Corynebacterium ulcerans Infections in Eurasian Beavers (Castor fiber)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Examined Beavers
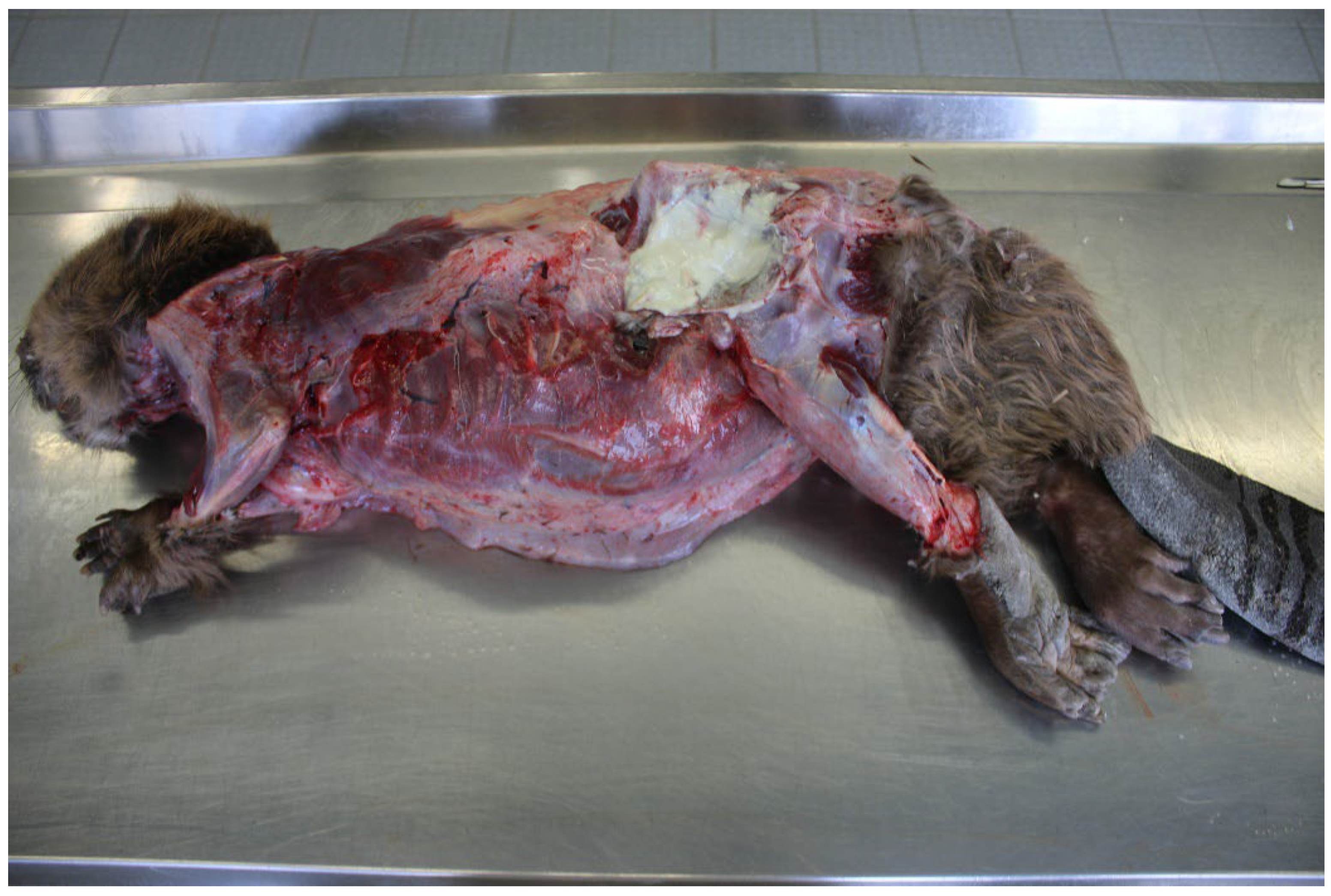
2.1.1. Beaver 1
2.1.2. Beaver 2
2.1.3. Beaver 3
2.2. Bacteriological Examinations
2.3. Identification and Characterization
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.5. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) Analysis
- (1)
- A pan-genomic C. ulcerans/C. pseudotuberculosis scheme with 193 species-overlapping target loci, as previously described in [23]. The addition of isolate typing profiles for C. pseudotuberculosis and C. silvaticum enables differentiation of the most closely related species.
