Adipose Tissue in Chagas Disease: A Neglected Component of Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
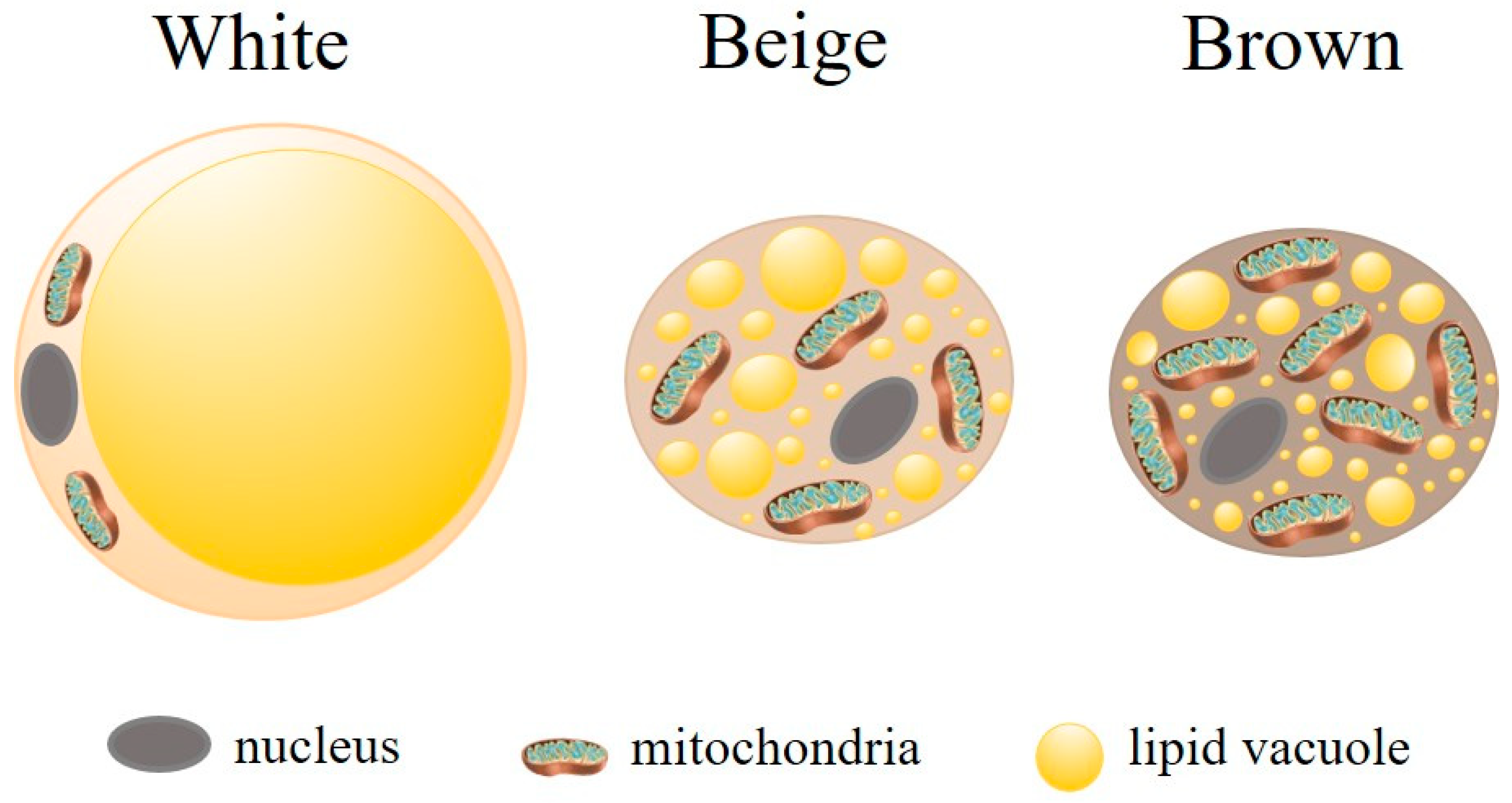
2. Complexity of Adipose Tissue: Structure and Function
3. Pathogens in White Adipose Tissue
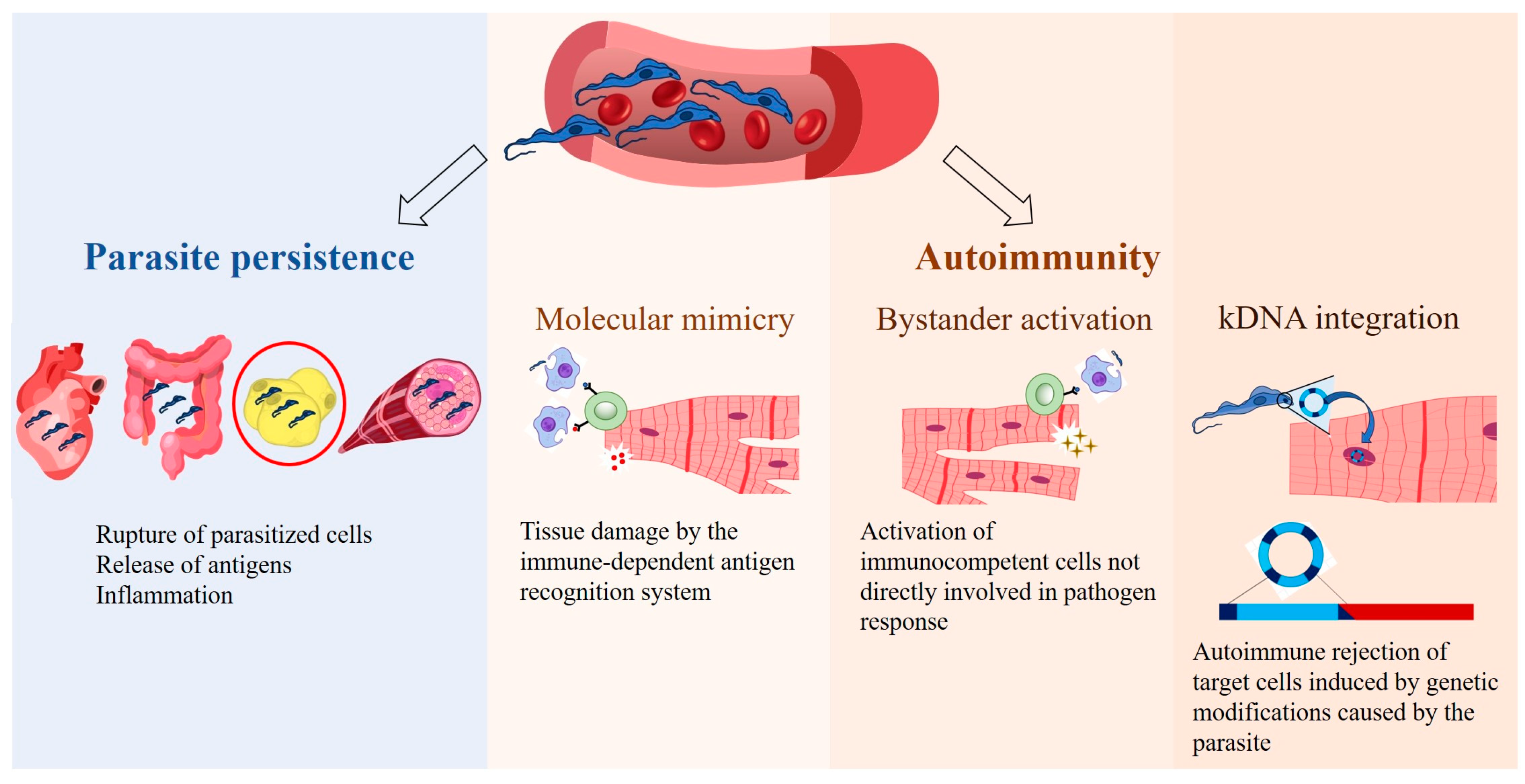
4. Consequences of T. cruzi Presence in Adipose Tissue
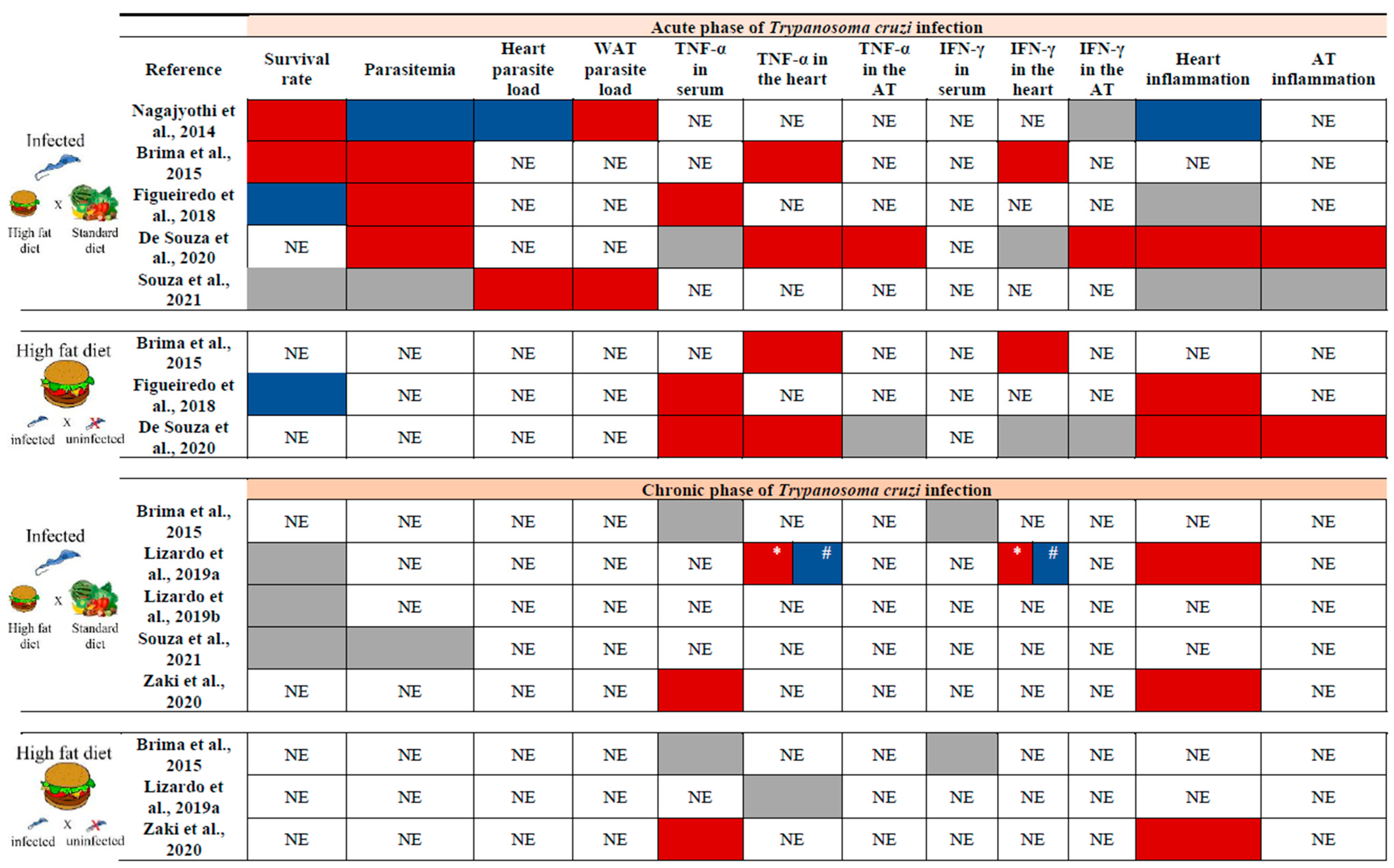
5. Influence of a High-Fat Diet on the Physiology of Adipose Tissue and Chagas Disease
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | Chagas disease |
| AT | adipose tissue |
| HFD | high-fat diet |
| qPCR | quantitative PCR |
| kDNA | kinetoplast DNA |
| CCC | chronic Chagas cardiomyopathy |
| WAT | white adipose tissue |
| BAT | brown adipose tissue |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| PAT | pink adipose tissue |
| PBMCs | peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| PPAR-γ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| AD | adiponectin |
| ATF-7 | activating transcription factor-7 |
| BMI | body mass index |
| dpi | days post-infection |
| MFD | medium-fat diet |
| IFN-γ | interferon-gamma |
| SD | standard diet |
| LDLr | low-density lipoprotein receptor |
References
- WHO Chagas Disease (Also Known as American Trypanosomiasis). 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chagas-disease-(american-trypanosomiasis) (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Fernandes, M.C.; Andrews, N.W. Host Cell Invation by T. cruzi: A Unique Strategy That Promotes Persistence. FEMS Microbiol. 2013, 36, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Escolano, J.; Marín, C.; Rosales, M.J.; Tsaousis, A.D.; Medina-Carmona, E.; Martín-Escolano, R. An Updated View of the T. cruzi Life Cycle: Intervention Points for an Effective Treatment. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarner, J. Chagas Disease as Example of a Reemerging Parasite. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 36, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, V.; Dias, N.; Paiva, T.; Hagström-Bex, L.; Nitz, N.; Pratesi, R.; Hecht, M. Current Trends in the Pharmacological Management of Chagas Disease. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2020, 12, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bona, E.; Lidani, K.C.F.; Bavia, L.; Omidian, Z.; Gremski, L.H.; Sandri, T.L.; de Messias Reason, I.J. Autoimmunity in Chronic Chagas Disease: A Road of Multiple Pathways to Cardiomyopathy? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, F.; Machado, F.S.; Burleigh, B.A.; Jelicks, L.A.; Scherer, E.; Mukherjee, S.; Lisanti, M.P.; Weiss, L.M.; Garg, N.J.; Tanowitz, H.B. Mechanisms of T. cruzi Persistence in Chagas Disease. Cell Microbiol 2012, 14, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Mazliah, D.; Ward, A.I.; Lewis, M.D. Host-Parasite Dynamics in Chagas Disease from Systemic to Hyper-Local Scales. Parasite Immunol. 2021, 43, e12786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.D.; Fortes Francisco, A.; Taylor, M.C.; Burrell-Saward, H.; Mclatchie, A.P.; Miles, M.A.; Kelly, J.M. Bioluminescence Imaging of Chronic T. cruzi Infections Reveals Tissue-Specific Parasite Dynamics and Heart Disease in the Absence of Locally Persistent Infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, M.D.; Kelly, J.M. Putting Infection Dynamics at the Heart of Chagas Disease. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Toloza, G.; Ferreira, A. T. cruzi Evades the Complement System as an Efficient Strategy to Survive in the Mammalian Host: The Specific Roles of Host/Parasite Molecules and T. cruzi Calreticulin. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverría, L.E.; Rojas, L.Z.; Rueda-Ochoa, O.L.; Gómez-Ochoa, S.A.; González Rugeles, C.I.; Díaz, M.L.; Marcus, R.; Morillo, C.A. Circulating T. cruzi Load and Major Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy: A Prospective Cohort Study. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2020, 25, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.; Langston, H.C.; Costa, F.C.; Olmo, F.; Taylor, M.C.; McCann, C.J.; Kelly, J.M.; Lewis, M.D. Local Association of T. cruzi Chronic Infection Foci and Enteric Neuropathic Lesions at the Tissue Micro-Domain Scale. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.T.; Schmidt, A.; da Silva, M.C.; Donadi, E.A.; da Silva, J.S.; Marin-Neto, J.A. Parasitic Load Correlates With Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Patients With Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 741347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcon, G.E.B.; de Albuquerque, D.M.; Batista, A.M.; Andrade, P.D.; Almeida, E.A.; Guariento, M.E.; Teixeira, M.A.B.; Costa, S.C.B. T. cruzi: Parasite Persistence in Tissues in Chronic Chagasic Brazilian Patients. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein, E.; Serna, C.; Fragoso, S.P.; Nagarkatti, R.; Debrabant, A. A Novel Nanoluciferase-Based System to Monitor T. cruzi Infection in Mice by Bioluminescence Imaging. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagajyothi, F.; Weiss, L.M.; Zhao, D.; Koba, W.; Jelicks, L.A.; Cui, M.H.; Factor, S.M.; Scherer, P.E.; Tanowitz, H.B. High Fat Diet Modulates T. cruzi Infection Associated Myocarditis. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanowitz, H.B.; Scherer, P.E.; Mota, M.M.; Figueiredo, L.M. Adipose Tissue: A Safe Haven for Parasites? Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, L.R.; Silva, A.C.; Oliveira, C.N.d.C.; Júnior, C.D.d.S.; Nascimento, A.V.; Oliveira, K.K.D.S.; Soares, A.K.d.A.; Saraiva, K.L.A.; Cavalcanti, M.d.P.; de Lorena, V.M.B. Benznidazole Treatment Decreases IL-6 Levels in T. cruzi-Infected Human Adipocytes Differentiated from Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2023, 118, e220295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Leone, J.L.; Vigliano, C.A. Chagas Disease: Historic Perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonney, K.M.; Engman, D.M. Autoimmune Pathogenesis of Chagas Heart Disease: Looking Back, Looking Ahead. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Buch, C.A.; Teixeira, A.R.L. The Immunology of Experimental Chagas’ Disease. J. Exp. Med. 1974, 140, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.R.L.; Hecht, M.M.; Guimaro, M.C.; Sousa, A.O.; Nitz, N. Pathogenesis of Chagas’ Disease: Parasite Persistence and Autoimmunity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 592–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley, M.; Moraes, A.; Rosa, A.d.C.; Carvalho, J.L.; Shiroma, T.; Vital, T.; Dias, N.; de Carvalho, B.; Rabello, D.D.A.; Borges, T.K.D.S.; et al. Correlation of Parasite Burden, Kdna Integration, Autoreactive Antibodies, and Cytokine Pattern in the Pathophysiology of Chagas Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, T.P.; Nagajyothi; Mukherjee, S.; De Almeida, C.J.; Jelicks, L.A.; Schubert, W.; Lin, Y.; Jayabalan, D.S.; Zhao, D.; Braunstein, V.L.; et al. The Adipocyte as an Important Target Cell for T. cruzi Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24085–24094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.V.M.; Segatto, M.; Menezesb, Z.; Macedo, A.M.; Gelaped, C.; de Oliveira Andrade, L.; Nagajyothif, F.; Schererg, P.E.; Teixeira, M.M.; Tanowitzf, H.B. Evidence for T. cruzi in Adipose Tissue in Human Chronic Chagas Disease. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabalén, M.E.; Cabral, M.F.; Sanmarco, L.M.; Andrada, M.C.; Onofrio, L.I.; Ponce, N.E.; Aoki, M.P.; Gea, S.; Cano, R.C. Chronic T. cruzi Infection Potentiates Adipose Tissue Macrophage Polarization toward an Anti-Inflammatory M2 Phenotype and Contributes to Diabetes Progression in a Diet-Induced Obesity Model. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13400–13415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Añez, N.; Crisante, G. The Tissue Specific Tropism in T. cruzi. Is It True? Acta Trop. 2021, 213, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.C.; Moreira, L.R.; Oliveira, C.N.d.C.; Júnior, C.D.d.S.; do Ó, K.P.; Oliveira, K.K.D.S.; Melo, M.G.N.D.; Soares, A.K.d.A.; Cavalcanti, M.d.P.; Vasconcelos, L.R.S.; et al. Dynamics of the T. cruzi Infection in Adipose Tissue: Assessing Gene Expression of PNPLA2, FASN, and ACAT1 under Benzonidazole Treatment and Indirect Mononuclear Immune Cells Interaction. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2024, 258, 111618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, L.R.; Silva, A.C.; Costa-Oliveira, C.N.d.; Silva-Júnior, C.D.d.; Oliveira, K.K.d.S.; Torres, D.J.L.; Barros, M.D.; Rabello, M.C.d.S.; de Lorena, V.M.B. Interaction between Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells and T. cruzi-Infected Adipocytes: Implications for Treatment Failure and Induction of Immunomodulatory Mechanisms in Adipose Tissue. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1280877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizcano, F.; Arroyave, F. Control of Adipose Cell Browning and Its Therapeutic Potential. Metabolites 2020, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, Z.; Gomez-Salazar, M.; Alexaki, V.I. Innate Immune Cells in the Adipose Tissue in Health and Metabolic Disease. J. Innate Immun. 2022, 14, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, V.; Dhurandhar, N.V. Microbes and Obesity-Interrelationship between Infection, Adipose Tissue and the Immune System. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Stern, J.H.; Scherer, P.E. The Cell Biology of Fat Expansion. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Bonorden, M.J.L.; Pandit, R.; Nkhata, K.J.; Bishayee, A. Infections and Immunity: Associations with Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2023, 57, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGown, C.; Birerdinc, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Sun, X. Effects of Multi-Organ Crosstalk on the Physiology and Pathology of Adipose Tissue. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1198984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, P.E. The Multifaceted Roles of Adipose Tissue—Therapeutic Targets for Diabetes and beyond: The 2015 Banting Lecture. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomou, T.; Mori, M.A.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Konishi, M.; Wolfrum, C.; Rao, T.N.; Winnay, J.N.; Grinspoon, S.K.; Gorden, P.; Kahn, C.R. Adipose-Derived Circulating MiRNAs Regulate Gene Expression in Other Tissues. Nature 2017, 542, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, J.; Bogard, G.; Wolowczuk, I. Beyond Energy Balance Regulation: The Underestimated Role of Adipose Tissues in Host Defense against Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1083191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimura, S.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Seale, P. Brown Adipose Tissue and Its Therapeutic Potential. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oelkrug, R.; Polymeropoulos, E.T.; Jastroch, M. Brown Adipose Tissue: Physiological Function and Evolutionary Significance. J. Comp. Physiol. B Biochem. Syst. Environ. Physiol. 2015, 185, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, L.H.; Heyn, G.S.; Magalhaes, K.G. The Impact of the Adipose Organ Plasticity on Inflammation and Cancer Progression. Cells 2019, 8, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, A.; Smorlesi, A.; Frontini, A.; Barbatelli, G.; Cint, S. White, Brown and Pink Adipocytes: The Extraordinary Plasticity of the Adipose Organ. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, R159–R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, M.W.; Scherer, P.E. Minireview: The Adipocyte—At the Crossroads of Energy Homeostasis, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyappan, J.P.; Ganapathi, U.; Lizardo, K.; Vinnard, C.; Nagajyothi, J.F.; Subbian, S.; Perlin, D.S. Adipose Tissue Regulates Pulmonary Pathology during TB Infection. MBio 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigier-Bompadre, M.; Montagna, G.N.; Kühl, A.A.; Lozza, L.; Weiner, J.; Kupz, A.; Vogelzang, A.; Mollenkopf, H.J.; Löwe, D.; Bandermann, S.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection Modulates Adipose Tissue Biology. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke-Fayard, B.; Janse, C.J.; Cunha-Rodrigues, M.; Ramesar, J.; Büscher, P.; Que, I.; Löwik, C.; Voshol, P.J.; Den Boer, M.A.M.; Van Duinen, S.G.; et al. Murine Malaria Parasite Sequestration: CD36 Is the Major Receptor, but Cerebral Pathology Is Unlinked to Sequestration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11468–11473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, P.; Humberto Treviño-Villarreal, J.; De Niz, M.; Meibalan, E.; Longchamp, A.; Reynolds, J.S.; Turnbull, L.B.; Opoka, R.O.; Roussilhon, C.; Spielmann, T.; et al. Adipose Tissue Parasite Sequestration Drives Leptin Production in Mice and Correlates with Human Cerebral Malaria. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, J.; Emous, M.; Heeringa, P.