Assessment of Microbiological Contamination and Prevalence of Pathogenic Strains in Cattle Carcasses from Romanian Slaughterhouses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Aerobic Colony Counts (ACCs) and Enterobacteriaceae
2.3. Bacterial Isolation Methods
2.3.1. E. coli Isolation Protocol
2.3.2. Salmonella spp. Isolation Protocol
2.3.3. Listeria spp. Isolation Protocol
2.3.4. Bacterial DNA Extraction
2.3.5. PCR Confirmation of Pathogenic Strains
2.3.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
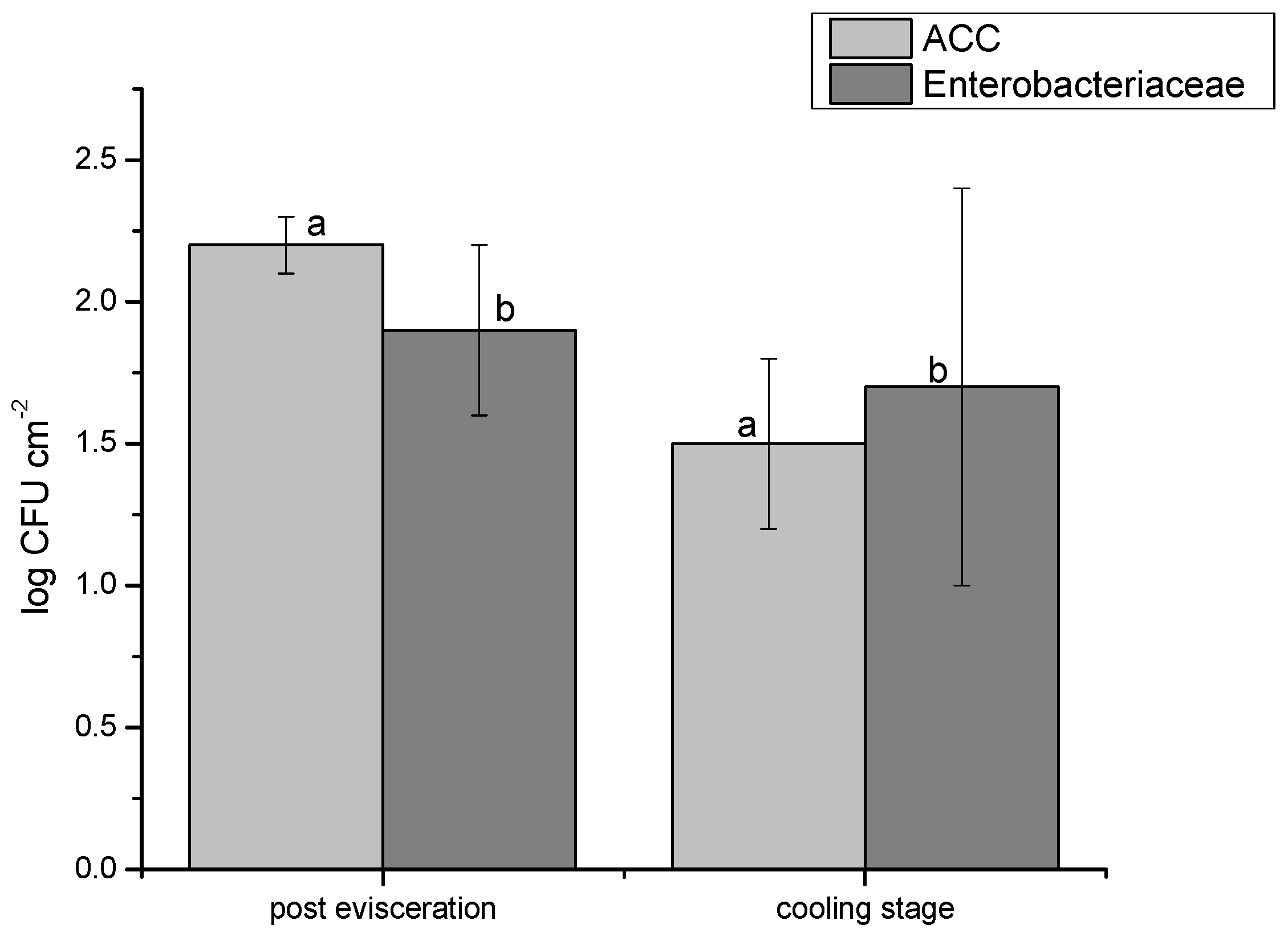
3.1. Results on the ACC and Enterobacteriaceae Loads
3.2. Results on the Prevalence of the Studied Bacteria in Fecal Samples
3.3. Results on Carcass Sample Prevalence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez-Melcón, C.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R. The One Health approach in food safety: Challenges and opportunities. Food Front. 2024, 5, 1837–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyashantha, H.; Vidanarachchi, J.K. Perspectives on value chain transformation towards resilient animal-source food systems in Sri Lanka. Cogent Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2384329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukkanen-Ninios, R.; Ghidini, S.; Gómez Laguna, J.; Langkabel, N.; Santos, S.; Maurer, P.; Meemken, D.; Alban, L.; Alvseike, O.; Vieira-Pinto, M. Additional post-mortem inspection procedures and laboratory methods as supplements for visual meat inspection of finishing pigs in Europe—Use and variability. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2022, 17, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, D.A.; Stewart, J.R. Microbial Indicators of Fecal Pollution: Recent Progress and Challenges in Assessing Water Quality. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, C.A.F.; Da Cruz, A.G.; Tavolaro, P.; Corassin, C.H. Chapter 10—Food Safety: Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Sanitation Standard Operating Procedures (SSOP), Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP). In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 10, pp. 129–139. ISBN 9780128007235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasijevic, I.; Boskovic, M.; Glisic, M. Chapter 29—Abattoir hygiene. In Present Knowledge in Food Safety; Knowles, M.E., Anelich, L.E., Boobis, A.R., Popping, B., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 29, pp. 412–438. ISBN 9780128194706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on the Hygiene of Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32004R0852 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 Laying Down Specific Hygiene Rules for Food of Animal Origin. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX:32004R0853 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Althaus, D.; Zweifel, C.; Stephan, R. Analysis of a poultry slaughter process: Influence of process stages on the microbiological contamination of broiler carcasses. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2017, 6, 7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Rao, W.; Han, M.; Deng, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Risk investigation and diversity of microbial contamination during slaughter processing of yellow-feathered broiler. LWT 2024, 210, 116801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzelli, A.; Osimani, A.; Pasquini, M.; Clementi, F.; Vetrano, V.; Paolini, F.; Foglini, M.; Micci, E.; Paoloni, A.; Tonucci, F. Trends in the microbial contamination of bovine, ovine and swine carcasses in three small-scale abattoirs in central Italy: A four-year monitoring. Meat Sci. 2016, 111, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, A.C.; Cossi, M.V.C.; Silva, W.P.D.; Bersot, L.D.S.; Landgraf, M.; Baranyi, J.; Franco, B.D.G.M.; Luís Augusto, N. Microbiological Testing for the Proper Assessment of the Hygiene Status of Beef Carcasses. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvseike, O.; Røssvoll, E.; Røtterud, O.