Abstract
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are a growing concern for human and animal health. The objective of this study was to determine the antimicrobial resistance and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase genes in Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas spp. and Acinetobacter spp. isolates from the uterus of healthy mares. For this purpose, 21 mares were swabbed for samples, which were later seeded on blood agar and MacConkey agar. The isolates were identified using MALDI-TOF and the antimicrobial susceptibility test was performed using the Kirby–Bauer technique. To characterize the resistance genes, a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) scheme was performed. Of the isolates identified as Gram-negative, 68.8% were Enterobacterales, represented by E. coli, Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter spp., and Klebsiella pneumoniae; 28.1% belonged to the genus Acinetobacter spp.; and 3.1% to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. A 9.3% of the isolates were multidrug-resistant (MDR), presenting resistance to antibiotics from three different classes, while 18.8% presented resistance to two or more classes of different antibiotics. The diversity of three genes that code for ESBL (blaTEM, blaCTX-M and blaSHV) was detected in 12.5% of the strains. The most frequent was blaSHV, while blaTEM and blaCTX-M were present in Citrobacter spp. and Klebsiella pneumoniae. These results are an alarm call for veterinarians and their environment and suggest taking measures to prevent the spread of these microorganisms.
1. Introduction
The presence of microorganisms in the uterus of mares without reproductive pathologies has shown the existence of a uterine microbiota, of which nearly 200 microorganisms have been identified by molecular techniques [1,2,3,4,5]. These microorganisms play fundamental roles [6] in processes such as embryo implantation, prevention of the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, and protection of the epithelium [7,8,9]. It has been described that alteration or dysbiosis is related to the direct entry of bacteria through mating, artificial insemination, gynecological examination [1,6,10,11], malformation of the vulva or perineal region [12,13], and lesions of the cervix or vagina. These situations have been positively associated with bacterial endometritis [9,14], where Streptococcus equi, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., and Pseudomonas spp. are the most frequently isolated microorganisms in this pathology [15,16,17,18,19].
In some countries in Europe, India, and the United States, bacteria such as Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas spp., and Acinetobacter spp. isolated from the uterus and vagina of healthy mares [11,16,18,20,21,22,23] show resistance or multidrug resistance (MDR) to antibiotics [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as critically important pathogens [32] and are among the main antimicrobial resistance (RAM) threats in humans [33,34] and animals [35,36,37,38,39]. These situations are a cause of concern for the medical environment due to the probable dissemination of microorganisms and the limitation of therapeutic options [40]. The objective of this study was to determine the antimicrobial resistance and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase genes in Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas spp., and Acinetobacter spp. isolates from the uterus of healthy mares.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
This research was approved by the Scientific Committee of Ethics of the Central-South macrozone of the Santo Tomás University, Chile (Approval number 60-21) and was carried out in the Maule region (35°25′ S, 71°39′ W) during October 2021.
2.2. Subjects and Criteria Selection
The group consisted of 21 purebred Chilean mares, between 4 and 15 years old, who were fed in a mixed meadow of ryegrass and white clover with free access to water. All participants were off antibiotic treatment for at least one month before being sampled
Clinically healthy mares in the ovulatory phase were included; this was determined by a gynecological clinical examination, transrectal ultrasound (Chison Eco 6 ultrasound, 5 MHz linear transducer), and cytology [13]. No mare presented a record of abortion, embryonic losses, endometritis, dystocia, or any reproductive pathology.
2.3. Uterine Samples, Collection, Isolation, and Identification
To avoid contamination, the tail was covered with sterile gauze and the fecal material was removed from the rectum. Subsequently, the perineum, clitoral fossa, and vulva were washed with soap and lukewarm water. The vulva was dried with bleached paper and the procedure was repeated until the area was visibly clean. Sample contamination was minimized using a sterile rectal glove, and a double-guarded occluded swab (IMV, Legler, Limoges, France) [18].
The uterine swabs were introduced directly in Amies transport medium (Linsan, Santiago, Chile) and were immediately transferred to the Clinic Microbiology and Microbiome laboratory, where they were seeded within 24 h on blood agar and MacConkey agar (Merk, Darmstadt, Germany). All plates were incubated at 37 °C for 18 to 24 h. Semi-quantitative evaluation of the different morphotypes was carried out, so that those that showed abundant growth in the second quadrant of the clock were selected with the help of a magnifying glass, observing standard patterns such as colony shape, borders, topography, color, and texture [41]. Later, each morphotype was isolated on blood agar (Linsan, Santiago, Chile) and was identified using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry analysis (MALDI Biotyper, Bruker, Singapore) following the manufacturer’s instructions and as described previously [42,43]. Importantly, Citrobacter spp. were analyzed as members of the C. freundii complex due to the impossibility of identification down to the species level using the MALDI-TOF technique [44].
