Abstract
As crucial vectors that transmit pathogens to humans and livestock, ticks pose substantial global health threats and economic burdens. We analyzed 328 tick genomes to explore the population’s genetic structure and the adaptive evolution of H. longicornis and R. microplus, two tick species with distinct life cycle characteristics. We observed distinct genetic structures in H. longicornis and R. microplus. Gene flow estimation revealed a closer genetic connection in R. microplus than H. longicornis, which was facilitated by geographical proximity. Notably, we identified a set of candidate genes associated with possible adaptations. Specifically, the immune-related gene DUOX and the iron transport gene ACO1 showed significant signals of natural selection in R. microplus. Similarly, H. longicornis exhibited selection in pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent enzyme genes associated with heme synthesis. Moreover, we observed significant correlations between the abundance of pathogens, such as Rickettsia and Francisella, and specific tick genotypes, which highlights the role of R. microplus in maintaining these pathogens and its adaptations that influence immune responses and iron metabolism, suggesting potential coevolution between vectors and pathogens. Our study highlights the vital genes involved in tick blood feeding and immunity, and it provides insights into the coevolution of ticks and tick-borne pathogens.
1. Introduction
Ticks, obligate bloodsucking, nonpermanent ectoparasitic arthropods, are one of the most important vectors for globally transmitting pathogens to humans and domestic animals [1,2]. Ticks include 702 species of hard ticks, 193 species of soft ticks, and 1 species of Nuttalliella [3]. Furthermore, ticks serve as a conduit for an extensive array of pathogenic microorganisms, surpassing the diversity transmitted by any other cohort of arthropod vectors. They often carry more than one pathogen and cause a series of tick-borne diseases (TBDs), including Lyme borreliosis, anaplasmosis, babesiosis, and ehrlichiosis [1,3,4,5,6]. Lyme disease cases treated in the United States number 476,000, and there are an estimated 700,000 human cases per year in the United States of America plus Europe [7,8]. Lyme borreliosis primarily spreads through multiple species of hard ticks, and each year, approximately 255,000 individuals worldwide fall ill due to this ailment, which is predominantly concentrated in Europe and North America, and approximately 30,000 cases are reported annually in northern China [9,10]. The economic repercussions of tick-borne illnesses are notable and consistently escalating [11,12,13,14]. These diseases affect nearly 80% of the global cattle population, resulting in estimated global costs of tick and tickborne disease ranging from USD 13.9 to 18.7 billion [15]. Thus, TBDs pose a grave threat to global public health and impose substantial economic burdens on the livestock industry.
The Asian long-horned tick, H. longicornis, has a remarkable capacity to endure a wide range of temperatures, from a developmental threshold of approximately 12 °C to a critical limit of nearly 40 °C [16]. H. longicornis, documented in ten countries, has a versatile host range and is a vector for numerous pathogens. At least 30 human pathogens have been associated with H. longicornis, including seven species of spotted fever group rickettsiae, species in the family of Anaplasmataceae, four genospecies in the complex Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, two Babesia species, six species of virus including severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, Jingmen tick virus, bocavirus, Nairobi sheep disease virus, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, and Francisella, Bartonella, Coxiella, and Toxoplasma, which were mainly reported in eastern Asia [17]. In China, H. longicornis is the most common tick species, with reports identifying at least 15 associated agents, 10 of which have potential pathogenicity to human health [18,19]. As a three-host invasive tick, H. longicornis has demonstrated rapid territorial expansion and robust proliferation within established habitats. Interestingly, this species has shown no discernible geographic structuring within mainland China, highlighting its ecological plasticity and dynamic population structure [20].
In contrast, the cattle tick, R. microplus, a one-host tick, exhibits a distinctive geographical dispersal strategy, resulting in significant economic implications for the cattle industry, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions across the globe. Moreover, R. microplus is a vector for the pathogens responsible for babesiosis (Babesia bovis and B. bigemina) and anaplasmosis (Anaplasma marginale) [21,22,23]. R. microplus has a more distinct population structure in China. A comprehensive comparative analysis of these two tick species in their native range, including analyzing their genetic structures and genomic attributes, influenced by their respective host interaction strategies, can yield valuable insights. Moreover, the difference in gene expression in their different tissues and development stages should be explored to provide a deeper understanding of their individual mechanisms [20].
Understanding the functional impact of pathogen colonization and transmission within tick carriers is imperative for developing innovative strategies to control ticks and tick-borne pathogens using targeted protein interventions [24]. The manipulation of host defenses by ticks is one of the elements that determines the branch of pathogen that a tick successfully transmits. The interaction of ticks and tick-borne pathogens at the host skin interface is critical to establishing an environment conducive to pathogen transmission and development. Ticks can promote blood feeding by inhibiting salivary secretion or regulating host defense [25]. There are several ways to regulate host defense, mainly reducing the host’s perception of pain through immunomodulatory responses in tick saliva. The saliva of some tick species contains kininase and amine (histamine)-binding lipid carrier proteins, which reduce pain and itch responses [26,27]. This is followed by tick inhibition of host hemostasis through the secretion of salivary vasodilators, platelet aggregation inhibitors, and molecules that delay or inhibit components of the clotting cascade and further regulate host wound healing inflammation, inhibit host immune response, and affect pathogen transmission [28,29,30,31]. In addition, different tick species may have multiple immune defense strategies to counteract the host’s major categories of defense regulation, which will be more conducive to pathogen transmission, establishment, and transmission environment [32,33].
The interaction between ticks and pathogens is very complex, including conflict and cooperation, and involves many metabolic pathways, such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and redox pathways. However, both ticks and pathogens benefit from these action mechanisms for survival [34]. Ticks can participate in phagocytosis of different microorganisms through cellular immunity mediated by blood cells [35]. Iron metabolism in ticks may have a role in microbial infection, which is central to host–pathogen interactions [36]. Ticks and pathogens have coevolved mechanisms for acquiring iron from each other, and this ’nutritional immunity’ is essential to maintain balance between ticks and pathogens [37]. Nevertheless, tick-borne pathogen infections induce transcriptional reprogramming, which affects several metabolic pathways in ticks, promoting infection, reproduction, and transmission [38]. They also help the tick complete its life cycle in harsh environments, improving its survival performance [39,40]. Therefore, in some specific cases, vector tolerance to pathogen infection is also a favorable feature of the coevolution of the two [41]. Notably, the most prevalent bacterial genera in ticks are Coxiella (60.5%) and Rickettsia (55.6%), with a broader distribution across tick species than any other genus [42]. Within tick organs, Rickettsia regulates the tick genome, manipulating robust anti-oxidant mechanisms to evade increases in reactive oxygen species (ROS) through a range of selenoproteins and non-selenoproteins (e.g., SOD, catalase, and glutathione reductase) [24]. These findings reveal the coevolution mechanism of ticks and pathogens, and further understanding of tick adaptation to survival, transmission, and tick–pathogen interactions provides an important opportunity to identify new therapeutic targets for tick-borne disease prevention and control [34].
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are the most fundamental form of DNA variation among individuals and can induce alterations in encoded amino acids (non-synonymous), remain silent with no effect on the amino acid sequence (synonymous), or manifest in non-coding regions [43]. These variations have considerable implications, revealing genomic evolutionary processes and inter-individual genetic disparities while also facilitating an in-depth analysis of mechanisms underlying diseases such as diabetes, bipolar disorder, and hypertension [43,44,45,46,47,48]. However, little is known about how SNPs affect the biological functions of ticks and the interactions between tick pathogens and hosts.
Since little is known about the genetic variations of ticks and the interactions between tick-borne pathogens and the genetic background of ticks, we generated high-quality SNP data from the 161 H. longicornis and 140 R. microplus genomes. Then, we performed a genetic analysis to examine the evolutionary history and local adaptation of the two tick species, with a particular focus on blood digestion and immune defense mechanisms, given that these species have distinct host-associated life cycles. Moreover, we carried out an association study on the potential interactions between ticks and pathogens to explore the coevolution between pathogens and tick genomes. Our study highlighted the genetic variations related to host adaptability traits, thereby enriching our understanding of the intricate genomic mechanisms driving tick adaptation to their respective hosts and dynamic environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Alignment
The re-sequenced data of 177 H. longicornis and 151 R. microplus were downloaded from the Genome Sequence Archive database (GSA: PRJCA002242) [20]. Reads of the 328 tick samples were aligned to the corresponding reference genome (ASM1333976v2 and ASM1333972v1, respectively) using Burrows–Wheeler Aligner (BWA) (version 0.7.17) [49]. The SNP callings were performed using the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) (version 4.2.4.1) [50]. Because of unknown sampling locations and a low genomic mapping rate (<50%), 15 H. longicornis and 11 R. microplus were filtered out. Finally, 161 samples of H. longicornis and 140 samples of R. microplus were retained for further analysis.
2.2. Alignment, Variant Calling, and Annotation
Sequencing reads were filtered by removing adaptors and low-quality bases using fastp (version 0.19.3) [51]. This study mapped only qualified pair-end reads to the reference genome (ASM1333976v2 and ASM1333972v1) using BWA-MEM with the -M parameter [52]. The resulting BAM files were marked as duplicates and locally realigned around indels using GATK (version 4.2.4.1) [50]. Because no whole-genome SNP dataset was available for the Base Quality Score Recalibrator (BQSR), we followed the approach recommended on the GTAK website for non-human data. An initial round of variant calling was performed using GATK HaplotypeCaller, and a joint genotyping step for comprehensive variation union was performed on the gVCF files with GATK GenotypeGVCFs. A hard filter was subsequently performed to filter the variants using GATK tools, and the parameters were set by default (for SNPs: QD < 2.0, FS > 60.0, MQ < 40.0, MQRankSum < 12.5, ReadPosRankSum < 8.0). The variants that passed the hard filter were used as a true positive set of variant sites for BQSR. Variant calling was repeated for the recalibrated BAM files, and then, the whole cohort was re-genotyped using GATK. We excluded sites with missing rates > 10% and MAF (minor allele frequency) < 5% in all samples using VCFtools (version 0.1.16) [53]. Functional annotation of SNPs was performed according to the tick genome using the software ANNOVAR (version 2020-6-7) [54].
