Reaction of Cornu aspersum Immune System against Different Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Developmental Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Larvae Suspension
2.2. Animals and Housing Conditions
2.3. Experimental Protocol
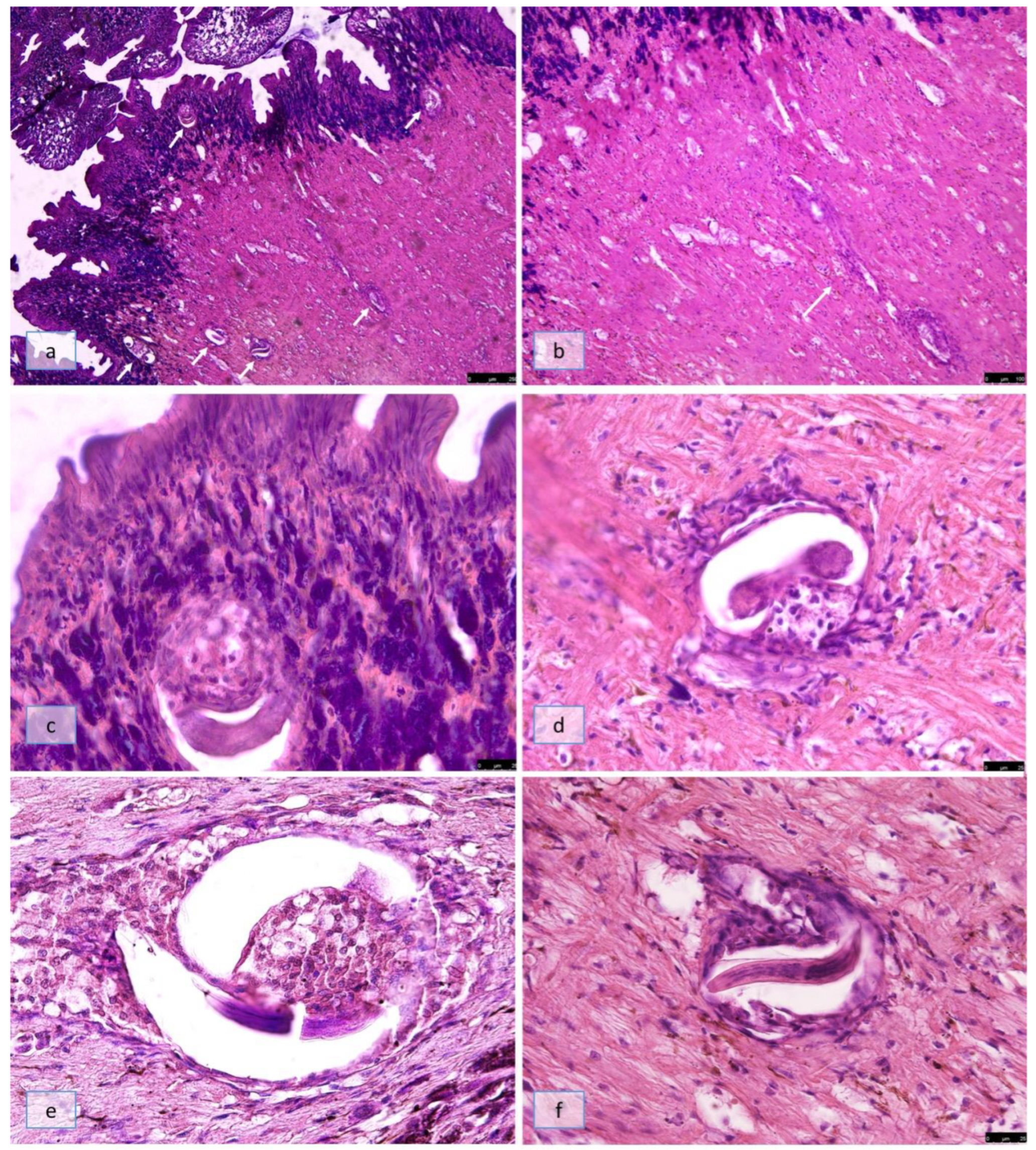
3. Results
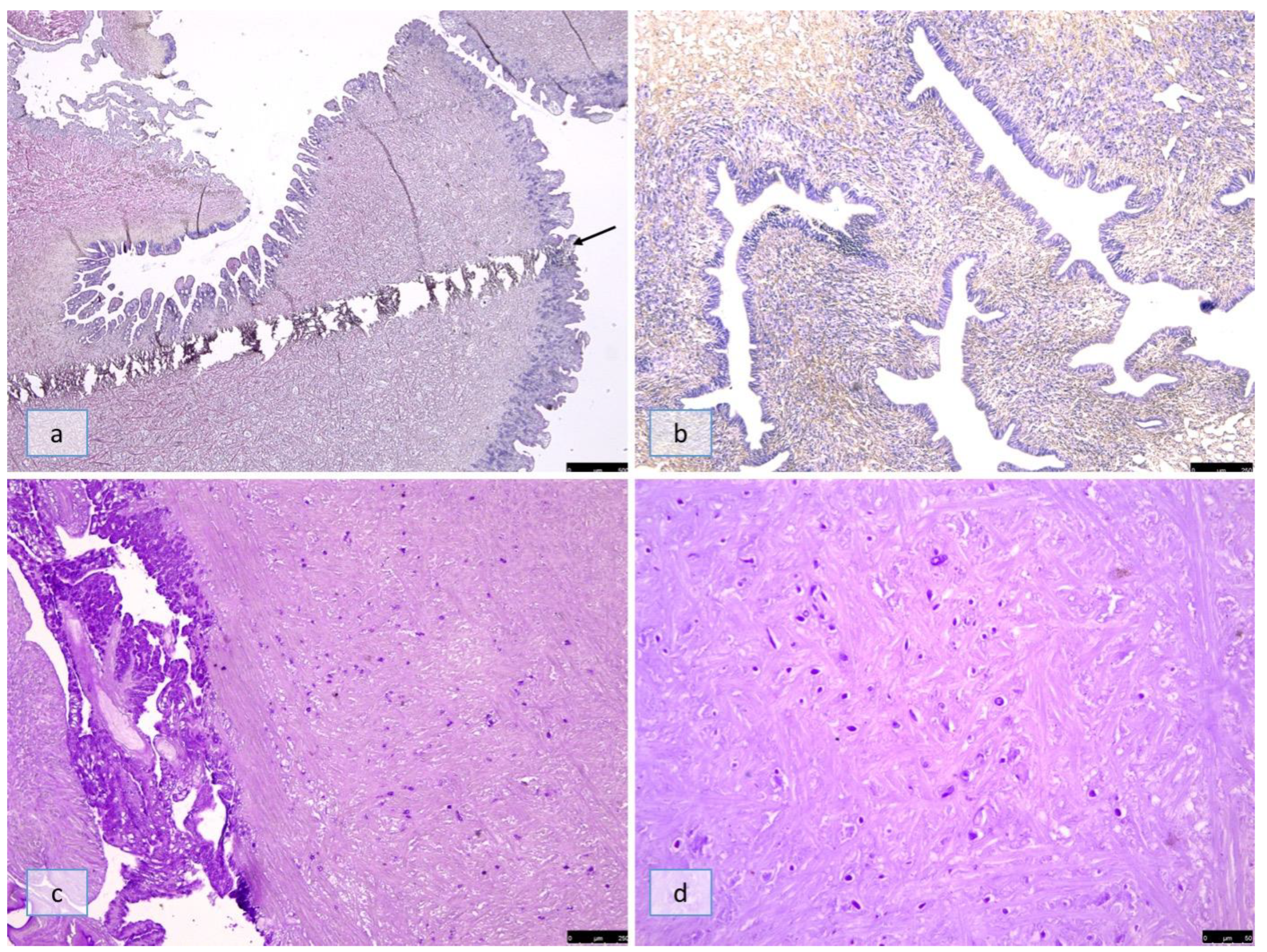
3.1. Group A
