Unravelling the Persistence of the Rare Serovar Salmonella Mikawasima in a Hospital Setting: A Whole-Genome Sequencing Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Clinical Cases and Isolates
2.3. Biochemical Characterization and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolates Metadata
3.2. Genomic Relatedness
3.3. AMR Gene Profile and Phenotypic Correlation
3.4. Virulence Genes as Biomarkers of Persistence
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Roggentin, P.; Mikoleit, M.; Guibourdenche, M.; de Pinna, E.; Nair, S.; Fields, P.I.; Weill, F.-X. Supplement 2008–2010 (No. 48) to the White–Kauffmann–Le Minor Scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimont, P.; Weill, F.-X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars, 9th ed.; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella, Institute Pasteur: Paris, France, 2007; pp. 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- Gunel, E.; Polat Kilic, G.; Bulut, E.; Durul, B.; Acar, S.; Alpas, H.; Soyer, Y. Salmonella Surveillance on Fresh Produce in Retail in Turkey. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 199, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, F.; Figueras, M.J.; Inza, I.; Sala, J.; Fleisher, J.M.; Guarro, J. Prevalence of Salmonella Serotypes in Environmental Waters and Their Relationships with Indicator Organisms. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1999, 75, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Gonzalez, N.; Mentaberre, G.; Porrero, C.M.; Serrano, E.; Mateos, A.; López-Martín, J.M.; Lavín, S.; Domínguez, L. Effect of Cattle on Salmonella Carriage, Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance in Free-Ranging Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) in Northeastern Spain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Tarifa, E.; Torralbo, A.; Borge, C.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Ayats, T.; Carbonero, A.; García-Bocanegra, I. Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter and Salmonella Strains Isolated from Decoys and Raptors. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Unusual Increase of Salmonella Mikawasima Infections in Humans. EFSA Support. Publ. 2013, 10, 512E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Communicable Disease Threats Report, 16-22 November 2024, Week 47. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/communicable-disease-threats-report-16-22-november-2024-week-47 (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- The European Surveillance System (TESSy). Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/european-surveillance-system-tessy (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Bobo, L.D.; Dubberke, E.R. Recognition and Prevention of Hospital-Associated Enteric Infections in the Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, S324–S334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.R.; Rowe, B. Investigation of Outbreaks of Salmonella in Hospitals. Br. Med. J. Clin. Res. Ed. 1983, 287, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, T.K.; Bamberg, W.M.; Ghosh, T.S.; Cronquist, A.; Fornof, M.E.; Cichon, M.K.; Gershman, K.; Vogt, R.L. Health Care-Associated Outbreak of Salmonella Tennessee in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Am. J. Infect. Control 2009, 37, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Smouse, S.L.; Tau, N.P.; Bamford, C.; Moodley, V.M.; Jacobs, C.; McCarthy, K.M.; Lourens, A.; Keddy, K.H. GERMS-SA Surveillance Network Laboratory-Acquired Infections of Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhi in South Africa: Phenotypic and Genotypic Analysis of Isolates. