Fatal Toxoplasmosis in Red Kangaroos (Macropus rufus) in East China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Signs and Sample Collection from the Dead Kangaroos
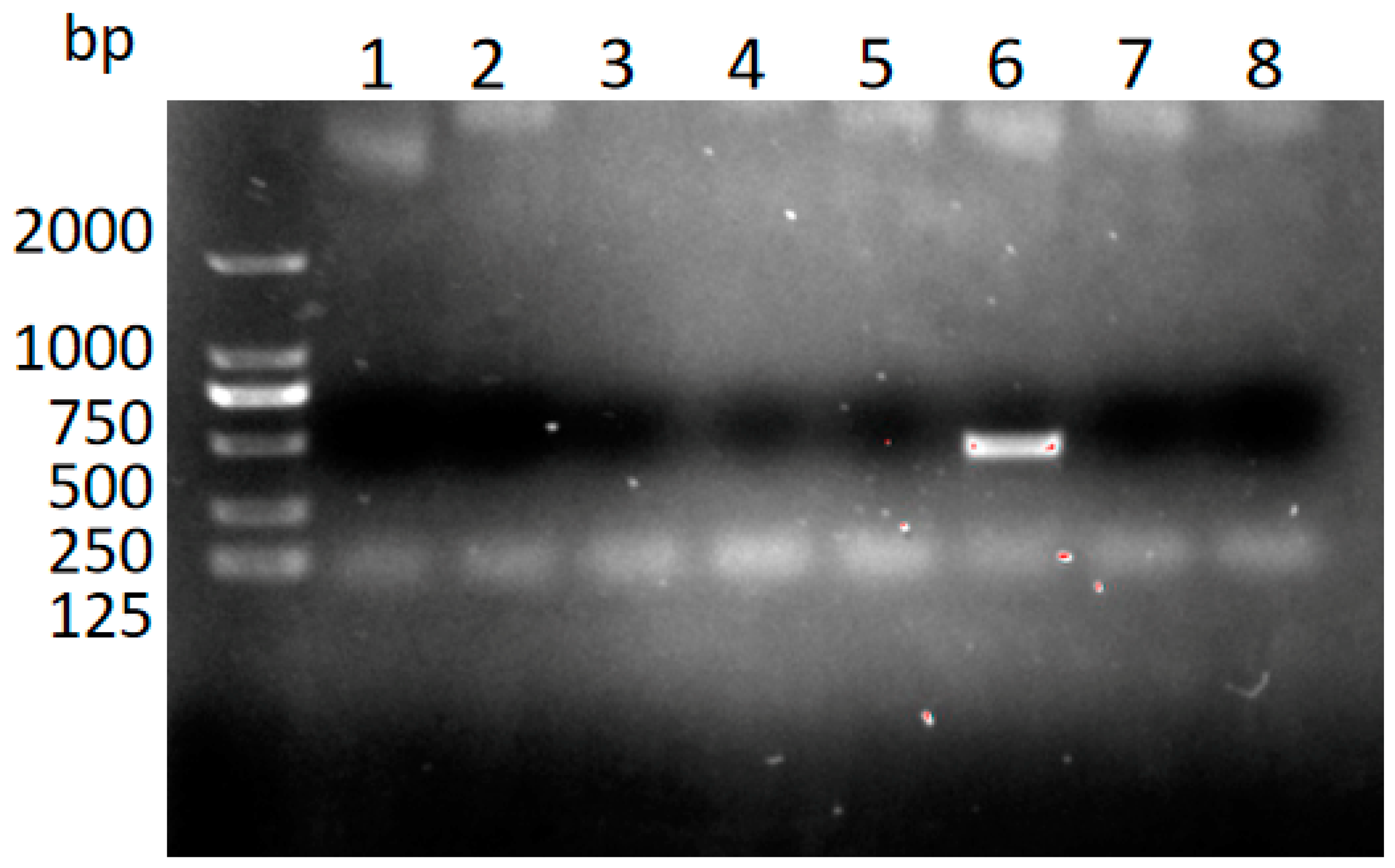
2.2. Identification of T. gondii in the Tissues and Body Fluids Using Nested PCR
2.3. IFAT Analysis of T. gondii in the Tissues
2.4. HE and IHC Staining of the Tissues
2.5. Detection of T. gondii in Stray Cats by Nested PCR
2.6. Treatment of the Infected Kangaroos
3. Results
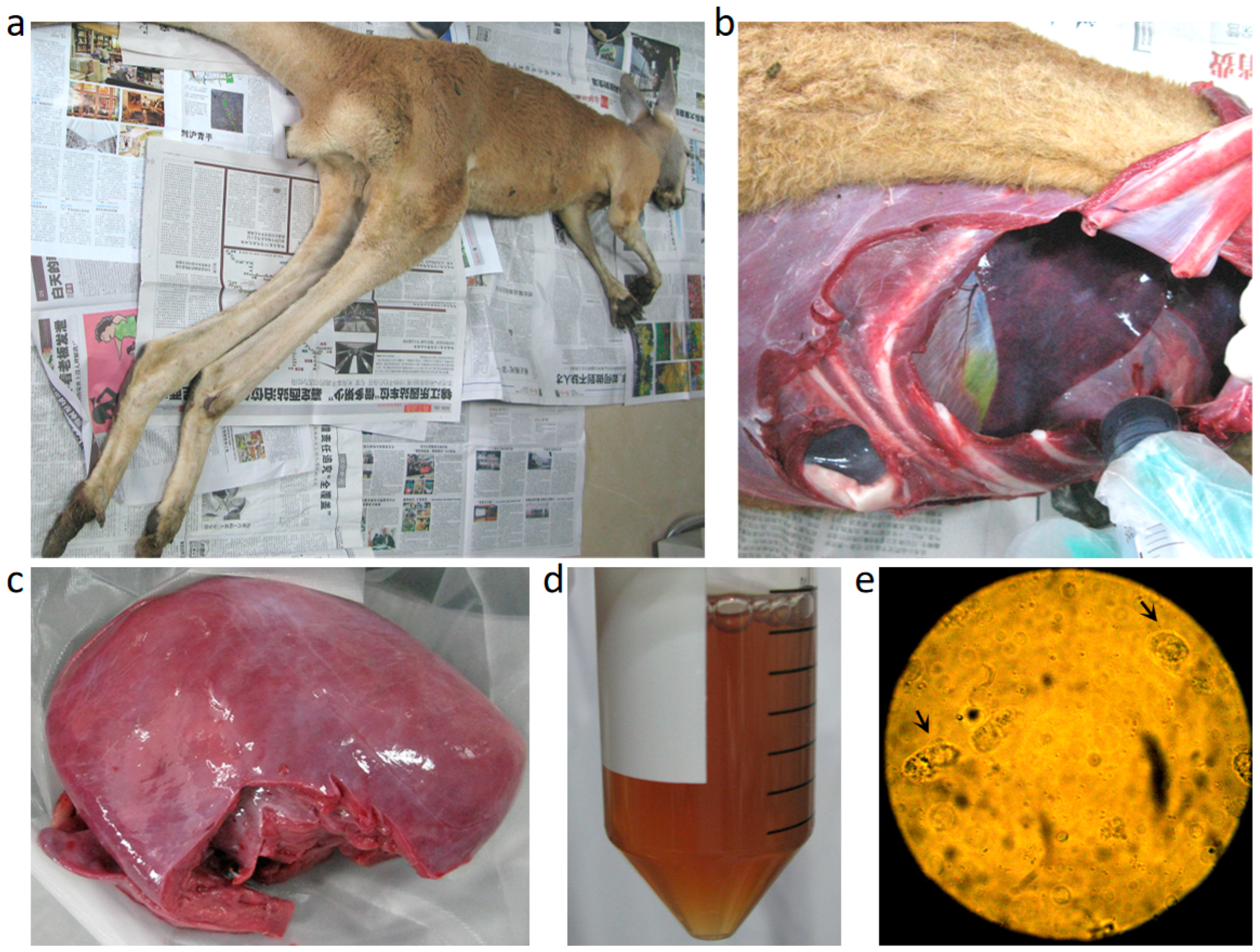
3.1. Clinical Signs and Necropsy Findings
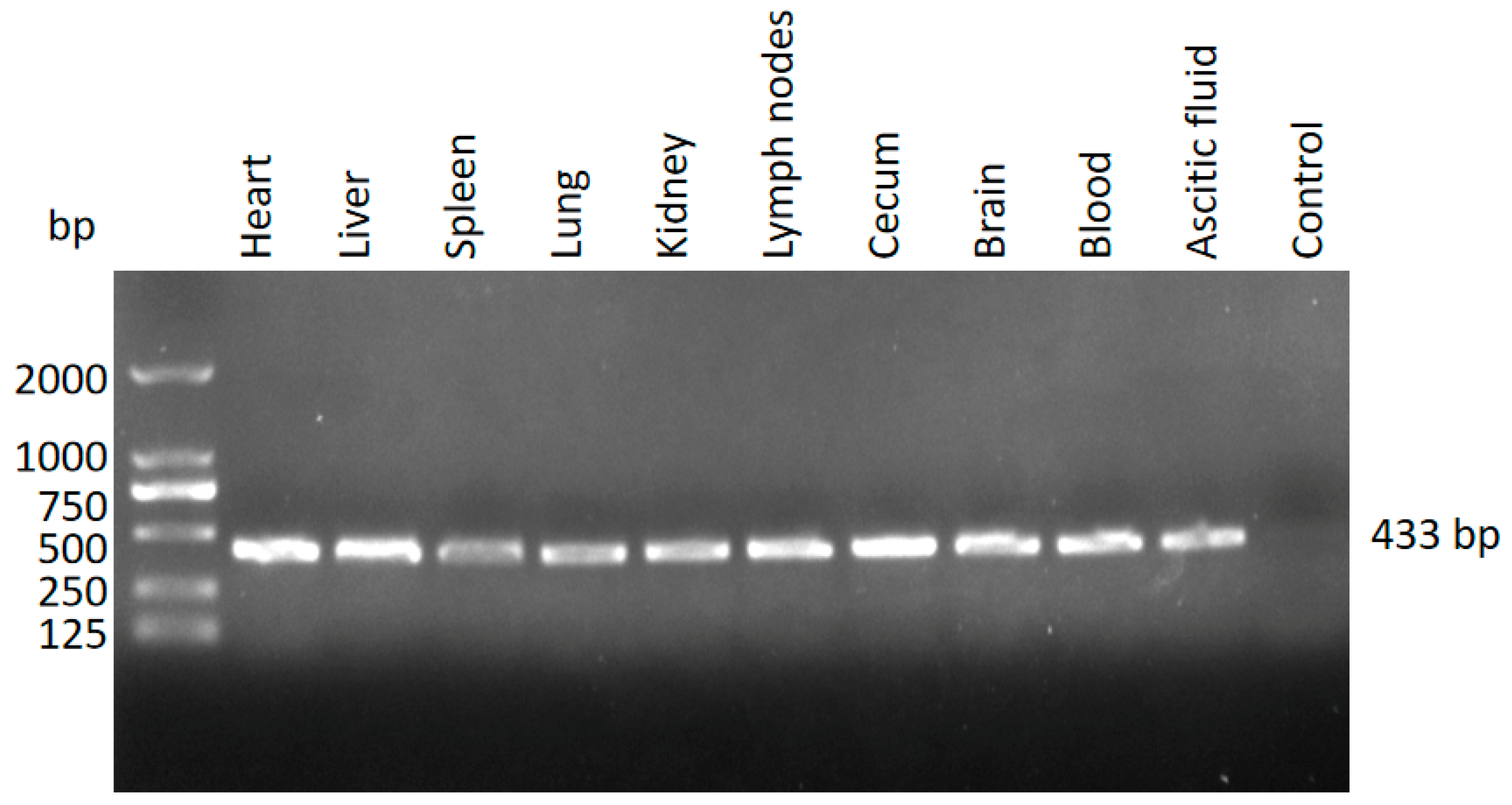
3.2. Identification of T. gondii in the Different Tissues from the Dead Kangaroos Using Nested PCR
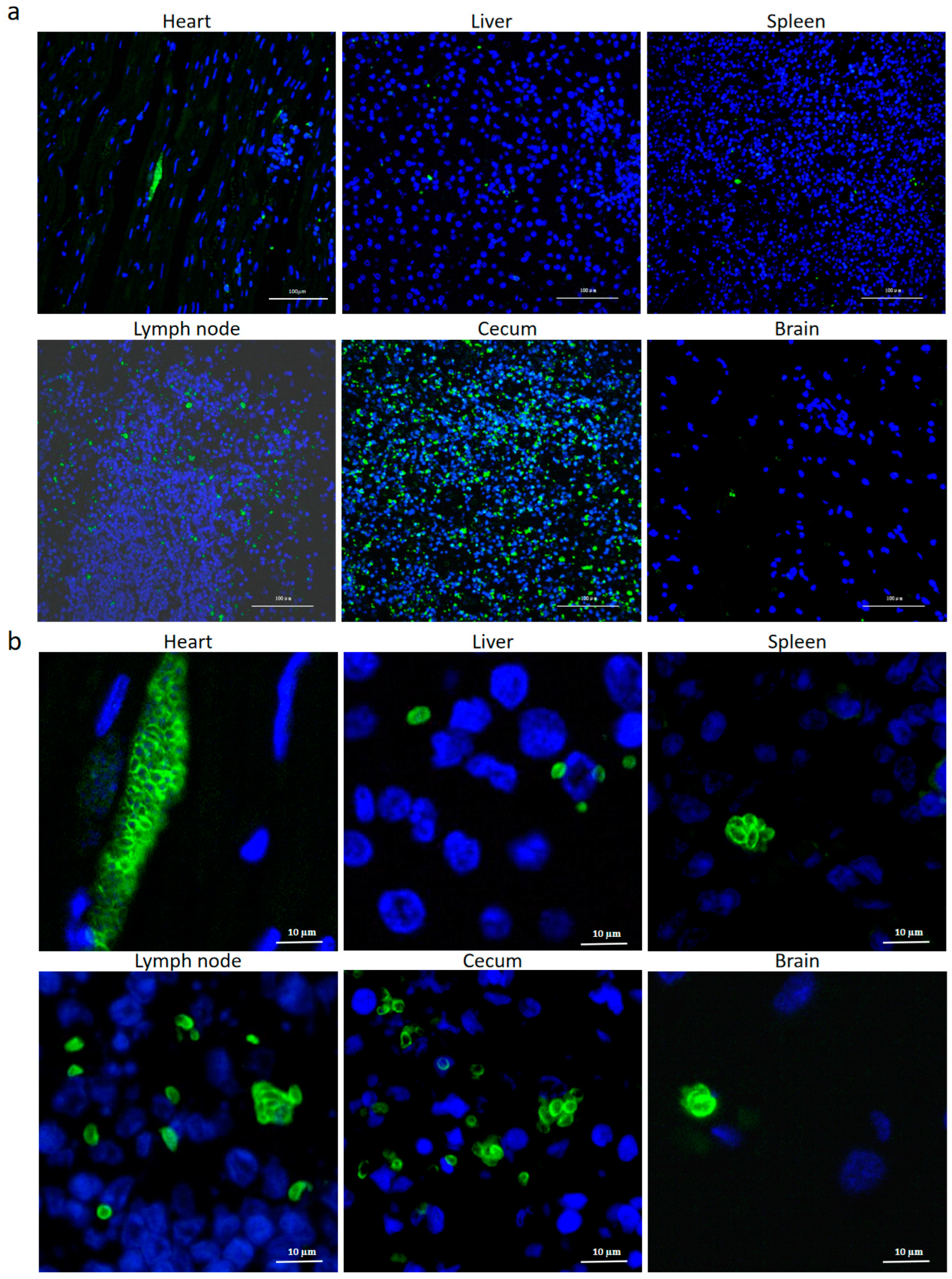
3.3. Identification of T.gondii in the Different Tissues from the Dead Kangaroos by IFAT
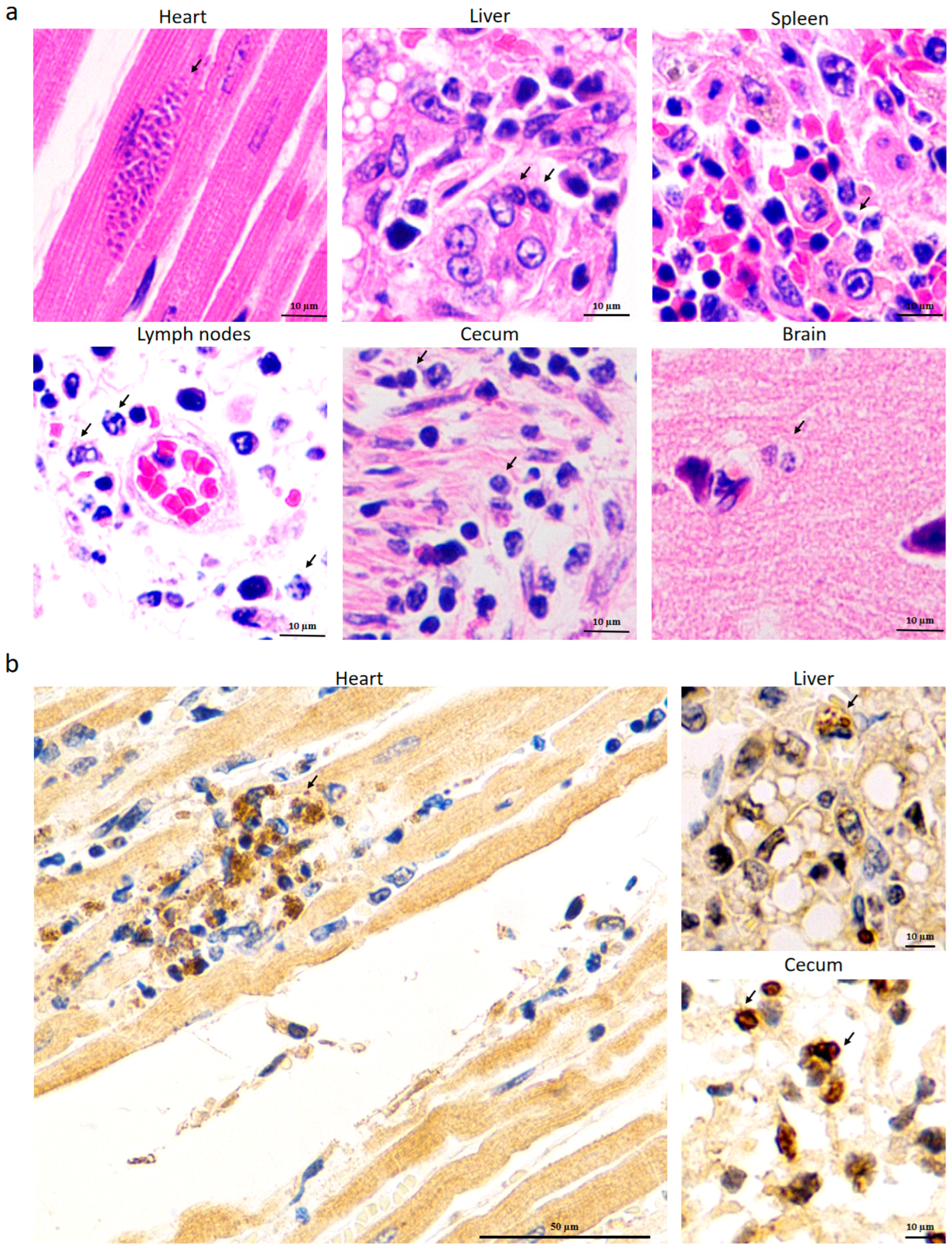
3.4. Identification of T. gondii in Different Tissues from the Dead Kangaroos by HE and IHC Staining
3.5. Detection of T. gondii in the Blood of a Native Stray Cat
3.6. Treatment Effect of SDZ and PYR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor and Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2010; Volume 112. [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Benavides Silván, J.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, E.; de Valk, H.; Villena, I.; Le Strat, Y.; Tourdjman, M. National perinatal survey demonstrates a decreasing seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection among pregnant women in France, 1995 to 2016: Impact for screening policy. Eur. Surveill. 