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
All isolates corresponding to Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas spp., and Acinetobacter spp. were tested against a panel of 13 antibiotics using the disk diffusion Kirby–Bauer method following CLSI guidelines in the M100 and VET01S [45,46]. Antibiotics tested included amikacin (AMK, 30 μg); ampicillin (AMP, 10 μg); amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (AUG 20/10 μg); ceftazidime (CAZ, 30 μg); ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 μg); ceftriaxone (CRO, 30 μg); doxycycline (DXT, 30 μg); enrofloxacin (ENR, 5 μg); ertapenem (ETP, 10 μg); gentamicin (GEN, 10 μg); imipenem (IPM, 10 μg); ampicillin/sulbactam (SAM, 10/10 μg); and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT, 1.25/23.75 μg). All of these were supplied by OXOID (Hampshire, UK). The AMP disc was not used for Pseudomonas spp., Enterobacter spp., Citrobacter spp., and Klebsiella spp. In addition, for Acinetobacter spp. we only tested carbapenems, within the group of beta-lactams [46].
The screening of organisms producing extended-spectrum b-lactamases (ESBLs) and/or AmpC was performed using Cefotaxime 30 μg (CTX), CTX + clavulanic acid, and CTX + cloxacillin disc (Liofilchem, Teramo, Italy). For Acinetobacter spp. and P. aeruginosa, CTX + clavulanic acid + cloxacillin disc (Liofilchem, Teramo, Italy) were used to inhibit the chromosomal AmpC b-lactamase, which can antagonize the synergistic effect with clavulanate [46].
In all experiments, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae ATCC 700603 and E. coli ATCC 25922 were used as resistant and susceptible controls, respectively. Bacterial isolates resistant to ≥1 agent in >3 antimicrobial different classes were cataloged as multidrug-resistant (MDR) following previously standardized criteria [47].
The genes encoding ESBLs (blaCTX-M, blaSHV, blaTEM, blaPER and blaGES) were detected by a conventional PCR scheme, as previously reported [30,48,49]. Briefly, PCR was performed in a volume of 25 µL in a Veriti® thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems). The reaction mix contained 1× Green GoTaq®Flexi Buffer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), PCR buffer, 800 nM of each primer (Table 1), 200 nM of dNTPs, 1.5 nM of MgCl2, 5 µL of DNA, and 1 U of Taq polymerase. The amplification program was an initial denaturation of 5 min at 94 °C, then 35 equal cycles of 40 s at 94 °C, 40 s at 52/57 °C, and 60 s at 72 °C. Finally, a final extension of 7 min at 72 °C occurred (Table 1). Tubes were stored at 4 °C until detection of the PCR product on 1.5% agarose gel. In cases where there was doubt that the size obtained in the PCR product was a non-specific amplification, it was decided to sequence them to confirm that they corresponded. For this, they were sequenced by the Sanger method using the BigDye® Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) in the SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems). The obtained sequences were compared with the GenBank database using the BLAST program. The sequences were deposited in the NCBI GenBank database (accession numbers OR242737, OR242738, OR242739, OR242740, and OR242741).

Table 1.
Primers used for ESBL PCRs.
2.5. Data Analysis
Data analysis was performed using Excel (Microsoft 365), open-source statistical computing package release 1.3.4; upset plots [50] were made employing the UpSetPlot package (https://github.com/jnothman/UpSetPlot, access on 25 April 2022), release 0.6.0.
3. Results
The group of 21 mares studied were composed of purebred Chilean females, with more than two births, between 4 and 15 years old, with an average age of 8 years.
As a result, each mare had a mixed bacterial growth in 100% of the cases, isolating at least two or three different bacteria, corresponding to 42.8% and 52.4%, respectively. In contrast, the largest bacterial population with four isolates was present in only one mare, representing 4.8%.
Of the 55 bacterial isolates, 39 (70.9%) were Gram-negative bacteria of which 22 (56.4%) belonged to Enterobacterales, represented by 17 Escherichia coli, 3 Enterobacter cloacae, 1 Citrobacter spp., and 1 Klebsiella pneumoniae; and 17 were Gram-negative non-fermenting rod bacteria, represented by 9 Acinetobacter spp. (2 A. lwoffii, 1 A. johnsonii, and 6 Acinetobacter spp.), 3 Brevundimonas diminuta, 3 Sphingobacterium spp., 1 Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and 1 Ochrobactrum anthropi. In contrast, 16 (29.1%) of the isolates were Gram-positive bacteria: 10 Enterococcus spp. (6 E. casseliflavus, 2 E. faecalis, and 2 E. faecium), 4 Streptococcus equi, and 1 Corynebaterium sp. (Figure 1).
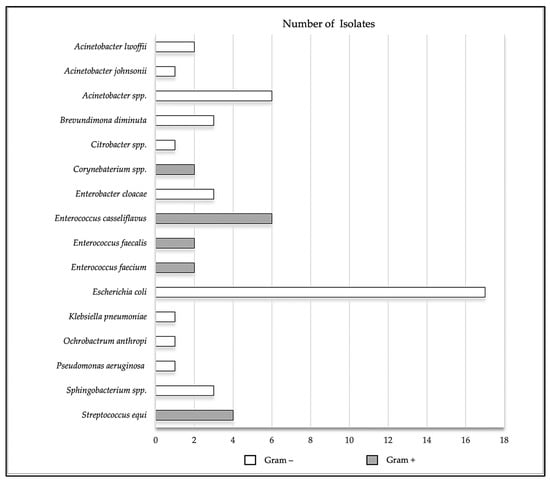
Figure 1.
