Molecular Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of Anaplasma marginale Moonlighting Proteins as Possible Antigenic Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic Identification of Moonlighting Proteins
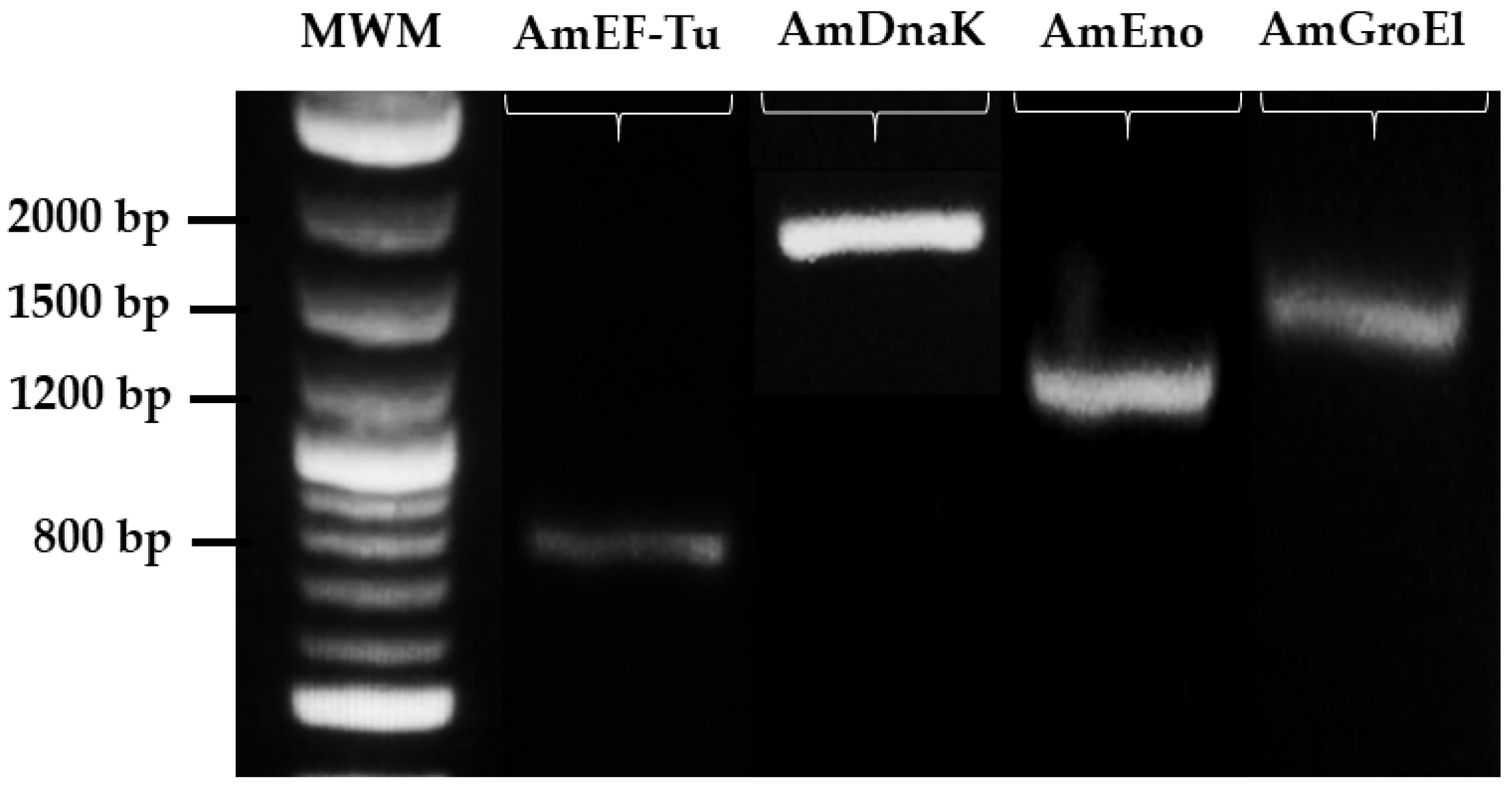
2.2. Identification of Moonlighting Genes by End-Point PCR
2.3. Functional Annotation
2.4. Three-Dimensional (3D) Modelling
2.5. Structural Homology Analysis
2.6. B-Cell Epitopes Prediction and Multiple Antigenic Peptides (MAPs) Design
2.7. Indirect Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (iELISA)
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Identification of Moonlighting Proteins
3.2. Identification of Moonlighting Proteins
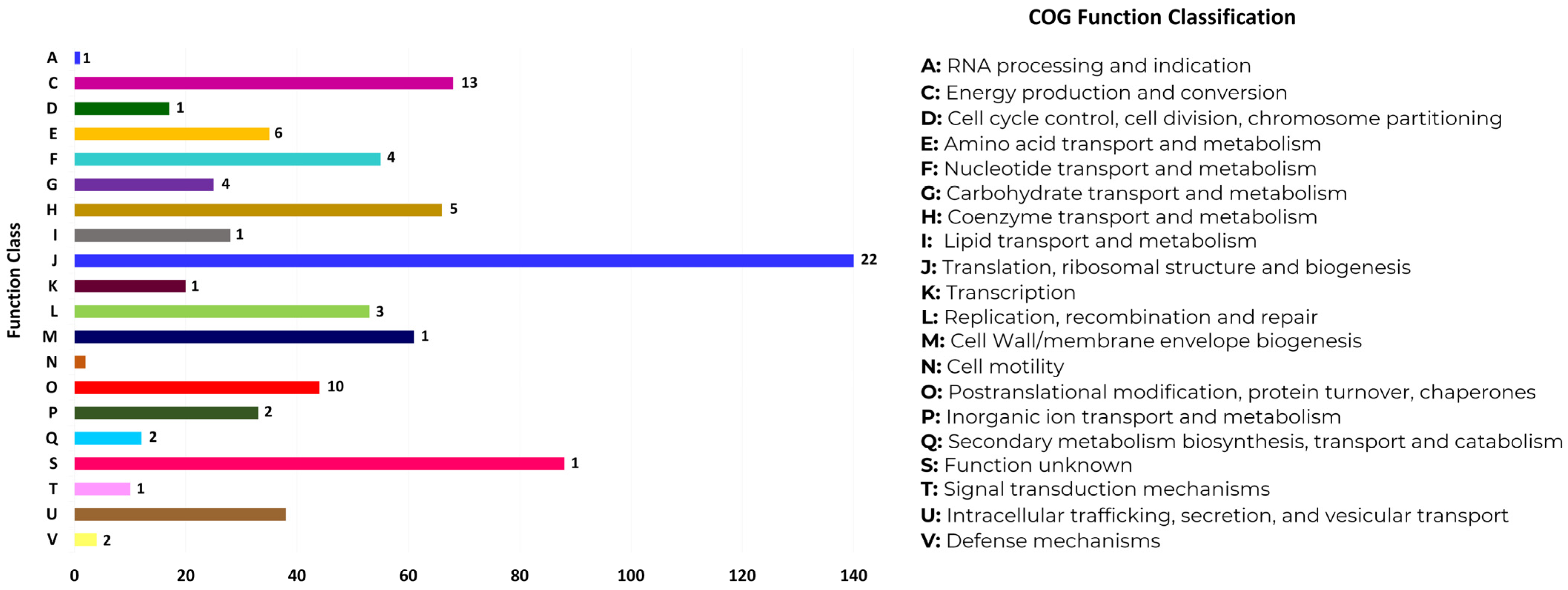
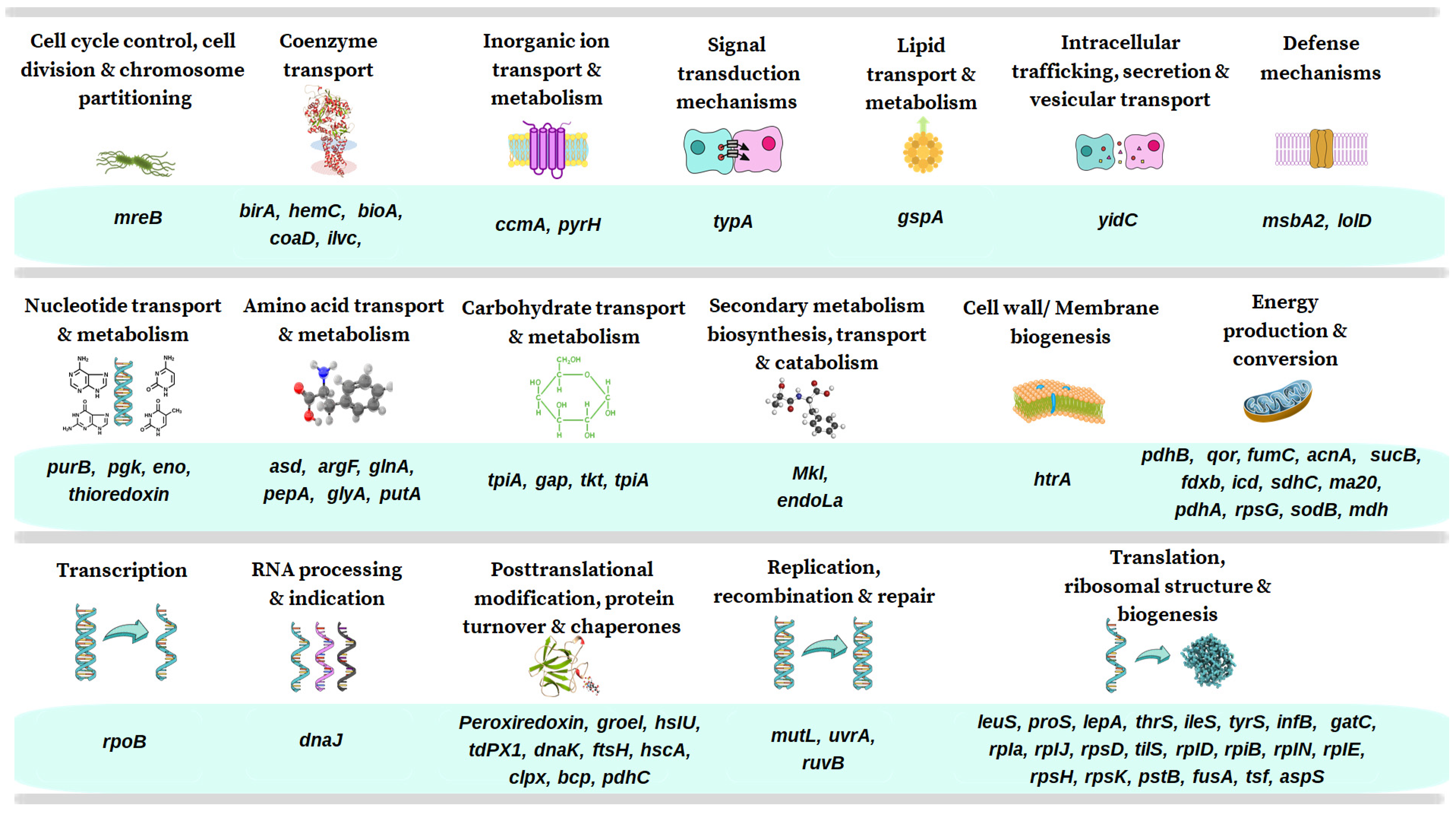
3.3. Functional Annotation of MLPs
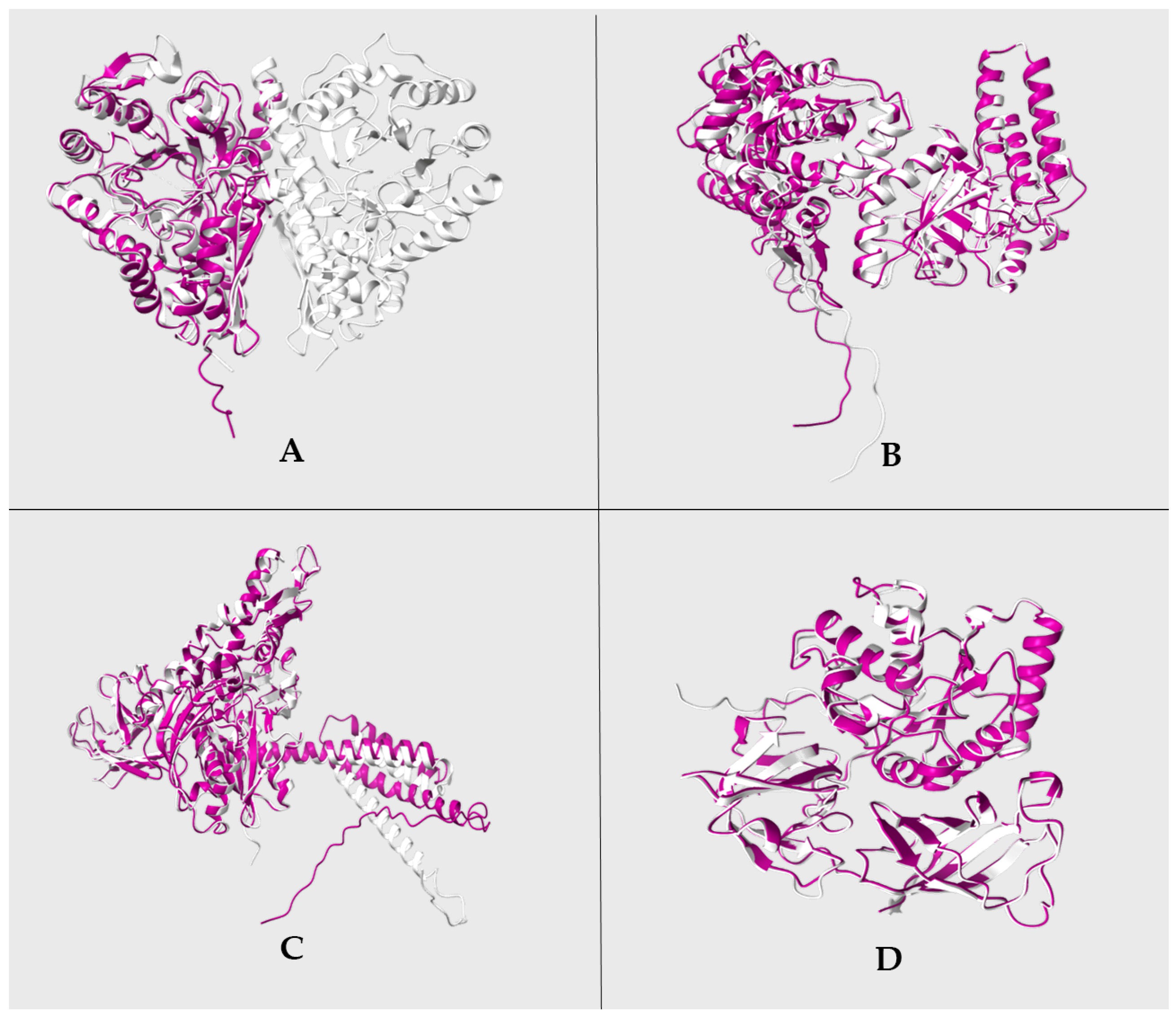
3.4. Three-Dimensional (3D) Modelling
3.5. Structural Homology Analysis
3.6. B-Cell Epitope Prediction
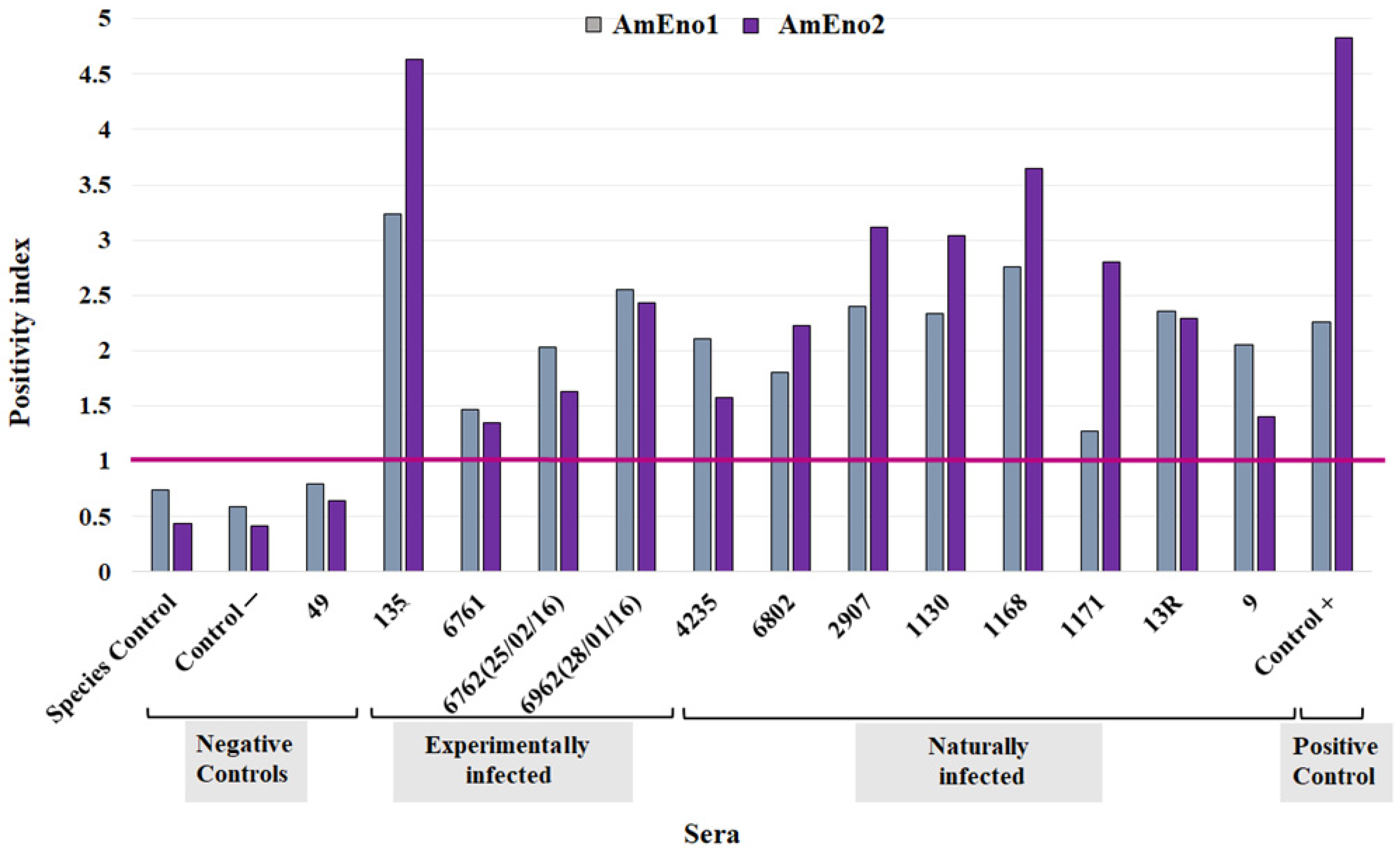
3.7. Antigenic Potential of AmEno1 and AmEno2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Coetzee, J.F.; Ewing, S.A. The Natural History of Anaplasma marginale. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WOAH. Bovine Anaplasmosis. In Manual of Diagnostic Test and Vaccines for Terrestrial Manual 2018; World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH): Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- de La Fuente, J.; Garcia-Garcia, J.C.; Blouin, E.F.; Rodríguez, S.D.; García, M.A.; Kocan, K.M. Evolution and Function of Tandem Repeats in the Major Surface Protein 1a of the Ehrlichial Pathogen Anaplasma marginale. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2001, 2, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangussu, A.S.R.; Mariúba, L.A.M.; Lalwani, P.; Pereira, K.D.E.S.; Astolphi-Filho, S.; Orlandi, P.P.; Epiphanio, S.; Viana, K.F.; Ribeiro, M.F.B.; Silva, H.M.; et al. A Hybrid Protein Containing MSP1a Repeats and Omp7, Omp8 and Omp9 Epitopes Protect Immunized BALB/c Mice against Anaplasmosis. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Mahony, D.; Cavallaro, A.S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Deringer, J.R.; Zhao, C.-X.; Brown, W.C.; Yu, C.; Mitter, N.; et al. Immunogenicity of Outer Membrane Proteins VirB9-1 and VirB9-2, a Novel Nanovaccine against Anaplasma marginale. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducken, D.R.; Brown, W.C.; Alperin, D.C.; Brayton, K.A.; Reif, K.E.; Turse, J.E.; Palmer, G.H.; Noh, S.M. Subdominant Outer Membrane Antigens in Anaplasma marginale: Conservation, Antigenicity, and Protective Capacity Using Recombinant Protein. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarli, M.; Novoa, M.B.; Mazzucco, M.N.; Signorini, M.L.; Echaide, I.E.; de Echaide, S.T.; Primo, M.E. A Vaccine Using Anaplasma marginale Subdominant Type IV Secretion System Recombinant Proteins Was Not Protective against a Virulent Challenge. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salje, J. Cells within Cells: Rickettsiales and the Obligate Intracellular Bacterial Lifestyle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.L.; Curto, P.; Simões, I. Moonlighting in Rickettsiales: Expanding Virulence Landscape. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Singh, R.; Sur, S.; Bansal, S.; Chaudhry, U.; Tandon, V. Moonlighting Proteins: Beacon of Hope in Era of Drug Resistance in Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 49, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Serrano, L.; Sánchez-Redondo, D.; Nájar-García, A.; Hernández, S.; Amela, I.; Perez-Pons, J.A.; Piñol, J.; Mozo-Villarias, A.; Cedano, J.; Querol, E. Pathogen Moonlighting Proteins: From Ancestral Key Metabolic Enzymes to Virulence Factors. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huberts, D.H.E.W.; van der Klei, I.J. Moonlighting Proteins: An Intriguing Mode of Multitasking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2010, 1803, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, C.J. Moonlighting Proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, C.J. Moonlighting Proteins: Complications and Implications for Proteomics Research. Drug Discov. Today Targets 2004, 3, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, C.J. Moonlighting Proteins—An Update. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, C.J. Protein Moonlighting: What Is It, and Why Is It Important? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Chen, Y.; Dong, T.; Hong, X.; Takeuchi, R.; Mori, H.; Kihara, D. Genome-Scale Identification and Characterization of Moonlighting Proteins. Biol. Direct 2014, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jeffery, C.J. Moonlighting Proteins in the Fuzzy Logic of Cellular Metabolism. Molecules 2020, 25, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatigorsky, J.; Wistow, G.J. Enzyme/Crystallins: Gene Sharing as an Evolutionary Strategy. Cell 1989, 57, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, N.J.; Patel, K.J.; Rizwan, A.; Jeffery, C.J. Moonlighting Proteins: Diverse Functions Found in Fungi. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satala, D.; Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Zelazna, A.; Rapala-Kozik, M.; Kozik, A. Moonlighting Proteins at the Candidal Cell Surface. