Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance Paradigm of Enterobacterales in Animal-Derived Food Sources: A One Health Disquiet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Study Settings
2.2. Sampling, Categorization, and Transportation
2.3. Isolation and Identification of Enterobacterales
2.4. MALDI-TOF
2.5. Identification of VAGs Among Enterobacterales
2.6. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.7. Rapid Polymyxin Test (RPT)
2.8. Carbapenemase Nordmann-Poirel CLSI (CarbaNP CLSI) Test
2.9. Identification of ARGs Among Isolates
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Biochemical Identification of Enterobacterales
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Enterobacterales from Animal-Based Foods
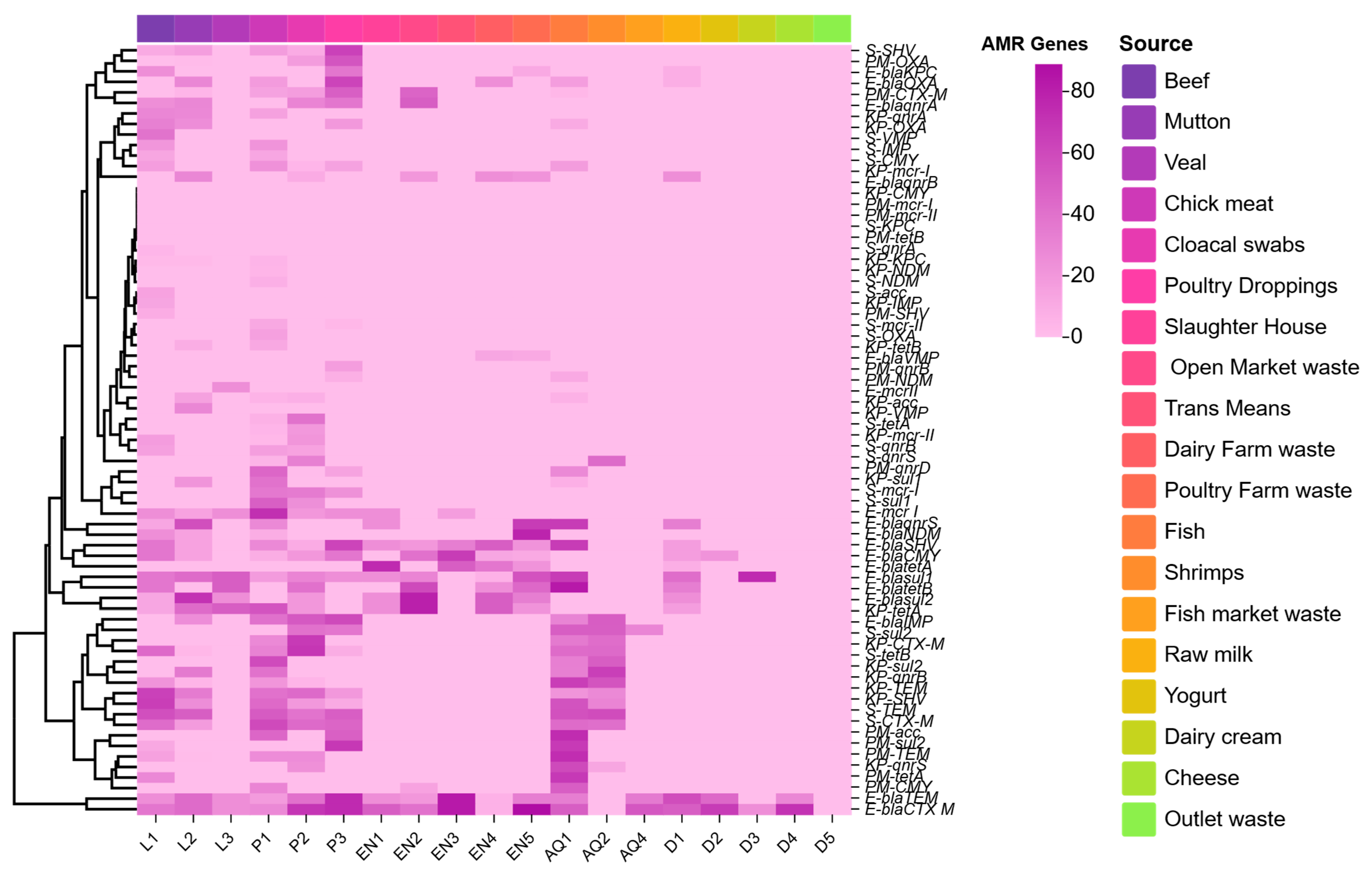
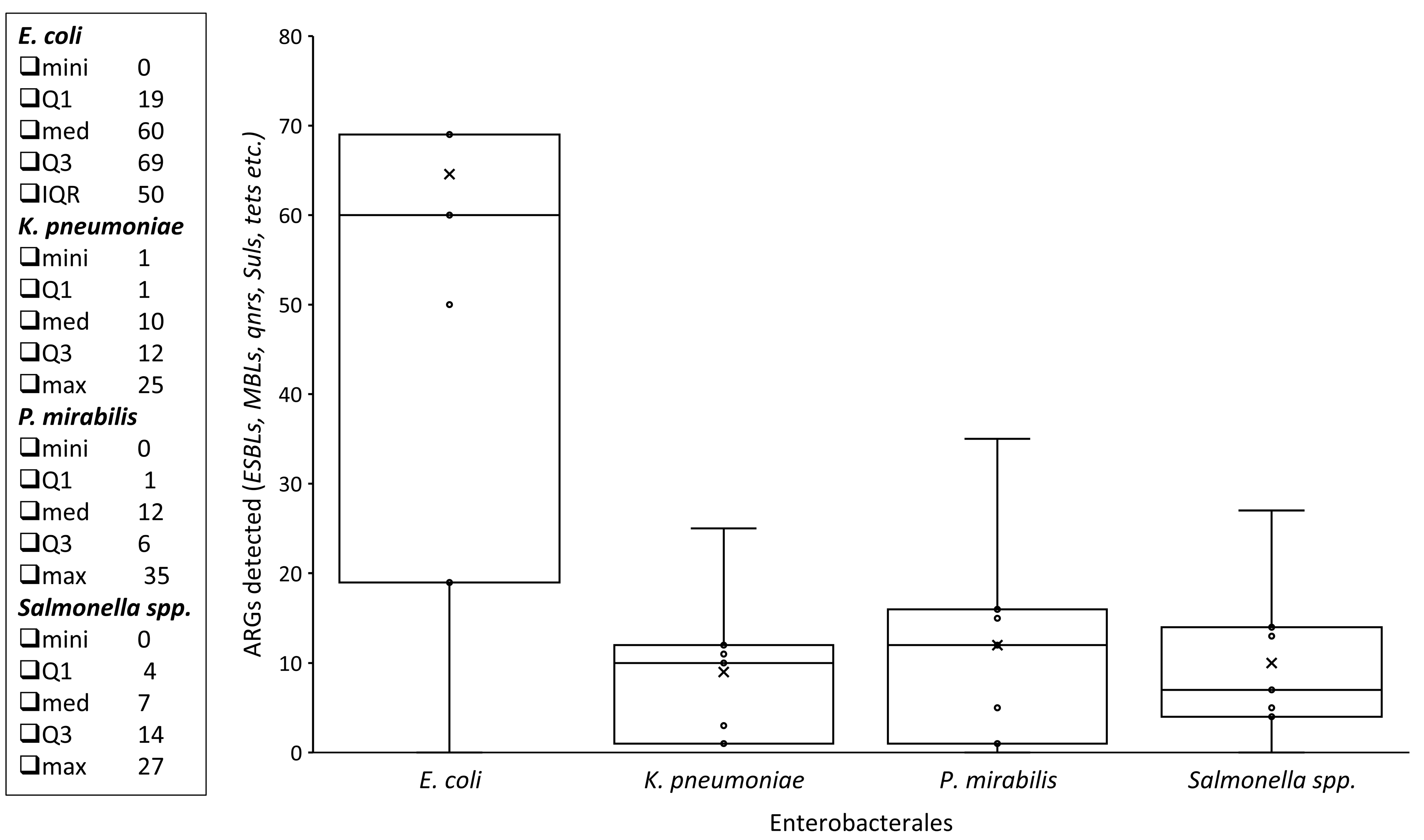
3.3. ARGs Among Enterobacterales Isolates
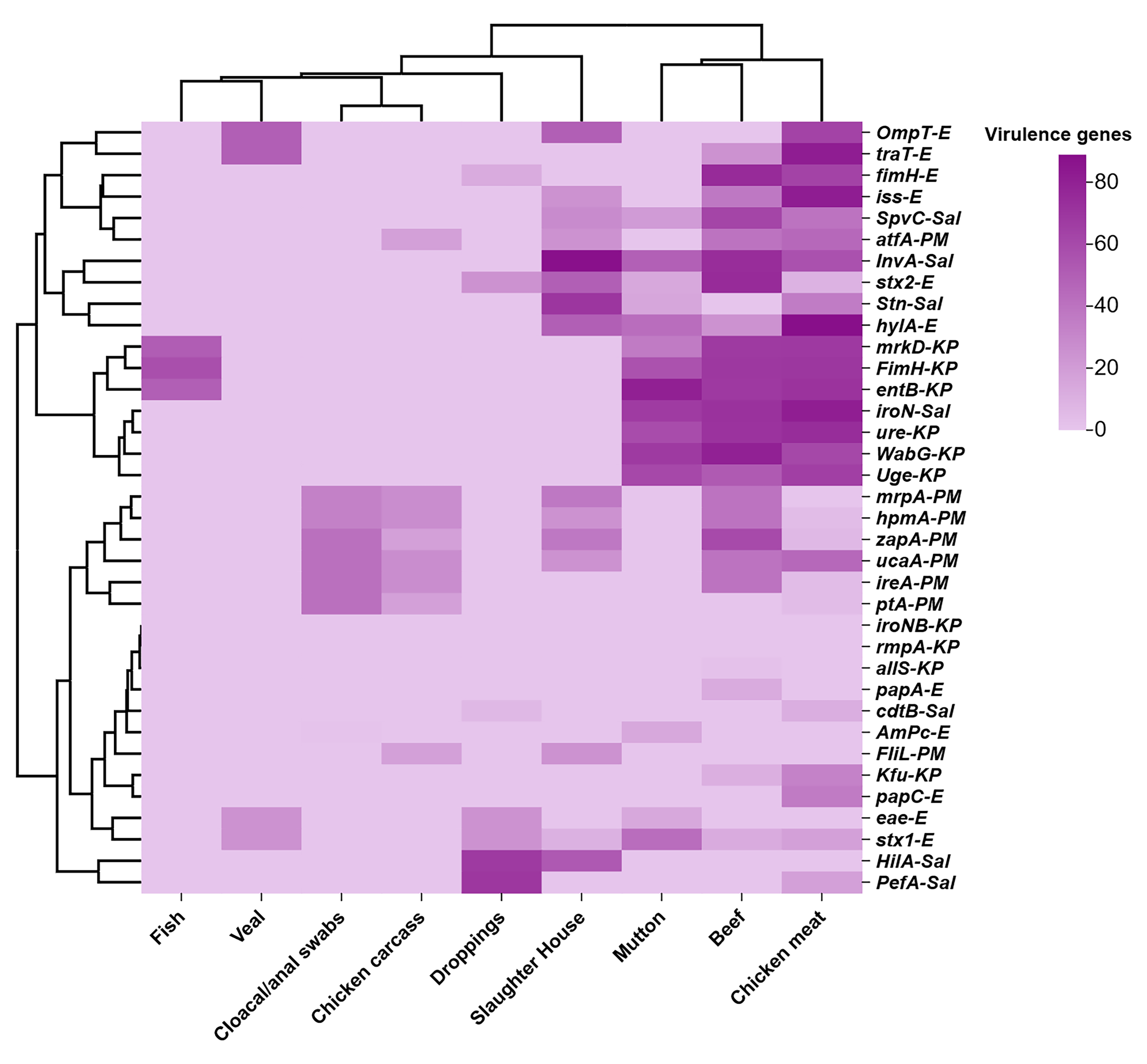
3.4. VAGs Among Enterobacterales Isolates
3.5. Co-Existence of blaNDM and mcr-1 Among Enterobacterales Isolated from Various Animal-Derived Foods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight |
| ARGs | Antibiotic resistance genes |
| VAGs | Virulence-associated genes |
References
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L. Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from One Health and Global Health perspectives. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Mas-Pla, J.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Čelić, M.; Castaño, M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Borrego, C.M.; Balcázar, J.L.; Petrović, M. Antibiotics, antibiotic resistance and associated risk in natural springs from an agroecosystem enviorment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 857, 159202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, T.; Trethewey, B. Agroecology for Structural One Health. Development 2023, 66, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.; Pencheon, D.; Squires, N. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and their implementation: A national global framework for health, development and equity needs a systems approach at every level. Br. Med. Bull. 2017, 124, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, P.; Brown, M.R. Screening for novel antimicrobial activity/compounds in the pharmaceutical industry. In Microbiological Quality Assurance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- Mulchandani, R.; Tiseo, K.; Nandi, A.; Klein, E.; Gandra, S.; Laxminarayan, R.; Van Boeckel, T. Global trends in inappropriate use of antibiotics, 2000–2021: Scoping review and prevalence estimates. BMJ Public Health 2025, 3, e002411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schar, D.; Klein, E.Y.; Laxminarayan, R.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okocha, R.C.; Olatoye, I.O.; Adedeji, O.B. Food safety impacts of antimicrobial use and their residues in aquaculture. Public Health Rev. 2018, 39, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Saleemi, M.K.; Umair, M.; Naseem, M.N.; He, C.; Khan, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Excessive use of medically important antimicrobials in food animals in Pakistan: A five-year surveillance survey. Glob. Health Action 2019, 12 (Suppl. 1), 1697541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial resistance: A one health perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Aslam, B.; Rasool, M.H.; Bekhit, M.M.S.; Sasanya, J. A Health Threat from Farm to Fork: Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Co-Harboring blaNDM-1 and mcr-1 in Various Sources of the Food Supply Chain. Pathogens 2024, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Leão, C.; Clemente, L.; Albuquerque, T.; Amaro, A. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profilesand Resistance Mechnasims of β-Lactams and Polymyxins of Escherchia coli from Briolers Raised under Intensive and Extensive Production Systems. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-F.; Lu, P.-L.; Tseng, S.-P. Clinical impact of the revised 2019 CLSI levofloxacin breakpoints in patients with Enterobacterales bacteremia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Mowlaboccus, S.; Jackson, B.; Cai, C.; Coombs, G.W. Antimicrobial resistance among clinically significant bacteria in wildlife: An overlooked one health concern. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 64, 107251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.; Stanton, I.C.; Tipper, H.J.; Read, D.S. Environment and Rural Affairs Monitoring & Modelling Programme-ERAMMP Report-55: Evidence Review on the Entry and Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in the Rural Water Environment in Wales; Centre for Ecology & Hydrology: Bangor, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Xi, L.; Wang, F.; Tian, J.; Luo, W. Antibiotic-resistance profiles and genetic diversity of Shigella isolates in China: Implications for control strategies. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2024, 21, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwike, I.E.; Ugwu, M.C.; Ejikeugwu, P.C.; Ujam, N.T.; Iroha, I.R.; Esimone, C.O. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. causing childhood diarrhoea in Awka, South-Eastern Nigeria. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2023, 47, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Khan, S.U.H.; Khan, M.J.; Khattak, B.; Fozia, F.; Ahmad, I.; Wadaan, M.A.; Khan, M.F.; Baabbad, A.; Goyal, S.M. Multiple-Drug Resistant Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli in Raw Milk of Dairy Bovine. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ullah, S.; Khan, S.U.H.; Ali, T.; Zeb, M.T.; Riaz, M.H.; Khan, S.; Goyal, S.M. Molecular characterization and antibiotic susceptibility of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) isolated from raw milk of dairy bovines in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmancier, H.; Domingues, C.P.F.; Rebelo, J.S.; Amaro, A.; Dionísio, F.; Pothier, J.; Serra, O.; Nogueira, T. Are Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Genes Linked? A Comprehensive Analysis of Bacterial Chromosomes and Plasmids. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shang, Z.; Zou, H.; Zhao, L.; Hou, X.; Wu, T.; Meng, M.; Li, X. Steady existence of Escherichia coli co-resistant to carbapenem and colistin in an animal breeding area even after the colistin forbidden. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Hoong, L.W.; Siong, Y.L.; Mustapha, Z.; Zalati, C.W.S.C.W.; Aklilu, E.; Mohamad, M.; Kamaruzzaman, N.F. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli isolated from broilers in the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas-Caldes, C.; Cisneros-Vásquez, E.; Zambrano, A.; Mosquera-Maza, A.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Rey, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Calvopiña, M.; de Waard, J.H. Co-harboring of beta-lactamases and mcr-1 genes in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from healthy carriers and backyard animals in rural communities in Ecuador. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 856. [Google Scholar]