2.3. Genetic Structure Analyses
First, we performed population structure analysis by filtering out the variants with a missing rate > 10% and MAF < 5% for all samples, and the LD was eliminated by using VCFtools and down-sampled according to the physical interval of no less than 5 kb between any two variants. Moreover, PCA was performed using PLINK (version 1.9) with the thinning SNP datasets [55]. We used the maximum likelihood tree-based approach implemented in IQtree (version 1.6.12) with the GTR+F+R6+ASC model [56]. The population genetic structure was inferred using ADMIXTIRE software (version 1.3.0) [57]. Ten independent runs for each K = 2–10 were carried out, and the process was repeated 10 times with different random seeds. The lowest cross-validation error (CV) value was found in R. microplus for K = 2, increasing for each value of K. We used AncestryPainter (version 1.1) to describe the summation and graphical representation of ADMIXTIRE outputs [58].
VCFtools (version 0.1.16) was used to calculate the nucleotide diversity (π) and fixation index (FST) based on all autosomal high-quality SNPs with a 10 kb window and a step size of 5 kb for every subpopulation [53]. We also calculated Tajima’s D in 10-kb non-overlapping windows across each autosome for each population. Tajima’s D values for each population were calculated using the same sliding window approach with an in-house script. Finally, LD decay was estimated using the PopLDdecay tool (version 3.42) that calculates the genotype correlation coefficient (r2) for pairs of all autosomal unphased SNPs at a maximum distance range of 300 kb [59]. For each subpopulation of H. longicornis and R. microplus, the LD decay was calculated separately and defined by the SubPop option. The LD decay was measured as the chromosomal distance at which the average pairwise r2 decreased to half its maximum value.
We used TreeMix (version 1.13) to estimate the flow of genes across each species [60]. Additionally, we used the estimated effective migration surface (EEMS) to estimate genetic migration patterns in specific geographic areas and compare geographic and genetic distances between different communities by calculating a genetic dissimilarity matrix and assigning geographic coordinates [61]. Finally, the R script provided by EEMS was used to visualize the result in space.
2.4. Detection of Genome-Wide Selection Signals
Multiple tests were used to investigate selection, including cross-population (FST and XP-EHH) and within-population methods (iHS and Tajima’s D) in H. longicornis and R. microplus. To identify the candidate regions of selection, we calculated FST in a 10 kb sliding window with a step size of 5 kb using VCFtools, and an empirical threshold of 1% was chosen as the outlier window. Statistical phasing was performed using Beagle (v. 5.4) [62]. Then, all the phased bi-allelic variants were used to calculate the integrated haplotype scores (iHS) and cross-population extended haplotype homozygosity (XP-EHH) using Selscan (v. 1.3.0) for each chromosome separately [63]. We also used the norm (v. 1.3.0) distributed with Selscan to normalize all Selscan outputs across all chromosomes. Moreover, the p-value of iHS and XP-EHH scores were calculated for 10 kb non-overlapping windows along each chromosome. Windows with a top 1% p-value were considered the selection signal. The same sliding windows with two or more significant SNPs were identified as selected genomic regions. Moreover, PBscan was applied to compute the population branching statistic (PBS) [64].
2.5. Association of Microbial Composition with Tick SNPs
Tick sequences were filtered using SAMtools (version 0.9.24) after mapping the reads of 301 specimens to tick genomes by BWA (version: 0.7.17), and all unmapped reads were retained for subsequent analysis [52,65]. Taxonomic classification was performed by aligning the filtered reads to the NR database using DIAMOND (version 0.9.24, parameters: -f 102 -top 10) [66]. To estimate the relative abundances of different microbial species, we extracted all taxonomic IDs according to the NCBI taxdump ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/taxonomy/taxdmp.zip (accessed on 12 August 2023) (Rickettsia: TaxID780, Anaplasma: TaxID768, Ehrlichia: TaxID 943, Borrelia: TaxID138, Babesia: TaxID 5864, Theileria: TaxID 5873, Francisella: TaxID262, Bartonella: TaxID 773, Coxiella: TaxID 776, Hepatozoon: TaxID 75741, Toxoplasma: TaxID 5810, and Candidatus Neoehrlichia: TaxID 467749). Sequence similarity (>70%) was used as the threshold to screen the alignment results. The union set of the metagenome species that had significantly different abundance between different regions in two ticks (p < 0.05, FDR < 10%, nonparametric two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test; Tables S8–S11) was retained for the correlation analysis. The union set of the host SNPs with the top 0.01 FST between SCC and SEC, SCC and SWC, SEC and SWC, and domestic and overseas populations of the two ticks was selected for the correlation analysis. To decrease the influence of LD, we filtered these SNPs using the tag SNP tagger from Paul de Bakker’s Tagger tag SNP selection algorithm in Haploview [67]. Thus, 28,133 filtered SNPs in R. microplus and 4229 in H. longicornis were recruited for the correlation analysis. Normalized abundance values of metagenome species were treated as quantitative traits for the rank-based Spearman correlation analysis to identify the correlation between the genotype of each SNP. The union set of the host SNPs with a strong selection signal in the two tick species was selected for the correlation analysis. Samples of a single ethnic group in R. microplus and H. longicornis were used to calculate the p-value of a single group using the Spearman correlation test, followed by a meta-analysis to produce the meta-p-value and the adjusted meta-p-value. The results were determined to be significant if meta-p < 0.05, adjusted meta-p < 0.05, and FDR < 10%.
2.6. Functional Enrichments and Differential Expression Analysis of Genes
The functional enrichments of the protein-coding genes were performed by using multiple gene annotation software, including eggNOG-mapper http://eggnog-mapper.embl.de/ (accessed on 9 January 2023), BlastKOALA in KEGG https://www.kegg.jp/blastkoala/ (accessed on 10 January 2023), and interproscan (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence/) (accessed on 10 January 2023) [68,69,70]. In addition, GO, KEGG, and the Retcome pathway were inferred by using the clusterProfiler package in R [71]. The threshold was set as a p-value < 0.01. Hematophagous traits of a tick include host questing, blood meal digestion, detoxification of xenobiotic factors, nutrient metabolism, and an immune response. Genes related to these traits were collected, including 1148 and 1028 genes for H. longicornis and R. microplus, respectively [20].
To further explore the gene expression in R. microplus, transcriptomes of samples from six tissues (ovary, synganglion, salivary gland, fat body, gut) at various stages of development (embryo, partially engorged, and fully engorged female) were downloaded from the NCBI database (project ID: PRJNA232001) [49]. Diverse software programs were put to use. Trim_galore software (version 0.6.7) https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore) (accessed on 15 April 2023) was used to filter out the low-quality reads and adapter sequences with the parameters “--length 70—quality 20—paired”. After quality control, HISAT2 (version 2.2.1) was applied so that the high-quality reads were aligned to the corresponding reference genome (ASM1333972v1) [72]. Afterwards, the read count of each gene was calculated for each sample by HTSeq (version 2.0.2) with parameters “-s no -r pos --mode=union --type exon --idattr gene_id” [73]. We used filterByExpr to filter out the low-expression genes, and calculated the counts per million (CPM) based on the trimmed mean of M-values (TMM) normalization by using the EdgeR package (version 3.38.2) [74]. To determine the gene’s differential expression in different tissues or development stages, we used GFOLD (version 1.1.4) without replicates [75]. A gene with a generalized fold change (GFOLD) value greater than or lower than zero (cutoff = 0.01) was considered differentially expressed [75]. Moreover, in order to understand the effectors that determine tick feeding activities, we downloaded the transcriptome of the tetracycline-treated H. longicornis nymph from the NCBI database (project ID: PRJNA 693137) and followed the same steps to process the transcriptome for subsequent analysis.
To investigate thoroughly the function of gene resistance to pathogen infection in R. microplus and H. longicornis, transcriptomes of the invertebrate pathogen Metarhizium anisopliae JEF-290-infected and uninfected nymph of H. longicornis were downloaded from the NCBI database (project ID: PRJNA714456) [76]. The high-quality reads were aligned to the corresponding reference genome (ASM1333976v2) using HISAT2 (version 2.2.1) [72]. In addition, transcriptomes of the sialotranscriptome profile of R. microplus in response to Theileria equi were downloaded from the NCBI database (project ID: PRJNA695199) [77]. The subsequent analysis followed the same detailed transcriptomic processing steps as previously described. BLASTP [78] https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 29 August 2023) was used to calculate the similarity between two proteins.
3. Results
3.1. Distinct Population Structures in R. microplus and H. longicornis
To understand the population structure and genetic analysis of R. microplus and H. longicornis, we selected available whole-genome sequencing data (mean read coverage of ~8X), including 161 H. longicornis from 14 regions and 140 R. microplus from 12 regions, for an in-depth analysis [20]. The population structure of the two tick species was characterized using a subset of autosomal variants including 177,208 variants in H. longicornis and 1,450,256 variants present in R. microplus by filtering out variants with missing rates of >10%, minor allele frequencies (MAF) of <5%, and a strong linkage disequilibrium (LD). Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the H. longicornis samples were divided into two subclades, and R. microplus samples were divided into three subclades in the two-dimensional PC plot (Figure 1A,B). Moreover, the phylogenetic tree implemented in IQtree (version 1.6.12) revealed the same distinct monophyletic clades for H. longicornis and R. microplus (Figure 1C and Figure S1A). Additionally, we performed ADMIXTURE analysis, which separates the study populations based on their geographic origins to determine the evolutionary history of the two tick populations by individual ancestry coefficients [57]. For R. microplus, the cross-validation error showed the lowest value at K = 2, regarded as the best number of ancestral populations to explain the variation for R. microplus (Figure 1D and Figure S1B,C). The individuals from these two sup-populations, Southeast China (SEC) and Southwest China (SWC), exhibited significantly different ancestral compositions, suggesting low gene flow due to geographic isolation. In contrast, the results for H. longicornis showed no substantial difference in ancestral composition between the identified clusters, which can likely be attributed to its facile invasion of new areas and prolific proliferation within established ranges, prioritizing dispersion over local competition [20].
