Campylobacter hepaticus Transcriptomics Identified Genes Involved in Spotty Liver Disease (SLD) Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. In Vitro Exposure of C. hepaticus to Chicken Bile
2.3. Chicken Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Epithelial Cells (LMH) and Infection
2.4. Liver Sample Collection from Spotty Liver Disease (SLD) Affected Chickens
2.5. RNA Extraction, rRNA Depletion, and mRNA Enrichment
2.6. Transcriptome Library Preparation, Sequencing, and Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.7. RT-qPCR Validation of RNA-Seq Results
2.8. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Overall Transcriptomic Response of C. hepaticus Across Different Host-Associated Environments
3.2. Transcriptomic Response of C. hepaticus to Bile Exposure
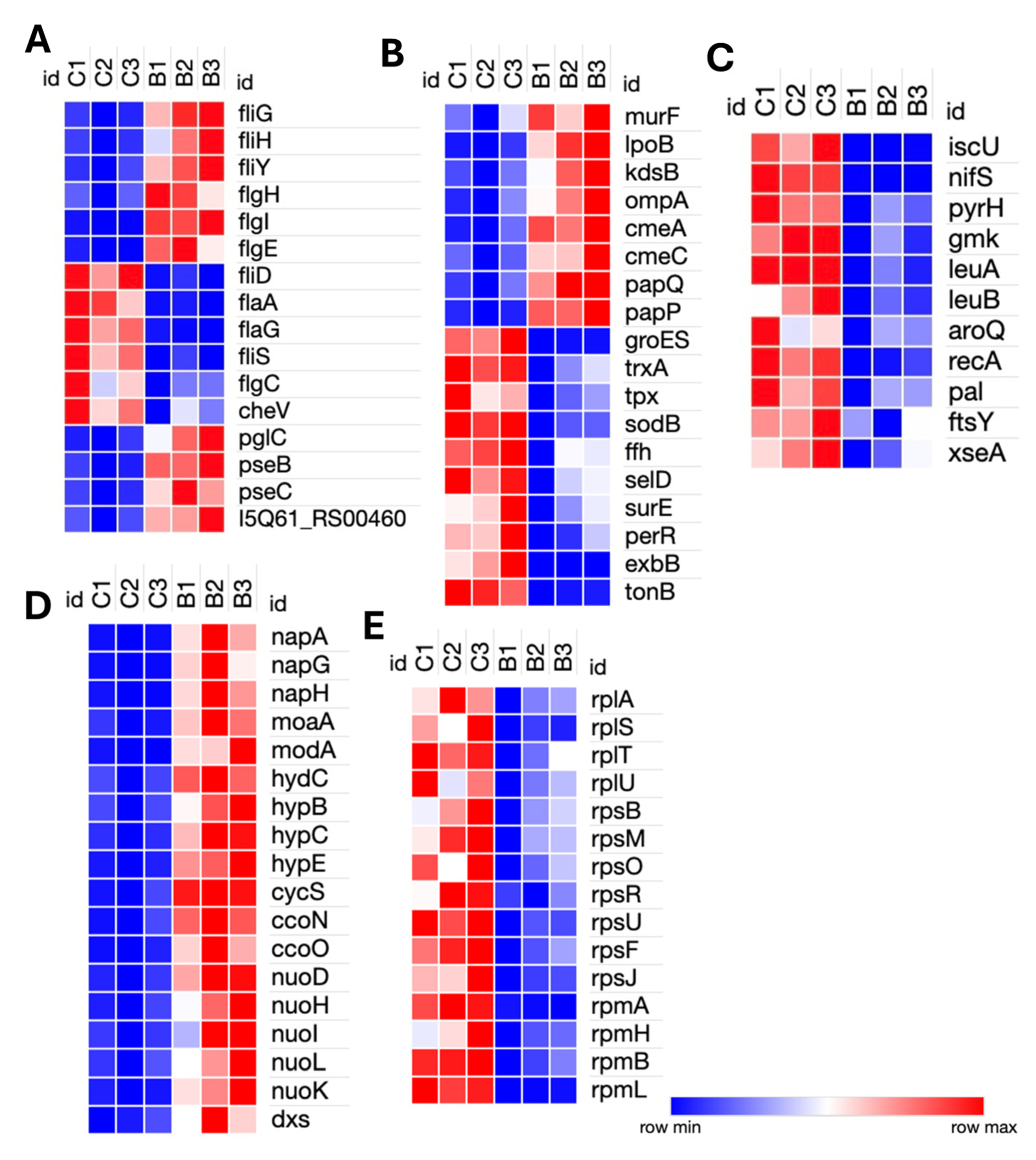
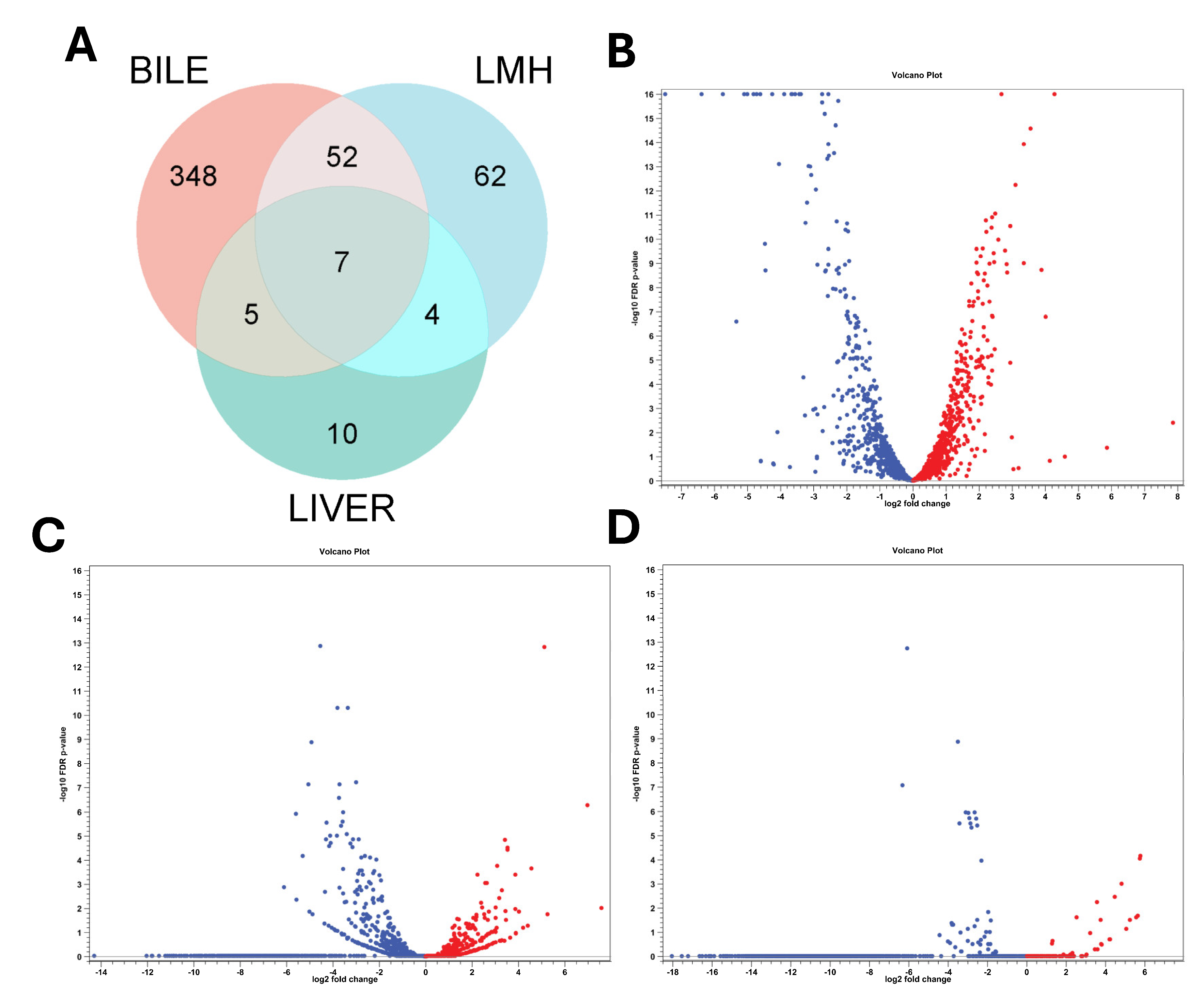

3.3. Transcriptomic Adaptation of C. hepaticus During In Vitro LMH Infection
3.4. Transcriptomic Analysis of C. hepaticus Isolated from Infected Livers
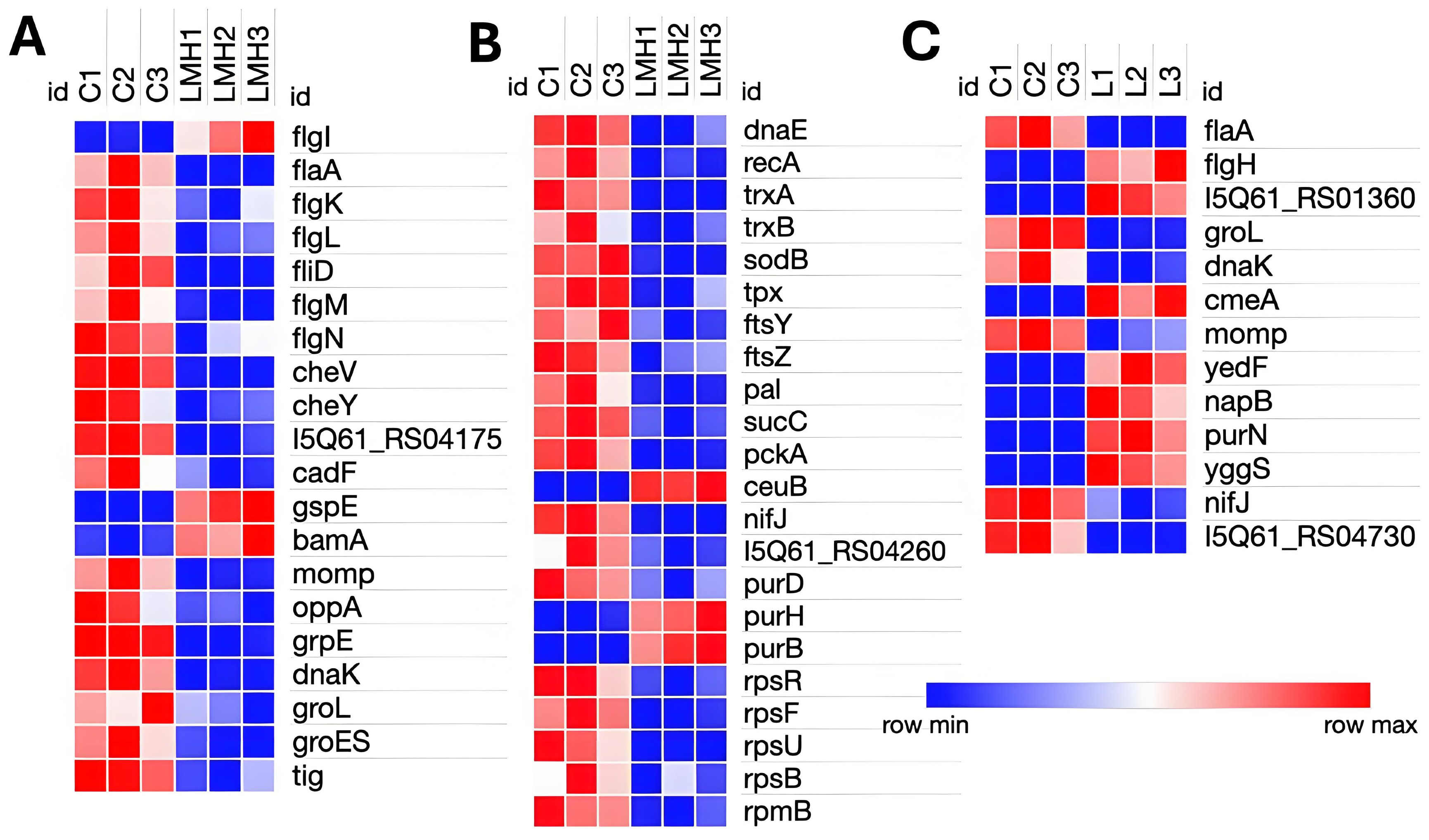
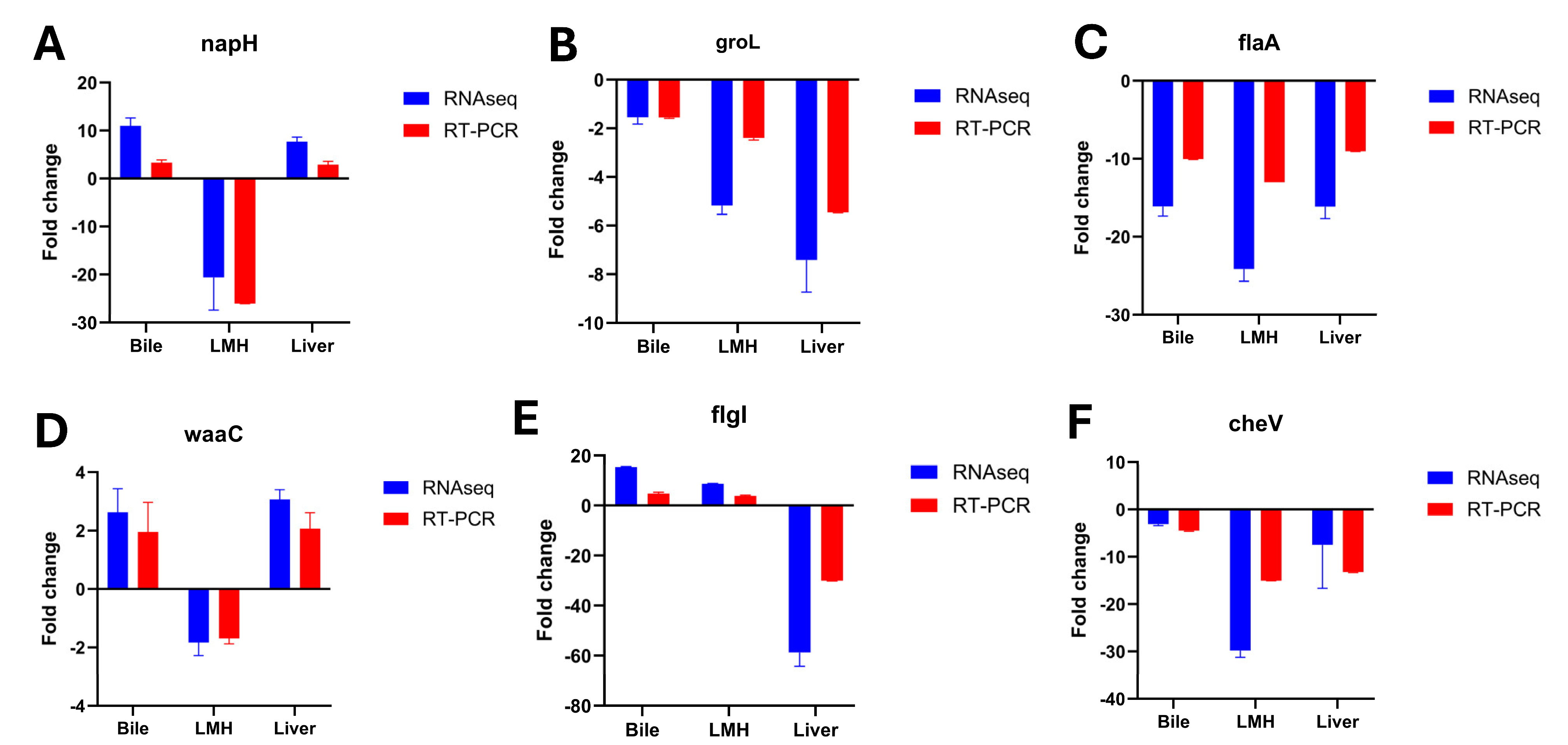
3.5. Confirmation of RNA-Seq Profiles by RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
4.1. Adaptation to Bile Exposure
4.2. Adaptation Within LMH
4.3. In Vivo Adaptation in the Liver
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SLD | Spotty liver disease |
| LMH | Chicken liver hepatocellular carcinoma epithelial cells |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene |
| RIN | RNA integrity number |
| FC | Fold change |
| LOS | Lipooligosaccharide |
| VBNC | Viable but non-culturable |
References
- Courtice, J.M.; Mahdi, L.K.; Groves, P.J.; Kotiw, M. Spotty Liver Disease: A Review of an Ongoing Challenge in Commercial Free-Range Egg Production. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 227, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, B.; Rautenschlein, S.; Hao Van, T.T.; Moore, R.J. Campylobacter hepaticus and Spotty Liver Disease in Poultry. Avian Dis. 2025, 68, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ienes-Lima, J.; Becerra, R.; Logue, C.M. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Campylobacter hepaticus Genomes Associated with Spotty Liver Disease, Georgia, United States. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1215769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, P.J.; Gao, Y.K.; Kotiw, M.; Wong, P.H.L.; Muir, W.I. Epidemiological Risk Factors and Path Models for Spotty Liver Disease in Australian Cage-Free Flocks Incorporating a Scratch Area. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtice, J.M.; Ahmad, T.B.; Wei, C.; Mahdi, L.K.; Palmieri, C.; Juma, S.; Groves, P.J.; Hancock, K.; Korolik, V.; Petrovsky, N.; et al. Detection, Characterization, and Persistence of Campylobacter hepaticus, the Cause of Spotty Liver Disease in Layer Hens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawshaw, T.R.; Chanter, J.I.; Young, S.C.L.; Cawthraw, S.; Whatmore, A.M.; Koylass, M.S.; Vidal, A.B.; Salguero, F.J.; Irvine, R.M. Isolation of a Novel Thermophilic Campylobacter from Cases of Spotty Liver Disease in Laying Hens and Experimental Reproduction of Infection and Microscopic Pathology. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.T.H.; Elshagmani, E.; Gor, M.C.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J. Campylobacter hepaticus sp. nov., Isolated from Chickens with Spotty Liver Disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4518–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.T.H.; Elshagmani, E.; Gor, M.C.; Anwar, A.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J. Induction of Spotty Liver Disease in Layer Hens by Infection with Campylobacter hepaticus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovska, L.; Tang, Y.; van Rensburg, M.J.J.; Cawthraw, S.; Nunez, J.; Sheppard, S.K.; Ellis, R.J.; Whatmore, A.M.; Crawshaw, T.R.; Irvine, R.M. Genome Reduction for Niche Association in Campylobacter hepaticus, a Cause of Spotty Liver Disease in Poultry. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.; Klein, B.; Sahin, O.; Girgis, G. Isolation and Characterization of Campylobacter hepaticus from Layer Chickens with Spotty Liver Disease in the United States. Avian Dis. 2018, 62, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, C.; Wilson, T.B.; Quinteros, J.A.