- Huda, M.N.U.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Tahir, A.H.; Ahmad, A.A.; Bin Zahoor, U.; Ahmad, W.; Raza, A.; Afzal, F.; Khalid, A.R.; Shabbir, M.A.B. Molecular detection and prevalence of colistin-resistant Escherichia coli in poultry and humans: A one health perspective. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Ye, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from retail foods in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; Feng, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhou, M.; Hou, S.; Wang, G.; Hao, H.; et al. Epidemiology, environmental risks, virulence, and resistance determinants of Klebsiella pneumoniae from dairy cows in Hubei, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, M.; Siddiqui, T.; Sengar, S.; Sahu, C. A comparative in vitro sensitivity study of “cefepime-tazobactam” and otherantibiotics against Gram-negative isolates from intensive care unit. J. Lab. Physician 2024, 16, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharidi, N.A.; Balta, I.; Houhoula, D.; Tsantes, A.G.; Lalliotis, G.P.; Polydera, A.C.; Stamatis, H.; Halvatsiotis, P. High prevalence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Greek meat products: Detection of virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes by molecular techniques. Foods 2022, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.U.; Fizza, K.; Chughtai, M.I.; Shafique, M.; Seytkhanova, B.; Yktiyarov, A.; Aatika; Saleem, Z.; Mustafa, S.; Tufail, Z.; et al. Food Safety Concerns in Pakistan: Monitoring of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria and Residue Contamination in Commercially Available Fish and Poultry Meat Samples. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.B.; Anwar, K.A. Phenotypic and genotypic detection of extended spectrum beta lactamase enzyme in Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267221. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaq, K.; Ahmad, A.; Rafique, A.; Aslam, R.