Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Serological Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
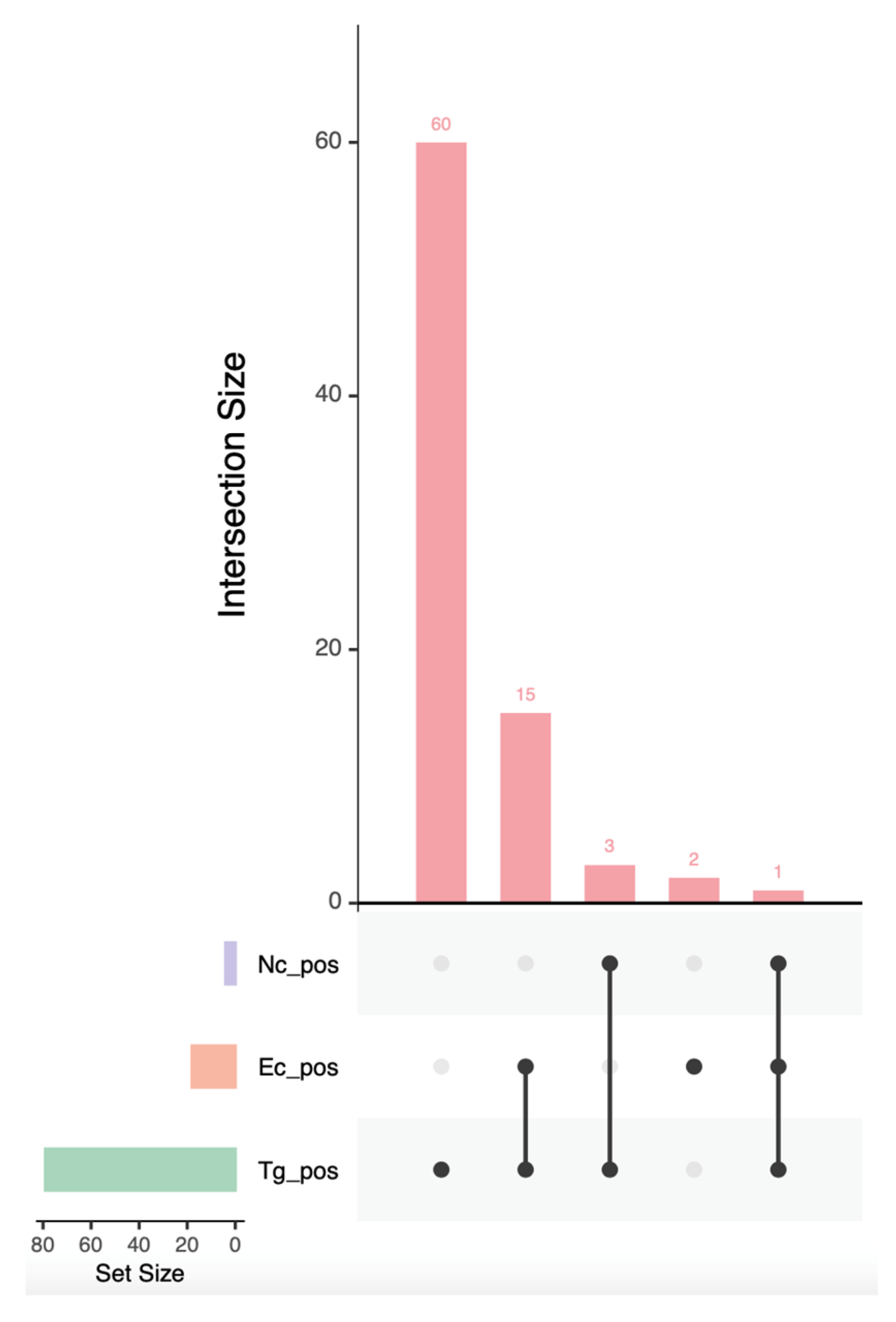
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IFAT | Immuno-Fluorescent Antibody Test |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay |
| DAT | Direct Agglutination Test |
References
- Simpson, V.R. Wild Animals as Reservoirs of Infectious Diseases in the UK. Vet. J. 2002, 163, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hůrková, L.; Modrý, D. PCR Detection of Neospora caninum, Toxoplasma gondii and Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Brains of Wild Carnivores. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsbury, C.D.; Statham, M.J. Red Fox Vulpes Vulpes (Linnaeus, 1758). In Handbook of the Mammals of Europe; Hackländer, K., Zachos, F.E., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard, É.; Sharma, R.; Hernández-Ortiz, A.; Buhler, K.; Al-Adhami, B.; Su, C.; Fenton, H.; G-Gouin, G.; Roth, J.D.; Rodrigues, C.W.; et al. Are Foxes (Vulpes spp.) Good Sentinel Species for Toxoplasma gondii in Northern Canada? Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didier, E.S.; Didier, P.J.; Snowden, K.F.; Shadduck, J.A. Microsporidiosis in Mammals. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, T.V.; Guy, E.C.; Roberts, K.E.; Joynson, D.H.M.; Hyde, J.E.; Sims, P.F.G. Molecular Evidence for Multiple Toxoplasma gondii Infections in Individual Patients in England and Wales: Public Health Implications. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, G.; Rigamonti, G.; Brustenga, L.; Calgaro, V.; Angeli, G.; Moretta, I.; Diaferia, M.; Veronesi, F. Exploring Similarities and Differences between Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum Infections in Dogs. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 3563–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.M.; Walochnik, J.; Hassl, A.; Moriarty, J.; Mooney, J.; Toolan, D.; Sanchez-Miguel, C.; O’Loughlin, A.; McAuliffe, A. Study on the Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora Caninum and Molecular Evidence of Encephalitozoon cuniculi and Encephalitozoon (Septata) intestinalis Infections in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Rural Ireland. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S. A Review of Neospora caninum and Neosporosis. Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 67, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trees, A.J.; Davison, H.C.; Innes, E.A.; Wastling, J.M. Towards Evaluating the Economic Impact of Bovine Neosporosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Review of Neospora caninum and Neosporosis in Animals. Korean J. Parasitol. 2003, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.K. An Outbreak of Toxoplasmosis in Farmed Mink (Mustela vison S.). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2001, 13, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, K.; Peper, R.L. Mammalian Microsporidiosis. Vet. Pathol. 2000, 37, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, A.; Weber, R.; Deplazes, P. Zoonotic Potential of the Microsporidia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S. Age Determination in the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes)—An Evaluation of Technique Efficiency as Applied to a Sample of Suburban Foxes. J. Zool. 1978, 184, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verin, R.; Mugnaini, L.; Nardoni, S.; Papini, R.A.; Ariti, G.; Poli, A.; Mancianti, F. Serologic, molecular, and pathologic survey of Toxoplasma gondii infection in free-ranging red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Central Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P.; Whitesell, L.E.; Culp, W.E.; Daye, S. Diagnosis and treatment of Neospora caninum –associated dermatitis in a red fox (Vulpes vulpes) with concurrent Toxoplasma gondii infection. J. Zoo. Wildl. Med. 2014, 45, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780470582473. [Google Scholar]
