Tracing the Zoonotic Origins of a Rare Human G5P[6] Rotavirus in Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Viral dsRNA Extraction and RT-PCR of the 11 Genome Segments
2.3. Sequencing and Genotyping
2.4. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
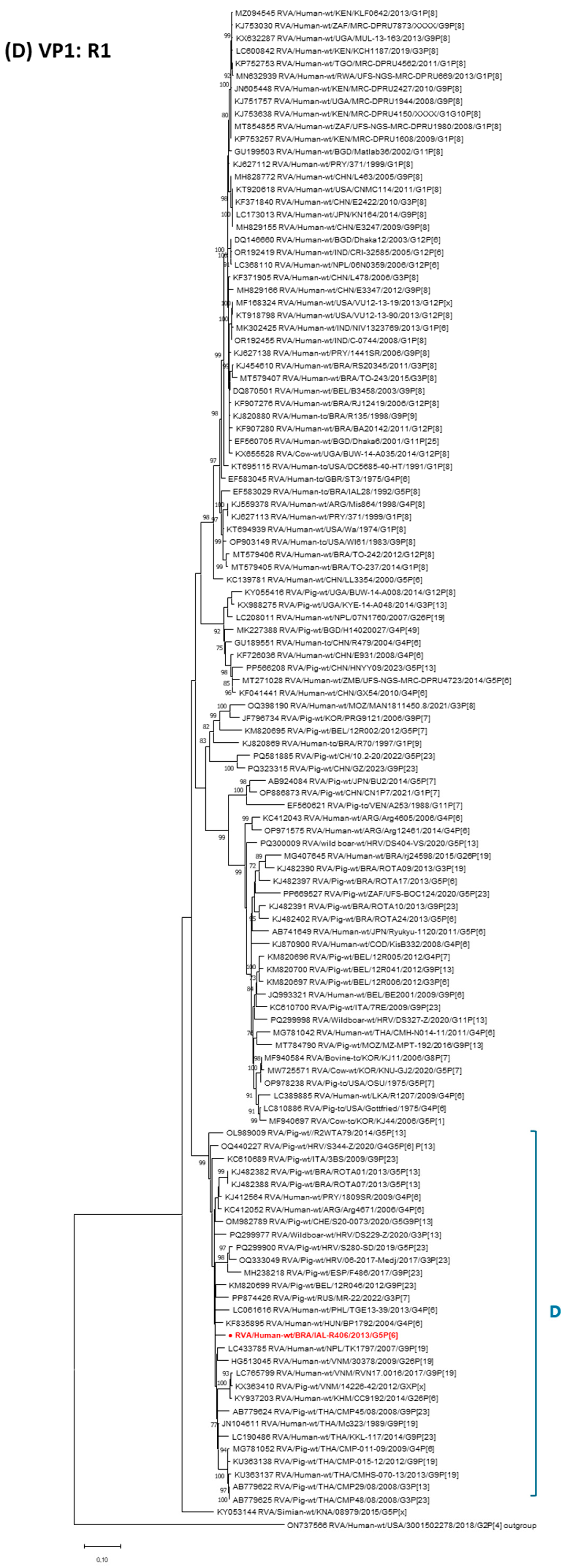
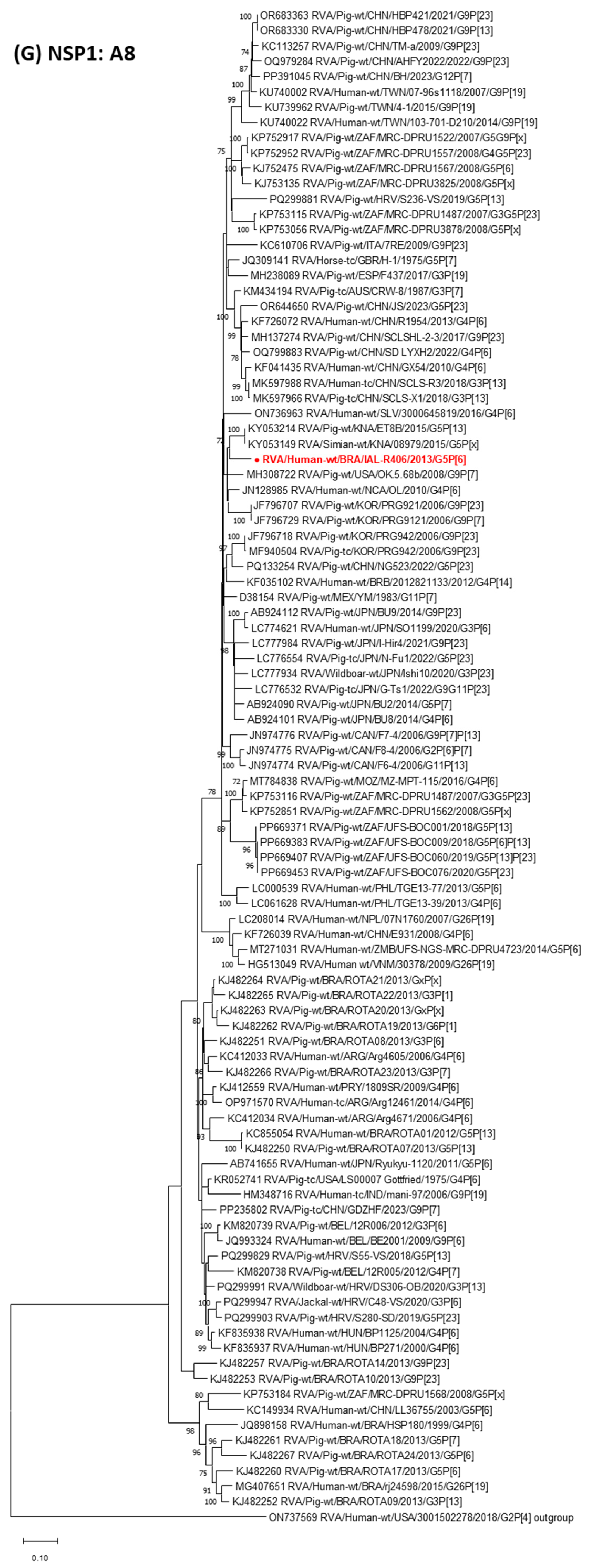
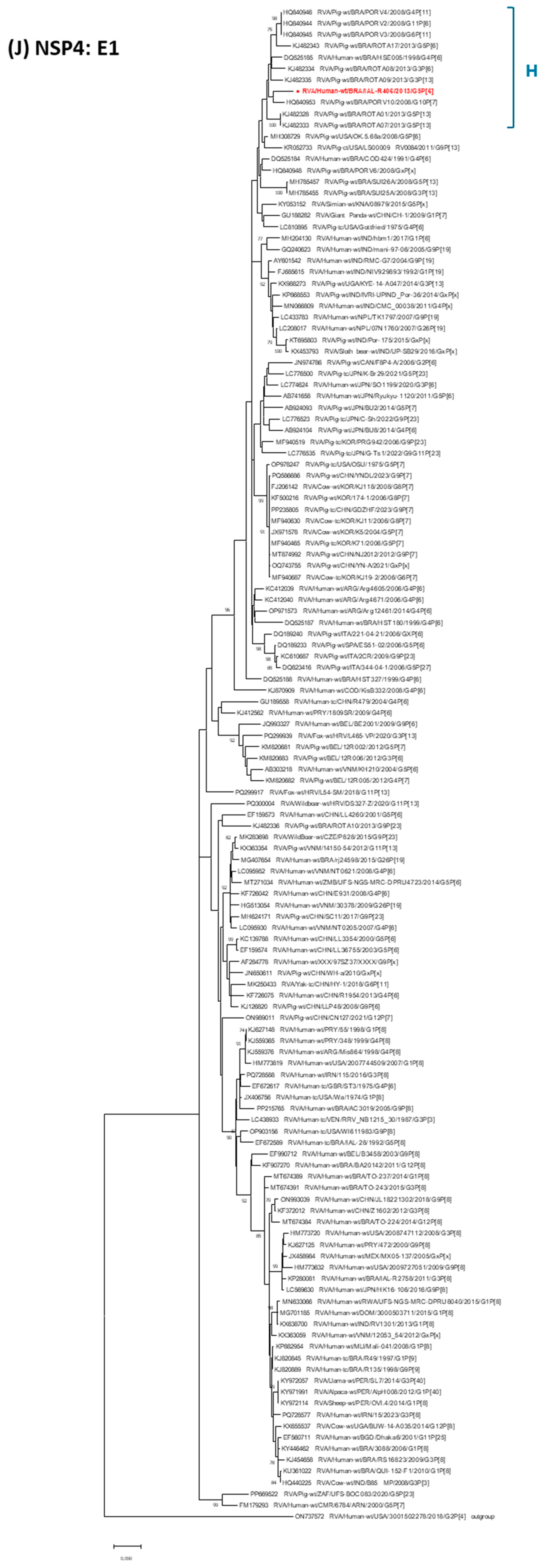
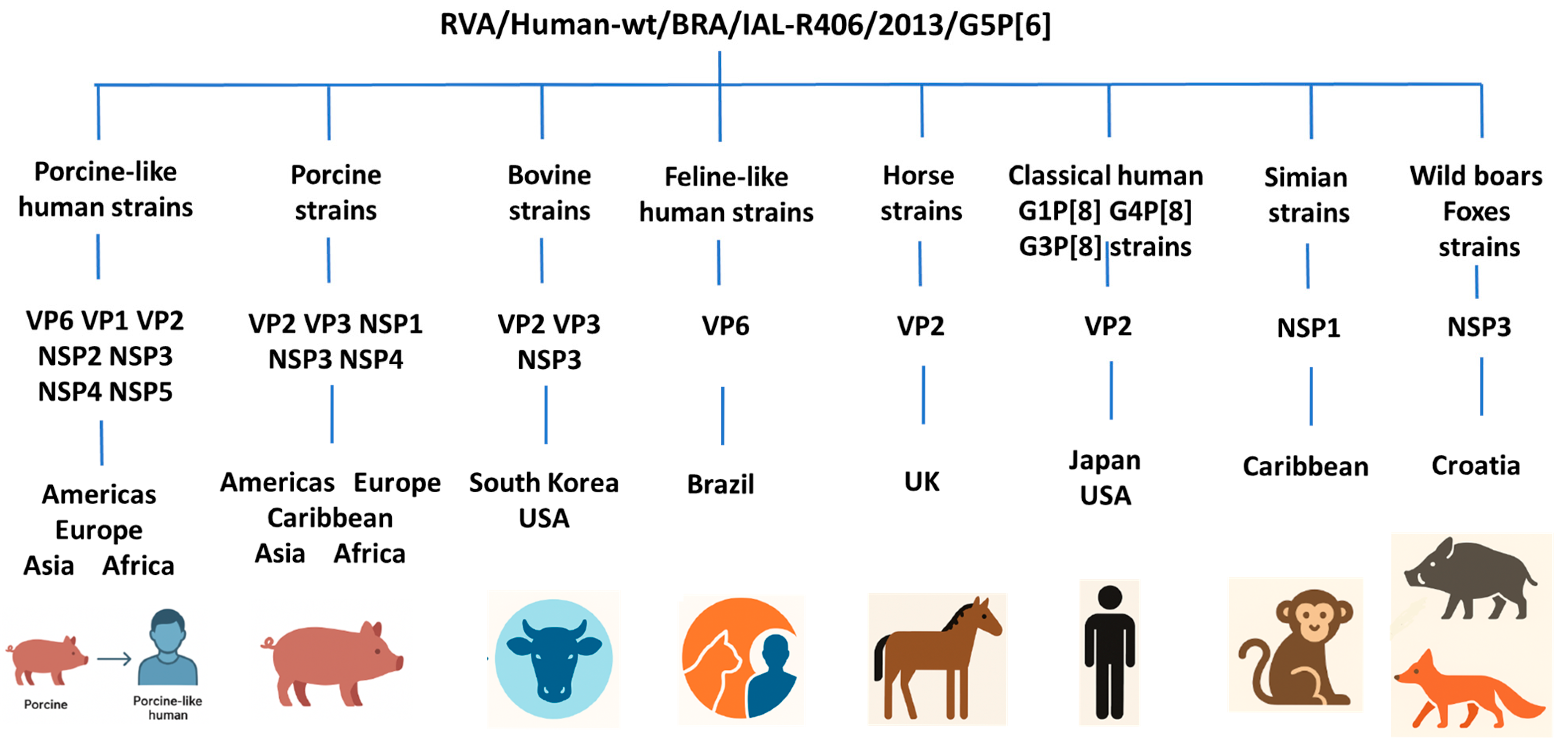
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walker, P.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; García, M.L.; Curtis Hendrickson, R.; et al. Recent changes to virus taxonomy ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2022). Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 2559–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šenica, P.; Žele Vengušt, D.; Vengušt, G.; Kuhar, U. Genomic revelations: Investigating rotavirus A presence in wild ruminants and its zoonotic potential. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1429654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunas, O.; Asare, E.O.; Sajewski, E.; Li, Y.; Pithawala, Z.; Weinberger, D.M.; Warren, J.L.; Armah, G.E.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; et al. Global estimates of rotavirus vaccine efficacy and effectiveness: A rapid review and meta-regression analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2025, 81, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Immunization Coverage. Key Facts. 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/immunization-coverage (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- De Jesus, M.C.S.; Santos, V.S.; Storti-Melo, L.M.; De Souza, C.D.F.; Barreto, Í.D.C.; Paes, M.V.C.; Lima, P.A.S.; Bohland, A.K.; Berezin, E.N.; Machado, R.L.D.; et al. Impact of a twelve-year rotavirus vaccine program on acute diarrhea mortality and hospitalization in Brazil: 2006–2018. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2020, 19, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Attoui, H.; Bányai, K.; Brussaard, C.P.D.; Danthi, P.; Del Vas, M.; Dermody, T.S.; Duncan, R.; Fāng, Q.; Johne, R.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Sedoreoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, e001782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esona, M.D.; Steele, D.; Kerin, T.; Armah, G.; Peenze, I.; Geyer, A.; Page, N.; Nyangao, J.; Agbaya, V.A.; Trabelsi, A.; et al. Determination of the G and P types of previously nontypeable rotavirus strains from the African Rotavirus Network, 1996–2004: Identification of unusual G types. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202 (Suppl. S1), S49–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Alarcón, R.G.; Salvatierra, K.; Gómez Quintero, E.; Liotta, D.J.; Parreño, V.; Miño, S.O. Complete genome classification system of Rotavirus alphagastroenteritidis: An updated analysis. Viruses 2025, 17, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.B.; Cates, J.E.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Ali, I.; Rodriguez, A.; Panjwani, J.; Tate, J.E.; Lopman, B.A.; Parashar, U.D. Rotavirus genotypes in the postvaccine era: A systematic review and meta-analysis of global, regional, and temporal trends by rotavirus vaccine introduction. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 229, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, Z.; Papp, H.; Lengyel, G.; Kisfali, P.; Steyer, A.; Steyer, A.F.; Esona, M.D.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Bányai, K. Detection of rare reassortant G5P[6] rotavirus, Bulgaria. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, C.; Liebert, U.G. Evidence for presumable feline origin of sporadic G6P[9] rotaviruses in humans. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 63, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsi, E.B.; Koukou, D.M.; Dellis, C.; Dourdouna, M.M.; Efthymiou, V.; Michos, A.; Syriopoulou, V. Epidemiological study of unusual rotavirus strains and molecular characterization of emerging P[14] strains isolated from children with acute gastroenteritis during a 15-year period. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandera, E.A.; Akari, Y.; Sang, C.; Njugu, P.; Khamadi, S.A.; Musundi, S.; Mutua, M.M.; Fukuda, S.; Murata, T.; Inoue, S.; et al. Full genome characterization of a Kenyan G8P[14] rotavirus strain suggests artiodactyl-to-human zoonotic transmission. Trop. Med. Health 2025, 53, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; McDonald, S.M.; Attoui, H.; Bányai, K.; Brister, J.R.; Buesa, J.; Esona, M.D.; Estes, M.K.; Gentsch, J.R.; et al. Uniformity of rotavirus strain nomenclature proposed by the Rotavirus Classification Working Group (RCWG). Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1397–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxie, I.; Dennehy, J.J. Intragenic recombination influences rotavirus diversity and evolution. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, vez059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoto, S.; Tacharoenmuang, R.; Guntapong, R.; Ide, T.; Sinchai, P.; Upachai, S.; Fukuda, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tharmaphornpilas, P.; Sangkitporn, S.; et al. Identification and characterization of a human G9P[23] rotavirus strain from a child with diarrhoea in Thailand: Evidence for porcine-to-human interspecies transmission. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, M.; Heylen, E.; De Coster, S.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J. Full genome characterization of a porcine-like human G9P[6] rotavirus strain isolated from an infant in Belgium. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.M.; da Silva, M.F.; Volotão, E.M.; Fialho, A.M.; Mazzoco, C.S.; Rocha, M.S.; Leite, J.P.G. G26P[19] rotavirus A strain causing acute gastroenteritis in the American continent. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2018, 113, e180344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.B.; de Assis, R.M.S.; Andrade, J.D.S.R.; Fialho, A.M.; Fumian, T.M. Rotavirus A during the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil, 2020–2022: Emergence of G6P[8] genotype. Viruses 2023, 15, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, F.M.; Falbo, A.R.; Germano, E.M.; Correia, N.B.; Souza, E.S.; Nakagomi, O.; Nakagomi, T.; Cuevas, L.E.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Correia, J.B. Reduction in Rotavirus Disease and Sustained Predominance of G2P[4] Rotavirus Strain following Introduction of Rotavirus Vaccine in Recife, Brazil. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2015, 61, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchs, A.; da Costa, A.C.; Cilli, A.; Komninakis, S.C.V.; Carmona, R.C.C.; Boen, L.; Morillo, S.G.; Sabino, E.C.; Timenetsky, M.D.C.S.T. Spread of the emerging equine-like G3P[8] DS-1-like genetic backbone rotavirus strain in Brazil and identification of potential genetic variants. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvea, V.; Santos, N. Rotavirus serotype G5: An emerging cause of epidemic childhood diarrhea. Vaccine 1999, 17, 1291–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.F.; Tort, L.F.; Gómez, M.M.; Assis, R.M.; Volotão, E.M.; de Mendonça, M.C.; Bello, G.; Leite, J.P.G. VP7 gene of human rotavirus A genotype G5: Phylogenetic analysis reveals the existence of three different lineages worldwide. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.D.; Duan, Z.J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, N.; Xie, Z.P.; Jiang, B.; Steele, D.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.S.; Fang, Z.Y. Molecular characterization of unusual human G5P[6] rotaviruses identified in China. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan-It, W.; Khamrin, P.; Saekhow, P.; Pantip, C.; Thongprachum, A.; Peerakome, S.; Ushijima, H.; Maneekarn, N. Multiple combinations of P[13]-like genotype with G3, G4, and G5 in porcine rotaviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.; Anh, D.D.; Nakagomi, O. Rotavirus G5P[6] in child with diarrhea, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1232–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoto, S.; Maeno, Y.; Tomita, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Ohfu, M.; Yodoshi, T.; Akeda, H.; Taniguchi, K. Whole genomic analysis of a porcine-like human G5P[6] rotavirus strain isolated from a child with diarrhoea and encephalopathy in Japan. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonietti, P.O.; Hora, A.S.; Silva, F.D.; Ruiz, V.L.; Gregori, F. Phylogenetic analyses of the VP4 and VP7 genes of porcine group A rotaviruses in Sao Paulo State, Brazil: First identification of G5P[23] in piglets. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2750–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maringa, W.M.; Mwangi, P.N.; Simwaka, J.; Mpabalwani, E.M.; Mwenda, J.M.; Peenze, I.; Esona, M.D.; Mphahlele, M.J.; Seheri, M.L.; Nyaga, M.M. Molecular Characterisation of a Rare Reassortant Porcine-Like G5P[6] Rotavirus Strain Detected in an Unvaccinated Child in Kasama, Zambia. Pathogens 2020, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvea, V.; de Castro, L.; Timenetsky, M.C.; Greenberg, H.; Santos, N. Rotavirus serotype G5 associated with diarrhea in Brazilian children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 1408–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, A.A.; Leite, J.P.; Nakagomi, O.; Kaga, E.; Woods, P.A.; Glass, R.I.; Gentsch, J.R. Characterization of human rotavirus genotype P[8]G5 from Brazil by probe-hybridization and sequence. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, J.D.; Linhares, A.C.; Gabbay, Y.B.; Leite, J.P. Detection and characterization of rotavirus G and P types from children participating in a rotavirus vaccine trial in Belém, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2002, 97, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, I.T.; Fialho, A.M.; de Assis, R.M.; Rocha, M.; Galvão, M.; Cruz, C.M.; Ferreira, M.S.R.; Leite, J.P.G. Rotavirus strain diversity in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Characterization of VP4 and VP7 genotypes in hospitalized children. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2002, 48, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, R.C.; Timenetsky, M.d.C.; da Silva, F.F.; Granato, C.F. Characterization of rotavirus strains from hospitalized and outpatient children with acute diarrhoea in São Paulo, Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, C.I.; Christofoletti, A.; Munford, V.; Rácz, M.L. G and P rotavirus genotypes in stool samples from children in Teresina, State of Piauí. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2007, 40, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, I.T.; Assis, R.M.; Fialho, A.M.; Mascarenhas, J.D.; Heinemann, M.B.; Leite, J.P. Brazilian P[8],G1, P[8],G5, P[8],G9, and P[4],G2 rotavirus strains: Nucleotide sequence and phylogenetic analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.F.; Tort, L.F.; Gómez, M.M.; Assis, R.M.; de Mendonça, M.C.; Volotão, E.M.; Leite, J.P.G. Phylogenetic analysis of VP1, VP2, and VP3 gene segments of genotype G5 group A rotavirus strains circulating in Brazil between 1986 and 2005. Virus Res. 2011, 160, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzetti, E.; da Silva Medeiros, T.N.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Genetic heterogeneity of wild-type G4P[6] porcine rotavirus strains detected in a diarrhea outbreak in a regularly vaccinated pig herd. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 154, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, H.; László, B.; Jakab, F.; Ganesh, B.; De Grazia, S.; Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Martella, V.; Bányai, K. Review of group A rotavirus strains reported in swine and cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.P.; Wu, F.T.; Bányai, K.; Wu, H.S.; Yang, D.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Lin, J.S.; Hsiung, C.A.; Huang, J.C.; Jiang, B.; et al. Identification of porcine rotavirus-like genotype P[6] strains in Taiwanese children. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Pang, B.B.; Ghosh, S.; Zhou, X.; Shintani, T.; Urushibara, N.; Song, Y.W.; He, M.Y.; Liu, M.Q.; Tang, W.F.; et al. Molecular epidemiology and genetic evolution of the whole genome of G3P[8] human rotavirus in Wuhan, China, from 2000 through 2013. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagula, N.B.; Esona, M.D.; Nyaga, M.M.; Stucker, K.M.; Halpin, R.A.; Stockwell, T.B.; Seheri, M.L.; Steele, A.D.; Wentworth, D.E.; Mphahlele, M.J. Whole genome analyses of G1P[8] rotavirus strains from vaccinated and non-vaccinated South African children presenting with diarrhea. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvea, V.; Glass, R.I.; Woods, P.; Taniguchi, K.; Clark, H.F.; Forrester, B.; Fang, Z.Y. Polymerase chain reaction amplification and typing of rotavirus nucleic acid from stool specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RIVM.Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu. Rotavirus A Genotyping Tool Version 0.1. Available online: https://mpf.rivm.nl/mpf/typingtool/rotavirusa/ (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martella, V.; Bányai, K.; Ciarlet, M.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Lorusso, E.; De Grazia, S.; Arista, S.; Decaro, N.; Elia, G.; Cavalli, A.; et al. Relationships among porcine and human P[6] rotaviruses: Evidence that the different human P[6] lineages have originated from multiple interspecies transmission events. Virology 2006, 344, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchs, A.; Cilli, A.; Morillo, S.G.; Gregório, D.S.; de Souza, K.A.; Vieira, H.R.; Fernandes, A.M.; Carmona, R.C.; Timenetsky, M.C. Detection of the emerging rotavirus G12P[8] genotype at high frequency in Brazil in 2014: Successive replacement of predominant strains after vaccine introduction. Acta Trop. 2016, 156, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulgheroff, A.C.; Silva, G.A.; Naveca, F.G.; Oliveira, A.G.; Domingues, A.L. Diversity of group A rotavirus genes detected in the Triângulo Mineiro region, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, S.F.S.; Soares, L.S.; Lobo, P.S.; Penha Júnior, E.T.; Sousa Júnior, E.C.; Bezerra, D.A.M.; Vaz, L.R.; Linhares, A.C.; Mascarenhas, J.D.P. Detection of a novel equine-like G3 rotavirus associated with acute gastroenteritis in Brazil. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 3131–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.S.; Nóbrega, F.A.; Soares, M.W.S.; Moreira, R.D.; Cuevas, L.E.; Gurgel, R.Q. Rotavirus Genotypes Circulating in Brazil Before and After the National Rotavirus Vaccine Program: A Review. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, e63–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Sales, M.; Leal, E.; Milagres, F.A.P.; Brustulin, R.; Morais, V.D.S.; Marcatti, R.; Araújo, E.L.L.; Witkin, S.S.; Deng, X.; Sabino, E.C.; et al. Genomic constellation of human Rotavirus A strains identified in Northern Brazil: A 6-year follow-up (2010–2016). Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2020, 62, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.B.; de Assis, R.M.S.; Arantes, I.; Fumian, T.M. Full genotype constellations analysis of unusual DS-1-like G12P[6] and G6P[8] rotavirus strains detected in Brazil, 2019. Virology 2022, 577, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.; Amarilla, A.A.; Galeano, M.E.; Aquino, V.H.; Fariña, N.; Russomando, G.; Parra, G.I. Predominance of rotavirus G2P[4] and emergence of G12P[9] strains in Asunción, Paraguay, 2006–2007. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tort, L.F.; Victoria, M.; Lizasoain, A.A.; Castells, M.; Maya, L.; Gómez, M.M.; Arreseigor, E.; López, P.; Cristina, J.; Leite, J.P.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of group A rotavirus among children admitted to hospital in Salto, Uruguay, 2011–2012: First detection of the emerging genotype G12. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degiuseppe, J.I.; Stupka, J.A. Genotype distribution of Group A rotavirus in children before and after massive vaccination in Latin America and the Caribbean: Systematic review. Vaccine 2020, 38, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggeri, F.M.; Delogu, R.; Petouchoff, T.; Tcheremenskaia, O.; De Petris, S.; Fiore, L. RotaNet-Italy Study Group. Molecular characterization of rotavirus strains from children with diarrhea in Italy, 2007–2009. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roczo-Farkas, S.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Bines, J.E. Enteric Virus Group, Murdoch Childrens Research Institute, Royal Children’s Hospital. Australian Rotavirus Surveillance Program: Annual Report, 2016. Commun. Dis. Intell. Q. Rep. 2017, 41, E455–E471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifacio, J.; Lupisan, S.; Roque, V., Jr.; Ducusin, M.J.; Grabovac, V.; Batmunkh, N.; Heffelfinger, J.D.; Fox, K.; Toda, K.; Castro, M.d.Q.; et al. Molecular characterization of rotavirus diarrhea among children aged under five years in the Philippines, 2013–2015. Vaccine 2018, 36, 7888–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandoker, N.; Thongprachum, A.; Takanashi, S.; Okitsu, S.; Nishimura, S.; Kikuta, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Sugita, K.; Baba, T.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of rotavirus gastroenteritis in Japan during 2014–2015: Characterization of re-emerging G2P[4] after rotavirus vaccine introduction. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana, A.; Jere, K.C.; Chaguza, C.; Montes, M.; Alkorta, M.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; Cilla, G. Molecular epidemiology of G12 rotavirus strains during eight consecutive epidemic seasons in the Basque Country (North of Spain), 2010–2018. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 71, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjate, F.; João, E.D.; Chirinda, P.; Garrine, M.; Vubil, D.; Nobela, N.; Kotloff, K.; Nataro, J.P.; Nhampossa, T.; Acácio, S.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Rotavirus Strains in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Children in Manhiça District, Southern Mozambique 2008–2019. Viruses 2022, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminu, M.; Page, N.A.; Ahmad, A.A.; Umoh, J.U.; Dewar, J.; Steele, A.D. Diversity of rotavirus VP7 and VP4 genotypes in Northwestern Nigeria. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, S198–S204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Galeano, M.E.; Akopov, A.; Palacios, R.; Russomando, G.; Kirkness, E.F.; Parra, G.I. Whole-genome analyses reveals the animal origin of a rotavirus G4P[6] detected in a child with severe diarrhea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degiuseppe, J.I.; Beltramino, J.C.; Millán, A.; Stupka, J.A.; Parra, G.I. Complete genome analyses of G4P[6] rotavirus detected in Argentinean children with diarrhoea provides evidence of interspecies transmission from swine. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, E367–E371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.D.; Espinoza, L.R.; Tonietti, P.O.; Barbosa, B.R.; Gregori, F. Whole-genomic analysis of 12 porcine group A rotaviruses isolated from symptomatic piglets in Brazil during the years of 2012–2013. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 32, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, S.F.S.; Fecury, P.C.M.S.; Bezerra, D.A.M.; Lobo, P.S.; Penha Júnior, E.T.; Sousa Júnior, E.C.; Mascarenhas, J.D.P.; Soares, L.S.; Justino, M.C.A.; Linhares, A.C. Emergence of G12P[6] rotavirus strains among hospitalized children with acute gastroenteritis in Belém, Northern Brazil, following introduction of a rotavirus vaccine. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, Y.; Medeiros, R.S.; Viana, E.; de Azevedo, L.S.; Guiducci, R.; da Costa, A.C.; Luchs, A. Genetic diversity and evolution of G12P[6] DS-1-like and G12P[9] AU-1-like Rotavirus strains in Brazil. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2024, 24, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupka, J.A.; Carvalho, P.; Amarilla, A.A.; Massana, M.; Parra, G.I. Argentinean National Surveillance Network for Diarrheas. National Rotavirus Surveillance in Argentina: High incidence of G9P[8] strains and detection of G4P[6] strains with porcine characteristics. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, J.D.; Linhares, A.C.; Gabbay, Y.B.; Lima, C.S.; Guerra, S.F.; Soares, L.S.; Oliveira, D.S.; Lima, J.C.; Macêdo, O.; Leite, J.P. Molecular characterization of VP4 and NSP4 genes from rotavirus strains infecting neonates and young children in Belém, Brazil. Virus Res. 2007, 126, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Heiman, E.; Arijs, I.; Delbeke, T.; McDonald, S.M.; Palombo, E.A.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Maes, P.; Patton, J.T.; et al. Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-Like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3204–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Urushibara, N.; Taniguchi, K.; Kobayashi, N. Whole genomic analysis reveals the porcine origin of human G9P[19] rotavirus strains Mc323 and Mc345. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucardo, F.; Rippinger, C.M.; Svensson, L.; Patton, J.T. Vaccine-derived NSP2 segment in rotaviruses from vaccinated children with gastroenteritis in Nicaragua. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1282–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Urushibara, N.; Chawla-Sarkar, M.; Krishnan, T.; Kobayashi, N. Whole genomic analyses of asymptomatic human G1P[6], G2P[6] and G3P[6] rotavirus strains reveal intergenogroup reassortment events and genome segments of artiodactyl origin. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 16, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K.I.; Roy, S.; Esona, M.D.; Jones, S.; Sobers, S.; Morris-Glasgow, V.; Rey-Benito, G.; Gentsch, J.R.; Bowen, M.D. Full genomic characterization of a novel genotype combination, G4P[14], of a human rotavirus strain from Barbados. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 28, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grazia, S.; Giammanco, G.M.; Dóró, R.; Bonura, F.; Marton, S.; Cascio, A.; Martella, V.; Bányai, K. Identification of a multi-reassortant G12P[9] rotavirus with novel VP1, VP2, VP3 and NSP2 genotypes in a child with acute gastroenteritis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 35, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, L.P.; Kaneko, M.; Nakagomi, T.; Gauchan, P.; Agbemabiese, C.A.; Dang, A.D.; Nakagomi, O. Molecular epidemiology of Rotavirus A causing acute gastroenteritis hospitalizations among children in Nha Trang, Vietnam, 2007–2008: Identification of rare G9P[19] and G10P[14] strains. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, M.; Do, L.P.; Doan, Y.H.; Nakagomi, T.; Gauchan, P.; Agbemabiese, C.A.; Dang, A.D.; Nakagomi, O. Porcine-like G3P[6] and G4P[6] rotavirus A strains detected from children with diarrhoea in Vietnam. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2261–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsuki, H.; Agbemabiese, C.A.; Nakagomi, T.; Pun, S.B.; Gauchan, P.; Muto, H.; Masumoto, H.; Atarashi, R.; Nakagomi, O.; Pandey, B.D. Whole genome characterisation of G11P[25] and G9P[19] rotavirus A strains from adult patients with diarrhoea in Nepal. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 69, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Matthijnssens, J.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Park, J.G.; Son, K.Y.; Ryu, E.H.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, W.S.; Kang, M.I.; et al. Full-length genomic analysis of porcine G9P[23] and G9P[7] rotavirus strains isolated from pigs with diarrhea in South Korea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel-Paradis, O.; Laurin, M.A.; Martella, V.; Sohal, J.S.; L’Homme, Y. Full-length genome analysis of G2, G9 and G11 porcine group A rotaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.G.; Kim, D.S.; Matthijnssens, J.; Kwon, H.J.; Zeller, M.; Alfajaro, M.M.; Son, K.Y.; Hosmillo, M.; Ryu, E.H.; Kim, J.Y.; et al. Comparison of pathogenicities and nucleotide changes between porcine and bovine reassortant rotavirus strains possessing the same genotype constellation in piglets and calves. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monini, M.; Zaccaria, G.; Ianiro, G.; Lavazza, A.; Vaccari, G.; Ruggeri, F.M. Full-length genomic analysis of porcine rotavirus strains isolated from pigs with diarrhea in Northern Italy. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 25, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.S.; Brandão, P.E.; Nishida, M.K.; Ruiz, V.L.A.; Gregori, F. Molecular analysis of NSP4 coding gene of porcine rotavirus in Brazil. Ars Vet. 2015, 31, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuns, S.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Roukaerts, I.D.; Desmarets, L.M.; Van Ranst, M.; Nauwynck, H.J.; Matthijnssens, J. Complete genome characterization of recent and ancient Belgian pig group A rotaviruses and assessment of their evolutionary relationship with human rotaviruses. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Navarro, R.; Malik, Y.S.; Willingham, A.L.; Kobayashi, N. Whole genomic analysis of a porcine G6P[13] rotavirus strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, R.; Aung, M.S.; Cruz, K.; Ketzis, J.; Gallagher, C.A.; Beierschmitt, A.; Malik, Y.S.; Kobayashi, N.; Ghosh, S. Whole genome analysis provides evidence for porcine-to-simian interspecies transmission of rotavirus-A. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 49, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.A.O.; Camargo, D.S.; Araújo, K.V.S.; Lobo, P.S.; Bandeira, R.S.; Soares, L.S.; Mascarenhas, J.D.P. Genomic Analysis of Rotavirus Species A Isolated from Swine, Amazon Region, Brazil. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 792–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, S.; Sydler, T.; Rosato, G.; Hilbe, M.; Kümmerlen, D.; Sidler, X.; Bachofen, C. Frequent occurrence of simultaneous infection with multiple rotaviruses in Swiss pigs. Viruses 2022, 14, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.J.; Agbemabiese, C.A.; Patton, J.T. Production of OSU G5P[7] Porcine Rotavirus Expressing a Fluorescent Reporter via Reverse Genetics. Viruses 2024, 16, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnikov, N.; Gulyukin, A.; Aliper, T.; Yuzhakov, A. Complete genome characterization by nanopore sequencing of rotaviruses A, B, and C circulating on large-scale pig farms in Russia. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, A.; Segone, N.; Coertze, R.; Barron, N.; Strydom, M.; O’Neill, H.G. Phylogenetic Analyses of Rotavirus A, B and C Detected on a Porcine Farm in South Africa. Viruses 2024, 16, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizawa, S.; Fukuda, F.; Kikkawa, Y.; Oi, T.; Takemae, H.; Masuda, T.; Ishida, H.; Murakami, H.; Sakaguchi, S.; Mizutani, T.; et al. Genomic diversity of group A rotaviruses from wild boars and domestic pigs in Japan: Wide prevalence of NSP5 carrying the H2 genotype. Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.C.; Kim, E.M.; Shin, S.U.; Park, J.; Choi, K.S. Molecular surveillance of rotavirus A associated with diarrheic calves from the Republic of Korea and full genomic characterization of bovine-porcine reassortant G5P[7] strain. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 100, 105266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.W.; Elleman, T.C.; Azad, A.A.; Dyall-Smith, M.L. Nucleotide sequence of gene segment 9 encoding a nonstructural protein of UK bovine rotavirus. Virology 1984, 134, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugawa, T.; Rainwater-Lovett, K.; Tsutsumi, H. Human G3P[9] rotavirus strains possessing an identical genotype constellation to AU-1 isolated at high prevalence in Brazil, 1997–1999. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Shintani, T.; Kobayashi, N. Evidence for the porcine origin of equine rotavirus strain H-1. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 158, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Kondo, K.; Nakata, S.; Morita, Y.; Adachi, N.; Kogawa, K.; Ukae, S.; Kudou, Y.; Adachi, S.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. Whole-genome analysis of human group A rotaviruses in 1980s Japan and evolutionary assessment of global Wa-like strains across half a century. J. Gen. Virol. 2024, 105, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; McDonald, P.W.; Thompson, T.A.; Dennis, A.F.; Akopov, A.; Kirkness, E.F.; Patton, J.T.; McDonald, S.M. Analysis of human rotaviruses from a single location over an 18-year time span suggests that protein coadaption influences gene constellations. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9842–9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, S.M.; Matthijnssens, J.; McAllen, J.K.; Hine, E.; Overton, L.; Wang, S.; Lemey, P.; Zeller, M.; Van Ranst, M.; Spiro, D.J.; et al. Evolutionary dynamics of human rotaviruses: Balancing reassortment with preferred genome constellations. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brnić, D.; Čolić, D.; Kunić, V.; Maltar-Strmečki, N.; Krešić, N.; Konjević, D.; Bujanić, M.; Bačani, I.; Hižman, D.; Jemeršić, L. Rotavirus A in domestic pigs and wild boars: High genetic diversity and interspecies transmission. Viruses 2022, 14, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolić, D.; Krešić, N.; Mihaljević, Ž.; Andreanszky, T.; Balić, D.; Lolić, M.; Brnić, D. A remarkable genetic diversity of Rotavirus A circulating in red fox population in Croatia. Pathogens 2021, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacharoenmuang, R.; Guntapong, R.; Upachai, S.; Singchai, P.; Fukuda, S.; Ide, T.; Hatazawa, R.; Sutthiwarakom, K.; Kongjorn, S.; Onvimala, N.; et al. Full genome-based characterization of G4P[6] rotavirus strains from diarrheic patients in Thailand: Evidence for independent porcine-to-human interspecies transmission events. Virus Genes 2021, 57, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akari, Y.; Hatazawa, R.; Kuroki, H.; Ito, H.; Negoro, M.; Tanaka, T.; Miwa, H.; Sugiura, K.; Umemoto, M.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Full genome-based characterization of an Asian G3P[6] human rotavirus strain found in a diarrheic child in Japan: Evidence for porcine-to-human zoonotic transmission. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 115, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Shimada, S.; Fujii, Y.; Moriyama, H.; Oba, M.; Katayama, Y.; Tsuchiaka, S.; Okazaki, S.; Omatsu, T.; Furuya, T.; et al. H2 genotypes of G4P[6], G5P[7], and G9[23] porcine rotaviruses show super-short RNA electropherotypes. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandera, E.A.; Hatazawa, R.; Tsutsui, N.; Kurokawa, N.; Kathiiko, C.; Mumo, M.; Waithira, E.; Wachira, M.; Mwaura, B.; Nyangao, J.; et al. Genomic characterization of an African G4P[6] human rotavirus strain identified in a diarrheic child in Kenya: Evidence for porcine-to-human interspecies transmission and reassortment. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 96, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyer, A.; Poljšak-Prijatelj, M.; Barlič-Maganja, D.; Marin, J. Human, porcine and bovine rotaviruses in Slovenia: Evidence of interspecies transmission and genome reassortment. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Strain | Genotypes | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VP7 | VP4 | VP6 | VP1 | VP2 | VP3 | NSP1 | NSP2 | NSP3 | NSP4 | NSP5 | |
