Post-Surgical Central Nervous System Infections in the Era of Multidrug Antibiotic Resistance in Greece—A Single-Center Experience of a Decade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Microbiology Data
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Outcomes
3.3. Survivors Vs. Non-Survivors
3.4. ICU Length of Stay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conen, A.; Walti, L.N.; Merlo, A.; Fluckiger, U.; Battegay, M.; Trampuz, A. Characteristics and treatment outcome of cerebrospinal fluid shunt-associated infections in adults: A retrospective analysis over an 11-year period. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2008, 47, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinchon, M.; Dhellemmes, P. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infection: Risk factors and long-term follow-up. Child’s Nerv. Syst. ChNS: Off. J. Int. Soc. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2006, 22, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Beek, D.; Drake, J.M.; Tunkel, A.R. Nosocomial bacterial meningitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.M.; Zimmermann, L.L.; Huynh, M.; Polage, C.R. Diagnostic Approach to Health Care- and Device-Associated Central Nervous System Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, K.; Hasbun, R. Central nervous system infections associated with neurologic devices. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 34, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, C.A.; Quigley, M.; Worel, A.M.; Post, C.; Zimmerli, S.; Ehrlich, G.; Veeh, R.H. Biofilm-related infections of cerebrospinal fluid shunts. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihawan, C.; Castelblanco, R.L.; Salazar, L.; Wootton, S.H.; Aguilera, E.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Sandberg, D.I.; Choi, H.A.; Lee, K.; Kitigawa, R.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Predictors of Adverse Outcome in Adult and Pediatric Patients With Healthcare-Associated Ventriculitis and Meningitis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, M.; Lipman, J.; Shorr, A.; Shankar, A. A meta-analysis of ventriculostomy-associated cerebrospinal fluid infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourbeti, I.S.; Vakis, A.F.; Ziakas, P.; Karabetsos, D.; Potolidis, E.; Christou, S.; Samonis, G. Infections in patients undergoing craniotomy: Risk factors associated with post-craniotomy meningitis. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citerio, G.; Signorini, L.; Bronco, A.; Vargiolu, A.; Rota, M.; Latronico, N. External Ventricular and Lumbar Drain Device Infections in ICU Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Italian Study. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Pu, K.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, Q. The Role of Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Shunt Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2017, 108, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korinek, A.M.; Baugnon, T.; Golmard, J.L.; van Effenterre, R.; Coriat, P.; Puybasset, L. Risk factors for adult nosocomial meningitis after craniotomy: Role of antibiotic prophylaxis. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strahm, C.; Albrich, W.C.; Zdravkovic, V.; Schöbi, B.; Hildebrandt, G.; Schlegel, M. Infection Rate after Cranial Neurosurgical Procedures: A Prospective Single-Center Study. World Neurosurg. 2018, 111, e277–e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruki, Y.; Hagiya, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Yukiue, T.; Tsuboi, N.; Sugiyama, T. Risk factors for Propionibacterium acnes infection after neurosurgery: A case-control study. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 23, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, P.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, D.; Ge, Z. Risk Factors and Outcomes of Central Nervous System Infection After Spinal Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. World Neurosurg. 2023, 170, e170–e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, J.G.; Rindler, R.S.; Chu, J.K.; Grossberg, J.A.; Pradilla, G.; Ahmad, F.U. Complications following cranioplasty and relationship to timing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 33, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyke, K.E.; Obasanjo, O.O.; Williams, M.A.; O’Brien, M.; Chotani, R.; Perl, T.M. Ventriculitis complicating use of intraventricular catheters in adult neurosurgical patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 2028–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Wen, L.; Zhu, Y. Prospective study evaluating post-operative central nervous system infections following cranial surgery. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 33, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, E.; Moore, J.; Cervantes-Arslanian, A.M. Neurosurgical Infections. Semin. Neurol. 2019, 39, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, F.; Walcott, B.P.; Kwon, C.S.; Sheth, S.A.; Asaad, W.; Nahed, B.V.; Eskandar, E.N.; Coumans, J.V. The Absence of Fever or Leukocytosis Does Not Exclude Infection Following Cranioplasty. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 42, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabi, Y.; Manca, A.; Ryan, J.; Elshawarby, A. Value of procalcitonin as a marker of surgical site infection following spinal surgery. Surgeon 2019, 17, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nau, R.; Sörgel, F.; Eiffert, H. Central nervous system infections and antimicrobial resistance: An evolving challenge. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2021, 34, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Shen, J.; Tong, Y.; Yu, H.; Wen, L. Post-operative central nervous system infections after cranial surgery in China: Incidence, causative agents, and risk factors in 1470 patients. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, S., III; Hall, W.A. Postoperative Central Nervous System Infection: Incidence and Associated Factors in 2111 Neurosurgical Procedures. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojak, R.; Koźba-Gosztyła, M.; Gaik, M.; Madej, M.; Majerska, A.; Soczyński, O.; Czapiga, B. Meningitis after elective intracranial surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, G.; Tumbarello, M.; Spanu, T.; Rosell, R.; Iacoangeli, M.; Scerrati, M.; Tacconelli, E. Risk factors and prognostic indicators of bacterial meningitis in a cohort of 3580 postneurosurgical patients. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, M.C.; Medeiros, E.A.; Ferraz, F.A. Hospital-acquired meningitis in patients undergoing craniotomy: Incidence, evolution, and risk factors. Am. J. Infect. Control 2002, 30, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Hsieh, M.K.; Lu, M.L.; Tsai, T.T.; Lai, P.L.; Fu, T.S.; Niu, C.C.; Chen, L.H. Postoperative meningitis after spinal surgery: A review of 21 cases from 20,178 patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (U.S.). CDC/NHSN Surveillance Definitions for Specific Types of Infections; Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Snowdin, J.W.; Mercuro, N.J.; Madaio, M.P.; Rawlings, S.A. Case report: Successful treatment of OXA-23 Acinetobacter baumannii neurosurgical infection and meningitis with sulbactam-durlobactam combination therapy. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1381123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofanopoulos, A.; Fermeli, D.; Vekios, D.; Bizos, A.; Marangos, M.; Constantoyannis, C.; Panagiotopoulos, V.; Assimakopoulos, S.F. Successful treatment of pan-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial meningitis/ventriculitis by combined intravenous and intrathecal colistin-tigecycline administration: A case series. Infez. Med. 2023, 31, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mounier, R.; Lobo, D.; Cook, F.; Martin, M.; Attias, A.; Aït-Mamar, B.; Gabriel, I.; Bekaert, O.; Bardon, J. From the skin to the brain: Pathophysiology of colonization and infection of external ventricular drain, a prospective observational study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e142320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, P.; Gordon, M.; Soriano, A.; Gil-Perotin, S.; Marti, V.; Gonzalez-Barbera, E.M. Assessment or the in vivo formation of biofilm on external ventricular drainages. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paharik, A.E.; Horswill, A.R. The Staphylococcal Biofilm: Adhesins, regulation, and host response. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 529–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompilio, A.; Scribano, D.; Sharsar, M.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Palamara, A.T.; Ambrosi, C. Gram-negative bacteria holding together in a biofilm: The Acinetobacter baumannii way. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, K.; Bitterman, R.; Shofty, B.; Paul, M.; Neuberger, A. Management of postneurosurgical meningitis: Narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, K.; Rabino, G.; Feder, O.; Eghbaryeh, H.; Zayyad, H.; Sviri, G.; Benenson, R.; Paul, M. Risk factors for meningitis in neurosurgical patients with cerebrospinal fluid drains: Prospective observational cohort study. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, M.; Franzoi, F.; Sergi, M.; De Cassai, A.; Geraldini, F.; Grandis, M.; Caravello, M.; Boscolo, A. Extensively drug-resistant and multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens in the neurocritical intensive care unit. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 164, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Li, L.; Deng, X.Y.; Cui, D.M.; Gao, L. Outcome following the treatment of ventriculitis caused by multi/extensive drug resistance Gram negative Bacilli; Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumonia. Front. Neurol. 2019, 9, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtaran, B.; Kuscu, F.; Ulu, A.; Inal, A.; Kömür, S.; Kibar, F.; Çetinalp, N.; Özsoy, K. The causes of postoperative meningitis: The comparison of Gram-negative and Gram-positive pathogens. Turk. Neurosurg. 2018, 28, 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, T.; Sok, K.; Erickson, T.; Aguilera, E.; Wootton, S.H.; Murray, K.O.; Hasbun, R. The comparison of Gram-positive and Gram-negative healthcare-associated ventriculitis and meningitis in adults and children. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2023–2021 Data; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and World Health Organization: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023.
