Trichomonas gallinae Kills Host Cells Using Trogocytosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell and Parasite Culture
2.2. LMH-Trichomonas gallinae Co-Culture Conditions
2.3. Trans-Well Assay
2.4. Trichomonas gallinae Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Determination of Trichomonas gallinae Viability
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Live Confocal Imaging
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
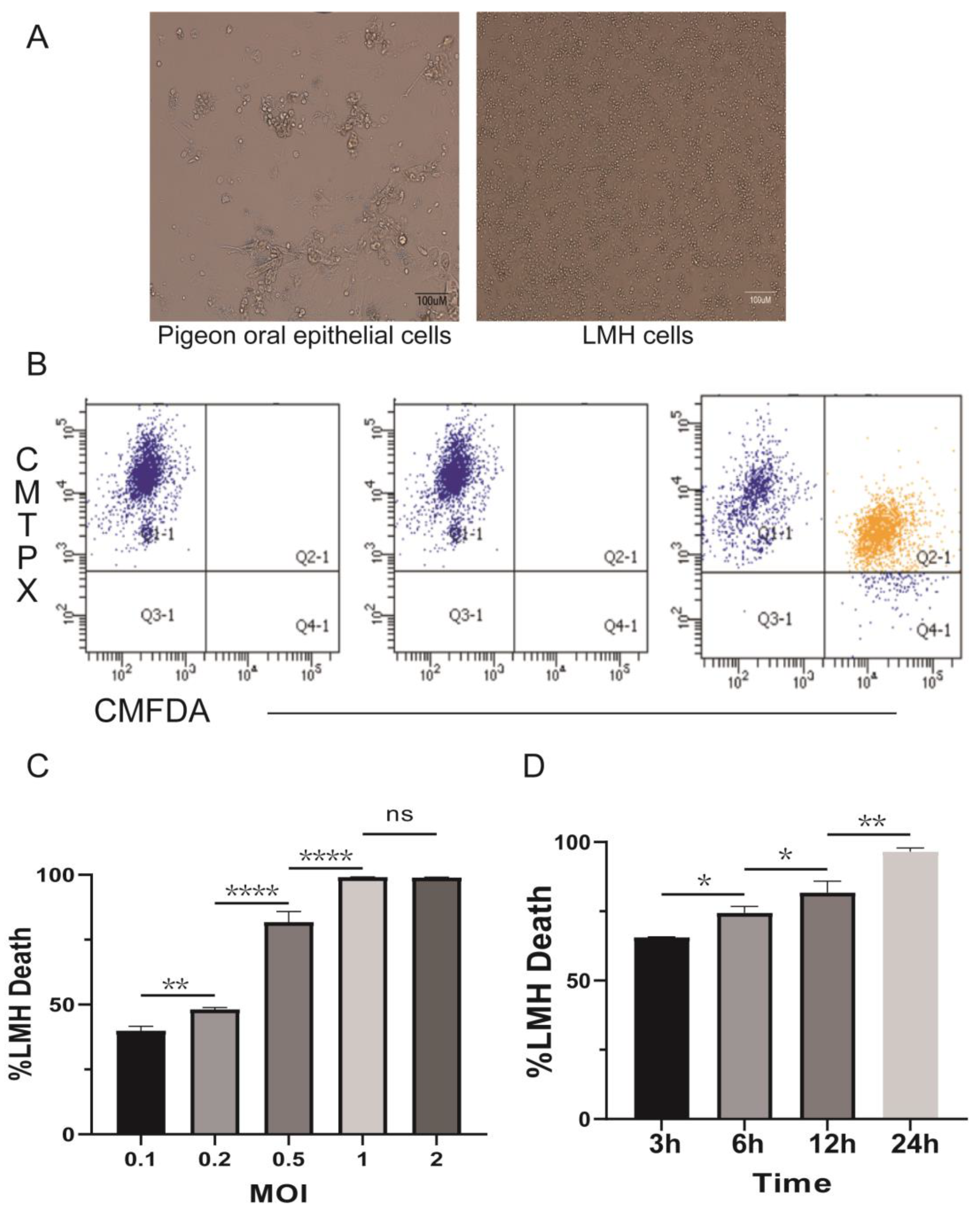
3.1. Trichomonas gallinae Damages Host Cells in a Time- and Concentration-Dependent Manner
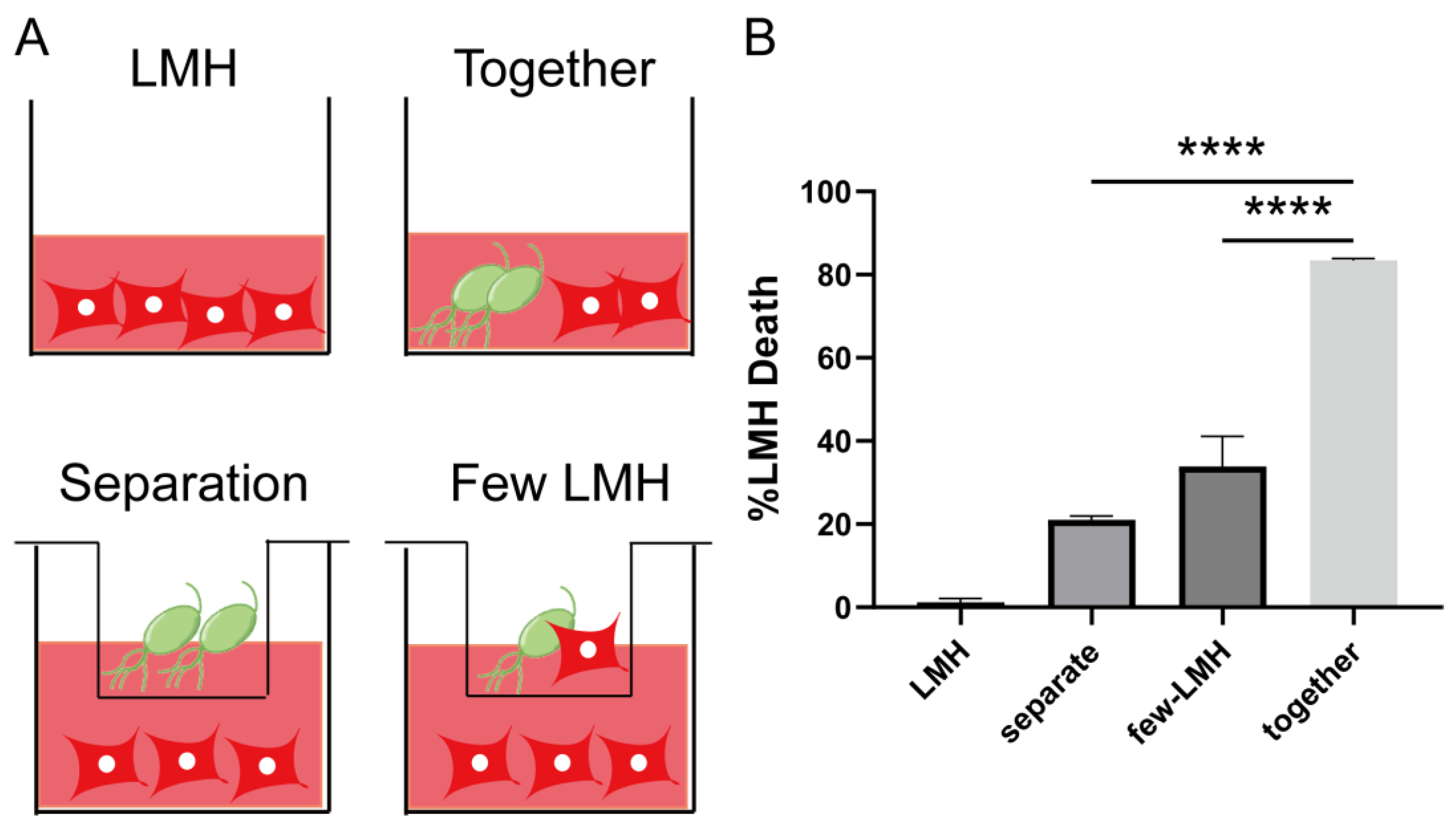
3.2. Trichomonas gallinae Killing of LMH Is Contact-Dependent
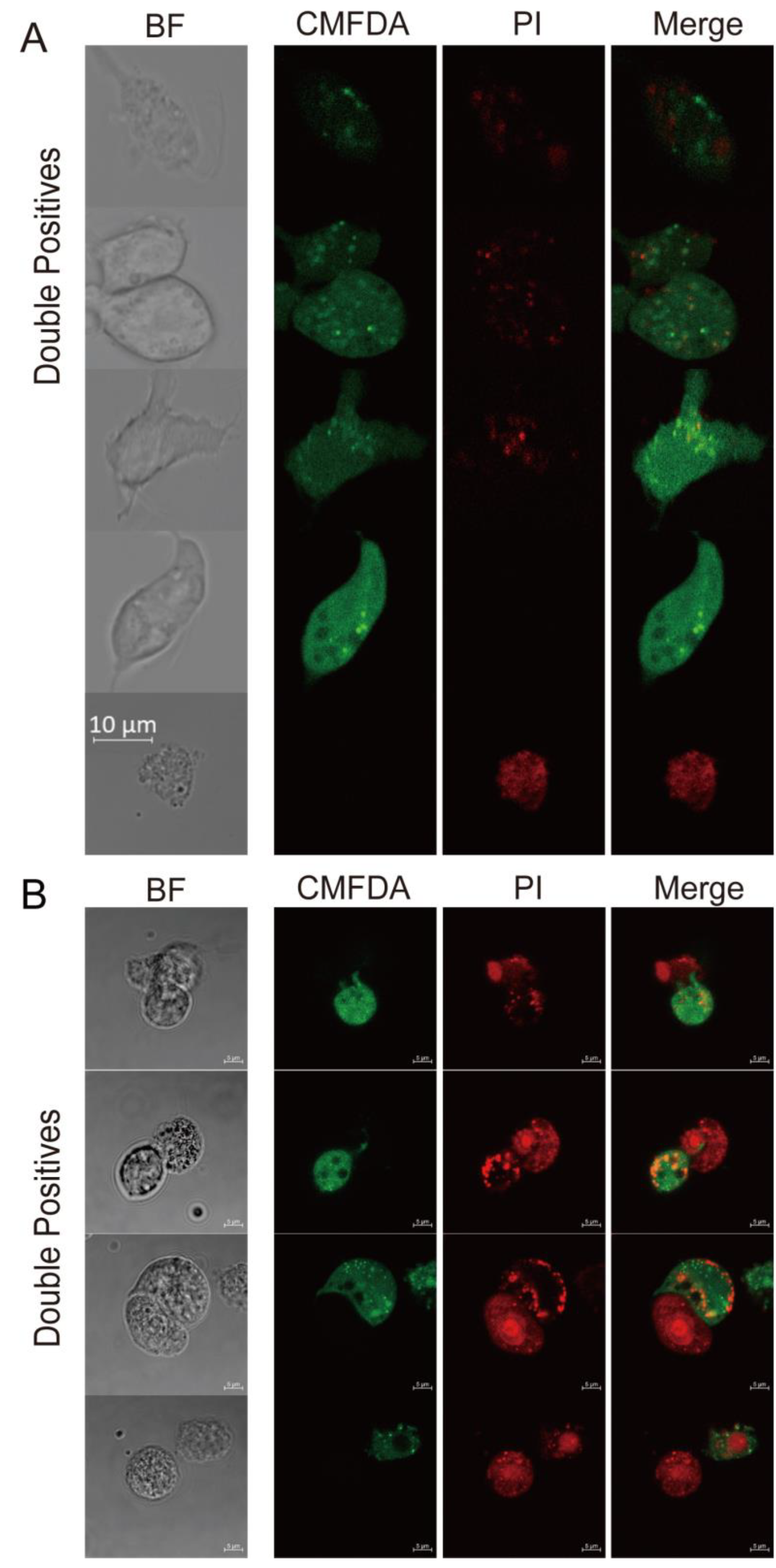
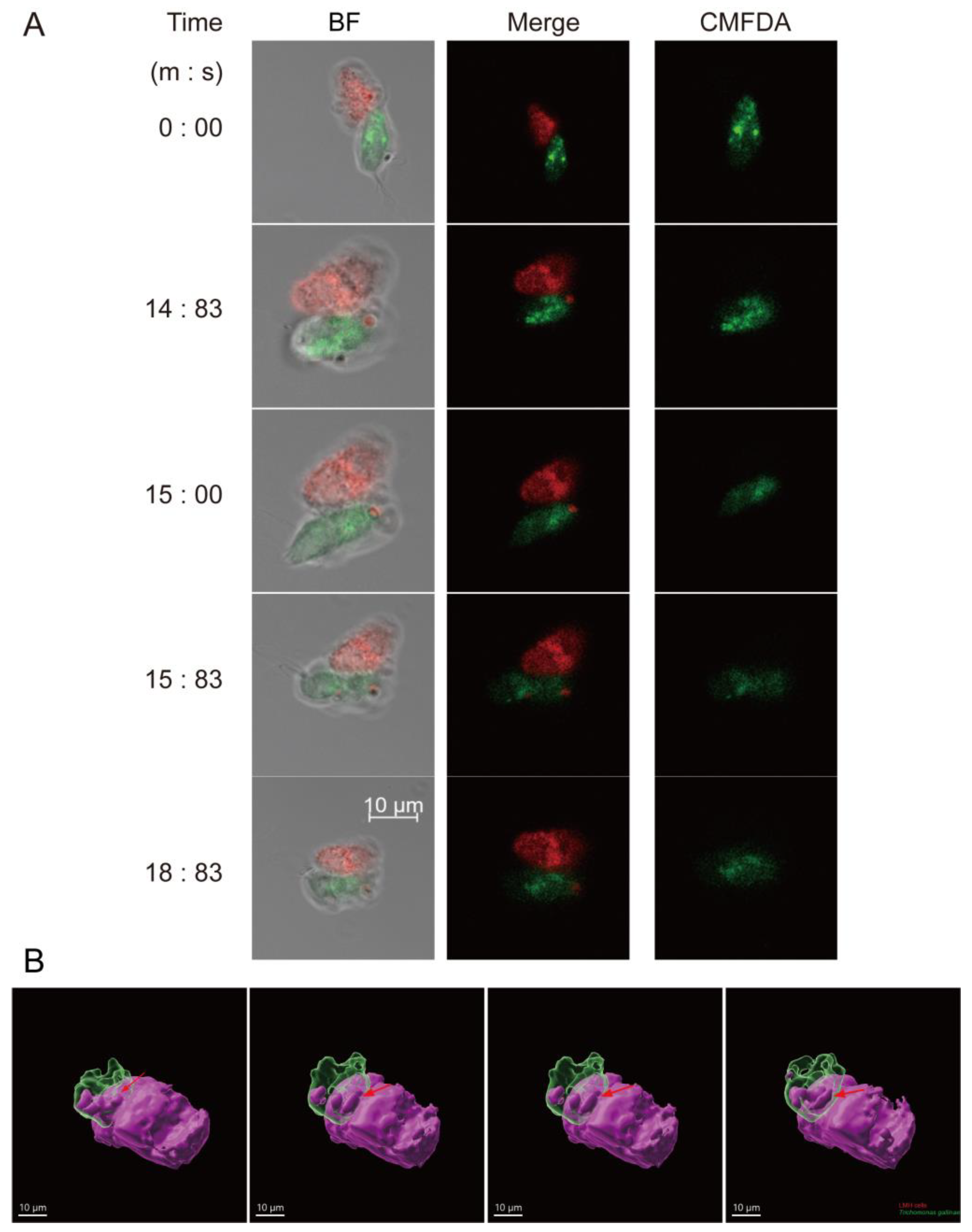
3.3. Trichomonas gallinae Kills LMH Cells by Swarming and Trogocytosis
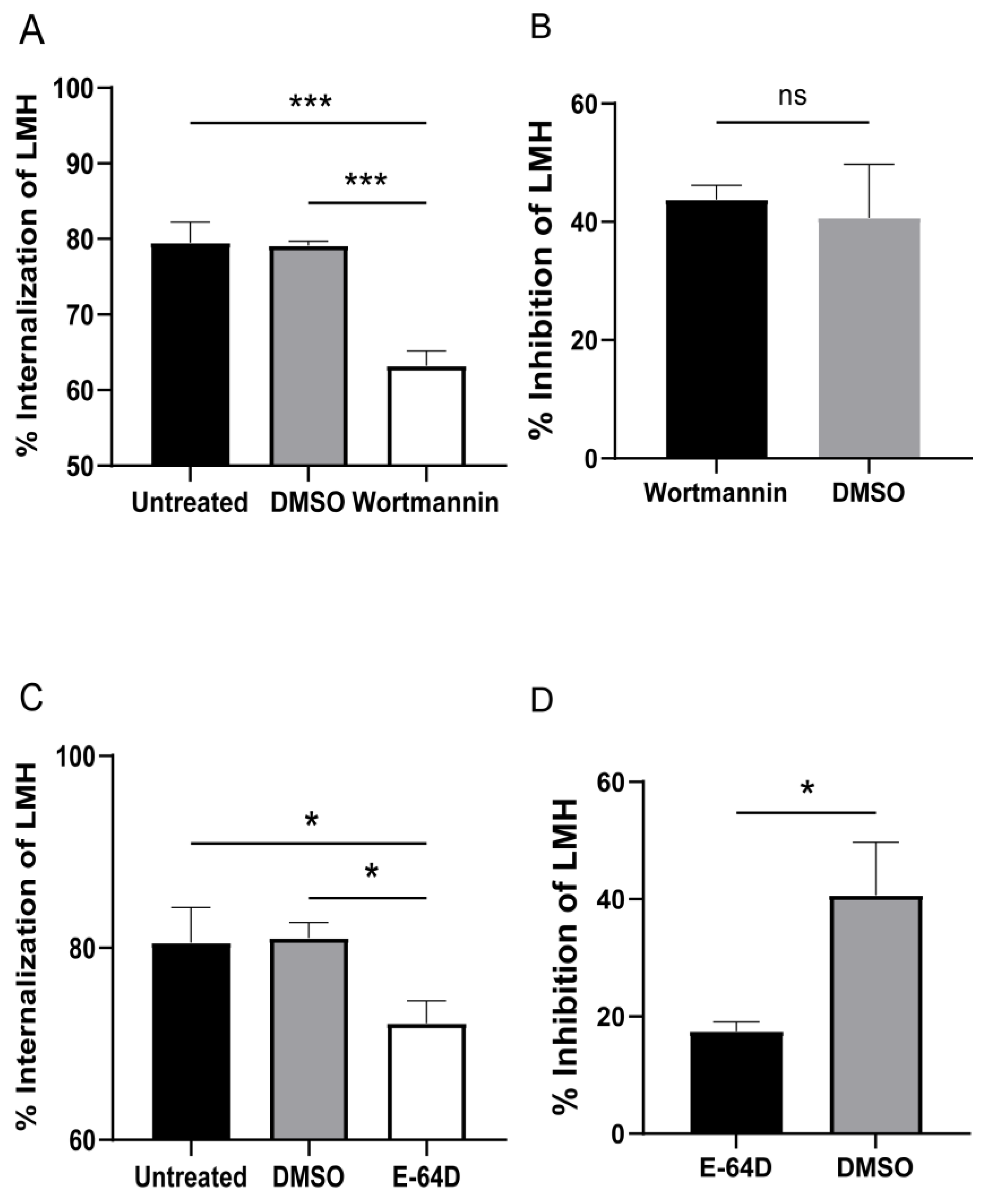
3.4. Cysteine Protease and PI3K Mediate T. gallinae Trogocytosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forzán, M.J.; Vanderstichel, R.; Melekhovets, Y.F.; McBurney, S. Trichomoniasis in finches from the Canadian Maritime provinces—An emerging disease. Can. Vet. J. = La Revue Veterinaire Canadienne 2010, 51, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R.A.; Lawson, B.; Toms, M.P.; Peck, K.M.; Kirkwood, J.K.; Chantrey, J.; Clatworthy, I.R.; Evans, A.D.; Hughes, L.A.; Hutchinson, O.C.; et al. Emerging infectious disease leads to rapid population declines of common British birds. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganas, P.; Jaskulska, B.; Lawson, B.; Zadravec, M.; Hess, M.; Bilic, I. Multi-locus sequence typing confirms the clonality of Trichomonas gallinae isolates circulating in European finches. Parasitology 2014, 141, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.L.; Grahn, R.A.; Van Hoosear, K.; Bondurant, R.H. Studies of trichomonad protozoa in free ranging songbirds: Prevalence of Trichomonas gallinae in house finches (Carpodacus mexicanus) and corvids and a novel trichomonad in mockingbirds (Mimus polyglottos). Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 161, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhold, R.W.; Yabsley, M.J.; Smith, A.J.; Ostergaard, E.; Mannan, W.; Cann, J.D.; Fischer, J.R. Molecular characterization of the Trichomonas gallinae morphologic complex in the United States. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecco, R.; Preis, I.S.; Vilela, D.A.R.; Luppi, M.M.; Malta, M.C.C.; Beckstead, R.B.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Gerhold, R.W. Molecular confirmation of Trichomonas gallinae and other parabasalids from Brazil using the 5.8S and ITS-1 rRNA regions. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Herrero, M.C.; Sansano-Maestre, J.; Azami-Conesa, I.; González-González, F.; Suárez Regalado, L.; Garijo-Toledo, M.M.; Gómez-Muñoz, M.T. Sequence subtyping of Trichomonas gallinae from Bonelli’s eagle (Aquila fasciata) during four years (2014–2017) reveals that MLS type is associated with lesions. Avian Pathol. 2021, 50, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, D.; Foster, G.; Atkinson, C. Parasitic diseases of wild birds. In Trichomonosis; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Borji, H.; Razmi, G.H.; Movassaghi, A.H.; Moghaddas, E.; Azad, M. Prevalence and pathological lesion of Trichomonas gallinae in pigeons of Iran. J. Parasit. Dis. 2011, 35, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, R.