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmadi, V.; Biswas, M. An Overview of Moonlighting Proteins in Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Bhalla, N. Moonlighting Proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2020, 54, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E.; Aguilar-Díaz, H.; Amaro-Estrada, I. An Alternative Vaccine Target for Bovine Anaplasmosis Based on Enolase, a Moonlighting Protein. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1225873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Xia, Y.; Cui, J.; Gu, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. The Roles of Moonlighting Proteins in Bacteria. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2014, 16, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz Castañeda, R.E.; Amaro Estrada, I.; Martínez Ocampo, F.; Rodríguez Camarillo, S.; Dantán González, E.; Cobaxin Cárdenas, M.; Preciado de la Torre, J.F. Draft Genome Sequence of Anaplasma marginale Strain Mex-01-001-01, a Mexican Strain That Causes Bovine Anaplasmosis. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e01101-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ocampo, F.; Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E.; Amaro-Estrada, I.; Dantán-González, E.; De La Torre, J.F.P.; Rodríguez-Camarillo, S. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Mexican Strains of Anaplasma marginale: An Approach to the Causal Agent of Bovine Anaplasmosis. Int. J. Genom. 2020, 2020, 5902029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ocampo, F.; Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E.; Amaro-Estrada, I.; Cobaxin Cárdenas, M.; Dantán-González, E.; Rodríguez-Camarillo, S. Draft Genome Sequences of Anaplasma marginale Strains MEX-15-099-01 and MEX-31-096-01, Two Mexican Isolates with Different Degrees of Virulence. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01184-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations Using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zabad, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Jeffery, C. MoonProt 2.0: An Expansion and Update of the Moonlighting Proteins Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D640–D644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. EggNOG-Mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, S.A.; Sokoli, A.; Felder, K.M.; Wittenbrink, M.M.; Schwarzenbach, S.; Guhl, B.; Hoelzle, K.; Hoelzle, L.E. The Surface-Localised α-Enolase of Mycoplasma suis Is an Adhesion Protein. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.D.; Takara, L.E.M.; Monaris, D.; Gonçalves, A.P.; Souza-Filho, A.F.; de Souza, G.O.; Heinemann, M.B.; Ho, P.L.; Abreu, P.A.E. GroEL Protein of the Leptospira Spp. Interacts with Host Proteins and Induces Cytokines Secretion on Macrophages. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, T.; Wei, Y.; Gan, Y.; Shao, J.; Shao, G.; Feng, Z.; et al. DnaK Functions as a Moonlighting Protein on the Surface of Mycoplasma hyorhinis Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 842058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archambaud, C.; Gouin, E.; Pizarro-Cerda, J.; Cossart, P.; Dussurget, O. Translation Elongation Factor EF-Tu Is a Target for Stp, a Serine-Threonine Phosphatase Involved in Virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 56, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting Modern Challenges in Visualization and Analysis. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Cheong, G.-W.; Zhang, S. Multifunctional Enzymes in Archaea: Promiscuity and Moonlight. Extremophiles 2013, 17, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligabue-Braun, R.; Carlini, C.R. Moonlighting Toxins: Ureases and Beyond. In Plant Toxins; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, W.; Mulders, J.W.; Bibby, M.A.; Slingsby, C.; Bloemendal, H.; de Jong, W.W. Duck Lens Epsilon-Crystallin and Lactate Dehydrogenase B4 Are Identical: A Single-Copy Gene Product with Two Distinct Functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7114–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.; Martin, A. Bacterial Virulence in the Moonlight: Multitasking Bacterial Moonlighting Proteins Are Virulence Determinants in Infectious Disease. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3476–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert, A.; Losse, J.; Gruszin, C.; Hühn, M.; Kaendler, K.; Mikkat, S.; Volke, D.; Hoffmann, R.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Seeberger, H.; et al. Immune Evasion of the Human Pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Elongation Factor Tuf Is a Factor H and Plasminogen Binding Protein. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2979–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antikainen, J.; Kuparinen, V.; Lähteenmäki, K.; Korhonen, T.K. Enolases from Gram-Positive Bacterial Pathogens and Commensal Lactobacilli Share Functional Similarity in Virulence-Associated Traits. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, G.H.; Barbet, A.F.; Cantor, G.H.; McGuire, T.C. Immunization of Cattle with the MSP-1 Surface Protein Complex Induces Protection against a Structurally Variant Anaplasma marginale Isolate. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 3666–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnes, J.T.; Brayton, K.A.; LaFollett, M.; Norimine, J.; Brown, W.C.; Palmer, G.H. Identification of Anaplasma Marginale Outer Membrane Protein Antigens Conserved between A. marginale Sensu Stricto Strains and the Live A. Marginale subsp. Centrale Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, C.J. Why Study Moonlighting Proteins? Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.E.; Hipp, M.S.; Bracher, A.; Hayer-Hartl, M.; Ulrich Hartl, F. Molecular Chaperone Functions in Protein Folding and Proteostasis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 323–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, W.; Walz, J.; Zühl, F.; Seemüller, E. The Proteasome: Paradigm of a Self-Compartmentalizing Protease. Cell 1998, 92, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J. Molecular Chaperones: Assisting Assembly in Addition to Folding. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensgraber, M.; Loos, M. A 66-Kilodalton Heat Shock Protein of Salmonella typhimurium Is Responsible for Binding of the Bacterium to Intestinal Mucus. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 3072–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, K.R.; Wilson, H.L. Understanding GroEL and DnaK Stress Response Proteins as Antigens for Bacterial Diseases. Vaccines 2020, 8, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, L.; Gründel, A.; Jacobs, E.; Dumke, R. The Surface-Displayed Chaperones GroEL and DnaK of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Interact with Human Plasminogen and Components of the Extracellular Matrix. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, T.B.M.; Thorson, L.M.; Speert, D.P.; Daffé, M.; Stokes, R.W. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Cpn60.2 and DnaK Are Located on the Bacterial Surface, Where Cpn60.2 Facilitates Efficient Bacterial Association with Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3389–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, P.K.; Bansal, A.; Sagi, S.S.K.; Mustoori, S.; Govindaswamy, I. Cloning, Expression and Characterization of Heat Shock Protein 60 (GroEL) of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi and Its Role in Protective Immunity against Lethal Salmonella Infection in Mice. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainulainen, V.; Korhonen, T.K. Dancing to Another Tune—Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins in Bacteria. Biology 2014, 3, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widjaja, M.; Harvey, K.L.; Hagemann, L.; Berry, I.J.; Jarocki, V.M.; Raymond, B.B.A.; Tacchi, J.L.; Gründel, A.; Steele, J.R.; Padula, M.P.; et al. Elongation Factor Tu Is a Multifunctional and Processed Moonlighting Protein. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K.L.; Jarocki, V.M.; Charles, I.G.; Djordjevic, S.P. The Diverse Functional Roles of Elongation Factor Tu (EF-Tu) in Microbial Pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Niu, X.; Mei, W.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Willias, S.P.; Yuan, C.; Bei, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Immunogenicity and Protective Capacity of EF-Tu and FtsZ of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 against Lethal Infection. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2581–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.E.; Siems, W.F.; Palmer, G.H.; Brayton, K.A.; McGuire, T.C.; Norimine, J.; Brown, W.C. Identification of Novel Antigenic Proteins in a Complex Anaplasma Marginale Outer Membrane Immunogen by Mass Spectrometry and Genomic Mapping. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 8109–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, V.; Fischetti, V.A. A-Enolase, a Novel Strong Plasmin(Ogen) Binding Protein on the Surface of Pathogenic Streptococci. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14503–14515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier Pérez De La Rosa, J.; Ureostegui, P.V.; Antonio Álvarez Martínez, J.; Rojas Martínez, C.; Manuel González Zuñiga, V.; Figueroa Millán, J.V. Identificación Inicial de Genes En Babesia Bigemina Mediante Análisis de Etiquetas de Secuencia Expresadas En El Estadio Intraeritrocítico Del Parásito. Rev. Mex. Ciencias Pecu. 2012, 3, 61–87. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas-Flores, A. Caracterización de La Proteína Enolasa de Babesia Bovis e Identificación de Epítopos Inmunogénicos; Universidad Autónoma de Querétaro: Querétaro, Mexico, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Seo, K.; Yang, M.; Cui, C.; Yang, M.; Xiang, S.; Yan, Z.; Wu, S.; Han, J.; Yu, X.; et al. Mycoplasma suis Alpha-Enolase Subunit Vaccine Induces an Immune Response in Experimental Animals. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NCBI ID | A. marginale Strain MEX-15-099-01 Proteins | Protein Name and Species in MoonProt 3.0 Database | Function 1 | Function 2 | E-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KAA8473050.1 | DNA mismatch repair endonuclease MutL | Mismatch repair endonuclease PMS2, Mus musculus | PMS2 mismatch repair enzyme introduces single-stranded breaks near the mismatch | Hypermutation of antibody variable chains | 1.43 × 10−28 |