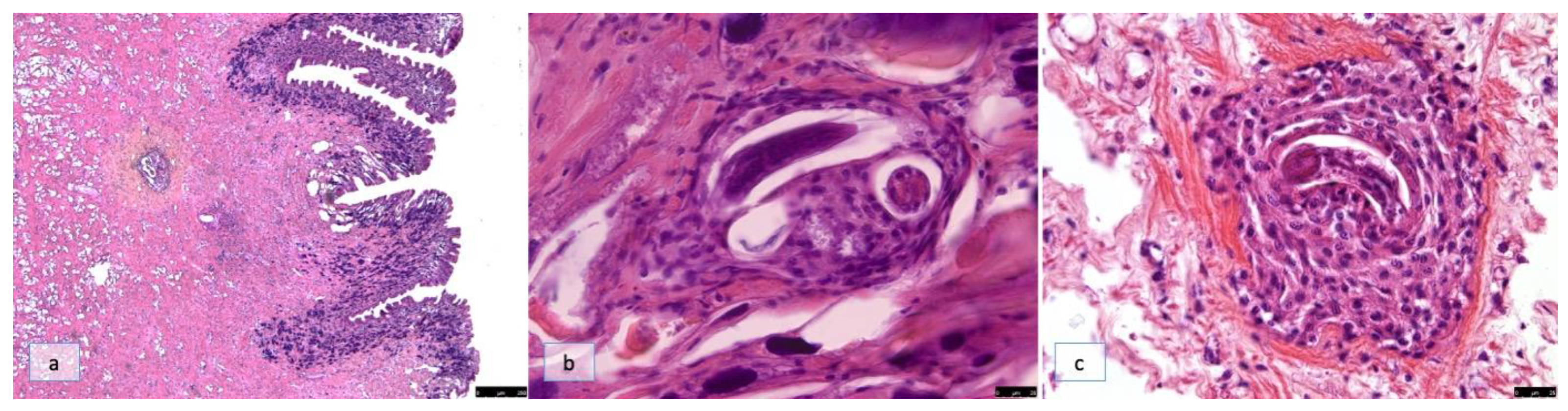
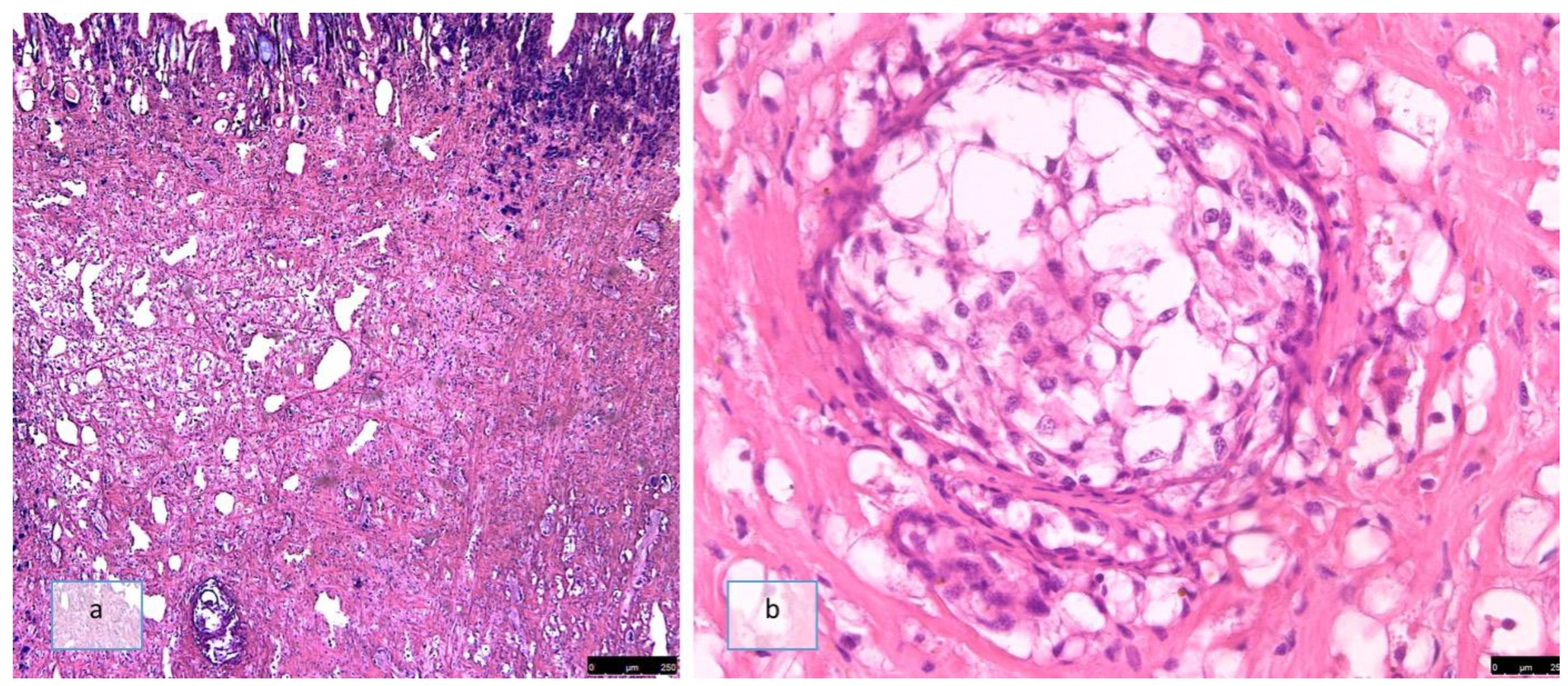
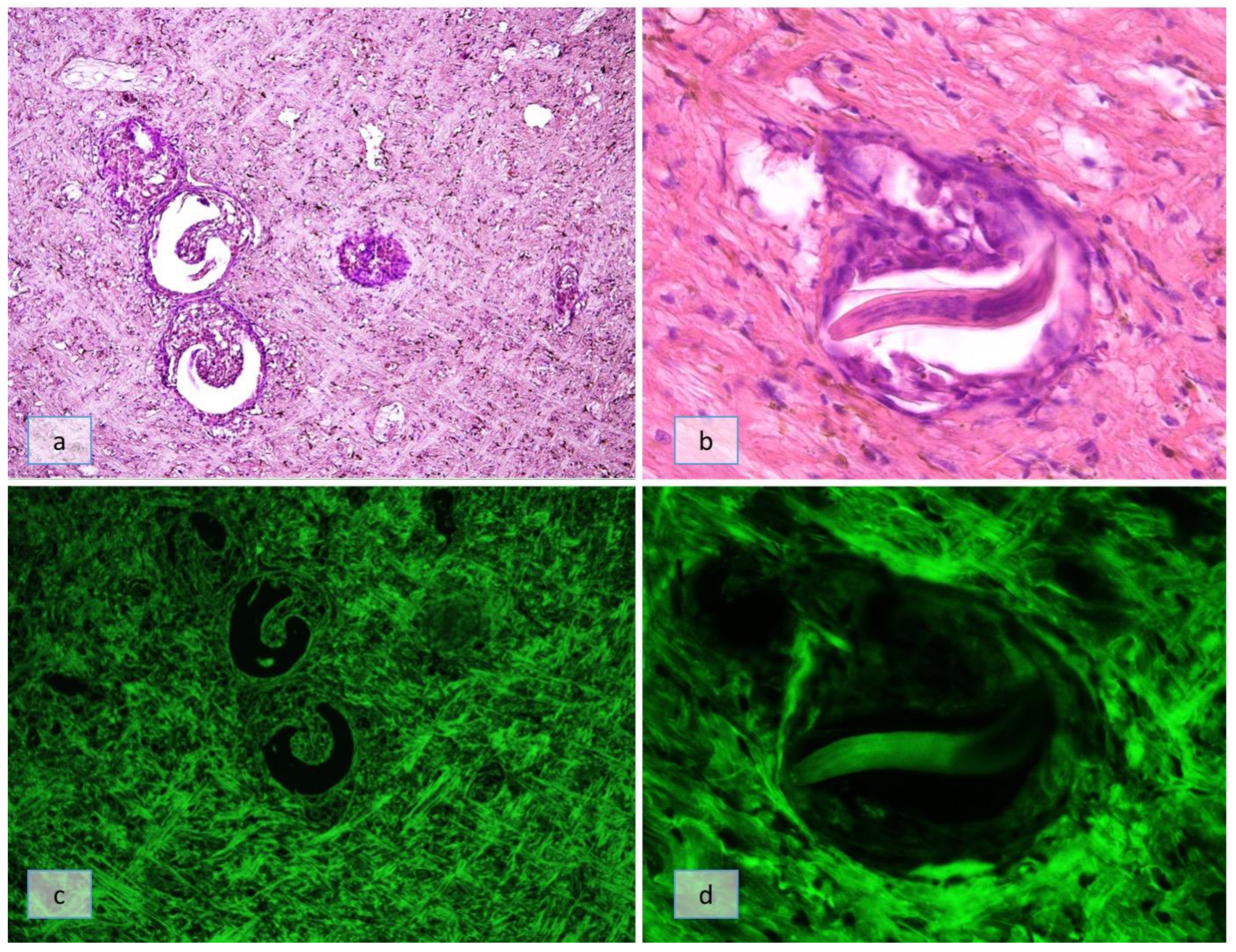
3.2. Groups B, C, and D
3.2.1. 4 h and 2 Days Post-Infection (SD2)
3.2.2. 10 Days Post-Infection (SD10)
3.2.3. 18 Days Post-Infection (SD18)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giannelli, A.; Colella, V.; Abramo, F.; Ramos, R.A.; Falsone, L.; Brianti, E.; Varcasia, A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Knaus, M.; Fox, M.T.; et al. Release of lungworm larvae from snails in the environment: Potential for alternative transmission pathways. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelli, A.; Capelli, G.; Joachim, A.; Hinney, B.; Losson, B.; Kirkova, Z.; René-Martellet, M.; Papadopoulos, E.; Farkas, R.; Napoli, E.; et al. Lungworms and gastrointestinal parasites of domestic cats: A European perspective. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.C. Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates: Their Development and Transmission; Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau International (CABI Publishing): Wallingford, UK, 2000.
