Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Drug-Resistant Salmonella Typhi in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sampling
2.2. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Analysis
2.3. Whole Genomic Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Patient Demographic and Clinical Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Hematological and Biochemical Parameters of the Infected Patients
3.3. Clinical Biomarkers and Age
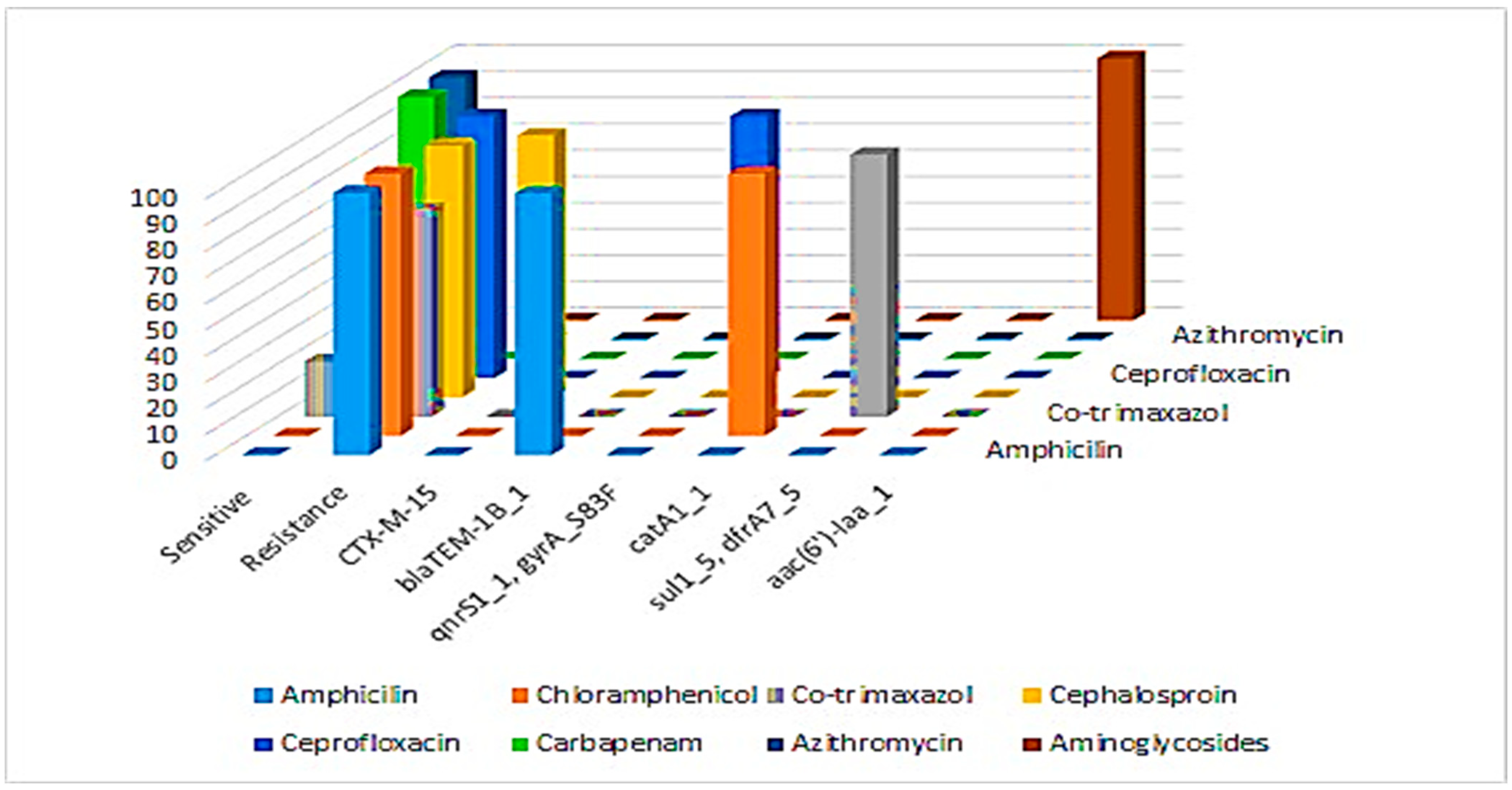
3.4. Phenotypic Antibiotic Susceptibility Profiles of S. typhi Isolates
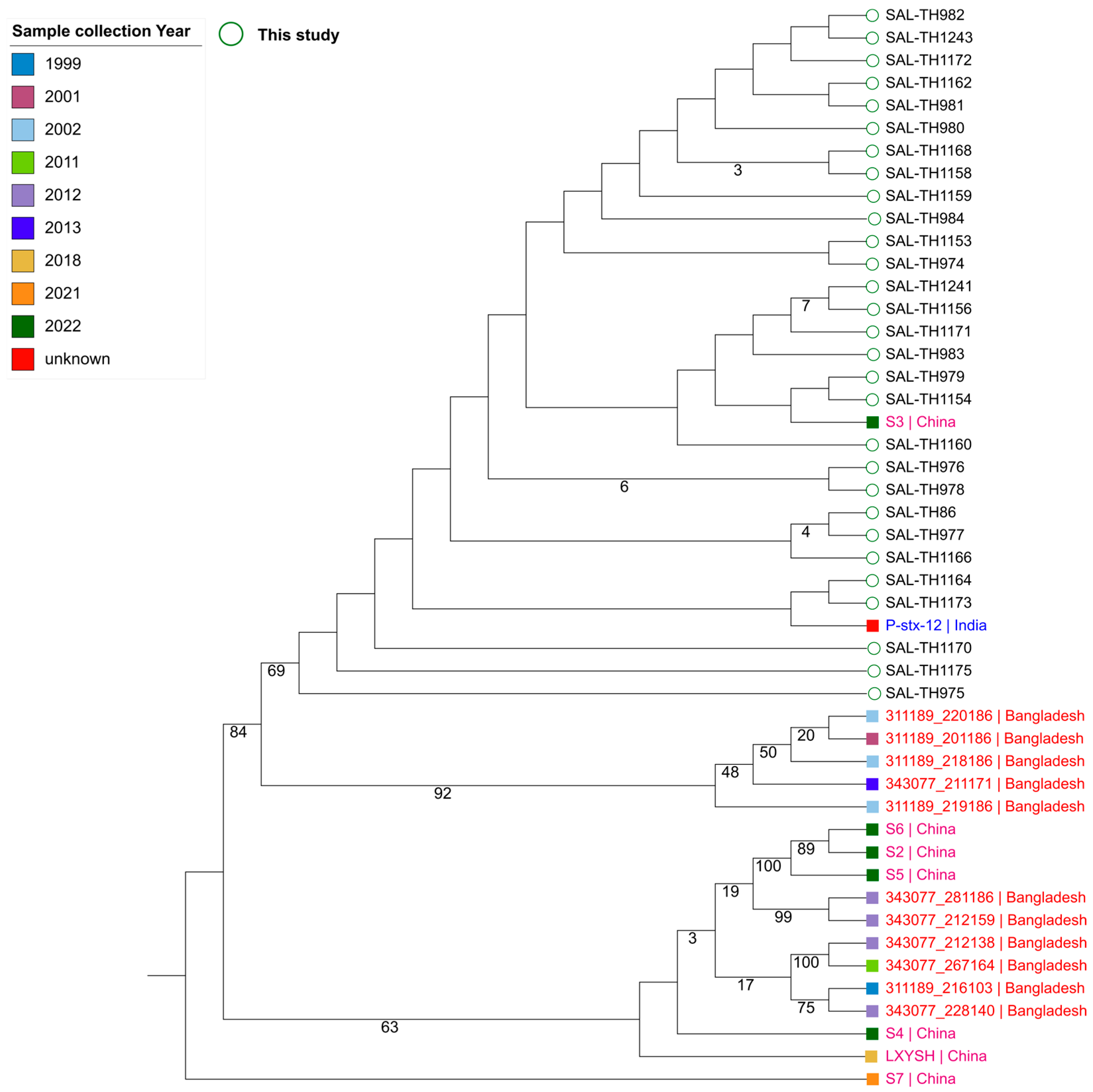
3.5. Analysis of Sequenced S. typhi Isolates
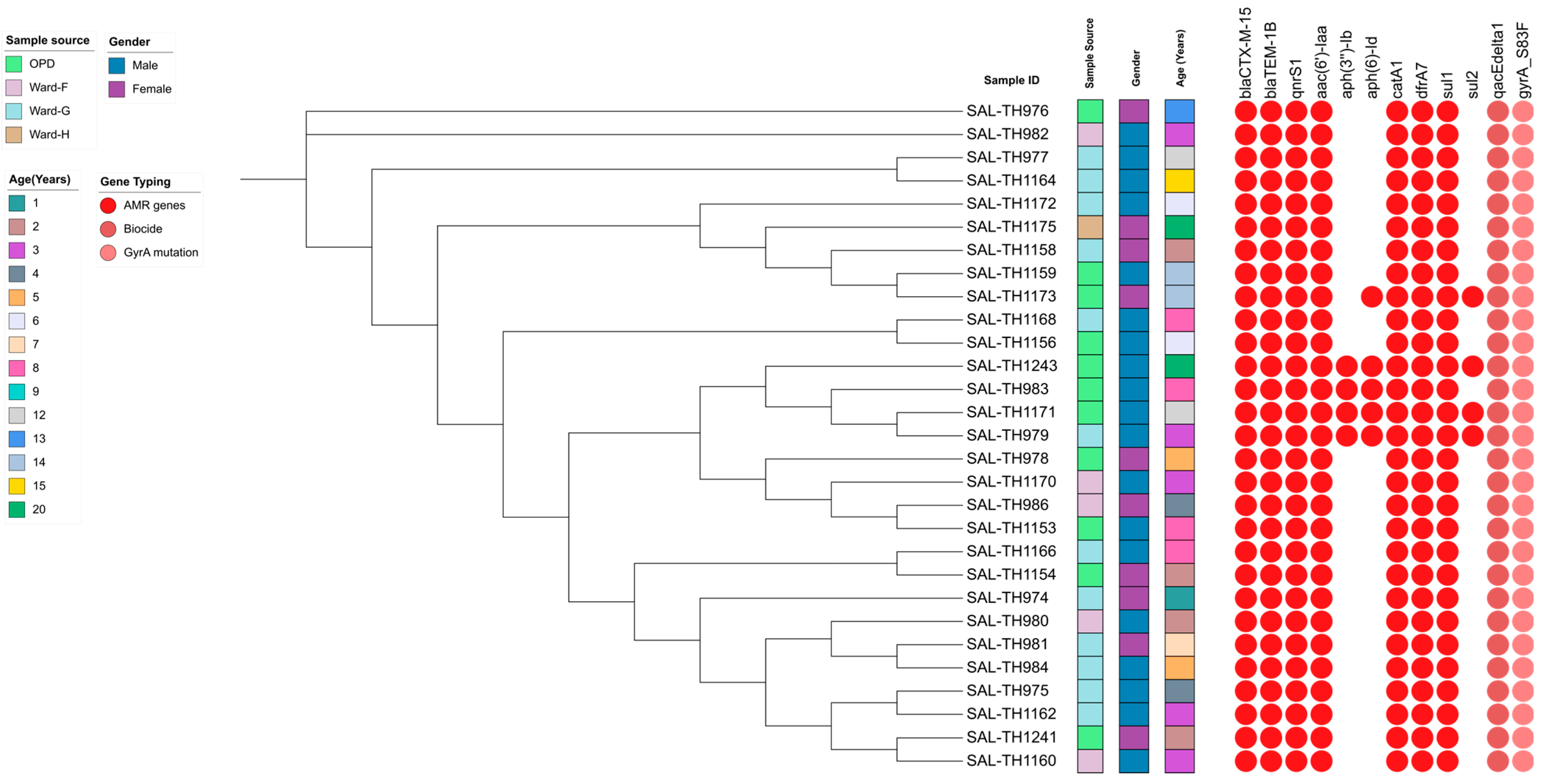
3.6. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in the Sequenced S. typhi Isolates
3.7. Virulence Gene Profile of the Sequenced S. typhi Isolates
3.8. Detection of Heavy Metal Resistance Genes in the Sequenced Isolates
3.9. Plasmid Distribution and Correlation of IncY Plasmid on Cephalosporin Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gashaw, T.; Jambo, A. Typhoid in Less Developed Countries: A Major Public Health Concern. In Hygiene and Health in Developing Countries-Recent Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qamar, F.N.; Hussain, W.; Qureshi, S. Salmonellosis including enteric fever. Pediatr. Clin. 2022, 69, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oludairo, O.O.; Kwaga, J.K.; Kabir, J.; Abdu, P.A.; Gitanjali, A.; Perrets, A.; Cibin, V.; Lettini, A.; Aiyedun, J. A review on Salmonella characteristics, taxonomy, nomenclature with special reference to non-Typhoidal and Typhoidal salmonellosis. Zag-Azig Vet. J. 2022, 50, 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Sijad-ur-Rehman, H.G.; Ahad, A.; Muhammad, N.; Bibi, R.; Ullah, I. Antimicrobial Sensitivity of Salmonella Species in Children-A Single-Centered Study. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2023, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, F.; Sayeed, M.A.; Choudhury, F.K.; Sheikh, A.; Ahmed, D.; Goswami, D.; Hossain, M.L.; Brooks, A.; Calderwood, S.B.; Charles, R.C. Typhoid fever in young children in Bangladesh: Clinical findings, antibiotic susceptibility pattern and immune responses. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, H.; Khan, M.N.; Rehman, T.; Hameed, M.F.; Yang, X. Antibiotic resistance in Pakistan: A systematic review of past decade. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, N.; Chapagain, R.; Thakur, C.K.; Basnet, A.; Amatya, I.; Singh, R.; Ghimire, R. Salmonella infection among the pediatric population at a tertiary care children’s hospital in central Nepal: A retrospective study. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1218864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Xie, X.