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.A. Mechanisms and Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2 Infection of the Adipose Tissue. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amisigo, C.M.; Amegatcher, G.; Sunter, J.D.; Gwira, T.M. Adipose and Skin Distribution of African Trypanosomes in Natural Animal Infections. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, H.; Bizarra-Rebelo, T.; Costa-Sequeira, M.; Trindade, S.; Carvalho, T.; Rijo-Ferreira, F.; Pacheco, B.R.; Serre, K.; Figueiredo, L.M. Trypanosoma Brucei Triggers a Broad Immune Response in the Adipose Tissue. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, S.; De Niz, M.; Costa-Sequeira, M.; Bizarra-Rebelo, T.; Bento, F.; Dejung, M.; Narciso, M.V.; López-Escobar, L.; Ferreira, J.; Butter, F.; et al. Slow Growing Behavior in African Trypanosomes during Adipose Tissue Colonization. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwing, A.; Pisani, D.F.; Pomares, C.; Majoor, A.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Jager, J.; Lemichez, E.; Marty, P.; Boyer, L.; Michel, G. Identification of Adipocytes as Target Cells for Leishmania Infantum Parasites. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trindade, S.; Rijo-Ferreira, F.; Carvalho, T.; Pinto-Neves, D.; Guegan, F.; Aresta-Branco, F.; Bento, F.; Young, S.A.; Pinto, A.; Van Den Abbeele, J.; et al. Trypanosoma Brucei Parasites Occupy and Functionally Adapt to the Adipose Tissue in Mice. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, F.; Desruisseaux, M.S.; MacHado, F.S.; Upadhya, R.; Zhao, D.; Schwartz, G.J.; Teixeira, M.M.; Albanese, C.; Lisanti, M.P.; Chua, S.C.; et al. Response of Adipose Tissue to Early Infection with T. cruzi (Brazil Strain). J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Aquino, G.P.; Gomes, M.A.M.; Salinas, R.K.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F. Lipid and Fatty Acid Metabolism in Trypanosomatids. Microb. Cell 2021, 8, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuzarte-Luís, V.; Mota, M.M. Parasite Sensing of Host Nutrients and Environmental Cues. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanowitz, H.B.; Jelicks, L.A.; Machado, F.S.; Esper, L.; Qi, X.; Desruisseaux, M.S.; Chua, S.C.; Scherer, P.E.; Nagajyothi, F. Adipose Tissue, Diabetes and Chagas Disease. Adv. Parasitol. 2011, 76, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevillard, C.; Nunes, J.P.S.; Frade, A.F.; Almeida, R.R.; Pandey, R.P.; Nascimento, M.S.; Kalil, J.; Cunha-Neto, E. Disease Tolerance and Pathogen Resistance Genes May Underlie T. cruzi Persistence and Differential Progression to Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, F.; Weiss, L.M.; Silver, D.L.; Desruisseaux, M.S.; Scherer, P.E.; Herz, J.; Tanowitz, H.B. T. cruzi Utilizes the Host Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor in Invasion. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizardo, K.; Ayyappan, J.P.; Cui, M.H.; Balasubramanya, R.; Jelicks, L.A.; Nagajyothi, J.F. High Fat Diet Aggravates Cardiomyopathy in Murine Chronic Chagas Disease. Microbes Infect. 2019, 21, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizardo, K.; Ayyappan, J.P.; Oswal, N.; Weiss, L.M.; Scherer, P.E.