Total number of isolates present in the uterus of healthy mares, represented by Escherichia coli (17), Enterobacter cloacae (3), Citrobacter spp. (1), Klebsiella pneumoniae (1), Acinetobacter spp. (9), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1), Brevundimonas diminuta (3), Sphingobacterium spp. (3), Ochrobactrum anthropi (1), E. casseliflavus (6), E. faecalis (2), E. faecium (2), Enterococcus spp. (10), Streptococcus equi (4) and Corynebaterium spp. (2).
Of all antibiotics tested against the Enterobacterales and Pseudomonas spp. (n = 23), the third generation cephalosporins were shown a 26.1% resistance, followed by GM. In the strains of the Acinetobacter spp. tested, AMP was shown the greatest resistance with 44.4% (Figure 2). Only 9.3% (n = 32) of isolates showed MDR, corresponding to Escherichia coli, Enterobacter cloacae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae; also, 18.8% of isolates presented resistance to two or more classes of antibiotics. On the contrary, the carbapenems IPM and ETP were sensitive to all isolates (Table 2).
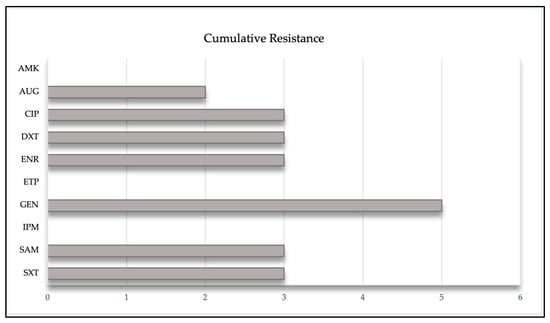
Figure 2.
Representation of the cumulative resistance of different antibiotics against Enterobacterales, Acinetobacter spp. and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, isolated from the uterus of mares.

Table 2.
Specific antibiotic resistance against 32 isolates: Enterobacterales, Acinetobacter spp. and Pseudomonas spp.
These results revealed the diversity of three ESBL genes (Table 3), blaTEM, blaCTX-M and blaSHV, in four isolates found (Escherichia coli, Acinetobacter spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae and Citrobacter spp.). The most frequent was blaSHV, being detected in all four isolates, while blaTEM and blaCTX-M were only present in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Citrobacter spp., which also exhibited coexistence of the three genes (blaCTX-M, blaSHV and blaTEM).

Table 3.
Genetic characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-positive bacterial isolates of equine origin.
4. Discussion
It is currently recognized that mares and their reproductive environment are a source of origin of different microorganisms, which can be disseminated to other animals and to humans through direct and indirect contact [40,51].
Of the group of mares sampled, all presented between two and four different bacterial isolates, information which is consistent with previous articles [4,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,52,53]. According to these results, the Enterobacterales group was the most predominant, with Escherichia coli being the most frequent bacterium [17,54,55,56]. Some studies indicate that the source of origin of this agent would be fecal matter that contaminates the vulva and perineum, associated with a bad anatomical conformation [12,13,15]. Likewise, Enterococcus spp., Acinetobacter spp., Streptococcus equi spp. and to a lesser extent Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [4,53,56,57,58,59,60,61].
A retrospective study carried out with bacteria isolated from the reproductive tract of 4122 mares with endometritis identified Escherichia coli and Streptococcus equi more frequently, adding that over the years the antimicrobial efficacy of cefquinome against E. coli decreased significantly, and the same is true of ampicillin, cefquinome, and penicillin against S. equi [22]. Previously, Pseudomonas spp. were reported in mares with fertility problems [62] in chronic endometritis and in those without response to antibiotic treatments [63,64]. On the other hand, Klebsiella pneumoniae has been frequently found in respiratory and digestive conditions in horses [65,66]. Enterococcus spp. are rare to find in the uterus of healthy mares; however, E. faecalis has been isolated from mares with chronic endometritis and infertility [67]. Acinetobacter baumannii has been found in the uterus of healthy mares, and in equine patients with wounds, septicemia, eye infections, bronchopneumonia, neonatal encephalopathy, and venous catheter [36,37,68,69]. Therefore, Lupo et al. indicate that A. baumannii has become a nosocomial pathogen in veterinary hospitals [70]. Finally, Citrobacter freundi, along with other species, has been detected in a case of uterine infection with purulent discharge [71] and another of endocarditis in a foal [72].
Although antimicrobial resistance (RAM) has been previously reported in bacteria from the equine reproductive tract [11,22,62,73], it is unknown whether its origin is related to local or systemic treatments. Similarly, it is considered that exposure to low levels of antibiotics through semen diluents would be a probable cause of antibiotic resistance in mares [62,73]. RAM has been identified as one of the major problems facing human and animal health [74,75,76]; in this regard, the British Equine Veterinary Association has indicated that the use of fluoroquinolones and third generation cephalosporins should be regulated in empirical or prophylactic therapies [77,78]. In addition, Benko et al., point out that microorganisms such as Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, and Escherichia coli are considered highly resistant to β-lactam class antibiotics and ampicillin [16].
These results exhibited high resistance to the third generation cephalosporins and ampicillin, which coincides with what was mentioned in other studies [79,80,81,82] and could be attributed to the empirical use of ceftiofur in equine Gram-negative bacterial infections [78,83,84,85,86]. Likewise, the use of broad-spectrum cephalosporins could be a selection factor for bacteria with ESBL. Generally, the resistance genes that code for the expression of this ESBL phenotype, such as blaCTX-M, blaSHV, blaTEM, and blaCTX-M, are in plasmids or integron-type structures, which would facilitate horizontal gene transfer [30,40,66,87,88,89,90].