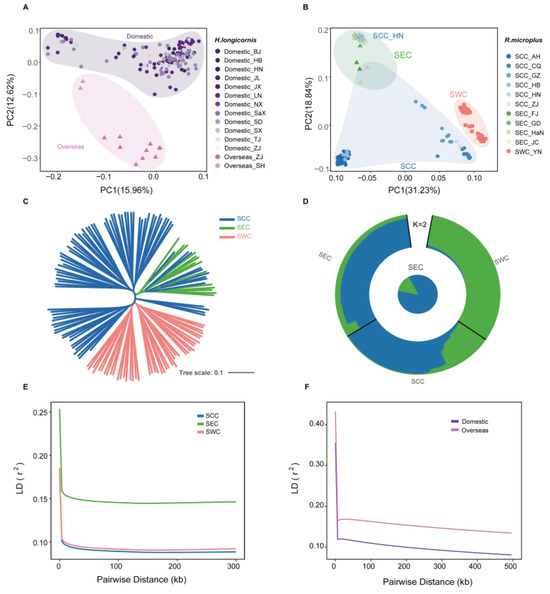
Figure 1.
Population structures of H. longicornis and R. microplus. (A,B) Principal component analysis (PCA) plot showing segregation of H. longicornis and R. microplus individuals, respectively. Differently colored shapes represent samples from different populations and provinces. SCC, South Central China; SEC, Southeast China; SWC, Southwest China. (C) Phylogenetic structure of R. microplus populations. (D) Population genetic structure of all R. microplus sample accessions, as estimated using ADMIXTURE with the best K = 2. The outer circle graphic shows the ancestry proportions of each individual, and the center pie chart highlights the ancestry proportions of the SEC population. Each color represents a different ancestral composition. (E,F) LD decay in different populations of H. longicornis and R. microplus.
The pair-wise LD for all high-quality SNPs was calculated to measure the genetic diversity among these subpopulations. For R. microplus, the LD decreased to half of its maximum value at 24 kb in SEC but was at 0.13 kb and 0.24 kb in South Central China (SCC) and SWC, respectively (Figure 1F). Specifically, the SEC population displayed a relatively slower rate of LD decay than the other populations, indicating lower genetic diversity in SEC and greater diversity in SCC. Conversely, for H. longicornis, the LD decay rate of domestic and overseas populations is basically the same (Figure 1E).
3.2. Genomic Diversity and Population Migration
The geographical distributions of the two tick species in China were apparently different (Figure 2A). We estimated the nucleotide diversity (π) and Tajima’s D in R. microplus and H. longicornis using multiple individuals (Figure 2B and Figure S2A). For R. microplus, the result suggested that the lowest nucleotide diversity was in the SEC population, which is indeed lower than in the other two populations (SCC and SWC) (Figure S2A). Moreover, Tajima’s D showed the same result (Figure 2B). These results suggest that the SEC population significantly differed from the other two populations. The FST value measures the degree of differentiation between the two populations, with the highest value observed between the SEC and SWC populations (Figure S2A). For H. longicornis, Tajima’s D values for both populations were above zero and higher in the domestic population, suggesting potential selection pressure (Figure 2B). However, no significant difference in nucleotide diversity between domestic and overseas was observed (Figure S2B). We examined the gene flow in different regions based on TreeMix and EEMS analyses of R. microplus and H. longicornis. For R. microplus, the Hunan branch, located in SCC, is more similar to the SEC population, possibly due to more accessible communication facilitated by geographical proximity. In contrast, communication with the South Central branch was hindered (Figure 2C,D). Conversely, for H. longicornis, the EEMS results show that the migration rates of the two populations overseas are relatively low (Figure S2C,D), indicating the communication between them and the domestic population is not close. These results appropriately explain the formation of different geographical populations of the two types of ticks, providing a foundation for studying the differences in tick life history and potential virus transmission mechanisms in different regions.
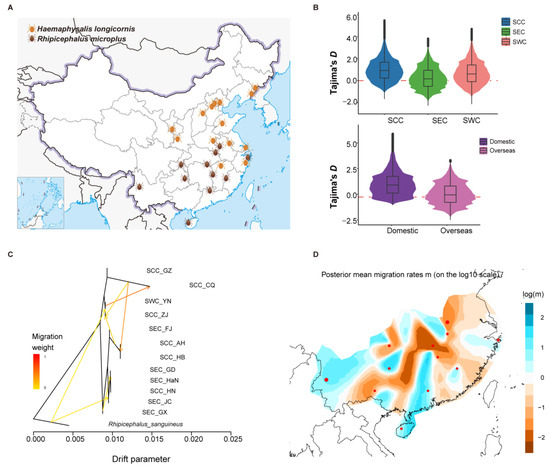
Figure 2.
Gene diversity and gene flow of H. longicornis and R. microplus in different geographical regions. (A) Regional distribution of the two tick species in China. (B) Tajima’s D values of the two tick species in different regions. (C) Gene flow between the different regions for R. microplus populations. (D) Migratory patterns of R. microplus based on EEMS (estimated effective migration surface).
3.3. Genetic Variations Contribute to Blood Meal Digestion and Vector–Pathogen Adaptation in R. microplus
Ingesting blood is a crucial process for tick survival and development, and the free-living stage of the hard tick R. microplus life cycle begins when the fully engorged female drops from the host, which involves a variety of homeostasis regulation mechanisms, including immune regulation [79]. To investigate the genomic signature responsible for the blood meal adaptation to different populations in R. microplus, strong genomic regions were identified using cross-population approaches (FST and XP-EHH) and one within-population approach (iHS). Accordingly, the FST calculation and XP-EHH analysis were used to detect 243 and 664 possible genomic selection regions, respectively, which overlapped 497 annotated protein-coding genes detected by at least one method mentioned above. Additionally, within-population natural selection tests identified 600 selection regions with significant (p < 0.05) iHS values, harboring 372 potentially selected protein-coding genes. Several genes bearing signals of positive selection in the SEC and SWC populations are associated with immune regulation in the stress response (e.g., SNRK, UBE2QL1, CTSC, Vacuolar H+ ATPases, MAPK, and Hsp60) and iron transport in the blood (e.g., Cytochrome.P450) (Table S1) [80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88]. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis showed that the selected genes were significantly enriched in the categories related to response to hydrogen peroxide, reactive oxygen species, protein tyrosine kinase activity, cell death, and T-cell activation (Table S2), indicating that these gene categories may play critical roles in tick development, reproduction, and survival when ticks are exposed to different environments [89].
We focused on the candidate gene DUOX because it has been identified as a robust selection signal through FST and iHS analysis in the whole genome, ranking seventh in the FST values of SEC and SWC populations (Figure 3A; Tables S1, S3 and S4). Moreover, it has been confirmed in multiple previous studies to be related to reduction–oxidation homeostasis during a blood meal in ticks. Additionally, we determined a specific site (chr9: g. 142,127,589 A > G) that ranked as the first value in the FST analysis. It showed a 0.1% maximal population branch statistic (PBS) value in the SEC population (Figure S3A), which indicated that it possibly plays an essential role in affecting and regulating the expression of DUOX. The variant 142,127,589 is located in the intron region of DUOX and may play an important role in regulating gene expression. According to our findings, the frequency of the G genotype of variant rs142127589 decreased from SEC to SCC and SWC, respectively. It was nearly absent in SEC, with the lowest alternative allele frequency of 0%, and no significant (p < 0.05) correlation was found between the variant rs142127589 genotype and overall pathogen abundance in different populations of R. microplus (Figure 3B and Figure S3B). Moreover, we observed distinct patterns in pathogen types carried by individuals with different genotypes of rs142127589, with Rickettsias more abundant in individuals with the G genotype (Figure 3C). Furthermore, extended haplotype homozygosity (EHH) around this SNP also indicated that the SEC population had slower homozygosity decay than other populations, confirming that the SEC population underwent a selective sweep in DUOX (Figure 3D). DUOX, a vital member of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase family, is crucial for maintaining mucosal immunity [90]. To further investigate and confirm the function of the DUOX gene, the transcriptomes from samples from multiple tissues at various stages of development were used for gene expression analysis, and we observed that the DUOX gene was highly expressed in the SGs (Figure 3E) [49]. Collectively, these findings suggest that DUOX plays a crucial role in immune response regulation and pathogen interactions, highlighting its potential as a key evolutionary driver of tick adaptation.
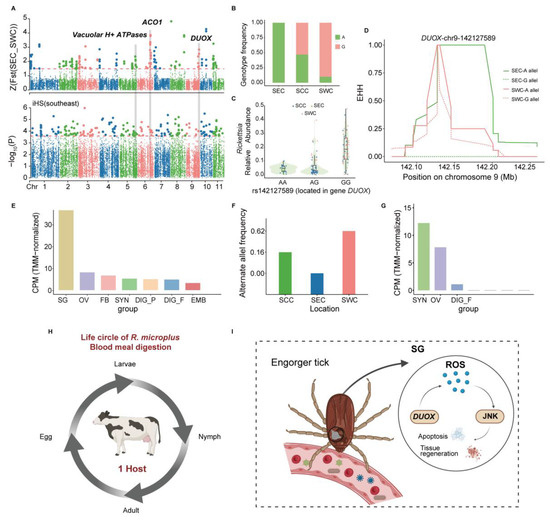
Figure 3.
