Dermatological Presentation of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Two Elderly Italian Inpatients
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Transient localized edema or urticaria where the filariform larva (L3, up to 600 µm long) enters the intact skin of the host
- -
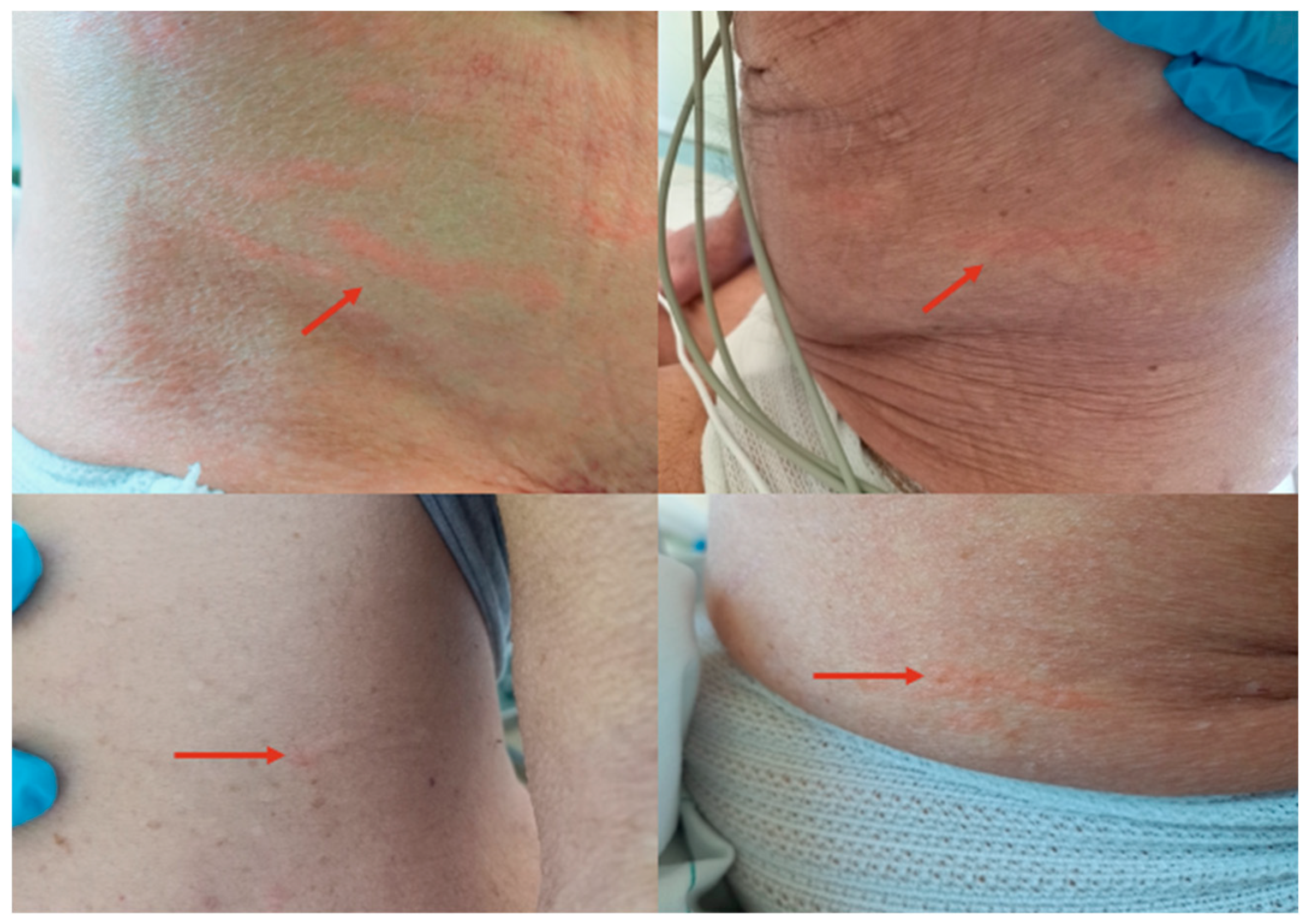
- Larva currens as a pathognomonic serpiginous urticarial running lesion (at least 1 cm/h) that appears mainly on the skin of the inferior abdomen, buttocks, or perineal area, caused by L3 larval passage through the dermal layer of the host [13];
- -
- -
- -
2. Case Report 1
3. Case Report 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). 2030 Targets for Soil-Transmitted Helminthiases Control Programmes. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330611 (accessed on 19 March 2022).