In 1998, the first ESBL strain was detected in bacteria of animal origin, an E. coli carrier of the SHV-12 gene [91]. Currently, there are several authors who report the presence of these bacteria in different animal species, emphasizing transmission to humans [26,28,29,87,92,93,94,95,96,97]. A study carried out from rectal swab samples in pairs of healthy mares and newborn foals reported the presence of ESBL in Escherichia coli strains in 25% and 29%, respectively, noting that during hospitalization this number increased significantly [98], the same as previously reported [99], suggesting an association with high use of antimicrobials, even in untreated animals [26], and nosocomial acquisition of ESBL in a hospital setting [100,101]. On the other hand, Klebsiella spp. have become a major health problem, leading to treatment failure in humans and animals. A previous report, carried out in healthy horses, reported only one K. pneumoniae isolate confirmed as a producer of ESBL (blaCTX-M) [92]. Another study carried out in the USA recovered E. coli isolates from clinical samples of equine patients over a period of five years, finding resistance to ceftiofur in 13 out of 48 of them, while the CTX-M and SHV genes were detected in 7 of them, which code for ESBL [84].
Interestingly, the literature reports that bacteria such as Acinetobacter spp., E. coli, Klebsiella spp., and Pseudomonas spp. can survive on inanimate surfaces for months [102,103]. The persistence of these bacteria ranges from 3 days to 5 months for Acinetobacter spp. [104], 1.5 h to 16 months for E. coli, 2 h to 30 months for Klebsiella spp., and 6 h to 16 months for Pseudomonas spp. [84,105,106]. The emergence of ESBL-producing bacteria is alarming, necessitating surveillance studies to understand the transmission and epidemiology of such microorganisms [30,84]. It is necessary to consider reinforcing measures such as hygiene, hand washing, identification of infected patients, cleaning, and disinfection of environmental sources of contamination.
ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae are a global public health alert, and so antimicrobial efficacy monitoring programs are crucial to consciously use antibiotics and preserve their effectiveness for both human and veterinary medicine.
The contribution of this study is its focus on antimicrobial resistance. So far, there is no evidence related to the presence of ESBL in isolates of Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas, and Acinetobacter obtained from a population of reproductively active mares in Chile. Although the group of animals studied was limited, the results revealed the diversity of three ESBL genes, blaTEM, blaCTX-M and blaSHV, which co-existed in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Citrobacter spp. It would be interesting to continue with these studies and apply them to a larger population to include other molecular techniques for the detection of resistance genes, such as the sequencing of the complete genome, to better understand the situation at the national level. This communication alerts us to the presence of multi-resistant bacteria in the uterus of healthy mares and urges us to emphasize cleaning and disinfection protocols to prevent dissemination at the animal–human–environment interface.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.T. and P.G.; methodology, P.T., P.G., C.M., C.d.R., R.C. and A.N.; formal analysis, P.T. and P.G.; investigation, P.T. and C.d.R.; resources, P.T.; writing—original draft preparation, C.d.R.; writing—review and editing, P.T., P.G. and C.M.; project administration, P.T.; funding acquisition, P.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research, together with the APC, was financed by ANID, PAI project # 77190079.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Universidad Santo Tomás, protocol code 60-21, on 7 July 2021.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank ANID, PAI project # 77190079, for the financial support given to this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rock, K.; Love, B.; DeSilva, U.; Rezabek, G.; Carrington, S.; Holyoak, G.; Carroll, B.; Gragg, D. Detectable differences in the endometrial microbiome between normal and susceptible mares using metagenomic profiling and conventional bacterial culture. In Proceedings of the Society of Theriogenology, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 11 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, R.; El-Hage, C.M.; Sansom, F.M.; Carrick, J.; Devlin, J.M.; Legione, A.R. Metagenomic investigation of potential abortigenic pathogens in foetal tissues from Australian horses. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holyoak, G.R. The Equine Endometrial Microbiome: A Brief Review. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res. 2021, 11, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holyoak, G.R.; Premathilake, H.U.; Lyman, C.C.; Sones, J.L.; Gunn, A.; Wieneke, X.; DeSilva, U. The healthy equine uterus harbors a distinct core microbiome plus a rich and diverse microbiome that varies with geographical location. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, P.; Pareja, J.; Núñez, A.; Santibáñez, R.; Castro, R. Characterization of microbial communities and predicted metabolic pathways in the uterus of healthy mares. Open Vet. J. 2022, 12, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Du, L.; Jia, Z.; Cui, X.; Yu, L.; Yang, J.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, B.; et al. Translocation of vaginal microbiota is involved in impairment and protection of uterine health. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathe, S.; Leiken, A.; Plummer, P. Metagenomic sequencing of the uterine microbial environment during estrus and early pregnancy in mares. Clin. Theriogenol. 2017, 9, 453. [Google Scholar]
