Circulation of RSV Subtypes A and B Among Mexican Children During the 2021–2022 and 2022–2023 Seasons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Case Definition, Inclusion, and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Multiplex RT-PCR for the Detection of Respiratory Viruses
2.5. Genotyping and Sequencing
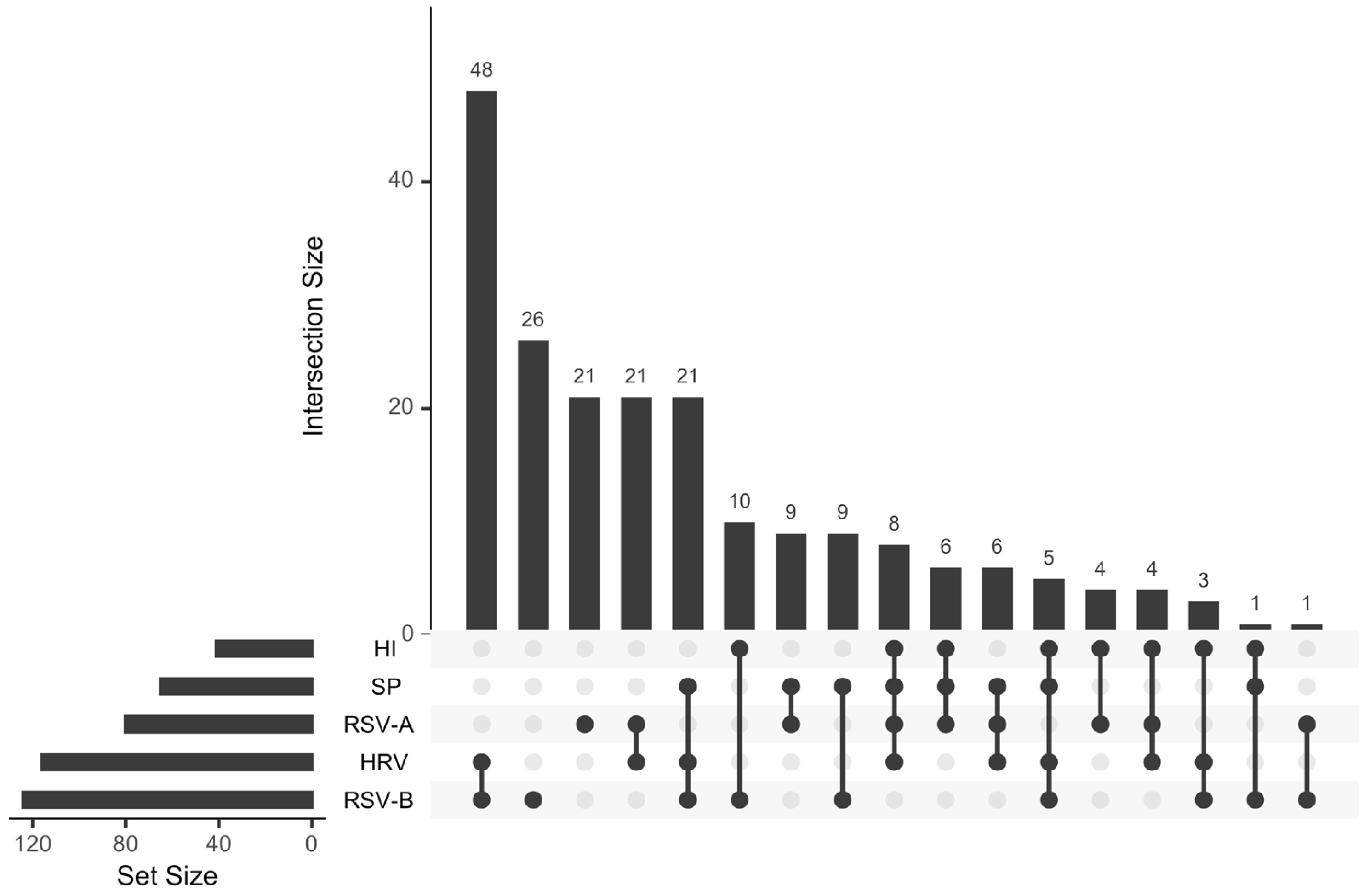
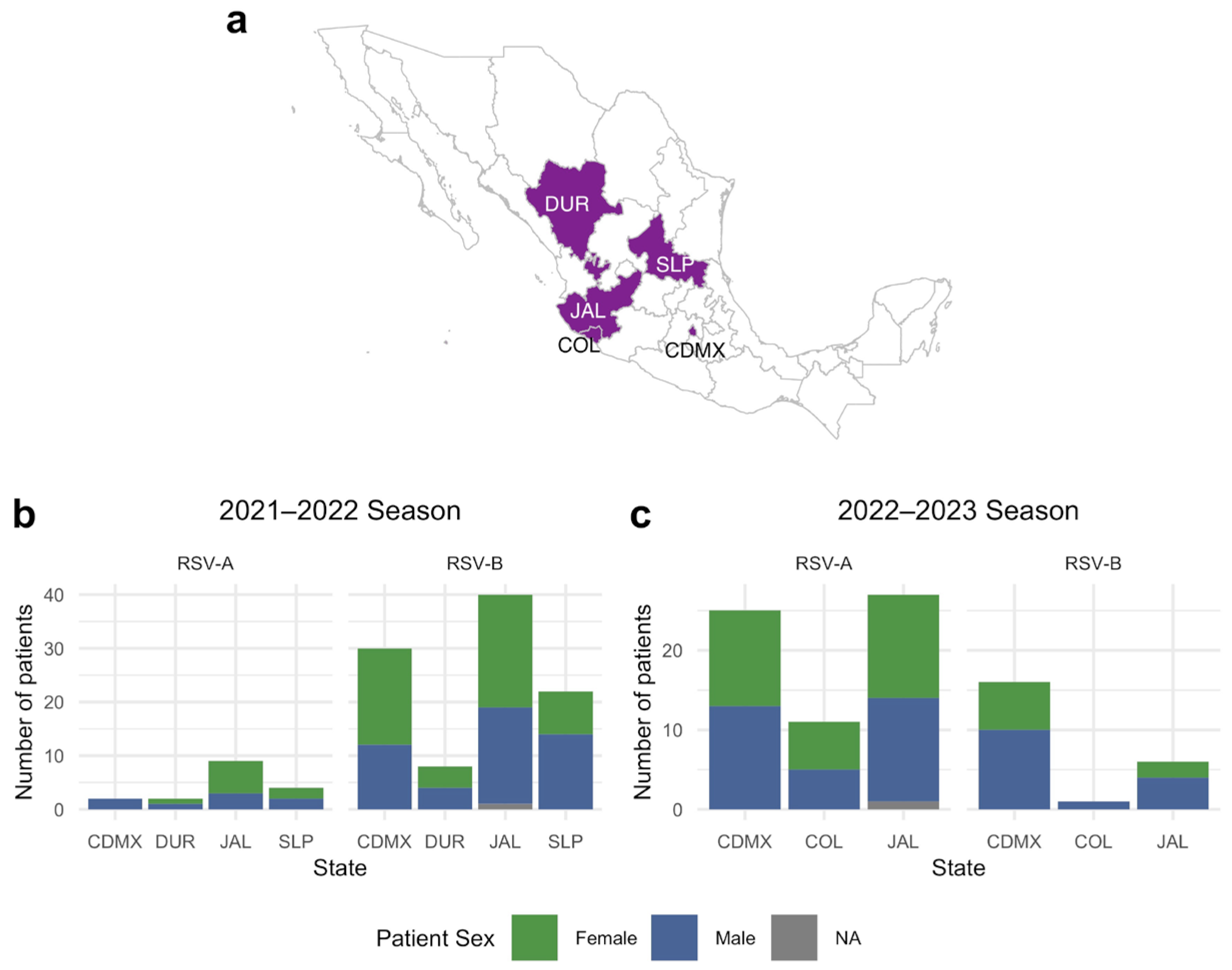
3. Results
3.1. Sample Data Analysis
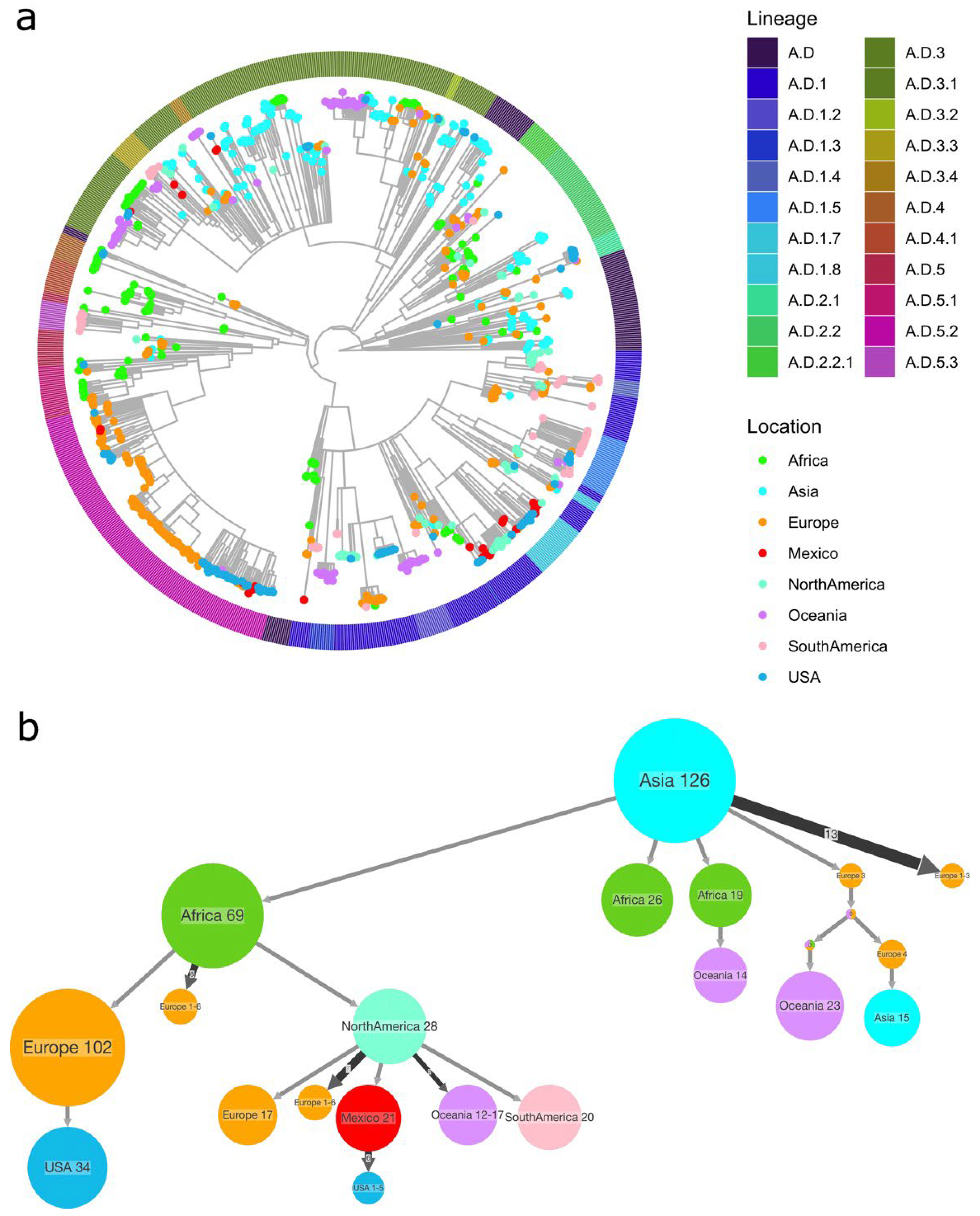
3.2. RSV Lineage Determination
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nuttens, C.; Moyersoen, J.; Curcio, D.; Aponte-Torres, Z.; Baay, M.; Vroling, H.; Gessner, B.D.; Begier, E. Differences Between RSV A and RSV B Subgroups and Implications for Pharmaceutical Preventive Measures. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2024, 13, 1725–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Reeves, R.M.; Wang, X.; Bassat, Q.; Brooks, W.A.; Cohen, C.; Moore, D.P.; Nunes, M.; Rath, B.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global Patterns in Monthly Activity of Influenza Virus, Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Parainfluenza Virus, and Metapneumovirus: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e1031–e1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard, M.N.; van de Ven, P.M.; Baraldi, B.; Kragten-Tabatabaie, L.; Bont, L.J.; Wildenbeest, J.G. International Changes in Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Epidemiology during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Association with School Closures. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2022, 16, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Guzman, E.; Simons, L.M.; Dean, T.J.; Agnes, F.; Pawlowski, A.; Alisoltanidehkordi, A.; Nam, H.H.; Ison, M.G.; Ozer, E.A.; Lorenzo-Redondo, R.; et al. Deviations in RSV epidemiological patterns and population structures in the United States following the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Commun. 