Molecular Survey of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Mammals of Southern Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.3. Molecular Analysis
2.4. Data Classification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bokaba, R.P.; Dermauw, V.; Morar-Leather, D.; Dorny, P.; Neves, L. Toxoplasma gondii in African Wildlife: A Systematic Review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Hayama, Y.; Yamaguchi, E.; Hanafusa, Y.; Osaki, M. First nationwide survey of the seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild boars in Japan. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, L.; Wek, R.C.; Sullivan, W.J. Host sensing and signal transduction during Toxoplasma stage conversion. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Benavides Silván, J.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Jones, J.L. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S.A.; Jones, J.L.; Conrad, P.A.; Patton, S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Epidemiology, feline clinical aspects, and prevention. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiling, S.; Dixon, B. Toxoplasma gondii: How an Amazonian parasite became an inuit health issue. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2019, 45, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, G.; Webster, J.P.; Walker, M. Toxoplasma gondii: An underestimated threat? Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. The History and Life Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. In Toxoplasma gondii; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Villa, L.; Lubian, E.; Ressegotti, S.; Grilli, G.; Raimondi, S.; Zanzani, S.A.; Manfredi, M.T. Molecular survey on Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora Caninum Infection in wild birds of prey admitted to recovery centers in northern Italy. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas-ramos, V.B.; Mori, E.; Bosso, L.; Ancillotto, L.; Russo, D. Zoonotic risk: One more good reason why cats should be kept away from bats. Pathogens 2021, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.G.; Lapen, D.R.; Mitchell, G.W.; Provencher, J.F.; Wilson, S. Interaction of diet and habitat predicts Toxoplasma gondii infection rates in wild birds at a global scale. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteves, F.; Aguiar, D.; Rosado, J.; Costa, M.L.; de Sousa, B.; Antunes, F.; Matos, O. Toxoplasma gondii prevalence in cats from Lisbon and in pigs from centre and south of Portugal. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, R.Á.; da Fonseca Lemos, J.; Farias, L.A.; Lopes, C.D.; dos Santos, K.R. Seroprevalence and risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection in pigs in southern Piauí. Rev. Bras. De Parasitol. Veterinária 2014, 23, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Formenti, N.; Trogu, T.; Pedrotti, L.; Gaffuri, A.; Lanfranchi, P.; Ferrari, N. Toxoplasma gondii infection in alpine red deer (Cervus elaphus): Its spread and effects on fertility. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gering, E.; Laubach, Z.M.; Weber, P.S.D.; Soboll Hussey, G.; Lehmann, K.D.S.; Montgomery, T.M.; Turner, J.W.; Perng, W.; Pioon, M.O.; Holekamp, K.E.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infections are associated with costly boldness toward felids in a wild host. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, K.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.; Dixon, B.; Dumètre, A.; de Wit, L.A.; VanWormer, E.; Villena, I. Environmental transmission of Toxoplasma gondii: Oocysts in water, soil and food. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natoli, E.; Maragliano, L.; Cariola, G.; Faini, A.; Bonanni, R.; Cafazzo, S.; Fantini, C. Management of feral domestic cats in the urban environment of Rome (Italy). Prev. Vet. Med. 2006, 77, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, G.; Rinaldi, L.; Guarino, A.