2021, 26, 1900710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, J.A.; Joiner, K.S.; Hilton, C.D.; Dubey, J.P.; Toivio-Kinnucan, M.; Minc, J.K.; Blagburn, B.L. Disseminated toxoplasmosis in a captive ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta). J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 904–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, W.; Edelhofer, R.; Zenker, W.; Möstl, K.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Prosl, H. Toxoplasmosis in Pallas’ cats (Otocolobus manul) raised in captivity. Parasitology 2005, 130, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, R.; Hidalgo-Hermoso, E.; Fredes, F.; Alegría-Morán, R.; Celis, S.; Ortiz-Tacci, C.; Kemec, I.; Mansell, M.; Verasay, J.; Ramírez-Toloza, G. Serological prevalence and risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii in zoo mammals in Chile. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 194, 105445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Ott-Joslin, J.; Torgerson, R.W.; Topper, M.J.; Sundberg, J.P. Toxoplasmosis in black-faced kangaroos (Macropus fuliginosus melanops). Vet. Parasitol. 1988, 30, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.M.; Roberts, H.; Munday, B.L. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibody in wild macropods. Aust. Vet. J. 1988, 65, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayberry, C.; Maloney, S.K.; Mitchell, J.; Mawson, P.R.; Bencini, R. Reproductive implications of exposure to Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in western grey kangaroos (Macropus fuliginosus