Prevalence of Rotavirus in Diarrheic Piglets on RVA-Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Farms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Farms Description
2.2. Sample Collection, Processing and Real-Time RT-PCR
2.2.1. Initial Screening for RVA, RVB and RVC
2.2.2. Longitudinal Testing in Two Farms
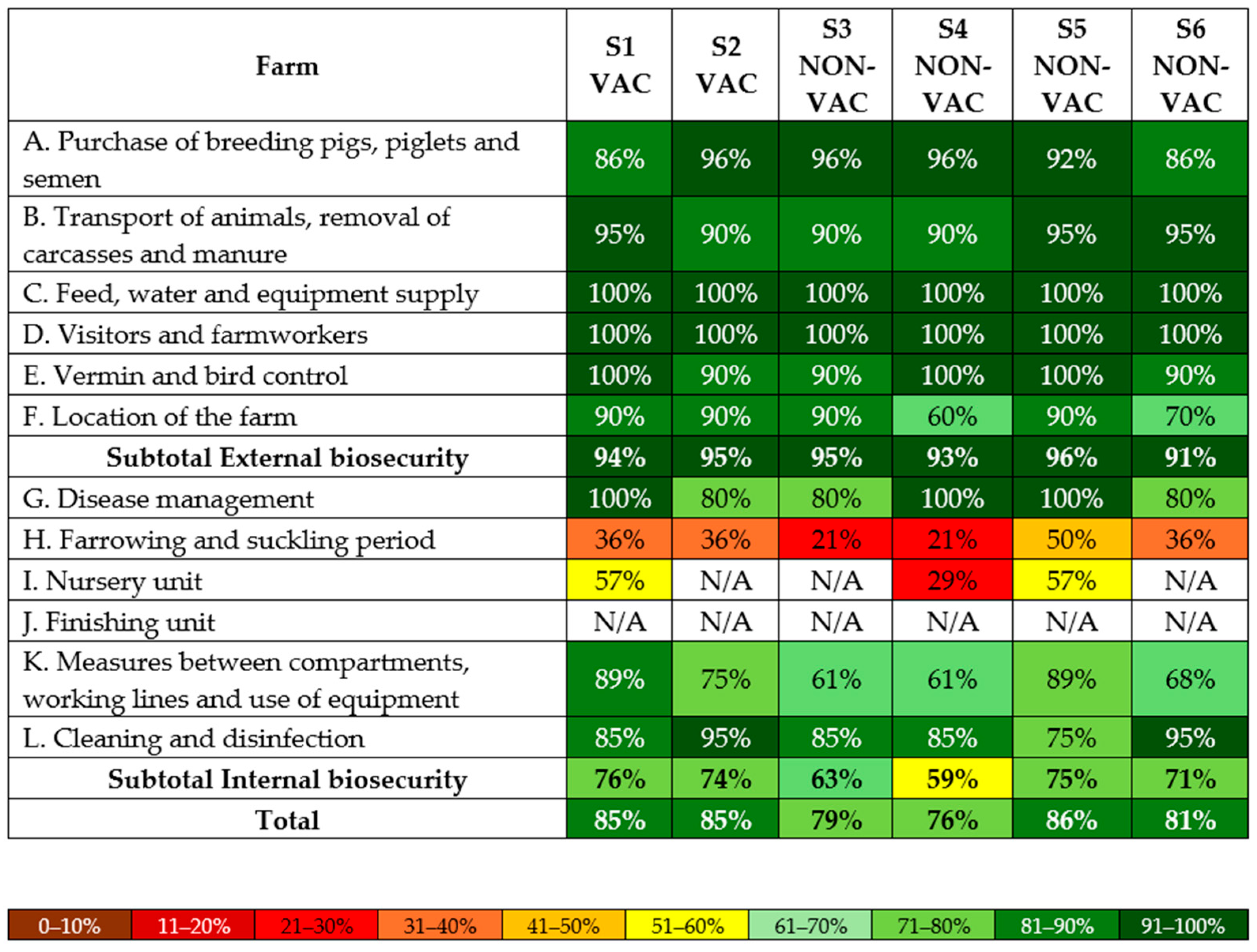
2.3. Biosecurity Scoring
2.4. Key Performance Indicators Assesment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
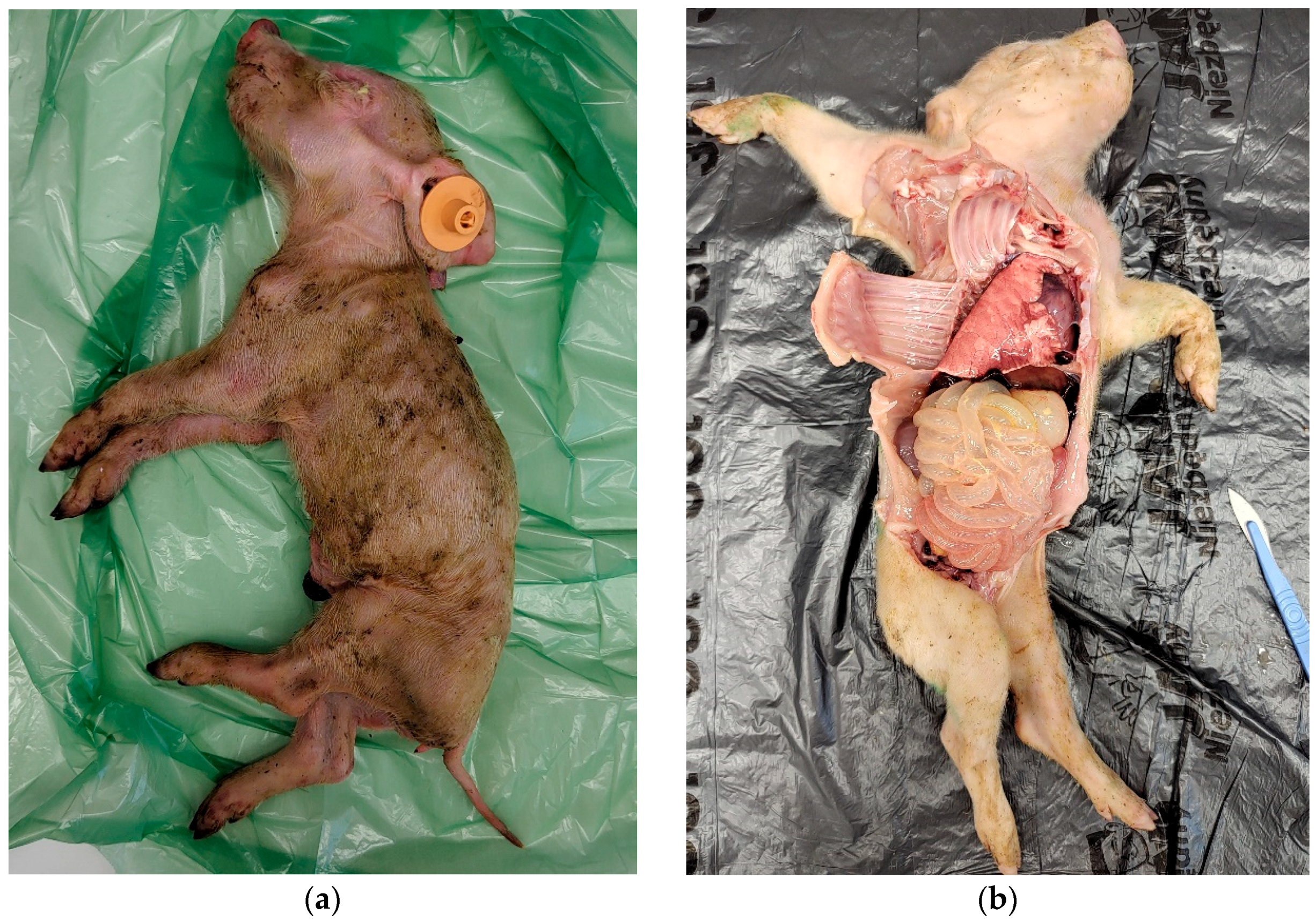
3.1. Detection of RVA, RVB and RVC with Real-Time RT-PCR
3.1.1. Initial Screening for RVs
| Farm ID | Date of Collection | No. of Collected Samples | No. of RVA-Positive Samples | No. of RVB-Positive Samples | No. of RVC-Positive Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 VAC | 17 July 2023 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 24 November 2023 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| S2 VAC | 24 November 2023 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| S3 NON-VAC | 5 July 2022 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 13 September 2023 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| 5 December 2023 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S4 NON-VAC | 28 August 2023 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 28 November 2023 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 3 | |
| S5 NON-VAC | 5 July 2022 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 5 December 2023 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| S6 NON-VAC | 5 July 2022 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 December 2023 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 4 | |