-J.; Nesbakken, T.; Skjerve, E.; Prieto, M.; Sandberg, M.; Johannessen, G.; Økland, M.; Urdahl, A.M.; et al. Slaughter hygiene in European cattle and sheep abattoirs assessed by microbiological testing and Hygiene Performance Rating. Food Control 2019, 101, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, M.T.; Getu, A.A. Assessment of bacteriological quality and safety of raw meat at slaughterhouse and butchers’ shop (retail outlets) in Assosa Town, Beneshangul Gumuz Regional State, Western Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX:32005R2073 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1441/2007 of 5 December 2007 Amending Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2007/1441/oj (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Haileselassie, M.; Taddele, H.; Adhana, K.; Kalayou, S. Food safety knowledge and practices of abattoir and butchery shops and the microbial profile of meat in Mekelle City, Ethiopia. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanal, G.; Poudel, S. Factors Associated with Meat Safety Knowledge and Practices among Butchers of Ratnanagar Municipality, Chitwan, Nepal: A Cross-Sectional Study. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2017, 29, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chepkemoi, S.; Lamuka, P.O.; Abong, G.O.; Matofari, J. Sanitation and hygiene meat handling practices in small and medium enterprise butcheries in Kenya-case study of Nairobi and Isiolo Counties. Internet J. Food Saf. 2015, 17, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sulleyman, K.; Adzitey, F.; Boateng, E. Knowledge and practices of meat safety by meat sellers in the Accra metropolis of Ghana. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 7, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Shilenge, L.B.; Shale, K.; Matodzi, T.; Machete, F.; Tshelane, C. A review of microbial hazards associated with meat processing in butcheries. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2017, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburi, P.A.S. Assessment of Hygiene Practices Used by Small Butchers and Slaughter Slabs in Beef Value Chain in Juba Town-South Sudan. In Van Hall Larenstein; University of Applied Science: Leeuwarden, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, A.; Hassan, A.; Kadarman, N.; Saleh, A.; Shu’Aibu, Y.B.; Lua, P.L. Food safety knowledge, attitude, and practice toward compliance with abattoir laws among the abattoir workers in Malaysia. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2016, 9, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Ståhl, K.; Boklund, A.E.; Podgórski, T.; Vergne, T.; Cortiñas Abrahantes, J.; Cattaneo, E.; Papanikolaou, A.; Mur, L. Epidemiological analysis of African swine fever in the European Union during 2023. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giucă, A.D.; Ursu, A.; Sterie, C.M.; Stoica, D.G.; Petre, L.I. Research on Animal Production Trends in 2014–2020 in Romania. Sci. Pap. Ser. Manag. Econ. Eng. Agric. Rural Dev. 2022, 22, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, P.J.; Mottet, A.; Opio, C.I.; Falcucci, A.; Teillard, F. Environmental impacts of beef production: Review of challenges and perspectives for durability. Meat Sci. 2015, 109, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, P.L. Review: An overview of beef production from pasture and feedlot globally, as demand for beef and the need for sustainable practices increase. Animal 2021, 15, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.B.; Gotoh, T.; Greenwood, P.L. Current situation and future prospects for global beef production: Overview of special issue. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cameron, A.; McAllister, T.A. Antimicrobial usage and resistance in beef production. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, K.; Brülisauer, F. The application of food safety interventions in primary production of beef and lamb: A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, S43–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eugène, N.; Ongol, M.P.; Kimonyo, A.; Sindic, M. Risk factors and control measures for bacterial contamination in the bovine meat chain: A review on Salmonella and pathogenic E. coli. J. Food Res. 2015, 4, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaisen, S.; Langkabel, N.; Thoene-Reineke, C.; Wiegard, M. Animal welfare during transport and slaughter of cattle: A systematic review of studies in the European legal framework. Animals 2023, 13, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, J. Sources of contamination during slaughter and measures for control. J. Food Saf. 1998, 18, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, J.C. Risks and prevention of contamination of beef carcasses during the slaughter process in the United States of America. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epizoot. 1997, 16, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buncic, S.; Nychas, G.-J.; Lee, M.R.F.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Hébraud, M.; Desvaux, M.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Bolton, D.; Blagojevic, B.; Antic, D. Microbial pathogen control in the beef chain: Recent research advances. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Ait Kaddour, A.; Sahar, A.; Cozzolino, D. Monitoring thermal treatments applied to meat using traditional methods and spectroscopic techniques: A review of advances over the last decade. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soepranianondo, K.; Wardhana, D.K. Analysis of bacterial contamination and antibiotic residue of beef meat from city slaughterhouses in East Java Province, Indonesia. Vet. World 2019, 12, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antic, D.; Houf, K.; Michalopoulou, E.; Blagojevic, B. Beef abattoir interventions in a risk-based meat safety assurance system. Meat Sci. 2021, 182, 108622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyamakwere, F.; Muchenje, V.; Mushonga, B.; Makepe, M.; Mutero, G. Assessment of Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Enterobacteriaceae, and aerobic colony counts contamination levels during the beef slaughter process. J. Food Saf. 2016, 36, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, T.M.; Bosilevac, J.M.; Nou, X.; Shackelford, S.D.; Wheeler, T.L.; Kent, M.P.; Jaroni, D.; Pauling, B.; Allen, D.M.; Koohmaraie, M.E. coli O157 prevalence and enumeration of aerobic bacteria, Enterobacteriaceae, and E. coli O157 at various steps in commercial beef processing plants. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imre, K.; Herman, V.; Morar, A. Scientific achievements in the study of the occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of major foodborne pathogenic bacteria in foods and food processing environments in Romania: Review of the last decade. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5134764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, C.O. Visible contamination on animals and carcasses and the microbiological condition of meat. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, C.J. Good hygiene practices for food handlers and consumers. In Food-Borne Pathogens: Hazards, Risk and Control; Blackburn, C.W., McClure, P.J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: London, UK, 2000; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, W.R.; Mead, G.C.; Hinton, M.N. Relevance of abattoir hygiene assessment to microbial contamination of British beef carcasses. Vet. Rec. 1996, 139, 587–589. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 4833-1:2013; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms, Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/53728.html (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- ISO 21528-2:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae, Part 2: Colony-Count Technique. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/63504.html (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- ISO 16654:2001; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Detection of Escherichia coli O157. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/29821.html (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Mooijman, K.A.; Pielaat, A.; Kuijpers, A.F.A. Validation of EN ISO 6579-1: Microbiology of the food chain—Horizontal method for the detection, enumeration, and serotyping of Salmonella. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 288, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO EN 11290/1/2:2005; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria spp. Part 1: Detection Method. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:60313:en (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Mihaiu, L.; Lăpuşan, A.; Tănăsuică, R.; Sobolu, R.; Mihaiu, R.; Oniga, O.; Mihaiu, M. First study of Salmonella in meat in Romania. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.B.; Galli, L.; Sankarapani, V.; Soler, M.; Rivas, M.; Torres, A.G. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli, enterohemorrhagic E. coli, and enteropathogenic E. coli strains. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujňáková, D.; Karahutová, L.; Kmeť, V. Escherichia coli Specific Virulence-Gene Markers Analysis for Quality Control of Ovine Cheese in Slovakia. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães de Freitas, C.; Santana, Â.P.; Caldeira da Silva, P.H.; Gonçalves, V.S.P.; Barros, M.A.F.; Torres, F.A.G.; Murata, L.S.; Perecmanis, S. PCR multiplex for detection of Salmonella enteritidis, Typhi and Typhimurium and occurrence in poultry meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpundu, P.; Muma, J.B.; Mukumbuta, N.; Mukubesa, A.N.; Muleya, W.; Kapila, P.; Hang’ombe, B.M.; Munyeme, M. Isolation, discrimination, and molecular detection of Listeria species from slaughtered cattle in Namwala District, Zambia. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germini, A.; Masola, A.; Carnevali, P.; Marchelli, R. Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O175, Salmonella spp., and Listeria monocytogenes by multiplex PCR. Food Control 2009, 20, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, S.; Alpigiani, I.; Tozzoli, R.; Vismarra, A.; Zecca, V.; Greppi, C.; Bacci, C.; Bruini, I.; Brindani, F. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157, O26, and O111 in cattle feces and hides in Italy. Vet. Rec. Open 2015, 2, e000061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmali, A.M.; Gannon, V.; Sargeant, J.M. Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli (VTEC). Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. STEC infection. In Annual Epidemiological Report for 2022; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nyabundi, D.; Onkoba, N.; Kimathi, R.; Nyachieo, A.; Juma, G.; Kinyanjui, P.; Kamau, J. Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance profiles of Salmonella isolated from fecal matter of domestic animals and animal products in Nairobi. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2017, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, S.; Bruini, I.; Magnani, R.; Cannistrà, N.; Brindani, F. Low prevalence of Salmonella enterica in cull dairy cattle at slaughter in Northern Italy. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2017, 6, 6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegan, N.; Vanderlinde, P.; Higgs, G.; Desmarchelier, P. Quantitation and prevalence of Salmonella in beef cattle presenting at slaughter. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunčić, S.; Sofos, J. Interventions to control Salmonella contamination during poultry, cattle, and pig slaughter. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunčić, S. The incidence of Listeria monocytogenes in slaughtered animals, in meat, and in meat products in Yugoslavia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1991, 12, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Hu, P.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Chang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Prevalence and transmission characteristics of Listeria species from ruminants in farm and slaughtering environments in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaître, N.; Van Damme, I.; De Zutter, L.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Rasschaert, G.; De Reu, K. Occurrence, distribution, and diversity of Listeria monocytogenes contamination on beef and pig carcasses after slaughter. Meat Sci. 2020, 169, 108–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Microorganism | Primer Sequence | Targeted Gene | Amplicon Size (pb) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | CTTTGACGGTAGTTCACTGGACTTC (F) GAAGACGTTATAGCCCAACATATTTTCAGG (R) | eae | 166 | [51] |