| RVA/Human-wt/BRA/IAL-R406/2013/G5P[6] a | G5 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/CHN/LL36755/2003/G5P[6] | G5 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/CHN/LL3354/2000/G5P[6] | G5 | P[6] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/CHN/LL4260/2001/G5P[6] | G5 | P[6] | I12 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/BGR/BG260/2008/G5P[6] | G5 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/ZMB/UFS-NGS-MRCDPRU4723/2014/G5P[6] | G5 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/JPN/Ryukyu-1120/2011/G5P[6] | G5 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/PRY/1809SR/2009/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/ARG/Arg4671/2006/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/ARG/Arg4605/2006/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/ARG/Arg12461/2014/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-tc/BRA/IAL28/1992/G5P[8] | G5 | P[8] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/CMR/6784/ARN/2000/G5P[7] | G5 | P[7] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-tc/GBR/ST3/1974/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-tc/CHN/R479/2004/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/CHN/E931/2008/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/COD/KisB332/2008/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/BRA/COD379/1991/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | Cx | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/CHN/GX54/2010/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/BRA/HSE005/1998/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A2 | N2 | T2 | E1 | H2 |
| RVA/Human-tc/BRA/R49/1997/G1P[9] | G1 | P[9] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M2 | A1 | N2 | T2 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/BEL/BE2001/2009/G9P[6] | G9 | P[6] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-tc/IND/mani-97/2006/G9P[19] | G9 | P[19] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/VNM/30378/2009/G26P[19] | G26 | P[19] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/BRA/rj24598/2015/G26P[19] | G26 | P[19] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-wt/PHL/TGE13-39/2013/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BEL/12R005/2012/G4P[7] | G4 | P[7] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-tc/USA/Gottfried/1975/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BEL/12R006/2012/G3P[6] | G3 | P[6] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/JPN/BU2/2014/G5P[7] | G5 | P[7] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BEL/12R002/2012/G5P[7] | G5 | P[7] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-tc/USA/OSU/1975/G5P[7] | G5 | P[7] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BRA/SUI13A/2008/G5P[13] | G5 | P[13] | I5 | R1 | C1 | Mx | A8 | Nx | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BRA/SUI24A/2008/G3P[13] | G3 | P[13] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M2 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BRA/ROTA01/2013/G5P[13] | G5 | P[13] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BRA/ROTA07/2013/G5P[13] | G5 | P[13] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BRA/ROTA17/2013/G5P[6] | G5 | P[6] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/BRA/ROTA24/2013/G5P[6] | G5 | P[6] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/IRL/R2WTA79/2014/G5P[13] | G5 | P[13] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N2 | T7 | E9 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/ITA/3BS/2009/G9P[23] | G9 | P[23] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/THA/CMP-011-09/2009/G4P[6] | G4 | P[6] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-tc/VEN/A131/1988/G3P[7] | G3 | P[7] | I5 | R1 | C2 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-tc/KOR/K71/2006/G5P[7] | G5 | P[7] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/KNA/ET8B/2015/G5P[13] | G5 | P[13] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Pig-wt/ITA/2CR/2009/G9P[23] | G9 | P[23] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Wildboar-wt/HRV/DS229-Z/2020/G3P[13] | G3 | P[13] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Wildboar-wt/HRV/DS306-OB/2020/G3P[13] | G3 | P[13] | I5 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A8 | N1 | T7 | Ex | H1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Azevedo, L.S.; Silva, V.C.M.; França, Y.; Guiducci, R.; Luchs, A. Tracing the Zoonotic Origins of a Rare Human G5P[6] Rotavirus in Brazil. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111172
de Azevedo LS, Silva VCM, França Y, Guiducci R, Luchs A. Tracing the Zoonotic Origins of a Rare Human G5P[6] Rotavirus in Brazil. Pathogens. 2025; 14(11):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111172
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Azevedo, Lais Sampaio, Vanessa Cristina Martins Silva, Yasmin França, Raquel Guiducci, and Adriana Luchs. 2025. "Tracing the Zoonotic Origins of a Rare Human G5P[6] Rotavirus in Brazil" Pathogens 14, no. 11: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111172
APA Stylede Azevedo, L. S., Silva, V. C. M., França, Y., Guiducci, R., & Luchs, A. (2025). Tracing the Zoonotic Origins of a Rare Human G5P[6] Rotavirus in Brazil. Pathogens, 14(11), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111172







