. Studies have shown that Viperin is highly expressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of SLE patients, and it reduces autoantibody production by inhibiting the TLR7/9 signaling pathway [93]. Furthermore, it has been shown that the absence of RSAD2 leads to a reduction in Th17 and Tfh cells, while the presence of RSAD2 promotes the differentiation of Th17 and Tfh cells in SLE individuals [94].
4.3. The Role of Viperin in Immunometabolic Reprogramming of Tumors
Metabolic reprogramming is a hallmark of malignancy that allows cancer cells to proliferate continuously using nutrients and energy [95,96,97,98]. Recent data support a role for IFN in the regulation of cancer metabolism; for example, IFN can activate the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in cancer cells to regulate metabolic processes and activate the tumor immune response [99,100,101,102]. In addition, IFN regulatory factors (IRFs) are involved in the regulation of cancer metabolism [103,104]. IFN upregulates the transcription of a large number of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), the products of which play a major role in the immune response [105].
It has been shown that ISG-encoded Viperin controls cancer metabolic reprogramming to promote cancer progression [106]. In recent years, it has been found that Viperin affects tumor progression by regulating lipid metabolism and glycolysis in the tumor microenvironment. This protein inhibits fatty acid β-oxidation in mitochondria, which in turn reduces ATP production and enhances glycolysis and lipogenesis during HCMV infection [46,74], suggesting that its function could be used to drive metabolic changes in cancer cells. In triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), Viperin promotes the self-renewal capacity of tumor stem cells (CSCs) by inhibiting fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) and enhancing lipid synthesis [106]. In addition, Viperin enhances the sugar uptake capacity of tumor cells by activating the HIF-1α signaling pathway and upregulating the expression of the glucose transporter protein GLUT1 [93]. Studies have shown that RSAD2 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cells, suggesting that it influences tumor progression through the regulation of energy metabolism [107]. These findings reveal a complex regulatory network of Viperin in tumor immunity, and its use as a prognostic marker or therapeutic target needs to be analyzed in combination with tumor type and the immune microenvironment. The ISG-encoded protein Viperin drives metabolic alterations in support of cancer proliferation, growth, and survival and is potentially important for the development of anticancer therapies targeting the cancer metabolism and IFN response [106,108,109].
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Viperin (RSAD2) is an important member of the family of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) that directly inhibit viral replication through multiple mechanisms. Its antiviral mechanism is mainly reflected in the direct inhibition of several aspects of viral replication, including interfering with viral RNA synthesis and affecting viral assembly and release [56]. Infection with different viruses leads to differences in RSAD2 expression levels. Some viruses induce upregulation of RSAD2 mRNA and protein expression during infection, but their antiviral activity is impaired. For example, EV71 or CSFV infection significantly increases RSAD2 mRNA and protein levels [33,110]; however, during Senecavirus A (SVA) infection, mRNA levels of RSAD2 are significantly increased, whereas its protein expression level is reduced [63]. Additionally, the HSV-1 UL41 protein significantly abrogated the antiviral activity of RSAD2 by reducing its mRNA expression level [111]. In addition, the expression level of Viperin is strongly correlated with the type I interferon signature of autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [16], and it can also be used to predict disease progression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [88]. Emerging evidence suggests that RSAD2 may play a role in atherosclerosis because it interferes with cellular processes that are critical in the development and progression of atherosclerosis [112]. These studies reveal that Viperin is not only a key molecule in antiviral defense but also an important bridge between innate immunity and disease pathology [113].