DUOX gene and ACO1 gene contribution to blood digestion and the immune response of R. microplus. (A) Whole-genome scan with FST and iHS for the SNPs around DUOX, ACO1, and Vacuolar H+ ATPases between the Southeast China (SEC) and Southwest China (SWC) populations. FST is normalized as Z scores for R. microplus. The horizontal red dashed lines represent the empirical threshold for the selected regions. (B) Genotype frequency of rs142127589 among the three R. microplus populations. (C) Correlation of a DUOX SNP (rs142127589) with the abundance of Rickettsias. (D) Haplotype decay around the DUOX-chr9-142127589 allele in SEC and SWC populations. (E) Gene expression of the DUOX gene in different tissues or development stages. Digestive cells from fully engorged female ticks (DIG_F); fat bodies from partially and fully engorged adult females (FB); synganglion from partially and fully engorged adult females (SYN); digestive cells from partially engorged female ticks (DIG_P); embryos (EMB); ovaries from partially and fully engorged adult females (OV); salivary glands from partially and fully engorged adult females (SG). (F) Alternative allele frequency across the three R. microplus populations. (G) Gene expression of ACO1 gene in different tissues or development stages. (H) Life circle of R. microplus blood meal digestion. (I) The DUOX gene contributes to blood digestion and the immune response in R. microplus.
Iron homeostasis is vital for hematophagous arthropods during blood feeding, as it profoundly impacts their reproduction and development [91,92,93]. The gene LOC119172490, identified through strong selection signals in FST and XP-EHH analyses (Figure 3A and Figure S4A,B and Tables S1, S3 and S5), exhibits a higher alternative allele frequency in the SWC population compared to others (Figure 3F). We observed distinct patterns in pathogen types carried by individuals with different genotypes of rs152825916, with Ehrlichia less abundant in individuals with the G genotype (Figure S4C). However, no significant (p < 0.05) correlation was found between the variant rs152825916 genotype and overall pathogen abundance in different populations of R. microplus (Figure S4D). Annotated as cytoplasmic aconitate hydratase-like (ACO1), this gene regulates cellular iron homeostasis by acting as IRP1 in its oxidized form (Figure S4E) [94,95,96,97,98]. Transcriptome analysis revealed high ACO1 expression in the synganglion and ovaries across developmental stages (Figure 3G). These results indicate that iron homeostasis regulation involving the ACO1 gene plays an important role in the physiology of ticks [49].
3.4. Genetic Variations of H. longicornis Contribute to Heme Synthesis and Correlate with Coxiella Abundance
H. longicornis, which is widely distributed and predominant in at least 17 provinces in China, has a complex genetic landscape that is closely linked to its geographic distribution [99]. It is critical to understand its genetic complexity and determine the links between its genomic variation and geographic distribution. To elucidate a potential genetic candidate for these differences, we used two cross-population approaches (FST and XP-EHH) and one within-population approach (iHS) to scan the genomic selective region between domestic and overseas populations. Notably, our FST and XP-EHH results did not show significant selection signals. We focused on the domestic population and identified 29 candidate genes detectable by the iHS (Table S6). The KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the selected genes were significantly (p < 0.05) enriched in the categories related to amino acid synthesis and metabolism (Table S7). The HaeL19522 gene was particularly of interest, with notable positive selection in the domestic population that ranked fourth, and it showed remarkable enrichment in the KEGG pathway (Figure 4A; Table S7). Moreover, this gene showed a noticeable difference in genotype frequency between domestic and overseas populations, with the AA genotype carrying a wider variety and abundance of pathogens in the domestic population (Figure 4B and Figure S5A). Interestingly, for variant rs65770851, the pathogen Coxiella exhibited a unique abundance pattern, which was more prevalent in individuals with the G genotype in both populations (Figure 4C).
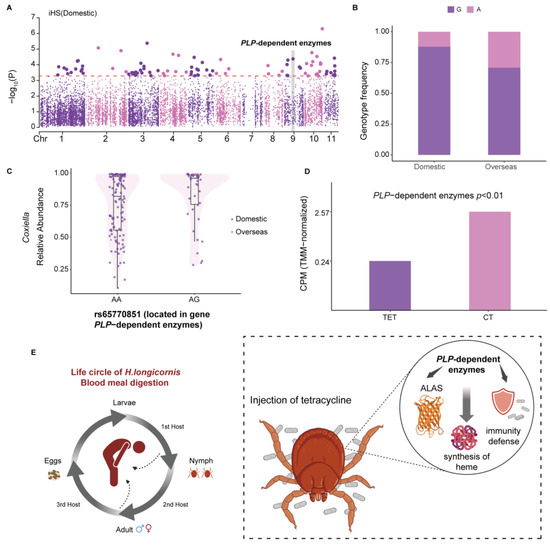
Figure 4.
PLP-dependent enzyme gene contributes to blood digestion in H. longicornis. (A) Whole-genome scan with iHS: top 1% windows; the horizontal red dashed lines represent the empirical threshold for the selected regions. (B) Genotype frequency of rs65770851 across H. longicornis populations. (C) Correlation of a PLP-dependent enzyme SNP (rs65770851) with the abundance of Coxiella. (D) PLP-dependent enzymes in nymphs treated with tetracycline (TET) versus controls (CT) (E) PLP-dependent enzyme genes contributing to blood digestion and heme synthesis in H. longicornis.
We annotated the HaeL19522 gene as a PLP-dependent enzyme through protein homologous analysis. PLP-dependent enzymes refer to a class of enzymes that rely on the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, also known as the active form of vitamin B6), which participate in many vital biochemical reactions in organisms, covering a wide range of metabolic pathways and biological functions [100,101]. To investigate the function of this gene in tick blood meal digestion, we compared gene expression data between H. longicornis nymphs treated with and without tetracycline. Treatment with tetracycline impacts the blood feeding of ticks, mainly by reducing the number of endosymbionts, such as Coxiella, which can promote tick blood feeding [102]. The expression of PLP-dependent enzymes was markedly reduced after tetracycline treatment, indicating that PLP-dependent enzymes play an essential role in blood feeding (Figure 4D,E). We also investigated the gene expression between the invertebrate pathogen M. anisopliae JEF-290-infected and uninfected ticks. PLP-dependent enzymes revealed a slightly lower expression in uninfected ticks compared with infected ones (|generalized fold change/GFOLD| = 0.584128 > 0.01) (Figure S5B). M. anisopliae JEF-290 significantly controls tick transmission, indicating that PLP-dependent enzymes have a particular role in tick immunity. The above results showed that the PLP-dependent enzymes/HaeL19522 gene are meaningful for H. longicornis during blood feeding and its immunological defense against pathogens.
3.5. Correlation Between Genetic Variants of Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogen Abundance
Understanding the interaction between pathogens and ticks is essential for elucidating the mechanisms of TBDs. We hypothesized that highly differentiated SNPs between tick populations may likely to influence the differentiated pathogens in ticks. Thus, we investigated the correlation between different tick genetic variates and microbiome species that were differentially prevalent across tick populations. In total, 28,133 filtered SNPs in R. microplus (see Section 2), 4229 in H. longicornis, and 12 filtered microbiome species (see Section 2) were selected for correlation analysis. Among these features, we identified significant correlations of SNPs with species using a meta-analysis of different populations in these two tick species. Our meta-analysis revealed no significant SNPs associated with pathogens in H. longicornis. In contrast, we identified several SNPs in functional genes related to blood feeding in R. microplus, suggesting significant differences in the association of pathogens with these two tick species (Table S12).
We found that a certain number of species and their correlated tick SNPs could affect tick immunity. For instance, the species Rickettsia was observed to be the most differentiated species between SCC and SWC (p = 9.48 × 10−10, Wilcox test; Table S9) and between SEC and SWC (p = 1.37 × 10−6; Wilcox test; Table S10). Rickettsia infection may trigger a series of innate immune responses in ticks, including three main immune signaling pathways of arthropods: Toll, IMD, and JAK/STAT [103]. Its correlated SNP (rs88416395, meta-p = 4 × 10−7, Spearman correlation test) is located in the immune-related gene TLR, which is a primary sensor of microbial pathogens that activates innate immune cells and initiates and orchestrates adaptive immune responses [104]. The correlation pattern of this locus with Rickettsia is opposite to that of Bartonella and Francisella (Figure 5A–C), indicating that different microbial species may induce distinct immune patterns, potentially influencing pathogen–host interactions, and this phenomenon that has been widely observed in other arthropod species as well [105]. Additionally, in the southwest region, the GA genotype frequency is higher than in the other two regions (Figure 5D), indicating different patterns of association between microbes and regions. This suggests the presence of specific microbial species in a given geographic region may exert selective pressure on the tick population, favoring certain genotypes that confer better resistance or tolerance to local pathogens.
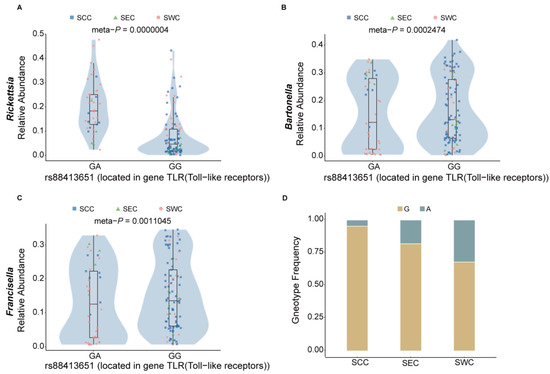
Figure 5.
