Disentangling the Causal Role of Gut Microbiota in Bacterial Liver Abscess: A Mendelian Randomization Study with Clinical Validation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source of Exposure and Outcome
2.2. The Selection of Instrumental Variables
2.3. Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization
2.4. Clinical Validation
2.4.1. Study Population
2.4.2. Sample Collection
2.4.3. Institutional Review Board Statement
2.4.4. 16S rDNA Sequencing of Gut Microbiota
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Result
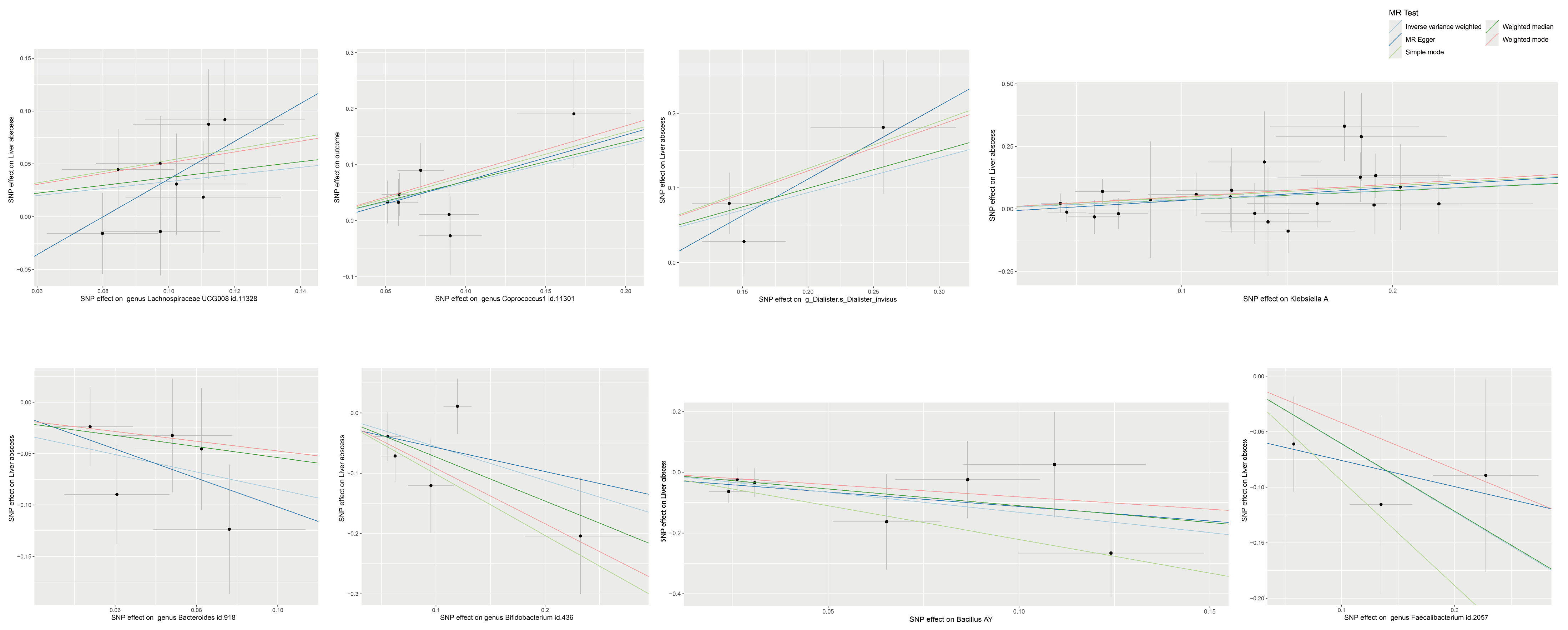
3.1. MR Analysis Results of Gut Microbiota on BLA
3.2. MR Analysis Results of Gut Microbial Metabolic Pathways on BLA
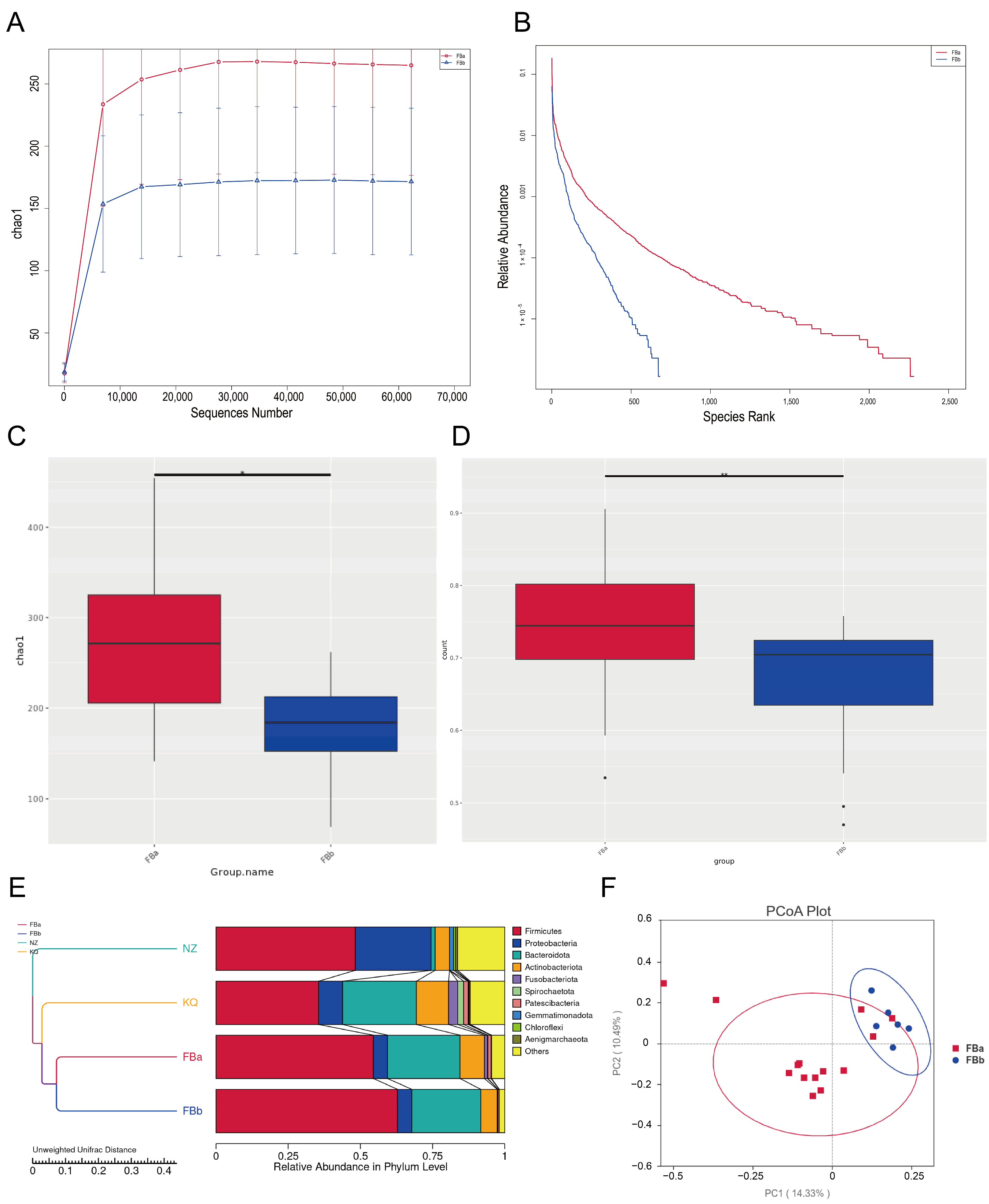
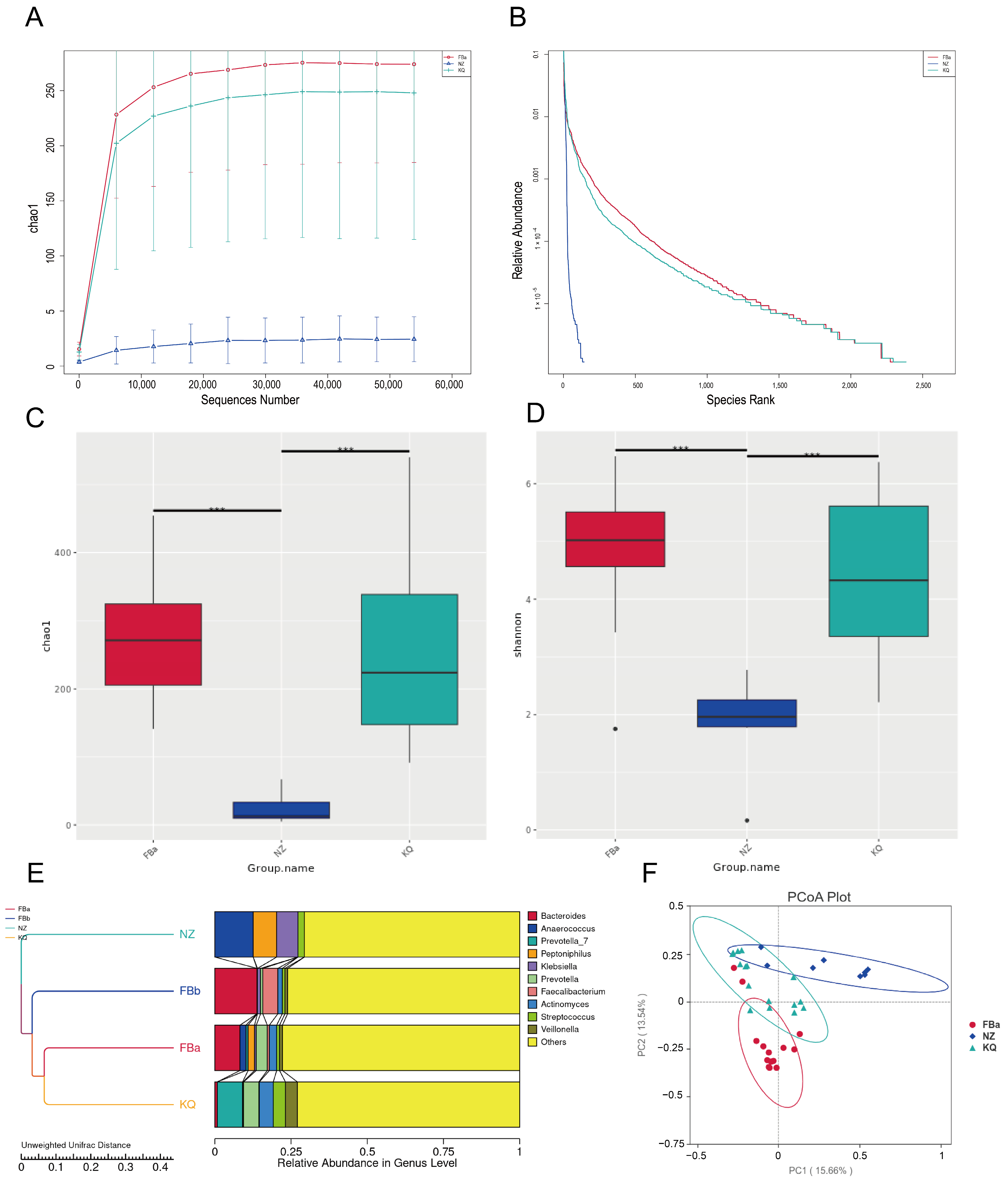
3.3. Gut Microbiota Diversity and Community Structure in BLA Patients and Controls
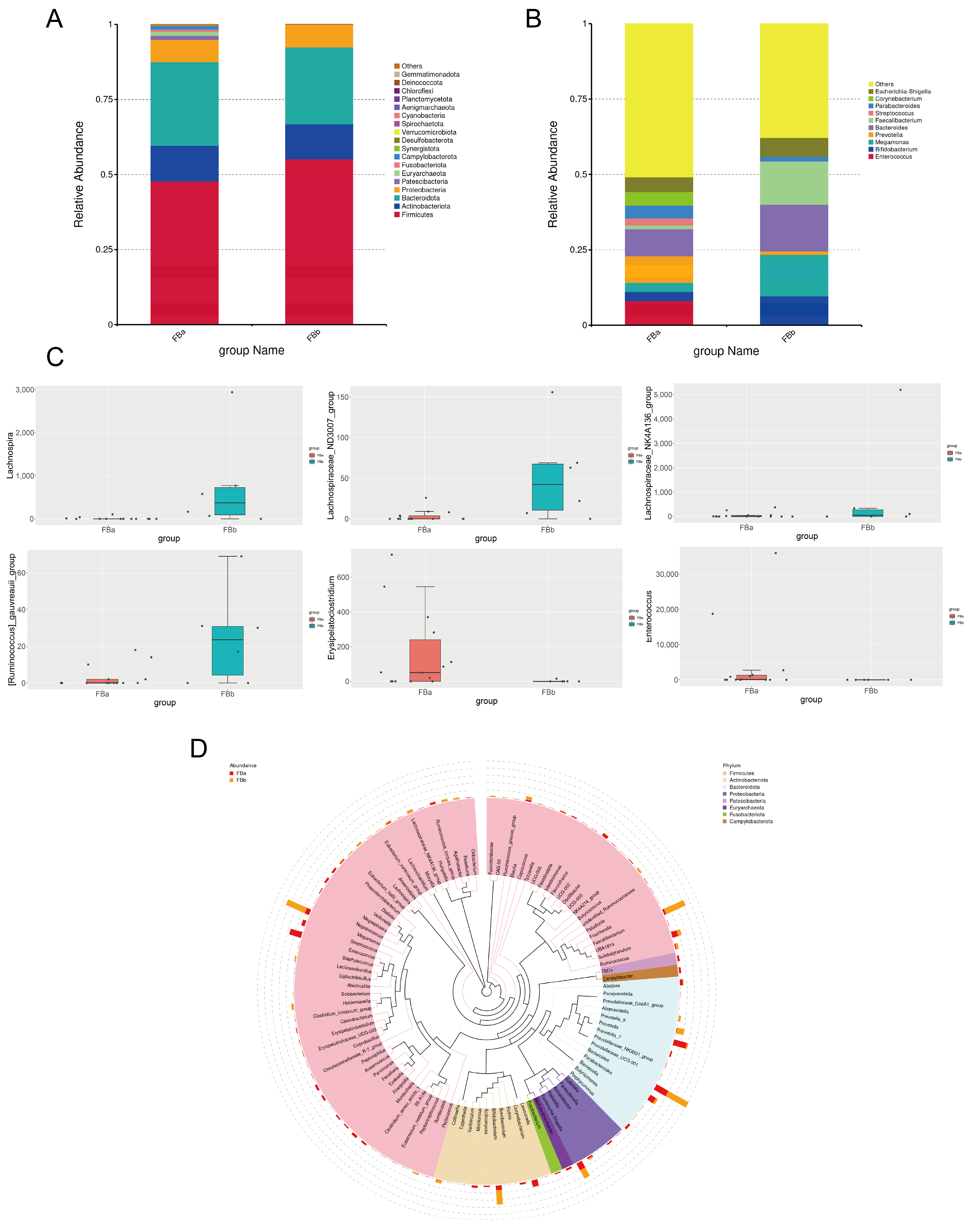
3.4. Significant Differences in Species Composition Between BLA Patients and Healthy Controls
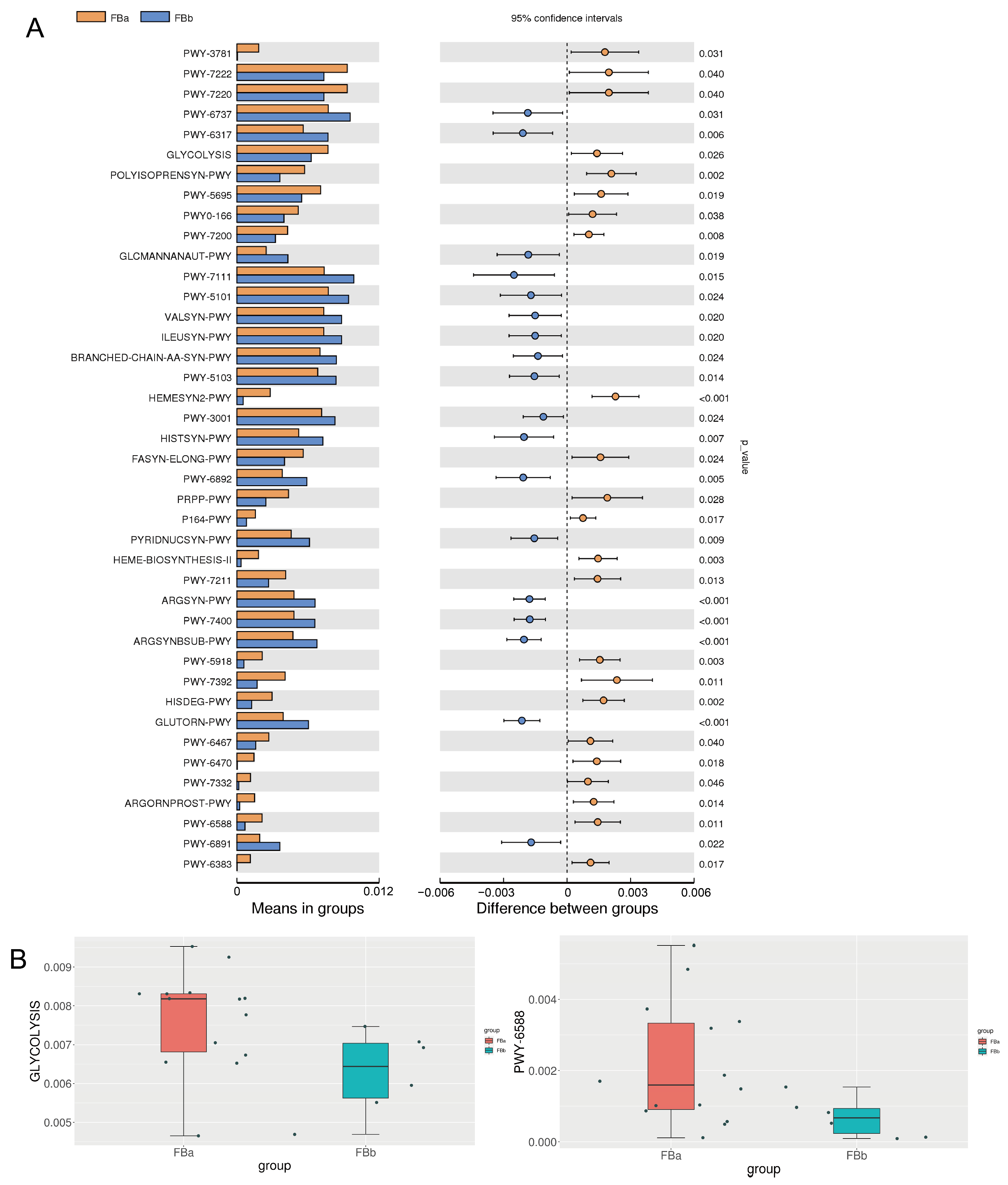
3.5. Key Differential Metabolic Pathways in BLA
3.6. Microbial Diversity Differs by Fecal, Oral, and Pus in BLA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johannsen, E.C.; Sifri, C.D.; Madoff, L.C. Pyogenic liver abscesses. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 14, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Dong, G.; Fang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhou, T. Clinical, microbiological, and molecular epidemiological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pyogenic liver abscess in southeastern China. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, J.; Bellot, P.; Roig, P.; Reus, S.; Carrascosa, S.; González-Alcaide, G.; Palazón, J.M.; Ramos, J.M. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of pyogenic liver abscess in people 65 years or older versus people under 65: A retrospective study. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Große, K.; Ohm, D.; Würstle, S.; Brozat, J.F.; Schmid, R.M.; Trautwein, C.; Stallmach, A.; Bruns, T.; Reuken, P.A. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with enterococcal liver abscess. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. The New Changes of Epidemiology, Etiology, and Clinical Characteristics of Pyogenic Liver Abscesses: A Retrospective Study in a Hospital in Northern China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 4013–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi-Rocca, J.; Rigothier, M.C.; Guillén, N. Host-microbe interactions and defense mechanisms in the development of amoebic liver abscesses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsett, P.A.; Huang, C.J.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Cameron, J.L.; Pitt, H.A. Fungal hepatic abscesses: Characterization and management. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 1997, 1, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Thaiss, C.A.; Elinav, E. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cui, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, P. Gut microbiota-an important contributor to liver diseases. J. South. Med. Univ. 2020, 40, 595–600. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Shen, W.; Li, J. Gut Microbiota Contributes to Host Defense Against Klebsiella pneumoniae-Induced Liver Abscess. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 5215–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, J.; Wei, Y. Gut microbes improve prognosis of Klebsiella pneumoniae pulmonary infection through the lung-gut axis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1392376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Bacigalupe, R.