Based on the important role of Viperin in antiviral immunity, the development of antiviral drugs targeting the Viperin pathway is of great clinical importance. Several studies have shown that Viperin not only plays an important role in antiviral immunity but may also be a potential target for antiviral therapy [114]. Interfering peptides (IPs) are recognized as a research avenue for new drug development. Researchers found that one of these interfering peptides, VIP-IP3, effectively blocked the interaction between UBE4A and Viperin and restored the ability of epithelial cells to produce the Viperin protein, revealing a defect in the inability of epithelial cells to efficiently produce Viperin proteins and carry out their antiviral functions [40]. Recently, it was reported that the small-molecule compound L-chicoric acid (LCA) could alleviate placental vascular injury and improve pregnancy outcomes in SLE patients by inhibiting RSAD2 activity [115,116]. Moreover, RNA biomarkers based on Viperin (such as RSAD2 and IFI27) can distinguish bacterial and viral co-infections in COVID-19 patients, providing a molecular basis for precise antiviral treatment [117]. These studies indicate that Viperin may become a potential target for antiviral therapy. Through regulating the expression or activity of Viperin, it may effectively inhibit the replication and transmission of viruses, thereby achieving the therapeutic purpose.
Despite the promising potential of Viperin in antiviral and immunomodulatory applications, challenges remain in its clinical use. Firstly, the pro-inflammatory properties of Viperin may exacerbate autoimmune responses, and tissue-specific delivery systems need to be developed to balance efficacy and safety. Secondly, the metabolic regulatory function of Viperin has been shown to have a dual role in cancer; for example, high expression of RSAD2 in colorectal cancer predicts a poor prognosis, but inhibition of its activity may enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy [118]. In addition, post-translational modifications of Viperin, such as ubiquitination and acetylation, provide new targets for its dynamic regulation. For example, targeting UBE4A can stabilize Viperin protein levels to enhance antiviral responses [40].
However, there are still many unknowns in the study of Viperin, and the specific functional differences of different transcript variants as well as the precise regulatory mechanisms in different tissues and cells have yet to be thoroughly investigated. Only through a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of these aspects can we fully explore the potential of Viperin as a therapeutic target and bring breakthroughs in the diagnosis and treatment of clinical diseases. Future studies need to integrate multi-omics techniques and organoid models to elucidate the functional heterogeneity of Viperin in different microenvironments and facilitate its transformation from basic research to clinical practice. In the future, the specific action mechanism of Viperin should be further explored, and antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs targeting the Viperin pathway should be developed. Through multidisciplinary cross-innovation, Viperin is anticipated to become a “multifunctional target” for antiviral, anti-tumor, and immune disease treatments, providing novel strategies and approaches for clinical therapy.
Funding
This work is supported by grants from The National Natural Science Foundation of China (32241009), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2025ZNSFSC1095), the Suzhou Medical College Basic Frontier lnnovation Cross Research Project (YXY2304060), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2024M750364), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DENV | Dengue virus |
| ZIKV | Zika virus |
| TBEV | Tick-borne encephalitis virus |
| WNV | West Nile virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| BUNV | Bunyamwera virus |
| EIAV | Equine infectious anemia virus |
| RABV | Rabies virus |
| SVA | Senecavirus A |
| IAV | Influenza A virus |
References
