Early-Life Skin Microbial Biomarkers for Eczema Phenotypes in Chinese Toddlers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
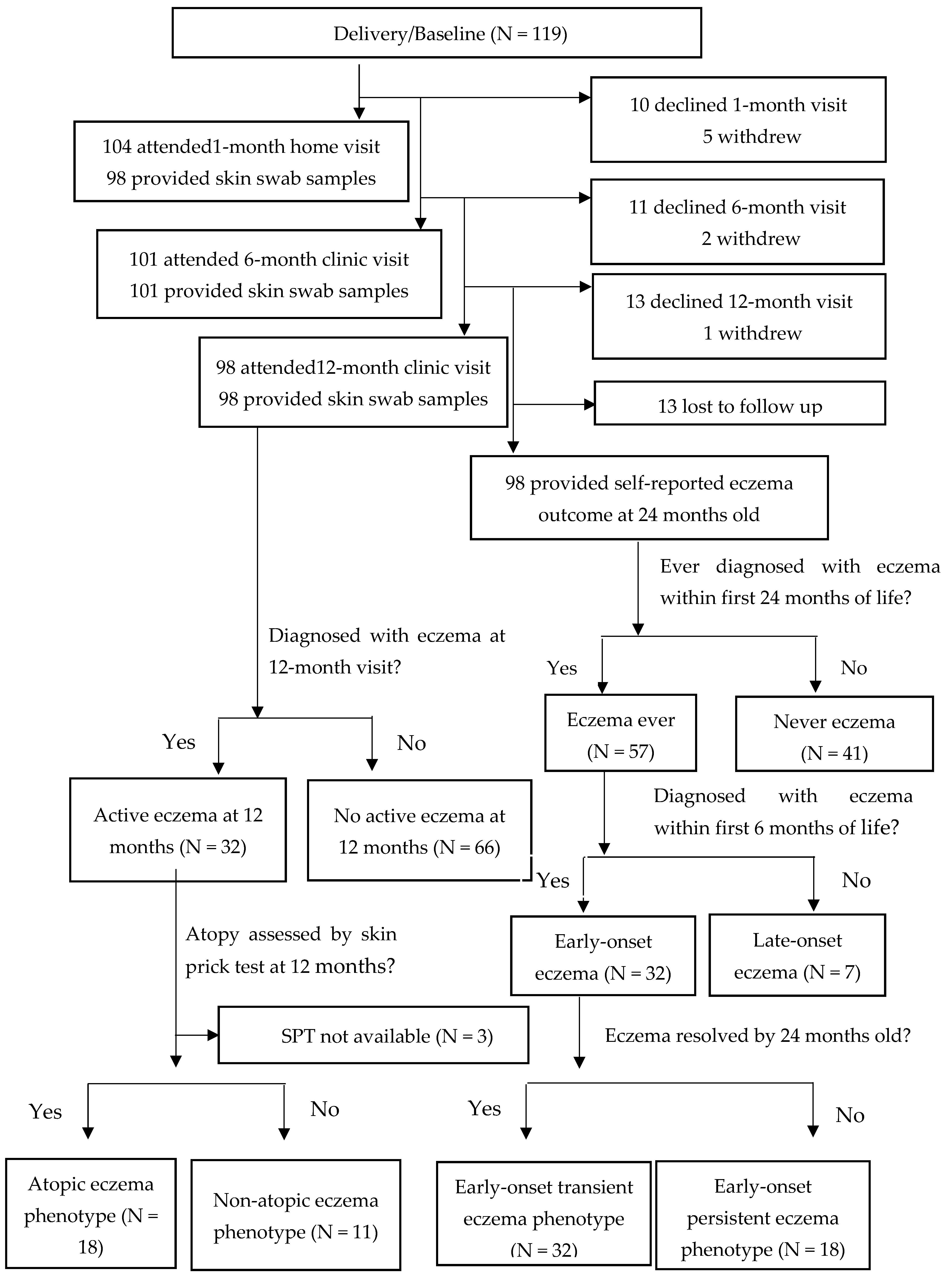
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Definition of Eczema Phenotypes
2.3. Sampling for Microbiome Analysis
2.4. Characterization of Skin Microbiome
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Population
3.2. Relationship between Atopy and Eczema Persistence
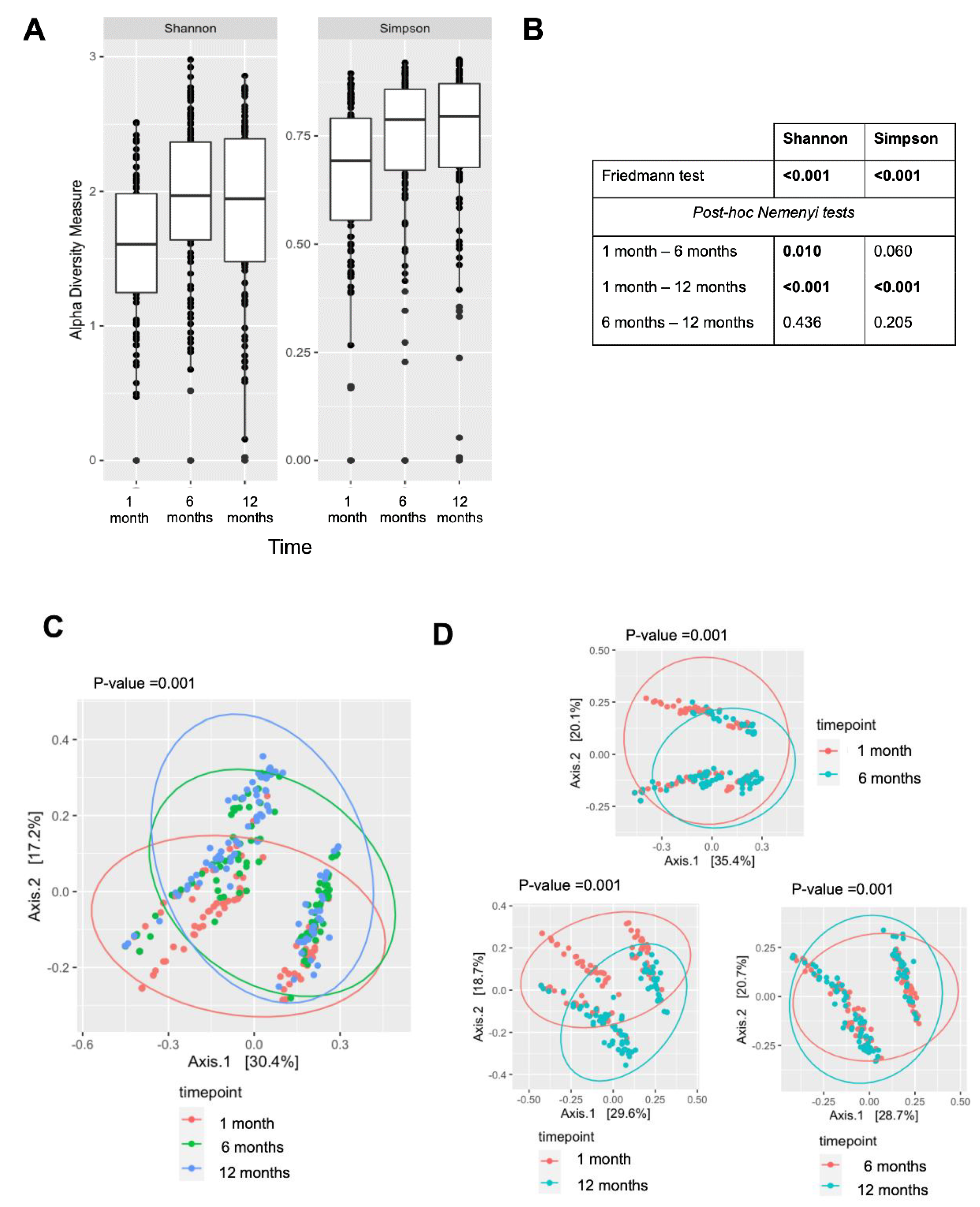
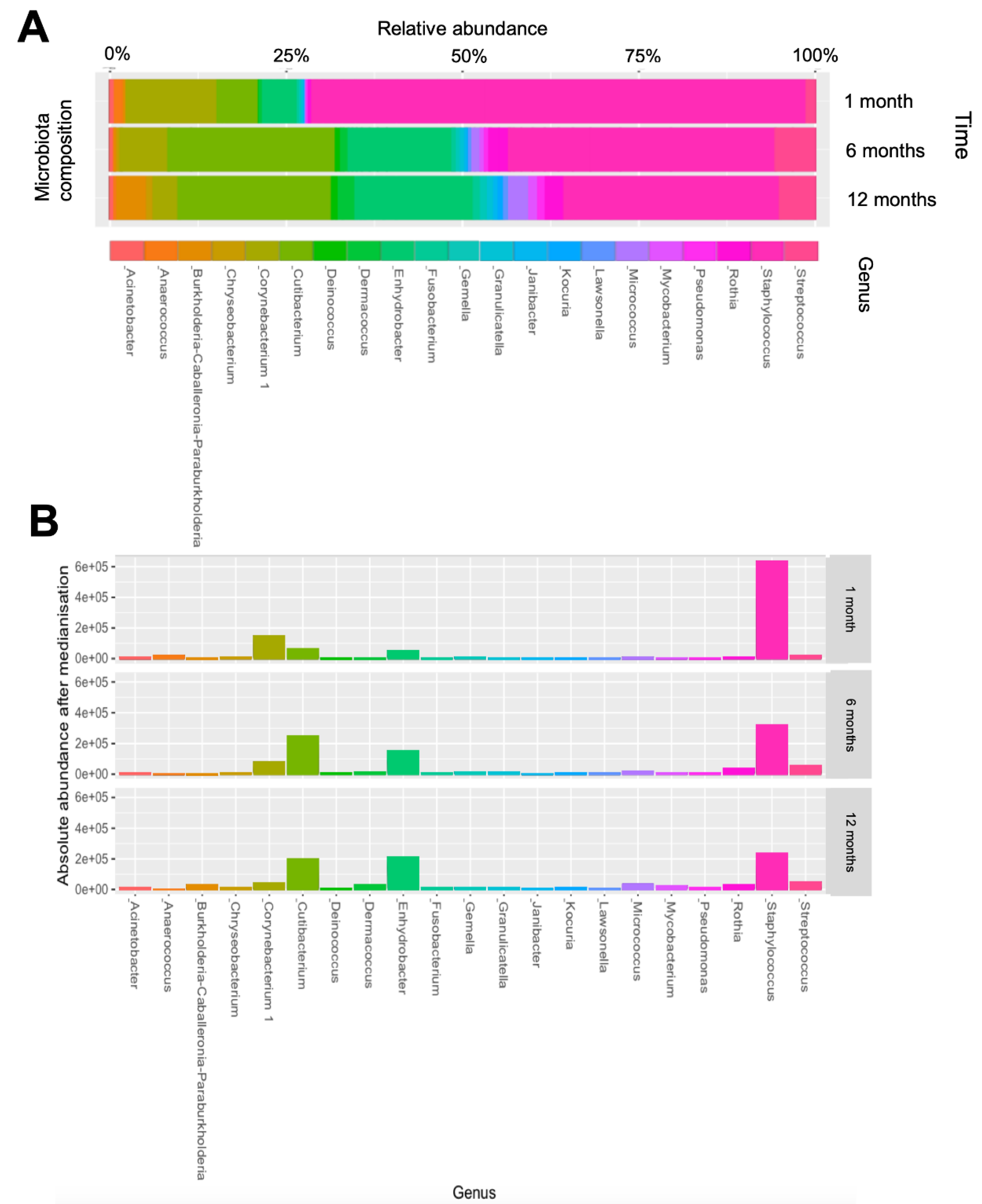
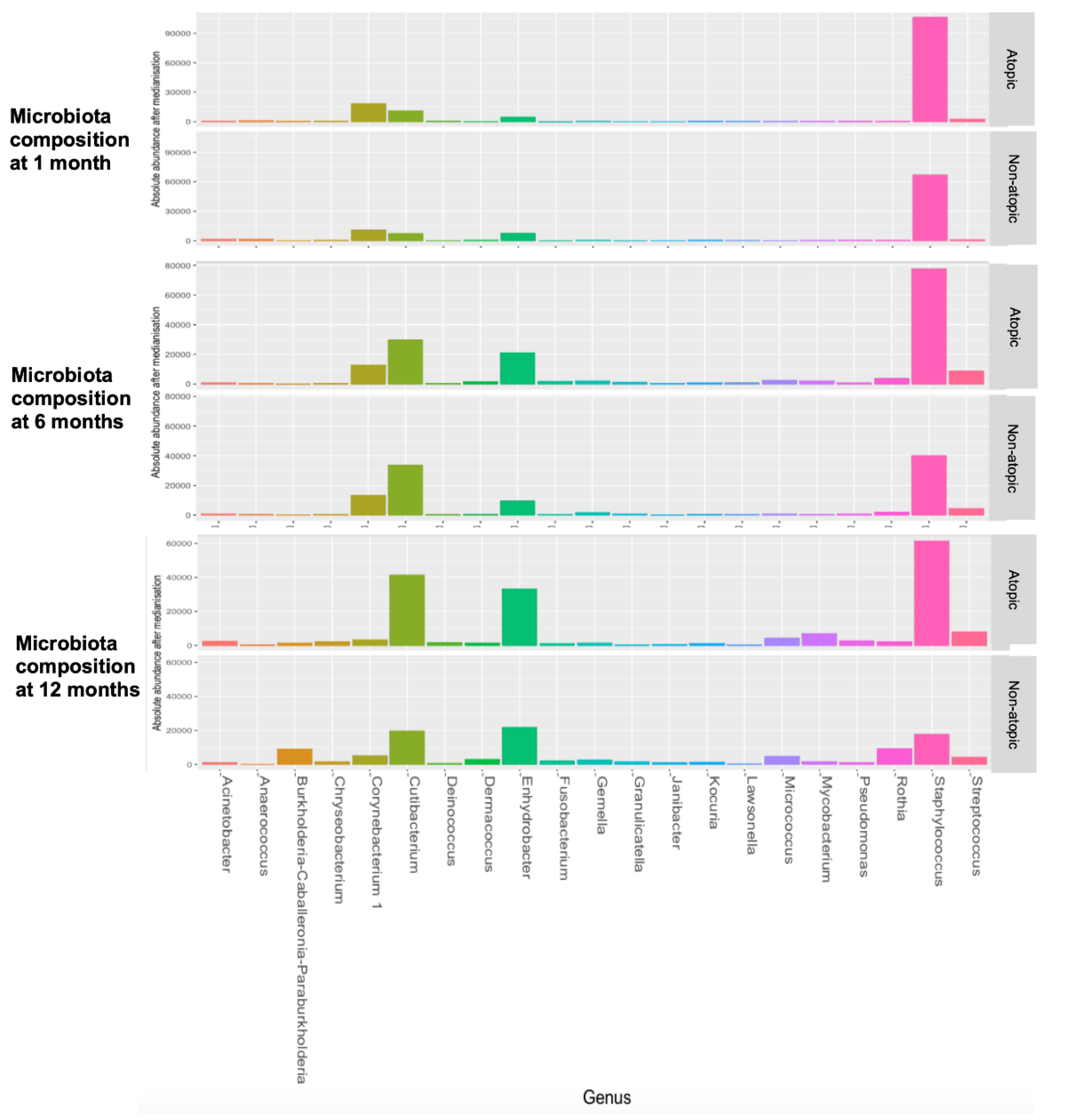
3.3. Evolution of Early-Life Skin Microbiome
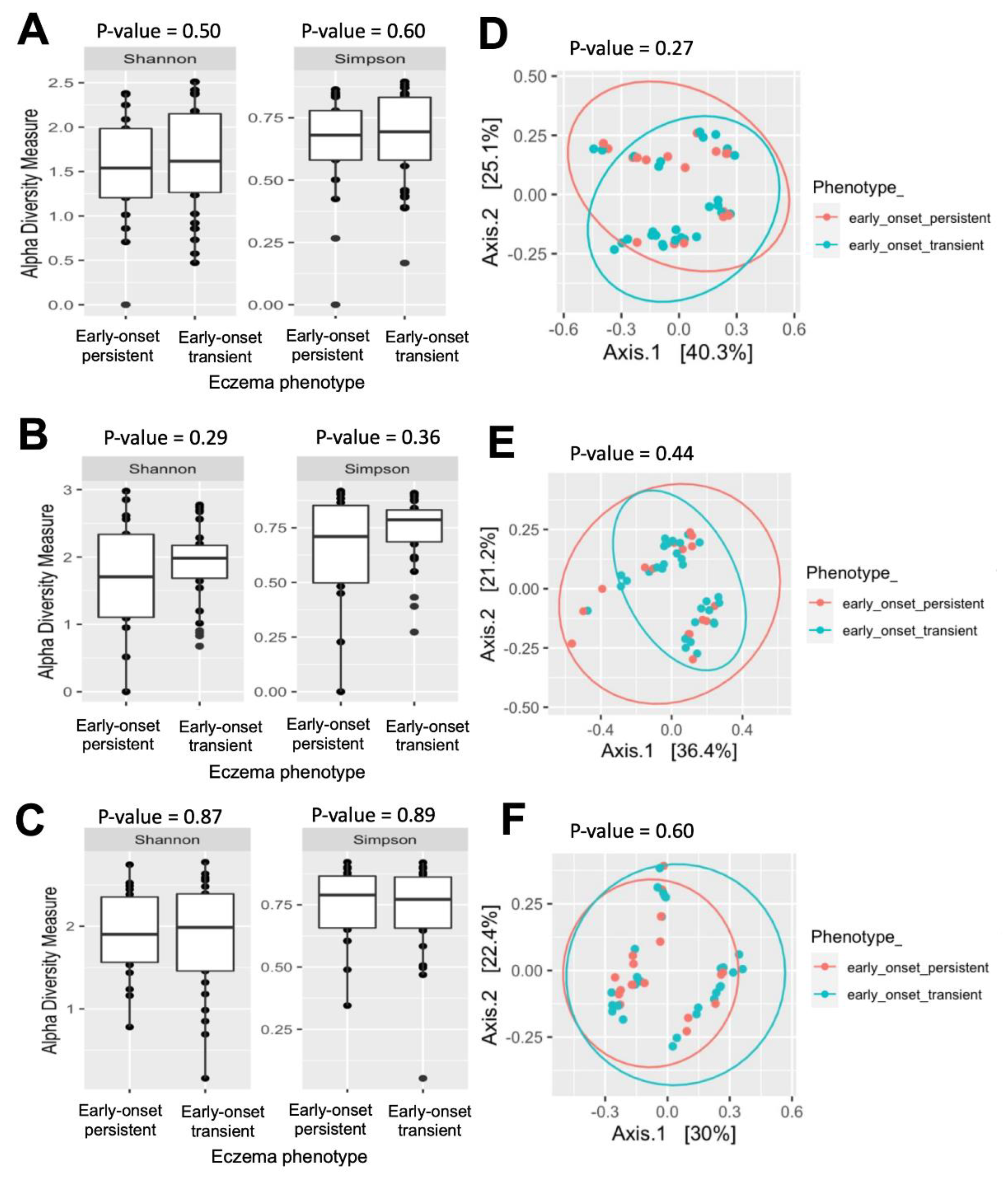
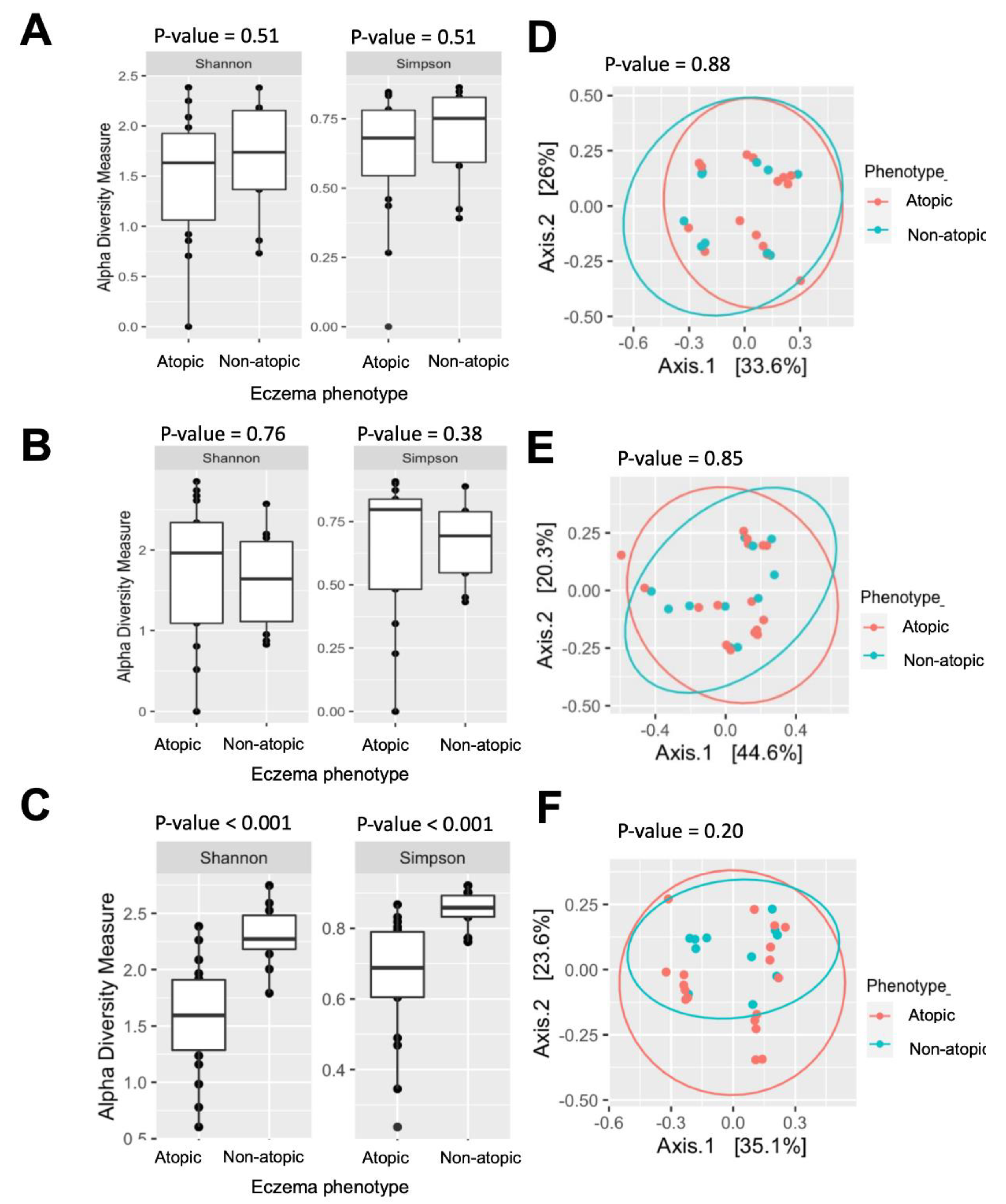
3.4. Temporal Effects of Skin-Microbial Diversity on Eczema Phenotypes
3.5. Skin Microbial Taxa Associated with Eczema Phenotypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Odhiambo, J.A.; Williams, H.C.; Clayton, T.O.; Robertson, C.F.; Asher, M.I. Global variations in prevalence of eczema symptoms in children from ISAAC Phase Three. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutten, S. Atopic dermatitis: Global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roduit, C.; Frei, R.; Depner, M.; Karvonen, A.M.; Renz, H.; Braun-Fahrländer, C.; Schmausser-Hechfellner, E.; Pekkanen, J.; Reidler, J.; Dalphin, J.