ocydromus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, R.; Faílde, L.D.; Losada, A.P.; Nieto, J.M.; Quiroga, M.I. Toxoplasmosis in Bennett’s wallabies (Macropus rufogriseus) in Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 160, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xin, S.; Zhu, N.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Yang, Y. Two viable Toxoplasma gondii isolates from red-necked wallaby (Macropus rufogriseus) and red kangaroo (M. rufus). Parasitol. Int. 2023, 92, 102687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabritz, H.A.; Conrad, P.A. Cats and Toxoplasma: Implications for public health. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.E.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii as a parasite in food: Analysis and control. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkens, Y. Toxoplasma gondii in Australian macropods (Macropodidae) and its implication to meat consumption. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2014, 16, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ren, H.; Zhu, N.; Mao, G.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Epidemiology and isolation of viable Toxoplasma gondii strain from macropods. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Dong, H.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Toxoplasma gondii in four captive kangaroos (Macropus spp.) in China: Isolation of a strain of a new genotype from an eastern grey kangaroo (Macropus giganteus). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Y.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Shi, J.L.; Li, X.T. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies, circulating antigens and DNA in stray cats in Shanghai, China. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portas, T.J. Toxoplasmosis in macropodids: A review. J. Zoo. Wildl. Med. 2010, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Su, C.; Grigg, M.E. Recent aspects on epidemiology, clinical disease, and genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii infections in Australasian marsupials. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dard, C.; Marty, P.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Garnaud, C.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Pelloux, H.; Pomares, C. Management of toxoplasmosis in transplant recipients: An update. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.L.; Sun, M.; Semple, B.D.; Tyebji, S.; Tonkin, C.J.; Mychasiuk, R.; Shultz, S.R. Catastrophic consequences: Can the feline parasite Toxoplasma gondii prompt the purrfect neuroinflammatory storm following traumatic brain injury? J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.R.; Bhaiyat, M.I.; de Allie, C.; Macpherson, C.N.; Sharma, R.N.; Sreekumar, C.; Vianna, M.C.; Shen, S.K.; Kwok, O.C.; Miska, K.B.; et al. Isolation, tissue distribution, and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from chickens in Grenada, West Indies. J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Sánchez-Anguiano, L.F.; Mendoza-Larios, A.; Hernández-Tinoco, J.; Pérez-Ochoa, J.F.; Antuna-Salcido, E.I.; Rábago-Sánchez, E.; Liesenfeld, O. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in brain and heart by Immunohistochemistry in a hospital-based autopsy series in Durango, Mexico. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 5, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadimoghaddam, Y.; Daryani, A.; Sharif, M.; Ahmadpour, E.; Hossienikhah, Z. Tissue tropism and parasite burden of Toxoplasma gondii RH strain in experimentally infected mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Tissue cyst tropism in Toxoplasma gondii: A comparison of tissue cyst formation in organs of cats, and rodents fed oocysts. Parasitology 1997, 115, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzib-Paredes, G.F.; Rosado-Aguilar, J.A.; Acosta-Viana, K.Y.; Ortega-Pacheco, A.; Hernández-Cortázar, I.B.; Guzman-Marín, E.; Jiménez-Coello, M. Seroprevalence and parasite load of Toxoplasma gondii in Mexican hairless pig (Sus. scrofa) tissues from the Southeast of Mexico. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 229, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Wang, Q. Seroepidemiological study of canine Leishmania infantum and Toxoplasma gondii infections in Shanghai, China, and analysis of risk factors. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2016, 23, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, H.; Mi, R.; Huang, Y.; Han, X.; Xia, L.; Li, S.; Jia, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, T.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in slaughter pigs in Shanghai, China. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 76, 102094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Diao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Serological survey for antibodies to Encephalitozoon cuniculi and Toxoplasma gondii in pet rabbits in eastern coastal areas of China. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Wei, M.X.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Yu, J.Y.; Shi, X.Q. Prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in the sera of rare wildlife in the Shanghai Zoological Garden, People’s Republic of China. Parasitol. Int. 2000, 49, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yin, J.; Jiang, N.; Xiang, M.; Hao, L.; Lu, H.; Sang, H.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Ankarklev, J.; et al. Seroepidemiology of human Toxoplasma gondii infection in China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romito, G.; Venturelli, E.; Tintorri, V.; Cipone, M. Reversible myocardial injury aggravated by complex arrhythmias in three Toxoplasma gondii-positive dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbaset, A.E.; Fox, B.A.; Karram, M.H.; Abd Ellah, M.R.; Bzik, D.J.; Igarashi, M. Lactate dehydrogenase in Toxoplasma gondii controls virulence, bradyzoite differentiation, and chronic infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, M.; Mehrzadi, S.; Sharif, M.; Sarvi, S.; Tanzifi, A.; Aghayan, S.A.; Daryani, A. Drug Resistance in Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.B.; Meurer, Y.S.; Andrade, J.M.; Costa, M.E.; Andrade, M.M.; Silva, L.A.; Lanza, D.C.; Vítor, R.W.; Andrade-Neto, V.F. Pathogenicity and phenotypic sulfadiazine resistance of Toxoplasma gondii isolates obtained from livestock in northeastern Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2016, 111, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doliwa, C.