-L.; Wang, W.-J.; Deng, L.; Shang, L.-H.; Xiong, L.-J.; Song, P.-P. Epidemiological Investigation of Salmonella enterica Isolates in children with diarrhea in Chengdu, China. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2021, 14, e119034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Afridi, M.A.R.; Awan, M.B.; Muhammad, I. New emerging pattern of sensitivity of Salmonella typhi: A single centre experience. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 32, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolutife, M.J. Bacterial Colonization of Laptop Keyboards Belonging to Caleb University Students Department of Biological Sciences and Biotechnology; Caleb University: Imota, Nigeria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, N. Synergistic Combinations Between Human-Derived Antimicrobial Peptides and Traditional Antibiotics Against Escherichia coli; Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Sharif, S.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, B. Antibiotic Resistance: Targeting Extensively Drug Resistant (XDR) Salmonella Typhi. Natl. J. Life Health Sci. 2024, 3, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghurnee, O.; Ghosh, A.K.; Abony, M.; Aurin, S.A.; Fatema, A.N.; Banik, A.; Ahmed, Z. Isolation of multi-drug resistant (MDR) and extensively drug resistant (XDR) Salmonella typhi from blood samples of patients attending tertiary medical centre in Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Adv. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnano San Lio, R.; Favara, G.; Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Agodi, A. How anti-microbial resistance is linked to climate change: An overview of two intertwined global challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Sultana, S.A.; Prova, S.R.; Uddin, T.M.; Islam, F.; Das, R.; Nainu, F.; Sartini, S.; Chidambaram, K.; Alhumaydhi, F.A. Investigating forthcoming strategies to tackle deadly superbugs: Current status and future vision. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 1309–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, F.; Chinni, S.V.; Samuggam, S.; Reddy, L.V.; Solayappan, M.; Su Yin, L. The complex mechanism of the Salmonella typhi biofilm formation that facilitates pathogenicity: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Wieczorek, K.; Dec, M.; Nowaczek, A.; Osek, J. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria—A review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinola, O.T.; Oyebamiji, A.K.; Oke, D.G.; Adekunle, D.O.; Olanrewaju, A.A.; Akintelu, S.A. In silico analysis on binding action of beta-lactam drugs against TEM and SHV class A beta-lactamases from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silago, V. Beta-lactam antibiotics and extended spectrum beta-lactamases. GSC Adv. Res. Rev. 2021, 9, 015–024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deekshit, V.K.; Srikumar, S. ‘To be, or not to be’—The dilemma of ‘silent’ antimicrobial resistance genes in bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2902–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokludová, L. Molecular Biology Perspective of Susceptibility and Resistance in Main Target Pathogens in the Respective Species and Antimicrobials of Concern. In Antimicrobials in Livestock 1: Regulation, Science, Practice: A European Perspective; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 281–359. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, D.G.; Lambert, P.A. Modes of Action of Antibacterial Agents. In Molecular Medical Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 597–614. [Google Scholar]
- Abushaheen, M.A.; Fatani, A.J.; Alosaimi, M.; Mansy, W.; George, M.; Acharya, S.; Rathod, S.; Divakar, D.D.; Jhugroo, C.; Vellappally, S. Antimicrobial resistance, mechanisms and its clinical significance. Disease-a-Month 2020, 66, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugaiyan, J.; Kumar, P.A.; Rao, G.S.; Iskandar, K.; Hawser, S.; Hays, J.P.; Mohsen, Y.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Awuah, W.A.; Jose, R.A.M. Progress in alternative strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance: Focus on antibiotics. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabeen, T. Challenges in the Prevention of Child Maltreatment in Pakistan: An Inter-play of the Culture and the Context. Int. J. Child Maltreatment Res. Policy Pract. 2021, 4, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M. Factors Influencing Access to Tuberculosis Diagnostic Services in Pakistan—An Analysis. Master’s Thesis, KIT (Royal Tropical Institute)/Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lubin, J.-B.; Green, J.; Maddux, S.; Denu, L.; Duranova, T.; Lanza, M.; Wynosky-Dolfi, M.; Flores, J.N.; Grimes, L.P.; Brodsky, I.E. Arresting microbiome development limits immune system maturation and resistance to infection in mice. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 554–570.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, K.E.; Date, K.; Hirani, N.; LeBoa, C.; Jayaprasad, N.; Borhade, P.; Warren, J.; Shim-pi, R.; Hoffman, S.A.; Mikoleit, M. Population structure and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella Typhi and Paratyphi A amid a phased municipal vac-cination campaign in Navi Mumbai, India. mBio 2023, 14, e0117923. [Google Scholar]