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, A.; Dzelalija, M.; Goic-Barisic, I.; Kovacic, A.; Pirija, M.; Maravic, A.; Radic, M.; Marinovic, J.; Rubic, Z.; Carev, M.; et al. Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of a Hospital Outbreak Clonal Lineage of Salmonella enterica Subspecies enterica Serovar Mikawasima Containing blaTEM-1B and blaSHV-2 That Emerged on a Neonatal Ward, During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Microb. Drug Resist. 2024, 30, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eucast: Previous Versions of Documents. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ast_of_bacteria/previous_versions_of_documents (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Babraham Bioinformatics—FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Chen, S. Ultrafast One-Pass FASTQ Data Preprocessing, Quality Control, and Deduplication Using Fastp. iMeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheenko, A.; Prjibelski, A.; Saveliev, V.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A. Versatile Genome Assembly Evaluation with QUAST-LG. Bioinforma. Oxf. Engl. 2018, 34, i142–i150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve Years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, N.A.; Wright, M.W.; Brister, J.R.; Ciufo, S.; Haddad, D.; McVeigh, R.; Rajput, B.; Robbertse, B.; Smith-White, B.; Ako-Adjei, D.; et al. Reference Sequence (RefSeq) Database at NCBI: Current Status, Taxonomic Expansion, and Functional Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D733–D745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Treangen, T.J.; Melsted, P.; Mallonee, A.B.; Bergman, N.H.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. Mash: Fast Genome and Metagenome Distance Estimation Using MinHash. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, C.K.; Kingsley, R.A.; Connor, T.R.; Harris, S.R.; Parry, C.M.; Al-Mashhadani, M.N.; Kariuki, S.; Msefula, C.L.; Gordon, M.A.; de Pinna, E.; et al. Intracontinental Spread of Human Invasive Salmonella Typhimurium Pathovariants in Sub-Saharan Africa. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, C.E.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Laing, C.R.; Lingohr, E.J.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Nash, J.H.E.; Taboada, E.N. The Salmonella In Silico Typing Resource (SISTR): An Open Web-Accessible Tool for Rapidly Typing and Subtyping Draft Salmonella Genome Assemblies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. mlst Github. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/mlst (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Pallen, M.J. Updating Benchtop Sequencing Performance Comparison. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Achtman, M. GrapeTree: Visualization of Core Genomic Relationships among 100,000 Bacterial Pathogens. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent Updates to the Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation Tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Nash, J.H.E. MOB-Suite: Software Tools for Clustering, Reconstruction and Typing of Plasmids from Draft Assemblies. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.H.K.; Bortolaia, V.; Tansirichaiya, S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Roberts, A.P.; Petersen, T.N. Detection of Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella enterica Using a Newly Developed Web Tool: MobileElementFinder. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Abricate, Github. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/abricate (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and Refined Dataset for Big Data Analysis—10 Years On. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roer, L.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Lukjancenko, O.; Kaas, R.S.; Hasman, H.; Aarestrup, F.M. Is the Evolution of Salmonella enterica Subsp. enterica Linked to Restriction-Modification Systems? mSystems 2016, 1, e00009-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Park, Y.-K.; Kim, J.F. PAIDB v2.0: Exploration and Analysis of Pathogenicity and Resistance Islands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D624–D630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Chen, R.; Li, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, R.; Shen, Y.; Guo, X. The Association between the Genetic Structures of Commonly Incompatible Plasmids in Gram-Negative Bacteria, Their Distribution and the Resistance Genes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1472876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VFDB—Pathogenesis of Salmonella. Available online: https://www.mgc.ac.cn/cgi-bin/VFs/genus.cgi?Genus=Salmonella (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Sheng, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Huang, X. Mig-14 May Contribute to Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Resistance to Polymyxin B by Decreasing the Permeability of the Outer-Membrane and Promoting the Formation of Biofilm. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 309, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs-Reitsma, W.F.; Maas, H.M.E. Eighteenth EURL-Salmonella Interlaboratory Comparison Study (2013) on Typing of Salmonella spp.; Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu RIVM: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Knegt, L.V.D.; Hald, T.; Boysen, L.; Pedersen, K.; Sørensen, A.I.V.; Korsgaard, H.; Perge, A.; Rosenquist, H. Annual Report on Zoonoses in Denmark 2013; DTU Food, National Food Institute: Lyngby, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, T.W.R.; Goulter, R.M.; McMeekin, T.; Dykes, G.A.; Fegan, N. Attachment of Different Salmonella Serovars to Materials Commonly Used in a Poultry Processing Plant. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, J.E.; Hahn, M.M.; D’Souza, S.J.; Vasicek, E.M.; Sandala, J.L.; Gunn, J.S.; McLachlan, J.B. Salmonella Biofilm Formation, Chronic Infection, and Immunity Within the Intestine and Hepatobiliary Tract. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 624622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laviniki, V.; Simoni, C.; Carloto, A.F.; Lopes, G.V. The Biofilm-Forming Ability of Salmonella Enterica Subsp. enterica Isolated from Swine-Feed Mills. Ciênc. Rural 2023, 54, e20230146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviria-Cantin, T.; Vargas, A.F.; Mouali, Y.E.; Jiménez, C.J.; Cimdins-Ahne, A.; Madrid, C.; Römling, U.; Balsalobre, C. Gre Factors Are Required for Biofilm Formation in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium by Targeting Transcription of the csgD Gene. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, C.; Kleefeld, A.; Lehnen, D.; Heintz, M.; Dobrindt, U.; Nagy, G.; Michaelis, K.; Emödy, L.; Polen, T.; Rachel, R.; et al. Regulation of Type 1 Fimbriae Synthesis and Biofilm Formation by the Transcriptional Regulator LrhA of Escherichia coli. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3287–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Zhang, P.; Piao, R.; Wang, Y. Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 (SPI-1) and Its Complex Regulatory Network. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramatla, T.; Khasapane, N.G.; Mlangeni, L.N.; Mokgokong, P.; Ramaili, T.; Ndou, R.; Nkhebenyane, J.S.; Lekota, K.; Thekisoe, O. Detection of Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands and Antimicrobial-Resistant Genes in Salmonella enterica Serovars Enteritidis and Typhimurium Isolated from Broiler Chickens. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneda, T.; Ishii, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Ohshima, K.; Iida, N.; Danbara, H.; Okada, N. Salmonella Type III Effector SpvC, a Phosphothreonine Lyase, Contributes to Reduction in Inflammatory Response during Intestinal Phase of Infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, M.E.; Quick, L.N.; Ubol, N.; Shrom, S.; Dollahon, N.; Wilson, J.W. Characterization of Salmonella Type III Secretion Hyper-Activity Which Results in Biofilm-Like Cell Aggregation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Lü, X.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S. Deletion of Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands SPI-1, 2 and 3 Induces Substantial Morphological and Metabolic Alternation and Protective Immune Potential. J. Integr. Agric. 2025, 24, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, J.R.; Paul, N.C.; Burin, R.; Guard, J.; Shah, D.H. Genomic Organization and Role of SPI-13 in Nutritional Fitness of Salmonella. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neonatal Infection: Antibiotics for Prevention and Treatment; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: Guidelines; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2024; ISBN 978-1-4731-5820-7.
- Pavelquesi, S.L.S.; de Oliveira Ferreira, A.C.A.; Rodrigues, A.R.M.; de Souza Silva, C.M.; Orsi, D.C.; da Silva, I.C.R. Presence of Tetracycline and Sulfonamide Resistance Genes in Salmonella spp.: Literature Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, W.; Hopkins, S.; Gayet-Ageron, A.; Holmes, A.; Sharland, M.; Suetens, C.; ECDC PPS Study Group. Health-Care-Associated Infections in Neonates, Children, and Adolescents: An Analysis of Paediatric Data from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Point-Prevalence Survey. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use in European Acute Care Hospitals: 2011–2012; Publications Office, LU: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use in European Acute Care Hospitals: 2016–2017; Publications Office, LU: Luxembourg, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä, A.V. Epidemiological and Microbiological Characteristics of Salmonella spp. Infections in Outpatients in Split-Dalmatia County in 2022: A Cross-Sectional Study. Master’s Thesis, School of Medicine, University of Split, Split, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Barač Juretić, K.; Carev, M. Najčešći Bakterijski i Virusni Uzročnici Gastrointestinalnih Infekcija u Splitskodalmatinskoj Županiji u Razdoblju 2021–2023. Javno Zdr. 2024, 1, 30–34. Available online: https://nzjz-split.hr/casopis-javno-zdravstvo/ (accessed on 21 April 2025).
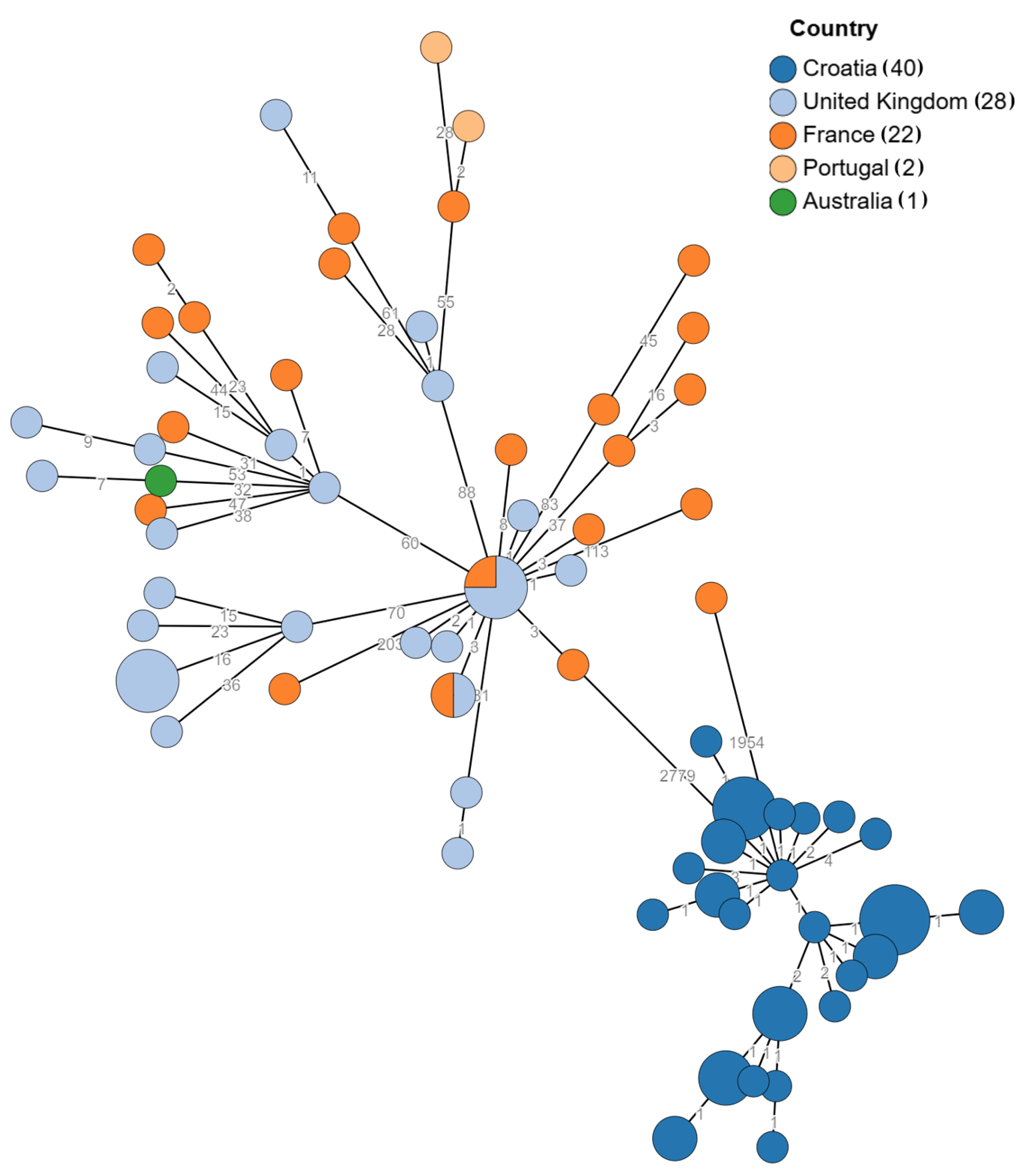
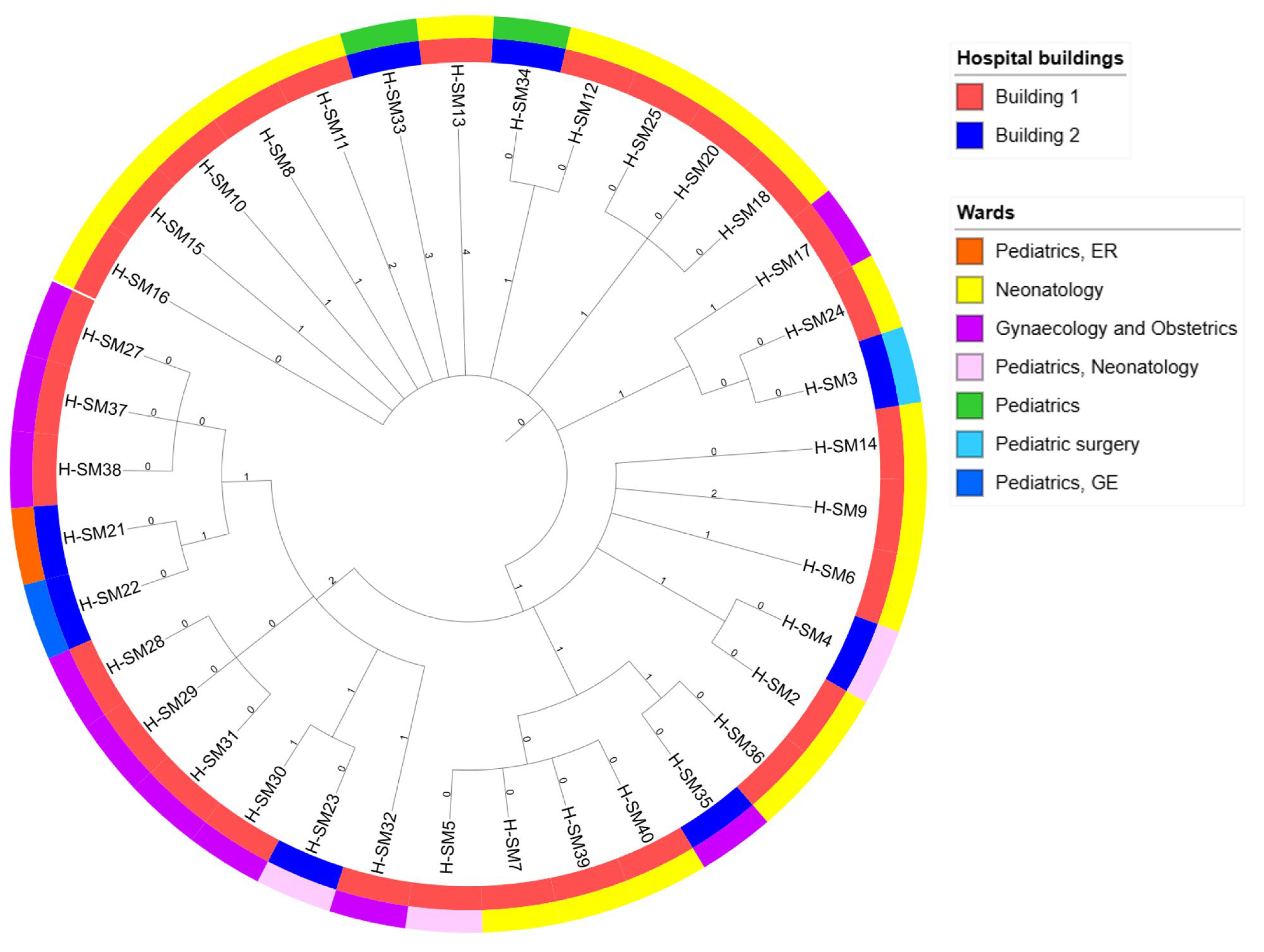
| Strain Code | Sampling Date | Age/Months | Sample | Symptoms | Unit | AMR Profile * | ESBL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H_SM2 | August 2023 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CRO, CAZ, CTX | positive |