- Crha, I.; Ventruba, P.; Žáková, J.; Ješeta, M.; Pilka, R.; Lousová, E.; Papíková, Z. Uterine microbiome and endometrial receptivity. Ceska Gynekol. 2019, 84, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Heil, B.A.; Paccamonti, D.L.; Sones, J.L. Role for the mammalian female reproductive tract microbiome in pregnancy outcomes. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemberg, E.; Lundeheim, N.; Einarsson, S. Retrospective study on vulvar conformation in relation to endometrial cytology and fertility in thoroughbred mares. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A Physiol. Pathol. Clin. Med. 2005, 52, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.A.; Stanton, M.B.; Thungrat, K.; Boothe, D.M. Uterine bacterial isolates from mares and their resistance to antimicrobials: 8296 cases (2003–2008). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 242, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M.; Causey, R. Clinical and subclinical endometritis in the mare: Both threats to fertility. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2009, 44, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katila, T. Evaluation of diagnostic methods in equine endometritis. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 16, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troedsson, M.H.T.; Woodward, E.M. Our current understanding of the pathophysiology of equine endometritis with an emphasis on breeding-induced endometritis. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 16, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontoso, R.; De Carlo, E.; Pasolini, M.; van der Meulen, K.; Pagnini, U.; Iovane, G.; De Martino, L. Retrospective study of bacterial isolates and their antimicrobial susceptibilities in equine uteri during fertility problems. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benko, T.; Boldizar, M.; Novotny, F.; Hura, V.; Valocky, I.; Dudrikova, K.; Karamanova, M.; Petrovic, V. Incidence of bacterial pathogens in equine uterine swabs, their antibiotic resistance patterns, and selected reproductive indices in English thoroughbred mares during the foal heat cycle. Vet. Med. 2015, 60, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.C.M.; Sánchez, R.A.C. Estimación de la integridad uterina en yeguas Pura Raza Chilena y su asociación con edad y número de partos. Rev. Investig. Vet. Perú 2018, 29, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.S.; Palomares, R. Aerobic uterine isolates and antimicrobial susceptibility in mares with post-partum metritis. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaioli, V.; Raffini, E.; Tamburini, M.; Galletti, G.; Frasnelli, M. Infectious Endometritis in Mares: Microbiological Findings in Field Samples. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 112, 103913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncagul, G.; Gocmen, H.; Yendim, S.K.; Yılmaz, K.; Intas, K.S. Bacteriologic and Cytologic Examination Results of Mares with Pneumovagina in Bursa Region. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 5, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Nocera, F.P.; Papulino, C.; Del Prete, C.; Palumbo, V.; Pasolini, M.P.; De Martino, L. Endometritis associated with Enterococcus casseliflavus in a mare: A case report. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisello, L.; Rampacci, E.; Stefanetti, V.; Beccati, F.; Hyatt, D.R.; Coletti, M.; Passamonti, F. Temporal efficacy of antimicrobials against aerobic bacteria isolated from equine endometritis: An Italian retrospective analysis (2010–2017). Vet. Rec. 2019, 185, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, K.; Subapriya, S.; Dinesh, N.M.; Partheban, P. Antibiotic sensitivity test on pathogens causing reproductive tract infection in thoroughbred mares. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 913–915. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J.G.; Jung, S.; Holman, R.C.; Marano, N.N.; McQuiston, J.H. Infection control practices and zoonotic disease risks among veterinarians in the United States. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 232, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weese, J.S. Infection control in veterinary practice; the time is now. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 52, 507–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, T.W.; Clegg, P.D.; Diggle, P.J.; Wedley, A.L.; Dawson, S.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; Williams, N.J. Cross-sectional study of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in horses. Part 1: Prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Equine Vet. J. 2012, 44, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, P.S. Evidence-based infection control in clinical practice: If you buy clothes for the emperor, will he wear them? J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, B.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Stamm, I.; Gehlen, H.; Barton, A.K.; Janßen, T.; Wieler, L.; Guenther, S. Fallbericht über vermutlich nosokomiale Infektionen durch multiresistente E. coli in einer pferdeklinik einschließlich extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-produzierender Isolate. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2014, 127, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Walther, B.; Tedin, K.; Lübke-Becker, A. Multidrug-resistant opportunistic pathogens challenging veterinary infection control. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, B.; Klein, K.-S.; Barton, A.-K.; Semmler, T.; Huber, C.; Wolf, S.A.; Tedin, K.; Merle, R.; Mitrach, F.; Guenther, S.; et al. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)producing Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter baumannii among horses entering a veterinary teaching hospital: The contemporary “Trojan Horse”. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perestrelo, S.; Correia Carreira, G.; Valentin, L.; Fischer, J.; Pfeifer, Y.; Werner, G.; Schmiedel, J.; Falgenhauer, L.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Chakraborty, T.; et al. Comparison of approaches for source attribution of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli in Germany. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Health Care Facilities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, N.B.; Mutters, N.; Marasca, G.; Conti, M.; Sifakis, F.; Vuong, C.; Voss, A.; Baño, J.; Tacconelli, E. Mandatory surveillance, and outbreaks reporting of the WHO priority pathogens for research & discovery of new antibiotics in European countries. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 943.e1–943.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial antibiotic resistance: The most critical pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endimiani, A.; Hujer, K.M.; Hujer, A.M.; Bertschy, I.; Rossano, A.; Koch, C.; Gerber, V.; Francey, T.; Bonomo, R.A.; Perreten, V. Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from pets and horses in Switzerland: Molecular characterization and clinical data. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S.; Janßen, T.; Wieler, L.H. Multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in veterinary medicine-emergence of an underestimated pathogen? Multiresistente Acinetobacter baumannii in der Veterinär-medizin-Vormarsch eines unterschätzten Krankheits-erregers? Berl. Münch. Tierärztl. Wochenschr 2014, 127, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van der Kolk, J.H.; Endimiani, A.; Graubner, C.; Gerber, V.; Perreten, V. Acinetobacter in veterinary medicine, with an emphasis on Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 16, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maboni, G.; Seguel, M.; Lorton, A.; Sanchez, S. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Acinetobacter spp. of animal origin reveal high rate of multidrug resistance. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 245, 108702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isgren, C.M.; Williams, N.J.; Fletcher, O.D.; Timofte, D.; Newton, R.J.; Maddox, T.W.; Clegg, P.D.; Pinchbeck, G.L. Antimicrobial resistance in clinical bacterial isolates from horses in the UK. Equine Vet. J. 2022, 54, 390–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyanwu, M.U.; Jaja, I.F.; Nwobi, O.C.; Mgbeahuruike, A.C.; Ikpendu, C.N.; Okafor, N.A.; Oguttu, J.W. Epidemiology and Traits of Mobile Colistin Resistance (mcr) Gene-Bearing Organisms from Horses. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera-Llantén, S.; Vásquez-Ponce, F.; Barrientos-Espinoza, B.; Mardones, F.O.; Marshall, S.H.; Olivares-Pacheco, J. Extended antibiotic treatment in salmon farms select multiresistant gut bacteria with a high prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchamba, C.N.; Rao, A.; Boyen, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Duprez, J.; Théron, L.; Thiry, D.; Mainil, J. Comparison of quantitative PCR and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry assays for identification of bacteria in milk samples from cows with subclinical mastitis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida-Fujii, E.; Niwa, H.; Kinoshita, Y.; Nukada, T. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for Identification of Bacterial Isolates from Horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 95, 103276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolínská, R.; Španělová, P.; Dřevínek, M.; Hrabák, J.; Žemličková, H. Species identification of strains belonging to genus Citrobacter using the biochemical method and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Folia Microbiol. 2015, 60, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI VET01S; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Test for Bacteria Isolate from Animals. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020.
- CLSI M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Supplement M100. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2023.
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogaerts, P.; Rezende de Castro, R.; de Mendonça, R.; Huang, T.D.; Denis, O.; Glupczynski, Y. Validation of carbapenemase and extended-spectrum β-lactamase multiplex endpoint PCR assays according to ISO 15189. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado-Caxito, M.; Benavides, J.A.; Munita, J.M.; Rivas, L.; García, P.; Listoni, F.J.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Paes, A.C. Risk factors associated with faecal carriage of extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Escherichia coli among dogs in Southeast Brazil. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 190, 105316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, R.L.; Sotman, T.E.; Czum, J.M.; Montner, S.M.; Meyer, C.A. Prevalence of Burnout among Cardiothoracic Radiologists: Stress Factors, Career Satisfaction, and Modality-specific Imaging Volumes. J. Thorac. Imaging 2022, 37, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.D.; Schwab, E. Current Usage of Symbiosis and Associated Terminology. Int. J. Biol. 2012, 5, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.M.; Troedsson, M.H.; Pedersen, M.R.; Bojesen, A.M.; Lehn-Jensen, H.; Zent, W.W. Diagnosis of Endometritis in the Mare Based on Bacteriological and Cytological Examinations of the Endometrium: Comparison of Results Obtained by Swabs and Biopsies. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2010, 30, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, G.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Zou, W.; Jin, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; et al. The normal vaginal and uterine bacterial microbiome in giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Microbiol. Res. 2017, 199, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, M.; Brandis, L.; Samuelsson, J.; Bojesen, A.M.; Troedsson, M.H.T.; Petersen, M.R. Diagnostic double-guarded low-volume uterine lavage in mares. Theriogenology 2015, 83, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego Rodríguez, R.S.; Ruiz Jaramillo, A.F.; Ruiz Buitrago, J.D. Frecuencia del aislamiento bacteriano y patrones de sensibilidad en yeguas criollas colombianas diagnosticadas con endometritis. Rev. Med. Vet. 2020, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.; Hambidge, M.; Firmanes, B.; Shabandri, A.M.; Wilsher, S. Bacteria Isolated from Equine Uteri in the United Arab Emirates: A Retrospective Study. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 115, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, M.M.; Magsig, J.; Stromberg, A.J. Use of a low-volume uterine flush for diagnosing endometritis in chronically infertile mares. Theriogenology 2007, 68, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyles, L.; Ortman, K.; Cardew, S.; Foster, G.; Rogerson, F.; Falsen, E. Corynebacterium uterequi sp. nov., a non-lipophilic bacterium isolated from urogenital samples from horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraelen, H.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Desimpel, F.; Jauregui, R.; Vankeirsbilck, N.; Weyers, S.; Verhelst, R.; De Sutter, P.; Pieper, D.H.; Van De Wiele, T. Characterisation of the human uterine microbiome in non-pregnant women through deep sequencing of the V1-2 region of the 16S rRNA gene. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.G.; Ericsson, A.C.; Poock, S.E.; Melendez, P.; Lucy, M.C. Hot topic: 16S rRNA gene sequencing reveals the microbiome of the virgin and pregnant bovine uterus. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4953–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSilva, U.; Lyman, C.C.; Holyoak, G.R.; Meinkoth, K.; Wieneke, X.; Chillemi, K.A. Canine endometrial and vaginal microbiomes reveal distinct and complex ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210157. [Google Scholar]