| Total | 53 | 4 | 5 | 31 |
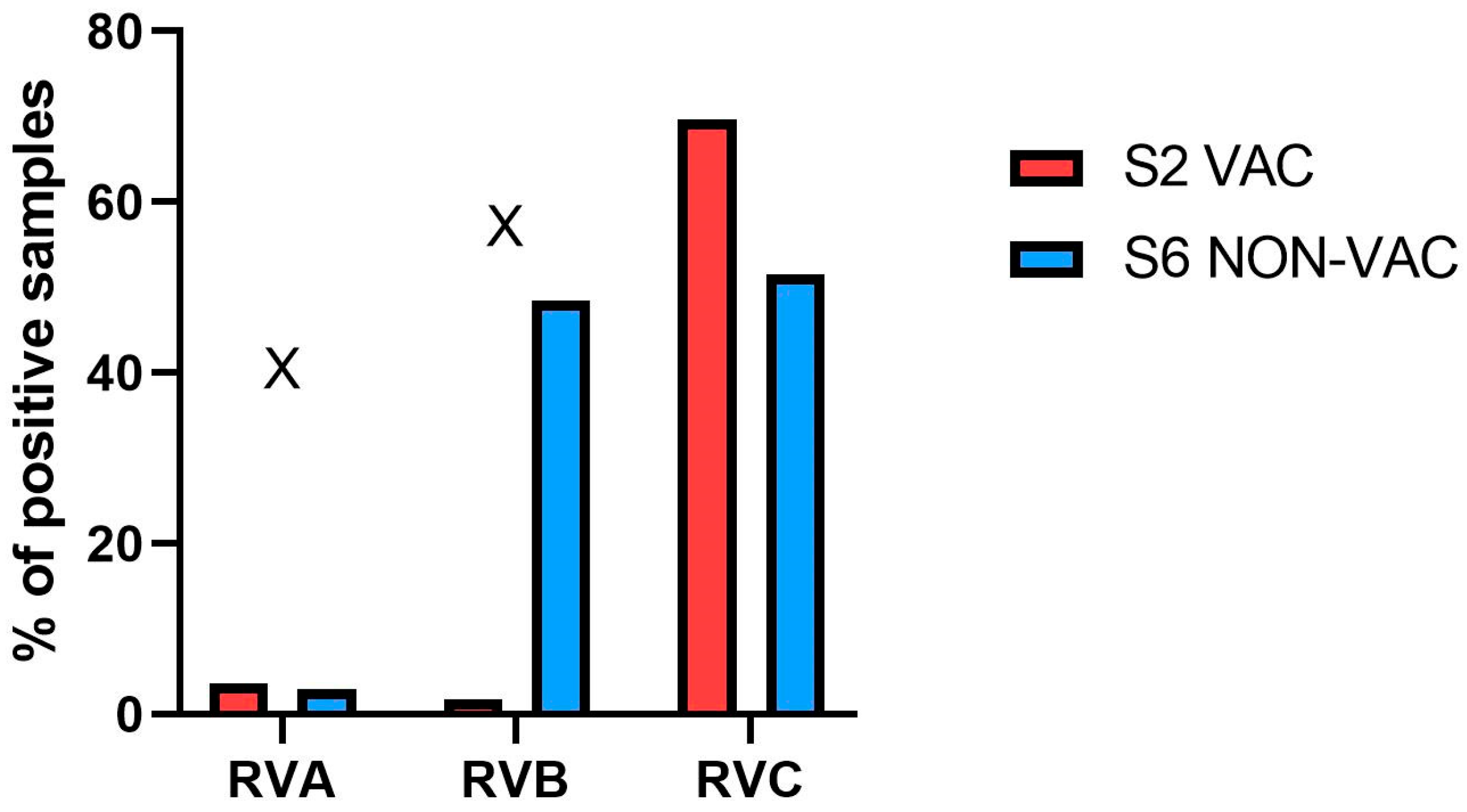
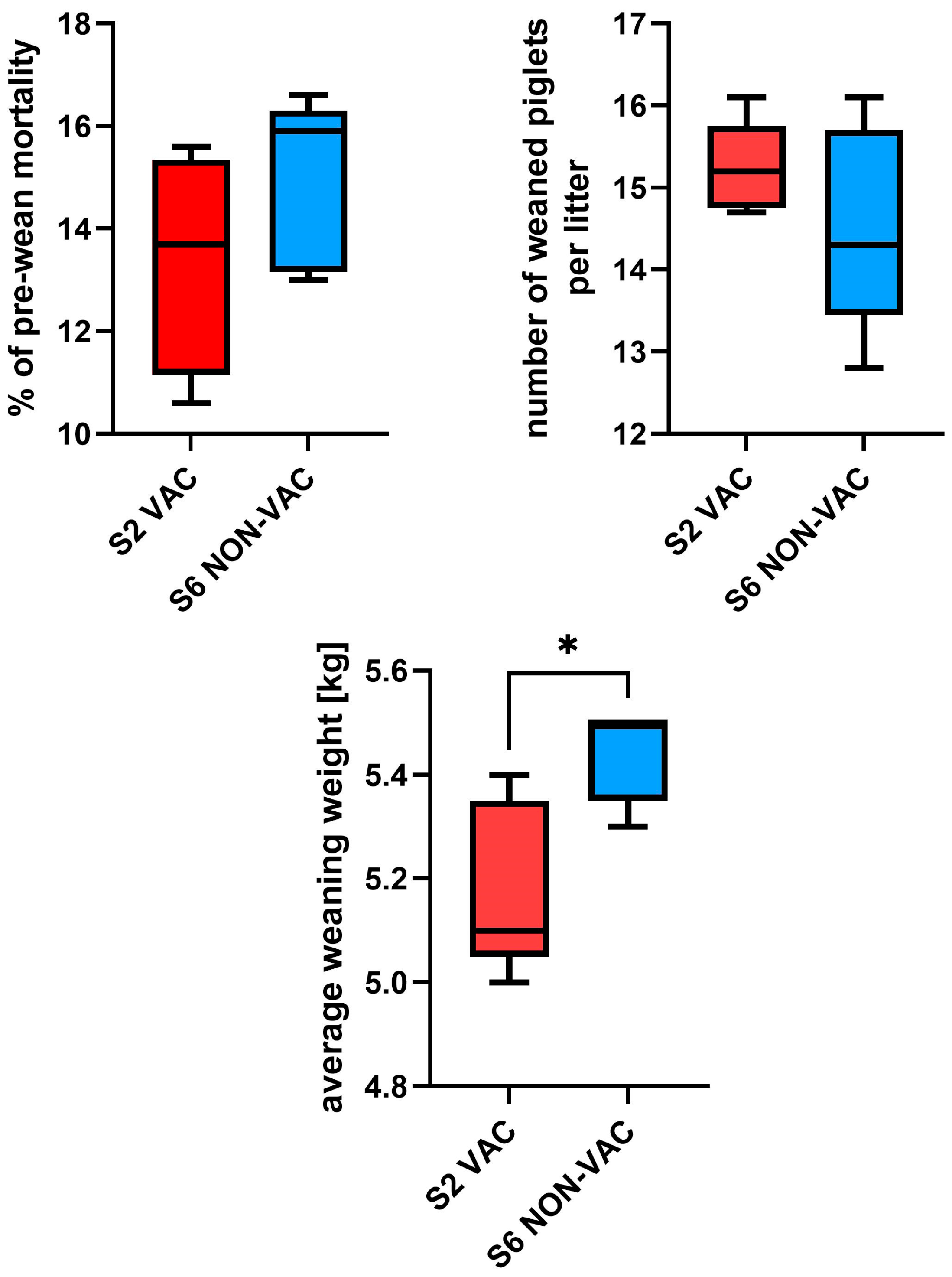
3.1.2. Longitudinal Testing
| Farm ID | Weekly Group | Sample Type | No. of Collected Samples | No. of RVA-Positive Samples | No. of RVB-Positive Samples | No. of RVC-Positive Samples | Pre-Wean Mortality [%] | No. of Weaned Piglets per Litter | Average Weaning Weight [kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2 VAC | 1 | feces | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 11.7 | 15.4 | 5.3 |
| ileum content | 8 | 1 | 0 | 5 | |||||
| 2 | feces | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 10.6 | 16.1 | 5.1 | |
| ileum content | 8 | 0 | 0 | 6 | |||||
| 3 | feces | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 15.6 | 15.2 | 5.4 | |
| ileum content | 8 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |||||
| 4 | feces | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 13.7 | 14.8 | 5.0 | |
| ileum content | 8 | 1 | 0 | 5 | |||||
| 5 | feces | 5 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 15.1 | 14.7 | 5.1 | |
| ileum content | 8 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |||||
| S6 NON-VAC | 1 | feces | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 13.0 | 12.8 | 5.3 |
| ileum content | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |||||
| 2 | feces | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 13.3 | 16.1 | 5.5 | |
| ileum content | 7 | 0 | 5 | 3 | |||||
| 3 | feces | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 16.6 | 14.3 | 5.5 | |