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Pesce, A.; Giuseppina, D.M.; Cringoli, G. Toxoplasma gondii in sheep from the Campania region (Italy). Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 149, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhimies, S. Directive 86/609/EEC on the protection of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes. ATLA Altern. Lab. Anim. 2002, 30, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, S.; Ianiro, G.; De Sabato, L.; Monini, M.; Angeloni, G.; Ponterio, E.; D’Agostino, C.; Di Bari, M.A.; Valeri, M.; Di Bartolo, I. Detection and whole genome sequencing of murine norovirus in animal facility in Italy. Anim. Biotechnol. 2022, 33, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baaert, L.; Wobus, C.E.; Van Coillie, E.; Thackray, L.B.; Debevere, J.; Uyttendaele, M. Detection of murine norovirus 1 by using plaque assay, transfection assay, and real-time reverse transcription-PCR before and after heat exposure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amoroso, M.G.; Serra, F.; Esposito, C.; D’Alessio, N.; Ferrara, G.; Cioffi, B.; Anzalone, A.; Pagnini, U.; de Carlo, E.; Fusco, G.; et al. Prevalence of Infection with Porcine Circovirus Types 2 and 3 in the Wild Boar Population in the Campania Region (Southern Italy). Animals 2021, 11, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgroi, G.; Viscardi, M.; Santoro, M.; Borriello, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Boccia, F.; Pacifico, L.; Fioretti, A.; Veneziano, V.; Fusco, G. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in wild boar (Sus scrofa) in southern Italy: Epidemiological survey and associated risk for consumers. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buesching, C.D.; Waterhouse, J.S.; Macdonald, D.W. Gas-chromatographic analyses of the subcaudal gland secretion of the European badger (Meles meles) Part I: Chemical Differences Related to Individual Parameters. J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, N.S.; Stollberg, K.; Mayer-Scholl, A.; Johne, A.; Nöckler, K.; Richter, M. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild boar and deer in Brandenburg, Germany. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skonhoft, A.; Friberg, V. Optimal harvesting in the presence of predation: An age-structured modelling approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero-Bernal, R.; Saugar, J.M.; Frontera, E.; Pe´rez-Martín, J.E.; Habela, M.A.; Serrano, F.J.; Reina, D.; Fuentes, I. Prevalence and genotype identification of Toxoplasma gondii in wild animals from southwestern Spain. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferroglio, E.; Bosio, F.; Trisciuoglio, A.; Zanet, S. Toxoplasma gondii in sympatric wild herbivores and carnivores: Epidemiology of infection in the western Alps. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, D. Prevalence mammals and of antibodies of Missouri to toxoplasma and central in Kansas: Biologic and ecologic considerations of transmission. J. Wildl. Dis. 1995, 31, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossi, F.; Ranc, N.; Moorcroft, P.; Bonanni, P.; Cagnacci, F. Ecological and behavioral drivers of supplemental feeding use by roe deer Capreolus capreolus in a peri-urban context. Animals 2020, 10, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Contreras, R.; Mentaberre, G.; Fernandez Aguilar, X.; Conejero, C.; Colom-Cadena, A.; Ráez-Bravo, A.; González-Crespo, C.; Espunyes, J.; Lavín, S.; López-Olvera, J.R. Wild boar in the city: Phenotypic responses to urbanisation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torretta, E.; Corradini, A.; Pedrotti, L.; Bani, L.; Bisi, F.; Dondina, O. Hide-and-seek in a highly human-dominated landscape: Insights into movement patterns and selection of resting sites of rehabilitated wolves (Canis lupus) in northern Italy. Animals 2022, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigozzi, G. The diet of the European badger in a Mediterranean coastal area. Acta Theriol. 