- Chicco, D.; Sichenze, A.; Jurman, G. A Simple Guide to the Use of Student’s t-Test, Mann-Whitney U Test, Chi-Squared Test, and Kruskal-Wallis Test in Biostatistics. BioData Min. 2025, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N.; Strobelt, H.; Vuillemot, R.; Pfister, H. UpSet: Visualization of Intersecting Sets. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2014, 20, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.-Y.; Gao, Y.; Lv, C.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Gong, Q.-L.; Zhang, X.-X. The Global Prevalence and Risk Factors of Toxoplasma gondii among Foxes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiterová, K.; Špilovská, S.; Čobádiová, A.; Hurníková, Z. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in Red Foxes in Slovakia. Acta Parasitol. 2016, 61, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, R.; Cabezón, O.; Millán, J.; Pabón, M.; Arnal, M.C.; Luco, D.F.; Gortázar, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Almeria, S. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Wild Carnivores from Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubek, E.-B.; Farkas, R.; Pálfi, V.; Mattsson, J.G. Prevalence of Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in Hungarian Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 144, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornacka, A.; Cybulska, A.; Bień, J.; Goździk, K.; Moskwa, B. The Usefulness of Direct Agglutination Test, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Animals. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 228, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártová, E.; Slezáková, R.; Nágl, I.; Sedlák, K. Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii; Antibodies in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in the Czech Republic. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 23, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroglio, E.; Bosio, F.; Trisciuoglio, A.; Zanet, S. Toxoplasma gondii in Sympatric Wild Herbivores and Carnivores: Epidemiology of Infection in the Western Alps. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakroub, H.; Sgroi, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Russo, D.; Serra, F.; Veneziano, V.; Rea, S.; Pucciarelli, A.; Lucibelli, M.G.; De Carlo, E.; et al. Molecular Survey of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Mammals of Southern Italy. Pathogens 2023, 12, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 9781003199373. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, P.; Bosco, A.; Capuano, F.; Baldi, L.; Giordano, A.; Mancusi, A.; Buonanno, M.; Morena, L.; Pinto, R.; Sarnelli, P.; et al. Towards an Integrated Approach for Monitoring Toxoplasmosis in Southern Italy. Animals 2021, 11, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, É.; Elmore, S.A.; Alisauskas, R.T.; Samelius, G.; Gajadhar, A.A.; Schmidt, K.; Ross, S.; Jenkins, E.J. Transmission dynamics of Toxoplasma gondii in arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus): A long-term mark-recapture serologic study at karrak lake, nunavut, canada. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukášová, R.; Marková, J.; Bártová, E.; Murat, J.-B.; Sedlák, K. Molecular Evidence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, and Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes). J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, A.L.; Cleaveland, S.C.; Brown, J.; Mahajan, A.; Shaw, D.J. Seroprevalence of Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Wild Rodents, Foxes and Domestic Cats in Three Sites in the United Kingdom. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinney, B.; Sak, B.; Joachim, A.; Kváč, M. More than a Rabbit’s Tale—Encephalitozoon spp. in Wild Mammals and Birds. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2016, 5, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoli, A.; Olfatifar, M.; Zaki, L.; Asghari, A.; Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Nowak, O.; Pirestani, M.; Diaz, D.; Cherati, M.G.; Eslahi, A.V.; et al. The Global Prevalence of Microsporidia Infection in Rabbits as a Neglected Public Health Concern: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2025, 234, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, C.N.; Zajac, A.M.; Snowden, K.S.; Lindsay, D.S. Direct Agglutination Test for Encephalitozoon cuniculi. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 135, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Künzel, F.; Peschke, R.; Tichy, A.; Joachim, A. Comparison of an Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Test with Western Blot for the Detection of Serum Antibodies against Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Cats. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 4457–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, T.R.; Pinto, F.F.; Queiroga, F.L. A Multidisciplinary Review about Encephalitozoon cuniculi in a One Health Perspective. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 2463–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, A.; Hogan, S.; Maguire, D.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Mulcahy, G.; Vaughan, L.; Wall, D.; Hayden, T.J. Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Ireland as Hosts for Parasites of Potential Zoonotic and Veterinary Significance. Vet. Rec. 2001, 149, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.M.; Gray, R.; Wright, S.E.; Gangadharan, B.; Laurenson, K.; Innes, E.A. Prevalence of Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from around the UK. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 130, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.S.; Gasser, R.B.; Ellis, J.; Reichel, M.P.; McMillan, D.; Trees, A.J. Prevalence of Antibodies to Neospora caninum in Different Canid Populations. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, D.; Maley, S.W.; Pastoret, P.P.; Brochier, B.; Innes, E.A. Examination of Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Belgium for Antibody to Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii. Vet. Rec. 1997, 141, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubek, E.-B.; Bröjer, C.; Regnersen, C.; Uggla, A.; Schares, G.; Björkman, C. Seroprevalences of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in Swedish Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 102, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanet, S.; Poncina, M.; Ferroglio, E. Congenital Transmission of Neospora caninum in Wild Ungulates and Foxes. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1109986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturaro, E.; Cocca, G.; Gallo, L.; Mrad, M.; Ramanzin, M. Livestock Systems and Farming Styles in Eastern Italian Alps: An on-Farm Survey. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almería, S.; Ferrer, D.; Pabón, M.; Castellà, J.; Mañas, S. Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) Are a Natural Intermediate Host of Neospora caninum. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 107, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almería, S. Neospora Caninum and Wildlife. ISRN Parasitol. 2013, 2013, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parasite | Risk Factor | Category | Ratio | Prevalence | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. gondii | Sex | Male | 45/70 | 64.3% | 52.6–74.5 |
| Female | 34/50 | 68.0% | 54.2–79.2 | ||
| Age class | Adult | 46/58 | 79.3% | 67.2–87.7 | |
| Juvenile | 33/62 | 53.2% | 41.0–65.1 | ||
| Location | Central Italy | 48/81 | 59.3% | 48.4–69.3 | |
| Southern Italy | 31/39 | 79.5% | 64.5–89.2 | ||
| Status | Alive | 33/60 | 55.0% | 42.3–67.2 | |
| Deceased | 46/60 | 76.7% | 64.8–86.6 | ||
| N. caninum | Sex | Male | 3/70 | 4.3% | 1.5–11.9 |
| Female | 1/50 | 2.0% | 0.4–10.5 | ||
| Age class | Adult | 3/58 | 5.2% | 1.8–14.1 | |
| Juvenile | 1/62 | 1.6% | 0.3–8.6 | ||
| Location | Central Italy | 3/81 | 3.7% | 1.3–10.3 | |
| Southern Italy | 1/39 | 2.6% | 0.5–13.2 | ||
| Status | Alive | 0/60 | 0.0% | 0.0–0.0 | |
| Deceased | 4/60 | 6.7% | 2.2–15.3 | ||
| E. cuniculi | Sex | Male | 10/70 | 14.3% | 7.9–24.3 |
| Female | 8/50 | 16.0% | 8.3–28.5 | ||
| Age class | Adult | 12/58 | 20.7% | 12.3–32.8 | |
| Juvenile | 6/62 | 9.7% | 4.5–19.5 | ||
| Location | Central Italy | 13/81 | 16.0% | 9.6–25.5 | |
| Southern Italy | 5/39 | 12.8% | 5.6–26.7 | ||
| Status | Alive | 8/60 | 13.3% | 6.4–23.7 | |
| Deceased | 10/60 | 16.7% | 8.8–27.7 |
| Risk Factor | Category | Seroprevalence | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age class | Juvenile | 53.2% (33/62) | 0.29 | 0.12–0.65 | 0.004 |
| Adult | 79.3% (46/58) | 1 (ref.) | - | - | |
| Location | Southern Italy | 79.5% (31/39) | 2.72 | 1.11–7.23 | 0.034 |
| Central Italy | 59.3% (48/81) | 1 (ref.) | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brustenga, L.; Scarcelli, S.; Rigamonti, G.; Moretta, I.; Diaferia, M.; Morganti, G.; D’Avino, N.; Gobbi, M.; Ranucci, A.; Sgroi, G.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Italy. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111175
Brustenga L, Scarcelli S, Rigamonti G, Moretta I, Diaferia M, Morganti G, D’Avino N, Gobbi M, Ranucci A, Sgroi G, et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Italy. Pathogens. 2025; 14(11):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111175
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrustenga, Leonardo, Stefano Scarcelli, Giulia Rigamonti, Iolanda Moretta, Manuela Diaferia, Giulia Morganti, Nicoletta D’Avino, Marco Gobbi, Alice Ranucci, Giovanni Sgroi, and et al. 2025. "Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Italy" Pathogens 14, no. 11: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111175
APA StyleBrustenga, L., Scarcelli, S., Rigamonti, G., Moretta, I., Diaferia, M., Morganti, G., D’Avino, N., Gobbi, M., Ranucci, A., Sgroi, G., Passamonti, F., & Veronesi, F. (2025). Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Encephalitozoon cuniculi in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Italy. Pathogens, 14(11), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111175