| ileum content | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | feces | 3 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 16.0 | 15.3 | 5.5 | |
| ileum content | 6 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 5 | feces | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 15.9 | 14.1 | 5.4 | |
| ileum content | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
3.2. Production Data
3.3. Biosecurity Scoring
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RVs | Rotaviruses |
| RVA | Rotavirus A |
| RVB | Rotavirus B |
| RVC | Rotavirus C |
| RVD | Rotavirus D |
| RVF | Rotavirus F |
| RVJ | Rotavirus J |
| RVK | Rotavirus K |
| RVL | Rotavirus L |
| PEDV | Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus |
| TGEV | Transmissible gastroenteritis virus |
| RVE | Rotavirus E |
| RVH | Rotavirus H |
| VAC | Vaccinated |
| NON-VAC | Non-vaccinated |
| SDCoV | Swine delta coronavirus |
| NPE | Natural planned exposure |
References
- Matthijnssens, J.; Otto, P.H.; Ciarlet, M.; Desselberger, U.; Van Ranst, M.; Johne, R. VP6-Sequence-Based Cutoff Values as a Criterion for Rotavirus Species Demarcation. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johne, R.; Tausch, S.H.; Grützke, J.; Falkenhagen, A.; Patzina-Mehling, C.; Beer, M.; Höper, D.; Ulrich, R.G. Distantly Related Rotaviruses in Common Shrews, Germany, 2004–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICTV. Rotavirus. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 2025. Available online: https://ictv.global/report/chapter/sedoreoviridae/sedoreoviridae/rotavirus (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Vlasova, A.N.; Amimo, J.O.; Saif, L.J. Porcine Rotaviruses: Epidemiology, Immune