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Li, J. Trichomonas gallinae induces heterophil extracellular trap formation in pigeons. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuska-Szalay, B.; Sipos, G.; Takacs, N.; Kontschan, J.; Sandor, A.D.; Peter, A.; Berta, K.; Kerek, A.; Jerzsele, A.; Votypka, J.; et al. Molecular epidemiological study of Trichomonas gallinae focusing on central and southeastern Europe. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1050561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, J.C.; Thomas, R.C.; Hipperson, H.; Sheehan, D.J.; Orsman, C.; Mallord, J.; Goodman, S.J. Evidence for strain-specific virulence of Trichomonas gallinae in African columbiformes. Parasitology 2023, 150, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, Z.; Liao, S.; Qi, N.; Li, J.; Lin, X.; et al. Prevalence and diversity of Trichomonas gallinae in meat pigeons (Columba livia) in Guangdong Province, People’s Republic of China. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Li, G.Q.; Su, R.Q.; Liang, G.; Chen, Z.H.; Hicham, W. Cloning and sequencing of adhesion protein gene of Trichomonas gallinae from pigeon. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Bilic, I.; Liebhart, D.; Hess, M. Trichomonads in birds—A review. Parasitology 2014, 141, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.S.; Solga, M.D.; Mackey-Lawrence, N.M.; Somlata; Bhattacharya, A.