Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Case–Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
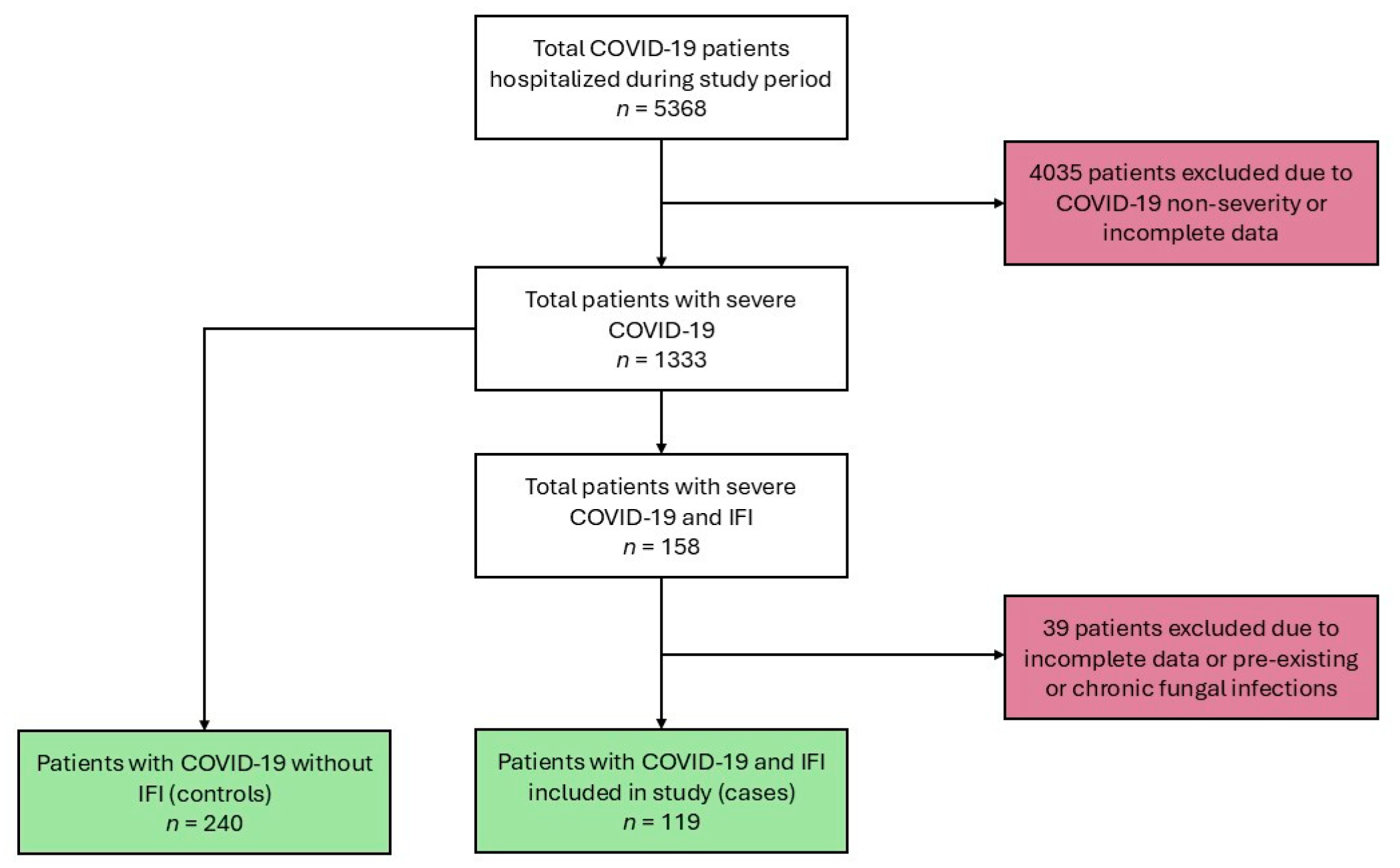
3. Results
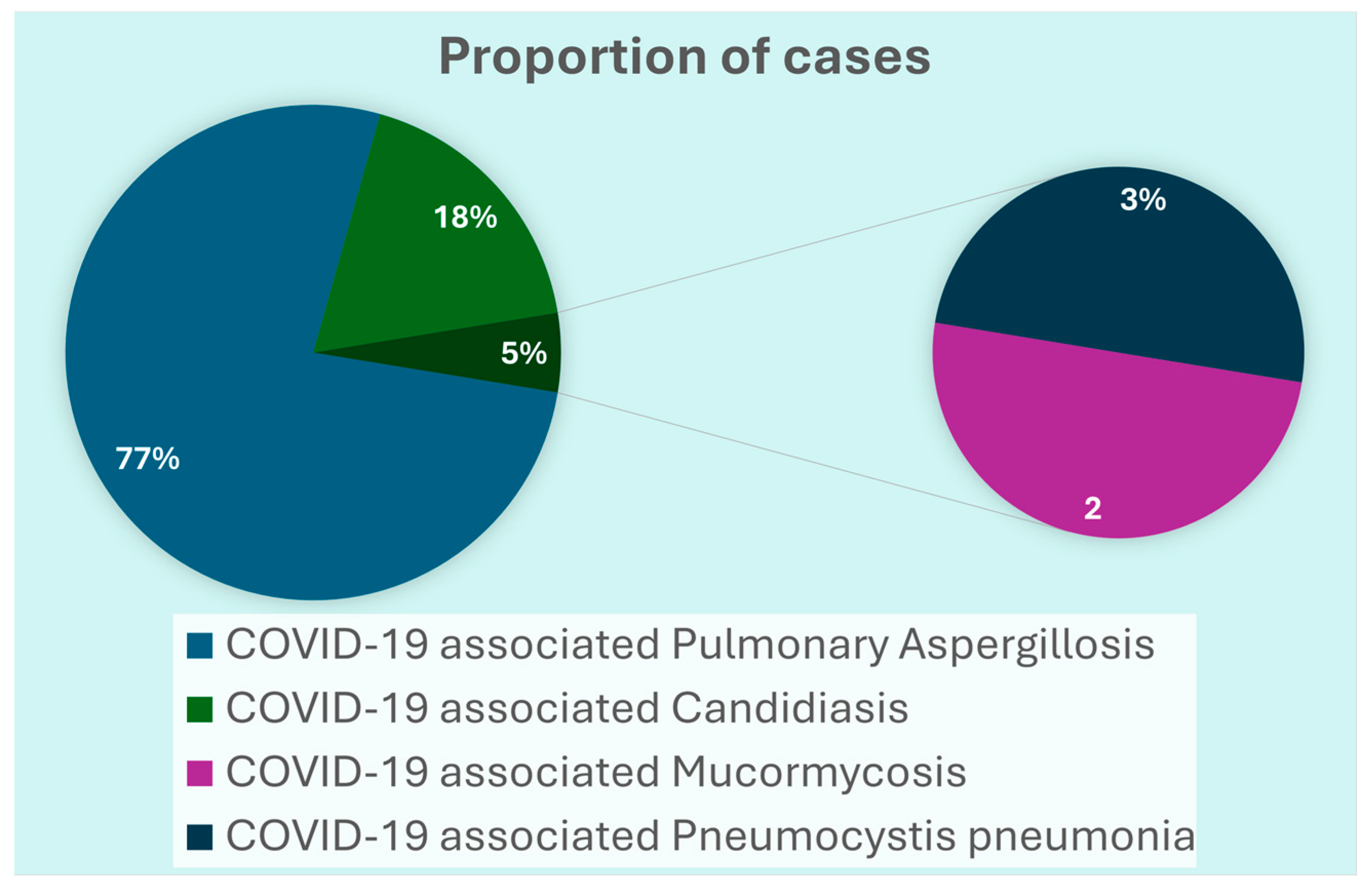
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients with IFIs
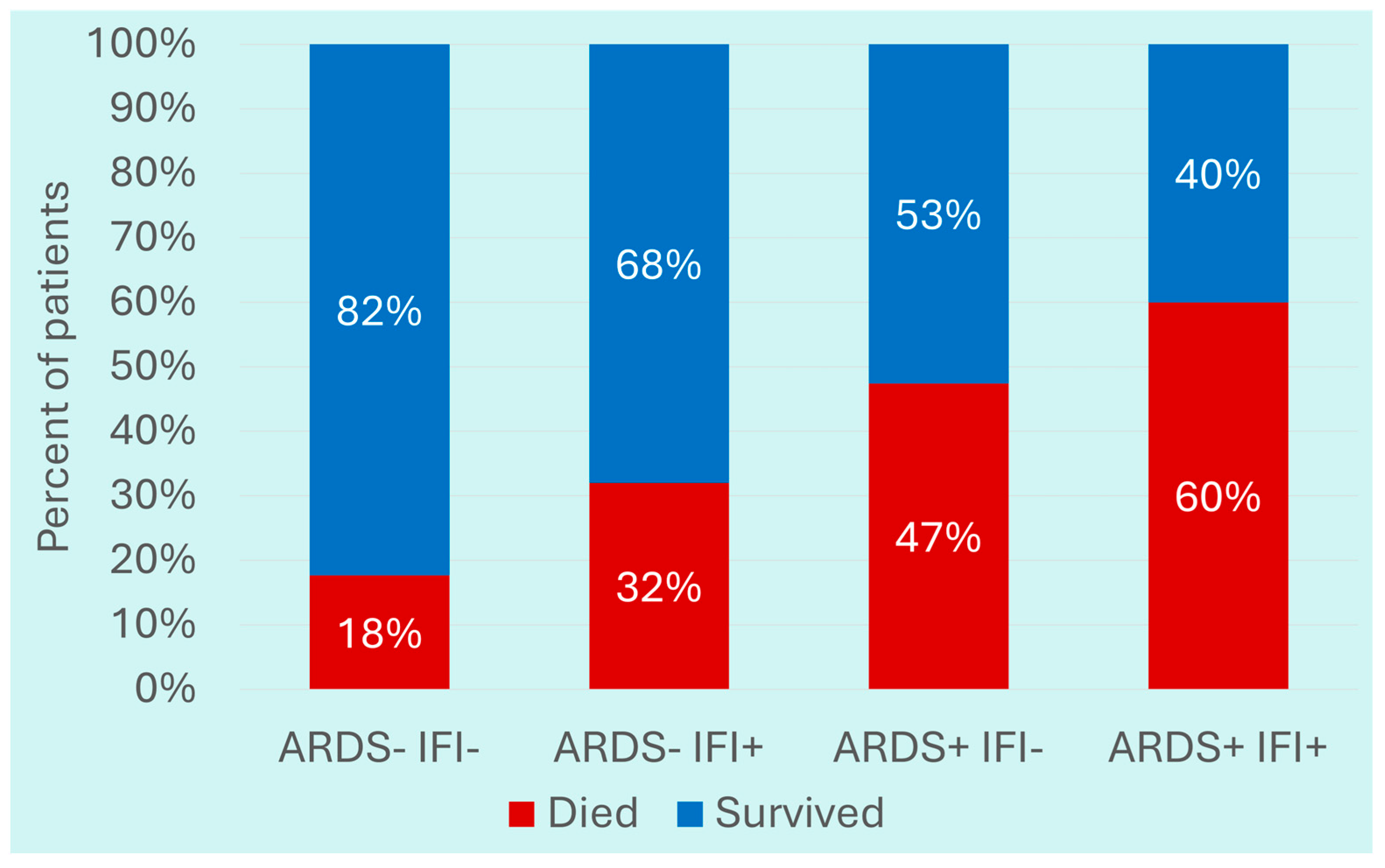
3.2. Comparison of Severe COVID-19 Patients with IFIs with Those Without IFIs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IFI | invasive fungal infection |
| CAPA | COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis |
| CAC | COVID-19-associated candidiasis |
| CAM | COVID-19-associated mucormycosis |
| PJP | Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia |
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| OR | odds ratio |
References
- Rovina, N.; Koukaki, E.; Romanou, V.; Ampelioti, S.; Loverdos, K.; Chantziara, V.; Koutsoukou, A.; Dimopoulos, G. Fungal Infections in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Inevitabile Malum. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalini, G.; Giacomelli, A.; Ridolfo, A.; Gervasoni, C.; Antinori, S. Invasive Fungal Infections Complicating COVID-19: A Narrative Review. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, A.A.; Mathew, M.; Baddley, J.W. Overview of COVID-19-Associated Invasive Fungal Infection. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2022, 16, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaelli, F.; Tanzarella, E.S.; De Pascale, G.; Tumbarello, M. Invasive Respiratory Fungal Infections in COVID-19 Critically Ill Patients. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, B.G.; Lakatos, B.; Bobek, I.; Szabo, E.; Szlavik, J.; Vályi-Nagy, I. Invasive Fungal Infections among Critically Ill Adult COVID-19 Patients: First Experiences from the National Centre in Hungary. J. Med. Mycol. 2021, 31, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.; Farooqi, J.; Mahmood, S.F.; Jabeen, K. COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA) in Patients Admitted with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: An Observational Study from Pakistan. Mycoses 2020, 63, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, T.M.; Jacob, C.N.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. When Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus and Severe COVID-19 Converge: The Perfect Storm for Mucormycosis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Singh, B.; Bhadada, S.K.; Banerjee, M.; Bhogal, R.S.; Hage, N.; Kumar, A. COVID-19-Associated Mucormycosis: An Updated Systematic Review of Literature. Mycoses 2021, 64, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, A.; Kamran, A.H.; Ammar, M.; Rahman, S. ur Frequency and Survival of COVID Associated Mucormycosis Patients at Tertiary Care Hospitals in Pakistan: A Retrospective Observational Study. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Clinical Management of COVID-19: Living Guideline; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2023; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Koehler, P.; Bassetti, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, S.C.A.; Colombo, A.L.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Oladele, R.O.; Vinh, D.C.; et al. Defining and Managing COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis: The 2020 ECMM/ISHAM Consensus Criteria for Research and Clinical Guidance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e149–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arastehfar, A.; Carvalho, A.; Nguyen, M.H.; Hedayati, M.T.; Netea, M.G.; Perlin, D.S.; Hoenigl, M. COVID-19-Associated Candidiasis (CAC): An Underestimated Complication in the Absence of Immunological Predispositions? J. Fungi 2020, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudramurthy, S.M.; Hoenigl, M.; Meis, J.F.; Cornely, O.A.; Muthu, V.; Gangneux, J.P.; Perfect, J.; Chakrabarti, A. ECMM and ISHAM ECMM/ISHAM Recommendations for Clinical Management of COVID-19 Associated Mucormycosis in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Mycoses 2021, 64, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornely, O.A.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Arenz, D.; Chen, S.C.A.; Dannaoui, E.; Hochhegger, B.; Hoenigl, M.; Jensen, H.E.; Lagrou, K.; Lewis, R.E.; et al. Global Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Mucormycosis: An Initiative of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology in Cooperation with the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e405–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoenigl, M.; Seidel, D.; Sprute, R.; Cunha, C.; Oliverio, M.; Goldman, G.H.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Carvalho, A. COVID-19-Associated Fungal Infections. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, P.; Kofteridis, D.P.; Alexakis, K.; Koutserimpas, C.; Papakitsou, I.; Maraki, S.; Samonis, G. Candida Species Isolation from Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19-A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Riad, A.; Singh, A.; Klugarová, J.; Antony, B.; Banna, H.; Klugar, M. Global Prevalence of COVID-19-Associated Mucormycosis (CAM): Living Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, A.G.B.; Lalla, U.; Taljaard, J.J.; Louw, E.H.; Koegelenberg, C.F.N.; Allwood, B.W. The Diagnostic Challenge of Pneumocystis Pneumonia and COVID-19 Co-Infection in HIV. Respirol. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e00725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Montes, C.M.; Bojorges-Aguilar, S.; Correl-Herrera, E.A.; Rangel-Cordero, A.; Díaz-Lomelí, P.; Cervantes-Sanchez, A.; Martinez-Guerra, B.A.; Rajme-López, S.; Tamez Torres, K.M.; Martínez-Gamboa, R.A.; et al. Fungal Infections in the ICU during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Mexico. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangneux, J.-P.; Dannaoui, E.; Fekkar, A.; Luyt, C.-E.; Botterel, F.; De Prost, N.; Tadié, J.-M.; Reizine, F.; Houzé, S.; Timsit, J.-F.; et al. Fungal Infections in Mechanically Ventilated Patients with COVID-19 during the First Wave: The French Multicentre MYCOVID Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.H.; Neu, K.P. Incidence, Diagnosis and Outcomes of COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA): A Systematic Review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 113, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoletti, M.; Pascale, R.; Cricca, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Maccaro, A.; Bussini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Tonetti, T.; Pizzilli, G.; Francalanci, E.; et al. Epidemiology of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Among Intubated Patients With COVID-19: A Prospective Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3606–e3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, L.; Topçu, U.; Manay, M.; Esen, B.H.; Bektas, S.N.; Aydın, S.; Özdemir, B.; Khostelidi, S.N.; Klimko, N.; Cornely, O.; et al. COVID-19–Associated Mucormycosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 958 Cases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdel, F.; Ahmadikia, K.; Salehi, M.; Tabari, A.; Jafari, R.; Mehrparvar, G.; Rezaie, Y.; Rajaeih, S.; Alijani, N.; Barac, A.; et al. Mucormycosis in Patients with COVID-19: A Cross-sectional Descriptive Multicentre Study from Iran. Mycoses 2021, 64, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, L.; Buonomo, A.R.; Iacovazzo, C.; Giaccone, A.; Scotto, R.; Viceconte, G.; Mercinelli, S.; Vargas, M.; Roscetto, E.; Cacciatore, F.; et al. Invasive Fungal Infections in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Non-Intensive Care Single-Centre Experience during the First Pandemic Waves. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.S.; McGwin, G.; Tushla, L.; Benedict, K.; Lyman, M.M.; Toda, M.; Baddley, J.W.; Pappas, P.G. Epidemiology of Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Fungal Infections in the Intensive Care Unit: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Mycopathologia 2025, 190, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuniga Moya, J.C.; Papadopoulos, B.; Mansoor, A.