Responses and Control Strategies. Viruses 2017, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, F.K.; Freeman, M.J.; Culhane, M.R.; Marthaler, D.G. Reoviruses (Rotaviruses and Reoviruses). In Diseases of Swine, 11th ed.; Zimmerman, J.J., Karriker, L.A., Ramirez, A., Schwartz, K.J., Stevenson, G.W., Zhang, J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 715–727. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, A.D.; Victor, J.C.; Carey, M.E.; Tate, J.E.; Atherly, D.E.; Pecenka, C.; Diaz, Z.; Parashar, U.D.; Kirkwood, C.D. Experiences with Rotavirus Vaccines: Can We Improve Rotavirus Vaccine Impact in Developing Countries? Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M. On the Infectious Causes of Neonatal Piglet Diarrhoea—A Review. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.; Martín-Valls, G.E.; Tello, M.; Mateu, E.; Martín, M.; Darwich, L. Prevalence of Enteric Pathogens in Diarrheic and Non-Diarrheic Samples from Pig Farms with Neonatal Diarrhea in the North East of Spain. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 237, 108419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antas, M.; Olech, M.; Szczotka-Bochniarz, A. Molecular characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) in Poland reveals the presence of swine enteric coronavirus (SeCoV) sequence in S gene. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, G.; D’Anza, E.; Rossi, A.; Improda, E.; Iovane, V.; Pagnini, U.; Iovane, G.; Montagnaro, S. A Serological Investigation of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome and Three Coronaviruses in the Campania Region, Southern Italy. Viruses 2023, 15, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antas, M.; Olech, M. First report of transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) and porcine respiratory coronavirus (PRCV) in pigs from Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, S.; Sydler, T.; Rosato, G.; Hilbe, M.; Kümmerlen, D.; Sidler, X.; Bachofen, C. Frequent Occurrence of Simultaneous Infection with Multiple Rotaviruses in Swiss Pigs. Viruses 2022, 14, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; Harrach, B.; Harrison, R.L.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Junglen, S.; et al. Changes to Virus Taxonomy and the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature Ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2019). Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthaler, D.; Homwong, N.; Rossow, K.; Culhane, M.; Goyal, S.; Collins, J.; Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M. Rapid Detection and High Occurrence of Porcine Rotavirus A, B, and C by RT-qPCR in Diagnostic Samples. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 209, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Shepherd, F.K.; Springer, N.L.; Mwangi, W.; Marthaler, D.G. Rotavirus Infection in Swine: Genotypic Diversity, Immune Responses, and Role of Gut Microbiome in Rotavirus Immunity. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malgarin, C.; de Grau, F. An investigation of group and subtype diversity and distribution of porcine rotaviruses in Canadian suckling piglets with diarrhea, 2019–2023. J. Swine Health Prod. 2024, 32, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuns, S.; Vyt, P.; Desmarets, L.M.B.; Roukaerts, I.D.M.