Antifungal Activity of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives Against Candida auris, Candida haemulonii, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Cryptococcus gattii Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds
2.2. Strains and Growth Conditions
2.3. Analysis of Antifungal Activity
2.4. Inhibition of Biofilm Formation by 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives
2.5. Evaluation of Cryptococcal Main Virulence Factors
2.6. Analysis of Synergistic Effects
2.7. Confocal Microscopy
2.8. Toxicity
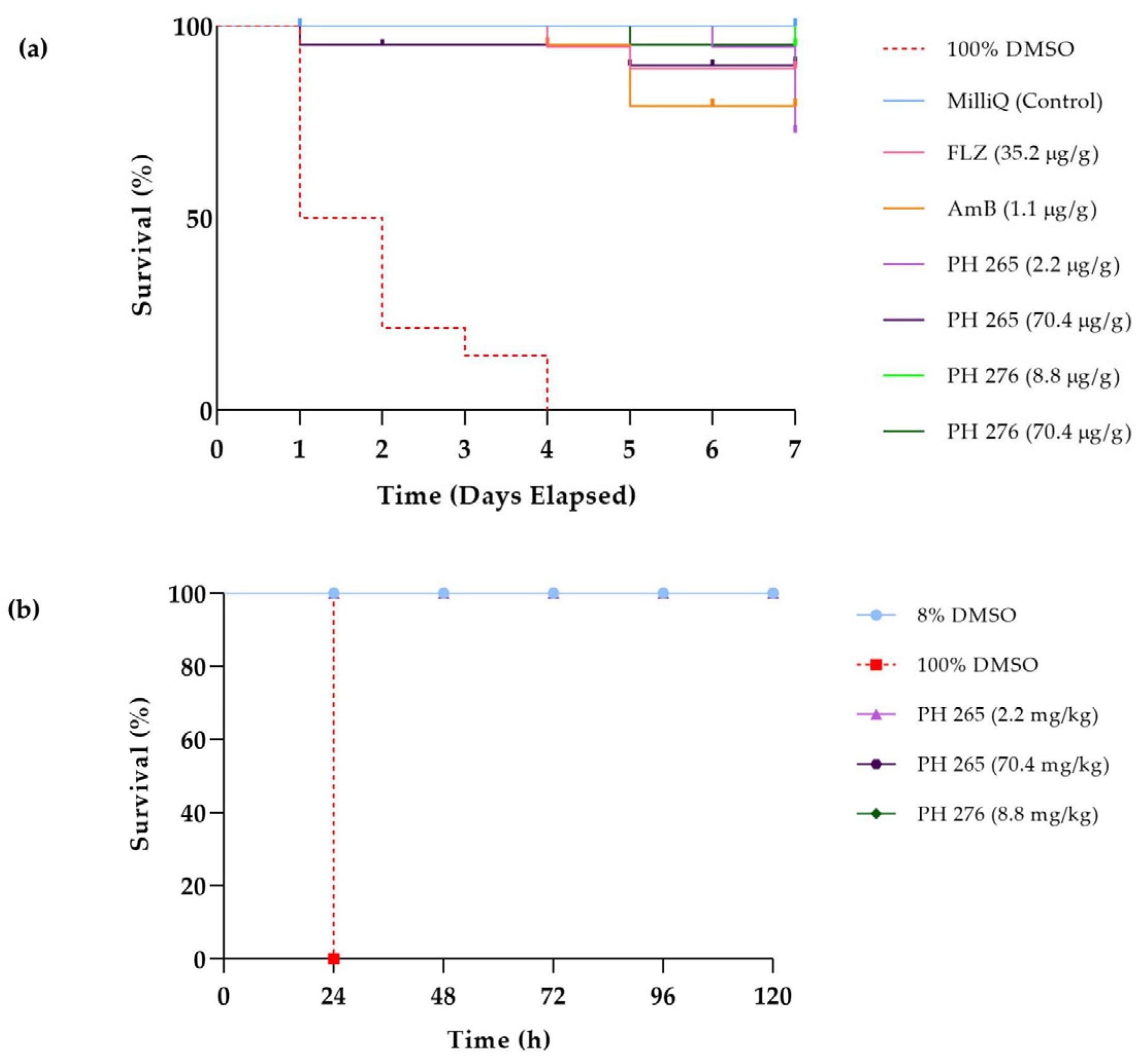
2.8.1. Toxicity in Tenebrio molitor
2.8.2. Toxicity in Galleria mellonella Larvae
2.8.3. Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity and Synergistic Potential of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives
3.2. PH265 and PH276 Modulate Capsule Formation in Cryptococcus spp.
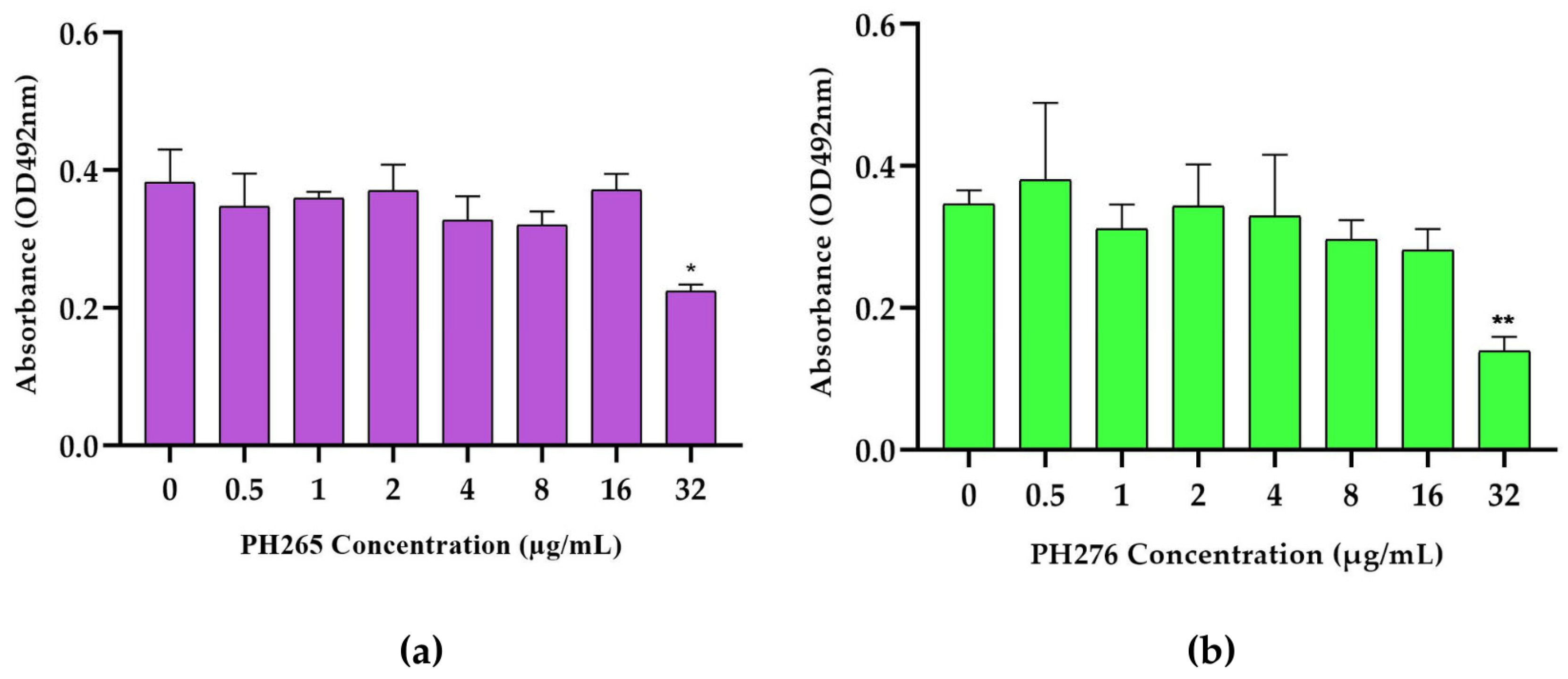
3.3. PH265 and PH276 Reduce Cryptococcus Biofilm Formation at High Concentrations
3.4. The Compounds PH265 and PH276 Demonstrated No Significant Toxicity Across All Tested Invertebrate Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 8HQ | 8-hydroxyquinoline |
| MIC | Minimal Inhibitory Concentration |
| MFC | Minimal Fungicidal Concentration |
References
- Denning, D.W.; Bromley, M.J. Infectious Disease. How to Bolster the Antifungal Pipeline. Science 2015, 347, 1414–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.L.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Fungal Diseases as Neglected Pathogens: A Wake-up Call to Public Health Officials. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ademe, M.; Girma, F. Candida auris: From Multidrug Resistance to Pan-Resistant Strains. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, A.; Voss, A.; Meis, J.F. Multidrug-Resistant Candida auris: “new Kid on the Block” in Hospital-Associated Infections? J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 94, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Bing, J.; Hu, T.; Ennis, C.L.; Nobile, C.J.; Huang, G. Candida auris: Epidemiology, Biology, Antifungal Resistance, and Virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Singh, P.; Wang, Y.; Yadav, A.; Pawar, K.; Singh, A.; Padmavati, G.; Xu, J.; Chowdhary, A. Environmental Isolation of Candida auris from the Coastal Wetlands of Andaman Islands, India. mBio 2021, 12, e03181-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongomin, F.; Oladele, R.O.; Gago, S.; Moore, C.B.; Richardson, M.D. A Systematic Review of Fluconazole Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Cryptococcus Species. Mycoses 2018, 61, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naicker, S.D.; Mpembe, R.S.; Maphanga, T.G.; Zulu, T.G.; Desanto, D.; Wadula, J.; Mvelase, N.; Maluleka, C.; Reddy, K.; Dawood, H.; et al. Decreasing Fluconazole Susceptibility of Clinical South African Cryptococcus neoformans Isolates over a Decade. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasingham, R.; Smith, R.M.; Park, B.J.; Jarvis, J.N.; Govender, N.P.; Chiller, T.M.; Denning, D.W.; Loyse, A.; Boulware, D.R. Global Burden of Disease of HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis: An Updated Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.R.; Casadevall, A. Biofilm Formation by Cryptococcus neoformans. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysan, D.J. Toward Improved Anti-Cryptococcal Drugs: Novel Molecules and Repurposed Drugs. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 78, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.L. Funding and Innovation in Diseases of Neglected Populations: The Paradox of Cryptococcal Meningitis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, D.J.; Dedicoat, M.J.; Lalloo, D.G. Treatment of Cryptococcal Meningitis in Resource Limited Settings. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 22, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkow, E.L.; Lockhart, S.R. Fluconazole Resistance in Candida Species: A Current Perspective. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 10, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpoza, E.; Rhein, J.; Abassi, M. Emerging Fluconazole Resistance: Implications for the Management of Cryptococcal Meningitis. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2018, 19, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, H.C.; Castelli, R.F.; Alves, L.R.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Salama, E.A.; Seleem, M.; Rodrigues, M.L. Identification of Four Compounds from the Pharmakon Library with Antifungal Activity against Candida auris and Species of Cryptococcus. Med. Mycol. 2022, 60, myac033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W. Echinocandin Antifungal Drugs. Lancet 2003, 362, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-On, W.; Huyen, N.T.B.; Songtawee, N.; Suwanjang, W.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Quinoline-Based Clioquinol and Nitroxoline Exhibit Anticancer Activity Inducing FoxM1 Inhibition in Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2033–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazovic, J.; Guo, L.; Nakashima, J.; Mirsadraei, L.; Yong, W.; Kim, H.J.; Ellingson, B.; Wu, H.; Pope, W.B. Nitroxoline Induces Apoptosis and Slows Glioma Growth in Vivo. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naber, K.G.; Niggemann, H.; Stein, G.; Stein, G. Review of the Literature and Individual Patients’ Data Meta-Analysis on Efficacy and Tolerance of Nitroxoline in the Treatment of Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. 8-Hydroxyquinolines: A Review of Their Metal Chelating Properties and Medicinal Applications. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdtrakulkiat, R.; Boonpangrak, S.; Sinthupoom, N.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Derivatives (Halogen, Nitro and Amino) of 8-Hydroxyquinoline with Highly Potent Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 6, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippi, B.; Loreto, E.S.; Merkel, S.; Joaquim, A.R.; Krummenauer, M.E.; Reginatto, P.; Vainstein, M.H.; Andrade, S.F.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Santurio, J.M.; et al. Pythium insidiosum: Insights into Biofilm Formation and Antibiofilm Activity of Antifungal Drugs. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2603–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, A.R.; Boff, R.T.; Adam, F.C.; Lima-Morales, D.; Cesare, M.A.; Kaminski, T.F.; Teixeira, M.L.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Andrade, S.F.; Martins, A.F. Antibacterial and Synergistic Activity of a New 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivative against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippi, B.; Zanette, R.A.; Joaquim, A.R.; Krummenauer, M.E.; Merkel, S.; Reginatto, P.; Vainstein, M.H.; Andrade, S.F.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Tondolo, J.S.M.; et al. Clioquinol and 8-Hydroxyquinoline-5-Sulfonamide Derivatives Damage the Cell Wall of Pythium insidiosum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, D.; Crater, A.K.; Lee, H.; Solomon, V.R.; Ananvoranich, S. The Potential of Quinoline Derivatives for the Treatment of Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 145, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, N.M.; Gentz, C. de B.; Reginatto, P.; Fernandes, T.H.M.; Kaminski, T.F.A.; Lopes, W.; Quatrin, P.M.; Vainstein, M.H.; Abegg, M.A.; Lopes, M.S.; et al. 8-Hydroxyquinoline 1,2,3-Triazole Derivatives with Promising and Selective Antifungal Activity. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentz, C.d.B.; Lopes, M.S.; Quatrin, P.M.; Gionbelli, M.P.; de Cesare, M.A.; Perin, A.P.; Lopes, W.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Vainstein, M.H.; Andrade, S.F.d. A Potent Fluorescent Derivative of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Suggests Cell Wall Damage as a Possible Cellular Action of the 5-Triazole 8-Hydroxyquinoline Class. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, S. The Genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta-de-la-Riva, M.; Fontrodona, L.; Villanueva, A.; Cerón, J. Basic Caenorhabditis elegans Methods: Synchronization and Observation. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 10, e4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.R.; Ntiamoah, P.; Gácser, A.; Casadevall, A.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Voriconazole Inhibits Melanization in Cryptococcus neoformans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4396–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, F.C.G.; Borges, B.S.; Jozefowicz, L.J.; Sena, B.A.G.; Garcia, A.W.A.; Medeiros, L.C.; Martins, S.T.; Honorato, L.; Schrank, A.; Vainstein, M.H.; et al. A Novel Protocol for the Isolation of Fungal Extracellular Vesicles Reveals the Participation of a Putative Scramblase in Polysaccharide Export and Capsule Construction in