1991, 36, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriggi, A.; Brangi, A.; Schenone, L.; Signorelli, D.; Milanesi, P. Changes of wolf (Canis lupus) diet in Italy in relation to the increase of wild ungulate abundance. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2011, 23, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballari, S.A.; Barrios-García, M.N. A review of wild boar Sus scrofa diet and factors affecting food selection in native and introduced ranges. Mammal Rev. 2014, 44, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, L.; Gracia, M.J.; Pérez-Arquillué, C.; Lázaro, R.; Herrera, M.; Herrera, A.; Bayarri, S. Toxoplasma gondii: Pig seroprevalence, associated risk factors and viability in fresh pork meat. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 224, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laguna, E.; Barasona, J.A.; Vicente, J.; Keuling, O.; Acevedo, P. Differences in wild boar spatial behaviour among land uses and management scenarios in Mediterranean ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saïd, S.; Tolon, V.; Brandt, S.; Baubet, E. Sex effect on habitat selection in response to hunting disturbance: The study of wild boar. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2012, 58, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, E.; Benatti, L.; Lovari, S.; Ferretti, F. What does the wild boar mean to the wolf? Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2017, 63, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-González, A.; Fernández-Gil, A.; Quevedo, M.; Revilla, E. Patterns and determinants of dispersal in grey wolves (Canis lupus). Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakban, F.M.; A’aiz, N.N. Investigate the Toxoplasma gondii infection in the consumed beef in al-diwaniyah province. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 34, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, B.F.; Oliveira, S.; Soares, H.S.; Pena, H.F.J.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Gennari, S.M. Isolation of viable Toxoplasma gondii from organs and Brazilian commercial meat cuts of experimentally infected pigs. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, A.; Riahi, S.M.; Fakhri, Y.; Saber, V.; Hanifehpour, H.; Valizadeh, S.; Gholizadeh, M.; Pouya, R.H.; Gamble, H.R. The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii among wild boars: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 244, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sabato, L.; Amoroso, M.G.; Ianiro, G.; Esposito, C.; De Grossi, L.; Fusco, G.; Barone, A.; Martini, E.; Ostanello, F.; Di Bartolo, I. Detection of Hepatitis E virus in livers and muscle tissues of wild boars in Italy. Food Environ. Virol. 2020, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, P.; Bosco, A.; Capuano, F.; Baldi, L.; Giordano, A.; Mancusi, A.; Buonanno, M.; Morena, L.; Pinto, R.; Sarnelli, P.; et al. Towards an integrated approach for monitoring toxoplasmosis in southern Italy. Animals 2021, 11, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrey, E.F.; Yolken, R.H. Toxoplasma gondii and schizophrenia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Prandovszky, E.; Kannan, G.; Pletnikov, M.V.; Dickerson, F.; Severance, E.G.; Yolken, R.H. Toxoplasma gondii: Biological parameters of the connection to schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepczyk, C.A.; Duffy, D.C.; Bird, D.M.; Calver, M.; Cherkassky, D.; Cherkassky, L.; Dickman, C.R.; Hunter, D.; Jessup, D.; Longcore, T.; et al. A science-based policy for managing free-roaming cats. Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 3693–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