2024, 15, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esparza-Miranda, L.A.; Juárez-Tobías, S.; Muñoz-Escalante, J.C.; Oliva-Jara, U.A.; Cadena-Mota, S.; Wong-Chew, R.M.; Noyola, D.E. Clinical and Epidemiologic Characteristics of Infants Hospitalized with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection During the 2022–2023 Season in Mexico. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, E382–E384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leija-Martínez, J.J.; Cadena-Mota, S.; González-Ortiz, A.M.; Muñoz-Escalante, J.C.; Mata-Moreno, G.; Hernández-Sánchez, P.G.; Vega-Morúa, M.; Noyola, D.E. Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Other Respiratory Viruses in Hospitalized Infants During the 2023–2024 Winter Season in Mexico. Viruses 2024, 16, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamiño-Arroyo, A.E.; Moreno-Espinosa, S.; Llamosas-Gallardo, B.; Ortiz-Hernández, A.A.; Guerrero, M.L.; Galindo-Fraga, A.; Galán-Herrera, J.F.; Prado-Galbarro, F.J.; Beigel, J.H.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; et al. Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections among Children and Adults in Mexico. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2017, 11, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcarra-Ugalde, S.; Rico-Hernández, M.; Monjarás-Ávila, C.; Bernal-Silva, S.; Garrocho-Rangel, M.E.; Ochoa-Pérez, U.R.; Noyola, D.E. Intensive Care Unit Admission and Death Rates of Infants Admitted with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Lower Respiratory Tract Infection in Mexico. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Guerra, D.; Piña-Flores, C.; Zamora-López, M.; Escalante-Padrón, F.; Lima-Rogel, V.; González-Ortiz, A.M.; Guevara-Tovar, M.; Bernal-Silva, S.; Benito-Cruz, B.; Castillo-Martínez, F.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Acute Respiratory Infection-Associated Hospitalizations in Preterm Mexican Infants: A Cohort Study. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2020, 14, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Auad, J.P.; Nava-Frías, M.; Casasola-Flores, J.; Johnson, K.M.; Nava-Ruiz, A.; Pérez-Robles, V.; Caniza, M.A. The Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children at a Public Pediatric Referral Hospital in Mexico. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, e508–e513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Hernández, J.X.; Núñez-López, M.; Comas-García, A.; Cherpitel, D.E.N.; Ocampo, M.C. Superinfection between Influenza and RSV Alternating Patterns in San Luis Potosí State, México. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyola, D.E.; Arteaga-Domínguez, G. Contribution of Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Influenza and Parainfluenza Viruses to Acute Respiratory Infections in San Luis Potosí, Mexico. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2005, 24, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Chew, R.M.; Noyola, D.E.; Solórzano-Santos, F.; Moreno-Espinosa, S.; Miranda-Novales, M.G.; Hein, E.O.; Galindo-Fraga, A.; Vilar-Compte, D.; Martinez-Aguilar, G.; Jiménez-Juárez, R.N.; et al. Mexican Interdisciplinary Consensus on the Diagnosis and Preventive Measures for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections. Arch. Med. Res. 2025, 56, 103183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Marrero, N.; Muñoz-Escalante, J.C.; Wong-Chew, R.M.; Torres-González, P.; García-León, M.L.; Bautista-Carbajal, P.; Martínez-Arce, P.A.; Espinosa-Sotero, M.d.C.; Tabla-Orozco, V.; Rojas-Larios, F.; et al. Genotypic Characterization of Human Respiratory Syncytial Viruses Detected in Mexico Between 2021 and 2024. Viruses 2025, 17, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Toledo, E.; Mejıa-Nepomuceno, F.; Mendoza-Ramırez, E.; Vera-Jimenez, A.; Becerril-Vargas, E.; Ahumada-Topete, V.H.; Castillejos-Lopez, M.; Perez-Orozco, F.B.; Benitez, G.; Salazar-Lezama, M.Á.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Mexico (Season 2023–2024) through Whole-Genome Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 27382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goya, S.; Ruis, C.; Neher, R.A.; Meijer, A.; Aziz, A.; Hinrichs, A.S.; von Gottberg, A.; Roemer, C.; Amoako, D.G.; Acuña, D.; et al. Standardized Phylogenetic Classification of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus below the Subgroup Level. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R Package for the Visualization of Intersecting Sets and Their Properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Use R! Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24275-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Gangavarapu, K.; Quick, J.; Matteson, N.L.; De Jesus, J.G.; Main, B.J.; Tan, A.L.; Paul, L.M.; Brackney, D.E.; Grewal, S.; et al. An Amplicon-Based Sequencing Framework for Accurately Measuring Intrahost Virus Diversity Using PrimalSeq and IVar. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbe, S.; Buckland-Merrett, G. Data, Disease and Diplomacy: GISAID’s Innovative Contribution to Global Health. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; McCauley, J. GISAID: Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data—From Vision to Reality. Euro Surveill. 2017, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-Hit: A Fast Program for Clustering and Comparing Large Sets of Protein or Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksamentov, I.; Roemer, C.; Hodcroft, E.B.; Neher, R.A. Nextclade: Clade Assignment, Mutation Calling and Quality Control for Viral Genomes. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, T.-H.; Jung, M.; Lycett, S.; Gascuel, O. Fast Dating Using Least-Squares Criteria and Algorithms. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.-Y. Ggtree: An r Package for Visualization and Annotation of Phylogenetic Trees with Their Covariates and Other Associated Data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.A.; Zhukova, A.; Iwasaki, W.; Gascuel, O.; Pupko, T. A Fast Likelihood Method to Reconstruct and Visualize Ancestral Scenarios. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2069–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelia, Y.; Procop, G.W.; Richter, S.S.; Worley, S.; Liu, W.; Esper, F. Dynamics and Predisposition of Respiratory Viral Co-Infections in Children and Adults. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 631.e1–631.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achten, N.B.; Wu, P.; Bont, L.; Blanken, M.O.; Gebretsadik, T.; Chappell, J.D.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Larkin, E.K.; Carroll, K.N.; et al. Interference between Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Human Rhinovirus Infection in Infancy. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickbakhsh, S.; Mair, C.; Matthews, L.; Reeve, R.; Johnson, P.C.D.; Thorburn, F.; Von Wissmann, B.; Reynolds, A.; McMenamin, J.; Gunson, R.N.; et al. Virus-Virus Interactions Impact the Population Dynamics of Influenza and the Common Cold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 27142–27150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, G.A.; Gálvez, N.M.S.; Soto, J.A.; Andrade, C.A.; Kalergis, A.M. Bacterial and Viral Coinfections with the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangeli, A.; Midulla, F.; Piralla, A.; Ferrari, G.; Nenna, R.; Pitrolo, A.M.G.; Licari, A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Abruzzese, D.; Pellegrinelli, L.; et al. Sequence Analysis of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Cases Reveals a Novel Subgroup -B Strain Circulating in North-Central Italy after Pandemic Restrictions. J. Clin. Virol. 2024, 173, 105681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nextstrain/Rsv/a/Genome/6y. Available online: https://nextstrain.org/rsv/a/genome/6y (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Nextstrain/Rsv/b/Genome/6y. Available online: https://nextstrain.org/rsv/b/genome/6y (accessed on 18 September 2025).


| Lineage | Season 2021–2022 | Season 2022–2023 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDMX | DUR | JAL | SLP | Total (%) | CDMX | COL | JAL | Total (%) | |
| RSV-A | |||||||||
| A.D.1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 6 | 1 | 7 (17.1) |
| A.D.1.8 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 (4.7) | 4 | 0 | 6 | 10 (24.4) |