The tick genetic variant rs88416395 is correlated with the abundance of tick-borne pathogens. (A–C) Correlation of a Toll-like receptors SNP (rs88418395) with Rickettsia, Bartonella, and Francisella abundance, respectively. (D) Genotype frequency of rs88418395 among the SCC, SEC, and SWC populations.
Moreover, the species Francisella has been reported to have successfully transitioned from mammalian to arthropod hosts by sensing changes in iron and/or altering the expression of iron-regulated genes in ticks [106]. Its associated SNP (rs210552537, meta-p = 1.91 × 10−3) is located in the UTR3 of protein-coding gene cytochrome P450 reductase, which is an essential redox partner for all cytochrome P450 enzymes, facilitating the transfer of electrons from NADPH into numerous physiological reactions [107]. The cytochrome P450 reductase complex, in conjunction with the iron component poly(rC)-binding protein 2, forms an auxiliary system that assists in heme catabolism and iron transfer [108]. Iron-regulated genes have been shown to play an essential role in regulating the virulence of Borrelia burgdorferi [109]. Under iron-limiting conditions, many differentially expressed genes of LVS of F. tularensis are related to virulence or intracellular replication. Our data showed that the frequency of the G genotype of the variant rs210552537 decreases from SCC to SEC and SWC populations (Figure S6A,B) [110]. This pattern of decreasing G allele frequency could indicate a selective pressure exerted by the regional differences in microbial communities, with implications for the ability of Francisella to adapt and survive in varying ecological niches.
4. Discussion
The differences between H. longicornis and R. microplus are significant in terms of their ecological roles, host interactions, and implications for disease transmission [111]. The geographical distribution and population interaction of H. longicornis and R. microplus exhibit strikingly different patterns, reflecting distinct ecological and biological traits between these two tick species, which is consistent with previous findings based on SNV and mtDNA data [20,112]. Building upon genetic structure analysis, we identified two distinct branches within H. longicornis, comprising domestic and overseas populations. In contrast, the geographical distribution pattern of R. microplus was more clearly delineated, with three branches, the south central, southeast, and southwest, mirroring previous population structure inferences [20]. Furthermore, population migration and gene flow analyses highlighted that gene flow between populations of R. microplus was more extensive compared to H. longicornis. The divergence in population structure and interaction can be attributed to differences in survival strategies, ecological niches, and life cycle characteristics [113]. H. longicornis displays remarkable adaptability, thriving across diverse habitats such as grasslands and forest edges in temperate regions, which supports its widespread distribution [114,115]. Its three-host life cycle facilitates rapid dispersal and reduces genetic differentiation among populations [20]. In addition, H. longicornis has the unique feature of having both parthenogenetic and bisexual populations [116]. Moreover, studies have shown that parthenogenetic populations spread more rapidly than bisexual ones, and phylogenetic analysis revealed distinct lineages for these populations, suggesting no gene flow between them [112,117]. However, this relationship could not be explored in the present study due to the lack of data on the absence of an assembled genome for parthenogenetic H. longicornis. In contrast, R. microplus is predominantly confined to warm, humid environments, typically in tropical and subtropical regions, where its distribution is closely tied to livestock farming [118]. This single-host species feeds primarily on cattle, and the regional differentiation of its populations may be influenced by variations in cattle breeds and associated farming practices across different regions [119,120]. The interplay of ecological and biological factors highlights the critical influence of species-specific traits, including life cycle strategies, host specialization, and environmental adaptability, in shaping the population structure and geographical distribution of tick species [121]. These findings underscore the importance of comprehensive genomic studies to uncover the genetic and evolutionary mechanisms driving tick ecology and to enhance our understanding of their roles in disease transmission and host interaction.
Differentiated habitats and species-specific traits are critical in shaping the genomic adaptations and evolutionary mechanisms of the two tick species, H. longicornis and R. microplus. Both species demonstrate genomic adaptations associated with blood feeding and coevolution with pathogens, yet they exhibit notable differences in the specificity of their adaptive evolution. For H. longicornis, statistical analyses across populations identified genes involved in heme synthesis, particularly PLP-dependent enzymes. PLP-dependent enzymes may play an essential role in heme synthesis. Previous research has reported that ALAS is a type of PLP-dependent enzyme, which is the starting enzyme of the heme synthesis pathway and catalyzes the reaction between histidine and pyruvate to form δ-aminoketoglutaric acid [122,123]. PLP-dependent enzymes exhibit significant genotype and allele frequency differences between domestic and overseas populations, reflecting distinct ecological adaptations. Furthermore, the genotype frequencies of PLP-dependent enzymes correlate positively with the abundance of Coxiella. Previous studies have shown that endosymbiont Coxiella is vital for regulating tick 5-HT biosynthesis and feeding [102]. Experimental treatment with tetracycline significantly reduced Coxiella abundance in H. longicornis and concomitantly decreased the expression levels of PLP-dependent enzyme genes, suggesting their critical role in reproductive development during blood feeding. In contrast, R. microplus displays a stronger association between its genomic features and host-specific adaptations. Genes critical for blood digestion and immune responses, such as LOC119178146/DUOX, have been identified. DUOX, an oxidative stress enzyme essential for mucosal immunity, plays a central role in tick–pathogen interactions, disease transmission, and blood meal processing [90]. In Drosophila, previous studies have shown that DUOX helps maintain intestinal redox homeostasis in the midgut [124]. In A. gambiae, the heme immunomodulatory peroxidase (IMPer), secreted by its intestinal epithelial cells, catalyzes the formation of a non-cellular molecular barrier called a dityrosine network (DTN), which blocks the transmission of epithelial immune elicitors and plays a vital role in intestinal epithelial cell immunity and maintaining host–microbial homeostasis [125]. Previous studies have shown that the DTN also exists in I. scapularis ticks [126]. RNAi-mediated DUOX knockdown reduces levels of B. burgdorferi persistence in ticks, with the absence of DTN formation [126]. Transcriptomic analysis revealed that the DUOX gene is highly expressed in the salivary glands of ticks [49]. Tick SGs are organs of osmoregulation in ticks. Both the SGs and saliva have been investigated mainly for their indispensable role in the response to pathogen infection and transmission, host hemostasis, and immune responses [127,128,129,130]. Previous studies have shown the same result, that a transcript annotated as DUOX A has been suggested to act in the trafficking of DUOX to the cell plasma membrane in mammalian liver, which has shown higher transcriptional levels in SGs from fully engorged adult female ticks [131]. Moreover, in the salivary glands of ticks, many signals related to degeneration and the onset of apoptosis have been described [132]. DUOX plays a key role in the JNK pathway. During the early stages of apoptosis in tick salivary gland cells, NADPH oxidase mediates the formation of ROS and activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, which in turn activates the moladietz (mol) gene [133,134]. JNK transcriptionally activates the gene that encodes the DUOX maturation factor (NPI), which is essential for ROS production, and in turn, triggers JNK activation during tissue regeneration, creating a feedback loop that maintains JNK activity throughout the regeneration process (Figure 3I) [131,133,134]. Furthermore, the enzyme produced by DUOX can directly damage pathogens by generating reactive oxygen species, produce antimicrobial peptides such as Duox/Mesh in the Lmd and JAK/STAT signaling pathways, mediate ROS expression, and trigger melanosis cascades [135]. This pathway involves various bactericidal substances and also plays a critical role in intestinal immunity [134]. Furthermore, the genotype frequencies of rs142127589 loci within DUOX are highly correlated with pathogen abundance and exhibit pronounced regional variation, aligning with tick ecological adaptations and pathogen transmission dynamics. Previous studies have reported that infection with Rickettsia parkeri affects the physiology and gene expression of Amblyoma maculatum ticks [136]. Thus, the frequency of the G genotype of the variant rs142127589 and its correlated Rickettsias might be one of the factors affecting the role of DUOX in different regions. Additionally, R. microplus demonstrates genomic adaptations linked to iron transport during blood-feeding. The gene LOC119172490/ACO1, encoding a key enzyme in iron and ROS metabolism, is highly expressed in the ganglia and ovaries, indicating its role in reproduction, development, and pathogen transmission [49,96]. Previous studies have confirmed that silencing IRP1-related genes, including ACO1, has been shown to reduce female hatching rates and post-blood-meal weights [137]. Notably, variation allele frequencies (VAF) for DUOX and ACO1 across the three R. microplus populations align with regional cattle breed distribution. Resistant cattle breeds predominate in the southern regions (lower VAF), while hybrid tick-resistant and susceptible breeds dominate the central and southwestern regions (higher VAF). This host specificity and regional variation underscore the coevolution of R. microplus with Asian cattle, as previously documented [138]. Together, these findings highlight both shared and divergent genomic adaptations in H. longicornis and R. microplus. While both species exhibit coevolutionary traits with pathogens and blood-feeding adaptations, R. microplus shows a stronger link between its genomic features and host-specific ecological variations, reflecting distinct pathways of adaptive evolution.