- Buonfrate, D.; Bisanzio, D.; Giorli, G.; Odermatt, P.; Fürst, T.; Greenaway, C.; French, M.; Reithinger, R.; Gobbi, F.; Montresor, A.; et al. The Global Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonfrate, D.; Baldissera, M.; Abrescia, F.; Bassetti, M.; Caramaschi, G.; Giobbia, M.; Mascarello, M.; Rodari, P.; Scattolo, N.; Napoletano, G.; et al. Epidemiology of Strongyloides stercoralis in northern Italy: Results of a multicentre case-control study, February 2013 to July 2014. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrescia, F.F.; Falda, A.; Caramaschi, G.; Scalzini, A.; Gobbi, F.; Angheben, A.; Gobbo, M.; Schiavon, R.; Rovere, P.; Bisoffi, Z. Reemergence of strongyloidiasis, northern Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1531–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirisi, M.; Salvador, E.; Bisoffi, Z.; Gobbo, M.; Smirne, C.; Gigli, C.; Minisini, R.; Fortina, G.; Bellomo, G.; Bartoli, E. Unsuspected strongyloidiasis in hospitalised elderly patients with and without eosinophilia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardini, G.; Froeschl, G.; Gurrieri, F.; De Francesco, M.A.; Cattaneo, C.; Marchese, V.; Piccinelli, G.; Corbellini, S.; Pagani, C.; Santagiuliana, M.; et al. Strongyloides stercoralis infection: An underlying cause of invasive bacterial infections of enteric origin. Results from a prospective cross-sectional study of a northern Italian tertiary hospital. Infection 2023, 51, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Gil, C.; Estrellas, B.; Middleton, J.R. Corticosteroid-induced asthma: A manifestation of limited hyperinfection syndrome due to Strongyloides stercoralis. South Med. J. 1995, 88, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costache, C.; Colosi, I.A.; Neculicioiu, V.S.; Florian, D.I.; Petrushev, B.; Vasvari, A.; Seicean, A. A Rare Case of Strongyloides stercoralis Hyperinfection in a Diabetic Patient from Romania-Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pathogens 2023, 12, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.N.; Oliveira, C.L.; Araujo, W.A.C.; Souza, A.B.S.; Silva, M.L.S.; da Cruz, I.D.R.; Sampaio, L.M.; Dos Santos, J.S.B.; Teixeira, M.C.A.; Soares, N.M. Strongyloides stercoralis in Alcoholic Patients: Implications of Alcohol Intake in the Frequency of Infection and Parasite Load. Pathogens 2020, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira Dias, O.; Belousova, N.; Sharif, N.; Brasg, I.; Singer, L.G.; Tikkanen, J.; Chaparro, C.; Rotstein, C. Strongyloides hyper-infection in a lung transplant recipient: Case report and review of the literature. J. Assoc. Med. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Can. 2022, 7, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutman, T.B. Human infection with Strongyloides stercoralis and other related Strongyloides species. Parasitology 2017, 144, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Zhang, Q.W.; Tang, S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.B. Co-infection with Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome and Klebsiella in a nephrotic syndrome patient: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e18247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feria, L.; Torrado, M.; Anton-Vazquez, V. Reactivation of Strongyloides stercoralis in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia receiving dexamethasone. Med. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 158, 242–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, R.; Rojas-Contreras, C.; De la Cruz-Ku, G.; Eyzaguirre-Sandoval, M.E.; Llanos, K.; Sotelo, C.; Alcantara, J.P.; Toledo, F.; Gayoso, M.; Valcarcel-Valdivia, B. Purpura due to Strongyloides stercoralis in an immunocompetent patient. Rev. Chilena Infectol. 2018, 35, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivoto Joao, G.A.; Alves Antunes, I.F.; Mendes Dos Santos, L. Fatal Disseminated Strongyloidiasis with Periumbilical Purpura. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 105, 860–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.J.; Cohen, P.R.; MacFarlane, D.F.; Grossman, M.E. Cutaneous manifestations of Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection in an HIV-seropositive patient. Skinmed 2011, 9, 199–202. [Google Scholar]