| H_SM3 | October 2023 | 13 | stool | diarrhoea | Clinic for paediatric surgery, Department for abdominal surgery | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM4 | November 2023 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Paediatrics, neonatology | AM, AMC, CTX, CAZ, CIP | positive |
| H_SM5 | November 2023 | 1 | stool | diarrhoea | Paediatrics, neonatology | AM, AMC, CRO, CAZ, CTX | positive |
| H_SM6 | November 2023 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CRO, CAZ, CTX | positive |
| H_SM7 | November 2023 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CTX, CAZ | positive |
| H_SM8 | January 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CTX | positive |
| H_SM9 | January 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | Missing data | positive |
| H_SM10 | January 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CTX | positive |
| H_SM11 | January 2024 | 2 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CTX | positive |
| H_SM12 | January 2024 | 1 | throat swab | asymptomatic colonisation | Neonatology | AM, AMC | positive |
| H_SM13 | January 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CTX | positive |
| H_SM14 | January 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM15 | January 2024 | 1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CAZ | positive |
| H_SM16 | February 2024 | 3 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM | positive |
| H_SM17 | February 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC, CTX | positive |
| H_SM18 | December 2023 | 2 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC | positive |
| H_SM20 | February 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CRO | positive |
| H_SM21 | March 2024 | 1 | stool | diarrhoea | Paediatrics, ER | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM22 | March 2024 | 1 | stool | diarrhoea | Paediatrics, GE | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM23 | March 2024 | 3 | stool | diarrhoea | Paediatrics, neonatology | AM, AMC | positive |
| H_SM24 | July 2024 | <1 | haemoculture | fever | Neonatology | AM, CAZ | positive |
| H_SM25 | July 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, CTX, CAZ | positive |
| H_SM27 | July 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM28 | August 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM29 | August 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM30 | August 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM31 | August 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM32 | August 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM33 | July 2024 | 1 | stool | diarrhoea | Paediatrics | AM, CTX | positive |
| H_SM34 | July 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Paediatrics | AM, CAZ | positive |
| H_SM35 | September 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM36 | September 2024 | 3 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CTX, CAZ | positive |
| H_SM37 | September 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM38 | September 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Gynaecology and Obstetrics | AM, AMC | negative |
| H_SM39 | September 2024 | <1 | rectal swab | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC, CTX, CAZ | positive |
| H_SM40 | October 2024 | <1 | stool | diarrhoea | Neonatology | AM, AMC | negative |
| August 2023 | October 2023 | November 2023 | December 2023 | January 2024 | February 2024 | March 2024 | July 2024 | August 2024 | September 2024 | October 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building 2 | |||||||||||