| A.D.3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 (2.4) |
| A.D.3.3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A.D.5.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 7 (17.1) |
| RSV-B | |||||||||
| B.D.E.1 | 17 | 5 | 19 | 13 | 54 (84.4) | 12 | 1 | 3 | 16 (39.0) |
| B.D.4.1.1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 (1.6) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zárate, S.; Taboada, B.; Torres-Rivera, K.; Bautista-Carbajal, P.; Garcia-León, M.L.; Tabla-Orozco, V.; Juárez-Tobías, M.S.; Noyola, D.E.; Martínez-Arce, P.A.; Espinosa-Sotero, M.d.C.; et al. Circulation of RSV Subtypes A and B Among Mexican Children During the 2021–2022 and 2022–2023 Seasons. Pathogens 2025, 14, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100996
Zárate S, Taboada B, Torres-Rivera K, Bautista-Carbajal P, Garcia-León ML, Tabla-Orozco V, Juárez-Tobías MS, Noyola DE, Martínez-Arce PA, Espinosa-Sotero MdC, et al. Circulation of RSV Subtypes A and B Among Mexican Children During the 2021–2022 and 2022–2023 Seasons. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100996
Chicago/Turabian StyleZárate, Selene, Blanca Taboada, Karina Torres-Rivera, Patricia Bautista-Carbajal, Miguel Leonardo Garcia-León, Verónica Tabla-Orozco, María Susana Juárez-Tobías, Daniel E. Noyola, Pedro Antonio Martínez-Arce, Maria del Carmen Espinosa-Sotero, and et al. 2025. "Circulation of RSV Subtypes A and B Among Mexican Children During the 2021–2022 and 2022–2023 Seasons" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100996
APA StyleZárate, S., Taboada, B., Torres-Rivera, K., Bautista-Carbajal, P., Garcia-León, M. L., Tabla-Orozco, V., Juárez-Tobías, M. S., Noyola, D. E., Martínez-Arce, P. A., Espinosa-Sotero, M. d. C., Martínez-Aguilar, G., Rojas-Larios, F., Sanchez-Flores, A., Arias, C. F., & Wong-Chew, R. M. (2025). Circulation of RSV Subtypes A and B Among Mexican Children During the 2021–2022 and 2022–2023 Seasons. Pathogens, 14(10), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100996