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Matthijnssens, J.; Nauwynck, H.J. Presence and Characterization of Pig Group A and C Rotaviruses in Feces of Belgian Diarrheic Suckling Piglets. Virus Res. 2016, 213, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E.; Salogni, C.; Martella, V.; Alborali, G.L.; Scaburri, A.; Boniotti, M.B. Assessing the Epidemiology of Rotavirus A, B, C and H in Diarrheic Pigs of Different Ages in Northern Italy. Pathogens 2022, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goecke, N.B.; Agerlin, M.V.; Skadborg, K.; Nielsen, E.O.; Haugegaard, S.; Weber, N.R.; Larsen, L.E. Occurrence and Diversity of Porcine Rotavirus Groups A, B, C and H in Danish Pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 307, 110615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekseev, K.P.; Penin, A.A.; Mukhin, A.N.; Khametova, K.M.; Grebennikova, T.V.; Yuzhakov, A.G.; Moskvina, A.S.; Musienko, M.I.; Raev, S.A.; Mishin, A.M.; et al. Genome Characterization of a Pathogenic Porcine Rotavirus B Strain Identified in Buryat Republic, Russia in 2015. Pathogens 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyabe, F.M.; Dall Agnol, A.M.; Leme, R.A.; Oliveira, T.E.S.; Headley, S.A.; Fernandes, T.; de Oliveira, A.G.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Porcine Rotavirus B as Primary Causative Agent of Diarrhea Outbreaks in Newborn Piglets. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulski, P.; Spiekermeier, I.; Rybkowska, W.; Rynkowski, J.; Stadejek, T. First Molecular Detection of Porcine Rotavirus B (RVB) in Poland—Case Study and Genome Analysis. Porcine Health Manag. 2025, submitted.