- (2)
- A C. ulcerans cgMLST scheme of 1211 target loci, previously described by Berger et al. [25], with the addition of other animal-based C. ulcerans isolate typing profiles.
3. Results
3.1. Post-Mortem and Bacteriological Examinations
3.1.1. Beaver 1 (County of Main–Spessart, Bavaria; 21 September 2015)
3.1.2. Beaver 2 (County of Soest, North Rhine–Westphalia, 7 April 2021)
3.1.3. Beaver 3 (District of Heilbronn, Baden-Wuerttemberg, 8 June 2022)
3.2. Identification and Characterization of the Corynebacterium sp.
3.3. Biochemical Investigations
3.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
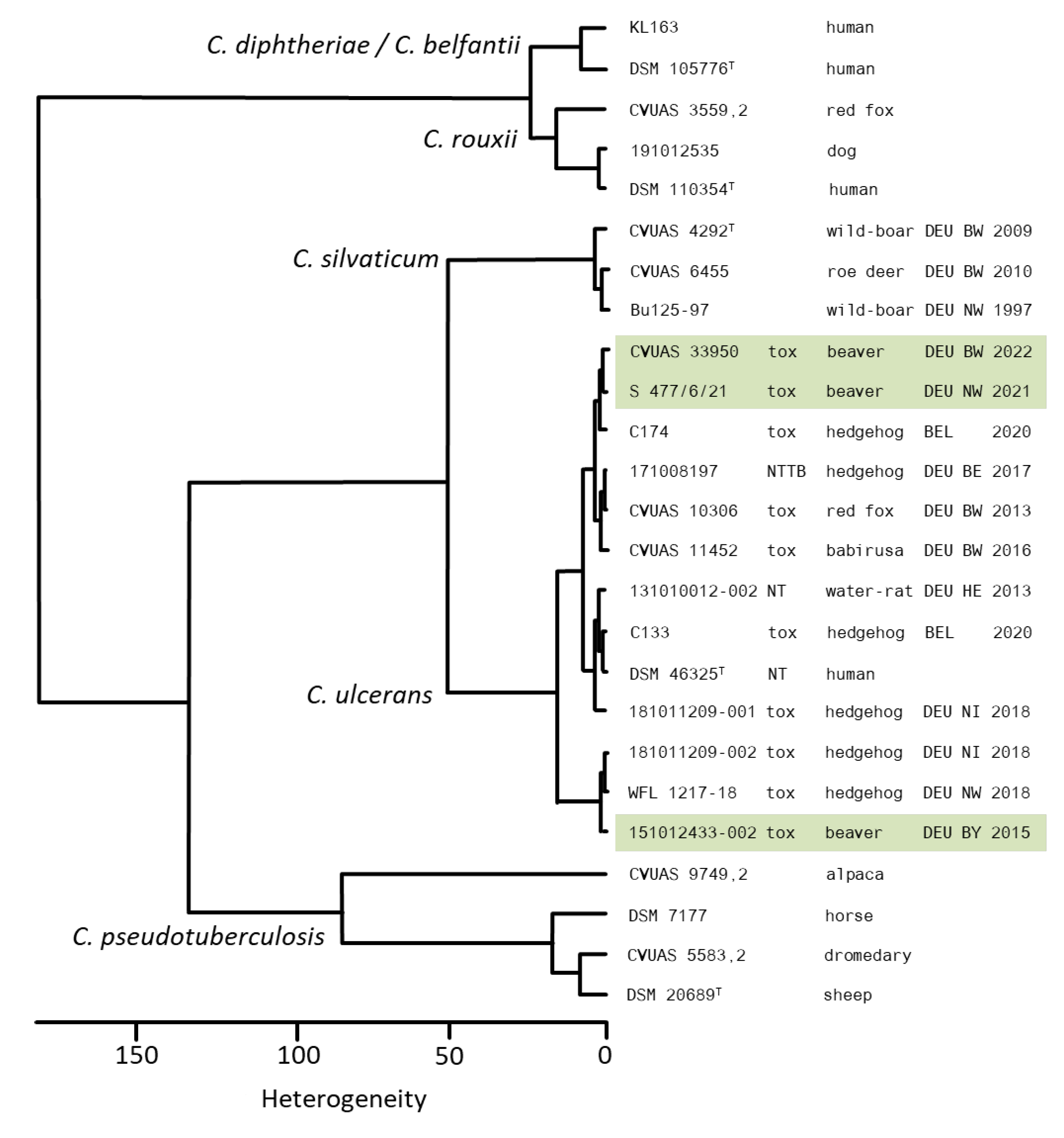
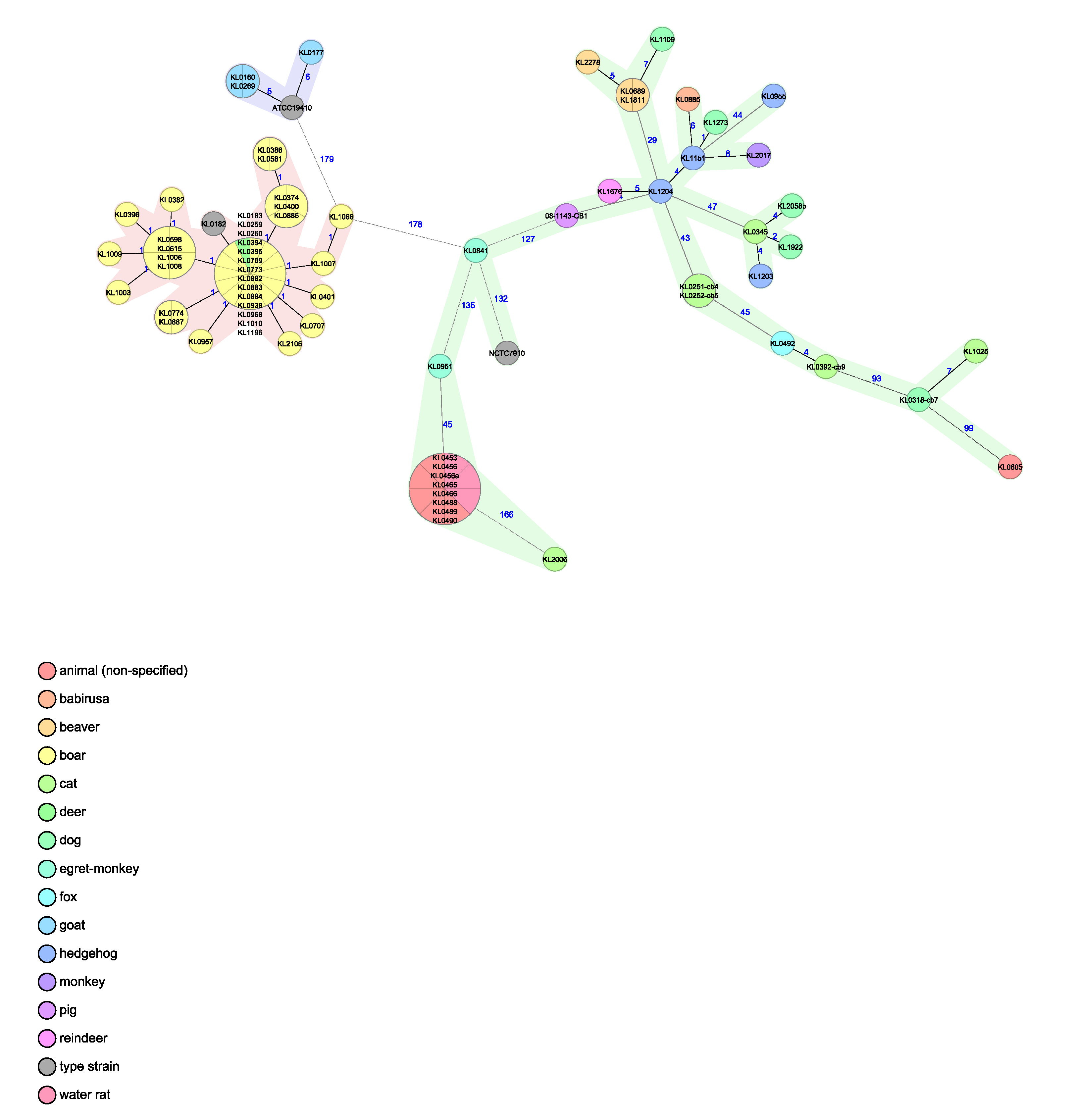
3.5. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nolet, B.A.; Rosell, F. Comeback of the beaver Castor fiber: An overview of old and new conservation problems. Biol. Conserv. 1998, 83, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halley, D.J.; Saveljev, A.P.; Rosell, F. Population and distribution of beavers Castor fiber and Castor canadensis in Eurasia. Mammal Rev. 2020, 51, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, G.; Schmidbauer, M. Beaver (Castor fiber L., Castoridae) management in Bavaria. Denisia 2003, 9, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wróbel, M. Population of Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber) in Europe. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batbold, J.; Batsaikhan, N.; Shar, S.; Hutterer, R.; Krystufek, B.; Yigit, N.; Mitsainas, G.; Palomo, L. Castor fiber (amended version of 2016 Assessment). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021. e.T4007A197499749. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T4007A197499749.en (accessed on 10 July 2023). [CrossRef]
- Maas, M.; Glorie, J.; Dam-Deisz, C.; de Vries, A.; Franssen, F.F.J.; Jaarsma, R.I.; Hengeveld, P.D.; Dierikx, C.M.; van der Giessen, J.W.B.; Opsteegh, M. Zoonotic Pathogens in Eurasian Beavers (Castor fiber) in the Netherlands. J. Wildl. Dis. 2022, 58, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCE-ZID). Zoonotic Diseases. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/onehealth/basics/zoonotic-diseases.html (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recht, J.; Schuenemann, V.J.; Sánchez-Villagra, M.R. Host Diversity and Origin of Zoonoses: The Ancient and the New. Animals 2020, 10, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Palmer, R.; Rosell, F.; Naylor, A.; Cole, G.; Mota, S.; Brown, D.; Fraser, M.; Pizzi, R.; Elliott, M.; Wilson, K.; et al. Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber) health surveillance in Britain: Assessing a disjunctive reintroduced population. Vet. Rec. 2021, 188, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girling, S.J.; Naylor, A.; Fraser, M.; Campbell-Palmer, R. Reintroducing beavers Castor fiberto Britain: A disease risk analysis. Mammal Rev. 2019, 49, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, C.W. (Ed.) A Review of the Evidence on the Interactions of Beavers with the Natural and Human Environment in Relation to England, 1st ed.; Natural England: Peterborough, UK, 2020; pp. 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, C.; Heuner, K.; Myrtennäs, K.; Karlsson, E.; Jacob, D.; Kutzer, P.; Große, K.; Forsman, M.; Grunow, R. High and novel genetic diversity of Francisella tularensis in Germany and indication of environmental persistence. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, F.; Rosef, O.; Parker, H. Investigations of Waterborne Pathogens in Eurasian Beaver (Castor fiber) from Telemark County, Southeast Norway. Acta Vet. Scand. 2001, 42, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Gomez, D.K.; Jung, T.S.; Park, S.C. Pleuritis and pericarditis associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber). Korean J. Vet. Res. 2008, 48, 501–503. [Google Scholar]
