BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphism Associated with Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection and Proviral Load in Holstein Cattle in Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sampling
2.2. Isolation of Genomic DNA from Whole Blood
2.3. Determination of BLV Infection and Quantification of BLV PVL Using the BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR-2 Assay
2.4. Genotyping of BoLA-DRB3
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genotyping of Holstein Cattle’s BoLA-DRB3
3.2. Analysis of the Association between BoLA-DRB3 and BLV Infection in Holstein Cows
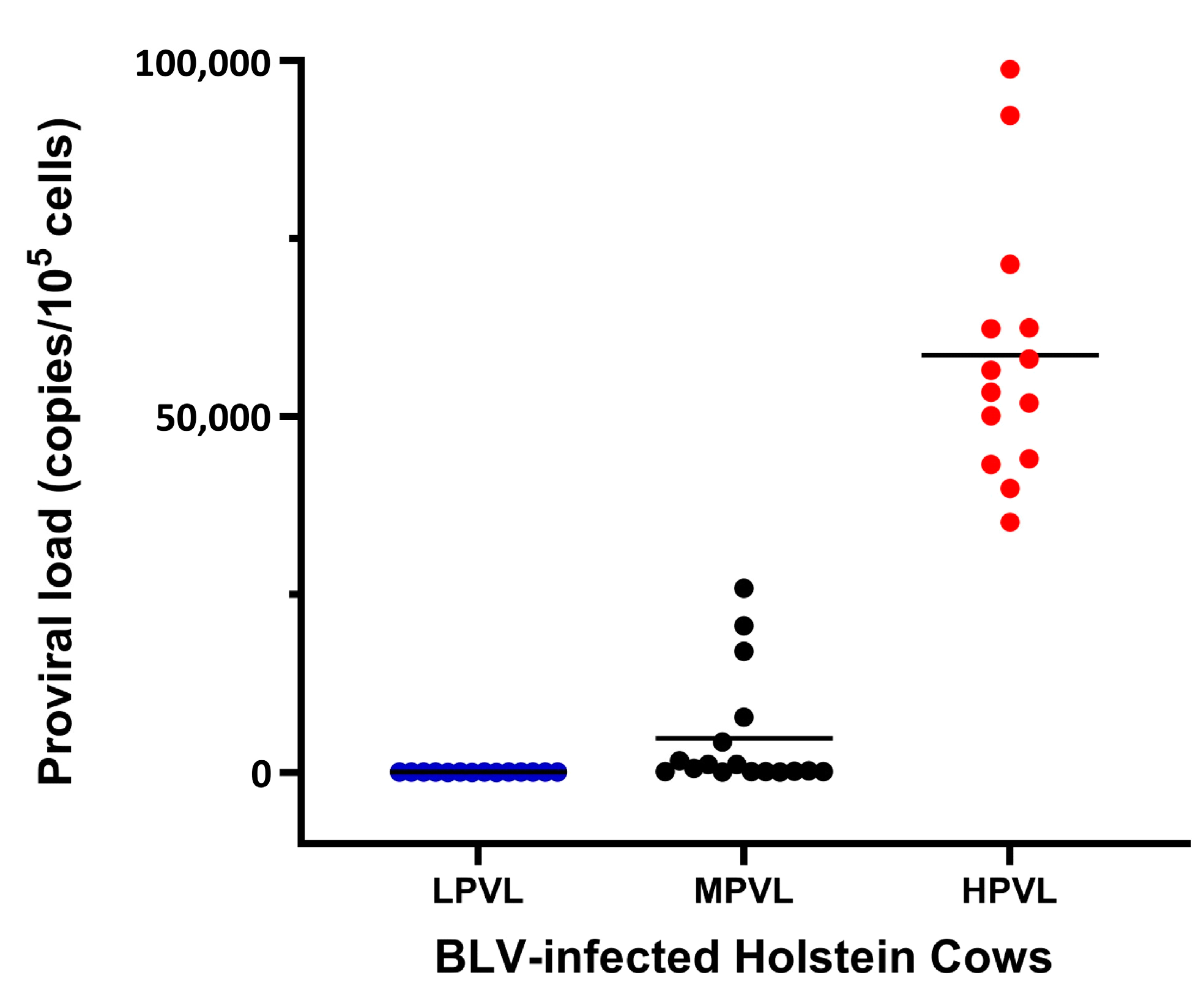
3.3. BLV PVL Estimation in Holstein Cattle and Classification into Three Groups by Categorizing PVL
3.4. Analysis of the Association between BoLA-DRB3 and BLV PVL in Holstein Cows
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aida, Y.; Murakami, H.; Takahashi, M.; Takeshima, S.N. Mechanisms of pathogenesis induced by bovine leukemia virus as a model for human T-cell leukemia virus. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, N.; Florins, A.; Boxus, M.; Burteau, C.; Nigro, A.; Vandermeers, F.; Balon, H.; Bouzar, A.-B.; Defoiche, J.; Burny, A. Mechanisms of leukemogenesis induced by bovine leukemia virus: Prospects for novel anti-retroviral therapies in human. Retrovirology 2007, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.K.; Pelzer, K.D.; Johnson, Y.J. Economic implications of bovine leukemia virus infection in mid-Atlantic dairy herds. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.L.; Moore, D.A. Reasons for whole carcass condemnations of cattle in the United States and implications for producer education and veterinary intervention. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 235, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekouei, O.; VanLeeuwen, J.; Stryhn, H.; Kelton, D.; Keefe, G. Lifetime effects of infection with bovine leukemia virus on longevity and milk production of dairy cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, S.L.; Johnson, R.; Wells, S.J. Association between bovine-leukosis virus seroprevalence and herd-level productivity on US dairy farms. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 61, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erskine, R.J.; Bartlett, P.C.; Byrem, T.M.; Render, C.L.; Febvay, C.; Houseman, J.T. Association between bovine leukemia virus, production, and population age in Michigan dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, Y.; Shanks, R.D.; Stewart, J.A.; Lewin, H.A. Milk and fat yields decline in bovine leukemia virus-infected Holstein cattle with persistent lymphocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6538–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norby, B.; Bartlett, P.C.; Byrem, T.M.; Erskine, R.J. Effect of infection with bovine leukemia virus on milk production in Michigan dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konnai, S.; Murata, S.; Ohashi, K. Immune exhaustion during chronic infections in cattle. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandev, N.; Koleva, M.; Binev, R.; Ilieva, D. Influence of enzootic bovine leukosis virus upon the incidence of subclinical mastitis in cows at a different stage of infection. Vet. Arh. 2004, 74, 411–416. [Google Scholar]
