Serosurvey of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection in Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
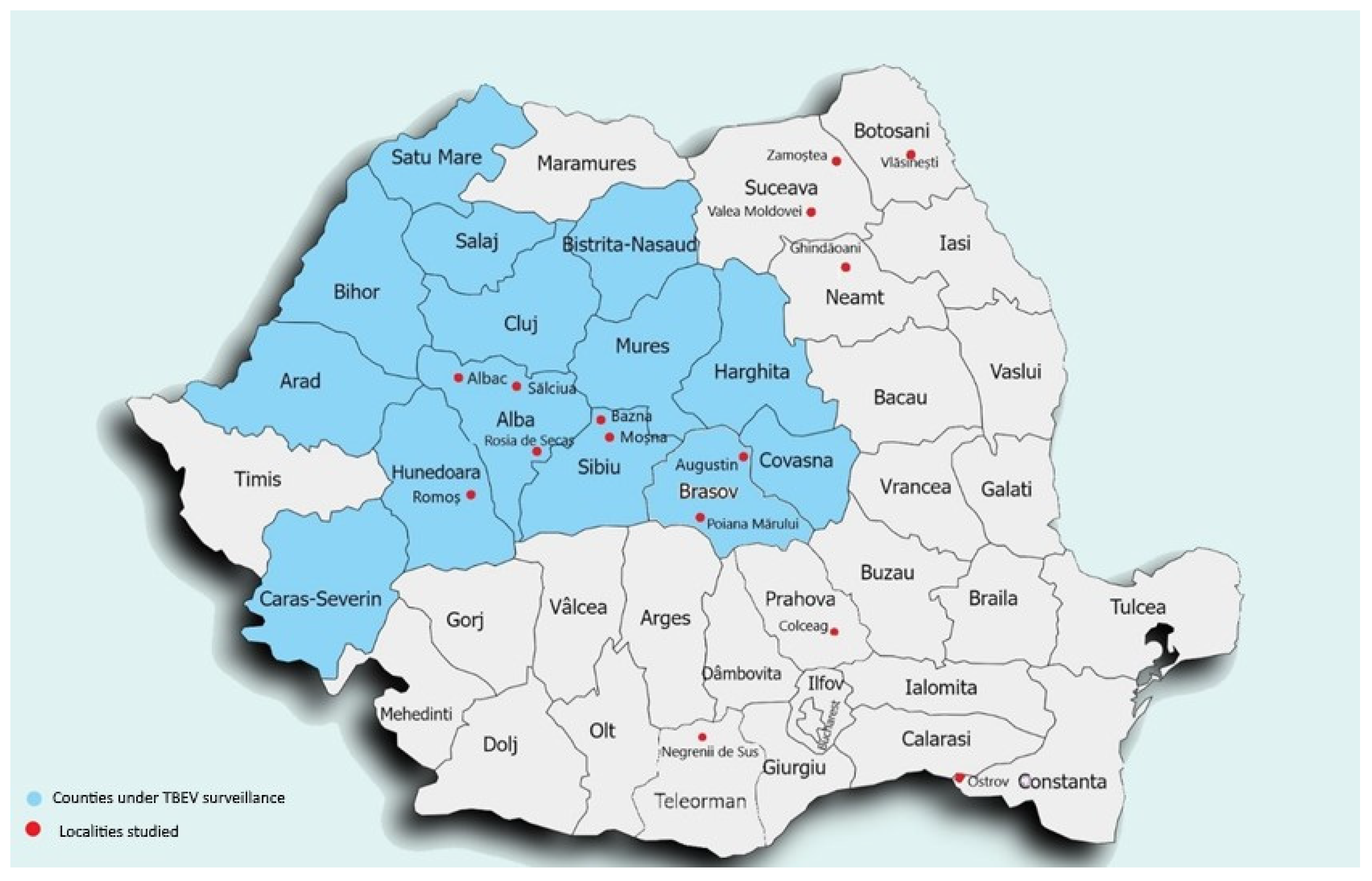
2.1. Blood Sampling and Data Collection
2.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) to Detect Anti-TBEV Antibodies
2.3. Neutralization Assay
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Anti-TBEV Antibody ELISA Results
3.3. Serum Neutralization Test Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindquist, L.; Vapalahti, O. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihalca, A.D.; Gherman, C.M.; Magdaş, C.; Dumitrache, M.O.; Györke, A.; Sándor, A.D.; Domşa, C.; Oltean, M.; Mircean, V.; Mărcuţan, D.I.; et al. Ixodes ricinus is the dominant questing tick in forest habitats in Romania: The results from a countrywide dragging campaign. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 58, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, A.K.; Springer, A.; Mischke, R.; Rieder, J.; Feige, K.; Ganter, M.; Nagel-Kohl, U.; Nordhoff, M.; Boelke, M.; Becker, S.; et al. Seroprevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in wild and domestic animals in northern Germany. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, L.; Alexse, A.; Ceianu, C.; Necsulescu, M.; Popescu, D.; Bicheru, S.; Dumitrescu, G.; Cumpănăşoiu, C.E.; Cumpănăşoiu, C.; Pasat, L.; et al. Investigation methods- used for identifing the presence of tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) in vector arthropods. Sci. Pap. Vet. Med. 2009, XLII, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Vladimirescu, A.; Dumitrescu, G.; Ionescu, L.; Necsulescu, M.; Moraru, V.; Popescu, D.; Bicheru, S.; Doina, D.; Baraitareanu, D.; Ciulacu-Purcarea, V.; et al. Real-Time PCR studies regarding the borrelia burgdorferi, francisella tularensis, tick borne encephalitis virus (TBEv) and crimeean congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFv) occurrence in the Romanian ticks. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 45, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salat, J.; Mihalca, A.D.; Mihaiu, M.; Modrý, D.; Ruzek, D. Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Sheep, Romania. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 2065–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suss, J. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and beyond--the epidemiological situation as of 2007. Eurosurveillance 2008, 26, 18916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, G.B.; Persecă, T.; Feder, A.; Păcuraru, D.; Marialaki, E.; Cojan, A. Evaluarea epidemiologică a emergenţei morbidităţii si focalităţii naturale cu virusul TBE-CEE in Transilvania [Epidemiological assessment of morbidity and natural foci of TBE-CEE virus infection in Transylvania]. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi. 2008, 112, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romanian National Center for Suerveillance of Transmitable Diseases—Suerveillance System for TBEV Infection (Centrul National de Supraveghere a Bolilor Transmisibile—Sistemul de Supraveghere al Infectiei cu Virusul Encefalitei Transmise de Capusa). Available online: https://www.cnscbt.ro/index.php/metodologii/tbe/477-tbe-metodologie/file (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Hristea, A.; Erber, W.; Jankovic, T.V. TBE in Romania Chapter12b. In The TBE Book, 2nd ed.; Dobler, G., Erber, W., Broker, M., Schmitt, H.J., Eds.; Global Health Press: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ganbold, D.; Uudus, B.; Nyamdavaa, N.; Chultemsuren, Y.; Zagd, A.; Tangad, M.; Badrakh, B.; Baldandorj, B.; Dogsom, O.; Lkunrev, R.; et al. Seroprevalence and risk factors of tick-borne encephalitis in Mongolia between 2016 and 2022. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2023, 22, e00318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VIROTECH FSME/TBE IgG/IgM ELISA—Gebrauchsanweisung/Instruction for Use (IFU). Available online: http://ifudownload.virotechdiagnostics.com/ELISA/EC117.00%20VIROTECH%20FSME_TBE%20IgGIgM%20ELISA/02%20EN/VIROTECH%20FSME,TBE%20IgG_IgM%20ELISA%20EN%20REV22.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Holzmann, H. Diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis. Vaccine 2003, 21 (Suppl. S1), S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VENICE II. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Surveillance Systems and Vaccination Recommendations in UE/EEA. Collaboration between VENICE II Project and ECDC. 2009. Available online: http://venice.cineca.org/final_report_TBE_19-01-2011.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Tick-borne encephalitis. In ECDC. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2017; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Tick-borne encephalitis. In ECDC. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2020; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Coroian, M.; Mihalca, A.D.; Dobler, G.; Euringer, K.; Girl, P.; Borșan, S.D.; Kalmár, Z.; Tincuța Briciu, V.; Flonta, M.; Topan, A.; et al. Seroprevalence Rates against West Nile, Usutu, and Tick-Borne Encephalitis Viruses in Blood-Donors from North-Western Romania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvik, Å.; Tveten, Y.; Pedersen, A.B.; Stiasny, K.; Andreassen, Å.K.; Grude, N. Low prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus antibodies in Norwegian blood donors. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borde, J.P.; Glaser, R.; Braun, K.; Riach, N.; Hologa, R.; Kaier, K.