Detection of Leishmania donovani DNA from Oral Swab in Visceral Leishmaniasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Cases for Specimens
2.2. Blood Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.3. Swab Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.4. Multiplex Real-Time PCR
2.5. Leishmania donovani Infection Model in Mice
2.6. Oral Swab Sampling from Mice and DNA Extraction
2.7. Detection of Leishmania DNA by LSU rRNA Gene from Oral Swab of L. donovani-Infected BALB/cA Mice
2.8. Sequencing of the LSU rRNA Gene
2.9. Determination of Spleen and Liver Parasite Burden of L. donovani-Infected BALB/cA Mice
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
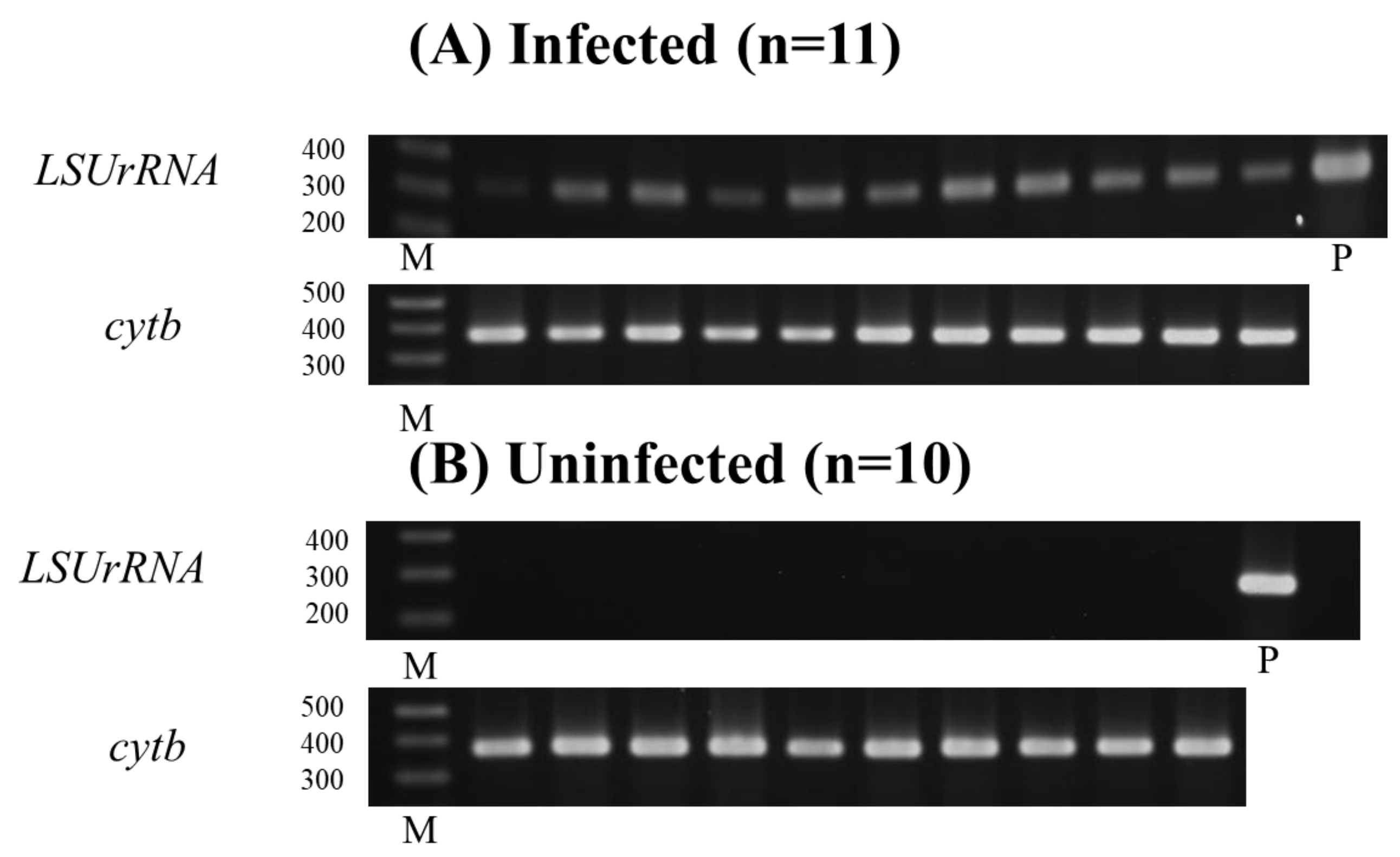
3.1. DNA Detection from Oral Swab and Buffy Coat Specimens by Real-Time PCR
3.2. Relation of Oral Swab PCR-Positive Cases with Their Symptoms of the Disease
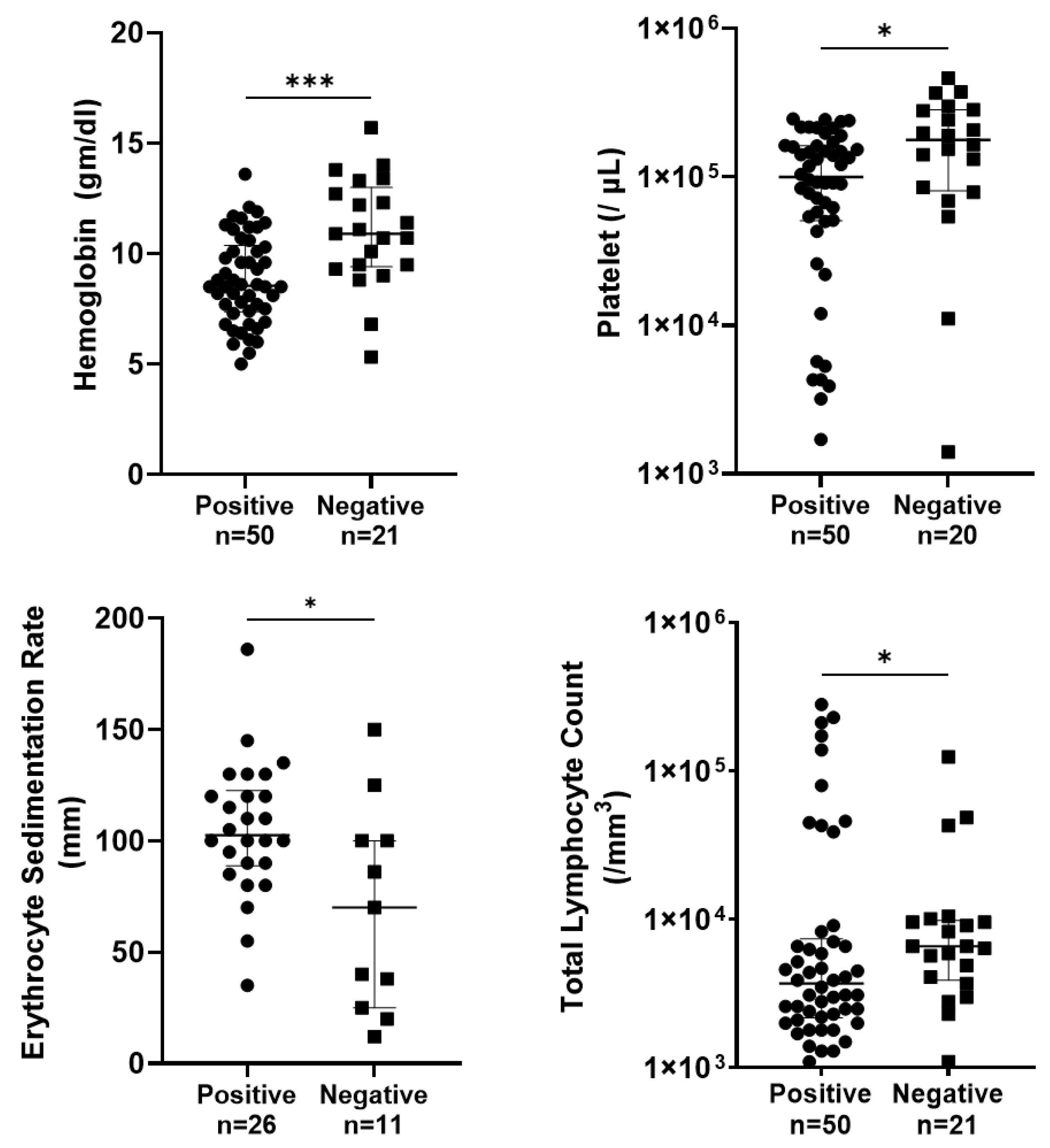
3.3. Relation of Oral Swab PCR-Positive Cases with Their Hematological Parameters
3.4. Parasitism and Molecular Detection in BALB/cA Mice Infected with L. donovani
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanoli, Z.M.; Rai, M.E.; Gandapur, A.S. Clinical presentation and management of visceral leishmaniasis. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2005, 17, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Leishmaniasis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Hirve, S.; Kroeger, A.; Matlashewski, G.; Mondal, D.; Banjara, M.R.; Das, P.; Be-Nazir, A.; Arana, B.; Olliaro, P. Towards Elimination of Visceral Leishmaniasis in the Indian Subcontinent—Translating Research to Practice to Public Health. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda, M.M.; Chowdhury, R.; Ghosh, D.; Dash, A.P.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Mondal, D. Visceral leishmaniasis-associated mortality in Bangladesh: A retrospective cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.; Banjara, M.R.; Singh, V.K.; Joshi, A.B.; Gurung, C.K.; Das, M.L.; Matlashewski, G.; Olliaro, P.; Kroeger, A. Barriers of Visceral Leishmaniasis reporting and surveillance in Nepal: Comparison of governmental VL-program districts with non-program districts. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2019, 24, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Mondal, D.; Chowdhury, V.; Faria, S.; Alvar, J.; Nabi, S.G.; Boelaert, M.; Dash, A.P. How Far Are We from Visceral Leishmaniasis Elimination in Bangladesh? An Assessment of Epidemiological Surveillance Data. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagi, N. Bangladesh eliminates visceral leishmaniasis. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reithinger, R.; Dujardin, J.C. Molecular diagnosis of leishmaniasis: Current status and future applications. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaï, Y.; Chabchoub, N.; Ben-Abid, M.; Ben-Abda, I.; Ben-Alaya-Bouafif, N.; Amri, A.; Aoun, A.; Bouratbine, A. Diagnosis of mediterranean visceral leishmaniasis by detection of leishmania antibodies and leishmania DNA in oral fluid samples collected using an Oracol device. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3150–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Figueroa, R.A.; Lozano, L.E.; Romero, I.C.; Cardona, M.T.; Prager, M.; Pacheco, R.; Diaz, Y.R.; Tellez, J.A.; Saraviaet, N.G. Detection of Leishmania in unaffected mucosal tissues of patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania (Viannia) species. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.C.A.; Celeste, B.J.; Lindoso, J.A.L.; Fujimori, M.; de Almeida, R.P.; Fortaleza, C.M.C.B.; Druzian, A.F.; Lemos, A.P.F.; Andrade de Melo, V.C.; Paniago, A.M.M.; et al. Performance of rK39-Based Immunochromatographic Rapid Diagnostic Test for Serodiagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis Using Whole Blood, Serum, and Oral Fluid. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Y.; Ito, S.; Adachi, Y.; Onodera, T.; Kageyama, T.; Takahasi, Y. Saliva as a useful tool for evaluating upper mucosal antibody response to influenza. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwakanma, D.C.; Gomez-Escobar, N.; Walther, M.; Crozier, S.; Dubovsky, F.; Malkin, E.; Locke, E.; Conway, D.J. Quantitative detection of Plasmodium falciparum DNA in saliva, blood, and urine. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, C.J.; Hallett, R. Detecting malaria parasites outside the blood. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaish, M.; Mehrotra, S.; Chakravarty, J.; Sundar, S. Noninvasive molecular diagnosis of human visceral leishmaniasis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2003–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Halder, A.; Rabidas, V.N.; Mandal, A.; Das, P. Specific noninvasive detection of Leishmania donovani in desquamated buccal cell swab samples from human visceral Leishmaniasis-HIV coinfected patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.A.; Almeida, G.G.; Silva, S.O.; Vogas, G.P.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Andrade, A.S.R.; Melo, M.N. Nasal, Oral and Ear Swabs for Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis Diagnosis: New Practical Approaches for Detection of Leishmania infantum DNA. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschar, M.O.E.T.; Laurenti, M.D.; Marcondes, M.; Tolezano, J.E.; Hiramoto, R.M.; Corbett, C.E.M.V.L. Value of the oral swab for the molecular diagnosis of dogs in different stages of infection with Leishmania infantum. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 225, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Closas, M.; Egan, K.M.; Abruzzo, J.; Newcomb, P.A.; Titus-Ernstoff, L.; Franklin, T.; Bender, P.K.; Beck, J.C.; Le Marchand, L.; Lum, A.; et al. Collection of genomic DNA from adults in epidemiological studies by buccal cytobrush and mouthwash. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2001, 10, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, E.R.; Gomez, M.A.; Scheske, L.; Rios, R.; Marquez, R.; Cossio, A.; Albertini, A.; Schallig, H.; Saravia, N.G. Sensitive diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis by lesion swab sampling coupled to qPCR. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlova, J.; Seblova, V.; Votypka, J.; Warburg, A.; Volf, P. Xenodiagnosis of Leishmania donovani in BALB/c mice using Phlebotomus orientalis: A new laboratory model. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, Y.; Aruga, H.; Sanjoba, C.; Takagi, H.; Paul, S.K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Noiri, E. Applicability of Multiplex Real-time PCR to Visceral Leishmaniasis. In Kala Azar in South Asia; Noiri, E., Jha, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccal Swab Genetic Testing Collection Instructions, Nutripath Intrigative Pathology Services, 2015, Version v3.0. Available online: https://nutripath.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/BUCCAL-SWAB-Collections-Instructions-V.3.0.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Pandey, K.; Yanagi, T.; Pandey, B.D.; Mallik, A.K.; Sherchand, J.B.; Kanbara, H. Characterization of Leishmania Isolates from Nepalese Patients with Visceral Leishmaniasis. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osada, Y.; Omachi, S.; Sanjoba, C.; Matsumoto, Y. Chapter 23, Animal Models of Visceral Leishmaniasis and Applicability to Disease Control. In Kala Azar in South Asia—Current Status and Sustainable Challenges, 2nd ed.; Noiri, E., Jha, T.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Bern, C.; Hightower, A.W.; Chowdhury, R.; Ali, M.; Amann, J.; Wagatsuma, Y.; Haque, R.; Kurkjian, K.; Vaz, L.E.; Begum, M.; et al. Risk Factors for Kala-Azar in Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijal, S.; Uranw, S.; Chappuis, F.; Picado, A.; Khanal, B.; Paudel, I.S.; Andersen, E.W.; Meheus, F.; Ostyn, B.; Das, M.L.; et al. Epidemiology of Leishmania donovani infection in high-transmission foci in Nepal. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2010, 15 (Suppl. S2), 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdousi, F.; Alam, M.S.; Hossain, M.S.; Ma, E.; Itoh, M.; Mondal, D.; Haque, R.; Wagatsuma, Y. Visceral Leishmaniasis Eradication is a Reality: Data from a Community-based Active Surveillance in Bangladesh. Trop. Med. Health 2012, 40, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Sur, D.; Singh, V.P.; Siddique, N.A.; Manna, B.; Lal, C.S.; Sinha, P.K.; Kishore, K.