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Wang, J.; Demirkan, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Garay, J.A.R.; Finnicum, C.T.; Liu, X.; et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopera-Maya, E.A.; Kurilshikov, A.; van der Graaf, A.; Hu, S.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Chen, L.; Vila, A.V.; Gacesa, R.; Sinha, T.; Collij, V.; et al. Author Correction: Effect of host genetics on the gut microbiome in 7738 participants of the Dutch Microbiome Project. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Havulinna, A.S.; Liu, Y.; Jousilahti, P.; Ritchie, S.C.; Tokolyi, A.; Sanders, J.G.; Valsta, L.; Brożyńska, M.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Author Correction: Combined effects of host genetics and diet on human gut microbiota and incident disease in a single population cohort. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.I. Prognosis of liver abscess with no identified organism. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wong, C.C.; Lai, S.C.; Lin, Z.H.; Zheng, W.L.; Zhao, H.; Pan, K.-H.; Chen, S.-J.; Si, J.-M. Klebsiella pneumoniae invasive liver abscess syndrome with purulent meningitis and septic shock: A case from mainland China. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Fu, L.; Jiang, C.; Peng, S. Demographics and Clinical Outcomes of Culture-Positive versus Culture-Negative Pyogenic Liver Abscess in an Asian Population. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Author Correction: Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaszak, M.; Górna, I.; Woźniak, D.; Przysławski, J.; Drzymała-Czyż, S. Association between Gut Dysbiosis and the Occurrence of SIBO, LIBO, SIFO and IMO. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Yang, X.X.; Tan, B.; Zhou, X.P.; Xia, H.M.; Xue, J.; Xu, X.; Qing, Y.; Li, C.-R.; Qiu, J.-F.; et al. Distribution of common pathogens in patients with pyogenic liver abscess in China: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.T.; Zhou, J.C.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, K.R.; Li, B.; Shen, P.; Wei, Z.-Q.; Yu, Y.-S. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in East China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Qian, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, X.; Feng, J.; Hu, J.; Fang, Y.; Jiao, F.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Functional vulnerability of liver macrophages to capsules defines virulence of blood-borne bacteria. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20212032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Cui, J.; Ning, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, W.; Yao, K.; Yuan, J.; Zhong, X. Alterations in gut microbiota and metabolite profiles in patients with infantile cholestasis. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Sun, C.; Miao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Lian, M.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; et al. Alterations of gut microbiome in autoimmune hepatitis. Gut 2020, 69, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Su, X.; Liang, X.; Liao, M.; Zhong, H.; Xu, J.; Gou, W.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Zheng, J.-S.; et al. Gut microbiome features and metabolites in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among community-dwelling middle-aged and older adults. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, W.; Chen, K.; Lu, C.; Li, X.; Li, Q. Elucidating the causal association between gut microbiota and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma through Mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1288525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaplana, T.; Miele, S.; Tolonen, A.C. Lachnospiraceae are emerging industrial biocatalysts and biotherapeutics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1324396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Kameyama, K.; Miyauchi, E.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kanaya, T.; Fujii, T.; Kato, T.; Sasaki, T.; Tachibana, N.; Negishi, H.; et al. Fatty acid overproduction by gut commensal microbiota exacerbates obesity. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 361–375.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, D.; Wu, D.; Gao, X.; Shao, F.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, W.; Qin, X.; et al. Tissue-resident Lachnospiraceae family bacteria protect against colorectal carcinogenesis by promoting tumor immune surveillance. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 418–432.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Cui, Z.; Ma, K.; Wu, D.; Luo, J.; Li, F.; Xiong, W.; Rao, S.; Xiang, Q.; et al. Lachnospiraceae-derived butyrate mediates protection of high fermentable fiber against placental inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.J.; Chang, H.C.; Sung, P.C.; Ge, M.C.; Tang, H.Y.; Cheng, M.L.; Cheng, H.-T.; Chou, H.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lin, W.-R.; et al. Oral fecal transplantation enriches Lachnospiraceae and butyrate to mitigate acute liver injury. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 113591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.K.; Tang, M.; Lei, L.; Li, J.R.; Sun, H.; Jiang, J.; Dong, B.; Li, H.-Y.; Jiang, J.-D.; et al. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron ameliorates mouse hepatic steatosis through regulating gut microbial composition, gut-liver folate and unsaturated fatty acids metabolism. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2304159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xiong, X.; Liu, M.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, G.; Shi, J.; Li, X. Bacteroides ovatus alleviates high-fat and high-cholesterol-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via gut-liver axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, C.; Guo, M.; Cui, X.; Jing, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, W.; Qi, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Bacteroides acidifaciens in the gut plays a protective role against CD95-mediated liver injury. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2027853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherid, M.; Samo, S.; Sulaiman, S.; Husein, H.; Sifuentes, H.; Sridhar, S. Liver abscess and bacteremia caused by Lactobacillus: Role of probiotics? Case report and review of the literature. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Qiu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, J.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zou, B.; Tang, D. Gut microbiota mediates the inhibition of lymphopoiesis in dietary-restricted mice by suppressing glycolysis. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2117509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguro-Igashira, E.; Murakami, M.; Mori, R.; Kuwahara, R.; Kihara, T.; Kohara, M.; Fujiwara, M.; Motooka, D.; Okuzaki, D.; Arase, M.; et al. The pyruvate-GPR31 axis promotes transepithelial dendrite formation in human intestinal dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2318767121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lan, R.; Zhao, L.; Pu, J.; Hu, D.; Yang, J.; Zhou, H.; Han, L.; Ye, L.; Jin, D.; et al. Prevotella copri alleviates hyperglycemia and regulates gut microbiota and metabolic profiles in mice. mSystems 2024, 9, e0053224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Yu, H.; Xue, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Shang, D. Disentangling the Causal Role of Gut Microbiota in Bacterial Liver Abscess: A Mendelian Randomization Study with Clinical Validation. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111173
Han J, Yu H, Xue H, Lu Y, Li S, Zhang Q, Liu J, Shang D. Disentangling the Causal Role of Gut Microbiota in Bacterial Liver Abscess: A Mendelian Randomization Study with Clinical Validation. Pathogens. 2025; 14(11):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111173
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jingrun, Han Yu, Haocheng Xue, Yifan Lu, Shuang Li, Qingkai Zhang, Jianjun Liu, and Dong Shang. 2025. "Disentangling the Causal Role of Gut Microbiota in Bacterial Liver Abscess: A Mendelian Randomization Study with Clinical Validation" Pathogens 14, no. 11: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111173
APA StyleHan, J., Yu, H., Xue, H., Lu, Y., Li, S., Zhang, Q., Liu, J., & Shang, D. (2025). Disentangling the Causal Role of Gut Microbiota in Bacterial Liver Abscess: A Mendelian Randomization Study with Clinical Validation. Pathogens, 14(11), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111173