| Paediatric, neonatology unit | 2 | 1 | |||||||||
| Paediatric, GE unit | 1 | ||||||||||
| Paediatric, ER | 1 | ||||||||||
| Clinic for paediatric surgery, Department for abdominal surgery | 1 | ||||||||||
| Paediatric | 2 | ||||||||||
| Building 1 | |||||||||||
| Neonatology Unit | 1 | 2 | 1 | 7 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Gynaecology and Obstetrics Unit | 1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |||||||
| ESBL | AMR Phenotypic Pattern | blaTEM-1B | blaSHV-2 | blaTEM-1B and blaSHV-2 | No. of Isolates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESBL-negative | Ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate | 13 | 1 | 14 | |
| ESBL-positive | Ampicillin | 1 | 1 | ||
| Ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, cefotaxime | 5 | 5 | |||
| Ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, cefotaxime, ceftazidime | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin | 1 | 1 | |||
| Ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, ceftazidime | 1 | 1 | |||
| Ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, ceftriaxone | 1 | 1 | |||
| Ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone | 3 | 3 | |||
| Ampicillin, cefotaxime | 1 | 1 | |||
| Ampicillin, cefotaxime, ceftazidime | 1 | 1 | |||
| Ampicillin, ceftazidime | 2 | 2 | |||
| Missing phenotypic data | 1 | 1 |
| Virulence Genes | |
|---|---|
| Adherence | csgA, csgB, csgC, csgD, csgE, csgF, csgG, fimC, fimD, fimF, fimH, fimI, misL, sinH, steA, steB, steC, |
| Effector delivery system | sipA, sipB, sipC, sipD, invC, sopA, sopB, sopD, sopD2, sopE2, prgH, prgI, prgJ, prgK, invA, invB, invE, invF, invG, invH, invI, invJ, sicA, sicP, spaO, spaP, spaQ, spaR, spaS, ssaA, ssaB, ssaC, ssaD, ssaE, ssaF, ssaG, ssaH, ssaI, ssaJ, ssaK, ssaL, ssaM, ssaN, ssaO, ssaP, ssaQ, ssaR, ssaS, ssaT, ssaU, ssaV, sscA, sscB, orgA, orgB, orgC, sptP, sseJ, sseK2, sseL, pipB, pipB2, sifA, sifB, avrA, spiC/ssaB, sprP |
| Exotoxin | cdtB |
| Nutritional/Metabolic factor | mgtC, mgtB |
| Antimicrobial activity and biofilm formation [40] | mig-14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferencak, I.; Gveric Grginic, A.; Juzbasic, T.; Tabain, I.; Tonkic, M.; Goic-Barisic, I.; Juric, D.; Jankovic, H.; Katic, L.; Novak, A. Unravelling the Persistence of the Rare Serovar Salmonella Mikawasima in a Hospital Setting: A Whole-Genome Sequencing Study. Pathogens 2025, 14, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050408
Ferencak I, Gveric Grginic A, Juzbasic T, Tabain I, Tonkic M, Goic-Barisic I, Juric D, Jankovic H, Katic L, Novak A. Unravelling the Persistence of the Rare Serovar Salmonella Mikawasima in a Hospital Setting: A Whole-Genome Sequencing Study. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050408
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerencak, Ivana, Ana Gveric Grginic, Tajana Juzbasic, Irena Tabain, Marija Tonkic, Ivana Goic-Barisic, Dragan Juric, Hrvojka Jankovic, Luka Katic, and Anita Novak. 2025. "Unravelling the Persistence of the Rare Serovar Salmonella Mikawasima in a Hospital Setting: A Whole-Genome Sequencing Study" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050408
APA StyleFerencak, I., Gveric Grginic, A., Juzbasic, T., Tabain, I., Tonkic, M., Goic-Barisic, I., Juric, D., Jankovic, H., Katic, L., & Novak, A. (2025). Unravelling the Persistence of the Rare Serovar Salmonella Mikawasima in a Hospital Setting: A Whole-Genome Sequencing Study. Pathogens, 14(5), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050408