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Aubert, D.; Velard, F.; Schmid, A.; Geers, R.; Villena, I. Induction of sulfadiazine resistance in vitro in Toxoplasma gondii. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 133, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alday, P.H.; Doggett, J.S. Drugs in development for toxoplasmosis: Advances, challenges, and current status. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2017, 11, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, H.; Wang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Qiu, S.; Chen, Z.; Han, X.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, W. Fatal Toxoplasmosis in Red Kangaroos (Macropus rufus) in East China. Pathogens 2025, 14, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020202
Gong H, Wang Q, Jin Y, Qiu S, Chen Z, Han X, Chen Z, Jiang W. Fatal Toxoplasmosis in Red Kangaroos (Macropus rufus) in East China. Pathogens. 2025; 14(2):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020202
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Haiyan, Quan Wang, Yinghong Jin, Suoping Qiu, Zhaoguo Chen, Xiangan Han, Zongyan Chen, and Wei Jiang. 2025. "Fatal Toxoplasmosis in Red Kangaroos (Macropus rufus) in East China" Pathogens 14, no. 2: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020202
APA StyleGong, H., Wang, Q., Jin, Y., Qiu, S., Chen, Z., Han, X., Chen, Z., & Jiang, W. (2025). Fatal Toxoplasmosis in Red Kangaroos (Macropus rufus) in East China. Pathogens, 14(2), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020202