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Dobler, G. Decoding the Geography of Natural TBEV Microfoci in Germany: A Geostatistical Approach Based on Land-Use Patterns and Climatological Conditions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Septfons, A.; Rigaud, E.; Bénézet, L.; Velay, A.; Zilliox, L.; Baldinger, L.; Gonzalez, G.; Figoni, J.; de Valk, H.; Deffontaines, G.; et al. Seroprevalence for Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and tick-borne encephalitis virus antibodies and associated risk factors among forestry workers in northern France, 2019 to 2020. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakimovski, D.; Mateska, S.; Dimitrova, E.; Bosilkovski, M.; Mijatović, D.; Simin, V.; Bogdan, I.; Grujić, J.; Budakov-Obradović, Z.; Meletis, E.; et al. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and Borrelia burgdorferi Seroprevalence in Balkan Tick-Infested Individuals: A Two-Centre Study. Pathogens 2023, 12, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunze, M.; Banović, P.; Bogovič, P.; Briciu, V.; Čivljak, R.; Dobler, G.; Hristea, A.; Kerlik, J.; Kuivanen, S.; Kynčl, J.; et al. Recommendations to Improve Tick-Borne Encephalitis Surveillance and Vaccine Uptake in Europe. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study Population and Counties N (%) | Total N = 1116 | Teleorman N = 56 (5) | Brasov N = 96 (8.6) | Alba N = 212 (19.0) | Sibiu N = 143 (12.8) | Suceava N = 182 (16.3) | Botosani N = 82 (7.3) | Constanta N = 74 (6.6) | Prahova N = 67 (6.0) | Hunedoara N = 111 (9.9) | Neamt N = 93 (8.3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex N (%) (95% CI) | 291 (26) (23.5–28.8) | 15 (26.8) | 14 (14.6) | 69 (32.5) | 38 (26.6) | 59 (32.4) | 16 (19.5) | 13 (17.6) | 21 (31.3) | 27 (24.3) | 19 (20.4) |
| Median age (IQR) (years) | 58 (47–70) | 65 (51–75) | 54 (40–69) | 60 (51–70) | 57 (49–66) | 56 (44–67) | 56 (46–69) | 47 (42–61) | 53 (41–69) | 59 (50–69) | 70 (59–76) |
| Profession at risk N (%) 1 (95% CI) | 230 (20.6) (18.3–23.1) | 10 (17.9) | 4 (4.2) | 66 (31.1) | 7 (4.9) | 58 (31.9) | 17 (20.7) | 10 (13.5) | 8 (11.9) | 8 (7.2) | 42 (45.2) |
| Mushroom collector N (%) (95% CI) | 266 (23.8) (21.4–26.5) | 1 (1.8) | 31 (32.3) | 73 (34.4) | 3 (2.1) | 101 (55.5) | 2 (2.4) | 6 (8.1) | 4 (6.0) | 29 (26.1) | 16 (17.2) |
| Consumption of unprocessed milk products N (%) (95% CI) | 561 (50.3) (47.3–53.3) | 22 (39.3) | 51 (53.1) | 131 (61.8) | 54 (37.8) | 112 (61.5) | 33 (40.2) | 41 (55.4) | 34 (50.7) | 21 (18.9) | 62 (66.7) |
| Tick bite history N (%) (95% CI) | 274 (24.5) (22.1–27.2) | 4 (7.1) | 26 (27.1) | 98 (46.2) | 26 (18.2) | 30 (16.5) | 7 (8.5) | 12 (16.2) | 5 (7.5) | 41 (36.9) | 25 (26.9) |
| Domestic animals in household N (%) 2 (95% CI) | 139 (12.4) (10.6–14.5) | 12 (21.4) | 13 (13.5) | 18 (8.4) | 12 (8.4) | 17 (9.3) | 34 (41.4) | 1 (1.4) | 5 (7.5) | 14 (12.6) | 13 (14.0) |
| ELISA TBEV+ samples N (%) (95% CI) | 26 (2.3) (1.5–3.4) | 0 | 0 | 3 (1.4) | 10 (6.9) | 5 (2.7) | 3 (3.6) | 0 | 3 (4.4) | 2 (1.8) | 0 |