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Risk factors for Indian kala-azar. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.; Singh, O.P. Molecular Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 22, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Ede, F.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Lima, H.C.; Thomaz-Soccol, A.; De Castro, E.A.; Mulinari-Brenner, F.; Queiroz-Telles, F.; Luz, E. Molecular diagnosis of leishmaniosis in the Paraná state of southern Brazil. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss-Ayali, D.; Jaffe, C.L.; Burshtain, O.; Gonen, L.; Baneth, G. Polymerase Chain Reaction Using Noninvasively Obtained Samples, for the Detection of Leishmania infantum DNA in Dogs. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1729–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.; Mallik, A.K.; Pyakurel, S.; Pun, S.B.; Pandey, B.D. Comparative study of microscopy and polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of suspected visceral leishmaniasis patients in Nepal. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. (KUMJ) 2013, 11, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ha, T.; Ferguson, D.A., Jr.; Chi, D.S.; Zhao, R.; Patel, N.R.; Krishnaswamy, G.; Thomas, E.A. A newly developed PCR assay of H. pylori in gastric biopsy, saliva, and feces. Evidence of high prevalence of H. pylori in saliva supports oral transmission. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Yoneda, M.; Naito, T.; Iwamoto, T.; Masuo, Y.; Yamada, K.; Hisama, K.; Okada, I.; Hirofuji, T. Detection of Helicobacter pylori DNA in the saliva of patients complaining of halitosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57 Pt 12, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phumee, A.; Kraivichian, K.; Chusri, S.; Noppakun, N.; Vibhagool, A.; Sanprasert, V.; Tampanya, V.; Wilde, H.; Siriyasatien, P. Detection of Leishmania siamensis DNA in saliva by polymerase chain reaction. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weerakoon, K.G.; McManus, D.P. Cell-Free DNA as a Diagnostic Tool for Human Parasitic Infections. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chappuis, F.; Sundar, S.; Hailu, A.; Ghalib, H.; Rijal, S.; Peeling, R.W.; Alvar, J.; Boelaert, M. Visceral leishmaniasis: What are the needs for diagnosis, treatment and control? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, P.G.; Singh, S.P.; Bern, C.; Hightower, A.W.; Sundar, S. Virgin soil: The spread of visceral leishmaniasis into Uttar Pradesh, India. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Griensven, J.; Carrillo, E.; López-Vélez, R.; Lynen, L.; Moreno, J. Leishmaniasis in immunosuppressed individuals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvar, J.; Vélez, I.D.; Bern, C.; Herrero, M.; Desjeux, P.; Cano, J.; Jannin, J.; den Boer, M.; WHO Leishmaniasis Control Team. Leishmaniasis Worldwide and Global Estimates of Its Incidence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, N.; Naseem, S. Hematologic changes in visceral leishmaniasis/kala azar. Indian. J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2010, 26, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulaki, A.; Piperaki, E.-T.; Voulgarelis, M. Effects of Visceralising Leishmania on the Spleen, Liver, and Bone Marrow: A Pathophyiological Perspective. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total (%) | Age | Sex | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <15 | 15–45 | 45< | Male | Female | |||
| Type of disease | PKA | 47 (58.8) | 8 | 27 | 12 | 24 | 23 |
| RKA | 33 (41.3) | 1 | 19 | 13 | 16 | 17 | |
| Total | 80 (100) | 9 | 46 | 25 | 40 | 40 | |
| qPCR | No. of Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| OS | BC | ||
| + | + | 46 | |
| + | − | 8 | |
| − | + | 4 | |
| − | − | 22 | |
| Positivity rate (%) | 67.5 | 62.5 | |
| (54/80) | (50/80) | ||
| Symptoms of the Disease | Number of Patient (%) | Result of OS PCR | Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (%) | Negative (%) | ||||
| Spleen | Palpable | 52 (67.5) | 45 (86.5) | 7 (13.5) | p < 0.001 |
| (n = 77) | Not palpable | 25 (32.5) | 9 (36) | 16 (64) | |
| Liver | Palpable | 24 (34.8) | 20 (83.3) | 4 (16.7) | NS |
| (n = 69) | Not palpable | 45 (65.2) | 30 (66.7) | 15 (33.3) | |
| Fever | Within 1 month | 24 (30) | 15 (62.5) | 9 (37.5) | NS |
| (n = 80) | >1 month | 56 (70) | 39 (69.6) | 17 (30.4) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarkar, S.R.; Hobo, R.; Shoshi, Y.; Paul, S.K.; Goto, Y.; Noiri, E.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sanjoba, C. Detection of Leishmania donovani DNA from Oral Swab in Visceral Leishmaniasis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020144
Sarkar SR, Hobo R, Shoshi Y, Paul SK, Goto Y, Noiri E, Matsumoto Y, Sanjoba C. Detection of Leishmania donovani DNA from Oral Swab in Visceral Leishmaniasis. Pathogens. 2025; 14(2):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020144
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarkar, Santana R., Rina Hobo, Yuki Shoshi, Shyamal K. Paul, Yasuyuki Goto, Eisei Noiri, Yoshitsugu Matsumoto, and Chizu Sanjoba. 2025. "Detection of Leishmania donovani DNA from Oral Swab in Visceral Leishmaniasis" Pathogens 14, no. 2: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020144
APA StyleSarkar, S. R., Hobo, R., Shoshi, Y., Paul, S. K., Goto, Y., Noiri, E., Matsumoto, Y., & Sanjoba, C. (2025). Detection of Leishmania donovani DNA from Oral Swab in Visceral Leishmaniasis. Pathogens, 14(2), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020144