| FCTTCGGTATCCTATTCCCGG (F) RGGATGCATCTCTGGTCATTG (R) | Stx-1 | 484 | [52] | |
| CCATGACAACGGACAGCAGTT (F) CCTGTC AACTGAGCAGCACTTTG (R) | Stx-2 | 779 | ||
| GGCGACAAATGCAGTATTGCTTGG GACGTTGGTTGCGGTAATTTTGGG | Cnf1 | 552 | ||
| AACGCTATTCGCCAGCTTGC (F) TCTCCCCATACCGTACGCTA (R) | ArpA | 400 | ||
| ATGGTACCGGACGAACCAAC (F) TGCCGCCAGTACCAAAGACA (R) | fhuA | 288 | ||
| CAAACGTGAAGTGTCAGGAG (F) AATGCGTTCCTCAACCTGTG (R) | YjaA | 211 | ||
| GCGCATTTGCTGATACTGTTG (F) CATCCAGACGATAAGCATGAGCA (R) | KspII | 272 | ||
| GACGGCTGTACTGCAGGGTGTGGCG (F) ATATCCTTTCTGCAGGGATGCAATA (R) | papC | 328 | ||
| CACACACAAACGGGAGCTGTT (F) CACACACAAACGGGAGCTGTT (R) | cvaC | 680 | ||
| Salmonella spp. | ATCGCTGACTTATGCAATCG (F) CGGGTTGCGTTATAGGTCTG (R) | Omp C | 204 | [53] |
| S. typhimurium | TTGTTCACTTTTTACCCCTGAA (F) CCCTGACAGCCGTTAGATATT (R) | Spy | 401 | |
| S. enteritidis | TGTGTTTTATCTGATGCAAGAGG (F) TGAACTACGTTCGTTCTTCTGG (R) | SdfI | 304 | |
| Listeria spp. | GCTGAAGAGATTGCGAAAGAAG (F) CAAAGAAACCTTGGATTTGCGG (R) | Prs | 370 | [54] |
| L.monocytogenes | TCATCGACGGCAACCTCGG (F) TGAGCAACGTATCCTCCAGAGT (R) | prfA | 217 | [55] |
| Targeted Gene | No. of Positive Samples/% |
|---|---|
| papC | 9/21.95 |
| fyuA | 9/21.95 |
| stx2 | 8/19.5 |
| cnf1 | 8/19.5 |
| kpsII | 5/12.1 |
| cvaC | 4/9.7 |
| stx1 | 4/9.7 |
| eaeA | 2/4.8 |
| ArpA | 0 |
| YjaA | 0 |
| Virulence Gene Detected | No. of Positive Strains | % of Positive Samples (n = 110) | Serogroup |
|---|---|---|---|
| papC | 1 | 0.9 | O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| fyuA | 4 | 3.63 | O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| Stx-2 | 2 | 1.8 | O26, O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| Cnf1, Stx-2 | 4 | 3.63 | O26, O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| Stx1, Stx-2 | 2 | 1.8 | O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| eaeA, Stx-1 | 2 | 1.8 | O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| Cnf1, kpsII | 1 | 0.9 | O26, O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| papC, fyuA | 2 | 1.8 | O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| cvaC, papC, kpsII, | 2 | 1.8 | O26, O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| papC, fyuA, cnf1 | 2 | 1.8 | O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| cvaC, papC, kpsII, cnf1 | 1 | 0.9 | O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
| fyuA, cvaC, papC, kpsII | 1 | 0.9 | O26, O101 ((K99)-F41-positive) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brătfelan, D.-O.; Tăbăran, A.; Dan, S.D.; Tăbăran, A.-F.; Mărgăoan, R.; Crişan-Reget, O.L.; Mihaiu, M. Assessment of Microbiological Contamination and Prevalence of Pathogenic Strains in Cattle Carcasses from Romanian Slaughterhouses. Pathogens 2025, 14, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030248
Brătfelan D-O, Tăbăran A, Dan SD, Tăbăran A-F, Mărgăoan R, Crişan-Reget OL, Mihaiu M. Assessment of Microbiological Contamination and Prevalence of Pathogenic Strains in Cattle Carcasses from Romanian Slaughterhouses. Pathogens. 2025; 14(3):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030248
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrătfelan, Dariana-Olivia, Alexandra Tăbăran, Sorin Daniel Dan, Alexandru-Flaviu Tăbăran, Rodica Mărgăoan, Oana Lucia Crişan-Reget, and Marian Mihaiu. 2025. "Assessment of Microbiological Contamination and Prevalence of Pathogenic Strains in Cattle Carcasses from Romanian Slaughterhouses" Pathogens 14, no. 3: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030248
APA StyleBrătfelan, D.-O., Tăbăran, A., Dan, S. D., Tăbăran, A.-F., Mărgăoan, R., Crişan-Reget, O. L., & Mihaiu, M. (2025). Assessment of Microbiological Contamination and Prevalence of Pathogenic Strains in Cattle Carcasses from Romanian Slaughterhouses. Pathogens, 14(3), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030248