Ticks and pathogens interact in complex ways that significantly influence the vectorial competence of ticks, playing a key role in TBDs [139]. Pathogens transmitted by ticks have evolved mechanisms to survive in their arthropod hosts by manipulating gene expression in specific environments like the midgut or salivary glands [140,141]. These interactions can impact various aspects of tick biology, including nutrition, fitness, development, reproduction, immune response, and tolerance to environmental stress [142]. The ecological and biological traits of different tick species can shape these interactions and influence their capacity to transmit pathogens [143]. H. longicornis exhibits a broad host range, infesting various mammals, including livestock, wildlife, and humans, which contributes to its potential as a vector for multiple pathogens, such as Borrelia spp. and Anaplasma spp. [1]. This versatility allows H. longicornis to adapt to diverse ecological niches, making it a notable concern for zoonotic diseases. In contrast, R. microplus is more specialized, primarily targeting cattle, and is responsible for transmitting significant pathogens such as Babesia bovis and Anaplasma marginale [144]. Life cycle dynamics further distinguish these ticks. H. longicornis follows a three-host life cycle, where each developmental stage (larva, nymph, adult) typically feeds on a different host [114]. This multi-host requirement can enhance its ability to spread pathogens across species [145]. In contrast, R. microplus is capable of completing its life cycle on a single host, allowing for increased reproduction rates and more efficient establishment in cattle populations [146]. This trait not only facilitates its persistence in endemic regions but also enhances its role in pathogen amplification [147]. Our analyses of pathogen abundance in the two tick species revealed further distinctions. We quantified the abundance of 12 pathogens and performed association studies between normalized pathogen loads and positively selected loci. In H. longicornis, no significant associations were identified. However, in R. microplus, we found two significant SNPs (rs88416395, meta-p = 4 × 10−7; rs210552537, meta-p = 1.91 × 10−3) that were strongly associated with the microbes Rickettsia and Francisella, and further studies have shown that the two genes are related to the immune system and iron metabolism of ticks (Table S12) [104,107]. Previous studies have shown that Rickettsia and Francisella, commonly found in species like R. microplus, are known to affect tick reproductive success and development by correlating with diverse pathogenic mechanisms subverting host immunity [148]. They may also enhance vector competence by directly interacting with host immune genes to balance pathogen clearance and microbial tolerance [148]. We further found through analysis that the three regions of R. microplus distribution had different genotype association patterns with Rickettsia and Francisella. The relationship between genotype and pathogen diversity also suggests that specific genetic variants may be selectively advantageous in certain regions, especially in the face of regionally distinct microbial communities [149]. In addition, we also observed that the genes involved in these two loci mentioned before were related to the immune defenses of tick, which further indicated the specific targeting of the immune adaptation of the genome under the ticks in different regions with different geographical habitats [20,111]. Moreover, these differences in pathogen associations between the two tick species may stem from their divergent life history traits. The one-host life cycle of R. microplus creates a stable host environment that supports the accumulation and retention of specific symbionts or pathogens, such as Rickettsia and Francisella. This stability may enhance its vector competence for certain pathogens [150]. In contrast, the multi-host life cycle of H. longicornis exposes it to diverse microbiomes and environmental factors across hosts, potentially leading to a broader but less stable pathogen community [34]. Furthermore, these interactions between ticks and pathogens reveal how pathogens activate and manipulate the biological responses of ticks to promote survival, while the tick must balance pathogen restriction with maintaining fitness and vector competence [103,151]. These results suggest that R. microplus may have evolved genetic adaptations that affect its ability to host and transmit certain pathogens, providing new insights into the molecular drivers of vector competence.
In summary, this study provides a comprehensive genomic perspective on the genetic diversity and variations within H. longicornis and R. microplus. We identified the gene HaeL19522 as a PLP-dependent enzyme associated with heme synthesis in H. longicornis. In R. microplus, during the blood-feeding process, we discovered two important immune-related genes, LOC119178146/DUOX, with the G allele frequency of rs142127589 showing a highly positive correlation with Rickettsia abundance. Additionally, we identified LOC119172490/ACO1, a gene related to iron transport. Interestingly, unlike the DUOX gene, the G allele frequency of rs152825916 in this gene displayed a negative correlation with Ehrlichia abundance. We also identified distinct patterns of pathogen associations in H. longicornis and R. microplus. Notably, we found two pathogens—Rickettsia and Francisella—that are significantly associated with R. microplus, playing crucial roles in immune response and iron metabolism, respectively. These findings enhance our understanding of the genomic adaptations and evolutionary mechanisms in both tick species, illuminating how specific genetic traits may facilitate pathogen transmission. Furthermore, our analysis strengthens the conceptual framework regarding the interactions between tick genetics and pathogen dynamics, highlighting potential molecular targets for controlling TBDs. By understanding these relationships, we can develop more effective strategies for managing tick populations and reducing the risk of pathogen transmission.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens14040306/s1.
Author Contributions
Y.L. and S.X. conceived and supervised this study. J.L. and A.Z. conducted computational analyses. J.L. drafted the manuscript. Q.L. and Y.G. assisted in data curation. Y.L. and S.X. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2023YFC2605400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grants (32288101, 32030020, 32470649), the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Program (23JS1410100), and the Office of Global Partnerships (Key Projects Development Fund). The computational work in this study was supported by the CFFF Computing Platform and the Human Phenome Data Center of Fudan University. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The whole-genome re-sequencing data of 177 H. longicornis and 151 R. microplus were downloaded from the NGDC database (project ID: PRJCA002242). The reference genomes ASM1333976v2 (H. longicornis) and ASM1333972v1 (R. microplus) were download from NGDC (project ID: PRJCA002240) or NCBI (project ID: PRJNA633311). The transcriptome data of two H. longicornis and seven R. microplus were downloaded from NCBI (project ID: PRJNA714456 and PRJNA232001, respectively).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no existing competing interests.
References
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Chomel, B.B.; Otranto, D. Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases: A One Health Perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfäffle, M.; Littwin, N.; Muders, S.V.; Petney, T.N. The Ecology of Tick-Borne Diseases. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1059–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Robbins, R.G.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Petney, T.N.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.G.; Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. The Argasidae, Ixodidae and Nuttalliellidae (Acari: Ixodida) of the World: A List of Valid Species Names. Zootaxa 2010, 2528, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneth, G. Tick-Borne Infections of Animals and Humans: A Common Ground. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brites-Neto, J.; Duarte, K.M.R.; Martins, T.F. Tick-Borne Infections in Human and Animal Population Worldwide. Vet. World 2015, 8, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlin, I.; Toledo, A. Emerging Tick-Borne Pathogens of Public Health Importance: A Mini-Review. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.R.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P. Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugeler, K.J.; Schwartz, A.M.; Delorey, M.J.; Mead, P.S.; Hinckley, A.F. Estimating the Frequency of Lyme Disease Diagnoses, United States, 2010–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radolf, J.D.; Caimano, M.J.; Stevenson, B.; Hu, L.T. Of Ticks, Mice and Men: Understanding the Dual-Host Lifestyle of Lyme Disease Spirochaetes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-B.; Na, R.-H.; Wei, S.-S.; Zhu, J.-S.; Peng, H.-J. Distribution of Tick-Borne Diseases in China. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Meltzer, M.I.; Peña, C.A.; Hopkins, A.B.; Wroth, L.; Fix, A.D. Economic Impact of Lyme Disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, J.J. Sustainable Tick and Tickborne Disease Control in Livestock Improvement in Developing Countries. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 71, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivaria, F.M. Estimated Direct Economic Costs Associated with Tick-Borne Diseases on Cattle in Tanzania. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2006, 38, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocaido, M.; Muwazi, R.T.; Opuda, J.A. Economic Impact of Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases on Cattle Production Systems around Lake Mburo National Park in South Western Uganda. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, J.J.; James, A.D.; Minjauw, B.; Di Giulio, G.U.; Permin, A.; Pegram, R.G.; Chizyuka, G.B.; Sinyangwe, P. Long-Term Studies on the Economic Impact of Ticks on Sanga Cattle in Zambia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1997, 21, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.C.G. Implications for New Zealand of Potentially Invasive Ticks Sympatric with Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann, 1901 (Acari: Ixodidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 18, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Cui, X.; Jia, N.; Wei, J.; Xia, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. Distribution of Haemaphysalis longicornis and Associated Pathogens: Analysis of Pooled Data from a China Field Survey and Global Published Data. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, e320–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.-Q.; Liu, K.; Li, X.-L.; Liang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yao, H.-W.; Sun, R.-X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.-J.; Zuo, S.-Q.; et al. Emerging Tick-Borne Infections in Mainland China: An Increasing Public Health Threat. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Luo, J. Ticks of Small Ruminants in China. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101 (Suppl. 2), S187–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Du, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, W.; Jiang, J.-F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ji, P.; et al. Large-Scale Comparative Analyses of Tick Genomes Elucidate Their Genetic Diversity and Vector Capacities. Cell 2020, 182, 1328–1340.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Venzal, J.; Kocan, K.; Sonenshine, D. Overview: Ticks as Vectors of Pathogens That Cause Disease in Humans and Animals. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.-L.; Guglielmone, A.; Horak, I.; Jongejan, F.; Latif, A.; Pegram, R.; Walker, A.R. The Known Distribution and Ecological Preferences of the Tick Subgenus Boophilus (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa and Latin America. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 38, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, R.J.; Van den Bossche, P.; Penzhorn, B.L.; Sharp, B. Tick, Fly, and Mosquito Control--Lessons from the Past, Solutions for the Future. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 132, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, S.; Kumar, D.; Budachetri, K. Recent Advances in Understanding Tick and Rickettsiae Interactions. Parasite Immunol. 