- Stertz, S.; Hale, B.G. Interferon system deficiencies exacerbating severe pandemic virus infections. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.E.; Hughes, J.; Gu, Q.; Behdenna, A.; Singer, J.B.; Dennis, T.; Orton, R.J.; Varela, M.; Gifford, R.J.; Wilson, S.J.; et al. Fundamental properties of the mammalian innate immune system revealed by multispecies comparison of type I interferon responses. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2004086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.S.; Liu, H.M. The Molecular Basis of Viral Inhibition of IRF- and STAT-Dependent Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savan, R.; Gale, M., Jr. Innate immunity and interferon in SARS-CoV-2 infection outcome. Immunity 2023, 56, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.D. Innate immunity, cytokine storm, and inflammatory cell death in COVID-19. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Subbian, S. Critical Determinants of Cytokine Storm and Type I Interferon Response in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00299-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.C.; Cresswell, P. Viperin (cig5), an IFN-inducible antiviral protein directly induced by human cytomegalovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15125–15130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, N.; Maddocks, S.; Turville, S.G.; Harman, A.N.; Woolger, N.; Helbig, K.J.; Wilkinson, J.; Bye, C.R.; Wright, T.K.; Rambukwelle, D.; et al. HIV-1 infection of human macrophages directly induces viperin which inhibits viral production. Blood 2012, 120, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szretter, K.J.; Brien, J.D.; Thackray, L.B.; Virgin, H.W.; Cresswell, P.; Diamond, M.S. The Interferon-Inducible Gene viperin Restricts West Nile Virus Pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11557–11566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Hoek, K.H.; Eyre, N.S.; Shue, B.; Khantisitthiporn, O.; Glab-Ampi, K.; Carr, J.M.; Gartner, M.J.; Jolly, L.A.; Thomas, P.Q.; Adikusuma, F.; et al. Viperin is an important host restriction factor in control of Zika virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hinson, E.R.; Cresswell, P. The Interferon-Inducible Protein Viperin Inhibits Influenza Virus Release by Perturbing Lipid Rafts. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, A.S.; Grove, T.L.; Arnold, J.J.; Jose, J.; Jangra, R.K.; Garforth, S.J.; Du, Q.; Cahill, S.M.; Dulyaninova, N.G.; Love, J.D.; et al. A naturally occurring antiviral ribonucleotide encoded by the human genome. Nature 2018, 558, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yin, Y.; Hu, T.; Wang, X.; Jia, T.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Meng, W.; Zhu, J.; Dai, C.; et al. UXT attenuates the CGAS-STING1 signaling by targeting STING1 for autophagic degradation. Autophagy 2023, 19, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A. The interferon inducible gene: Viperin. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, K.J.; Beard, M.R. The Role of Viperin in the Innate Antiviral Response. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-Y.; Yaneva, R.; Cresswell, P. Viperin: A Multifunctional, Interferon-Inducible Protein that Regulates Virus Replication. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, E.R.; Cresswell, P. The antiviral protein, viperin, localizes to lipid droplets via its N-terminal amphipathic alpha-helix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20452–20457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, T.-S.; Foo, S.-S.; Simamarta, D.; Lum, F.-M.; Teo, T.-H.; Lulla, A.; Yeo, N.K.W.; Koh, E.G.L.; Chow, A.; Leo, Y.-S.; et al. Viperin restricts chikungunya virus replication and pathology. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4447–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, E.R.; Cresswell, P. The N-terminal amphipathic alpha-helix of viperin mediates localization to the cytosolic face of the endoplasmic reticulum and inhibits protein secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4705–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-D.; Na, L.; Zhu, C.-H.; Shen, N.; Yang, F.; Fu, X.-Q.; Wang, Y.-H.; Fu, L.-H.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lin, Y.-Z.; et al. Equine Viperin Restricts Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Replication by Inhibiting the Production and/or Release of Viral Gag, Env, and Receptor via Distortion of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12296–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunkemeyer, T.J.; Ghosh, S.; Patel, A.M.; Sajja, K.; Windak, J.; Basrur, V.; Kim, Y.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Kennedy, R.T.; Marsh, E.N.G. The antiviral enzyme viperin inhibits cholesterol biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, M.K.; Li, Y.; Cresswell, P.; Modis, Y.; Ealick, S.E. Structural studies of viperin, an antiviral radical SAM enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6806–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton-Smith, C.; Elliott, R.M. Viperin, MTAP44, and Protein Kinase R Contribute to the Interferon-Induced Inhibition of Bunyamwera Orthobunyavirus Replication. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11548–11557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Guo, H.; Xu, C.; Chang, J.; Gu, B.; Wang, L.