- Campanha, J.E.T.; Possatti, F.; Lorenzetti, E.; de Almeida Moraes, D.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Longitudinal study of rotavirus C VP6 genotype I6 in diarrheic piglets up to 1 week old. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.V.; Shepherd, F.; Dominguez, F.; Pittman, J.S.; Marthaler, D.; Karriker, L.A. Evaluating natural planned exposure protocols on rotavirus shedding patterns in gilts and the impact on their suckling pigs. J. Swine Health Prod. 2023, 31, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo, L.V.; Benito, A.A.; Lázaro-Gaspar, S.; Arnal, J.L.; Martin-Jurado, D.; Menjon, R.; Quílez, J. Occurrence of Rotavirus A Genotypes and Other Enteric Pathogens in Diarrheic Suckling Piglets from Spanish Swine Farms. Animals 2022, 12, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall Agnol, A.M.; Guimarães, N.S.; Leme, R.A.; da Costa, A.R.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. The Vaccination Changed the Profile of Rotavirus Infection with the Increase of Non-Rotavirus A Species Diagnosis in One-Week-Old Diarrheic Piglets. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chepngeno, J.; Takanashi, S.; Diaz, A.; Michael, H.; Paim, F.C.; Rahe, M.C.; Hayes, J.R.; Baker, C.; Marthaler, D.; Saif, L.J.; et al. Comparative Sequence Analysis of Historic and Current Porcine Rotavirus C Strains and Their Pathogenesis in 3-Day-Old and 3-Week-Old Piglets. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, P.H.; Rosenhain, S.; Elschner, M.C.; Hotzel, H.; Machnowska, P.; Trojnar, E.; Hoffmann, K.; Johne, R. Detection of Rotavirus Species A, B and C in Domestic Mammalian Animals with Diarrhoea and Genotyping of Bovine Species A Rotavirus Strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rybkowska, W.; Woźniak, A.; Goecke, N.B.; Larsen, L.E.; Cybulski, P.; Stadejek, T. Prevalence of Rotavirus in Diarrheic Piglets on RVA-Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Farms. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101055
Rybkowska W, Woźniak A, Goecke NB, Larsen LE, Cybulski P, Stadejek T. Prevalence of Rotavirus in Diarrheic Piglets on RVA-Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Farms. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101055
Chicago/Turabian StyleRybkowska, Weronika, Aleksandra Woźniak, Nicole Bakkegård Goecke, Lars Erik Larsen, Piotr Cybulski, and Tomasz Stadejek. 2025. "Prevalence of Rotavirus in Diarrheic Piglets on RVA-Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Farms" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101055
APA StyleRybkowska, W., Woźniak, A., Goecke, N. B., Larsen, L. E., Cybulski, P., & Stadejek, T. (2025). Prevalence of Rotavirus in Diarrheic Piglets on RVA-Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Farms. Pathogens, 14(10), 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101055