| 2 | KAA8473081.1 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | MalK, Escherichia coli | ATP binding/hydrolysis protein of MalEFGK maltose/maltodextrin transporter (importer), an ABC transporter ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate | Transcription regulation binds to MalT activator of mal regulon and prevents its action | 2.73 × 10−48 |
| 3 | KAA8473084.1 | Biotin-[acetyl-CoA-carboxylase] ligase | birA biotin sythetase, Escherichia coli | birA biotin synthetase, enzyme biotin-acetyl-CoA-carboxylase] ligase ATP + biotin + apo-[acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming)] = AMP + diphosphate + [acetyl-CoA:carbon-dioxide ligase (ADP-forming)] | Bio-operon repressor activity depends on cellular concentration of biotin | 6.49 × 10−19 |
| 4 | KAA8473103.1 | Porphobilinogen synthase | Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase, Homo sapiens | 5-aminolaevulinate dehydratase, enzyme converts 2 (5-aminolevulinate) to porphobilinogen + 2H2O. Porphyrin-containing compound metabolism, protoporphyrin-IX biosynthesis | Proteasome inhibitor noncompetitively blocks proteolysis of certain protein substrates | 1.14 × 10−56 |
| 5 | KAA8473122.1 | Leucine-tRNA ligase | Leucyl-tRNA synthetase, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Leucyl-tRNA synthetase, enzyme ATP + L-leucine + tRNA (Leu) ⇒ AMP + diphosphate + L-leucyl-tRNA (Leu) protein synthesis | Intron splicing, RNA splicing group I intron splicing | 1.53 × 10−14 |
| 6 | KAA8473129.1 | excinuclease ABC subunit UvrA | MDR1, Homo sapiens | Transmembrane transporter efflux pump, uses ATP for energy expels drugs and other small molecule compounds ATP + H2O + xenobiotic (Inside) => ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic (Outside) | Regulator of volume-activated chloride channels | 2.23 × 10−6 |
| 7 | KAA8473164.1 | Proline-tRNA ligase | Threonyl-tRNA synthetase, Escherichia coli | Threonine-tRNA ligase, enzyme ATP + L-threonine + tRNA (Thr) => AMP + diphosphate + L-threonyl-tRNA (Thr) | Binds mRNA encoding threonyl-tRNA synthetase, controls expression of its own gene at the translational level | 6.82 × 10−12 |
| 8 | KAA8473168.1 | Alkyl hydroperoxide reductase subunit C-like protein | Mitochondrial 2-cysteine peroxiredoxin Leishmania infantum | Peroxidase activity, detoxification of reactive oxygen species (ROS), removal of peroxide, uses redox active cysteine residue (peroxidatic Cys) to reduce substrates like H2O2 | Chaperone and activators of signal transduction cascades, prevents thermal aggregation of citrate synthase in vitro, lack of expression makes promastigotes more sensitive to temperature in the mammalian host (37 °C) | 1.27 × 10−52 |
| 9 | KAA8473177.1 | Translation elongation factor LepA | Elongation factor 2, Homo sapiens | Translation elongation factor | Binding partner for Akt2 signaling molecule | 6.10 × 10−24 |
| 10 | KAA8473193.1 | Triosephosphate isomerase | Triose phosphate isomerase, Staphylococcus aureus | Triose phosphate isomerase, enzyme D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate ⇔ dihydroxyacetone phosphate Carbohydrate degradation, glycolysis Carbohydrate biosynthesis, gluconeogenesis | Adhesin, contact-mediated killing of Cryptococcus | 4.52 × 10−45 |
| 11 | KAA8473199.1 | Adenylosuccinate lyase | Argininosuccinate lyase, Anas platyrhynchos | Argininosuccinate lyase, enzyme Catalyzes the breakdown of argininosuccinate to produce arginine and fumarate. It is the fourth enzyme of the urea cycle. Argininosuccinase is involved in biosythesis of arginine in all species and production of urea in ureotelic organisms. 2-(N(omega)-L-arginino)succinate => fumarate + L-arginine Amino-acid biosynthesis, arginine biosynthesis | Delta-2 Crystallin in the lens of the eye—only in birds and reptiles | 6.71 × 10−7 |
| 12 | KAA8473204.1 | Aspartate aminotransferase | MalY, Escherichia coli | Beta-cystathionase, enzyme cleavage of cystathionine to homocysteine, ammonia, and pyruvate L-cystathionine + H2O => L-homocysteine + NH3 + pyruvate Amino-acid biosynthesis, methionine biosynthesis | Transcription regulation binds to MalT activator of mal regulon and prevents its action | 1.42 × 10−7 |
| 13 | KAA8473206.1 | Rod shape-determining protein | DnaK, Lactococcus lactis | Chaperone | Binding to invertase, a hyperglycosylated mannoprotein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 3.82 × 10−9 |
| 14 | KAA8472839.1 | Phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase | Phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase, Schizosaccharomyces pombe | Phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase, decarboxylation of phosphopahtothenoyl-L-cysteine, in CoA biosynthesis, PPCDC | Inhibitor of serine/threoinine phosphatase Pzh1 | 7.40 × 10−25 |
| 15 | KAA8472842.1 | Phosphoglycerate kinase | Phosphoglycerate kinase, Streptococcus anginosus and S. oralis | Phosphoglycerate kinase, enzyme ADP + 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate => ATP + 3-phospho-D-glycerate Carbohydrate degradation, glycolysis | Plasminogen binding | 2.25 × 10−81 |
| 16 | KAA8472854.1 | Ketol-acid reductoisomerase | Acetohydroxyacid isomerase, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Acetohydroxyacid reductoisomerase, enzyme Amino-acid biosynthesis, L-leucine, L-isoleucine and L-valine biosynthesis (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate + NADP+ => (S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH (2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoate + NADP+ => (S)-2-hydroxy-2-ethyl-3-oxobutanoate + NADPH Cofactor | maintain mitochondrial DNA stability enzyme catalytic Function not needed for this role | 1.24 × 10−25 |