- Gerichter, C.B. Studies on the nematodes parasitic in the lungs of Felidae in Palestine. Parasitology 1949, 39, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, E.; Arfuso, F.; Gaglio, G.; Abbate, J.M.; Giannetto, S.; Brianti, E. Effect of different temperatures on survival and devel-opment of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Railliet, 1898) larvae. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansart, A.; Guiller, A.; Madec, L. (Eds.) CABI Invasive Species Compendium: Cornu aspersum; CABI: London, UK, 2019.
- Hobmaier, M.; Hobmaier, A. Intermediate hosts of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus of the cat. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1935, 32, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Crisi, P.E.; Di Giulio, E.; Veronesi, F.; Frangipane di Regalbono, A.; Talone, T.; Traversa, D. Larval development of the feline lungworm Aelurostrongylus abstrusus in Helix aspersa. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3101–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelli, A.; Ramos, R.A.; Annoscia, G.; Di Cesare, A.; Colella, V.; Brianti, E.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Mutafchiev, Y.; Otranto, D. Development of the feline lungworms Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Troglostrongylus brevior in Helix aspersa snails. Parasitology 2014, 141, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, E.; Falsone, L.; Gaglio, G.; Colella, V.; Otranto, D.; Giannetto, S.; Brianti, E. Evaluation of different methods for the experimental infection of the land snail Helix aspersa with Aelurostrongylus abstrusus lungworm. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 225, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.K.; Penagos-Tabares, F.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Gärtner, U.; Mejer, H.; Schaper, R.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Gastropod-derived haemocyte extracellular traps entrap metastrongyloid larval stages of Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Troglostrongylus brevior. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, N.A. Invertebrate immunity a primer for the non-specialist. Immunol. Lett. 1985, 10, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, B.H.; Peatman, E. Mucosal Health in Aquaculture; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.C. A classification of molluscan hemocytes based on functional evidences. In Invertebrate Blood; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, K.; Nomoto, A.M.; Nishijima, M.; Maruyama, T. Morphological and functional characterization of hemocytes in the giant clam Tridacna crocea. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1997, 69, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matricon-Gondran, M.; Letocart, M. Internal defenses of the snail Biomphalaria glabrata: I. Characterization of hemocytes and fixed phagocytes. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1999, 74, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, M.; Doenhoff, M.; Kirschfink, M.; Ruppel, A. Serine protease and phenoloxidase activities in hemocytes of Biomphalaria glabrata snails with varying susceptibility to infection with the parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Souza, R.L.; Pereira, C.A.J.; Martins Filho, O.A.; Coelho, P.M.Z.; Corrêa, A., Jr.; Negrão-Corrêa, D. Differential lectin labelling of circulating hemocytes from Biomphalaria glabrata and Biomphalaria tenagophila resistant or susceptible to Schistosoma mansoni infection. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101 (Suppl. I), 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavodna, M.; Sandland, G.J.; Minchella, D.J. Effects of intermediate host genetic background on parasite transmission dynamics: A case study using Schistosoma mansoni. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 120, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, C. Parasitism: The Ecology and Evolution of Intimate Interactions; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix, M.C. Diagnostic Veterinary Parasitology; Mosby: St. Luis, MO, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brianti, E.; Gaglio, G.; Giannetto, S.; Annoscia, G.; Latrofa, M.S.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Traversa, D.; Otranto, D. Troglostrongylus brevior and Troglostrongylus subcrenatus (Strongylida: Crenosomatidae) as agents of broncho-pulmonary infestation in domestic cats. Parasites Vectors 2012, 23, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brianti, E.; Giannetto, S.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Lungworms of the genus Troglostrongylus (Strongylida: Crenoso-matidae): Neglected parasites for domestic cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 202, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pila, E.A.; Li, H.; Hambrook, J.R.; Wu, X.; Hanington, P.C. Schistosomiasis from a Snail’s Perspective: Advances in Snail Immunity. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.; Madec, L. Dual strategy for immune defense in the land snail Cornu aspersum (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2011, 84, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penagos-Tabares, F.; Lange, M.K.; Seipp, A.; Gärtner, U.; Mejer, H.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Novel approach to study gastropod-mediated innate immune reactions against metastrongyloid parasites. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangassalo, K.; Valtonen, T.M.; Roff, D.; Pölkki, M.; Dubovskiy, I.M.; Sorvari, J.; Rantala, M.J. Intra- and trans-generational effects of larval diet on susceptibility to an entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana, in the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella. J. Evol. Biol. 2015, 28, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krams, I.; Kecko, S.; Kangassalo, K.; Moore, F.R.; Jankevics, E.; Inashkina, I.; Krama, T.; Lietuvietis, V.; Meija, L.; Rantala, M.J. Effects of food quality on trade-offs among growth, immunity and survival in the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella. J. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojda, I. Immunity of the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella. Insect Sci. 2016, 24, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, V.; Giannelli, A.; Brianti, E.; Ramos, R.A.; Cantacessi, C.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Feline lungworms unlock a novel mode of parasite transmission. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montresor, L.C.; Vidigal, T.H.; Mendonça, C.L.; Fernandes, A.A.; de Souza, K.N.; Carvalho, O.S.; Caputo, L.F.; Mota, E.M.; Lenzi, H.L. Angiostrongylus costaricensis (Nematoda: Protostrongylidae): Migration route in experimental infection of Omalonyx sp. (Gastropoda: Succineidae). Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, C.L.; Carvalho, O.S.; Mota, E.M.; Pelajo-Machado, M.; Caputo, L.F.; Lenzi, H.L. Penetration sites and migratory routes of Angiostrongylus costaricensis in the experimental intermediate host (Sarasinula marginata). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1999, 94, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacif-Pimenta, R.; de Mattos, A.C.; Orfanó, A.S.; Barbosa, L.; Pimenta, P.F.; Coelho, P.M. Schistosoma mansoni in susceptible and resistant snail strains Biomphalaria tenagophila: In vivo tissue response and in vitro hemocyte interactions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubila, L.; Rollinson, D. Snail–parasite compatibility and prevalence of Schistosoma haematobium on the shores of Lake Ka-riba, Zambia. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2002, 96, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, M.; Arouna, N. Studies on the morphology and compatibility between Schistosoma hematobium and the Bulinus sp. complex (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Cameroon. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Kirinoki, M.; Matsumoto, J.; Kawai, S.; Otake, H.; Chigusa, Y.; Matsuda, H. Histological observation of an elimination process of Schistosoma japonicum Mindoro (Philippines) strain in Oncomerania nosophora Yamanashi strain. Parasitol. Int. 2000, 45, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y.; Furuta, E.; Kirinoki, M.; Seo, N.; Matsuda, H. Comparative studies on the internal defense system of schistosome-resistant and—Susceptible amphibious snail Oncomelania nosophora. Comparative morphological and functional studies on hemocytes from both snails. Zool. Sci. 2003, 20, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, C.M.; Borges, C.C.; Andrade, Z.A. Changes induced in Biomphalaria glabrata (Say, 1818) following trials for artificial stimulation of its internal defence system. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Napoli, E.; Sfacteria, A.; Rifici, C.; Mazzullo, G.; Gaglio, G.; Brianti, E. Reaction of Cornu aspersum Immune System against Different Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Developmental Stages. Pathogens 2023, 12, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040542
Napoli E, Sfacteria A, Rifici C, Mazzullo G, Gaglio G, Brianti E. Reaction of Cornu aspersum Immune System against Different Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Developmental Stages. Pathogens. 2023; 12(4):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040542
Chicago/Turabian StyleNapoli, Ettore, Alessandra Sfacteria, Claudia Rifici, Giuseppe Mazzullo, Gabriella Gaglio, and Emanuele Brianti. 2023. "Reaction of Cornu aspersum Immune System against Different Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Developmental Stages" Pathogens 12, no. 4: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040542
APA StyleNapoli, E., Sfacteria, A., Rifici, C., Mazzullo, G., Gaglio, G., & Brianti, E. (2023). Reaction of Cornu aspersum Immune System against Different Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Developmental Stages. Pathogens, 12(4), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040542






