Genetic Diversity of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Clonal Transmission (ST92) in Critical Care Units at Hospital Juárez de México: MLST and Virulence Profiling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains and Biochemical Identification
2.2. Genetic Confirmation of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains by 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Resistance Profiles of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains
2.4. In Vitro Formation of Mature Biofilms of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains
2.5. Virutyping of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains
2.6. Multilocus Sequence Typing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
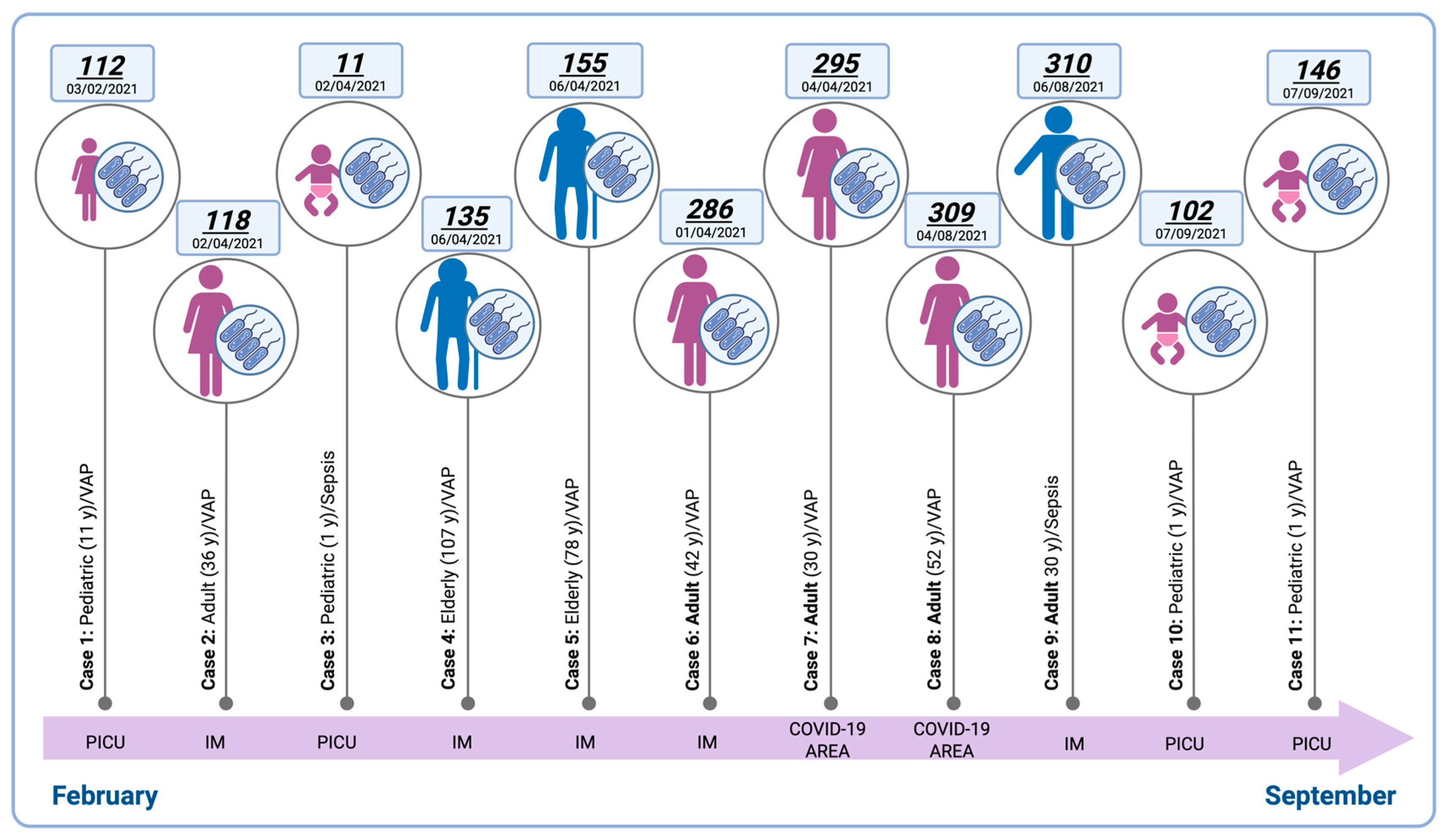
3.1. Epidemiological Distribution of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates
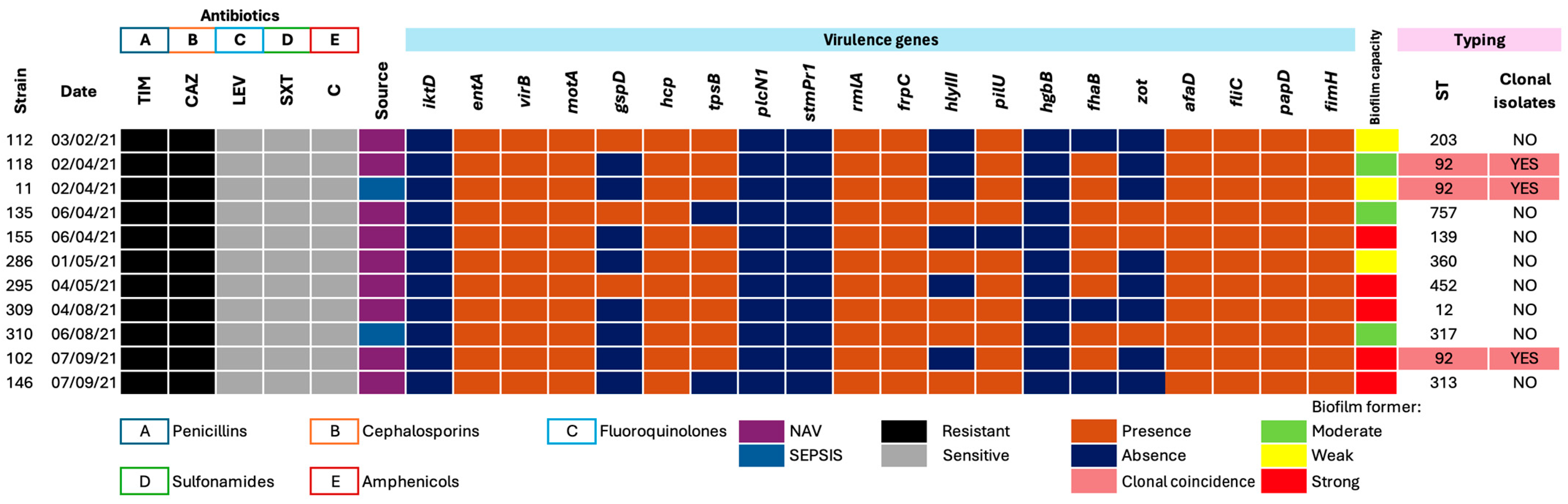
3.2. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles
3.3. Distribution of Virulence Genes
3.4. Clonal Typing and Relationships Among Isolates
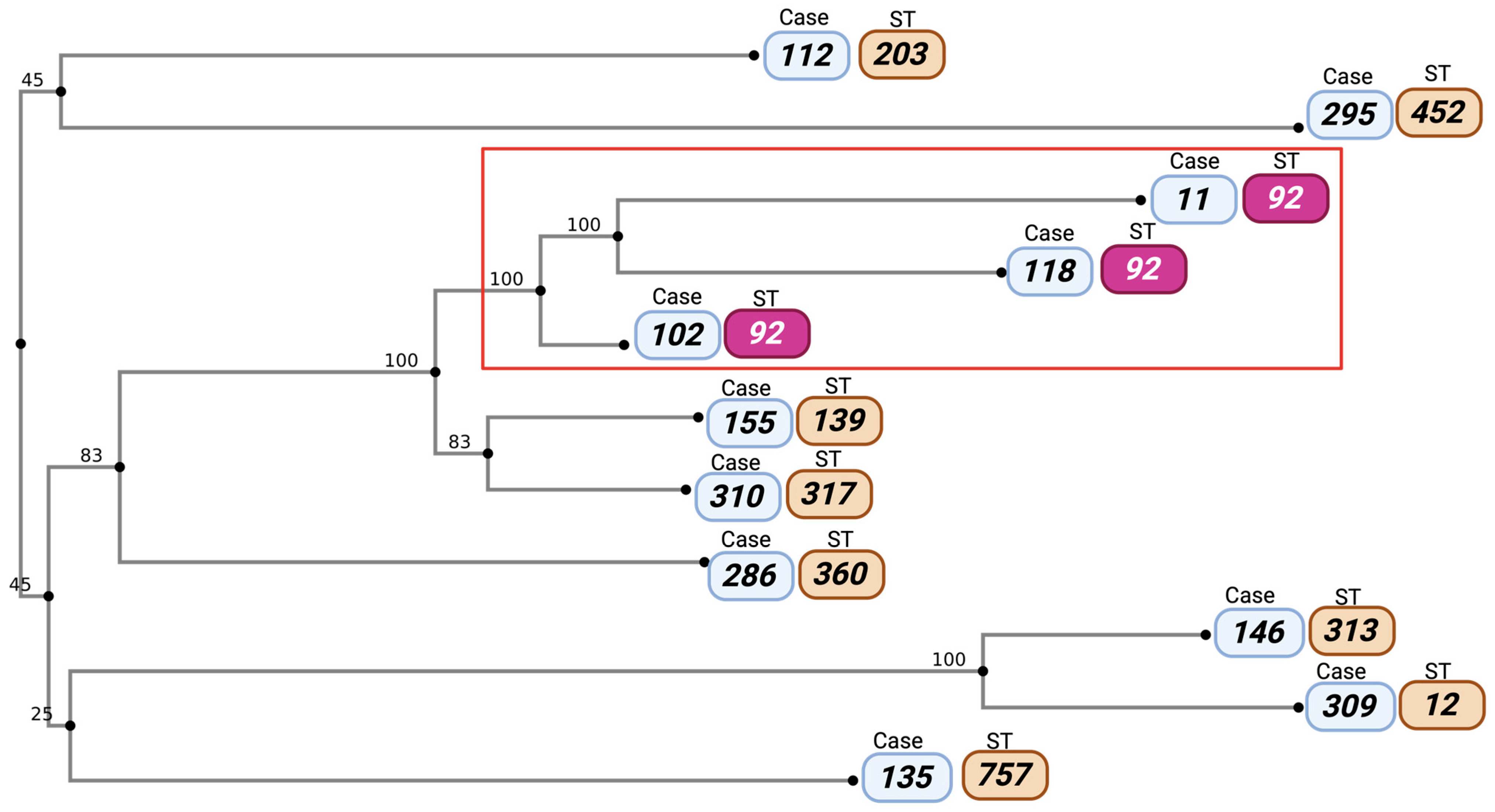
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denton, M.; Kerr, K.G. Microbiological and clinical aspects of infection associated with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jeong, S.J.; Ku, N.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Yeom, J.-S.; Song, Y.G. Risk factors for mortality in patients with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia and clinical impact of quinolone–resistant strains. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ji, S.; Cho, D.; Lee, A.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.E.; Park, K.H.; Jung, S.I.; Kim, U.J.; et al. Persistence of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in Patients with Bacteremia: Incidence, Clinical and Microbiologic Characters, and Outcomes. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Bartilotti Matos, F.; Gorgulho, A.; Gonçalves, C.; Figueiredo, C.; Coutinho, D.; Teixeira, T.; Pargana, M.; Abreu, G.; Malheiro, L. Determinants of Clinical Cure and Mortality in Patients with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections: A Retrospective Analysis. Cureus 2025, 17, e86294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezen, A.I.; Ozdemir, Y.E.; Yeşilbağ, Z.; Borcak, D.; Canbolat Ünlü, E.; Bayrak Erdem, F.; Çizmeci, Z.; Topcu, E.; Kart Yasar, K. Seven-year evaluation of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia in a university-affiliated hospital. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2025, 19, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J.S. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An emerging global opportunistic pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 2–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamek, M.; Linke, B.; Schwartz, T. Virulence genes in clinical and environmental Stenotrophomas maltophilia isolates: A genome sequencing and gene expression approach. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 67–68, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuMont, A.L.; Cianciotto, N.P. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Serine Protease StmPr1 Induces Matrilysis, Anoikis, and Protease-Activated Receptor 2 Activation in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00544-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo-Delgado, J.E.; Gómez-Mateos, J.M. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, un patógeno nosocomial de importancia creciente Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, an increasingly important nosocomial pathogen. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clín. 2006, 24, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, T.A.; Aldawood, E.; Albloshi, A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Mubaraki, M.A.; Alyami, A.S.; Aldriwesh, M.G. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Epidemiology, Resistance Characteristics, and Clinical Outcomes: Understanding of the Recent Three Years’ Trends. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-Franco, V.; Lacayo-Pallais, M.I. Neumonía por Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Acta Médica Costarric. 2012, 56, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, I.B.; Simões, L.C.; Simões, M. The effects of emerging environmental contaminants on Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolated from drinking water in planktonic and sessile states. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J.S. Advances in the Microbiology of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0003019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, S.; Ji, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Lu, Z.; You, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zha, L. Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in China, 2014–2021. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2025, 14, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojica, M.F.; Humphries, R.; Lipuma, J.J.; Mathers, A.J.; Rao, G.G.; Shelburne, S.A.; Fouts, D.E.; Van Duin, D.; Bonomo, R.A. Clinical challenges treating Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections: An update. JAC-Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 4, dlac040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.L.; Dersch-Mills, D.; Clark, D. Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole for Treatment of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Pneumonia in a Neonate. Can. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2013, 66, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Treviño, S.; Bocanegra-Ibarias, P.; Camacho-Ortiz, A.; Morfín-Otero, R.; Salazar-Sesatty, H.A.; Garza-González, E. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia biofilm: Its role in infectious diseases. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2019, 17, 877–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Córdova, A.; Mancilla-Rojano, J.; Luna-Pineda, V.M.; Escalona-Venegas, G.; Cázares-Domínguez, V.; Ormsby, C.; Franco-Hernández, I.; Zavala-Vega, S.; Hernández, M.A.; Medina-Pelcastre, M.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Traits of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains Associated with an Outbreak in a Mexican Tertiary Care Hospital. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adefila, W.O.; Osie, I.; Keita, M.L.; Wutor, B.M.; Yusuf, A.O.; Hossain, I.; Molfa, M.; Barjo, O.; Salaudeen, R.; Mackenzie, G. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia neonatal sepsis: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2024, 18, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyükcam, A.; Bıçakcigil, A.; Cengiz, A.B.; Sancak, B.; Ceyhan, M.; Kara, A. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia in children—A 10-year analysis. Bacteriemia por Stenotrophomonas maltophilia en niños: Análisis de 10 años. Arch. Argent. Pediatría 2020, 118, e317–e323. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaumik, R.; Aungkur, N.Z.; Anderson, G.G. A guide to Stenotrophomonas maltophilia virulence capabilities, as we currently understand them. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 11, 131322853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailovich, V.; Heydarov, R.; Zimenkov, D.; Chebotar, I. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia virulence: A current view. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1385631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.Z.; Poole, K. SmeDEF multidrug efflux pump contributes to intrinsic multidrug resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3497–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekan, M.; Tabaraie, B.; Akhoundtabar, L.; Afrough, P.; Behrouzi, A. Distribution of Class I Integron and smqnr Resistance Gene Among Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolated from Clinical Samples in Iran. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2017, 9, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, P.; Corona, F.; Martínez, J.L. Involvement of the RND efflux pump transporter SmeH in the acquisition of resistance to ceftazidime in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrasa, H.; Morán, M.A.; Fernández-Ciriza, L.; Isla, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Canut-Blasco, A.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A. Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections in Critically Ill Patients: A Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Approach. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woh, P.Y.; Zhang, X. The burden of ESKAPE pathogen-related hospital-acquired infections: Clinical and financial perspective from a systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2025, 162, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, C.V.; Varga, C.; Gheorghe-Barbu, C.; Pope, C.D.; Kovács, Á.T. The type VI secretion system of the emerging pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia complex has antibacterial properties. mSphere 2023, 8, e00584-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgarm Shams-Abadi, A.; Ramazanzadeh, R.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A.; Paterson, D.L.; Arash, R.; Asadi Farsani, E.; Taji, A.; Heidari, H.; Shahini Shams Abadi, M. The prevalence of colistin resistance in clinical Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Brodie, E.L.; Moberg, J.P.; Zubieta, I.X.; Piceno, Y.M.; Andersen, G.L. High-density universal 16S rRNA microarray analysis reveals broader diversity than typical clone library when sampling the environment. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 53, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory standard institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024; ISBN 978-1-68440-105-5. [Google Scholar]
- ATCC 25923; Complete Genome Sequence of the Quality Control Strain Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus. ATCC: Manassas, VA, USA, 2014.