- VanLeeuwen, J.A.; Haddad, J.P.; Dohoo, I.R.; Keefe, G.P.; Tiwari, A.; Tremblay, R. Associations between reproductive performance and seropositivity for bovine leukemia virus, bovine viral-diarrhea virus, Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis, and Neospora caninum in Canadian dairy cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 2010, 94, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kohara, J.; Adachi, Y.; Makita, K. Estimation of economic loss by carcass weight reduction of Japanese dairy cows due to infection with bovine leukemia virus. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 198, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, O.J.; Norby, B.; Bartlett, P.C.; Maeroff, J.E.; Grooms, D.L. Impact of bovine leukemia virus infection on beef cow longevity. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 181, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettmann, R.; Portetelle, D.; Mammerickx, M.; Cleuter, Y.; Dekegel, D.; Galoux, M.; Ghysdael, J.; Burny, A.; Chantrenne, H. Bovine leukemia virus: An exogenous RNA oncogenic virus? Hamatol. Bluttransfus. 1976, 19, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, G.; Rodríguez, S.M.; De Brogniez, A.; Gillet, N.; Golime, R.; Burny, A.; Jaworski, J.P.; Alvarez, I.; Vagnoni, L.; Trono, K.; et al. Vaccination against δ-retroviruses: The bovine leukemia virus paradigm. Viruses 2014, 6, 2416–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimba, M.; Takeshima, S.N.; Matoba, K.; Endoh, D.; Aida, Y. BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR: Quantitation of bovine leukemia virus proviral load using the CoCoMo algorithm. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somura, Y.; Sugiyama, E.; Fujikawa, H.; Murakami, K. Comparison of the copy numbers of bovine leukemia virus in the lymph nodes of cattle with enzootic bovine leukosis and cattle with latent infection. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2693–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Inagaki, Y.; Ohnuki, N.; Sato, R.; Murakami, S.; Imakawa, K. Increasing Bovine leukemia virus (BLV) proviral load is a risk factor for progression of Enzootic bovine leucosis: A prospective study in Japan. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 178, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Watanuki, S.; Murakami, H.; Sato, R.; Ishizaki, H.; Aida, Y. Development of a luminescence syncytium induction assay (LuSIA) for easily detecting and quantitatively measuring bovine leukemia virus infection. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Borjigin, L.; Sato, H.; Takeshima, S.; Asaji, S.; Ishizaki, H.; Kawashima, K.; Obuchi, Y.; Sunaga, S.; Ando, A.; et al. Kinetic Study of BLV Infectivity in BLV Susceptible and Resistant Cattle in Japan from 2017 to 2019. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, A.; Takeshima, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Aida, Y. Risk factors associated with increased bovine leukemia virus proviral load in infected cattle in Japan from 2012 to 2014. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panei, C.J.; Takeshima, S.; Omori, T.; Nunoya, T.; Davis, W.C.; Ishizaki, H.; Matoba, K.; Aida, Y. Estimation of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) proviral load harbored by lymphocyte subpopulations in BLV-infected cattle at the subclinical stage of enzootic bovine leucosis using BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Kitamura-Muramatsu, Y.; Saito, S.; Ishizaki, H.; Nakano, M.; Haga, S.; Matoba, K.; Ohno, A.; Murakami, H.; Takeshima, S. Detection of the BLV provirus from nasal secretion and saliva samples using BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR-2: Comparison with blood samples from the same cattle. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanuki, S.; Takeshima, S.N.; Borjigin, L.; Sato, H.; Bai, L.; Murakami, H.; Sato, R.; Ishizaki, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Aida, Y. Visualizing bovine leukemia virus (BLV)-infected cells and measuring BLV proviral loads in the milk of BLV seropositive dams. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuchi, A.; Watanuki, S.; Borjigin, L.; Sato, H.; Bai, L. BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphism Controls Proviral Load and Infectivity of Bovine Leukemia Virus (BLV) in Milk. Pathogens 2022, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohara, J.; Bai, L.; Takeshima, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Hirai, T.; Aida, Y. Correlation between the Biodistribution of Bovine Leukemia Virus in the Organs and the Proviral Load in the Peripheral Blood during Early Stages of Experimentally Infected Cattle. Pathogens 2023, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliarena, M.A.; Barrios, C.N.; Ceriani, M.C.; Esteban, E.N. Hot topic: Bovine leukemia virus (BLV)-infected cows with low proviral load are not a source of infection for BLV-free cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4586–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, S.N.; Ohno, A.; Aida, Y. Bovine leukemia virus proviral load is more strongly associated with bovine major histocompatibility complex class II DRB3 polymorphism than with DQA1 polymorphism in Holstein cow in Japan. Retrovirology 2019, 16, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.-W.; Borjigin, L.; Saito, S.; Fukunaga, K.; Saitou, E.; Okazaki, K.; Mizutani, T.; Wada, S.; Takeshima, S.; Aida, Y. BoLA-DRB3 polymorphism is associated with differential susceptibility to bovine leukemia virus-induced lymphoma and proviral load. Viruses 2020, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, T.; Takeshima, S.; Jimba, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Matsuhashi, T. Identification of bovine leukocyte antigen class II haplotypes associated with variations in bovine leukemia virus proviral load in Japanese Black cattle. Tissue Antigens 2013, 81, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, S.; Aida, Y. Structure, function and disease susceptibility of the bovine major histocompatibility complex. Anim. Sci. J. 2006, 77, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Furuta, H.; Kondo, Y.; Mukoyama, H. Association of BoLA-DRB3 alleles with mastitis resistance and susceptibility in Japanese Holstein cows. Anim. Sci. J. 2012, 83, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, R.; Hernandez, A.; Mallard, B.A. Association of Bovine Leukocyte Antigen (BoLA) DRB3.2 with Immune Response, Mastitis, and Production and Type Traits in Canadian Holsteins. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashmi, M.; Qanbari, S.; Ghorashi, S.A.; Sharifi, A.R.; Simianer, H. Analysis of relationship between bovine lymphocyte antigen DRB3.2 alleles, somatic cell count and milk traits in Iranian Holstein population. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2009, 126, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, S.; Mallard, B.A.; Wilkie, B.N.; Sargeant, J.M.; Scott, H.M.; Dekkers, J.C.M.; Leslie, K.E. Associations of the bovine major histocompatibility complex DRB3 (BoLA-DRB3) alleles with occurrence of disease and milk somatic cell score in Canadian dairy cattle. Anim. Genet. 1998, 29, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, J.-C.; Berthier, D.; Chantal, I.; Thevenon, S.; Sidibé, I.; Stachurski, F.; Belemsaga, D.; Razafindraïbé, H.; Elsen, J.-M. Selection assisted by a BoLA-DR/DQ haplotype against susceptibility to bovine dermatophilosis. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2003, 35, S193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangjinda, M.; Jindatajak, Y.; Tipvong, W.; Sriwarothai, J.; Pattarajinda, V.; Katawatin, S.; Boonkum, W. Association of BoLA-DRB3 alleles with tick-borne disease tolerance in dairy cattle in a tropical environment. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.L.; Machado, M.A.; Nascimento, C.S.; Silva, M.; Teodoro, R.L.; Furlong, J.; Prata, M.C.A.; Campos, A.L.; Guimarães, M.F.M.; Azevedo, A.L.S. Association of BoLA-DRB3.2 alleles with tick (Boophilus microplus) resistance in cattle. Genet. Mol. Res 2006, 5, 513–524. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, O.E.; Khodary, M.G.; El-Deeb, A.H.; Hussein, H.A. Five BoLA-DRB3 genotypes detected in Egyptian buffalo infected with Foot and Mouth disease virus serotype O. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.P.A.; López-Herrera, A.; Zuluaga, J.E. Association of BoLA DRB3 gene polymorphisms with BoHV-1 infection and zootechnical traits. Open Vet. J. 2020, 10, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Mallard, B.A.; Wilkie, B.N.; Sargeant, J.M.; Scott, H.M.; Dekkers, J.C.M.; Leslie, K.E. Associations of the bovine major histocompatibility complex DRB3 (BoLA-DRB3) with production traits in Canadian dairy cattle. Anim. Genet. 1999, 30, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, J.A.; Echeverri, J.Z.; López-Herrera, A. Association of gene BoLA DRB3.2 with production traits in a dairy herd of Antioquia, Colombia. Rev. MVZ Cordoba 2014, 19, 4116–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballingall, K.T.; Luyai, A.; Rowlands, G.J.; Sales, J.; Musoke, A.J.; Morzaria, S.P.; McKeever, D.J. Bovine leukocyte antigen major histocompatibility complex class II DRB3*2703 and DRB3*1501 alleles are associated with variation in levels of protection against Theileria parva challenge following immunization with the sporozoite p67 antigen. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2738–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, R.; Craigmile, S.C.; Haley, C.; Douglas, A.J.; Williams, J.L.; Glass, E.J. BoLA-DR peptide binding pockets are fundamental for foot-and-mouth disease virus vaccine design in cattle. Vaccine 2009, 28, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borjigin, L.; Lo, C.-W.; Bai, L.; Hamada, R.; Sato, H.; Yoneyama, S.; Yasui, A.; Yasuda, S.; Yamanaka, R.; Mimura, M. Risk assessment of bovine major histocompatibility complex class II DRB3 alleles for perinatal transmission of bovine leukemia virus. Pathogens 2021, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forletti, A.; Juliarena, M.A.; Ceriani, C.; Amadio, A.F.; Esteban, E.; Gutiérrez, S.E. Identification of cattle carrying alleles associated with resistance and susceptibility to the Bovine Leukemia Virus progression by real-time PCR. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliarena, M.A.; Poli, M.; Sala, L.; Ceriani, C.; Gutierrez, S.; Dolcini, G.; Rodriguez, E.M.; Marino, B.; Rodríguez-Dubra, C.; Esteban, E.N. Association of BLV infection profiles with alleles of the BoLA-DRB3.2 gene. Anim. Genet. 2008, 39, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützelschwab, C.M.; Forletti, A.; Cepeda, R.; Esteban, E.N.; Confalonieri, O.; Gutiérrez, S.E. Co-infection with Mycobacterium bovis does not alter the response to bovine leukemia virus in BoLA DRB3*0902, genetically resistant cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 109, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marawan, M.A.; Alouffi, A.; El Tokhy, S.; Badawy, S.; Shirani, I.; Dawood, A.; Guo, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Alshammari, F.A.; Selim, A. Bovine leukaemia virus: Current epidemiological circumstance and future prospective. Viruses 2021, 13, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghawa, A.; Beier, D.; Abd El-Rahim, I.H.A.; El-Ballal, S.; Karim, I.; Conraths, F.J.; Marquardt, O. An outbreak of enzootic bovine leukosis in upper egypt: Clinical, laboratory and molecular–epidemiological studies. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2002, 49, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaher, K.; Ahmed, W. Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection in Dairy Cows in Egypt. Acad. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 7, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, A.; Marawan, M.A.; Ali, A.F.; Manaa, E.; AbouelGhaut, H.A. Seroprevalence of bovine leukemia virus in cattle, buffalo, and camel in Egypt. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 52, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metwally, S.; Hamada, R.; Ali, A.O.; Mahmoud, H.Y.A.H.; Baker, N.M.; Mohamed, A.E.A.; Wada, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Aida, Y. Detection and molecular characterization of bovine leukemia virus in beef cattle presented for slaughter in Egypt. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, R.; Metwally, S.; Polat, M.; Borjigin, L.; Ali, A.O.; Abdel-Hady, A.A.A.; Mohamed, A.E.A.; Wada, S.; Aida, Y. Detection and molecular characterization of bovine leukemia virus in Egyptian dairy cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, S.; Kitamura-Muramatsu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Polat, M.; Saito, S.; Aida, Y. BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR-2: Improvements to the BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR assay for bovine leukemia virus by reducing primer degeneracy and constructing an optimal standard curve. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjigin, L.; Watanuki, S.; Hamada, R.; Bai, L.; Hirose, T.; Sato, H.; Yoneyama, S.; Yasui, A.; Yasuda, S.; Yamanaka, R.; et al. Effectiveness of innovative bovine leukemia virus eradication strategies utilizing cattle carrying resistant and susceptible histocompatibility complex class II DRB3 alleles. J. Dairy Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimba, M.; Takeshima, S.; Murakami, H.; Kohara, J.; Kobayashi, N.; Matsuhashi, T.; Ohmori, T.; Nunoya, T.; Aida, Y. BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR: A useful tool for evaluating bovine leukemia virus infection status. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, S.N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Miyasaka, T.; Arainga-Ramirez, M.; Saito, H.; Onuma, M.; Aida, Y. A new method for typing bovine major histocompatibility complex class II DRB3 alleles by combining two established PCR sequence-based techniques. Tissue Antigens 2011, 78, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, T.; Vu, L.; Nguyen, S.; Duy, C.L.; Dao, T.; Bui, N.V.; Ogawa, H.; Imai, K.; Sugiura, K.; Aida, Y. Association between BoLA-DRB3 polymorphism and bovine leukemia virus proviral load in Vietnamese Holstein Friesian cattle. HLA 2022, 99, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stear, M.J.; Bishop, S.C.; Mallard, B.A.; Raadsma, H.; Road, B.; Canada, O. The sustainability, feasibility and desirability of breeding livestock for disease resistance. Res. Veter.-Sci. 2001, 71, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkie, B.N.; Mallard, B. Genetic aspects of health and disease in pigs. In Breeding for Disease Resistance in Farm Animals, 2nd ed.; Axford, R.F.E., Bishop, S.C., Nicholas, F.W., Owen, J.B., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2000; pp. 379–396. [Google Scholar]
- Mallard, B.; Wilkie, B.N.; Kennedy, B.W.; Gibson, J.P.; Quinton, M. Immune responsiveness in swine: Eight generations of selection for high and low immune response in Yorkshire pigs. In Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, Armidale, Australia, 11–16 January 1998; Volume 27, pp. 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.M.; Van der Maaten, M.J. Bovine leukosis—Its importance to the dairy industry in the United States. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 2194–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Abubakar, M.; Arshed, M.J.; Aslam, R.; Sattar, S.; Shah, N.A.; Javed, S.; Tariq, A.; Bostan, N.; Manzoor, S. Molecular investigation of possible relationships concerning bovine leukemia virus and breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, A.; Roushdy, S.; Beillard, M.J.; Agricultural, S.R. Egypt Livestock and Products Annual 2019 Egyptian Beef Prices Stable, US Beef Imports Challenged; USDA, Foreign Agricultural Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; GAIN Report Number: EG-190162.