-C.; et al. Phenotypes of atopic dermatitis depending on the timing of onset and progression in childhood. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternoster, L.; Savenije, O.E.; Heron, J.; Evans, D.M.; Vonk, J.M.; Brunekreef, B.; Wijga, A.H.; Henderson, A.J.; Koppelman, G.H.; Brown, S.J. Identification of atopic dermatitis subgroups in children from 2 longitudinal birth cohorts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Duijts, L.; Erler, N.S.; Elbert, N.J.; Piketty, C.; Bourdès, V.; Blanchet-Réthoré, S.; de Jongste, J.C.; Pasmans, S.G.; Felix, J.F.; et al. Most associations of early-life environmental exposures and genetic risk factors poorly differentiate between eczema phenotypes: The Generation R Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; Simon, D.; Simon, H.U.; Akdis, C.A.; Wüthrich, B. Epidemiology, clinical features, and immunology of the “intrinsic” (non-IgE-mediated) type of atopic dermatitis (constitutional dermatitis). Allergy 2001, 56, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.H.; Oh, J.; Deming, C.; Conlan, S.; Grice, E.A.; Beatson, M.A.; Nomicos, E.; Polley, E.C.; Komarow, H.D.; Murray, P.R.; et al. Temporal shifts in the skin microbiome associated with disease flares and treatment in children with atopic dermatitis. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.A.; Connolly, J.; Hourihane, J.O.; Fallon, P.G.; McLean, W.H.; Murray, D.; Jo, J.