2021, 43, e12830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischknecht, F. The Skin as Interface in the Transmission of Arthropod-borne Pathogens. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paesen, G.C.; Adams, P.L.; Nuttall, P.A.; Stuart, D.L. Tick Histamine-Binding Proteins: Lipocalins with a Second Binding Cavity. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1482, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Mather, T.N. Ixodes Scapularis: Salivary Kininase Activity Is a Metallo Dipeptidyl Carboxypeptidase. Exp. Parasitol. 1998, 89, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francischetti, I.M.B. Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors from Hematophagous Animals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1482, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theilgaard-Monch, K.; Knudsen, S.; Follin, P.; Borregaard, N. The Transcriptional Activation Program of Human Neutrophils in Skin Lesions Supports Their Important Role in Wound Healing. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 7684–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, S.; Sakaguchi, T.; You, M.; Xuan, X.; Fujisaki, K. Tick Troponin I-like Molecule Is a Potent Inhibitor for Angiogenesis. Microvasc. Res. 2006, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.; Nahmias, Z.; Norman, D.D.; Mulvihill, T.A.; Coons, L.B.; Cole, J.A. Dermacentor Variabilis: Regulation of FIbroblast Migration by Tick Salivary Gland Extract and Saliva. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovius, J.W.R. Spitting Image: Tick Saliva Assists the Causative Agent of Lyme Disease in Evading Host Skin’s Innate Immune Response. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2337–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikel, S.K. Tick Modulation of Host Immunity: An Important Factor in Pathogen Transmission. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Villar, M.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Ayllón, N.; Alberdi, P. Tick–Host–Pathogen Interactions: Conflict and Cooperation. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajdusek, O.; Sima, R.; Ayllon, N.; Jalovecka, M.; Perner, J.; De La Fuente, J.; Kopacek, P. Interaction of the Tick Immune System with Transmitted Pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, G.; Sakamoto, K.; Soares, M.P. Innate Nutritional Immunity. J. Immunol. 2019, 201, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galay, R.L.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Mochizuki, M.; Fujisaki, K.; Tanaka, T. Iron Metabolism in Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae): The Antidote to Their Toxic Diet. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Espinosa, P.; Alberdi, P.; Fuente, J. de la Tick–Pathogen Interactions: The Metabolic Perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busby, A.; Ayllón, N.; Kocan, K.; Blouin, E.; de la Fuente, G.; Galindo, R.; Villar, M.; de la Fuente, J. Expression of Heat Shock Proteins and Subolesin Affects Stress Responses, Anaplasma phagocytophilum Infection and Questing Behaviour in the Tick, Ixodes Scapularis. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2011, 26, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Rego, R.O.M.; De la Fuente, J. Tick-Pathogen Ensembles: Do Molecular Interactions Lead Ecological Innovation? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.K.; Tate, A.T.; Schneider, D.S.; Levashina, E.A.; Kagan, J.C.; Pal, U.; Fikrig, E.; Pedra, J.H.F. Vector Immunity and Evolutionary Ecology: The Harmonious Dissonance. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duron, O.; Binetruy, F.; Noël, V.; Cremaschi, J.; McCoy, K.D.; Arnathau, C.; Plantard, O.; Goolsby, J.; Pérez de León, A.A.; Heylen, D.J.A.; et al. Evolutionary Changes in Symbiont Community Structure in Ticks. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2905–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shastry, B.S. SNPs: Impact on Gene Function and Phenotype. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 578, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altshuler, D.; Donnelly, P. The International HapMap Consortium A Haplotype Map of the Human Genome. Nature 2005, 437, 1299–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, A.J. The Essence of SNPs. Gene 1999, 234, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, P.R.; Clayton, D.G.; Cardon, L.R.; Craddock, N.; Deloukas, P.; Duncanson, A.; Kwiatkowski, D.P.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ouwehand, W.H.; Samani, N.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of 14,000 Cases of Seven Common Diseases and 3,000 Shared Controls. Nature 2007, 447, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioli, L.C.; Menelaou, A.; Pulit, S.L.; van Dijk, F.; Palamara, P.F.; Elbers, C.C.; Neerincx, P.B.T.; Ye, K.; Guryev, V.; Kloosterman, W.P.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequence Variation, Population Structure and Demographic History of the Dutch Population. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignal, A.; Milan, D.; SanCristobal, M.; Eggen, A. A Review on SNP and Other Types of Molecular Markers and Their Use in Animal Genetics. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2002, 34, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirloni, L.; Braz, G.; Nunes, R.D.; Gandara, A.C.P.; Vieira, L.R.; Assumpcao, T.C.; Sabadin, G.A.; Da Silva, R.M.; Guizzo, M.G.; Machado, J.A.; et al. A Physiologic Overview of the Organ-Specific Transcriptome of the Cattle Tick Rhipicephalus microplus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce Framework for Analyzing next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The Variant Call Format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional Annotation of Genetic Variants from High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-Generation PLINK: Rising to the Challenge of Larger and Richer Datasets. GigaSci 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast Model-Based Estimation of Ancestry in Unrelated Individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Lu, D.; Xu, S. AncestryPainter: A Graphic Program for Displaying Ancestry Composition of Populations and Individuals. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, S.-S.; Xu, J.-Y.; He, W.-M.; Yang, T.-L. PopLDdecay: A Fast and Effective Tool for Linkage Disequilibrium Decay Analysis Based on Variant Call Format Files. Bioinformatics 2018, 35, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of Population Splits and Mixtures from Genome-Wide Allele Frequency Data. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, D.; Novembre, J.; Stephens, M. Visualizing Spatial Population Structure with Estimated Effective Migration Surfaces. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, B.L.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. Fast Two-Stage Phasing of Large-Scale Sequence Data. Am. J. Human. Genet. 2021, 108, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpiech, Z.; Hernandez, R. Selscan: An Efficient Multithreaded Program to Perform EHH-Based Scans for Positive Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2824–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämälä, T.; Savolainen, O. Genomic Patterns of Local Adaptation under Gene Flow in Arabidopsis lyrata. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2557–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve Years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and Sensitive Protein Alignment Using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and Visualization of LD and Haplotype Maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-Mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; Mcanulla, C.; Mcwilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-Scale Protein Function Classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes Among Gene Clusters. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-Based Genome Alignment and Genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-Genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python Framework to Work with High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Meyer, C.A.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Shirley Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. GFOLD: A Generalized Fold Change for Ranking Differentially Expressed Genes from RNA-Seq Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2782–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.; Kim, J.C.; Park, S.E.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, J.S. Interactive Gene Expression Between Metarhizium Anisopliae JEF-290 and Longhorned Tick Haemaphysalis Longicornis at Early Stage of Infection. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 643389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, P.; Vitari, G.; Rezende, A.; Couto, J.; Antunes, S.; Domingos, A.; Peckle, M.; Massard, C.; Araújo, F.; Santos, H. Characterization of the Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) Microplus Sialotranscriptome Profile in Response to Theileria equi Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. BLAST: Improvements for Better Sequence Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W6–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzer, C. Gene Expression Profiling of Adult Female Tissues in Feeding Rhipicephalus microplus Cattle Ticks. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sharma, P.; Singh, R.; Tiwari, R.; Singh, G. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Sucrose Nonfermenting-1-Related Protein Kinase (SnRK) Genes in Triticum Aestivum in Response to Abiotic Stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, S.; Ueyama, T.; Tsujibe, S.; Saito, N.; Korzeniowska, A.; Leto, T. Duox Maturation Factors Form Cell Surface Complexes with Duox Affecting the Specificity of Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-S.; Wu, S.-B.; Lee, W.-Y.; Cheng, J.-S.; Wei, Y.-H. Response to the Increase of Oxidative Stress and Mutation of Mitochondrial DNA in Aging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerver, L.; Papadopoulos, C.; Liu, B.; Kravic, B.; Rota, G.; Brecht, L.; Veenendaal, T.; Polajnar, M.; Bluemke, A.; Ehrmann, M.; et al. The Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme UBE2QL1 Coordinates Lysophagy in Response to Endolysosomal Damage. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e48014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, M.J.; Lipsky, P.; Thiele, D. Generation of Active Myeloid and Lymphoid Granule Serine Proteases Requires Processing by the Granule Thiol Protease Dipeptidyl Peptidase I. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 2458–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, T.; Forgac, M. The Vacuolar (H+)-ATPases--Nature’s Most Versatile Proton Pumps. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Gibson, T.B.; Xu, B.-E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Pathways: Regulation and Physiological Functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.A.; Webb, A.J. Nitrite Reduction and Cardiovascular Protection. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 73, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Macario, E.C.; Yohda, M.; Macario, A.J.L.; Robb, F.T. Bridging Human Chaperonopathies and Microbial Chaperonins. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. Investigating the Functional Role of Tick Antioxidants in Hematophagy and Vector Competence. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southern Mississippi, Hattiesburg, MS, USA, 2016; p. 905. [Google Scholar]