| 17 | KAA8472865.1 | Molecular chaperone DnaJ | Zuotin, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Component of a chaperone complex component of the ribosome-associated complex (RAC) that helps in folding of nascent polypeptide chains | Activator of a transcription factor activates Pdr1 transcription factor | 1.46 × 10−6 |
| 18 | KAA8472874.1 | NAD-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAPDH, Bacillus anthracis | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, enzyme catalyzes the oxidative phosphorylation of D-glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate (G-3-P) to 1,3-diphosphoglycerate in the presence of NAD+/NADP+ and inorganic phosphate (Pi) | Plasminogen binding | 2.06 × 10−99 |
| 19 | KAA8472877.1 | Aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase | Arg5,6, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Enzyme in the arginine biosynthetic pathway N-acetyl-gamma phosphate reductase and acetyl glutamate kinase | Arg5 binds to mitochondrial and nuclear DNA in vivo and regulates gene expression, regulator of transcription for several genes | 1.16 × 10−6 |
| 20 | KAA8472881.1 | Threonine-tRNA ligase | Threonyl-tRNA synthetase, Escherichia coli | Threonine-tRNA ligase, enzyme ATP + L-threonine + tRNA(Thr) => AMP + diphosphate + L-threonyl-tRNA(Thr) | Binds mRNA binds mRNA encoding threonyl-tRNA synthetase, controls expression of its own gene at the translational level | 0 |
| 21 | KAA8472917.1 | Ornithine carbamoyltransferase | Ornithine carbamoyltransferase, Staphylococcus epidermidis | Ornithine carbamoyltransferase, enzyme Carbamoyl phosphate + L-ornithine => phosphate + L-citrulline | Bind fibronectin | 2.49 × 10−16 |
| 22 | KAA8472922.1 | ATP-binding cassette domain-containing protein | MalK, Escherichia coli | ATP binding/hydrolysis protein of MalEFGK maltose/maltodextrin transporter (importer) an ABC transporter ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate | Transcription regulation binds to MalT activator of mal regulon and prevents its action | 2.98 × 10−23 |
| 23 | KAA8472925.1 | Glutamine synthetase | Glutamine synthetase, Bifidobacterium | Glutamine synthetase, enzyme ATP + L-glutamate + NH3 => ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine | Plasminogen binding | 2.53 × 10−140 |
| 24 | KAA8472933.1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 subunit, Bacillus thuringiensis | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 subunit, dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase | DNA binding, transcription regulation | 3.95 × 10−54 |
| 25 | KAA8472947.1 | Valine-tRNA ligase | Leucyl-tRNA synthetase, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Leucyl-tRNA synthetase, enzyme ATP + L-leucine + tRNA (Leu) => AMP + diphosphate + L-leucyl-tRNA (Leu) protein synthesis | Intron splicing, RNA splicing group I intron splicing | 1.53 × 10−14 |
| 26 | KAA8472967.1 | Tyrosine-tRNA ligase | Tyrosyl tRNA synthetase, Neurospora crassa | Tyrosyl tRNA synthetase, enzyme attaches tyrosine to tRNA (Tyr) ATP + L-tyrosine + tRNA (Tyr) = AMP + diphosphate + L-tyrosyl-tRNA(Tyr) | Promotes folding of group 1 introns | 1.46 × 10−56 |
| 27 | KAA8472719.1 | Quinone oxidoreductase | NADPH quinone oxidoreductase, Zeta-crystallin, Hyla japonica | NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase, enzyme | Zeta crystallin (Also in camel, llamas and Guinea pig) | 5.67 × 10−29 |
| 28 | KAA8472720.1 | Type I secretion system permease/ATPase | MDR1, Homo sapiens | Transmembrane transporter efflux pump, uses ATP for energy expels drugs and other small molecule compounds ATP + H2O + xenobiotic (Inside) => ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic (Outside) | Regulator of volume-activated chloride channels | 1.96 × 10−32 |
| 29 | KAA8472725.1 | Class II fumarate hydratase | Aspartate ammonia lyase, aspartase, Haemophilus influenzae | Aspartate ammonia lyase, aspartase, enzyme L-aspartate => fumarate + NH3 | Binds plasminogen | 1.48 × 10−101 |
| 30 | KAA8472731.1 | Chaperonin GroEL | Hsp60, Helicobacter pylori | Chaperonin, prevents protein misfolding, promotes the refolding and proper assembly of unfolded proteins | Adhesin—to host cells | 6.77 × 10−169 |
| 31 | KAA8472736.1 | Cytosol aminopeptidase PepA | PepA, Escherichia coli | Aminopeptidase, enzyme removes amino-terminal amino acid, preferentially if it is Leu | Transcriptional repressor binds DNA, binds car operator DNA represses the carAB operon | 1.55 × 10−84 |
| 32 | KAA8472754.1 | NAD(P)H-dependent glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, Candida albicans | Glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, functions in glycerol accumulation | Plasminogen binding | 1.38 × 10−18 |
| 33 | KAA8472760.1 | ATP-dependent protease ATPase subunit HslU | FtsH, Shigella flexneri | Chaperone | Metalloprotease, enzyme ATP-dependent zinc metallopeptidase, hydrolyzes cytoplasmic and transmembrane proteins | 1.3 × 10−6 |
| 34 | KAA8472784.1 | Aconitate hydratase AcnA | Aconitase, Bos taurus | Aconitase, enzyme 4Fe-4S cluster in active site when cellular iron levels are high Citrate <=> isocitrate Citric acid cycle | Iron-responsive element binding protein when cellular iron concentrations are low, loses 4Fe-4S cluster and binds to iron-responsive elements (IRES) in mRNA that encodes proteins that are involved in iron uptake and use | 0 |