- Arch, E.L.; Schaefer, J.T.; Dahiya, A. Cutaneous manifestation of disseminated strongyloidiasis in a patient coinfected with HTLV-I. Dermatol. Online J. 2008, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez-Gomez, L.; Comeche, B.; Subirats, M. Strongyloidiasis: An Important Coinfection in the COVID-19 Era. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 105, 1134–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifdini, M.; Kia, E.B.; Ashrafi, K.; Hosseini, M.; Mirhendi, H.; Mohebali, M.; Kamranrashani, B. An Analysis of Clinical Characteristics of Strongyloides stercoralis in 70 indigenous patients in Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2014, 9, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchese, V.; Crosato, V.; Gulletta, M.; Castelnuovo, F.; Cristini, G.; Matteelli, A.; Castelli, F. Strongyloides infection manifested during immunosuppressive therapy for SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. Infection 2021, 49, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoffi, Z.; Buonfrate, D.; Sequi, M.; Mejia, R.; Cimino, R.O.; Krolewiecki, A.J.; Albonico, M.; Gobbo, M.; Bonafini, S.; Angheben, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of five serologic tests for Strongyloides stercoralis infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Canales, M.; Polman, K.; Ziem, J.; Brienen, E.A.; Polderman, A.M.; van Lieshout, L. Molecular diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis in faecal samples using real-time PCR. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfrate, D.; Requena-Mendez, A.; Angheben, A.; Cinquini, M.; Cruciani, M.; Fittipaldo, A.; Giorli, G.; Gobbi, F.; Piubelli, C.; Bisoffi, Z. Accuracy of molecular biology techniques for the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection-A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacal, E.; Saugar, J.M.; Soler, T.; Azcárate, J.M.; Jiménez, M.S.; Merino, F.J.; Rodríguez, E. Parasitological versus molecular diagnosis of strongyloidiasis in serial stool samples: How many? J. Helminthol. 2018, 92, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfrate, D.; Salas-Coronas, J.; Muñoz, J.; Maruri, B.T.; Rodari, P.; Castelli, F.; Zammarchi, L.; Bianchi, L.; Gobbi, F.; Cabezas-Fernández, T.; et al. Multiple-dose versus single-dose ivermectin for Strongyloides stercoralis infection (Strong Treat 1 to 4): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled superiority trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gardini, G.; Froeschl, G.; Puzzi, P.R.; Gambino, S.; Erne, E.M. Dermatological Presentation of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Two Elderly Italian Inpatients. Pathogens 2024, 13, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080658
Gardini G, Froeschl G, Puzzi PR, Gambino S, Erne EM. Dermatological Presentation of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Two Elderly Italian Inpatients. Pathogens. 2024; 13(8):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080658
Chicago/Turabian StyleGardini, Giulia, Guenter Froeschl, Petra Rosa Puzzi, Silvia Gambino, and Elke Maria Erne. 2024. "Dermatological Presentation of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Two Elderly Italian Inpatients" Pathogens 13, no. 8: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080658
APA StyleGardini, G., Froeschl, G., Puzzi, P. R., Gambino, S., & Erne, E. M. (2024). Dermatological Presentation of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Two Elderly Italian Inpatients. Pathogens, 13(8), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080658