- Donkó, Á.; Péterfi, Z.; Sum, A.; Leto, T.; Geiszt, M. Dual Oxidases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 2301–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galay, R.L.; Aung, K.M.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Maeda, H.; Matsuo, T.; Kawaguchi, H.; Miyoshi, N.; Suzuki, H.; Xuan, X.; Mochizuki, M.; et al. Multiple Ferritins Are Vital to Successful Blood Feeding and Reproduction of the Hard Tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pantopoulos, K. Regulation of Cellular Iron Metabolism. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Kohlhepp, P.; Geiser, D.; Frasquillo, M.d.C.; Vazquez-Moreno, L.; Winzerling, J.J. Fate of Blood Meal Iron in Mosquitoes. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Wan, D. Regulation of Iron Homeostasis and Related Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 6062094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.P.; Shen, M.; Eisenstein, R.S.; Leibold, E.A. Mammalian Iron Metabolism and Its Control by Iron Regulatory Proteins. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 1468–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, G.; Recalcati, S.; Pietrangelo, A.; Minotti, G. The Iron Regulatory Proteins: Targets and Modulators of Free Radical Reactions and Oxidative Damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, G.; Ronchi, R.; Recalcati, S.; Campanella, A.; Minotti, G. Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite Activate the Iron Regulatory Protein-1 of J774A.1 Macrophages by Direct Disassembly of the Fe-S Cluster of Cytoplasmic Aconitase. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7435–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentze, M.W.; Kühn, L.C. Molecular Control of Vertebrate Iron Metabolism: mRNA-Based Regulatory Circuits Operated by Iron, Nitric Oxide, and Oxidative Stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8175–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z. Morphological, Biological and Molecular Characteristics of Bisexual and Parthenogenetic Haemaphysalis longicornis. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 189, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, G.A.; Ferreira, G.C. 5-Aminolevulinate Synthase: Catalysis of the First Step of Heme Biosynthesis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2009, 55, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Percudani, R.; Peracchi, A. A Genomic Overview of Pyridoxal-Phosphate-Dependent Enzymes. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhong, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Wang, J. Symbiont-Regulated Serotonin Biosynthesis Modulates Tick Feeding Activity. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1545–1557.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogaça, A.C.; Sousa, G.; Pavanelo, D.B.; Esteves, E.; Martins, L.A.; Urbanová, V.; Kopáček, P.; Daffre, S. Tick Immune System: What Is Known, the Interconnections, the Gaps, and the Challenges. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 628054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo-Diaz, M.A.; Song, C.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, H.; Wahl, L.M.; Radulovic, S.; Medvedev, A.E. Involvement of TLR2 and TLR4 in Cell Responses to Rickettsia akari. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldhaar, H.; Gross, R. Immune Reactions of Insects on Bacterial Pathogens and Mutualists. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Tamilselvam, B.; Hansen, E.J.; Daefler, S. Modulation of Iron Homeostasis in Macrophages by Bacterial Intracellular Pathogens. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadahunsi, A.I. Biochemical Characterisation of Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase from the Cattle Tick, Rhipicephalus microplus, Highlights Potential New Acaricide Target. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanatori, I.; Richardson, D.R.; Toyokuni, S.; Kishi, F. The Iron Chaperone Poly(rC)-Binding Protein 2 Forms a Metabolon with the Heme Oxygenase 1/Cytochrome P450 Reductase Complex for Heme Catabolism and Iron Transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 13205–13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Deka, R.K.; Norgard, M.V. BosR (BB0647) Controls the RpoN-RpoS Regulatory Pathway and Virulence Expression in Borrelia Burgdorferi by a Novel DNA-Binding Mechanism. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Blick, R.J.; Liu, W.; Hansen, E.J. Identification of Francisella Tularensis Genes Affected by Iron Limitation. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4224–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, K.; Xie, B.; Gao, Y.; Xu, S.; Lu, Y. Mapping Structural Variations in Haemaphysalis longicornis and Rhipicephalus microplus Reveals Vector-Pathogen Adaptation. iScience 2023, 26, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cai, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Zheng, A. Comparative Analysis of Bisexual and Parthenogenetic Populations in Haemaphysalis longicornis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; He, F. Advances in Species Coexistence Theory. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Du, L.; Ye, R.-Z.; Zhao, F.; Cao, W.-C. Haemaphysalis Longicornis. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, A. Biology, Ecology and Distribution of the Tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann (Acari: Ixodidae) in New Zealand. Vet. J. 2016, 64, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Yu, Z.; Guo, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J. Multiple Lines of Evidence on the Genetic Relatedness of the Parthenogenetic and Bisexual Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, G.; Yu, T.; Lawrence, K.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Yang, Z.; Ye, L.; et al. Rapid Spread of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus by Parthenogenetic Asian Longhorned Ticks. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungirai, M.; Moyo, D.; De Clercq, P.; Madder, M.; Vanwambeke, S.; De Clercq, E. Modelling the Distribution of Rhipicephalus microplus and R. decoloratus in Zimbabwe. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 14, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Hu, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Whole-Genome Resequencing Reveals World-Wide Ancestry and Adaptive Introgression Events of Domesticated Cattle in East Asia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lian, L.-S.; Wen, J.-K.; Shi, X.-W.; Zhu, F.-X.; Nie, L.; Zhang, Y.-P. Genetic Diversity and Relationship of Yunnan Native Cattle Breeds and Introduced Beef Cattle Breeds. Biochem. Genet. 2004, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccoy, K.; Léger, E.; Dietrich, M. Host Specialization in Ticks and Transmission of Tick-Borne Diseases: A Review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Layer, G.; Reichelt, J.; Jahn, D.; Heinz, D.W. Structure and Function of Enzymes in Heme Biosynthesis. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 1137–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.U.; Brown, B.L. Structural Basis for Allostery in PLP-Dependent Enzymes. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 884281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, E.-M.; Lee, K.-A.; Seo, Y.Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Lim, J.-H.; Oh, B.-H.; Kim, J.; Lee, W.-J. Coordination of Multiple Dual Oxidase–Regulatory Pathways in Responses to Commensal and Infectious Microbes in Drosophila Gut. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Molina-Cruz, A.; Gupta, L.; Rodrigues, J.; Barillas-Mury, C. A Peroxidase/Dual Oxidase System Modulates Midgut Epithelial Immunity in Anopheles Gambiae. Science 2010, 327, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Smith, A.A.; Williams, M.S.; Pal, U. A Dityrosine Network Mediated by Dual Oxidase and Peroxidase Influences the Persistence of Lyme Disease Pathogens within the Vector. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12813–12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, A.S.; Sauer, J.R. Tick Salivary Glands: Function, Physiology and Future. Parasitology 2004, 129, S67–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Renneker, S.; Beyer, D.; Kullmann, B.; Seitzer, U.; Ahmed, J.; Bakheit, M.A. Identification and Partial Characterization of a Salp15 Homolog from Ixodes Ricinus. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mans, B.J. Evolution of Vertebrate Hemostatic and Inflammatory Control Mechanisms in Blood-Feeding Arthropods. J. Innate Immun. 2011, 3, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimo, L.; Kazimirova, M.; Richardson, J.; Bonnet, S.I. The Essential Role of Tick Salivary Glands and Saliva in Tick Feeding and Pathogen Transmission. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabadin, G.A.; Salomon, T.B.; Leite, M.S.; Benfato, M.S.; Oliveira, P.L.; da Silva Vaz, I. An Insight into the Functional Role of Antioxidant and Detoxification Enzymes in Adult Rhipicephalus microplus Female Ticks. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 81, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.R.J.; Rosa, R.M.; Moura, D.J.; Seitz, A.L.; Colodel, E.M.; Driemeier, D. Cell Death during Preoviposition Period in Boophilus microplus Tick. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 144, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, R.; Becker, S.; Eberle, A.; Grether-Beck, S.; Häussinger, D. Involvement of NADPH Oxidase Isoforms and Src Family Kinases in CD95-Dependent Hepatocyte Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27179–27194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.J.; Abidi, S.N.F.; Skinner, A.; Tian, Y.; Smith-Bolton, R.K. The Drosophila Duox Maturation Factor Is a Key Component of a Positive Feedback Loop That Sustains Regeneration Signaling. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.J.; Jiggins, F.M. Comparative Genomics Reveals the Origins and Diversity of Arthropod Immune Systems. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2111–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizzo, M.G.; Budachetri, K.; Adegoke, A.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Karim, S. Rickettsia Parkeri Infection Modulates the Sialome and Ovariome of the Gulf Coast Tick, Amblyomma maculatum. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1023980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdusek, O.; Sojka, D.; Kopacek, P.; Buresova, V.; Franta, Z.; Sauman, I.; Winzerling, J.; Grubhoffer, L. Knockdown of Proteins Involved in Iron Metabolism Limits Tick Reproduction and Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, A.E.; Ali, A.; Rehman, G.; Rocha Garcia, G.; Zangirolamo, A.F.; Malardo, T.; Jonsson, N.N. Cattle Tick Rhipicephalus microplus-Host Interface: A Review of Resistant and Susceptible Host Responses. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, S.I.; Nijhof, A.M.; de la Fuente, J. Editorial: Tick-Host-Pathogen Interactions. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas-Jerónimo, S.; Villar, M.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Valdés, J.J.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Alberdi, P. Functional Evolution of Subolesin/Akirin. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Mulenga, A.; Vaz, I.S.J. Editorial: Tick and Tick-Borne Pathogens: Molecular and Immune Targets for Control Strategies. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiewra, D.; Krysmann, A. Interactions between Hard Ticks (Ixodidae) and Bacterial Tick-Borne Pathogens. Ann. Parasitol. 2023, 69, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Antunes, S.; Bonnet, S.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Domingos, A.G.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Johnson, N.; Kocan, K.M.; Mansfield, K.L.; Nijhof, A.M.; et al. Tick-Pathogen Interactions and Vector Competence: Identification of Molecular Drivers for Tick-Borne Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, A.S. Cattle Ticks and Associated Tick-Borne Pathogens in Burkina Faso and Benin: Apparent Northern Spread of Rhipicephalus Microplus in Benin and First Evidence of Theileria velifera and Theileria annulata. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerton, M. A Life Stage-Targeted Acaricide Application Approach for the Control of Haemaphysalis longicornis. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, N.; Piper, P.; Constantinoiu, C. Host Resistance in Cattle to Infestation with the Cattle Tick Rhipicephalus microplus. Parasite Immunol. 2014, 36, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toure, A.; Sanogo, M.; Sghiri, A.; Sahibi, H. Incidences of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) Microplus (Canestrini, 1888) Transmitted Pathogens in Cattle in West Africa. Acta Parasitol 2022, 67, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K. Rickettsia-Host-Tick Interactions: Knowledge Advances and Gaps. Infect. Immun. 2022, 90, e00621-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Tian, H.; Li, C.; Ma, R.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, X.; Mo, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Species Composition, Genetic Structure, and Pathogen Prevalence in Tick Populations in Guangxi, China. Zoonoses 2025, 5, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, S.I. The Tick Microbiome: Why Non-Pathogenic Microorganisms Matter in Tick Biology and Pathogen Transmission. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillas-Mury, C.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Valenzuela, J.G. Understanding Pathogen Survival and Transmission by Arthropod Vectors to Prevent Human Disease. Science 2022, 377, eabc2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).