| 35 | KAA8472802.1 | Methionine-tRNA ligase | Methionyl-tRNA synthetase, Homo sapiens | Methionyl-tRNA synthetase, enzyme ATP + L-methionine + tRNA(Met) => AMP + diphosphate + L-methionyl-tRNA(Met) protein synthesis | Biogenesis of rRNA in nucleoli translocation to nucleolus triggered by growth factors | 4.55 × 10−40 |
| 36 | KAA8472628.1 | Superoxide dismutase | Superoxide dismutase, Mycobacterium avium | Superoxide dismutase, enzyme antioxidant converts superoxide anion radicals into O2 and H2O2 | Adhesin | 2.06 × 10−31 |
| 37 | KAA8472646.1 | Molecular chaperone DnaK | DnaK, Bifidobacterium(Bifidobacterium lactis, B. bifidum, and B. longum) | Chaperone | Plasminogen binding | 0 |
| 38 | KAA8472652.1 | Transketolase | Transketolase, Escherichi coli | Transketolase, enzyme Pentose Phosphate Pathway Sedoheptulose 7-phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate <=> D-ribose 5-phosphate + D-xylulose 5-phosphate | Transcriptional regulator derepresses the marRAB multiple antibiotic resistance operon by binding to the MarR repressor, a “trigger enzyme” | 0 |
| 39 | KAA8472657.1 | Glutamate-tRNA ligase | Glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase, Homo sapiens | Glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase, enzyme an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase catalyze the attachment of amino acids to cognate tRNAs ATP + L-glutamate + tRNA(Glu) => AMP + diphosphate + L-glutamyl-tRNA(Glu) ATP + L-proline + tRNA(Pro) => AMP + diphosphate + L-prolyl-tRNA(Pro) | Translation inhibition part of GAIT complex: interferon (IFN)-gamma-activated inhibitor of translation silences ceruloplasmin mRNA translation | 1.85 × 10−15 |
| 40 | KAA8472519.1 | HtrA protease/chaperone protein | DegP, Escherichia coli | Peptidase at higher temperatures | Chaperone at low temperatures | 3.81 × 10−72 |
| 41 | KAA8472533.1 | Hihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase component (E2) of 2- oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex | Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase E2, Trypanosoma brucei | Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase E2, in Krebs cycle, dihydrolipoyl succinyltransferase | Mitochondrial DNA inheritance | 1.24 × 10−87 |
| 42 | KAA8472539.1 | Metalloprotease | DegP, Escherichia coli | Peptidase at higher temperatures. | Chaperone at low temperatures | 9.6 × 10−7 |
| 43 | KAA8472556.1 | ATP-dependent metallopeptidase FtsH/Yme1/Tma family protein | FtsH, Shigella flexneri | Chaperone | Metalloprotease, enzyme ATP-dependent zinc metallopeptidase, hydrolyzes cytoplasmic and transmembrane proteins | 0 |
| 44 | KAA8472563.1 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase | Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Isocitrate dehydrogenase, enzyme isocitrate + NAD+ = 2-oxoglutarate + CO2 + NADH Citric acid cycle | Binds mRNA specifically to 5′-untranslated leaders of mitochondrial mRNAs | 6.43 × 10−74 |
| 45 | KAA8472473.1 | Hsp70 family protein | DnaK, Neisseria meningitidis | Chaperone | Plasminogen binding protein | 4.09 × 10−106 |
| 46 | KAA8472398.1 | 50S ribosomal protein L1 | L1 ribosomal protein, Escherichia coli | Ribosomal protein, part of the 50S subunit | Translational repressor binds to the mRNA of the L11 operon | 2.37 × 10−56 |
| 47 | KAA8472399.1 | 50S ribosomal protein L10 | L10 ribosomal protein, Escherichia coli | Ribosomal protein part of the 50S subunit | Translation inhibitor autogenous regulation of translation | 6.83 × 10−10 |
| 48 | KAA8472401.1 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta | DNA-directed RNA polymerase beta subunit, Streptococcus gordonii | Beta subunit of DNA-directed RNA polymerase | Muc7 binding protein | 7.26 × 10−41 |
| 49 | KAA8472421.1 | Succinate dehydrogenase, cytochrome b556 subunit | Succinate dehydrogenase subunit 3, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Subunit of succinate dehydrogenase in the respiratory chain, electron transport in respiratory complex II | Part of TIM22 complex (carrier translocase, mitochondrial inner membrane translocase) in mitochondria, helps in biogenesis and assembly of membrane-integral subunits of TIM22 complex | 2.33 × 10−9 |
| 50 | KAA8472432.1 | ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit ClpX | FtsH, Shigella flexneri | Chaperone | Metalloprotease, enzyme ATP-dependent zinc metallopeptidase, hydrolyzes cytoplasmic and transmembrane proteins | 6.18 × 10−7 |
| 51 | KAA8472433.1 | Endopeptidase La | FtsH, Shigella flexneri | Chaperone | Metalloprotease, enzyme ATP-dependent zinc metallopeptidase, hydrolyzes cytoplasmic and transmembrane proteins | 8.2 × 10−9 |
| 52 | KAA8472438.1 | 30S ribosomal protein S4 | S4 ribosomal protein, Escherichia coli | S4 ribosomal protein part of the 30S subunit, helps nucleate assembly of the 30S subunit by binding directly to the 16S rRNA | Translational repressor binds mRNA of operon encoding S3, S11, S4 | 6.05 × 10−41 |
| 53 | KAA8472355.1 | Isoleucine-tRNA ligase | Leucyl-tRNA synthetase, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Leucyl-tRNA synthetase, enzyme ATP + L-leucine + tRNA (Leu) => AMP + diphosphate + L-leucyl-tRNA (Leu) protein synthesis | Intron splicing, RNA splicing group I intron splicing | 4.64 × 10−14 |