-R.; Mazi, P.B.; Rauseo, A.M.; Spec, A.; Consortium, N. Incidence and Mortality of COVID-19 Associated Invasive Fungal Infections Among Critically-Ill Intubated Patients: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melenotte, C.; Chavarot, N.; L’Honneur, A.-S.; Bodard, S.; Cheminant, M.; Flahault, A.; Nguyen, Y.; Burgard, M.; Dannaoui, E.; Bougnoux, M.-E.; et al. Increased Risk of Invasive Aspergillosis in Immunocompromised Patients With Persistent SARS-CoV-2 Viral Shedding >8 Weeks, Retrospective Case-Control Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.; Farooqi, J.; Mahmood, S.F.; Jabeen, K. COVID-19 Associated Mucormycosis: A Life-Threatening Complication in Patients Admitted with Severe to Critical COVID-19 from Pakistan. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1704–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.; Farooqi, J.; Zubair, S.M.; Ayub, M.; Khan, S.; Wiqar, M.H.; Mahmood, S.F.; Jabeen, K. Comparison of Risk Factors and Outcome of Patients with and without COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis from Pakistan: A Case–Control Study. Mycoses 2023, 66, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pates, K.; Periselneris, J.; Russell, M.D.; Mehra, V.; Schelenz, S.; Galloway, J.B. Rising Incidence of Pneumocystis Pneumonia: A Population-Level Descriptive Ecological Study in England. J. Infect. 2023, 86, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amstutz, P.; Bahr, N.C.; Snyder, K.; Shoemaker, D.M. Pneumocystis Jirovecii Infections Among COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series and Literature Review. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Y. Demographic Characteristics and Risk Factors for Invasive Fungal Sinusitis in the Context of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2024, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqtadar, S.; Hashmat, M.; Chaudhry, M.N.A.; Mumtaz, S.U.; Abaidullah, S.; Pascual-Figal, D.A.; Khan, A. Unnecessary Use of Corticosteroids for Managing Early Mild Symptoms of COVID-19 May Lead to Rhino-Ortibal-Cerebral Mucormycosis in Patients with Diabetes—A Case Series from Lahore, Pakistan. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, 20499361221097417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, S.; Nasir, N. Aspergillosis and Mucormycosis in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2022, 32, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezeokoli, O.T.; Gcilitshana, O.; Pohl, C.H. Risk Factors for Fungal Co-Infections in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients, with a Focus on Immunosuppressants. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juyal, D.; Pal, S.; Negi, N.; Singh, M.; Kumar, M.; Singhal, S. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)-Associated Mucormycosis (CAM): The Unholy Triad of COVID-19, Diabetes Mellitus, and Corticosteroid Therapy. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2023, 12, 2538–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M.; Goli, M. Predisposing Factors of Important Invasive Fungal Coinfections in COVID-19 Patients: A Review Article—Mohammadali Zia, Mohammad Goli, 2021. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 3000605211043413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva-Lozano, H.; Treviño-Rangel, R.d.J.; González, G.M.; Ramírez-Elizondo, M.T.; Lara-Medrano, R.; Aleman-Bocanegra, M.C.; Guajardo-Lara, C.E.; Gaona-Chávez, N.; Castilleja-Leal, F.; Torre-Amione, G.; et al. Outbreak of Candida Auris Infection in a COVID-19 Hospital in Mexico. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, D.; Farrugia, J.; Azzopardi, C.M. SARS-CoV-2 Related ARDS and Invasive Fungal Infections in Intensive Care Patients. Clin. Infect. Pract. 2022, 13, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeshima, K.; Yamamoto, R.; Matsumura, K.; Kaito, D.; Homma, K.; Yamakawa, K.; Tagami, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Ogura, T.; Hirayama, A.; et al. Fungal Infection-Related Conditions and Outcomes in Severe COVID-19: A Nationwide Case-Control Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenigl, M.; Seidel, D.; Carvalho, A.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Arastehfar, A.; Gangneux, J.-P.; Nasir, N.; Bonifaz, A.; Araiza, J.; Klimko, N.; et al. The Emergence of COVID-19 Associated Mucormycosis: A Review of Cases from 18 Countries. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e543–e552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayaaslan, B.; Eser, F.; Kaya Kalem, A.; Bilgic, Z.; Asilturk, D.; Hasanoglu, I.; Ayhan, M.; Tezer Tekce, Y.; Erdem, D.; Turan, S.; et al. Characteristics of Candidemia in COVID-19 Patients; Increased Incidence, Earlier Occurrence and Higher Mortality Rates Compared to non-COVID-19 Patients. Mycoses 2021, 64, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.; Ray, A.; Sarda, S.; Vyas, S.; Singh, G.; Jorwal, P.; Kodan, P.; Khanna, P.; Xess, I.; Sinha, S. COVID-19-associated Subacute Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Mycoses 2022, 65, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Than, H.M.; Dao, T.V.; Cao, T.V.; Duong, T.V.; Pham, T.N.; Nguyen, C.T.; Vu, P.D.; Le, N.V.; Do, B.N.; Nguyen, P.V.; et al. Factors Associated with Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation and 30-Day Mortality in Intubated COVID-19 Patients with Invasive Fungal Infections: A Retrospective Observational Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | IFIs (n = 119) | No IFIs (n = 240) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median Age (IQR) years | 64 (54–70) | 60 (52–69) | 1.01 (0.99–1.03) | 0.317 |
| Sex n (%) | ||||
| Male | 85 (71.4) | 159 (66.3) | 1.27 (0.79–2.06) | 0.375 |
| Female | 34 (28.6) | 81 (33.6) | Ref | |
| Comorbidity n (%) | ||||
| DM | 56 (47.1) | 134 (55.8) | 0.70 (0.45–4.13) | 0.118 |
| HTN | 65 (54.6) | 141 (58.7) | 0.85 (0.54–1.32) | 0.457 |
| IHD | 8 (6.72) | 16 (6.70) | 1.01 (0.42–2.43) | 0.984 |
| CKD | 19 (19.0) | 9 (3.8) | 1.25 (0.54–1.32) | 0.422 |
| Chronic Lung Disease | 13 (10.9) | 20 (8.3) | 1.30 (0.65–2.82) | 0.425 |
| Malignancy | 6 (5.0) | 10 (4.2) | 1.22 (0.43–3.44) | 0.706 |
| Medications n (%) | ||||
| Tocilizumab | 35 (29.4) | 53 (22.1) | 1.47 (0.89–2.42) | 0.130 |
| Steroids | 117 (98.3) | 233 (97.1) | 1.76 (0.36–8.59) | 0.486 |
| Antibiotic given n (%) | 118 (99.2) | 229 (95.4) | 5.67 (0.72–44.4) | 0.099 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation n (%) | 56 (47.1) | 63 (26.2) | 2.48 (1.57–3.96) | <0.001 |
| Hemodialysis n (%) | 24 (20.2) | 25 (10.4) | 2.17 (1.18–3.99) | 0.013 |
| ARDS n (%) | 62 (52.1) | 87 (36.3) | 1.91 (1.23–2.99) | 0.004 |
| In-hospital Mortality n (%) | 49 (46.7) | 61 (28.5) | 2.19 (1.35–3.56) | 0.001 |
| Length of hospital stay (median (IQR)) | 14 (8–20) | 8 (5–13) | 1.06 (1.04–1.09) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasir, N.; Kazmi, S.A.M.; Farooqi, J.; Irfan, M.; Jabeen, K. Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Case–Control Study. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101064
Nasir N, Kazmi SAM, Farooqi J, Irfan M, Jabeen K. Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Case–Control Study. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101064
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasir, Nosheen, Syed Abbas Moazzam Kazmi, Joveria Farooqi, Muhammad Irfan, and Kauser Jabeen. 2025. "Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Case–Control Study" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101064
APA StyleNasir, N., Kazmi, S. A. M., Farooqi, J., Irfan, M., & Jabeen, K. (2025). Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Case–Control Study. Pathogens, 14(10), 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101064