- Chidambaram, S.; Nair, M.N.; Krishnan, S.S.; Cai, L.; Gu, W.; Vasudevan, M.C. Postoperative Central Nervous System Infection After Neurosurgery in a Modernized, Resource-Limited Tertiary Neurosurgical Center in South Asia. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Durkin, J.; Byers, K.E.; Snyderman, C.H.; Gardner, P.A.; Shields, R.K. Microbiologic and Clinical Description of Postoperative Central Nervous System Infection After Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2023, 175, e434–e438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, S.R.; Baharvahdat, H.; Spetzler, R.F.; Sauvageau, E.; Chang, S.W.; Stiefel, M.F.; Park, M.S.; Bambakidis, N.C. Operative intracranial infection following craniotomy. Neurosurg. Focus. 2008, 24, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, L.J.; Chen, W.L.; Chang, Y.J.; Wang, S.H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Yen, H.C. Risk factors associated with postcraniotomy meningitis: A retrospective study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvouniaris, M.; Brotis, A.; Tsiakos, K.; Palli, E.; Koulenti, D. Current Perspectives on the Diagnosis and Management of Healthcare-Associated Ventriculitis and Meningitis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 697–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Goda, R.; Borkar, S.A.; Katiyar, V.; Agarwal, S.; Kumar, A.; Mohapatra, S.; Kapil, A.; Suri, A. Outcome following postneurosurgical Acinetobacter meningitis: An institutional experience of 72 cases. Neurosurg. Focus. 2019, 47, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvouniaris, M.; Brotis, A.G.; Tsiamalou, P.; Fountas, K.N. The role of intraventricular antibiotics in the treatment of nosocomial ventriculitis/meningitis from Gram-negative pathogens: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018, 120, e637–e650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Gao, L. Treatment of severe ventriculitis caused by extensively drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii by intraventricular lavage and administration of colistin. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzi, M.; Karvouniaris, M.; Makris, D.; Tsimitrea, E.; Gatos, C.; Tasiou, A.; Mantzarlis, K. Bundle of measures for external cerebral ventricular drainage-associated ventriculitis. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek Senturk, G.; Ozay, R.; Kul, G.; Altay, F.A.; Kuzi, S.; Gurbuz, Y.; Tutuncu, E.; Eser, T. Evaluation of post-operative meningitis: Comparison of meningitis caused by Acinetobacter spp. And other possible causes. Turk. Neurosurg. 2019, 29, 804–810. [Google Scholar]