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.A.; Sarwar, N.; Aslam, M.A.; Aslam, B.; Arshad, M.I. Occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis from chicken carcass. Pak. Vet. J. 2022, 42, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagar, S.; Qambrani, N.A. Bacteriological quality assessment of poultry chicken meat and meat contact surfaces for the presence of targeted bacteria and determination of antibiotic resistance of Salmonella spp. in Pakistan. Food Control 2023, 151, 109786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Rasoo, M.H.; Khurshid, M.; Aslam, B. Genetic outlook of Colistin resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium recovered from Poultry-Environment Interface: A One Health Standpoint. Pak. Vet. J. 2025, 45, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Xu, J.; Yin, D.; Sun, C.; Liu, D.; Zhai, W.; Bai, R.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, S.; et al. Transmission of bla NDM in Enterobacteriaceae among animals, food and human. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2337678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenović, K.G.; Grujović, M.Ž.; Kiš, M.; Furmeg, S.; Tkalec, V.J.; Stefanović, O.D.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.D. Enterobacteriaceae in food safety with an emphasis on raw milk and meat. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Niu, D. foodborne Enterobacteriaceae of animal origin. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 772359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
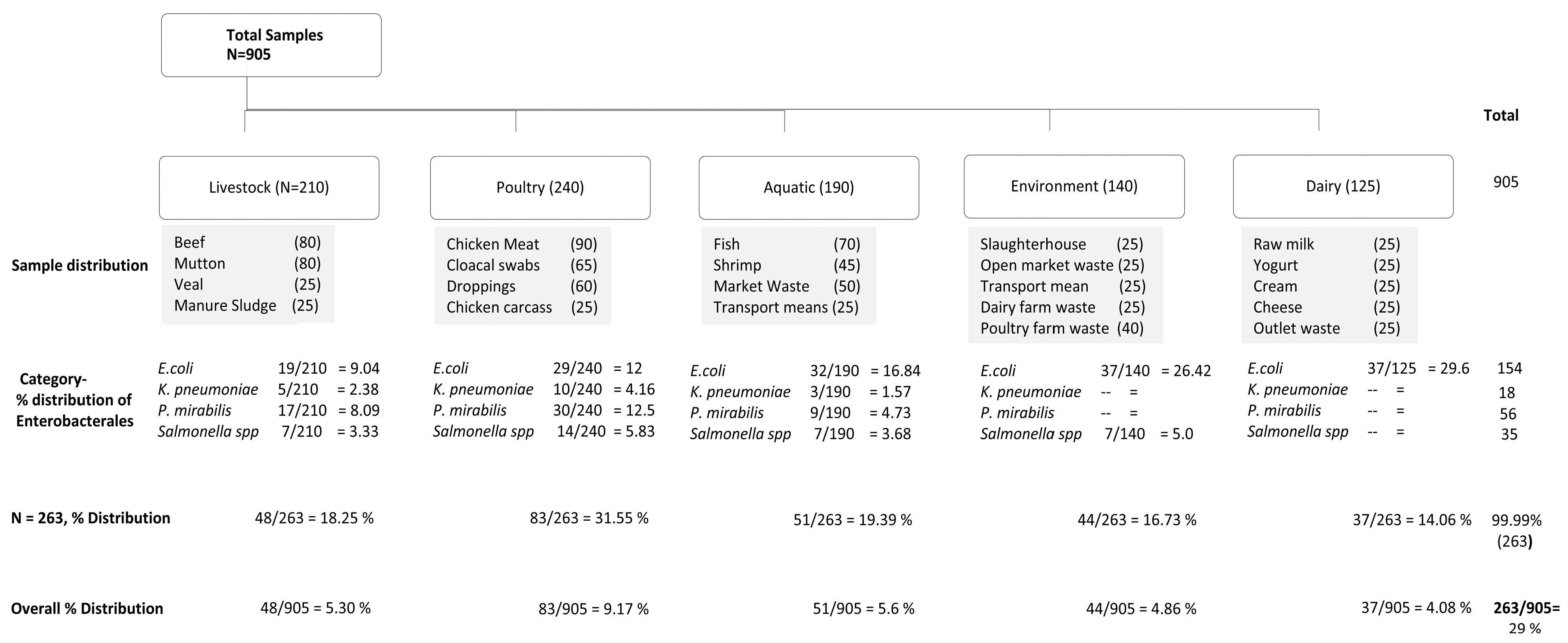


| Enterobacterales | Sample Categories * | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Livestock | Poultry | Aquatic | Environment | Dairy | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| Bf | Mt | Vl | MS | mt | Sbs | CC | Dpg | Fis | Shri | Mkt | Trp | SH | OPW | TM | DFW | PFW | RM | YGT | Cr | CHS | OW | ||
| E. coli | 8 | 7 | 4 | -- | 11 | 10 | -- | 8 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 17 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 12 | 9 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 154 |
| K. pneumoniae | 2 | 3 | -- | -- | 5 | 2 | -- | 3 | 2 | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 18 |
| P. mirabilis | 5 | 4 | -- | 8 | 7 | 12 | 11 | -- | 4 | -- | 5 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 56 |
