‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ Predicted Effector SAP11-like Alters Morphology of Transformed Arabidopsis Plants and Interacts with AtTCP2 and AtTCP4 Plant Transcription Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growth
2.2. Codon Optimization, Cloning, and Transformation of Arabidopsis Plants
2.3. Phenotypic Analysis of Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana Plants with SAP11-like Overexpression
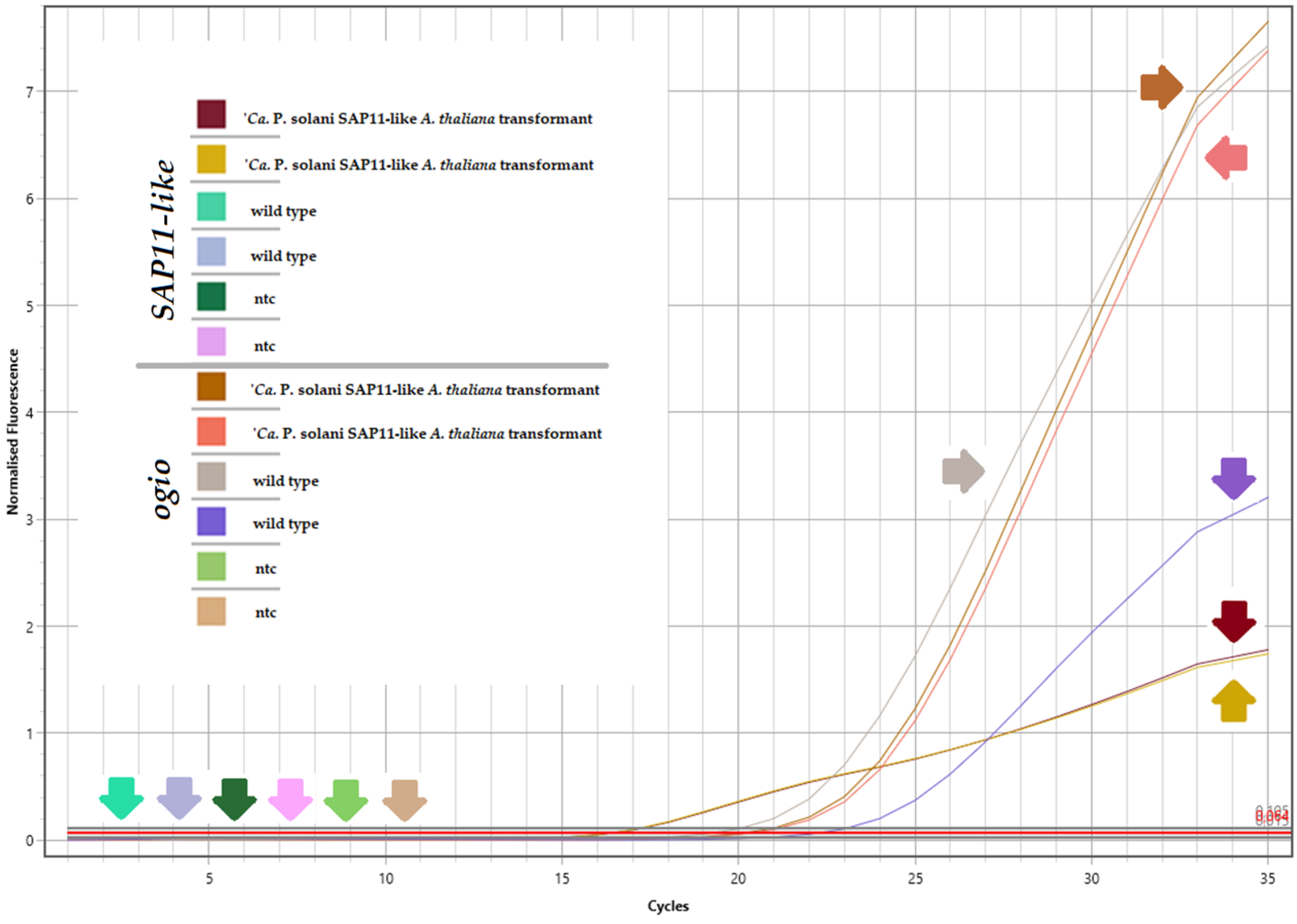
2.4. Quantification of SAP11-like Gene Expression in Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana Lines
2.5. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) in Nicotiana benthamiana Leaf Epidermal Cells
3. Results
3.1. Regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana Plants Overexpressing SAP11-like Transgene
3.2. SAP11-like Gene Presence and Expression in Transformed A. thaliana Plants
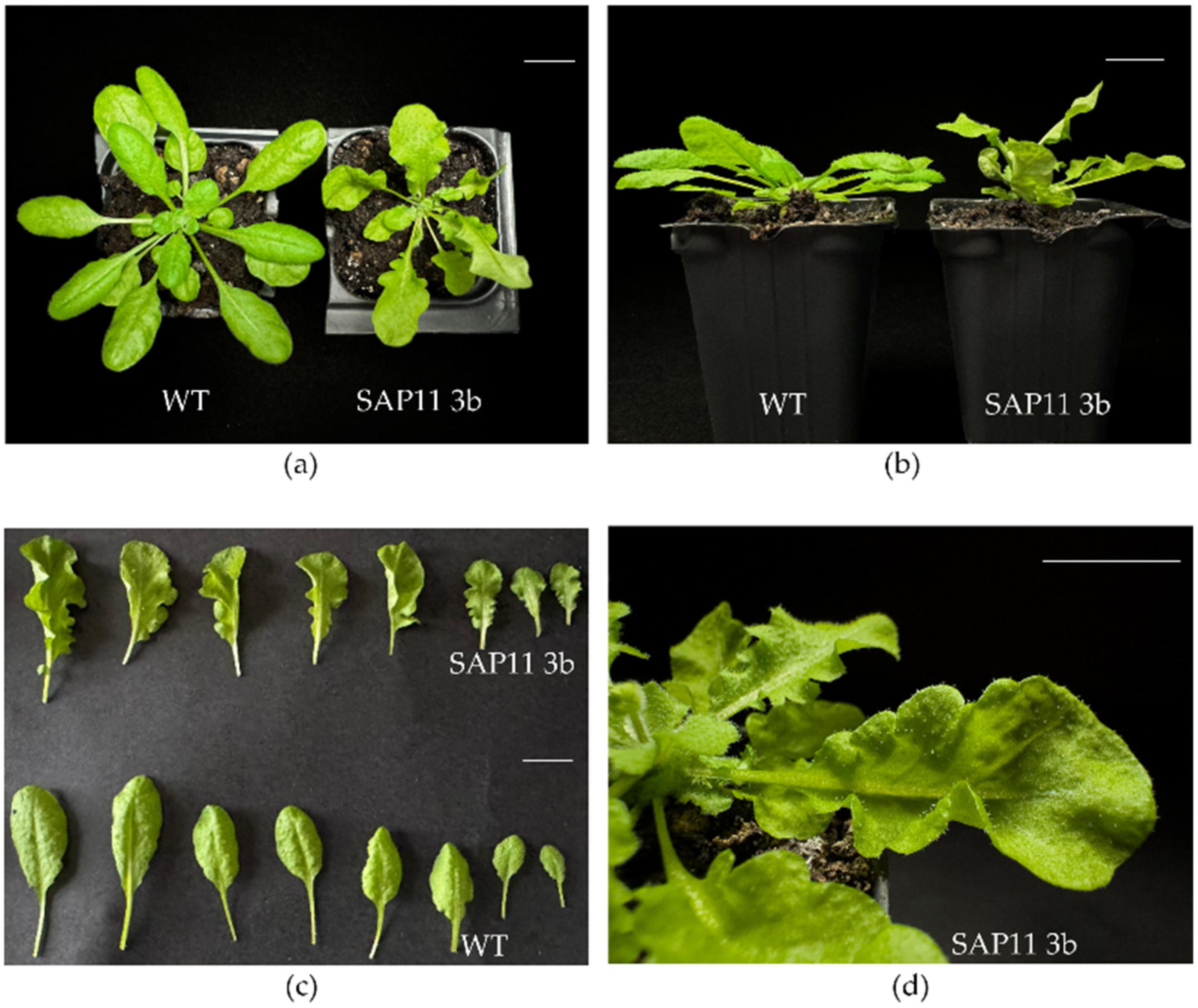
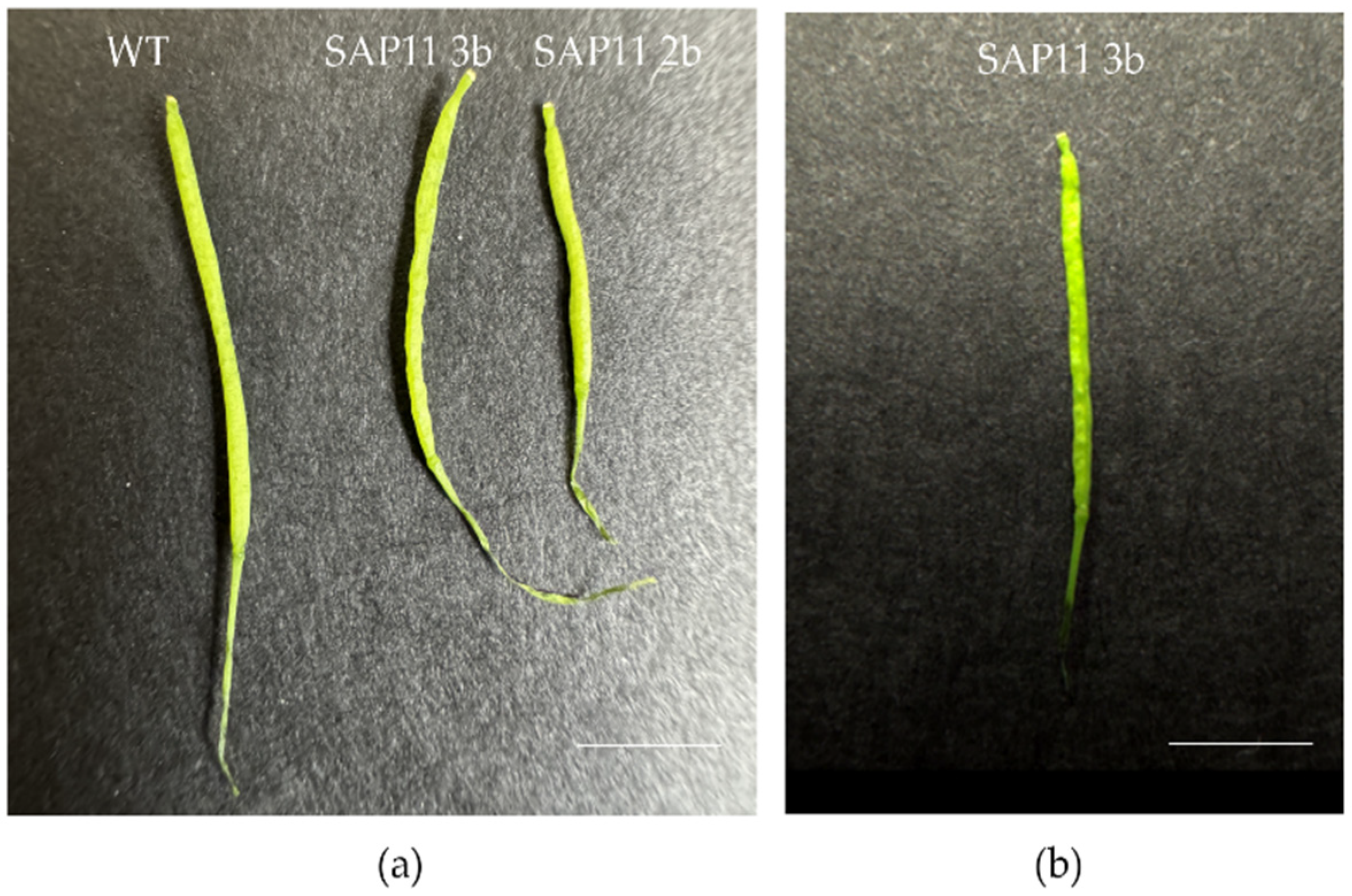
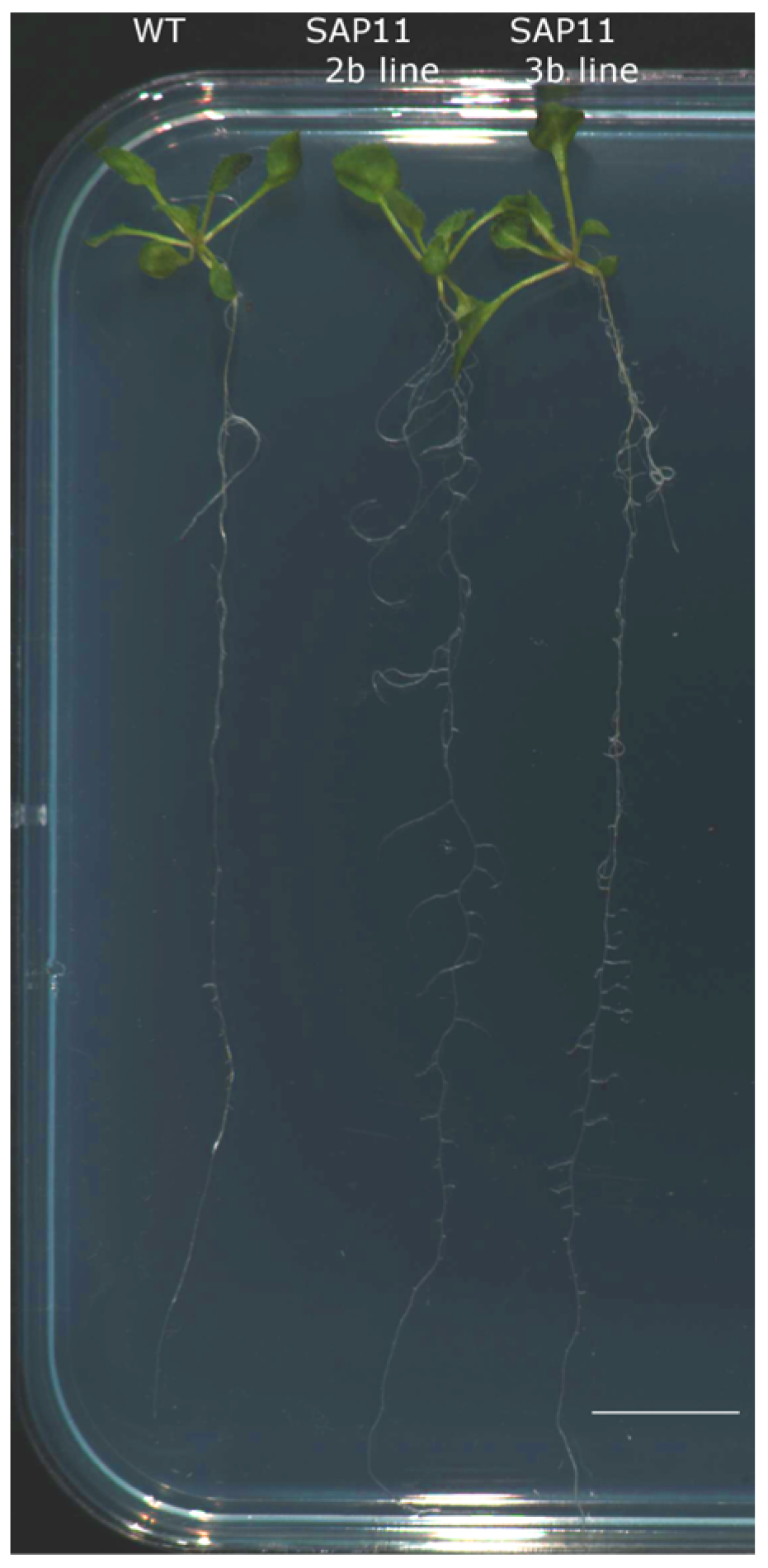
3.3. SAP11-like Overexpressing Arabidopsis thaliana Plants Show Significant Phenotypic Changes
3.4. In Planta SAP11-like Interact with AtTCP2 and AtTCP4 Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navrátil, M.; Válová, P.; Fialová, R.; Lauterer, P.; Šafářová, D.; Starý, M. The Incidence of Stolbur Disease and Associated Yield Losses in Vegetable Crops in South Moravia (Czech Republic). Crop Prot. 2009, 28, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E. Phytoplasma Research Begins to Bloom. Science 2009, 325, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogenhout, S.A.; Oshima, K.; Ammar, E.D.; Kakizawa, S.; Kingdom, H.N.; Namba, S. Phytoplasmas: Bacteria That Manipulate Plants and Insects. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, S. Molecular and Biological Properties of Phytoplasmas. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2019, 95, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogenhout, S.A.; Loria, R. Virulence Mechanisms of Gram-Positive Plant Pathogenic Bacteria. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Trillo, M.; Cubas, P. TCP Genes: A Family Snapshot Ten Years Later. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, C. Molecular Biology and Pathogenicity of Phytoplasmas. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 165, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Correa, V.R.; Toruño, T.Y.; Ammar, E.D.; Kamoun, S.; Hogenhout, S.A. AY-WB Phytoplasma Secretes a Protein That Targets Plant Cell Nuclei. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008, 22, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, A.; Oshima, K.; Kakizawa, S.; Ishii, Y.; Ozeki, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Komatsu, K.; Kagiwada, S.; Yamaji, Y.; Namba, S. A Unique Virulence Factor for Proliferation and Dwarfism in Plants Identified from a Phytopathogenic Bacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6416–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, S.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. Functional Genomics of Phytoplasmas. In Phytoplasmas: Genomes, Plant Hosts and Vectors; CAB International: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Reyes-Caldas, P.; Mann, M.; Seifbarghi, S.; Kahn, A.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Béven, L.; Heck, M.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Coaker, G. Bacterial Vector-Borne Plant Diseases: Unanswered Questions and Future Directions. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; MacLean, A.M.; Sugio, A.; Maqbool, A.; Busscher, M.; Cho, S.T.; Kamoun, S.; Kuo, C.H.; Immink, R.G.H.; Hogenhout, S.A. Parasitic Modulation of Host Development by Ubiquitin-Independent Protein Degradation. Cell 2021, 184, 5201–5214.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugio, A.; MacLean, A.M.; Kingdom, H.N.; Grieve, V.M.; Manimekalai, R.; Hogenhout, S.A. Diverse Targets of Phytoplasma Effectors: From Plant Development to Defense against Insects. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecher, P.; Moro, G.; Canale, M.C.; Capdevielle, S.; Singh, A.; MacLean, A.; Sugio, A.; Kuo, C.H.; Lopes, J.R.S.; Hogenhout, S.A. Phytoplasma SAP11 Effector Destabilization of TCP Transcription Factors Differentially Impact Development and Defence of Arabidopsis versus Maize. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, 1008035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogenhout, S.A.; Van Der Hoorn, R.A.L.; Terauchi, R.; Kamoun, S. Emerging Concepts in Effector Biology of Plant-Associated Organisms. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, A.M.; Orlovskis, Z.; Kowitwanich, K.; Zdziarska, A.M.; Angenent, G.C.; Immink, R.G.H.; Hogenhout, S.A. Phytoplasma Effector SAP54 Hijacks Plant Reproduction by Degrading MADS-Box Proteins and Promotes Insect Colonization in a RAD23-Dependent Manner. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, 1001835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maejima, K.; Iwai, R.; Himeno, M.; Komatsu, K.; Kitazawa, Y.; Fujita, N.; Ishikawa, K.; Fukuoka, M.; Minato, N.; Yamaji, Y.; et al. Recognition of Floral Homeotic MADS Domain Transcription Factors by a Phytoplasmal Effector, Phyllogen, Induces Phyllody. Plant J. 2014, 78, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugio, A.; Kingdom, H.N.; MacLean, A.M.; Grieve, V.M.; Hogenhout, S.A. Phytoplasma Protein Effector SAP11 Enhances Insect Vector Reproduction by Manipulating Plant Development and Defense Hormone Biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E1254–E1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, K.; Mithöfer, A.; Raffeiner, M.; Stellmach, H.; Hause, B.; Schlink, K. An Effector of Apple Proliferation Phytoplasma Targets TCP Transcription Factors-a Generalized Virulence Strategy of Phytoplasma? Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglino, F.; Zhao, Y.; Casati, P.; Bulgari, D.; Bianco, P.A.; Wei, W.; Davis, R.E. “Candidatus Phytoplasma solani”, a Novel Taxon Associated with Stolbur-and Bois Noir-Related Diseases of Plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2879–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixner, M.; Ahrens, U.; Seemüller, E. Detection of the German Grapevine Yellows (Vergilbungskrankheit) MLO in Grapevine, Alternative Hosts and a Vector by a Specific PCR Procedure. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1995, 101, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jović, J.; Cvrković, T.; Mitrović, M.; Krnjajić, S.; Petrović, A.; Redinbaugh, M.G.; Pratt, R.C.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Toševski, I. Stolbur Phytoplasma Transmission to Maize by Reptalus Panzeri and the Disease Cycle of Maize Redness in Serbia. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seruga Music, M.; Samarzija, I.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Haryono, M.; Cho, S.T.; Kuo, C.H. The Genome of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ Strain SA-1 Is Highly Dynamic and Prone to Adopting Foreign Sequences. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 42, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugio, A.; Maclean, A.M.; Hogenhout, S.A. The Small Phytoplasma Virulence Effector SAP11 Contains Distinct Domains Required for Nuclear Targeting and CIN-TCP Binding and Destabilization. New Phytol. 2014, 202, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S. The Arabidopsis Thaliana TCP Transcription Factors: A Broadening Horizon beyond Development. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e1044192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, K.; Kakizawa, S.; Nishigawa, H.; Jung, H.Y.; Wei, W.; Suzuki, S.; Arashida, R.; Nakata, D.; Miyata, S.I.; Ugaki, M.; et al. Reductive Evolution Suggested from the Complete Genome Sequence of a Plant-Pathogenic Phytoplasma. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.T.; Li, M.Y.; Cheng, K.T.; Tan, C.M.; Su, L.W.; Lin, W.Y.; Shih, H.T.; Chiou, T.J.; Yang, J.Y. Transgenic Plants That Express the Phytoplasma Effector SAP11 Show Altered Phosphate Starvation and Defense Responses. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1456–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelberg, C.; Hause, B.; Janki, K. The ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma Mali’ Effector Protein SAP11CaPm Interacts with MdTCP16, AclassII CYC/TB1transcriptionfactorthatishighlyexpressedduringphytoplasmainfection. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonrod, K.; Strohmayer, A.; Schwarz, T.; Braun, M.; Tropf, T.; Krczal, G. Beyond Destabilizing Activity of SAP11-like Effector of Candidatus Phytoplasma Mali Strain PM19. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bio Assays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plant 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Nielsen, H.; Von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Improved Prediction of Signal Peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral Dip: A Simplified Method for Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škiljaica, A.; Jagić, M.; Vuk, T.; Leljak Levanić, D.; Bauer, N.; Markulin, L. Evaluation of Reference Genes for RT-QPCR Gene Expression Analysis in Arabidopsis Thaliana Exposed to Elevated Temperatures. Plant Biol. 2022, 24, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.; Chaban, C.; Schütze, K.; Batistic, O.; Weckermann, K.; Näke, C.; Blazevic, D.; Grafen, C.; Schumacher, K.; Oecking, C.; et al. Visualization of Protein Interactions in Living Plant Cells Using Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation. Plant J. 2004, 40, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, J.; Kamoun, S. PCB301-P19: A Binary Plasmid Vector to Enhance Transient Expression of Transgenes by Agroinfiltration. Plant J. 2003, 33, 949–956. [Google Scholar]
- Jagić, M. Domain-Specific Interactions of BPM1 with DMS3 and RDM1 in RNAdirected DNA Methylation. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Win, J.; Chaparro-Garcia, A.; Belhaj, K.; Saunders, D.G.O.; Yoshida, K.; Dong, S.; Schornack, S.; Zipfel, C.; Robatzek, S.; Hogenhout, S.A.; et al. Effector Biology of Plant-Associated Organisms: Concepts and Perspectives. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2012, 77, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohmayer, A.; Schwarz, T.; Braun, M.; Krczal, G.; Boonrod, K. The Effect of the Anticipated Nuclear Localization Sequence of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma Mali’ SAP11-like Protein on Localization of the Protein and Destabilization of TCP Transcription Factor. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelberger, C.; Moser, M.; Hause, B.; Janik, K. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma Mali’ SAP11-like Protein Modulates Expression of Genes Involved in Energy Production, Photosynthesis, and Defense in Nicotiana Occidentalis Leaves. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, M.; Challa, K.R.; Sarvepalli, K.; Nath, U. CINCINNATA-like TCP Transcription Factors in Cell Growth—An Expanding Portfolio. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 825341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Yin, L.; Zeng, Z.; Xiang, J.; Liu, S. Identification of a Consensus DNA-Binding Site for the TCP Domain Transcription Factor TCP2 and Its Important Roles in the Growth and Development of Arabidopsis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yang, H.; Yin, Z.; Liu, W.; Sun, L.; Wu, Y. Phytoplasma Effector SWP1 Induces Witches’ Broom Symptom by Destabilizing the TCP Transcription Factor BRANCHED1. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 2623–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Tan, C.M.; Wu, C.T.; Lin, T.H.; Jiang, S.Y.; Liu, R.C.; Tsai, M.C.; Su, L.W.; Yang, J.Y. Alterations of Plant Architecture and Phase Transition by the Phytoplasma Virulence Factor SAP11. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 5389–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresso, E.G.; Chorostecki, U.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Palatnik, J.F.; Schommer, C. Spatial Control of Gene Expression by MiR319-Regulated TCP Transcription Factors in Leaf Development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1694–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedle-Bauer, M.; Brader, G. Effects of Insecticides and Repellents on the Spread of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ under Laboratory and Field Conditions. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2023, 130, 1057–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, P.A.; Romanazzi, G.; Mori, N.; Myrie, W.; Bertaccini, A. Integrated Management of Phytoplasma Diseases. In Phytoplasmas: Plant Pathogenic Bacteria—II; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Jaouannet, M.; Dempsey, D.A.; Imani, J.; Coustau, C.; Kogel, K.H. RNA-Based Technologies for Insect Control in Plant Production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 39, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schutter, K.; Taning, C.N.T.; Van Daele, L.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Dubruel, P.; Smagghe, G. RNAi-Based Biocontrol Products: Market Status, Regulatory Aspects, and Risk Assessment. Front. Insect Sci. 2021, 1, 818037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


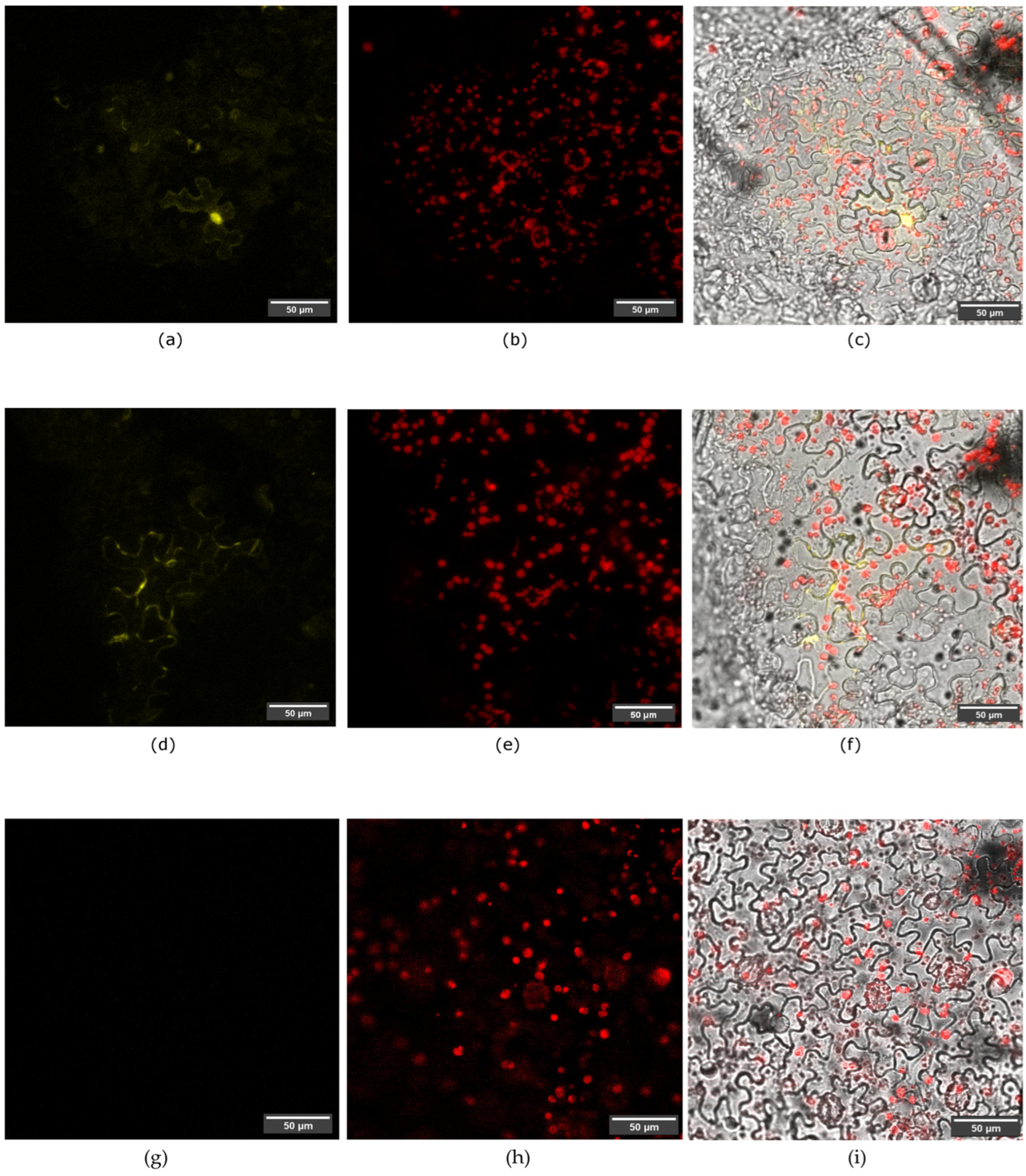
| No. of A. tumefaciens Combination | Plasmid Constructs in Agroinfiltration Mixture | Type of Sample |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | pSPYNE-SAP11-like pSPYCE-AtTCP2 pCB301-p19 | Experimental sample |
| 2 | pSPYNE-SAP11-like pSPYCE-AtTCP4 pCB301-p19 | Experimental sample |
| 3 | pSPYNE-SAP11-like pCB301-p19 | Negative control |
| 4 | pSPYCE-AtTCP2 pCB301-p19 | Negative control |
| 5 | pSPYCE-AtTCP4 pCB301-p19 | Negative control |
| 6 | pB7WGR2.0-EGFP-DMS3 pCB301-p19 | Positive control of agroinfiltration |
| Plant | Gene | Cq | Cq | Average Cq | ΔCq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAP11-like transgenic A. thaliana | ogio | 20.08 | 20.25 | 20.17 | −3.85 |
| SAP11-like | 16.34 | 16.29 | 16.32 | ||
| ntc | 0 | 0 | 0 | Not applicable | |
| Wild-type A. thaliana | ogio | 19.18 | 22.19 | 20.69 | Not applicable |
| SAP11-like | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| ntc | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Measurement | WT | SAP11-like 2b | SAP11-like 3b |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh shoot mass 1 (g) | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.27 ± 0.02 ** | 0.50 ± 0.06 * |