- ATCC 25922; Complete Genome Assembly of Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, a Serotype O6 Reference Strain. ATCC: Manassas, VA, USA, 2014.
- ATCC 27,853; Draft Genome Sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain. ATCC: Manassas, VA, USA, 2012.
- Qi, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Liang, B.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Du, X.; Liu, X.; Qiu, S.; Song, H. Relationship between Antibiotic Resistance, Biofilm Formation, and Biofilm-Specific Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, S.; Biehler, K.; Jonas, D.A. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia multilocus sequence typing scheme for inferring population structure. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2934–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.Y.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Lei, H.P.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, D. Using PhyloSuite for molecular phylogeny and tree-based analyses. iMeta 2023, 2, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Treviño, S.; Gutiérrez-Ferman, J.L.; Morfín-Otero, R.; Rodríguez-Noriega, E.; Estrada-Rivadeneyra, D.; Rivas-Morales, C.; Llaca-Díaz, J.M.; Camacho-Ortíz, A.; Mendoza-Olazarán, S.; Garza-González, E. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in Mexico: Antimicrobial resistance, biofilm formation and clonal diversity. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Girón, J.A.; Yañez, J.A.; Cedillo, M.L. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Its Ability to Form Biofilms. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Plascencia-Nieto, E.S.; Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Nolasco-Rojas, A.E.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Gómez-Zamora, E.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, M.C.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, Y.d.J.; et al. Gram-Negative ESKAPE Bacteria Surveillance in COVID-19 Pandemic Exposes High-Risk Sequence Types of Acinetobacter baumannii MDR in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Pathogens 2024, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Márquez-Valdelamar, L.M.; Bravata-Alcántara, J.C.; Cortés-Ortíz, I.A.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Fernández-Sánchez, V.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; et al. ESKAPE bacteria characterization reveals the presence of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa outbreaks in COVID-19/VAP patients. Am. J. Control 2023, 51, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Bravata-Alcantará, J.C.; Sosa-Hernández, O.; Delgado-Balbuena, L.; León-García, G.; Cortés-Ortíz, I.A.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; et al. Clonal dispersion of Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit designed to patients COVID-19. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Ortíz, I.A.; Juárez-Gómez, J.C.; Cu-Quijano, C.; Flores-Paz, R.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Gutiérrez-Muñoz, V.H.; Sosa-Hernández, O.; Escobar-Escamilla, N.; Bravata-Alcántara, J.C.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae blaNDM-1 carrying a class 1 integron causing a hospital outbreak in a Mexican attention center. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Gaytán-Cervantes, J.; González-Torres, C.; Quiroga-Vargas, E.; Calzada-Mendoza, C.C.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Fernández-Sánchez, V.; et al. Massive sequencing of the V3-V4 hypervariable region of bronchoalveolar lavage from patients with COVID-19 and VAP reveals the collapse of the pulmonary microbiota. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 001634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Nowroozi, J.; Abiri, R.; Mohajeri, P. Multilocus Sequence Typing for Molecular Epidemiology of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Clinical and Environmental Isolates from a Tertiary Hospital in West of Iran. Iran. Biomed. J. 2022, 26, 142–152. [Google Scholar]
- Bostanghadiri, N.; Ghalavand, Z.; Fallah, F.; Yadegar, A.; Ardebili, A.; Tarashi, S.; Pournajaf, A.; Mardaneh, J.; Shams, S.; Hashemi, A. Characterization of Phenotypic and Genotypic Diversity of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains Isolated from Selected Hospitals in Iran. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, A.; Pompilio, A.; Bettua, C.; Crocetta, V.; Giacobazzi, E.; Fiscarelli, E.; Jousson, O.; Di Bonaventura, G. Evolution of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in Cystic Fibrosis Lung over Chronic Infection: A Genomic and Phenotypic Population Study. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zając, O.M.; Tyski, S.; Laudy, A.E. Phenotypic and Molecular Characteristics of the MDR Efflux Pump Gene-Carrying Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Strains Isolated in Warsaw, Poland. Biology 2022, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizi, K.S.; Jamehdar, S.A.; Sasan, M.S.; Ghazvini, K.; Aryan, E.; Safdari, H.; Farsiani, H. Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and carbapenemases in clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in the northeast of Iran. Gene Rep. 2024, 34, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, J.; Wong, D.W. Antimicrobial Treatment Strategies for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A Focus on Novel Therapies. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaba, S.M.; White, R.C.; Cianciotto, N.P. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia encodes a type II protein secretion system that promotes detrimental effects on lung epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3210–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalidasan, V.; Joseph, N.; Kumar, S.; Awang Hamat, R.; Neela, V.K. Iron and Virulence in Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia: All We Know So Far. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamet, A.; Nassif, X. New players in the toxin field: Polymorphic toxin systems in bacteria. mBio 2015, 6, e00285-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nas, M.Y.; White, R.C.; DuMont, A.L.; Lopez, A.E.; Cianciotto, N.P. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Encodes a VirB/VirD4 Type IV Secretion System That Modulates Apoptosis in Human Cells and Promotes Competition against Heterologous Bacteria, Including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00457-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompilio, A.; Ranalli, M.; Piccirilli, A.; Perilli, M.; Vukovic, D.; Savic, B.; Krutova, M.; Drevinek, P.; Jonas, D.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; et al. Biofilm Formation among Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates Has Clinical Relevance: The ANSELM Prospective Multicenter Study. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkő, R.; Gajdács, M.; Matuz, M.; Bodó, G.; Lázár, A.; Hajdú, E.; Papfalvi, E.; Hannauer, P.; Erdélyi, P.; Pető, Z. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance of ESKAPE Pathogens Isolated in the Emergency Department of a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital in Hungary: A 5-Year Retrospective Survey. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolas-Sayago, L.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; Ortíz-López, M.G.; Jiménez-Zamarripa, C.A.; Rojas-Bernabé, A.; Nieto-Velázquez, N.G.; Tolentino-Sánchez, E.; Bravata-Alcántara, J.C.; et al. Genetic Diversity of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Clonal Transmission (ST92) in Critical Care Units at Hospital Juárez de México: MLST and Virulence Profiling. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111125
Nicolas-Sayago L, Cruz-Cruz C, Durán-Manuel EM, Castro-Escarpulli G, Ortíz-López MG, Jiménez-Zamarripa CA, Rojas-Bernabé A, Nieto-Velázquez NG, Tolentino-Sánchez E, Bravata-Alcántara JC, et al. Genetic Diversity of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Clonal Transmission (ST92) in Critical Care Units at Hospital Juárez de México: MLST and Virulence Profiling. Pathogens. 2025; 14(11):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111125
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolas-Sayago, Liliana, Clemente Cruz-Cruz, Emilio M. Durán-Manuel, Graciela Castro-Escarpulli, María G. Ortíz-López, Carlos A. Jiménez-Zamarripa, Araceli Rojas-Bernabé, Nayeli G. Nieto-Velázquez, Eduardo Tolentino-Sánchez, Juan C. Bravata-Alcántara, and et al. 2025. "Genetic Diversity of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Clonal Transmission (ST92) in Critical Care Units at Hospital Juárez de México: MLST and Virulence Profiling" Pathogens 14, no. 11: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111125
APA StyleNicolas-Sayago, L., Cruz-Cruz, C., Durán-Manuel, E. M., Castro-Escarpulli, G., Ortíz-López, M. G., Jiménez-Zamarripa, C. A., Rojas-Bernabé, A., Nieto-Velázquez, N. G., Tolentino-Sánchez, E., Bravata-Alcántara, J. C., Castañeda-Ortega, J. C., Hernández-Castellanos, B., López-Ornelas, A., Márquez-Valdelamar, L. M., Razo Blanco-Hernández, D. M., Puente-Rivera, J., Calzada-Mendoza, C. C., Tamayo-Ordóñez, Y. d. J., Tamayo-Ordóñez, M. C., ... Bello-López, J. M. (2025). Genetic Diversity of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Clonal Transmission (ST92) in Critical Care Units at Hospital Juárez de México: MLST and Virulence Profiling. Pathogens, 14(11), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14111125