- Platt-Samoraj, A.; Syczyło, K.; Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Giżejewska, A.; Szweda, W. Yersinia enterocolitica strains isolated from beavers (Castor fiber). Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 18, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girling, S.J.; Goodman, G.; Burr, P.; Pizzi, R.; Naylor, A.; Cole, G.; Brown, D.; Fraser, M.; Rosell, F.N.; Schwab, G.; et al. Evidence of Leptospira species and their significance during reintroduction of Eurasian beavers (Castor fiber) to Great Britain. Vet. Rec. 2019, 185, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauková, A.; Strompfová, V.; Kandričáková, A.; Ščerbová, J.; Semedo-Lemsaddek, T.; Miltko, R.; Belzecki, G. Virulence factors genes in enterococci isolated from beavers (Castor fiber). Folia Microbiol. 2015, 60, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Feßler, A.T.; Burgold-Voigt, S.; Krüger, H.; Mühldorfer, K.; Wibbelt, G.; Liebler-Tenorio, E.M.; Reinicke, M.; Braun, S.D.; Hanke, D.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Eurasian Beavers (Castor fiber) carry a novel phage-borne bicomponent leukocidin related to the Panton-Valentine leukocidin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Palmer, R.; Schwab, G.; Girling, S.; Lisle, S.; Gow, D. Managing Wild Eurasian Beavers: A Review of European Management Practices with Consideration to Application in Scotland; Scott, J., Ed.; Commissioned Report No. 812 ed.; Scottish Natural Heritage: Inverness, UK, 2015; pp. 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Prygiel, M.; Polak, M.; Mosiej, E.; Wdowiak, K.; Formińska, K.; Zasada, A.A. New Corynebacterium Species with the Potential to Produce Diphtheria Toxin. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlez, K.; Eisenberg, T.; Rau, J.; Dubielzig, S.; Kornmayer, M.; Wolf, G.; Berger, A.; Dangel, A.; Hoffmann, C.; Ewers, C.; et al. Corynebacterium rouxii, a recently described member of the C. diphtheriae group isolated from three dogs with ulcerative skin lesions. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangel, A.; Berger, A.; Rau, J.; Eisenberg, T.; Kampfer, P.; Margos, G.; Contzen, M.; Busse, H.-J.; Konrad, R.; Peters, M.; et al. Corynebacterium silvaticum sp. nov., a unique group of NTTB corynebacteria in wild boar and roe deer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3614–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dover, L.G.; Thompson, A.R.; Sutcliffe, I.C.; Sangal, V. Phylogenomic Reappraisal of Fatty Acid Biosynthesis, Mycolic Acid Biosynthesis and Clinical Relevance among Members of the Genus Corynebacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 802532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Dangel, A.; Peters, M.; Mühldorfer, K.; Braune, S.; Eisenberg, T.; Szentiks, C.A.; Rau, J.; Konrad, R.; Hörmansdorfer, S.; et al. Tox-positive Corynebacterium ulcerans in hedgehogs, Germany. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, E.; Antunes, C.