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T. Identification of three interferon-inducible cellular enzymes that inhibit the replication of hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Weidner, J.M.; Qing, M.; Pan, X.B.; Guo, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Birk, A.; Chang, J.; Shi, P.Y.; et al. Identification of five interferon-induced cellular proteins that inhibit west nile virus and dengue virus infections. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8332–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.S.; Vonderstein, K.; Pichlmair, A.; Stehling, O.; Bennett, K.L.; Dobler, G.; Guo, J.-T.; Superti-Furga, G.; Lill, R.; Överby, A.K.; et al. Viperin is an iron-sulfur protein that inhibits genome synthesis of tick-borne encephalitis virus via radical SAM domain activity. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J.; Gu, F.; Ling, L.; Tolfvenstam, T.; Olfat, F.; Chin, K.C.; Aw, P.; George, J.; Kuznetsov, V.A.; Schreiber, M.; et al. Host gene expression profiling of dengue virus infection in cell lines and patients. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2007, 1, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, M.K.; Su, D.; Dong, M.; Lin, H.; Ealick, S.E. Structural Basis of the Substrate Selectivity of Viperin. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.M.; Marsh, E.N.G. The Antiviral Enzyme, Viperin, Activates Protein Ubiquitination by the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase, TRAF6. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4910–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Feng, L.; Chen, P.; Li, A.; Guo, S.; Jiao, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhong, K.; et al. Viperin inhibits classical swine fever virus replication by interacting with viral nonstructural 5A protein. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.C.; Laurent-Rolle, M.; Pawlak, J.B.; Xia, H.; Kunte, A.; Hee, J.S.; Lim, J.; Harris, L.D.; Wood, J.M.; Evans, G.B.; et al. Viperin triggers ribosome collision-dependent translation inhibition to restrict viral replication. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 1631–1642.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, L.; Su, J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. Transcriptional Regulation of Antiviral Interferon-Stimulated Genes. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, P.; Jin, H.; Luo, R. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of duck Janus kinase 1. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 117, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, S.; Kriss, M.; Golden-Mason, L.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Stone, A.E.; Soto-Gutierrez, A.; Mitchell, A.; Khetani, S.R.; Yamane, D.; Stoddard, M.; et al. Hepatitis C virus infection induces autocrine interferon signaling by human liver endothelial cells and release of exosomes, which inhibits viral replication. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 392–402.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, S.; Olejnik, A.; Sikorski, K.; Pelisek, J.; Błaszczyk, K.; Aoqui, C.; Nowicka, H.; Zernecke, A.; Heemann, U.; Wesoly, J.; et al. STAT1-dependent signal integration between IFNγ and TLR4 in vascular cells reflect pro-atherogenic responses in human atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.S.; Jatta, K.; Wågsäter, D.; Gredmark, S.; Hedin, U.; Paulsson-Berne, G.; Söderberg-Nauclér, C.; Hansson, G.K.; Sirsjö, A. The antiviral cytomegalovirus inducible gene 5/viperin is expressed in atherosclerosis and regulated by proinflammatory agents. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, e113–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Miao, Y.; Qian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Zuo, Y.; Feng, Q.; Guo, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Targeting UBE4A Revives Viperin Protein in Epithelium to Enhance Host Antiviral Defense. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 734–747.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Miao, Y.; Ren, T.; Huang, F.; Qian, L.; Chen, X.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, H.G.; He, J.; Qiao, C.; et al. High salt activates p97 to reduce host antiviral immunity by restricting Viperin induction. EMBO Rep. 2021, 23, e53466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Qian, L.; Miao, Y.; Cui, Q.; Cao, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Ren, T.; et al. Targeting Viperin prevents coxsackievirus B3-induced acute heart failure. Cell Discov. 2025, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.B.; Lu, Z.L.; Wei, X.K.; Zhong, T.Z.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Ouyang, L.X.; Luo, Y.; Xing, X.W.; Liao, F.; Peng, K.K.; et al. Viperin inhibits rabies virus replication via reduced cholesterol and sphingomyelin and is regulated upstream by TLR4. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Takaoka, A.; Taniguchi, T. Type I interferon [corrected] gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 2006, 25, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Gjinaj, E.; Bachu, M.; Squire, E.; Novatt, H.; Ozato, K.; Rabin, R.L. IRF1 Maintains Optimal Constitutive Expression of Antiviral Genes and Regulates the Early Antiviral Response. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Yaneva, R.; Hinson, E.R.; Cresswell, P. Human cytomegalovirus directly induces the antiviral protein viperin to enhance infectivity. Science 2011, 332, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudinot, P.; Riffault, S.; Salhi, S.; Carrat, C.; Sedlik, C.; Mahmoudi, N.; Charley, B.; Benmansour, A. Vesicular stomatitis virus and pseudorabies virus induce a vig1/cig5 homologue in mouse dendritic cells via different pathways. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2675–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Sun, H.; Fan, H.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Tang, H. MiR-23a facilitates the replication of HSV-1 through the suppression of interferon regulatory factor 1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.K.; Sali, T.; Alvarado, D.; Gatti, E.; Pierre, P.; Streblow, D.; Defilippis, V.R. Chikungunya virus induces IPS-1-dependent innate immune activation and protein kinase R-independent translational shutoff. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantisitthiporn, O.; Shue, B.; Eyre, N.S.; Nash, C.W.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Van der Hoek, K.H.; Helbig, K.J.; Beard, M.R. Viperin interacts with PEX19 to mediate peroxisomal augmentation of the innate antiviral response. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 4, e202000915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattijssen, S.; Pruijn, G.J. Viperin, a key player in the antiviral response. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.-L.; Chang, T.-H.; Liao, C.-L.; Lin, Y.-L. The Cellular Antiviral Protein Viperin Is Attenuated by Proteasome-Mediated Protein Degradation in Japanese Encephalitis Virus-Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10455–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panayiotou, C.; Lindqvist, R.; Kurhade, C.; Vonderstein, K.; Pasto, J.; Edlund, K.; Upadhyay, A.S.; Överby, A.K. Viperin Restricts Zika Virus and Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Replication by Targeting NS3 for Proteasomal Degradation. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02054-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwalscappel, B.; Tada, T.; Landau, N.R. Toll-like receptor agonist R848 blocks Zika virus replication by inducing the antiviral protein viperin. Virology 2018, 522, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, R.; Överby, A.K. The Role of Viperin in Antiflavivirus Responses. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 37, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, K.J.; Carr, J.M.; Calvert, J.K.; Wati, S.; Clarke, J.N.; Eyre, N.S.; Narayana, S.K.; Fiches, G.N.; McCartney, E.M.; Beard, M.R. Viperin is induced following dengue virus type-2 (DENV-2) infection and has anti-viral actions requiring the C-terminal end of viperin. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarti, A.; Selvadurai, K.; Shahoei, R.; Lee, H.; Fatma, S.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Huang, R.H. Reconstitution and substrate specificity for isopentenyl pyrophosphate of the antiviral radical SAM enzyme viperin. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14122–14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwalscappel, B.; Gadea, G.; Desprès, P. A Viperin Mutant Bearing the K358R Substitution Lost its Anti-ZIKA Virus Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Hong, S.; Seo, J.Y. A Cysteine Residue of Human Cytomegalovirus vMIA Protein Plays a Crucial Role in Viperin Trafficking to Control Viral Infectivity. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0187422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonderstein, K.; Nilsson, E.; Hubel, P.; Nygård Skalman, L.; Upadhyay, A.; Pasto, J.; Pichlmair, A.; Lundmark, R.; Överby, A.K.; Pfeiffer, J.K. Viperin Targets Flavivirus Virulence by Inducing Assembly of Noninfectious Capsid Particles. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01751-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, K.J.; Eyre, N.S.; Yip, E.; Narayana, S.; Li, K.; Fiches, G.; McCartney, E.M.; Jangra, R.K.; Lemon, S.M.; Beard, M.R. The antiviral protein viperin inhibits hepatitis C virus replication via interaction with nonstructural protein 5A. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Pan, T.; Song, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, Z. Viperin inhibits hepatitis C virus replication by interfering with binding of NS5A to host protein hVAP-33. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, P.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhou, J.; Song, J.; Liu, J. RSAD2 suppresses viral replication by interacting with the Senecavirus A 2 C protein. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.A.; Marineau, A.; Doyon, P.; Acevedo, M.; Durette, É.; Gingras, A.C.; Servant, M.J. TRK-Fused Gene (TFG), a protein involved in protein secretion pathways, is an essential component of the antiviral innate immune response. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, K.S.; Eom, J.; Lee, J.B.; Seo, J.Y. Viperin Differentially Induces Interferon-Stimulated Genes in Distinct Cell Types. Immune Netw. 2019, 19, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severa, M.; Coccia, E.M.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Toll-like Receptor-dependent and -independent Viperin Gene Expression and Counter-regulation by PRDI-binding Factor-1/BLIMP1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26188–26195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, T.; Satoh, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Antiviral Protein Viperin Promotes Toll-like Receptor 7- and Toll-like Receptor 9-Mediated Type I Interferon Production in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Immunity 2011, 34, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhu, T. Knockdown of RSAD2 attenuates B cell hyperactivity in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) via suppressing NF-κb signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 2029–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F. Innate immunity: The bacterial connection. Trends Immunol. 2023, 44, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, W.; Pu, J.; Jiang, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, X. A Novel Role for the Regulatory Nod-Like Receptor NLRP12 in Anti-Dengue Virus Response. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 744880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Pan, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, B. 5-Methoxyflavone-induced AMPKα activation inhibits NF-κB and P38 MAPK signaling to attenuate influenza A virus-mediated inflammation and lung injury in vitro and in vivo. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbig, K.J.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Semendric, L.; Harley, H.A.J.; Beard, M.R. Analysis of ISG Expression in Chronic Hepatitis C Identifies Viperin as a Potential Antiviral Effector. Hepatology 2005, 42, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Liao, Y.; Pei, M.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Jin, D.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Yang, X. RSAD2 Is an Effective Target for High-Yield Vaccine Production in MDCK Cells. Viruses 2022, 14, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Cresswell, P. Viperin regulates cellular lipid metabolism during human cytomegalovirus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, S.; Daga, S.; Fallerini, C.; Baldassarri, M.; Benetti, E.; Picchiotti, N.; Fava, F.; Gallì, A.; Zibellini, S.; Bruttini, M.; et al. Rare variants in Toll-like receptor 7 results in functional impairment and downregulation of cytokine-mediated signaling in COVID-19 patients. Genes Immun. 2022, 23, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinthapatla, R.; Sotoudegan, M.; Srivastava, P.; Anderson, T.K.; Moustafa, I.M.; Passow, K.T.; Kennelly, S.A.; Moorthy, R.; Dulin, D.; Feng, J.Y.; et al. Interfering with nucleotide excision by the coronavirus 3′-to-5′ exoribonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yan, Q.; Cao, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. Identification of key molecules in COVID-19 patients significantly correlated with clinical outcomes by analyzing transcriptomic data. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 930866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; He, J.; Zhou, X.; Pan, H.; He, F.; Du, A.; Yu, B.; Jiang, N.; Li, X.; Yuan, K.; et al. Discovering common pathogenetic processes between COVID-19 and tuberculosis by bioinformatics and system biology approach. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1280223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassan, M.; Collesei, A.; Angerilli, V.; Sbaraglia, M.; Fortarezza, F.; Pezzuto, F.; De Gaspari, M.; Businello, G.; Moni, M.; Rizzo, S.; et al. Multi-Design Differential Expression Profiling of COVID-19 Lung Autopsy Specimens Reveals Significantly Deregulated Inflammatory Pathways and SFTPC Impaired Transcription. Cells 2022, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ye, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, S.; Yang, Q.; Qian, H.; Gao, S.; Hua, C. Crucial Roles of RSAD2/viperin in Immunomodulation, Mitochondrial Metabolism and Autoimmune Diseases. Inflammation 2025, 48, 520–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Nature reviews. Nephrology 2023, 19, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rönnblom, L.; Leonard, D. Interferon pathway in SLE: One key to unlocking the mystery of the disease. Lupus Sci. Med. 2019, 6, e000270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Romo, G.S.; Caielli, S.; Vega, B.; Connolly, J.; Allantaz, F.; Xu, Z.; Punaro, M.; Baisch, J.