- Tunkel, A.R.; Hasbun, R.; Bhimraj, A.; Byers, K.; Kaplan, S.L.; Scheld, W.M.; van de Beek, D.; Bleck, T.P. 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America’s clinical practice guidelines for healthcare-associated Ventriculitis and meningitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, e34–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaiskos, I.; Galani, L.; Baziaka, F.; Giamarellou, H. Intraventricular and intrathecal colistin as the last therapeutic resort for the treatment of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ventriculitis and meningitis: A literature review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2013, 41, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Spandidos, D.A.; Papalexis, P.; Gkoufa, A.; Aravantinou-Fatorou, A.; Angelopoulou, E.; Trakas, I.; Trakas, N.; Fotakopoulos, G. Outcomes in meningitis-ventriculitis treated with intravenous or intrathecal plus intravenous colistin: A meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adapa, A.R.; Linzey, J.R.; Moriguchi, F.; Daou, B.J.; Khalsa, S.S.; Ponnaluri-Wears, S. Risk factors and morbidity associated with surgical site infection subtypes following adult neurosurgical procedures. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 38, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozier, A.P.; Sciacca, R.R.; Romagnoli, M.F.; Connolly, E.S., Jr. Ventriculostomy-related infections: A critical review of the literature. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotakopoulos, G.; Makris, D.; Chatzi, M.; Tsimitrea, E.; Zakynthinos, E.; Fountas, K. Outcomes in meningitis/ventriculitis treated with intravenous or intraventricular plus intravenous colistin. Acta Neurochir. 2016, 158, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, A.; Shofty, B.; Bishop, B.; Naffaa, M.E.; Binawi, T.; Babich, T.; Rappaport, Z.H.; Zaaroor, M.; Sviri, G.; Yahav, D.; et al. Risk factors associated with death or neurological deterioration among patients with Gram-negative postneurosurgical meningitis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 573.e1–573.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bonis, P.; Lofrese, G.; Scoppettuolo, G.; Spanu, T.; Cultrera, R.; Labonia, M.; Cavallo, M.A.; Mangiola, A.; Anile, C.; Pompucci, A. Intraventricular versus intravenous colistin for the treatment of extensively drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii meningitis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remeš, F.; Tomáš, R.; Jindrák, V.; Vaniš, V.; Setlík, M. Intraventricular and lumbar intrathecal administration ofantibiotics in postneurosurgical patients with meningitis and/or ventriculitis in a serious clinical state. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Lin, P.C.; Chou, C.H.; Ho, C.M.; Lin, K.H.; Tsai, C.T.; Wang, J.H.; Chi, C.Y.; Ho, M.W. Intraventricular antimicrobial therapy in postneurosurgical Gram-negative bacillary meningitis or ventriculitis: A Hospital-based retrospective study. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2014, 47, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. Treatment of ventriculitis and meningitis after neurosurgery caused by Carbapenem-Resistant enterobacteriaceae (CRE): A challenging topic. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 3807–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfisterer, W.; Mühlbauer, M.; Czech, T.; Reinprecht, A. Early diagnosis of external ventricular drainage infection: Results of a prospective study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefnagel, D.; Dammers, R.; Ter Laak-Poort, M.P.; Avezaat, C.J. Risk factors for infections related to external ventricular drainage. Acta Neurochir. 2008, 150, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.R.; Peterson, K.D.; Andrus, M.L.; Tolson, J.S.; Goulding, J.S.; Dudeck, M.A.; Mincey, R.B.; Pollock, D.A.; Horan, T.C. NHSN Facilities: National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Report, data summary for 2006, issued June 2007. Am. J. Infect. Control 2007, 35, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatos, C.; Fotakopoulos, G.; Chatzi, M.; Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Spandidos, D.A.; Makris, D.; Fountas, K.N. Investigation of risk factors for external ventricular drainage-associated central nervous system infections in patients undergoing neurosurgery. Med. Int. 2023, 3, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, R.P.; Schinkel, J.; Visser, L.G.; Van Dijk, J.M.; Voormolen, J.H.; Kuijper, E.J. Bacterial meningitis caused by the use of ventricular or lumbar cerebrospinal fluid catheters. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
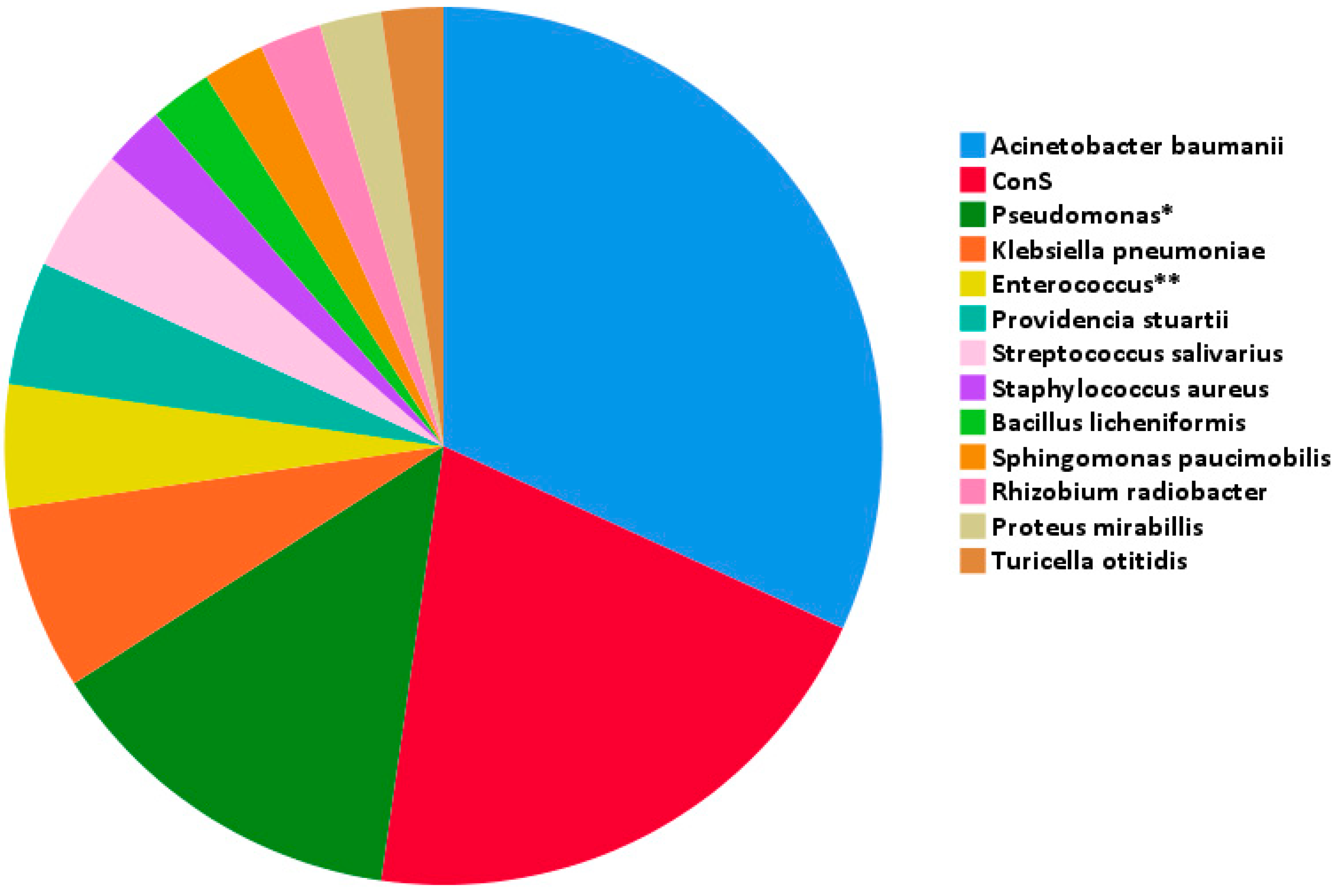
| Pathogen | N | Type of Procedure (No. of Cases) | Type of Infection (No. of Cases) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 14 |
|
|
| ConS | 9 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas spp. * | 6 |
|
|
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 3 |
|
|
| Enterococcus spp. ** | 2 |
|
|
| Providencia stuartii | 2 |
|
|
| Streptococcussalivarius | 2 |
|
|
| Bacilluslicheniformis | 1 |
|
|
| Proteus mirabilis | 1 |
|
|
| Rhizobium radiobacter | 1 |
|
|
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis | 1 |
|
|
| Staphylococcus aureus | 1 |
|
|
| Turicella otitidis | 1 |
|
|
| Acinetobacter | ConS | Pseudomonas | Klebsiella | Enterococcus | Providencia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDR | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ||
| XDR | 9 | 2 | 2 | |||
| PDR | 3 | 1 | ||||
| MRSE | 3 |
| Characteristics | Survivors | Non-Survivors | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 32 (10.8–52.8) | 56 (45–65) | <0.01 |