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Fat Tissue Regulates the Pathogenesis and Severity of Cardiomyopathy in Murine Chagas Disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0008964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavel, H.; Dhanyalayam, D.; Kim, M.; Lizardo, K.; Sidrat, T.; Lopez, J.G.; Wang, X.; Bansal, S.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Adipocyte-Released Adipomes in Chagas Cardiomyopathy: Impact on Cardiac Metabolic and Immune Regulation. iScience 2024, 27, 109672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, J.F.; Weiss, L.M. Advances in Understanding the Role of Adipose Tissue and Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in T. cruzi Infection. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.-J.; Nagajyothi, F.; Machado, F.S.; Weiss, L.M.; Scherer, P.E.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Garg, N.J. Markers of Oxidative Stress in Adipose Tissue during T. cruzi Infection. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyappan, J.P.; Lizardo, K.; Wang, S.; Yurkow, E.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Inhibition of SREBP Improves Cardiac Lipidopathy, Improves Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Modulates Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, F.; Desruisseaux, M.S.; Thiruvur, N.; Weiss, L.M.; Braunstein, V.L.; Albanese, C.; Teixeira, M.M.; De Almeida, C.J.; Lisanti, M.P.; Scherer, P.E.; et al. T. cruzi Infection of Cultured Adipocytes Results in an Inflammatory Phenotype. Obesity 2008, 16, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brima, W.; Eden, D.J.; Mehdi, S.F.; Bravo, M.; Wiese, M.M.; Stein, J.; Almonte, V.; Zhao, D.; Kurland, I.; Pessin, J.E.; et al. The Brighter (and Evolutionarily Older) Face of the Metabolic Syndrome: Evidence from T. cruzi Infection in CD-1 Mice. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, V.P.; Junior, E.S.L.; Lopes, L.R.; Simões, N.F.; Penitente, A.R.; Bearzoti, E.; Vieira, P.M.d.A.; Schulz, R.; Talvani, A. High Fat Diet Modulates Inflammatory Parameters in the Heart and Liver during Acute T. cruzi Infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 64, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizardo, K.; Ayyappan, J.P.; Ganapathi, U.; Dutra, W.O.; Qiu, Y.; Weiss, L.M.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Diet Alters Serum Metabolomic Profiling in the Mouse Model of Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 4956016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, D.M.S.; de Paula Costa, G.; Leite, A.L.J.; de Oliveira, D.S.; de Castro Pinto, K.M.; Farias, S.E.B.; Simões, N.F.; de Paiva, N.C.N.; de Abreu Vieira, P.M.; da Silva, C.A.M.; et al. A High-Fat Diet Exacerbates the Course of Experimental T. cruzi Infection That Can Be Mitigated by Treatment with Simvastatin. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1230461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, D.M.S.d.; Silva, M.C.; Farias, S.E.B.; Menezes, A.P.d.J.; Milanezi, C.M.; Lúcio, K.d.P.; Paiva, N.C.N.; Abreu, P.M.d.; Costa, D.C.; Pinto, K.M.d.C.; et al. Diet Rich in Lard Promotes a Metabolic Environment Favorable to T. cruzi Growth. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 667580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, P.; Domingues, E.L.; Amjad, F.M.; Narde, M.B.; Gonçalves, K.R.; Viana, M.L.; de Paula, H.; de Lima, W.G.; Huang, H.; Bahia, M.T.; et al. The Role of Fat on Cardiomyopathy Outcome in Mice Models of Chronic T. cruzi Infection. Parasitol Res. 2020, 119, 1829–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.D.; Francisco, A.F.; Taylor, M.C.; Jayawardhana, S.; Kelly, J.M. Host and Parasite Genetics Shape a Link between T. cruzi Infection Dynamics and Chronic Cardiomyopathy. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría, M.H.; Ríos, L.D.; Corral, R.S. T. cruzi Down-Regulates Adiponectin Expression in Mouse Adipocytes via the NFAT Signaling Pathway. Microbes Infect. 2021, 23, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, F.B.; Villar, S.R.; Toneatto, J.; Pacini, M.F.; Márquez, J.; D’Attilio, L.; Bottasso, O.A.; Piwien-Pilipuk, G.; Pérez, A.R. Immune Response Triggered by T. cruzi Infection Strikes Adipose Tissue Homeostasis Altering Lipid Storage, Enzyme Profile and Adipokine Expression. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Qi, Y.; Yi, H.; Mao, C.; Meng, Q.; Wang, H.; Zheng, C. The Roles of Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Human Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 908749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, F.; Zhao, D.; Machado, F.S.; Weiss, L.M.; Gary, J.; Desruisseaux, M.S.; Zhao, Y.; Factor, S.M.; Albanese, C.; Teixeira, M.M.; et al. Crucial Role of the Central Leptin Receptor in Murine T. cruzi Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, F.; Villar, S.; D’Attilio, L.; Leiva, R.; Marquez, J.; Lioi, S.; Beloscar, J.; Bottasso, O.; Perez, A.R. Dysregulated Network of Immune, Endocrine and Metabolic Markers Is Associated to More Severe Human Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy. Neuroimmunomodulation 2018, 25, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Shibata, R.; Walsh, K. Targeting Adiponectin for Cardioprotection. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2006, 10, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z. Adipokines in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Adipocyte 2023, 12, 2202976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, F.; Dantas, S.; Ianni, B.M.; Ramires, F.J.A.; Buck, P.; Salemi, V.M.C.; Lopes, H.F.; Mady, C. Leptin Levels in Different Forms of Chagas’ Disease. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2007, 40, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Ferreira, J.M.; Mady, C.; Ianni, B.M.; Lopes, H.F.; Ramires, F.J.A.; Salemi, V.M.C.; Grupi, C.J.; Hachul, D.T.; Fernandes, F. Dysregulation of Autonomic Nervous System in Chagas’ Heart Disease Is Associated with Altered Adipocytokines Levels. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabarian, A.L.; Mady, C.; Barbosa-Ferreira, J.M.; Ianni, B.M.; Hotta, V.T.; Ramires, F.J.A.; Lopes, H.F.; Buck, P.d.C.; Pessoa, F.G.; Fonseca, K.C.B.; et al. Dysregulation of Insulin Levels in Chagas Heart Disease Is Associated with Altered Adipocytokine Levels. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, Z.A.; Silva, H.R. Parasitism of Adipocytes by T. cruzi. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1995, 90, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, J.P.; Hoffman, R.V., Jr.; Huffman, D.G. T. cruzi: Preference for Brown Adipose Tissue in Mice by the Tulahuen Strain. Exp. Parasitol. 1970, 27, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyappan, J.P.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Diet Modulates Adipose Tissue Oxidative Stress in a Murine Acute Chagas Model. JSM Atheroscler. 2017, 2, 1030. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Lizardo, K.; Cui, M.H.; Ambadipudi, K.; Lora, J.; Jelicks, L.A.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Antagonistic Effect of Atorvastatin on High Fat Diet Induced Survival during Acute Chagas Disease. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M.; Reardon, T. Obesity and the Food System Transformation in Latin America. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1028–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraix, J.; Ardisson, L.P.; Marcondes-Machado, J.; Pereira, P.C.M. Clinical and Nutritional Profile of Individuals with Chagas Disease. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janoschek, R.; Handwerk, M.; Hucklenbruch-Rother, E.; Schmitz, L.; Bae-Gartz, I.; Kasper, P.; Lackmann, J.W.; Kretschmer, T.; Vohlen, C.; Mesaros, A.; et al. Heterogeneous Effects of Individual High-Fat Diet Compositions on Phenotype, Metabolic Outcome, and Hepatic Proteome Signature in BL/6 Male Mice. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estadella, D.; Oyama, L.M.; Dâmaso, A.R.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Oller Do Nascimento, C.M. Effect of Palatable Hyperlipidic Diet on Lipid Metabolism of Sedentary and Exercised Rats. Nutrition 2004, 20, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, S.; Kumar, V.; Murphy, E.A.; Enos, R.T.; Singh, U.P. High Fat Diet-Induced CD8+ T Cells in Adipose Tissue Mediate Macrophages to Sustain Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 680944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, S.; Manabe, I.; Nagasaki, M.; Eto, K.; Yamashita, H.; Ohsugi, M.; Otsu, M.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Sugiura, S.; et al. CD8+ Effector T Cells Contribute to Macrophage Recruitment and Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johndrow, C.; Nelson, R.; Tanowitz, H.; Weiss, L.; Nagajyothi, F. T. cruzi Infection Results in an Increase in Intracellular Cholesterol. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pessoa, V.F.d.S.; Hecht, M.; Nitz, N.; Hagström, L. Adipose Tissue in Chagas Disease: A Neglected Component of Pathogenesis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040339
Pessoa VFdS, Hecht M, Nitz N, Hagström L. Adipose Tissue in Chagas Disease: A Neglected Component of Pathogenesis. Pathogens. 2025; 14(4):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040339
Chicago/Turabian StylePessoa, Vitória França dos Santos, Mariana Hecht, Nadjar Nitz, and Luciana Hagström. 2025. "Adipose Tissue in Chagas Disease: A Neglected Component of Pathogenesis" Pathogens 14, no. 4: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040339
APA StylePessoa, V. F. d. S., Hecht, M., Nitz, N., & Hagström, L. (2025). Adipose Tissue in Chagas Disease: A Neglected Component of Pathogenesis. Pathogens, 14(4), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040339