| Salmonella spp. | 3 | 4 | -- | -- | 6 | -- | -- | 8 | 4 | 3 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 7 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 35 |
| Total | 18 | 18 | 4 | 8 | 29 | 24 | 11 | 19 | 16 | 6 | 12 | 17 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 8 | 16 | 12 | 9 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 263 |
| % Distribution from positive samples (n = 263) | 6.84 | 6.84 | 1.52 | 3.0 | 11.0 | 9.12 | 4.18 | 7.22 | 6.0 | 2.28 | 4.56 | 6.46 | 1.52 | 3.80 | 2.28 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 4.56 | 3.42 | 1.52 | 2.66 | 1.90 | |
| Overall % Distribution (n = 905) | 1.98 | 1.98 | 0.40 | 0.88 | 3.20 | 2.65 | 1.21 | 2.09 | 1.76 | 0.66 | 1.32 | 1.87 | 0.44 | 1.10 | 0.66 | 0.88 | 1.76 | 1.32 | 0.99 | 0.44 | 0.77 | 0.55 | 29% |
| Statistical Analysis | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p-value | F crit | |||||||||||||||||
| Between Groups | 881.16 | 21 | 41.96 | 1.71 | 0.037 | 1.637 | |||||||||||||||||
| Within Groups | 3242.96 | 132 | 24.57 | 1.64 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 4124.13 | 153 | 66.53 | 3.34 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Isolates | Specimen Category | Samples Sources | Total Samples | Positive Samples | blaNDM | mcr-1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | Livestock | Beef | 25 | 8 | 3 (37.5%) | 2 (25%) | <0.05 |
| Mutton | 25 | 7 | 1 (14.28%) | 1 (14.28%) | |||
| Veal | 25 | 4 | ND | 1 (25%) | |||
| Poultry | Chicken meat | 25 | 11 | 3 (27.27%) | 8 (72.72%) | ||
| Cloacal/anal swabs | 25 | 10 | 1 (10%) | 2 (20%) | |||
| Droppings | 25 | 8 | 5 (62.5%) | 2 (25%) | |||
| Environment | Slaughterhouse | 25 | 4 | 1 (25%) | 1 (25%) | ||
| Open market waste | 25 | 10 | 1 (20%) | ND | |||
| Transport Means | 25 | 6 | 2 (33.33%) | 1 (16.67%) | |||
| Dairy farm waste | 25 | 8 | 4 (50%) | ND | |||
| Poultry farm waste | 25 | 9 | 2 (22.22%) | ND | |||
| Aquatic | Fish | 25 | 6 | 4 (66.67%) | ND | ||
| Shrimps | 25 | 2 | ND | ND | |||
| Market waste | 25 | 7 | ND | ND | |||
| Transport means | 25 | 17 | ND | ND | |||
| Dairy | Raw milk | 25 | 12 | 2 (16.67%) | ND | ||
| Yogurt | 25 | 9 | ND | ND | |||
| Dairy cream | 25 | 4 | ND | ND | |||
| Cheese | 25 | 7 | ND | ND | |||
| Outlet waste | 25 | 5 | ND | ND | |||
| K. pneumoniae | Livestock | Beef | 15 | 2 | ND | 17.11 | |
| Mutton | 15 | 3 | ND | ND | |||