| Height (cm) | 36.00 ± 0.99 | 23.79 ± 0.74 ** | 28.78 ± 0.91 ** |
| Rosette diameter (cm) | 6.42 ± 0.36 | 4.48 ± 0.19 ** | 6.09 ± 0.32 |
| Length of rosette 2 leaf (cm) | 2.19 ± 0.11 | 1.32 ± 0.05 ** | 1.94 ± 0.07 * |
| Width of rosette leaf 2 (cm) | 1.16 ± 0.045 | 0.75 ± 0.03 ** | 1.03 ± 0.08 |
| Length of siliques (cm) | 1.34 ± 0.47 | 0.88 ± 0.23 ** | 0.89 ± 0.27 ** |
| Ʃ axillary shoots | 4.2 ± 0.33 | 9.56 ± 0.59 ** | 10.76 ± 0.85 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drcelic, M.; Skiljaica, A.; Polak, B.; Bauer, N.; Seruga Music, M. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ Predicted Effector SAP11-like Alters Morphology of Transformed Arabidopsis Plants and Interacts with AtTCP2 and AtTCP4 Plant Transcription Factors. Pathogens 2024, 13, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100893
Drcelic M, Skiljaica A, Polak B, Bauer N, Seruga Music M. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ Predicted Effector SAP11-like Alters Morphology of Transformed Arabidopsis Plants and Interacts with AtTCP2 and AtTCP4 Plant Transcription Factors. Pathogens. 2024; 13(10):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100893
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrcelic, Marina, Andreja Skiljaica, Bruno Polak, Natasa Bauer, and Martina Seruga Music. 2024. "‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ Predicted Effector SAP11-like Alters Morphology of Transformed Arabidopsis Plants and Interacts with AtTCP2 and AtTCP4 Plant Transcription Factors" Pathogens 13, no. 10: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100893
APA StyleDrcelic, M., Skiljaica, A., Polak, B., Bauer, N., & Seruga Music, M. (2024). ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’ Predicted Effector SAP11-like Alters Morphology of Transformed Arabidopsis Plants and Interacts with AtTCP2 and AtTCP4 Plant Transcription Factors. Pathogens, 13(10), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100893