Cryptococcus gattii. mSphere 2019, 4, e00080-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Wickes, B.L.; Booth, J.L.; Vishniac, H.S.; Bennett, J.E. Urease Inhibition by EDTA in the Two Varieties of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 1751–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-W.; Campbell, L.T.; Wilkins, M.R.; Pang, C.N.I.; Chen, S.; Carter, D.A. Synergy and Antagonism between Iron Chelators and Antifungal Drugs in Cryptococcus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffe, L.S.; Schneider, R.; Lopes, W.; Azevedo, R.; Staats, C.C.; Kmetzsch, L.; Schrank, A.; Del Poeta, M.; Vainstein, M.H.; Rodrigues, M.L. The Anti-Helminthic Compound Mebendazole Has Multiple Antifungal Effects against Cryptococcus neoformans. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, N.S.; Dos Santos, F.M.; Garcia, A.W.A.; Ferrareze, P.A.G.; Fabres, L.F.; Schrank, A.; Kmetzsch, L.; Rott, M.B.; Vainstein, M.H.; Staats, C.C. Modulation of Zinc Homeostasis in Acanthamoeba castellanii as a Possible Antifungal Strategy against Cryptococcus gattii. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.G.; de Curcio, J.S.; Silva-Bailão, M.G.; Lima, R.M.; Tomazett, M.V.; de Souza, A.F.; Cruz-Leite, V.R.M.; Sbaraini, N.; Bailão, A.M.; Rodrigues, F.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Siderophore Biosynthesis in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. IMA Fungus 2020, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Ramos, F.; Martins, D.M.; Nunes Sagini, J.P.; Quines, C.B.; de Oliveira Pereira, F.S.; de Ávila, D.S.; Zanzarin, D.; Pilau, E.J.; de Lima Postiga, I.A.; Tostes, J.; et al. Soybeans Agroindustrial Residues as Staphylococcus epidermidis and S. aureus Biofilm Inhibitors. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.P.; Tamagno, W.A.; Alves, C.; Mesacasa, L.; Santin, L.F.; Sutorillo, N.T.; Bilibio, D.; Müller, C.; Galon, L.; Kaizer, R.R. Neuroprotective Potential of Cannabis sativa-Based Oils in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limited Availability of Generic Antifungals Across the World. Available online: https://gaffi.org/limited-availability-of-generic-antifungals-across-the-world/41 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Deray, G. Amphotericin B Nephrotoxicity. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 49 (Suppl. 1), 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, J.F.; Chowdhary, A. Candida auris-“Ten Years After”. J. Fungi 2019, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, A.R.; Pippi, B.; de Cesare, M.A.; Rocha, D.A.; Boff, R.T.; Staudt, K.J.; Ruaro, T.C.; Zimmer, A.R.; de Araújo, B.V.; Silveira, G.P.; et al. Rapid Tools to Gain Insights into the Interaction Dynamics of New 8-Hydroxyquinolines with Few Fungal Lines. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 93, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ballesta, M.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á.; García-Viguera, C.; Domínguez-Perles, R. Nanoparticles and Controlled Delivery for Bioactive Compounds: Outlining Challenges for New “Smart-Foods” for Health. Foods 2018, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosanchuk, J.D.; Ovalle, R.; Casadevall, A. Glyphosate Inhibits Melanization of Cryptococcus neoformans and Prolongs Survival of Mice after Systemic Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
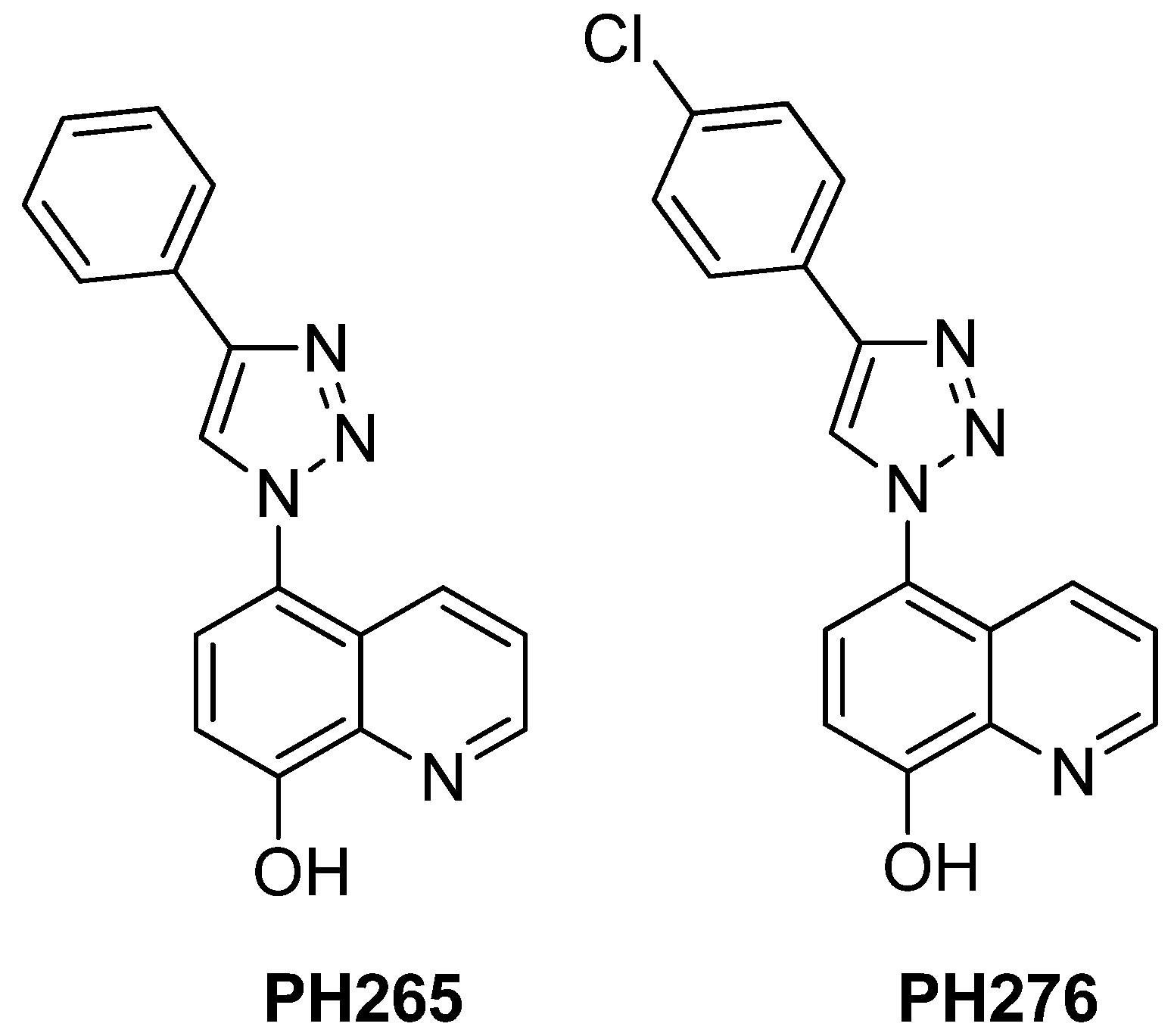


| PH265 | PH276 | Amphotericin B * | Fluconazole | Caspofungin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate | µM | µg/mL | µM | µg/mL | µM | µg/mL | µM | µg/mL | µM | µg/mL | |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | H99 | 3 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 208.9 | 8 | - | - |
| Cryptococcus deneoformans | B3501 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 12.38 | 4 | 0.135 | 0.125 | 6.525 | 2 | - | - |
| Cryptococcus deuterogattii | R265 | 3 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 26.12 | 8 | - | - |
| Candida haemulonii | LipCh12 | 3 | 1 | 24.76 | 8 | 2.165 | 2 | 26.12 | 8 | 3.65 | 4 |
| Candida auris | Ca446 | 3 | 1 | 24.76 | 8 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 26.12 | 8 | 1.82 | 2 |
| PH265 | PH276 | Amphotericin B | Fluconazole | Caspofungin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate | µM | µg/mL | µM | µg/mL | µM | µg/mL | µM | µg/mL | µM | µg/mL | |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | H99 | 24.6 | 8 | 6.19 | 2 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 208.9 | 64 | - | - |
| Cryptococcus deneoformans | B3501 | >49.5 | >16 | 49.5 | 16 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 104.4 | 32 | - | - |
| Cryptococcus deuterogattii | R265 | >49.5 | >16 | 6.19 | 2 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 208.9 | >64 | - | - |
| Candida haemulonii | LipCh12 | >49.5 | >16 | >49.5 | >16 | 2.165 | 2 | 208.9 | >64 | 7.31 | 8 |
| Candida auris | Ca446 | >49.5 | >16 | >49.5 | >16 | 0.54 | 0.5 | 208.9 | >64 | >32 | >29.26 |
| Drug A | Drug B | Drug A | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | Molecule | MIC Alone (µg/mL) | MIC Combined (µg/mL) | MIC Alone (µg/mL) | MIC Combined (µg/mL) | FIC 1 | |
| C. neoformans H99 | PH265 | 8 | 1 | FLZ | 8 | 8 | 1.125 |
| PH265 | 1 | 1 | AmB | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | |
| PH276 | 0.5 | 0.0312 | FLZ | 8 | 8 | 1.06 | |
| PH276 | 0.5 | 0.5 | AmB | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | |
| C. auris Ca446 | PH265 | 1 | 0.125 | FLZ | 8 | 8 | 1.12 |
| PH265 | 1 | 1 | AmB | 0.5 | 0.06 | 1.12 | |
| PH265 | 1 | 1 | Caspo | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| PH276 | 8 | 0.5 | FLZ | 8 | 8 | 1 | |
| PH276 | 8 | 8 | AmB | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | |
| PH276 | 8 | 8 | Caspo | 1 | 0.5 | 1.5 | |
| C. haemulonii LipCh12 | PH265 | 1 | 1 | FLZ | 8 | 4 | 1.5 |
| PH265 | 1 | 1 | AmB | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| PH265 | 1 | 0.5 | Caspo | 4 | 0.5 | 0.75 | |
| PH276 | 8 | 1 | FLZ | 8 | 2 | 0.37 | |
| PH276 | 8 | 8 | AmB | 2 | 0.06 | 1 | |
| PH276 | 8 | 2 | Caspo | 4 | 1 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krummenauer, M.E.; Camargo, M.d.S.; Gentz, C.d.B.; Silva Lopes, M.; Feliciani da Luz, L.; Silva Trentin, D.d.; Ávila Rodrigues, B.; Rigon Zimmer, K.; Fernandes de Andrade, S.; Henning Vainstein, M. Antifungal Activity of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives Against Candida auris, Candida haemulonii, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Cryptococcus gattii Complex. Pathogens 2025, 14, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100999
Krummenauer ME, Camargo MdS, Gentz CdB, Silva Lopes M, Feliciani da Luz L, Silva Trentin Dd, Ávila Rodrigues B, Rigon Zimmer K, Fernandes de Andrade S, Henning Vainstein M. Antifungal Activity of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives Against Candida auris, Candida haemulonii, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Cryptococcus gattii Complex. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100999
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrummenauer, Maria Eduarda, Matheus da Silva Camargo, Caroline de Bem Gentz, Marcela Silva Lopes, Letícia Feliciani da Luz, Danielle da Silva Trentin, Belisa Ávila Rodrigues, Karine Rigon Zimmer, Saulo Fernandes de Andrade, and Marilene Henning Vainstein. 2025. "Antifungal Activity of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives Against Candida auris, Candida haemulonii, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Cryptococcus gattii Complex" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100999
APA StyleKrummenauer, M. E., Camargo, M. d. S., Gentz, C. d. B., Silva Lopes, M., Feliciani da Luz, L., Silva Trentin, D. d., Ávila Rodrigues, B., Rigon Zimmer, K., Fernandes de Andrade, S., & Henning Vainstein, M. (2025). Antifungal Activity of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives Against Candida auris, Candida haemulonii, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Cryptococcus gattii Complex. Pathogens, 14(10), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100999