| Poultry | Chicken meat | 20 | 5 | ND | 2 (23.21) | ||
| Cloacal swabs | 15 | 2 | ND | 4.01 | |||
| Poultry droppings | 15 | 3 | ND | 1 (14.36) | |||
| Aquatic | Fish | 10 | 2 | ND | 17.45 | ||
| Shrimp | 10 | 1 | ND | ND | |||
| P. mirabilis | Poultry | Chicken meat | 25 | 7 | ND | ND | |
| Chicken carcass | 25 | 11 | ND | ND | |||
| cloacal/anal swabs | 25 | 12 | 1 (8%) | ND | |||
| Livestock | Beef | 25 | 5 | ND | ND | ||
| Mutton | 25 | 4 | ND | ND | |||
| Manure sludge | 25 | 8 | ND | ND | |||
| Aquatic | Raw fish | 25 | 4 | 0 (11.23%) | ND | ||
| Fish Market sludge/waste | 25 | 5 | ND | ND | |||
| Salmonella spp. | Livestock | Beef | 15 | 3 | ND | ND | |
| Mutton | 15 | 4 | ND | ND | |||
| Poultry | chicken meat | 20 | 6 | ND | 2 (36.4) | ||
| poultry farm | 15 | 7 | ND | 2 (34.67) | |||
| poultry droppings | 20 | 8 | ND | 2 (23.45) | |||
| Aquatic | Fish | 10 | 4 | ND | ND | ||
| shrimp | 10 | 3 | ND | ND | |||
| Total | 905 | 263 | 30 | 27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarwar, A.; Aslam, B.; Rasool, M.H.; Shafique, M.; Khurshid, M.; Sasanya, J.J.; Aljasir, S.F. Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance Paradigm of Enterobacterales in Animal-Derived Food Sources: A One Health Disquiet. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101040
Sarwar A, Aslam B, Rasool MH, Shafique M, Khurshid M, Sasanya JJ, Aljasir SF. Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance Paradigm of Enterobacterales in Animal-Derived Food Sources: A One Health Disquiet. Pathogens. 2025; 14(10):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101040
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarwar, Ayesha, Bilal Aslam, Muhammad Hidayat Rasool, Muhammad Shafique, Mohsin Khurshid, James Jacob Sasanya, and Sulaiman F. Aljasir. 2025. "Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance Paradigm of Enterobacterales in Animal-Derived Food Sources: A One Health Disquiet" Pathogens 14, no. 10: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101040
APA StyleSarwar, A., Aslam, B., Rasool, M. H., Shafique, M., Khurshid, M., Sasanya, J. J., & Aljasir, S. F. (2025). Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance Paradigm of Enterobacterales in Animal-Derived Food Sources: A One Health Disquiet. Pathogens, 14(10), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14101040