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L.; Burkovski, A.; Tauch, A. Corynebacterium ulcerans, an emerging human pathogen. Futur. Microbiol. 2016, 11, 1191–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, L.; Collins, S.; de Zoysa, A.; White, J.; Mandal, S.; Efstratiou, A. Molecular and Epidemiological Review of Toxigenic Diphtheria Infections in England between 2007 and 2013. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, C.M.; Scobie, A.; Fry, N.K.; Litt, D.J.; Cameron, J.C.; Chand, M.; Brown, C.S.; Collins, S.; White, J.M.; Ramsay, M.; et al. The changing epidemiology of diphtheria in the United Kingdom, 2009 to 2017. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 1900462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, H.; Soetens, O.; Litt, D.; Fry, N.K.; Detemmerman, L.; Wybo, I.; Desombere, I.; Efstratiou, A.; Piérard, D. Diphtheria in Belgium: 2010–2017. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakikhany, K.; Efstratiou, A. Diphtheria in Europe: Current problems and new challenges. Futur. Microbiol. 2012, 7, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.; Eisenberg, T.; Peters, M.; Berger, A.; Kutzer, P.; Lassnig, H.; Hotzel, H.; Sing, A.; Sting, R.; Contzen, M. Reliable differentiation of a non-toxigenic tox gene-bearing Corynebacterium ulcerans variant frequently isolated from game animals using MALDI-TOF MS. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 237, 108399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, A.; Boyen, F.; Rau, J.; Eisenberg, T.; Sing, A.; Berger, A.; Chiers, K.; Van Praet, S.; Verbanck, S.; Vervaeke, M.; et al. Widespread Disease in Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Caused by Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2686–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barksdale, L.; Linder, R.; Sulea, I.T.; Pollice, M. Phospholipase D activity of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis (Corynebacterium ovis) and Corynebacterium ulcerans, a distinctive marker within the genus Corynebacterium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1981, 13, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. rpoB Gene Sequencing for Identification of Corynebacterium Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3925–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L. Similarity analysis of rRNAs. In Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; Gerhardt, P., Murray, R.G.E., Wood, W.A., Krieg, N.R., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 683–700. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, D.E.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Acinas, S.G.; Gautier, C.; Bertilsson, S.; Polz, M.F. Evaluation of 23S rRNA PCR Primers for Use in Phylogenetic Studies of Bacterial Diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Brown, G.R.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI Reference Sequences (RefSeq): Current status, new features and genome annotation policy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 40, D130–D135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhegger, R.; Kugler, R.; Sing, A. Pitfalls with Diphtheria-like Illness due to Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, V.G.; Berger, A.; Sing, A. Detection of diphtheria toxin production by toxigenic corynebacteria using an optimized Elek test. Infection 2022, 50, 1591–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST (European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, Corynebacterium diphtheriae and C. ulcerans. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Andrews, S. FASTQC. A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; Braham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, F.; Cassiday, P.; Tondella, M.L.; DeZoysa, A.; Efstratiou, A.; Sing, A.; Zasada, A.; Bernard, K.; Guiso, N.; Badell, E.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing Identifies Evidence for Recombination and Two Distinct Lineages of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4177–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, C.; Meinel, D.M.; Margos, G.; Konrad, R.; Sing, A. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Corynebacterium ulcerans Provides Evidence for Zoonotic Transmission and for Increased Prevalence of Certain Sequence Types among Toxigenic Strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4318–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.-M.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, A.A.; Santos, L.S.; Sabbadini, P.S.; Santos, C.S.; Silva Junior, F.C.; Napoleão, F.; Nagao, P.E.; Villas-Bôas, M.H.; Hirata Junior, R.; Guaraldi, A.L. Corynebacterium ulcerans diphtheria: An emerging zoonosis in Brazil and worldwide. Rev. Saude Publica 2011, 45, 1176–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guaraldi, A.L.D.M.; Hirata, R.; Azevedo, V.a.D.C. Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis—General aspects. In Corynebacterium Diphtheriae and Related Toxigenic Species, 1st ed.; Burkovski, A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 15–37. [Google Scholar]
- Konrad, R.; Hörmansdorfer, S.; Sing, A. Possible human-to-human transmission of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, Y.; Efstratiou, A.; Brennan, G.; Hallanan, S.; Leggett, B.; Leonard, F.C.; Markey, B.K.; Tuite, C.; Fry, N.K. Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans associated with upper respiratory infections in cats and dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 61, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsukawa, C.; Komiya, T.; Umeda, K.; Goto, M.; Yanai, T.; Takahashi, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Iwaki, M. Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans isolated from a hunting dog and its diphtheria toxin antibody titer. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 60, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frosch, C.; Kraus, R.H.S.; Angst, C.; Allgöwer, R.; Michaux, J.; Teubner, J.; Nowak, C. The Genetic Legacy of Multiple Beaver Reintroductions in Central Europe. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.A.; Silva, F.C., Jr.; Pereira, G.A.; Souza, M.C.; Camello, T.C.; Damasceno, J.A.; Pacheco, L.G.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V.A.; Hirata, R., Jr.; et al. Corynebacterium ulcerans Isolated from an Asymptomatic Dog Kept in an Animal Shelter in the Metropolitan Area of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsukawa, C.; Kawahara, R.; Inoue, K.; Ishii, A.; Yamagishi, H.; Kida, K.; Nishino, S.; Nagahama, S.; Komiya, T.; Iwaki, M.; et al. Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans Isolated from the Domestic Dog for the First Time in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 62, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Huber, I.; Merbecks, S.S.; Ehrhard, I.; Konrad, R.; Hörmansdorfer, S.; Hogardt, M.; Sing, A. Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans in Woman and Cat. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1767–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandentorren, S.; Guiso, N.; Badell, E.; Boisrenoult, P.; Micaelo, M.; Troché, G.; Lecouls, P.; Moquet, M.J.; Patey, O.; Belchior, E. Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans in a fatal human case and her feline contacts, France, March 2014. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 20910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; Patterson, T.; Howie, F.; Simpson, V.; Davison, N.; Efstratiou, A.; Lai, S. Corynebacterium ulcerans in free-ranging otters. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 524. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, T.; Mauder, N.; Contzen, M.; Rau, J.; Ewers, C.; Schlez, K.; Althoff, G.; Schauerte, N.; Geiger, C.; Margos, G.; et al. Outbreak with clonally related isolates of Corynebacterium ulcerans in a group of water rats. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.E.; Goemans, I.; Bolingbroke, D.; Lundberg, S. Gangrenous dermatitis caused by Corynebacterium ulcerans in Rich-ardson ground squirrels. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1988, 193, 367–368. [Google Scholar]
- Konrad, R.; Berger, A.; Huber, I.; Boschert, V.; Hörmansdorfer, S.; Busch, U.; Hogardt, M.; Schubert, S.; Sing, A. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry as a tool for rapid diagnosis of potentially toxigenic Corynebacterium species in the laboratory management of diphtheria-associated bacteria. Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 19699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasada, A.A.; Mosiej, E. Contemporary microbiology and identification of Corynebacteria spp. causing infections in human. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 66, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.C.; Boyette, M.; Goforth, C.; Sperry, K.V.; Greene, S.R. Comparison of the Biolog OmniLog Identification System and 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing for accuracy in identification of atypical bacteria of clinical origin. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 79, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, M.; Kämpfer, P.; Busse, H.J.; Trujillo, M.E.; Suzuki, K.; Ludwig, W.; Whitman, W.B. The Actinobacteria. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai-Yuki, A.; Komiya, T.; Suzaki, Y.; Ami, Y.; Katsukawa, C.; Takahashi, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Yamada, Y.K. Isolation and characterization of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans from 2 closed colonies of cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis) in Japan. Comp. Med. 2013, 63, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Marosevic, D.V.; Berger, A.; Kahlmeter, G.; Payer, S.K.; Hörmansdorfer, S.; Sing, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans in Germany 2011–17. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.; Männig, A.; Hiller, E.; Mauder, N.; Wind, C.; Horlacher, S.; Kadlec, K.; Schwarz, S.; Contzen, M. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for reliable identification of bacteria—A validation based on Staphylococcaceae field isolates. Asp. Food Control. Anim. Health 2016, 2016, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sting, R.; Geiger, C.; Rietschel, W.; Blazey, B.; Schwabe, I.; Rau, J.; Schneider-Bühl, L. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Infections in Alpacas (Vicugna pacos). Animals 2022, 12, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangel, A.; Berger, A.; Konrad, R.; Sing, A. NGS-based phylogeny of diphtheria-related pathogenicity factors in different Corynebacterium spp. implies species-specific virulence transmission. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Museux, K.; Arcari, G.; Rodrigo, G.; Hennart, M.; Badell, E.; Toubiana, J.; Brisse, S. Corynebacteria of the Diphtheriae Species Complex in Companion Animals: Clinical and Microbiological Characterization of 64 Cases from France. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0000623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, P.A.; Foster, G.; Falsen, E.; Markopoulos, S.J.; Collins, M.D. Streptococcus castoreus sp. nov., isolated from a beaver (Castor fiber). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühldorfer, K.; Rau, J.; Fawzy, A.; Heydel, C.; Glaeser, S.P.; van der Linden, M.; Kutzer, P.; Knauf-Witzens, T.; Hanczaruk, M.; Eckert, A.S.; et al. Streptococcus castoreus, an uncommon group A Streptococcus in beavers. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, C.; Kutzer, P.; Winterhoff, N.; Engelhardt, A.; Bilk, S.; Teubner, J. Isolation and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus castoreus isolated from carcasses of European beavers (Castor fiber) in Germany. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2015, 128, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.D.; Hutson, R.; Hoyles, L.; Falsen, E.; Nikolaitchouk, N.; Foster, G. Streptococcus ovis sp. nov., isolated from sheep. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sting, R.; Schwalm, A.; Contzen, M.; Roller, M.; Rau, J. Actinomycetes associated with abscess formation in a goat, a llama and two alpacas. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2020, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.G.; Tóth, I.; Rózsa, B.; Dubecz, A.; Patai, A.V.; Németh, T.; Kaplan, S.; Kovács, E.G.; Makrai, L.; Solymosi, N. Canine Saliva as a Possible Source of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.; Kaur, S.; Wang, Q.; Hennessy, D.; Luo, L.; Octavia, S.; Tanaka, M.M.; Sintchenko, V.; Lan, R. Multilevel genome typing: Genomics-guided scalable resolution typing of microbial pathogens. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 1900519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürch, A.; Arredondo-Alonso, S.; Willems, R.; Goering, R. Whole genome sequencing options for bacterial strain typing and epidemiologic analysis based on single nucleotide polymorphism versus gene-by-gene–based approaches. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, J.; Huhulescu, S.; Stoeger, A.; Allerberger, F.; Ruppitsch, W. Draft genome sequences of six Corynebacterium ulcerans strains isolated from humans and animals in Austria, 2013 to 2019. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00946-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, L.I.; Barbut, F.; Chopin, D.; Rondeau, P.; Lalande, V.; Jolivet, S.; Badell, E.; Brisse, S.; Lacombe, K.; Surgers, L. Cutaneous diphtheria: Three case-reports to discuss determinants of re-emergence in resource-rich settings. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 2300–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, R.; Kolodkina, V.; Sutcliffe, I.; Simpson-Louredo, L.; Hirata, R., Jr.; Titov, L.