Antibacterial and Biofilm Production Inhibition Activity of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil against Salmonella spp. Isolates from Reptiles
Abstract
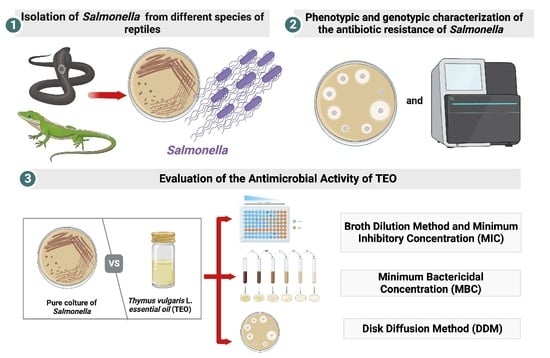
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection
2.2. Bacteriological Analysis
2.3. PCR Characterization
2.4. In Vitro Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.5. Genomic Analysis
2.6. EO—Compound Identification and Dilution Design
2.7. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of TEO
2.7.1. Broth Dilution Method and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.7.2. Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
2.7.3. Bactericidal and Bacteriostatic Effects
2.8. Disk Diffusion Method (DDM)
2.9. Detection of Biofilm and TEO Activity
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bacteriological Analysis
3.2. AMR
3.3. TEO Antibacterial Activity
3.4. Biofilm Production and TEO Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Authority, E.F.S.; ECfD Prevention. The European Union One Health 2020 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchello, C.S.; Birkhold, M.; Crump, J.A.; Martin, L.B.; Ansah, M.O.; Breghi, G.; Canals, R.; Fiorino, F.; Gordon, M.A.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Complications and Mortality of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Invasive Disease: A Global Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.R.; Kingsley, R.A. Evolution of Salmonella within Hosts. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Corrente, M.; Otranto, D. Zoonotic Pathogens of Reptiles: An Unregarded Slithery Matter. In Zoonoses: Infections Affecting Humans and Animals; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, M.A.; Shane, S.M. Salmonella in Reptiles. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet Med. 2001, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warwick, C.; Lambiris, A.J.L.; Westwood, D.; Steedman, C. Reptile-Related Salmonellosis. J. R. Soc. Med. 2001, 94, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagre, A.C.; Pabilonia, K.L.; Johnston, M.S.; Morley, P.S.; Burgess, B.A. Comparison of Detection Methods for Salmonella enterica Shedding among Reptilian Patients at a Veterinary Teaching Hospital. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrente, M.; Sangiorgio, G.; Grandolfo, E.; Bodnar, L.; Catella, C.; Trotta, A.; Martella, V.; Buonavoglia, D. Risk for Zoonotic Salmonella Transmission from Pet Reptiles: A Survey on Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Reptile-Owners Related to Reptile Husbandry. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 146, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrente, M.; Madio, A.; Friedrich, K.G.; Greco, G.; Desario, C.; Tagliabue, S.; D’Incau, M.; Campolo, M.; Buonavoglia, C. Isolation of Salmonella Strains from Reptile Faeces and Comparison of Different Culture Media. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J.R.; Goggins, J.A.; McLachlan, J.B. Salmonella Infection: Interplay between the Bacteria and Host Immune System. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 190, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, M.; Skarżyńska, M.; Lalak, A.; Kwit, R.; Śmiałowska-Węglińska, A.; Pasim, P.; Szulowski, K.; Wasyl, D. Salmonella in Captive Reptiles and Their Environment-Can We Tame the Dragon? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu Rajendran, N.; Mutters, N.T.; Marasca, G.; Conti, M.; Sifakis, F.; Vuong, C.; Voss, A.; Baño, J.R.; Tacconelli, E. COMBACTE-MAGNET-EPI-Net Consortium Mandatory Surveillance and Outbreaks Reporting of the WHO Priority Pathogens for Research & Discovery of New Antibiotics in European Countries. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 943.e1–943.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitten, T.; Bender, J.B.; Smith, K.; Leano, F.; Scheftel, J. Reptile-Associated Salmonellosis in Minnesota, 1996–2011. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; Laso, O.; Villora-Gonzalez, J.; Vega, S. Pet Reptiles: A Potential Source of Transmission of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 613718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, S.S.R.; Turcotte, M.R.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wolfe, K.L.; Gao, F.; Benton, C.S.; Andam, C.P. Population Analysis of Heavy Metal and Biocide Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica from Human Clinical Cases in New Hampshire, United States. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 983083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Leone, P.; Solimando, A.G.; Fasano, R.; Malerba, E.; Prete, M.; Corrente, M.; Prati, C.; Vacca, A.; Racanelli, V. Antibiotics or No Antibiotics, That Is the Question: An Update on Efficient and Effective Use of Antibiotics in Dental Practice. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, G. Biocidal Agents Used for Disinfection Can Enhance Antibiotic Resistance in Gram-Negative Species. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Millezi, A.F.; das Cardoso, M.G.; Alves, E.; Piccoli, R.H. Reduction of Aeromonas Hidrophyla Biofilm on Stainless Stell Surface by Essential Oils. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galgano, M.; Pellegrini, F.; Fracchiolla, G.; Mrenoshki, D.; Zarea, A.A.K.; Bianco, A.; Del Sambro, L.; Capozzi, L.; Schiavone, A.; Saleh, M.S.; et al. Pilot Study on the Action of Thymus Vulgaris Essential Oil in Treating the Most Common Bacterial Contaminants and Salmonella enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Derby in Poultry Litter. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgano, M.; Capozza, P.; Pellegrini, F.; Cordisco, M.; Sposato, A.; Sblano, S.; Camero, M.; Lanave, G.; Fracchiolla, G.; Corrente, M.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Evaluated In Vitro against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological Effects of Essential Oils—A Review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Ye, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, D. Exploring the Antibacterial Mechanism of Essential Oils by Membrane Permeability, Apoptosis and Biofilm Formation Combination with Proteomics Analysis against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillín, Y.; Cáceres, M.; Torres, R.; Stashenko, E.; Ortiz, C. Effect of Essential Oils on the Inhibition of Biofilm and Quorum Sensing in Salmonella Enteritidis 13076 and Salmonella Typhimurium 14028. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Przychodna, M.; Sopata, S.; Bodalska, A.; Fecka, I. Thymol and Thyme Essential Oil—New Insights into Selected Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ed-Dra, A.; Nalbone, L.; Filali, F.R.; Trabelsi, N.; El Majdoub, Y.O.; Bouchrif, B.; Giarratana, F.; Giuffrida, A. Comprehensive Evaluation on the Use of Thymus Vulgaris Essential Oil as Natural Additive against Different Serotypes of Salmonella Enterica. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Nawaz, M.S.; Khan, S.A.; Cerniglia, C.E. Detection of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 by Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 182, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: BIGSdb Software, the PubMLST.Org Website and Their Applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, F.W.; Villar, R.G.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.; Swaminathan, B. Salmonella Nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2465–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.K.; Padmanabhan, B.R.; Diene, S.M.; Lopez-Rojas, R.; Kempf, M.; Landraud, L.; Rolain, J.-M. ARG-ANNOT, a New Bioinformatic Tool To Discover Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Bacterial Genomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Frye, J.G.; Haendiges, J.; Haft, D.H.; Hoffmann, M.; Pettengill, J.B.; Prasad, A.B.; Tillman, G.E.; et al. AMRFinderPlus and the Reference Gene Catalog Facilitate Examination of the Genomic Links among Antimicrobial Resistance, Stress Response, and Virulence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Raphenya, A.R.; Alcock, B.; Waglechner, N.; Guo, P.; Tsang, K.K.; Lago, B.A.; Dave, B.M.; Pereira, S.; Sharma, A.N.; et al. CARD 2017: Expansion and Model-Centric Curation of the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D566–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using Plasmid Finder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amouei, H.; Ferronato, G.; Qotbi, A.A.A.; Bouyeh, M.; Dunne, P.G.; Prandini, A.; Seidavi, A. Effect of Essential Oil of Thyme (Thymus Vulgaris L.) or Increasing Levels of a Commercial Prebiotic (TechnoMOS®) on Growth Performance and Carcass Characteristics of Male Broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Dool, H.; Kratz, P.D. A Generalization of the Retention Index System Including Linear Temperature Programmed Gas—Liquid Partition Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1963, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectorscopy, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing Corp: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Raybaudi-Massilia, R.M.; Mosqueda-Melgar, J.; Martín-Belloso, O. Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils on Salmonella enteritidis, Escherichia coli, and Listeria innocua in Fruit Juices. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarrino, G.; Paparella, A.; Chaves-López, C.; Faberi, A.; Sergi, M.; Sigismondi, C.; Compagnone, D.; Serio, A. Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes Inactivation Dynamics after Treatment with Selected Essential Oils. Food Control 2015, 50, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloff, J. A Sensitive and Quick Microplate Method to Determine the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration of Plant Extracts for Bacteria. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozturk, S.; Ercisli, S. The Chemical Composition of Essential Oil and in Vitro Antibacterial Activities of Essential Oil and Methanol Extract of Ziziphora Persica Bunge. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L. Pharmacologic Principles. In Equine Internal Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 79–137. [Google Scholar]
- Tzanetakis, G.N.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Zachaki, S.; Panopoulos, P.; Kontakiotis, E.G.; Madianos, P.N.; Divaris, K. Comparison of Bacterial Community Composition of Primary and Persistent Endodontic Infections Using Pyrosequencing. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamed, E.A.; Abdelaty, M.F.; Sorour, H.K.; Elmasry, D.M.A.; Abdelmagid, M.A.; Saleh, M.A.M.; AbdelRahman, M.A.A. A Pilot Study on the Effect of Thyme Microemulsion Compared with Antibiotic as Treatment of Salmonella enteritidis in Broiler. Vet. Med. Int. 2022, 2022, 3647523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raad, N.; Tandon, D.; Hapfelmeier, S.; Polacek, N. The Stationary Phase-Specific SRNA FimR2 Is a Multifunctional Regulator of Bacterial Motility, Biofilm Formation and Virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 11858–11875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, G.D.; Simpson, W.A.; Younger, J.J.; Baddour, L.M.; Barrett, F.F.; Melton, D.M.; Beachey, E.H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: A quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 22, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiley, H.; Gardner, M.G.; Ross, K. A Review of Salmonella and Squamates (Lizards, Snakes and Amphisbians): Implications for Public Health. Pathogens 2017, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meletiadis, A.; Biolatti, C.; Mugetti, D.; Zaccaria, T.; Cipriani, R.; Pitti, M.; Decastelli, L.; Cimino, F.; Dondo, A.; Maurella, C.; et al. Surveys on Exposure to Reptile-Associated Salmonellosis (RAS) in the Piedmont Region—Italy. Animals 2022, 12, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauteur, P.M.M.; Relly, C.; Hug, M.; Wittenbrink, M.M.; Berger, C. Risk Factors for Invasive Reptile-Associated Salmonellosis in Children. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamas, A.; Miranda, J.M.; Regal, P.; Vázquez, B.; Franco, C.M.; Cepeda, A. A Comprehensive Review of Non-Enterica Subspecies of Salmonella enterica. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.; Le Hello, S.; Weill, F.-X.; De Thoisy, B.; Berger, F. Salmonella Serotypes in Reptiles and Humans, French Guiana. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wybo, I.; Potters, D.; Plaskie, K.; Covens, L.; Collard, J.M.; Lauwers, S. Salmonella Enterica Subspecies Houtenae Serotype 44:Z4, Z23:—As a Rare Cause of Meningitis. Acta Clin. Belg. 2004, 59, 232–234. [Google Scholar]
- Giner-Lamia, J.; Vinuesa, P.; Betancor, L.; Silva, C.; Bisio, J.; Soleto, L.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Puente, J.L.; García-del Portillo, F. Genome Analysis of Salmonella enterica Subsp. Diarizonae Isolates from Invasive Human Infections Reveals Enrichment of Virulence-Related Functions in Lineage ST1256. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seepersadsingh, N.; Adesiyun, A.A. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella spp. in Pet Mammals, Reptiles, Fish Aquarium Water, and Birds in Trinidad. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2003, 50, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; You, L.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, D. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Genotyping of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Clinical Isolates from Guizhou Province of Southwestern China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, R.; Barh, D.; Weimer, B.C.; Viana, M.V.C.; Profeta, R.; Sousa, T.J.; Aburjaile, F.F.; Quino, W.; Souza, R.P.; Mestanza, O.; et al. WGS-Based Lineage and Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern of Salmonella typhimurium Isolated during 2000–2017 in Peru. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekshun, M.N.; Levy, S.B. The Mar Regulon: Multiple Resistance to Antibiotics and Other Toxic Chemicals. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcicki, M.; Świder, O.; Daniluk, K.J.; Średnicka, P.; Akimowicz, M.; Roszko, M.Ł.; Sokołowska, B.; Juszczuk-Kubiak, E. Transcriptional Regulation of the Multiple Resistance Mechanisms in Salmonella—A Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braoudaki, M.; Hilton, A.C. Adaptive Resistance to Biocides in Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli O157 and Cross-Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guyomard-Rabenirina, S.; Weill, F.-X.; Le Hello, S.; Bastian, S.; Berger, F.; Ferdinand, S.; Legreneur, P.; Loraux, C.; Malpote, E.; Muanza, B.; et al. Reptiles in Guadeloupe (French West Indies) Are a Reservoir of Major Human Salmonella enterica Serovars. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soni, K.A.; Oladunjoye, A.; Nannapaneni, R.; Schilling, M.W.; Silva, J.L.; Mikel, B.; Bailey, R.H. Inhibition and Inactivation of Salmonella typhimurium Biofilms from Polystyrene and Stainless Steel Surfaces by Essential Oils and Phenolic Constituent Carvacrol. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, R.; Low, K.H.; Hashim, N.B.; Ahmad, W.; Nasharuddin, M.N.A. Characterization of Sulfur-Compounds as Chemotaxonomic Markers in the Essential Oils of Allium Species by Solvent-Free Microwave Extraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akermi, S.; Smaoui, S.; Fourati, M.; Elhadef, K.; Chaari, M.; Mtibaa, A.C.; Mellouli, L. In-Depth Study of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil: Towards Understanding the Antibacterial Target Mechanism and Toxicological and Pharmacological Aspects. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 3368883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čabarkapa, I.; Čolović, R.; Đuragić, O.; Popović, S.; Kokić, B.; Milanov, D.; Pezo, L. Anti-Biofilm Activities of Essential Oils Rich in Carvacrol and Thymol against Salmonella Enteritidis. Biofouling 2019, 35, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in Vitro Evaluating Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klančnik, A.; Piskernik, S.; Jeršek, B.; Možina, S.S. Evaluation of Diffusion and Dilution Methods to Determine the Antibacterial Activity of Plant Extracts. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 81, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reptiles | Animals | Sex | Weight (g) | Theca | Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snakes | Royal python (P1) | F | 1500 | Shared * | CS |
| Royal python (P2) | M | 850 | Shared * | CS | |
| Royal python (P3) | F | 1880 | Shared * | CS | |
| Royal python (P4) | F | 400 | Single | CS | |
| Small royal snake | M | 310 | Single | CS | |
| Large royal snake | F | 1290 | Single | CS | |
| Albino coral snake | M | 156 | Single | CS | |
| Bull snake | M | 110 | Single | CS | |
| False coral snake | F | 400 | Single | CS | |
| Pink boa | F | 200 | Single | CS | |
| Saurians | Tiliqua | F | 386 | Single | CS + Feces |
| Gerrhosaurus major | M | 360 | Single | CS | |
| Bearded dragon | F | 320 | Single | CS + Feces |
| Positive Animals | Detected Salmonella | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID Sample | Species and Subspecies | Serotype | Antimicrobial Resistance Gene 1 | |
| Large royal snake | Salmonella 1 | S. enterica subsp. diarizonae | 51:k:z35 | marA; soxS; soxR; CRP; emrB; ACC(6′)-Iy; baeR; bacA; msbA; E.coliUhpT; E.coliGlpT |
| Bull snake | Salmonella 2 | S. enterica subsp. diarizonae | Z:z35:z35 | marA; soxS; soxR; CRP; emrB; ACC(6′)-Iy; bacA; msbA; E.coliUhpT; E.coliGlpT |
| Small royal snake | Salmonella 3 | S. enterica subsp. diarizonae | 51:k:z35 | marA; soxS; soxR; CRP; emrB; ACC(6′)-Iy; baeR; bacA; msbA; E.coliUhpT; E.coliGlpT |
| Gerrohsaurus major | Salmonella 4 | S. enterica subsp. salamae | F:g,m,s,t:1,5 | marA; soxS; soxR; CRP; emrB; arcB; mdtK; baeR; bacA; msbA; sdiA; E.coliUhpT; E.coliGlpT |
| False coral snake | Salmonella 5 | S. enterica subsp. diarizonae | Z:z35:z35 | marA; soxS; soxR; CRP; emrB; arcB; mdtK; ACC(6′)-Iy; baeR; bacA; msbA; sdiA; E.coliUhpT; E.coliGlpT |
| Coral snake | Salmonella 6 | S. enteric subsp. diarizonae | 53:z10:z35 | marA; soxS; soxR; CRP; emrB; ACC(6′)-Iy; baeR; bacA; msbA; sdiA; E.coliUhpT |
| Pink boa | Salmonella 7 | S. enterica subsp. enterica | Muenchen | marA; soxS; soxR; CRP; acrB; mdtK; ACC(6′)-Iy; baeR; bacA; msbA; sdiA; E.coliUhpT; E.coliGlpT |
| Royal python 4 | Salmonella 8 | S. enterica subsp. houtenae | 44:z4,z23:- | marA; CRP; acrB; ACC(6′)-Iy; baeR; bacA; msbA; E.coliUhpT |
| Royal python 2 | Salmonella 9 | ND | ND | marA; soxS; soxR; CRP; emrB; ACC(6′)-Iy; baeR; bacA; msbA; E.coliUhpT; E.coliGlpT |