| County | Serum Sample N | ELISA TBEV % | Calculated Sample Size | Locality | Serum Samples N (%) | ELISA TBEV+ Samples N (%); 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sibiu | 142 | 7 | 278 | Mosna | 72 (6.4) | 9 (12.5); (5.9–22.4) |
| Bazna | 71 (6.3) | 1 (1.4); (0–7.6) | ||||
| Brasov | 96 | 0 | 43 | Augustin | 44 (3.9) | 0; (0–8) |
| Poiana Marului | 52 (4.6) | 0; (0–6.8) | ||||
| Alba | 212 | 1 | 43 | Rosia de Secas | 50 (4.5) | 3 (6.0); (1.3-16.5) |
| Albac | 93 (8.3) | 0; (0–3.9) | ||||
| Salciua | 69 (6.1) | 0; (0–5.2) | ||||
| Suceava | 182 | 2.5 | 104 | Zamostea | 100 (8.9) | 4 (4.0); (1.1–9.9) |
| Valea Moldovei | 82 (7.3) | 1 (1.2); (0–6.6) | ||||
| Botosani | 82 | 3 | 125 | Vlasinesti | 82 (7.3) | 3 (3.6); (0.8–10.3) |
| Teleorman | 56 | 0 | 43 | Negrenii de Sus | 56 (5.0) | 0; (0–6.4) |
| Constanta | 74 | 0 | 43 | Ostrov | 74 (6.6) | 0; (0–4.9) |
| Prahova | 67 | 3 | 125 | Colceag | 67 (6.0) | 3 (4.4); (0.9–12.5) |
| Hunedoara | 111 | 2 | 84 | Romos | 111 (9.9) | 2 (1.8); (0.2–6.4) |
| Neamt | 93 | 0 | 43 | Ghindaoani | 93 (8.3) | 0; (0–3.9) |
| Total | 1116 (100) | 26 (2.3); (1.5–3.4) |
| Positive TBE N = 7 | Negative TBE N = 65 | OR (95% CI) p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex N (%) | 2 (28.6) | 16 (24.6) | 1.22 (0.21–6.93) 0.81 |
| Age Median (IQR) | 59 (53–65) | 60(51-67) | 0.57 |
| Profession at risk N (%) | 1 (14.3) | 4 (6.2) | 2.54 (0.24–26.55) 0.42 |
| Mushroom collector N (%) | 0 | 3 (4.6) | 1.11 (1.02–1.20) 0.56 |
| Consumption of unprocessed milk products N (%) | 2 (28.6) | 23 (35.4) | 0.73 (0.13–4.06) 0.71 |
| Tick bite history N(%) | 0 | 14 (21.5) | 1.13 (1.03–1.25) 0.17 |
| Domestic animals in household N (%) | 0 | 8 (12.3) | 1.12 (1.03–1.22) 0.32 |
| History of recreational activities in nature N (%) | 0 | 2 (3.1) | 1.11 (1.02–1.20) 0.63 |
| Knowledge about diseases spread by ticks N (%) | 3 (42.9) | 50 (76.9) | 0.22 (0.04–1.1) 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panciu, A.M.; Cheran, C.A.; Militaru, E.D.; Rîciu, C.D.; Hristea, A. Serosurvey of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection in Romania. Pathogens 2024, 13, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13030231
Panciu AM, Cheran CA, Militaru ED, Rîciu CD, Hristea A. Serosurvey of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection in Romania. Pathogens. 2024; 13(3):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13030231
Chicago/Turabian StylePanciu, Andreea Mădălina, Cristina Alexandra Cheran, Eliza Daniela Militaru, Claudia Doina Rîciu, and Adriana Hristea. 2024. "Serosurvey of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection in Romania" Pathogens 13, no. 3: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13030231
APA StylePanciu, A. M., Cheran, C. A., Militaru, E. D., Rîciu, C. D., & Hristea, A. (2024). Serosurvey of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection in Romania. Pathogens, 13(3), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13030231