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J.; Van, T.T.H. Enhancement of Campylobacter hepaticus Culturing to Facilitate Downstream Applications. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao Van, T.T.; Lacey, J.A.; Vezina, B.; Phung, C.; Anwar, A.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J. Survival Mechanisms of Campylobacter hepaticus Identified by Genomic Analysis and Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of in Vivo and in Vitro Derived Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiarpinitnun, P.; Iwakiri, A.; Fuke, N.; Pongsawat, P.; Miyanishi, C.; Sasaki, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Matsui, Y.; Luangtongkum, T.; Yamada, K.; et al. Involvement of Campylobacter Species in Spotty Liver Disease-like Lesions in Broiler Chickens Detected at Meat Inspections in Miyazaki Prefecture, Japan. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.K.; Singh, M.; Muir, W.I.; Kotiw, M.; Groves, P.J. Identification of Epidemiological Risk Factors for Spotty Liver Disease in Cage-Free Layer Flocks in Houses with Fully Slatted Flooring in Australia. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; McMullen, L.; Jeon, B. Impact of Oxidative Stress Defense on Bacterial Survival and Morphological Change in Campylobacter jejuni under Aerobic Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palyada, K.; Sun, Y.Q.; Flint, A.; Butcher, J.; Naikare, H.; Stintzi, A. Characterization of the Oxidative Stress Stimulon and PerR Regulon of Campylobacter jejuni. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.F. Roles of Fe Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase in Resistance of Campylobacter coli to Freeze-Thaw Stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3110–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cagliero, C.; Guo, B.; Barton, Y.W.; Maurel, M.C.; Payot, S.; Zhang, Q. Bile Salts Modulate Expression of the CmeABC