| 54 | KAA8472356.1 | Thiol peroxidase (Peroxiredoxin) | Peroxiredoxin, Neisseria meningitidis | Peroxiredoxin, antioxidant | Plasminogen binding | 1.29 × 10−34 |
| 55 | KAA8472364.1 | NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit NuoI | Pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase, Trichomonas vaginalis | Pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase, enzyme oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to yield acetyl-CoA and CO2 | Cell surface adherence protein | 9.65 × 10−5 |
| 56 | KAA8472372.1 | Translational GTPase TypA | EF-G, Streptococcus gordonii | Elongation factor in translation catalyzes translocation step, uses GTP | Adhesin, binds salivary mucin MUC7 | 7.93 × 10−27 |
| 57 | KAA8472305.1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E1 component subunit beta | Pyruvate dehydrogenase, Mycoplasma pneumoniae | Pyruvate dehydrogenase, enzyme, the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion pyruvate => acetyl-CoA and CO2. Pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1) is one of the enzyme components of the complex | Fibrinogen binding | 1.09 × 10−56 |
| 58 | KAA8472326.1 | Lipoprotein releasing (ABC transporter ATP-binding protein) | MalK, Escherichia coli | ATP binding/hydrolysis protein of MalEFGK maltose/maltodextrin transporter (importer) an ABC transporter ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate | Transcription regulation binds to MalT activator of mal regulon and prevents its action | 8.20 × 10−23 |
| 59 | KAA8472251.1 | Holliday junction branch migration DNA helicase RuvB | Regulatory particle triple-A ATPase subunit 5b, Arabidopsis thaliana | Part of the regulatory ATPase complex of the 26S proteasome, confers substrate specificity and need for ATP to the proteasome | Binds to hexokinase 1 and VHA B1 to modulate transcription of specific target genes | 3.89 × 10−6 |
| 60 | KAA8472256.1 | ABC transporter (ATP-binding cassette domain-containing protein) | MDR1, Homo sapiens | Transmembrane transporter efflux pump, uses ATP for energy expels drugs and other small molecule compounds ATP + H2O + xenobiotic (Inside) => ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic (Outside) | Regulator of volume-activated chloride channels | 6.69 × 10−79 |
| 61 | KAA8472258.1 | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, Homo sapiens | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, enzyme 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + glycine + H2O <=> tetrahydrofolate + L-serine one-carbon metabolism, tetrahydrofolate interconversion | Binds mRNA binds the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) of its own mRNA | 1.29 × 10−103 |
| 62 | KAA8472274.1 | Heme ABC exporter ATP-binding protein CcmA | MalK, Escherichia coli | ATP binding/hydrolysis protein of MalEFGK maltose/maltodextrin transporter (importer) an ABC transporter ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate | Transcription regulation binds to MalT activator of mal regulon and prevents its action | 1.29 × 10−14 |
| 63 | KAA8472191.1 | 50S ribosomal protein L4 | L4 ribosomal protein, Escherichia coli | Ribosomal protein, part of the 50S subunit | Transcriptional repressor causes premature termination of transcription within S10 operon | 2.13 × 10−26 |
| 64 | KAA8472193.1 | 50S ribosomal protein L2 | L2 ribosomal protein, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Component of the ribosome large subunit (60S) | Regulates accumulation of L2 mRNA, shortens half-life of L2 mRNA | 2.66 × 10−24 |
| 65 | KAA8472200.1 | 50S ribosomal protein L14 | L14 ribosomal protein, Escherichia coli | Ribosomal protein part of the 30S subunit binds to the 23S rRNA | Binds DNA, stimulates unwinding of DNA by Rep helicase protein | 3.07 × 10−40 |
| 66 | KAA8472202.1 | 50S ribosomal protein L5 | L11 ribosomal protein, Mus musculus | Ribosomal protein, part of 60S subunit | Binds to and inhibits HDM2, a ubiquitin ligase, which results in stabilization of p53 tumor suppressor protein | 1.31 × 10−13 |
| 67 | KAA8472204.1 | 30S ribosomal protein S8 | S8 ribosomal protein, Escherichia coli | S8 ribosomal protein part of the 30S subunit binds to 16S rRNA | Translational repressor inhibits expression of some proteins encoded by the spc operon | 7.13 × 10−41 |
| 68 | KAA8472212.1 | 30S ribosomal protein S11 | S14 ribosomal protein, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Component of the ribosome small subunit (40S) | Represses expression of RPS14B gene, rpS14 binds directly to RNA, binds to an RNA stem-loop structure in RPS14B pre-mRNA | 1.5 × 10−9 |
| 69 | KAA8472223.1 | Phosphate ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | MDR1, Homo sapiens | Transmembrane transporter efflux pump, uses ATP for energy, expels drugs and other small molecule compounds ATP + H2O + xenobiotic (Inside) => ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic (Outside) | Regulator of volume-activated chloride channels | 6.61 × 10−31 |
| 70 | KAA8472142.1 | UMP kinase | PyrH, Escherichia coli | UMP kinase, enzyme phosphorylates UMP to UDP ATP + UMP <=> ADP + UDPde novo biosynthetic pathway of pyrimidine nucleotides | Transcriptional regulator involved in pyrimidine-specific repression of the carAB operon binds to PepA | 1.55 × 10−74 |