-H.; Segre, J.A.; Kong, H.H.; Irvine, A.D. Skin microbiome before development of atopic dermatitis: Early colonization with commensal Staphylococci at 2 months is associated with a lower risk of atopic dermatitis at 1 year. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, P.; Lang, C.; Mermoud, S.; Johannsen, A.; Norrenberg, S.; Hohl, D.; Vial, Y.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G.; Kypriotou, M.; et al. Skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus precedes the clinical diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in infancy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HanifIn, J.M. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1980, 92, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.F.; Yung, E.; Wong, Y.S.; Lam, C.W.; Wong, G.W. Parent-reported adverse food reactions in Hong Kong Chinese preschoolers: Epidemiology, clinical spectrum and risk factors. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2009, 20, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.F.; Yung, E.; Wong, Y.S.; Li, C.Y.; Wong, G.W. Quality-of-life assessment in Chinese families with food allergic children. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Leung, A.S.; Li, R.M.; Leung, T.F.; Lau, C.S.; Wong, G.W. Increasing incidence of anaphylaxis in Hong Kong from 2009 to 2019—Discrepancies of anaphylaxis care between adult and pediatric patients. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2020, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.A.; Fontanella, S.; Boakes, E.; Belgrave, D.; Shaw, A.G.; Cornwell, E.; Fernandez-Crespo, R.; Fink, C.G.; Custovic, A.; Kroll, J.S. Temporal association of the development of oropharyngeal microbiota with early life wheeze in a population-based birth cohort. EBioMedicine 2019, 46, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlert, T. PMCMRplus: Calculate Pairwise Multiple Comparisons of Mean Rank Sums Extended. R Package Version 1.9.4. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=PMCMRplus (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, E.; Park, Y.M.; Hong, S.J. Microbiome in the gut-skin axis in atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.G.; Wu, J.R.; Gloor, G.B. Expanding the UniFrac toolbox. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogai, K.; Nana, B.C.; Lloyd, Y.M.; Arios, J.P.; Jiyarom, B.; Awanakam, H.; Esemu, L.F.; Hori, A.; Matsuoka, A.; Nainu, F.; et al. Skin microbiome profile of healthy Cameroonians and Japanese. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, S.; Zhang, K. Bacteremia caused by Janibacter melonis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3537–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Natal, M.I.; Sáez-Nieto, J.A.; Medina-Pascual, M.J.; Valdezate-Ramos, S.; Guerra-Laso, J.M.; Rodríguez-Pollán, R.H.; Soriano, F. First report of bacteremia by Janibacter terrae in humans. Infection 2015, 43, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Hu, N. Whole genome sequencing of first Janibacter indicus isolate in China revealed three unique genomic islands compared with saprophytic strains. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 5351–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.W.H.; Chan, J.Y.W.; Leung, T.F.; Choi, K.C.; Tsui, S.K.W.; Wong, C.L.; Chow, K.M. Altered gut microbiome and environmental factors associated with development of eczema in Hong Kong infants: A 4-month pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.W.H.; Leung, T.F.; Choi, K.C.; Tsui, S.K.W.; Wong, C.L.; Chow, K.M.; Chan, J.Y.W. Association of early-life gut microbiome and lifestyle factors in the development of eczema in Hong Kong infants. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Sy, H.; Kwok, J.; Tam, W.; Hon, K.; Tung, C.; Wong, G.; Tsui, S.; Leung, T. Eczema susceptibility and composition of faecal microbiota at 4 weeks of age: A pilot study in Chinese infants. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Census and Statistics Department, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. Hong Kong Annual Digest of Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://www.censtatd.gov.hk/en/data/stat_report/product/B1010003/att/B10100032022AN22B0100.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Department of Health, Hong kong Special Administrative Region. Breastfeeding Survery 2021. 2021. Available online: https://www.fhs.gov.hk/english/reports/files/BF_survey_2021.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Lee, S.L.; Lau, Y.L.; Wong, W.H.S.; Tian, L.W. Childhood wheeze, allergic rhinitis, and eczema in Hong Kong ISAAC Study from 1995 to 2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 16503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, R.J.; Boucher, Y.; Dahllöf, I.; Holmström, C.; Doolittle, W.F.; Kjelleberg, S. Use of 16S rRNA and rpoB genes as molecular markers for microbial ecology studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Maternal characteristics | |
| Received education level higher than secondary school, n/N (%) | 63/119 (52.9) |
| History of allergy, n/N (%) | 42/119 (35.3) |
| Paternal characteristics | |
| Received education level higher than secondary school, n/N (%) | 60/119 (50.4) |
| History of allergy, n/N (%) | 32/109 (29.4) |
| Child characteristics | |
| Male, n/N (%) | 63/119 (52.9) |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 39.3 ± 1.2 (N = 119) |
| Birth weight (g) | 3145 ± 340 (N = 119) |
| Born by vaginal delivery, n/N (%) | 91/119 (76.5) |
| Exclusive breastfeeding at 1 month, n/N (%) | 26/109 (23.9) |
| Mixed breast and formula feeding at 1 month, n/N (%) | 74/109 (67.9) |
| Furry pets at home at 1 month (yes), n/N (%) | 23/109 (21.1) |
| Exposure to household smoking at 1 month (yes), n/N (%) | 34/109 (31.2) |
| Eczema diagnosis, n/N (%) | |
| Eczema at 6 months | 40/101 (39.6) |
| Eczema at 12 months | 32/98 (32.7) |
| Eczema at 24 months | 22/98 (22.4) |
| Atopy by skin-prick test at 12 months, n/N (%) | 26/82 (31.7) |
| Sensitization to single tested allergen | 15/82 (18.3) |
| Sensitization to multiple tested allergens | 11/82 (13.4) |
| Received intrapartum antibiotics, n/N(%) | 60/119 (50.4) |
| Received postnatal antibiotics, n/N (%) | |
| Within 1 month after birth | 12/109 (11.0) |
| 1 month to 6 months of age | 18/100 (18.0) |
| 6 to 12 months of age | 22/98 (22.4) |
| 12 to 24 months of age | 31/86 (36.0) |
| Non-Atopic Eczema–Atopic Eczema | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa at genus level | Skin Microbiome at 1 Month | Skin Microbiome at 6 Months | Skin Microbiome at 12 Months | |||
| Beta coefficient | Adjusted p-value | Beta coefficient | Adjusted p-value | Beta coefficient | Adjusted p-value | |