| Sex (male/female) | 10/4 | 19/8 | 1 |
| Susceptibility to empirical treatment (%) | 71.4% | 59.3% | 0.44 |
| Leukocytes (/mm3) | 131 (54.5–218) | 460 (61–1075) | 0.15 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 44 (24–66) | 36 (24–79) | 0.7 |
| Protein (mg/dL) | 80 (54.4–435.3) | 95 (61.3–209.1) | 0.82 |
| Leukocytes (/μL) | 10,510 (6450–15,800) | 10,535 (6665–15,805) | 0.83 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.53 (0.48–0.95) | 0.65 (0.39–0.84) | 0.35 |
| PCT (ng/mL) | 0.57 (0.29–0.81) | 0.19 (0.11–0.4) | 0.015 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 40 (19–40) | 22 (16.5–101.7) | 0.63 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.03 (1.47–3.26) | 2.7 (2.27–2.76) | 0.93 |
| ICU length of stay (days) | 1 (0–16.5) | 25 (18.5–34.5) | <0.01 |
| CCI | 0 (0–1) | 1 (0–2) | 0.14 |
| Time to infection (days of PM) | 10 (6.3–21.5) | 17 (9–24) | 0.49 |
| Previous hospitalization | 6 | 8 | 0.48 |
| Previous antibiotic treatment | 6 | 6 | 0.16 |
| Previous head surgery | 2 | 6 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markakis, K.; Kapiki, K.; Edric, A.A.A.; Pappas, A.A.; Feretos, G.; Nanoudis, S.; Pilalas, D.; Michailidis, T.; Protonotariou, E.; Skoura, L.; et al. Post-Surgical Central Nervous System Infections in the Era of Multidrug Antibiotic Resistance in Greece—A Single-Center Experience of a Decade. Pathogens 2025, 14, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040390
Markakis K, Kapiki K, Edric AAA, Pappas AA, Feretos G, Nanoudis S, Pilalas D, Michailidis T, Protonotariou E, Skoura L, et al. Post-Surgical Central Nervous System Infections in the Era of Multidrug Antibiotic Resistance in Greece—A Single-Center Experience of a Decade. Pathogens. 2025; 14(4):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040390
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkakis, Konstantinos, Konstantina Kapiki, Angela Ava Arbelle Edric, Asimina Aphrodite Pappas, Georgios Feretos, Sideris Nanoudis, Dimitrios Pilalas, Theodoros Michailidis, Efthymia Protonotariou, Lemonia Skoura, and et al. 2025. "Post-Surgical Central Nervous System Infections in the Era of Multidrug Antibiotic Resistance in Greece—A Single-Center Experience of a Decade" Pathogens 14, no. 4: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040390
APA StyleMarkakis, K., Kapiki, K., Edric, A. A. A., Pappas, A. A., Feretos, G., Nanoudis, S., Pilalas, D., Michailidis, T., Protonotariou, E., Skoura, L., Foroglou, N., Metallidis, S., & Tsachouridou, O. (2025). Post-Surgical Central Nervous System Infections in the Era of Multidrug Antibiotic Resistance in Greece—A Single-Center Experience of a Decade. Pathogens, 14(4), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040390