| Salmonella Strain | Logarithmic Phase 24 h | Logarithmic Phase 48 h | Logarithmic Phase Ratio | ||
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MBC/MIC | |
| Salmonella 1 | 0.312 | 0.312 | 0.078 | 0.312 | 1.6 |
| Salmonella 2 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 1 |
| Salmonella 3 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 1 |
| Salmonella 4 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 1 |
| Salmonella 5 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 6 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 7 | 0.156 | 0.312 | 0.156 | 0.312 | 2 |
| Salmonella 8 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 9 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 1 |
| Salmonella Strain | Stationary Phase 24 h | Stationary Phase 48 h | Stationary Phase Ratio | ||
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MBC/MIC | |
| Salmonella 1 | 0.312 | 0.312 | 0.156 | 0.312 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 2 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 1 |
| Salmonella 3 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 1 |
| Salmonella 4 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 5 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 6 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 7 | 0.312 | 0.312 | 0.156 | 0.312 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 8 | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 1.3 |
| Salmonella 9 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 1 |
| % TEO | Alone Inhibition Diameter (mm) (Logarithmic Phase) | ||||||||
| S. 1 | S. 2 | S. 3 | S. 4 | S. 5 | S. 6 | S. 7 | S. 8 | S. 9 | |
| 5 | 14 | 10 | 14 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 13.5 | 15 |
| 2.5 | 12 | 9 | 12 | 9 | n.i. | 9 | 8 | 10 | 9 |
| 1.25 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | n.i. | 8 | 7 | 9 | 7 |
| 0.625 | 8 | 7 | 9 | 7 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.312 | 8 | n.i. | 8 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.156 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.078 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.039 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| % TEO | Alone Inhibition Diameter (mm) (Stationary Phase) | ||||||||
| S. 1 | S. 2 | S. 3 | S. 4 | S. 5 | S. 6 | S. 7 | S. 8 | S. 9 | |
| 5 | 12 | 11.75 | 13.25 | 10 | 9.5 | 14 | 16.75 | 13.5 | 12 |
| 2.5 | 9 | 9.5 | 10 | 9 | n.i. | 8.5 | 9.25 | 9 | 8.25 |
| 1.25 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 9,5 | n.i | n.i. | n.i. | 7.25 | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.625 | 7.5 | 7 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.312 | 7 | n.i. | n.i | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.156 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.078 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 0.039 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galgano, M.; Mrenoshki, D.; Pellegrini, F.; Capozzi, L.; Cordisco, M.; Del Sambro, L.; Trotta, A.; Camero, M.; Tempesta, M.; Buonavoglia, D.; et al. Antibacterial and Biofilm Production Inhibition Activity of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil against Salmonella spp. Isolates from Reptiles. Pathogens 2023, 12, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060804
Galgano M, Mrenoshki D, Pellegrini F, Capozzi L, Cordisco M, Del Sambro L, Trotta A, Camero M, Tempesta M, Buonavoglia D, et al. Antibacterial and Biofilm Production Inhibition Activity of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil against Salmonella spp. Isolates from Reptiles. Pathogens. 2023; 12(6):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060804
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalgano, Michela, Daniela Mrenoshki, Francesco Pellegrini, Loredana Capozzi, Marco Cordisco, Laura Del Sambro, Adriana Trotta, Michele Camero, Maria Tempesta, Domenico Buonavoglia, and et al. 2023. "Antibacterial and Biofilm Production Inhibition Activity of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil against Salmonella spp. Isolates from Reptiles" Pathogens 12, no. 6: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060804
APA StyleGalgano, M., Mrenoshki, D., Pellegrini, F., Capozzi, L., Cordisco, M., Del Sambro, L., Trotta, A., Camero, M., Tempesta, M., Buonavoglia, D., Laricchiuta, P., Catella, C., Pratelli, A., Buonavoglia, A., & Corrente, M. (2023). Antibacterial and Biofilm Production Inhibition Activity of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil against Salmonella spp. Isolates from Reptiles. Pathogens, 12(6), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060804