| Janibacter | N/A | N/A | −1.085 | <0.001 T | −0.123 | 1.000 F |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yau, J.W.K.; Chan, K.C.C.; Leung, A.S.Y.; Chan, O.M.; Yeung, A.C.M.; Yuen, C.L.Y.; Chan, P.K.S.; et al. Early-Life Skin Microbial Biomarkers for Eczema Phenotypes in Chinese Toddlers. Pathogens 2023, 12, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050697
Chen Y, Song Y, Chen Z, Yau JWK, Chan KCC, Leung ASY, Chan OM, Yeung ACM, Yuen CLY, Chan PKS, et al. Early-Life Skin Microbial Biomarkers for Eczema Phenotypes in Chinese Toddlers. Pathogens. 2023; 12(5):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050697
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yehao, Yuping Song, Zigui Chen, Jennifer Wing Ki Yau, Kate Ching Ching Chan, Agnes Sze Yin Leung, Oi Man Chan, Apple Chung Man Yeung, Connie Lai Yuk Yuen, Paul Kay Sheung Chan, and et al. 2023. "Early-Life Skin Microbial Biomarkers for Eczema Phenotypes in Chinese Toddlers" Pathogens 12, no. 5: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050697
APA StyleChen, Y., Song, Y., Chen, Z., Yau, J. W. K., Chan, K. C. C., Leung, A. S. Y., Chan, O. M., Yeung, A. C. M., Yuen, C. L. Y., Chan, P. K. S., Tam, W. H., & Leung, T. F. (2023). Early-Life Skin Microbial Biomarkers for Eczema Phenotypes in Chinese Toddlers. Pathogens, 12(5), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050697