- Malaluang, P.; Wilén, E.; Lindahl, J.; Hansson, I.; Morrell, J.M. Antimicrobial Resistance in Equine Reproduction. Animals 2021, 11, 3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Bertrana Sánchez, M.L. Estudio Microbiológico de Infertilidad en Yeguas; Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria: Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, J.; Katila, T. Use of antimicrobials in the treatment of reproductive diseases in cattle and horses. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2014, 49, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, K.; Eskola, K.; Eklund, M.; Suominen, K.; Määttä, M.; Junnila, J.; Nykäsenoja, S.; Niinistö, K.; Grönthal, T.; Rantala, M. Characterisation of and risk factors for extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacterales (ESBL-E) in an equine hospital with a special reference to an outbreak caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307:CTX-M-1. Acta Vet. Scand. 2022, 64, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, A.A.; Hedia, R.H.; Dorgham, S.M.; Ibrahim, E.S.; Bakry, M.A.; Abdalhamed, A.M.; Abuelnaga, A.S.M. Determination of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from horses with respiratory manifestation. Vet. World 2022, 15, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Extracellular superoxide produced by Enterococcus faecalis reduces endometrial receptivity via inflammatory injury. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2021, 86, e13453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneechoutte, M.; Devriese, L.A.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Lamote, B.; Deprez, P.; Verschraegen, G.; Haesebrouck, F. Acinetobacter baumannii-infected vascular catheters collected from horses in an equine clinic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4280–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y.; Murray, G.L.; Peleg, A.Y. Acinetobacter baumannii: Evolution of antimicrobial resistance-treatment options. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lupo, A.; Haenni, M.; Madec, J.-Y. Antimicrobial Resistance in Acinetobacter spp. and Pseudomonas spp. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhne, M.; Tönissen, A.; Unruh, C.; Pruß, D.; Sieme, H. Occurrence of Intrauterine Purulent Concernments in a Maiden Mare-A Case Report. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 95, 103278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, E.E.A.; Thomas, A.; Cadoré, J.L.; Smith, A.B. Citrobacter freundii induced endocarditis in a yearling colt. Can. Vet. J. 2016, 57, 767. [Google Scholar]
- Malaluang, P.; Wilén, E.; Frosth, S.; Lindahl, J.; Hansson, I.; Morrell, J.M. Vaginal Bacteria in Mares and the Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, L.B. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: No ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Ginocchio, F.; Mikulska, M. New treatment options against gram-negative organisms. Crit. Care 2011, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Khurshid, M.; Arshad, M.I.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.; Yasmeen, N.; Shah, T.; Chaudhry, T.H.; Rasool, M.H.; Shahid, A.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance: One Health One World Outlook. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, C.; Moreno, L.; Fumuso, E.; García, J.; Rivulgo, M.; Confalonieri, A.; Sparo, M.; Bruni, S.S. Enrofloxacin-based therapeutic strategy for the prevention of endometritis in susceptible mares. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 33, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorph, K.; Haughan, J.; Robinson, M.; Redding, L.E. Critically important antimicrobials are frequently used on equine racetracks. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2022, 260, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenni, M.; Bour, M.; Châtre, P.; Madec, J.Y.; Plésiat, P.; Jeannot, K. Resistance of animal strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to carbapenems. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrina, M.A.B.; Cosentino, L.A.; Wiesenfeld, H.C.; Darville, T.; Hillier, S.L. Susceptibility of endometrial isolates recovered from women with clinical pelvic inflammatory disease or histological endometritis to antimicrobial agents. Anaerobe 2019, 56, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasi, U.L.; Sebola, D.; Oguttu, J.W.; Qekwana, D.N. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from canine clinical cases at a veterinary academic hospital in South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2020, 91, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dégi, J.; Moțco, O.-A.; Dégi, D.M.; Suici, T.; Mareș, M.; Imre, K.; Cristina, R.T. Antibiotic Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Canine Isolates from a Multicentric Study in Romania. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragesser, L.A.; Wittum, T.E.; Funk, J.A.; Winokur, P.L.; Rajala-Schultz, P.J. Association between ceftiofur use and isolation of Escherichia coli with reduced susceptibility to ceftriaxone from fecal samples of dairy cows. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 1696–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Gillis, D.C.; Gurrola-Rodriguez, T.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Murray, S.A.; Ohta, N.; Scott, H.M.; et al. The Occurrence and Characterization of Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Clinical Diagnostic Specimens of Equine Origin. Animals 2019, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Dollen, K.A.; Jones, M.; Beachler, T.; Harris, T.L.; Papich, M.G.; Lyle, S.K.; Bailey, C.S. Antimicrobial Activity of Ceftiofur and Penicillin with Gentamicin against Escherichia coli and Streptococcus equi Subspecies zooepidemicus in an Ex Vivo Model of Equine Postpartum Uterine Disease. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2019, 79, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradella, G.D.; Taschetto, P.M.; Duarte, C.A.; da Silva Azevedo, M.; Góss, G.C. Ceftiofur Side Effect in a Mare-Case Report. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 95, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Coque, T.M. The CTX-M beta-lactamase pandemic. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasakopoulou, Z.; Reinicke, M.; Diezel, C.; Sofia, M.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Braun, S.D.; Reissig, A.; Spyrou, V.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli Isolates from Animals in Greece. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongtawan, T.; Narinthorn, R.; Sontigun, N.; Sansamur, C.; Petcharat, Y.; Fungwithaya, P.; Saengsawang, P.; Blackall, P.J.; Thomrongsuwannakij, T. Characterizing the antimicrobial resistance profile of Escherichia coli found in sport animals (fighting cocks, fighting bulls, and sport horses) and soils from their environment. Vet. World 2022, 15, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir, A.; Abdel-Moein, K.A.; Zaher, H.M. The Public Health Burden of Virulent Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Isolated from Diseased Horses. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 22, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshager, T.; Domínguez, L.; Moreno, M.A.; Saénz, Y.; Torres, C.; Cardeñosa, S. solation of an SHV-12 beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli strain from a dog with recurrent urinary tract infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 3483–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukmawinata, E.; Uemura, R.; Sato, W.; Thu Htun, M.; Sueyoshi, M. Multidrug-Resistant ESBL/AmpC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Healthy Thoroughbred Racehorses in Japan. Animals 2020, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijs, A.P.; Gijsbers, E.F.; Hengeveld, P.D.; Dierikx, C.M.; de Greeff, S.C.; van Duijkeren, E. ESBL/pAmpC-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae carriage among veterinary healthcare workers in the Netherlands. Antimicrob Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, V.; Nykäsenoja, S.; Myllyniemi, A.L.; Rossow, H.; Heikinheimo, A. Genomic characterization of ESBL/AmpC-producing and high-risk clonal lineages of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in imported dogs with shelter and stray background. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 30, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossair, M.A.; Abd El Baqy, F.A.; Rizk, M.S.Y.; Elaadli, H.; Mansour, A.M.; Abd El-Aziz, A.H.; Alkhedaide, A.; Soliman, M.M.; Ramadan, H.; Shukry, M.; et al. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases and AmpC β-lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae among Human, Cattle, and Poultry. Pathogens 2022, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, Y.; Thahir, S.S.A.; Rajendiran, S.; Hock, L.K.; Ahmad, N.; Muthu, V.; Shaharudin, R. Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria and Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from the Poultry Farm Environment. Microbiol Spectr. 2022, 10, e0269421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinyuy, J.F.; Ali, I.M.; Ousenu, K.; Tume, C.B. Molecular characterization of antimicrobial resistance related genes in E. coli, Salmonella and Klebsiella isolates from broilers in the West Region of Cameroon. PLoS ONE. 2023, 18, e0280150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnaiderman-Torban, A.; Paitan, Y.; Arielly, H.; Kondratyeva, K.; Tirosh-Levy, S.; Abells-Sutton, G.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Steinman, A. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Hospitalized Neonatal Foals: Prevalence, Risk Factors for Shedding and Association with Infection. Animals 2019, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damborg, P.; Marskar, P.; Baptiste, K.E.; Guardabassi, L. Faecal shedding of CTX-M-producing Escherichia coli in horses receiving broad-spectrum antimicrobial prophylaxis after hospital admission. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 154, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, T.W.; Williams, N.J.; Clegg, P.D.; O’Donnell, A.J.; Dawson, S.; Pinchbeck, G.L. Longitudinal study of antimicrobial-resistant commensal Escherichia coli in the faeces of horses in an equine hospital. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 100, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, A.; Sturlesi, N.A.; Fallach, N.; Zilberman-Barzilai, D.; Hussein, O.; Blum, S.E.; Klement, E.; Schwaber, M.J.; Carmeli, Y. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Transmission Dynamics of Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae: A National Survey of Cattle Farms in Israel in 2013. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3515–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad, A.; Heritage, J.; Snelling, A.M.; Gascoyne-Binzi, D.M.; Hawkey, P.M. Influence of relative humidity and suspending menstrua on survival of Acinetobacter spp. on dry surfaces. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Schwebke, I.; Kampf, G. How long do nosocomial pathogens persist on inanimate surfaces? A systematic review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, A.D.; Romero, R.; Gervasi, M.T.; Gomez-Lopez, N.; Tran, M.R.; Garcia-Flores, V.; Pacora, P.; Jung, E.; Hassan, S.S.; Hsu, C.D.; et al. Does the endometrial cavity have a molecular microbial signature? Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, A.N. A survey of gram-negative bacteria survival on hospital fabrics and plastics. J. Burn. Care Rehabil. 2000, 21, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bălan, G.G.; Roșca, I.; Ursu, E.-L.; Doroftei, F.; Bostănaru, A.-C.; Hnatiuc, E.; Năstasă, V.; Șandru, V.; Ștefănescu, G.; Trifan, A.; et al. Plasma-activated water: A new and effective alternative for duodenoscope reprocessing. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).