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Trogocytosis by Entamoeba histolytica contributes to cell killing and tissue invasion. Nature 2014, 508, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utter, C.; Serrano, A.E.; Glod, J.W.; Leibowitz, M.J. Association of Plasmodium falciparum with Human Endothelial Cells in vitro. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Nozaki, T. Trogocytosis in Unicellular Eukaryotes. Cells 2021, 10, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M. Antigen Presentation by MHC-Dressed Cells. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.; De Pasquale, C.; Carrega, P.; Ferlazzo, G.; Bonaccorsi, I. Cross-dressing: An alternative mechanism for antigen presentation. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 168, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.P.; Lindorfer, M.A. Fcγ-receptor-mediated trogocytosis impacts mAb-based therapies: Historical precedence and recent developments. Blood 2015, 125, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andoh, M.; Ikegaya, Y.; Koyama, R. Synaptic Pruning by Microglia in Epilepsy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dance, A. Core Concept: Cells nibble one another via the under-appreciated process of trogocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17608–17610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettadapur, A.; Miller, H.W.; Ralston, K.S. Biting Off What Can Be Chewed: Trogocytosis in Health, Infection, and Disease. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.-J.; Wu, C.-H.; Lu, C.-H.; Shen, C.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-M.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Yu, C.-L. Trogocytosis between Non-Immune Cells for Cell Clearance, and among Immune-Related Cells for Modulating Immune Responses and Autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriek, P.; Villadangos, J.A. Trogocytosis and cross-dressing in antigen presentation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2023, 83, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-L.; Chen, J.-F.; Zhong, X.-R.; Liang, P.; Lin, W. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies on Trichomonas vaginalis adhering to and phagocytizing genitourinary epithelial cells. Chin. Med. J. 2004, 117, 376–381. [Google Scholar]
- Cybulski, W.; Radko, L.; Rzeski, W. Cytotoxicity of monensin, narasin and salinomycin and their interaction with silybin in HepG2, LMH and L6 cell cultures. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2015, 29, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, M.A.; Youssefi, M.R.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Antitrichomonal activity of Peganum harmala alkaloid extract against trichomoniasis in pigeon (Columba livia domestica). Br. Poult. Sci. 2017, 58, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.E.S.; Parsamand, T.; Kelly, R.W.; Simoes-Barbosa, A. An improved quantitative method to assess adhesive properties of Trichomonas vaginalis to host vaginal ectocervical cells using flow cytometry. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 92, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.; Hadano, S.; Kojima, A.; Yorisaki, M.; Yasuda, M.; Ike, K.; Tokiwa, T. Genetic characterization of Trichomonas gallinae (Rivolta, 1878) in companion birds in Japan and the genotypical relationship in the Asia region. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. = Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi 2022, 55, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Nöbauer, K.; Patzl, M.; Berger, E.; Hess, M.; Bilic, I. Cysteine peptidases, secreted by Trichomonas gallinae, are involved in the cytopathogenic effects on a permanent chicken liver cell culture. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.-J.; Wu, C.-H.; Shen, C.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-M.; Yu, C.-L.; Hsieh, S.-C. Membrane Transfer from Mononuclear Cells to Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils Transduces Cell Survival and Activation Signals in the Recipient Cells via Anti-Extrinsic Apoptotic and MAP Kinase Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valgardsdottir, R.; Cattaneo, I.; Klein, C.; Introna, M.; Figliuzzi, M.; Golay, J. Human neutrophils mediate trogocytosis rather than phagocytosis of CLL B cells opsonized with anti-CD20 antibodies. Blood 2017, 129, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmartin, A.A.; Ralston, K.S.; Petri, W.A. Inhibition of Amebic Cysteine Proteases Blocks Amebic Trogocytosis but Not Phagocytosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Bilic, I.; Berger, E.; Hess, M. Trichomonas gallinae, in comparison to Tetratrichomonas gallinarum, induces distinctive cytopathogenic effects in tissue cultures. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Ozuna, J.F.T.; Rivera-Rivas, L.A.; Cárdenas-Guerra, R.E.; Hernández-García, M.S.; Rodríguez-Cruz, S.; González-Robles, A.; Chavez-Munguía, B.; Arroyo, R. Glucose-restriction increases Trichomonas vaginalis cellular damage towards HeLa cells and proteolytic activity of cysteine proteinases (CPs), such as TvCP2. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, R.; Capdet, J.; Mirshahi, P.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Dagonnet, F.; Klein, C.; Mirshahi, M.; Fournie, J.J.; Rafii, A.; Poupot, M. Oncologic trogocytosis with Hospicells induces the expression of N-cadherin by breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, M.A.; Pozniak, B.; Youssefi, M.R.; Sarvandani, M.R.R.; Giorgi, M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of metronidazole in healthy and Trichomonas gallinae infected pigeons (Columba livia, var. domestica). Br. Poult. Sci. 2021, 62, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Guo, K.; Jiang, D.; Xiao, J.; Liang, D. Design, Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Epoxysuccinyl-Peptide Derivatives as Cathepsin B Inhibitors. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, C.; Li, Y.; Jing, S.; Han, S.; He, H. Trichomonas gallinae Kills Host Cells Using Trogocytosis. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081008
Xiang C, Li Y, Jing S, Han S, He H. Trichomonas gallinae Kills Host Cells Using Trogocytosis. Pathogens. 2023; 12(8):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081008
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Chen, Yi Li, Shengfan Jing, Shuyi Han, and Hongxuan He. 2023. "Trichomonas gallinae Kills Host Cells Using Trogocytosis" Pathogens 12, no. 8: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081008
APA StyleXiang, C., Li, Y., Jing, S., Han, S., & He, H. (2023). Trichomonas gallinae Kills Host Cells Using Trogocytosis. Pathogens, 12(8), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081008