- Kryzhevskyi, V.; Strokous, V.; Lifshyts, Y.; Rybianets, Y.; Oberniak, A.; Krikunov, A.; Iungin, O.; Potochilova, V.; Rudnieva, K.; Petakh, P.; et al. Case report: Azithromycin-meropenem combination therapy as a low-cost approach to combat PDR gram-negative infections of war wounds in Ukraine. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1264492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodise, T.P.; Bhavnani, S.M.; Ambrose, P.G.; Sader, H.S.; Andes, D.; Pogue, J.M. Piperacillin/tazobactam susceptibility test interpretive criteria for Enterobacterales: Recommendations from the United States Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 79, ciae328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, F.; Hu, X.; Saxena, A.; Mou, K.; Shen, H.; Ali, H.; Ghauri, M.A.; Sarwar, Y.; Ali, A.; Li, G. Analyzing Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria from Wastewater in Pakistan Using Whole-Genome Sequencing. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Gorden, P.J.; Xia, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, G. Whole-genome analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae from bovine mastitis milk in the US. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 1183–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Yan, S.; Jiang, F.; Cai, W.; Li, G. Whole genome sequencing analysis of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli from China. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 259, 109158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chklovski, A.; Parks, D.H.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM2: A rapid, scalable and accurate tool for assessing microbial genome quality using machine learning. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Den Bakker, H.C.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Lane, C.; Lauer, A.; Fields, P.I.; Deng, X. SeqSero2: Rapid and improved Salmonellas erotype determination using whole-genome sequencing data. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01746-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhimiukor, O.O.; Oaikhena, A.O.; Afolayan, A.O.; Fadeyi, A.; Kehinde, A.; Ogunleye, V.O.; Aboderin, A.O.; Oduyebo, O.O.; Elikwu, C.J.; Odih, E.E. Genomic characterization of invasive typhoidal and non-typhoidal Salmonella in southwestern Nigeria. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Fedorov, B.; Haft, D.H.; Prasad, A.B.; Klimke, W. Curation of the AMRFinderPlus databases: Applications, functionality and impact. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kille, B.; Nute, M.G.; Huang, V.; Kim, E.; Phillippy, A.M.; Treangen, T.J. Parsnp 2.0: Scalable core-genome alignment for massive microbial datasets. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, gkae268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, P.; Machado, J.; Sousa, J.C.; Peixe, L. Dissemination of sulfonamide re-sistance genes (sul1, sul2, and sul3) in Portuguese Salmonella enterica strains and relation with integrons. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, J.R.; Rup, A.R.; Dash, A.K.; Sahu, S.K.; Gaurav, A.; Gupta, A. Clinical and Laboratory Profile of Enteric Fever in Children from a Tertiary Care Centre in Odisha, Eastern India. Cureus 2021, 13, e12826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabasa, A.; Mava, Y.; Pius, S.; Timothy, S.; Baba, U. Typhoid fever in children: Clinical presentation and risk factors. Niger. J. Paediatr. 2013, 40, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malini, A.; Barathy, C.; Madhusudan, N.S.; Johnson, C. Clinical and microbiologi-cal profile of enteric fever among pediatric patients in a tertiary care center in South India: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Sci. 2020, 17, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndako, J.A.; Dojumo, V.T.; Akinwumi, J.A.; Fajobi, V.O.; Owolabi, A.O.; Olatinsu, O. Changes in some haematological parameters in typhoid fever patients attending Landmark University Medical Center, Omuaran-Nigeria. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Latif, I.; Neupane, D.P.; Lee, G.Y.; Kwon, R.S.; Batool, A.; Ahmed, Q.; Qamar, M.U.; Song, J. The molecular basis of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella Typhi isolates from pediatric septicemia patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchello, C.S.; Carr, S.D.; Crump, J.A. A Systematic Review on Antimicrobial Resistance among Salmonella Typhi Worldwide. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelquesi, S.L.S.; de Oliveira Ferreira, A.C.A.; Rodrigues, A.R.M.; de Souza Silva, C.M.; Orsi, D.C.; da Silva, I.C.R. Presence of Tetracycline and Sulfonamide Re-sistance Genes in Salmonella spp.: Literature Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, O.A.; Asghar, Z.; Aftab, R.M.; Amin, S.; Shaikh, G.; Nashwan, A.J. Anti-microbial resistant strains of Salmonella typhi: The role of illicit antibiotics sales, misuse, and self-medication practices in Pakistan. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, K.E.; Tanmoy, A.M.; Pragasam, A.K.; Iqbal, J.; Sajib, M.S.I.; Mutreja, A.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Tamrakar, D.; Qamar, F.N.; Dougan, G. The internation-al and intercontinental spread and expansion of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella Typhi: A genomic epidemiology study. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e567–e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.; Chaguza, C.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Carey, M.; Baker, S.; Khan, K.; Bogoch, I.I.; Pitzer, V.E. Assessing the global risk of typhoid outbreaks caused by extensively drug resistant Salmonella Typhi. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, E.J.; Shakoor, S.; Page, A.J.; Qamar, F.N.; Judge, K.; Saeed, D.K.; Wong, V.K.; Dallman, T.J.; Nair, S.; Baker, S. Emergence of an extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi clone harboring a promiscuous plasmid encoding resistance to fluoroquinolones and third-generation cephalosporins. mBio 2018, 9, e00105-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.E.; Phan, M.D.; Baker, S.; Duy, P.T.; Nga, T.V.T.; Nair, S.; Turner, A.K.; Walsh, C.; Fanning, S.; Farrell-Ward, S. Emergence of a globally dominant IncHI1 plasmid type associated with multiple drug resistant typhoid. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewska, M.; Błażejewska, A.; Gawor, J.; Adamska, D.; Goryca, K.; Szeląg, M.; Kalinowski, P.; Popowska, M. A newly identified IncY plasmid from multi-drug-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from dairy cattle feces in Poland. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e00877-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Barba, S.; Top, E.M.; Stalder, T. Plasmids, a molecular cornerstone of antimicrobial resistance in the One Health era. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Mean | SD | Min–Max | Ref. Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 8.93 | 5.61 | 1–20 | - |
| Hb (g/dL) | 11.09 | 1.49 | 7.2–16.4 | 11.5–15.5 |
| TLC (103/µL) | 6.56 | 2.18 | 2.57–15.65 | 4.50–13.50 |
| ALT (U/L) | 76.83 | 109.12 | 13–855 | 5–50 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 10.80 | 10.78 | 0.59–57.2 | 0.0–0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riaz, M.; Ahmad, S.; Sattar, F.; Li, G.; Din, Z.U.; Ahmad, S.; Azra; Waheed, A.; Ul Haq, I.; Phelan, J.E.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Drug-Resistant Salmonella Typhi in Children. Pathogens 2025, 14, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100967
Riaz M, Ahmad S, Sattar F, Li G, Din ZU, Ahmad S, Azra, Waheed A, Ul Haq I, Phelan JE, et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Drug-Resistant Salmonella Typhi in Children. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100967
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiaz, Muhammad, Shabir Ahmad, Fazal Sattar, Ganwu Li, Zia Ud Din, Sajjad Ahmad, Azra, Aiman Waheed, Ihtisham Ul Haq, Jody E. Phelan, and et al. 2025. "Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Drug-Resistant Salmonella Typhi in Children" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100967
APA StyleRiaz, M., Ahmad, S., Sattar, F., Li, G., Din, Z. U., Ahmad, S., Azra, Waheed, A., Ul Haq, I., Phelan, J. E., Rani, G. F., Cabral-Marques, O., Campino, S., Khan, T. A., & Clark, T. G. (2025). Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Drug-Resistant Salmonella Typhi in Children. Pathogens, 14(10), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14100967