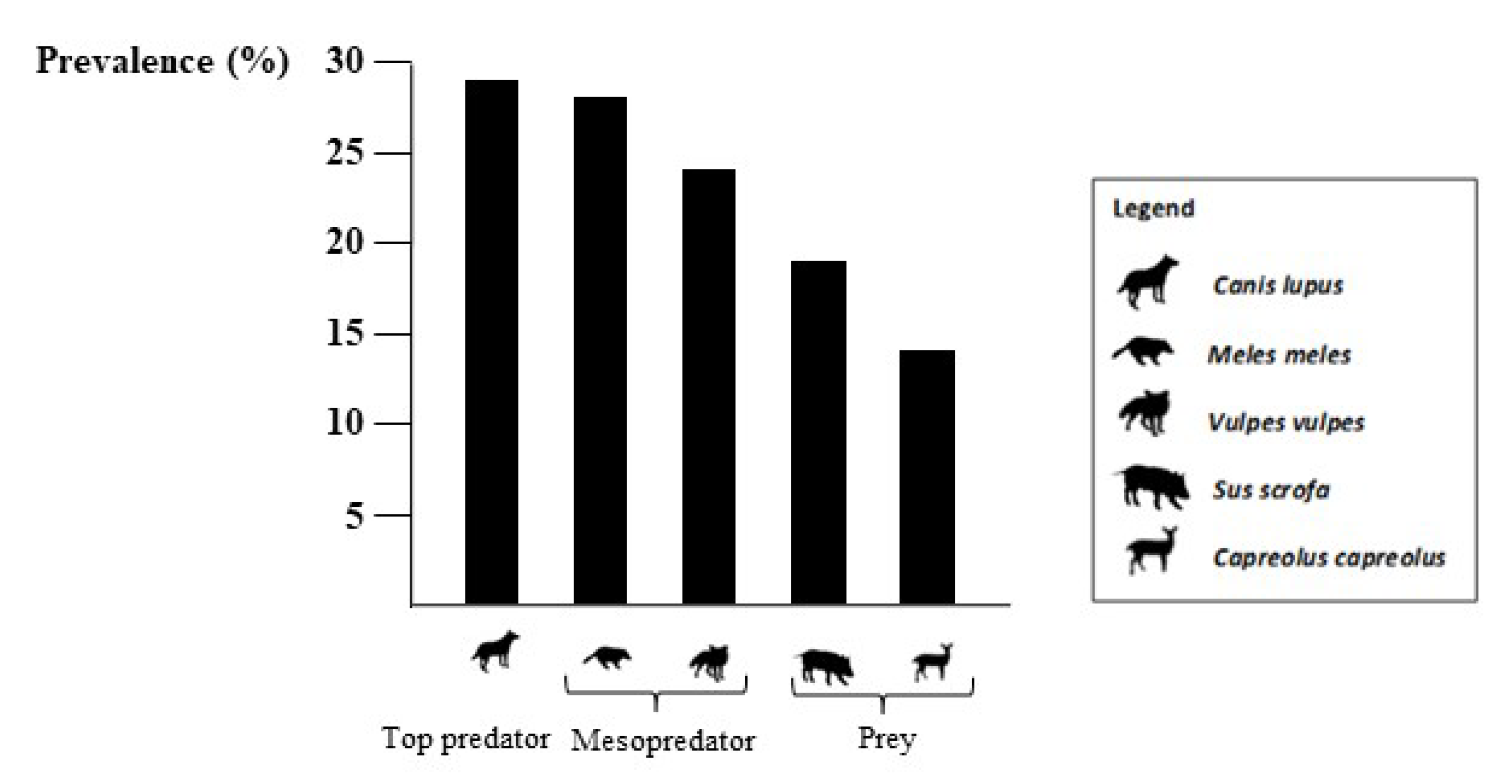

| Species | p |
|---|---|
| Wolf vs. fox | 0.740 |
| Wolf vs. wild boar | 0.474 |
| Wolf vs. roe deer | 0.648 |
| Wolf vs. badger | 1.000 |
| Fox vs. wild boar | 0.444 |
| Fox vs. roe deer | 0.726 |
| Badger vs. fox | 0.781 |
| Wild boar vs. roe deer | 1.000 |
| Badger vs. wild boar | 0.388 |
| Badger vs. roe deer | 0.441 |
| Top predators vs. mesopredators | 0.748 |
| Top predators vs. mammal prey | 0.470 |
| Mesopredator vs. mammal prey | 0.299 |
| Variable | Species | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolf Pos/Tot (%) | Fox Pos/Tot (%) | Wild Boar Pos/Tot (%) | Roe Deer Pos/Tot (%) | Badger Pos/Tot (%) | |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 2/5 (40.0) | 9/39 (23.1) | 11/37 (29.7) | 2/12 (16.7) | 5/15 (33.3) |
| Female | 2/9 (22.2) | 8/32 (25.0) | 6/53 (11.3) | 0/2 (0) | 1/7 (14.3) |
| p = 0.580 | p = 1.000 | p = 0.053 | p = 1.000 | p = 0.616 | |
| Age | |||||
| Juvenile | - | 3/15 (20.0) | 1/10 (10.0) | - | 1/2 (50.0) |
| Sub-adult | 0/2 (0) | 3/15 (20.0) | 10/52 (19.2) | 0/5 (0) | 1/5 (20.0) |
| Adult | 4/12 (33.3) | 11/41 (26.8) | 6/28 (21.4) | 2/9 (22.2) | 4/15 (26.7) |
| p = 1.000 | p = 0.866 | p = 0.858 | p = 1.000 | p = 0.799 | |
| Dominant land use | |||||
| Urban | - | 3/16 (18.7) | 0/7 (-) | - | 0/1 (-) |
| Peri-urban | 1/10 (10) | 9/40 (22.5) | 10/26 (38.5) | 1/10 (10.0) | 4/15 (26.7) |
| Rural | 3/4 (75.0) | 5/15 (33.3) | 7/57 (12.3) | 1/4 (25.0) | 2/6 (33.3) |
| p = 0.040 | p = 0.695 | p = 0.010 | p = 0.505 | p = 1.000 |
| Species | p-Value | Organs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Pos/Tot (%) | Brain Pos/Tot (%) | Muscle Pos/Tot (%) | ||
| Wolf | p = 0.822 | 3/11 (27.3) | 1/11 (9.1) | 1/7 (14.3) |
| Fox | p = 0.485 | 8/48 (16.7) | 4/48 (8.3) | 6/61 (9.8) |
| Wild boar | p = 0.580 | 10/82 (12.2) | 5/37 (13.5) | 7/86 (8.1) |
| Roe deer | p = 0.405 | 1/4 (25.0) | Not performed | 1/14 (7.1) |
| Badger | p = 0.100 | 3/18 (16.7) | 2/16 (12.5) | 3/22 (13.6) |
| Total | p = 0.228 | 25/163 (15.3) | 12/112 (10.7) | 18/190 (9.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dakroub, H.; Sgroi, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Russo, D.; Serra, F.; Veneziano, V.; Rea, S.; Pucciarelli, A.; Lucibelli, M.G.; De Carlo, E.; et al. Molecular Survey of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Mammals of Southern Italy. Pathogens 2023, 12, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030471
Dakroub H, Sgroi G, D’Alessio N, Russo D, Serra F, Veneziano V, Rea S, Pucciarelli A, Lucibelli MG, De Carlo E, et al. Molecular Survey of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Mammals of Southern Italy. Pathogens. 2023; 12(3):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030471
Chicago/Turabian StyleDakroub, Hiba, Giovanni Sgroi, Nicola D’Alessio, Danilo Russo, Francesco Serra, Vincenzo Veneziano, Simona Rea, Alessia Pucciarelli, Maria Gabriella Lucibelli, Esterina De Carlo, and et al. 2023. "Molecular Survey of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Mammals of Southern Italy" Pathogens 12, no. 3: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030471
APA StyleDakroub, H., Sgroi, G., D’Alessio, N., Russo, D., Serra, F., Veneziano, V., Rea, S., Pucciarelli, A., Lucibelli, M. G., De Carlo, E., Fusco, G., & Amoroso, M. G. (2023). Molecular Survey of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Mammals of Southern Italy. Pathogens, 12(3), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12030471