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.; Burkovski, A.; Sangal, V. Genomic analyses reveal two distinct lineages of Corynebacterium ulcerans strains. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 25, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, D.M.; Margos, G.; Konrad, R.; Krebs, S.; Blum, H.; Sing, A. Next generation sequencing analysis of nine Corynebacterium ulcerans isolates reveals zoonotic transmission and a novel putative diphtheria toxin-encoding pathogenicity island. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antimicrobials | MIC Range | MIC Results of C. ulcerans Isolates | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beaver 1 151012433-002 | Beaver 2 S 477/6/21 | Beaver 3 CVUAS 33950 | DSM 46325T (NCTC 7910T) | ||
| AMC | 0.063/0.031–16/8 | ≤0.063/0.031 | ≤0.063/0.031 | ≤0.063/0.031 | ≤0.063/0.031 |
| AMP | 0.125–8 | ≤0.125 | ≤0.125 | ≤0.125 | ≤0.125 |
| CFV | 0.25–4 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 |
| CEX | 0.5–16 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 |
| CMP | 1–16 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 |
| CLI | 0.031–1 | >2 | >2 | >2 | >2 |
| ENR | 0.016–2 | =0.063 | =0.063 | =0.031 | =0.031 |
| ERY | 0.023–4 | =0.047 | =0.064 | =0.023 | =0.047 |
| GEN | 0.063–4 | =2 | =4 | =4 | =4 |
| OXA | 0.063–2 | =1 | =1 | =1 | =1 |
| PEN | 0.063–4 | ≤0.063 | ≤0.063 | ≤0.063 | ≤0.063 |
| PRX | 0.004–1 | =0.031 | =0.016 | =0.008 | =0.008 |
| TET | 0.063–8 | =0.25 | =0.25 | =0.25 | =0.25 |
| T/S | 0.25/4.75–2/38 | =0.5/9.5 | =0.5/9.5 | ≤0.25/4.25 | ≤0.25/4.25 |
| Type Strain Genome | Species | Beaver 1 151012433-002 | Beaver 2 S 477/6/21 | Beaver 3 CVUA S33950 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSM 46325T (NCTC 7910T) | C. ulcerans | 0.988 | 0.987 | 0.987 |
| KL 0182T (DSM 109166 T, CVUAS 4292 T) | C. silvaticum | 0.904 | 0.902 | 0.904 |
| ATCC 19410T (DSM 20689T) | C. pseudotuberculosis | 0.845 | 0.844 | 0.845 |
| NCTC 11397T | C. diphtheriae | 0.742 | 0.742 | 0.742 |
| FRC 0190T | C. rouxii | 0.741 | 0.741 | 0.740 |
| FRC 0043T | C. belfantii | 0.740 | 0.739 | 0.739 |
| DSM 45586T | C. epidermidicanis | 0.732 | 0.732 | 0.732 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sting, R.; Pölzelbauer, C.; Eisenberg, T.; Bonke, R.; Blazey, B.; Peters, M.; Riße, K.; Sing, A.; Berger, A.; Dangel, A.; et al. Corynebacterium ulcerans Infections in Eurasian Beavers (Castor fiber). Pathogens 2023, 12, 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12080979
Sting R, Pölzelbauer C, Eisenberg T, Bonke R, Blazey B, Peters M, Riße K, Sing A, Berger A, Dangel A, et al. Corynebacterium ulcerans Infections in Eurasian Beavers (Castor fiber). Pathogens. 2023; 12(8):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12080979
Chicago/Turabian StyleSting, Reinhard, Catharina Pölzelbauer, Tobias Eisenberg, Rebecca Bonke, Birgit Blazey, Martin Peters, Karin Riße, Andreas Sing, Anja Berger, Alexandra Dangel, and et al. 2023. "Corynebacterium ulcerans Infections in Eurasian Beavers (Castor fiber)" Pathogens 12, no. 8: 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12080979
APA StyleSting, R., Pölzelbauer, C., Eisenberg, T., Bonke, R., Blazey, B., Peters, M., Riße, K., Sing, A., Berger, A., Dangel, A., & Rau, J. (2023). Corynebacterium ulcerans Infections in Eurasian Beavers (Castor fiber). Pathogens, 12(8), 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12080979