Multidrug Efflux Pump in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 7417–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottapu, C.; Sahin, O.; Edison, L.K.; Srednik, M.E.; Kariyawasam, S. Complete Genome Sequences of Campylobacter hepaticus Strains USA1 and USA5 Isolated from a Commercial Layer Flock in the United States. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2025, 14, e0091924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arukha, A.; Denagamage, T.N.; Butcher, G.; Kariyawasam, S. Complete Genome Sequence of Campylobacter hepaticus Strain UF2019SK1, Isolated from a Commercial Layer Flock in the United States. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Sahin, O.; Zhang, Q. Complete Genome Sequence of Campylobacter hepaticus USA52, Associated with Chicken Spotty Liver Disease. Genome Announc. 2021, 10, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.T.H.; Phung, C.; Anwar, A.; Wilson, T.B.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J. Campylobacter bilis, the Second Novel Campylobacter Species Isolated from Chickens with Spotty Liver Disease, Can Cause the Disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 276, 109603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, L.K.; Kudva, I.T.; Kariyawasam, S. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 on Bovine Rectoanal Junction Cells and Human Colonic Epithelial Cells during Initial Adherence. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, L.K.; Kariyawasam, S. From the Gut to the Brain: Transcriptomic Insights into Neonatal Meningitis Escherichia Coli Across Diverse Host Niches. Pathogens 2025, 14, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, M.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Hill, C. The Interaction between Bacteria and Bile. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 625–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremers, C.M.; Knoefler, D.; Vitvitsky, V.; Banerjee, R.; Jakob, U. Bile Salts Act as Effective Protein-Unfolding Agents and Instigators of Disulfide Stress in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1610–E1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negretti, N.M.; Gourley, C.R.; Clair, G.; Adkins, J.N.; Konkel, M.E. The Food-Borne Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni Responds to the Bile Salt Deoxycholate with Countermeasures to Reactive Oxygen Species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, S.L.; Maier, R.J.; Sawers, R.G.; Greening, C. Molecular Hydrogen Metabolism: A Widespread Trait of Pathogenic Bacteria and Protists. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, N.; Ding, X.; Peng, L.; Deng, X. The Molybdate-Binding Protein ModA Is Required for Proteus Mirabilis-Induced UTI. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1156273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.C.; Freel Meyers, C.L. DXP Synthase Function in a Bacterial Metabolic Adaptation and Implications for Antibacterial Strategies. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakur, S.G.J.; Williamson, S.L.; Pavic, A.; Gao, Y.K.; Harris, T.; Kotiw, M.; Muir, W.I.; Groves, P.J. Developing a Selective Culturing Approach for Campylobacter hepaticus. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajam, I.A.; Dar, P.A.; Shahnawaz, I.; Jaume, J.C.; Lee, J.H. Bacterial Flagellin-a Potent Immunomodulatory Agent. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmi, A.; Nasher, F.; Dorrell, N.; Wren, B.; Gundogdu, O. Revisiting Campylobacter jejuni Virulence and Fitness Factors: Role in Sensing, Adapting, and Competing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 607704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friman, V.P.; Lindstedt, C.; Hiltunen, T.; Laakso, J.; Mappes, J. Predation on Multiple Trophic Levels Shapes the Evolution of Pathogen Virulence. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.A.; Bogacz, M.; El Abbar, F.M.; Browning, D.D.; Hsueh, B.Y.; Waters, C.M.; Lee, V.T.; Thompson, S.A. The Campylobacter jejuni Response Regulator and Cyclic-Di-GMP Binding CbrR Is a Novel Regulator of Flagellar Motility. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotkov, K.V.; Sandkvist, M.; Hol, W.G.J. The Type II Secretion System: Biogenesis, Molecular Architecture and Mechanism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Gao, B.; Novik, V.; Galán, J.E. Quantitative Proteomics of Intracellular Campylobacter jejuni Reveals Metabolic Reprogramming. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allameh, A.; Niayesh-Mehr, R.; Aliarab, A.; Sebastiani, G.; Pantopoulos, K. Oxidative Stress in Liver Pathophysiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randaisi, V.R.; Bunch, M.L.; Beavers, W.N.; Rogers, T.; Mesler, R.; Ashurst, T.D.; Donohoe, D.R.; Monteith, A.J.; Johnson, J.G. Efficient Gastrointestinal Colonization by Campylobacter jejuni Requires Components of the ChuABCD Heme Transport System. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.E.; Williams, P.H.; Ketley, J.M. Pumping Iron: Mechanisms for Iron Uptake by Campylobacter. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3157–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdaneta, V.; Casadesús, J. Interactions between Bacteria and Bile Salts in the Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Tracts. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomfield, S.J.; Midwinter, A.C.; Biggs, P.J.; French, N.P.; Marshall, J.C.; Hayman, D.T.S.; Carter, P.E.; Mather, A.E.; Fayaz, A.; Thornley, C.; et al. Genomic Adaptations of Campylobacter jejuni to Long-Term Human Colonization. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Makino, F.; Miyata, T.; Minamino, T.; Kato, T.; Namba, K. Structure of the Molecular Bushing of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutourina, O.A.; Bertin, P.N. Regulation Cascade of Flagellar Expression in Gram-Negative Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. The Role of Fecal Sulfur Metabolome in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 311, 151513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Bu, T.; Zhang, J.; Lu, M.; Ha, N.C.; Quan, C.; Nam, K.H.; et al. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Pyridoxal Phosphate Homeostasis Protein YggS from Fusobacterium Nucleatum. Molecules 2022, 27, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzieciol, M.; Wagner, M.; Hein, I. CmeR-Dependent Gene Cj0561c Is Induced More Effectively by Bile Salts than the CmeABC Efflux Pump in Both Human and Poultry Campylobacter jejuni Strains. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, E.M.; Raftery, M.; Goodchild, A.; Mendz, G.L. Campylobacter jejuni Response to Ox-Bile Stress. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.J.; Semchenko, E.A.; Korolik, V. Glycoconjugates Play a Key Role in Campylobacter jejuni Infection: Interactions between Host and Pathogen. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.; Allan, E.; Coates, A.R.M. Stress Wars: The Direct Role of Host and Bacterial Molecular Chaperones in Bacterial Infection. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3693–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figaj, D. The Role of Heat Shock Protein (Hsp) Chaperones in Environmental Stress Adaptation and Virulence of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bommineni, V.; Edison, L.K.; Gottapu, C.; Butcher, G.D.; Kariyawasam, S. Campylobacter hepaticus Transcriptomics Identified Genes Involved in Spotty Liver Disease (SLD) Pathogenesis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101048
Bommineni V, Edison LK, Gottapu C, Butcher GD, Kariyawasam S. Campylobacter hepaticus Transcriptomics Identified Genes Involved in Spotty Liver Disease (SLD) Pathogenesis. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101048
Chicago/Turabian StyleBommineni, Varsha, Lekshmi K. Edison, Chaitanya Gottapu, Gary D. Butcher, and Subhashinie Kariyawasam. 2025. "Campylobacter hepaticus Transcriptomics Identified Genes Involved in Spotty Liver Disease (SLD) Pathogenesis" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101048
APA StyleBommineni, V., Edison, L. K., Gottapu, C., Butcher, G. D., & Kariyawasam, S. (2025). Campylobacter hepaticus Transcriptomics Identified Genes Involved in Spotty Liver Disease (SLD) Pathogenesis. Pathogens, 14(10), 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101048