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R.L.; et al. Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, D.; Hong, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Fu, B.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Shen, W.; et al. Expression characteristics of interferon-stimulated genes and possible regulatory mechanisms in lupus patients using transcriptomics analyses. EBioMedicine 2021, 70, 103477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehar-Belaid, D.; Hong, S.; Marches, R.; Chen, G.; Bolisetty, M.; Baisch, J.; Walters, L.; Punaro, M.; Rossi, R.J.; Chung, C.H.; et al. Mapping systemic lupus erythematosus heterogeneity at the single-cell level. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1094–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarras, A.; Wittmann, M.; Vital, E.M. Emerging concepts of type I interferons in SLE pathogenesis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, W.; Xu, D.; Fu, M.; Kang, Y. Screening of gene signatures for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raterman, H.G.; Vosslamber, S.; de Ridder, S.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Lems, W.F.; Boers, M.; van de Wiel, M.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Verweij, C.L.; Voskuyl, A.E. The interferon type I signature towards prediction of non-response to rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübbers, J.; Brink, M.; van de Stadt, L.A.; Vosslamber, S.; Wesseling, J.G.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Verweij, C.L. The type I IFN signature as a biomarker of preclinical rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Duan, C.; Xie, C.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, T. Identification of key interferon-stimulated genes for indicating the condition of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 962393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezin, T.; Vorobyev, A.; Sadik, C.D.; Zillikens, D.; Gupta, Y.; Ludwig, R.J. Gene Expression Analysis Reveals Novel Shared Gene Signatures and Candidate Molecular Mechanisms between Pemphigus and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in CD4(+) T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, G.; Ren, D.; Liu, F.; Dong, G.; Hou, Y. Gender differences of B cell signature related to estrogen-induced IFI44L/BAFF in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 181, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, A.G.; Godet, I.; Gilkes, D.M. The rise of viperin: The emerging role of viperin in cancer progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e165907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; He, Z.; Mei, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yang, M.; Wu, H. Interferon-α regulates abnormally increased expression of RSAD2 in Th17 and Tfh cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2350420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Sato, T.; Nomura, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Ito, S.; Kurosawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sugiura, Y.; et al. PKM1 Confers Metabolic Advantages and Promotes Cell-Autonomous Tumor Cell Growth. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 355–367.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elstrom, R.L.; Bauer, D.E.; Buzzai, M.; Karnauskas, R.; Harris, M.H.; Plas, D.R.; Zhuang, H.; Cinalli, R.M.; Alavi, A.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Akt stimulates aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3892–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, J.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Mole, D.R.; Lee, S.; Torres-Cabala, C.; Chung, Y.L.; Merino, M.; Trepel, J.; Zbar, B.; Toro, J.; et al. HIF overexpression correlates with biallelic loss of fumarate hydratase in renal cancer: Novel role of fumarate in regulation of HIF stability. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, M.A.; Chandriani, S.; O’Connell, B.; Petrenko, O.; Kotenko, I.; Beavis, A.; Sedivy, J.M.; Cole, M.D. A functional screen for Myc-responsive genes reveals serine hydroxymethyltransferase, a major source of the one-carbon unit for cell metabolism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5793–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.Z.; Bonner, J.A. Bridging Radiotherapy to Immunotherapy: The IFN-JAK-STAT Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Cassol, E. Role of cellular metabolism in regulating type I interferon responses: Implications for tumour immunology and treatment. Cancer Lett. 2017, 409, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 2012, 36, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, K.; Miasari, M.; Shi, W.; Xin, A.; Henstridge, D.C.; Preston, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Belz, G.T.; Smyth, G.K.; Febbraio, M.A.; et al. The transcription factor IRF4 is essential for TCR affinity-mediated metabolic programming and clonal expansion of T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Takami, M.; Yamada, A.; Wang, X.; Koga, T.; Hu, X.; Tamura, T.; Ozato, K.; Choi, Y.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; et al. Interferon regulatory factor-8 regulates bone metabolism by suppressing osteoclastogenesis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, A.J.; Williams, B.R. Interferon-inducible antiviral effectors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.M.; Kim, J.J.; Yoo, J.; Kim, K.S.; Gu, Y.; Eom, J.; Jeong, H.; Kim, K.; Nam, K.T.; Park, Y.S.; et al. The interferon-inducible protein viperin controls cancer metabolic reprogramming to enhance cancer progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e157302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiang, D.; Dai, Z.; Zhu, J.; Du, Y.; Fu, G.; Chu, X. Unveiling the immunogenomic landscape of cholangiocarcinoma: Identifying new prognostic markers and therapeutic targets based on CCL5 expression. J. Gene Med. 2024, 26, e3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.W.; Wisniewska, K.; King, C.M.; Li, S.; Coffey, A.; Kelly, M.R.; Regner, M.J.; Franco, H.L. Enhancer RNA Transcription Is Essential for a Novel CSF1 Enhancer in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, X.; Du, K.; Yang, Q.; Xia, T. The m6A-regulation and single cell effect pattern in sunitinib resistance on clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Identification and validation of targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1131610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zheng, C.; Sun, J.; Luo, D.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, H. Viperin Inhibits Enterovirus A71 Replication by Interacting with Viral 2C Protein. Viruses 2018, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Cai, M.; Li, M.-l.; Zheng, C.; Sandri-Goldin, R.M. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Counteracts Viperin via Its Virion Host Shutoff Protein UL41. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12163–12166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayderi, A.; Kumawat, A.K.; Shavva, V.S.; Dreifaldt, M.; Sigvant, B.; Petri, M.H.; Kragsterman, B.; Olofsson, P.S.; Sirsjö, A.; Ljungberg, L.U. RSAD2 is abundant in atherosclerotic plaques and promotes interferon-induced CXCR3-chemokines in human smooth muscle cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shomar, H.; Georjon, H.; Feng, Y.; Olympio, B.; Guillaume, M.; Tesson, F.; Cury, J.; Wu, F.; Bernheim, A. Viperin immunity evolved across the tree of life through serial innovations on a conserved scaffold. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 8, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennelly, S.A.; Sawyer, J.M.; Payne, A.F.; Ciota, A.T.; Harki, D.A. Development of 3′-Deoxy-3′,4′-didehydro-nucleoside Prodrug Inhibitors of West Nile and Zika Viruses. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xu, X.; Hu, X.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ke, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. RSAD2: A pathogenic interferon-stimulated gene at the maternal-fetal interface of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 101974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negatu, S.G.; Jurado, K.A. Targeting pathogenic interferon-stimulated gene RSAD2 improves pregnancy outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus models. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, P.D.; Wargowsky, R.; Gonzalez-Almada, A.; Sifontes, E.P.; Shaykhinurov, E.; Jaatinen, K.; Jepson, T.; Lafleur, J.E.; Yamane, D.; Perkins, J.; et al. Blood RNA Biomarkers Identify Bacterial and Biofilm Coinfections in COVID-19 Intensive Care Patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 39, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, J.; Guo, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X. RSAD2, a pyroptosis-related gene, predicts the prognosis and immunotherapy response for colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2024, 14, 2507–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