| 71 | KAA8472163.1 | Thioredoxin | Thioredoxin, Escherichia coli | Thioredoxin antioxidant aids the reduction of other proteins by cysteine thiol-disulfide exchange | Subunit of T7 DNA polymerase (maybe not strictly considered moonlighting because adopted by a phage to be part of a protein complex) | 6.18 × 10−26 |
| 72 | KAA8472099.1 | Glutamine synthetase | Glutamine synthetase, Bifidobacterium (Bifidobacterium lactis, B. bifidum, and B. longum) | Glutamine synthetase, enzyme ATP + L-glutamate + NH3 => ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine | Plasminogen binding | 3.53 × 10−16 |
| 73 | KAA8472120.1 | 30S ribosomal protein S7 | S7 ribosomal protein, Escherichia coli | Ribosomal protein binds to 16S rRNA part of the 30S subunit | Translational repressor regulates the expression of two proteins encoded by the str operon | 2.05 × 10−46 |
| 74 | KAA8472121.1 | Elongation factor G | EF-G, Streptococcus gordonii | Elongation factor in translation catalyzes translocation step, uses GTP | Adhesin, binds salivary mucin MUC7 | 0 |
| 75 | KAA8471941.1 | Elongation factor Tu | Translation elongation factor Tu, Streptococcus gordonii | Translation elongation factor Tu | Mucin (MUC7)-binding protein | 3.29 × 10−12 |
| 76 | KAA8472015.1 | Aspartate tRNA ligase | Lysyl-tRNA synthetase, Homo sapiens | Lysyl-tRNA synthetase, enzyme ATP + L-lysine + tRNA (Lys) = AMP + diphosphate + L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys) protein synthesis | Cytokine binds to macrophages and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, increases TNF-alpha Production by target cells increases target cell migration | 5.64 × 10−14 |
| 77 | KAA8472021.1 | Cytochrome c family protein | Cytochrome C, Equus caballus | Electron carrier protein component of the mitochondrial electron-transport chain | Binding to apoptosis protease activation factor-1 (Apaf-1), promotes apoptosis release from mitochondria, allows interaction with apoptosis proteins | 2.04 × 10−26 |
| 78 | KAA8471995.1 | Bifunctional proline dehydrogenase/L-glutamate gamma-semialdehyde dehydrogenase | PutA, Salmonella typhimurium | Proline dehydrogenase/Proline oxidase pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid dehydrogenase activity | Transcriptional repressor of the put operon | 0 |
| 79 | KAA8472002.1 | Phosphopyruvate hydratase | Enolase, Bacillus anthracis | Enolase, enzyme 2-phospho-D-glycerate => phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O, catalyzes the reversible conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate into phosphoenolpyruvate, carbohydrate degradation, glycolysis | Binds plasminogen and laminin | 8.84 × 10−171 |
| 80 | KAA8471950.1 | Malate dehydrogenase | Lactate dehydrogenase isozyme M, Mus musculus | Enzyme, lactate + NAD+ -> pyruvate + NADH | RNA binding protein, post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression, AU-rich element (ARE, binding to these kinds of elements can be involved in affecting RNA stability) binding protein (AUBP), role may also involve binding to AUF1 protein, binds the 3-UTR of GM-CSF RNA | 3.98 × 10−52 |
| MLPs | B-Cell Epitopes | |
|---|---|---|
| BCEPred | SVMTrip | |
| AmEno | YNVIISHRSGETEDVTIA VSPFDQRAVDEILLSLDGTKNKSKLG YKLKEVLKKMGHSTNTGDEGGFA PNLENNTDVLDVLVEAIERSGYRASSDV | DIEGWKAVTKRLGDKIQL (1.0) CAEVFYKLKEVLKKMGHSTN (0.861) SYKFSGKCLTSGELIACYED (0.859) |
| AmEF-Tu | LLRGIKKEDVERGQVL GQIRSYKAFKAEVYILKKEEGGRHTPF KIELPVREKDKPFLM | SEKIMELVGALEKIELPVRE (1.0) |
| AmGroEl | QIKSQIEVSSSDYDKEKLKERLAKL QCVREVGKDGVITVEESK GFKDLEVERTDGMQF | KKINLVQSILPVLENVARSG (1.0) MANVVVTGEALDKSIREVVR (0.975) EDEIAQVATISANGDKNIGG (0.809) |
| AmDnaK | AFTENERLVGELAKRQANINAQNTIYASKRIIGRRYDDMRDVKCPY AKHLSLKLTRAKFEGLVSELIERTIEPCKKALDDAGIKDTSKIDE SDTSGNPEERVVDSEYQEIKKDDEDKK | GDKISSADKSGIEAAIKELR (1.0) VLEIAEGVFEVKATNGDTKL (0.999) GAKHLSLKLTRAKFEGLVSE (0.867) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E.; Aguilar-Díaz, H.; Coronado-Villanueva, E.; Catalán-Ochoa, D.I.; Amaro-Estrada, I. Molecular Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of Anaplasma marginale Moonlighting Proteins as Possible Antigenic Targets. Pathogens 2024, 13, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100845
Quiroz-Castañeda RE, Aguilar-Díaz H, Coronado-Villanueva E, Catalán-Ochoa DI, Amaro-Estrada I. Molecular Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of Anaplasma marginale Moonlighting Proteins as Possible Antigenic Targets. Pathogens. 2024; 13(10):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100845
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuiroz-Castañeda, Rosa Estela, Hugo Aguilar-Díaz, Eduardo Coronado-Villanueva, Diego Israel Catalán-Ochoa, and Itzel Amaro-Estrada. 2024. "Molecular Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of Anaplasma marginale Moonlighting Proteins as Possible Antigenic Targets" Pathogens 13, no. 10: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100845
APA StyleQuiroz-Castañeda, R. E., Aguilar-Díaz, H., Coronado-Villanueva, E., Catalán-Ochoa, D. I., & Amaro-Estrada, I. (2024). Molecular Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of Anaplasma marginale Moonlighting Proteins as Possible Antigenic Targets. Pathogens, 13(10), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100845