- Ali, A.F.; Selim, A.; Manaa, E.A.; Abdelrahman, A.; Sakr, A. Oxidative state markers and clinicopathological findings associated with bovine leukemia virus infection in cattle. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 136, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Rahim, I.H.A.; El-Ballal, S.S. Introduction of bovine leukaemia virus (BLV) into Egypt. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 1999, 42, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sebaie, A.H.; Hofmann, W.; Nafie, E.; Nafady, A. Enzootic bovine leukosis as a herd problem in a Holstein-Friesian cattle herd in Assiut, Egypt. Prakt. Tierarzt 1999, 80, 789–795. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, S.M.; Florins, A.; Gillet, N.; de Brogniez, A.; Sánchez-Alcaraz, M.T.; Boxus, M.; Boulanger, F.; Gutiérrez, G.; Trono, K.; Alvarez, I.; et al. Preventive and therapeutic strategies for bovine leukemia virus: Lessons for HTLV. Viruses 2011, 3, 1210–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lairmore, M.D. Animal models of bovine leukemia virus and human T-lymphotrophic virus type-1: Insights in transmission and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2014, 2, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliarena, M.A.; Barrios, C.N.; Lützelschwab, C.M.; Esteban, E.N.; Gutiérrez, S.E. Bovine leukemia virus: Current perspectives. Virus Adapt. Treat. 2017, 9, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahata, H. Bovine leukocyte adhesion deficiency (BLAD): A review. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2004, 66, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, G.C.; Davies, C.J.; Andersson, L.; Ellis, S.A.; Hensen, E.J.; Lewin, H.A.; Mikko, S.; Muggli-Cockett, N.E.; Van der Poel, J.J. BoLA class II nucleotide sequences, 1996: Report of the ISAG BoLA Nomenculature Committee. Anim. Genet. 1997, 28, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, G.C.; Fraser, D.C.; Craigmile, S.; Oliver, R.A.; Dutia, B.M.; Glass, E.J. Sequence and transfection of BoLA-DRB3 cDNAs. Anim. Genet. 2000, 31, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigurdardottir, S.; Borsch, C.; Gustafsson, K.; Andersson, L. Cloning and sequence analysis of 14 DRB alleles of the bovine major histocompatibility complex by using the polymerase chain reaction. Anim. Genet. 1991, 22, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikko, S.; Anderson, L. Extensive MHC class II DRB3 diversity in African and European cattle. Immunogenetics 1995, 42, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyasaka, T.; Takeshima, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Matsuhashi, T. The diversity of bovine MHC class II DRB3 and DQA1 alleles in different herds of Japanese Black and Holstein cattle in Japan. Gene 2011, 472, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, S.; Giovambattista, G.; Okimoto, N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Acosta, T.J. Characterization of bovine MHC class II DRB3 diversity in South American Holstein cattle populations. Tissue Antigens 2015, 86, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikbakht Brujeni, G.; Ghorbanpour, R.; Esmailnejad, A. Association of BoLA-DRB3.2 alleles with BLV infection profiles (persistent lymphocytosis/lymphosarcoma) and lymphocyte subsets in Iranian Holstein cattle. Biochem. Genet. 2016, 54, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victoria, M.; Farias, N.; Caffaro, M.E.; Lendez, P.A.; Passucci, J.; Poli, M.; Ceriani, M.C.; Dolcini, G. A novel association of BoLA DRB3 alleles in BLV infected cattle with different proviral loads. Archives 2017, 0201, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Tsutsui, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Hayama, Y.; Kameyama, K.I.; Konishi, M.; Murakami, K. Risk factors associated with within-herd transmission of bovine leukemia virus on dairy farms in Japan. BMC Vet. Res. 2010, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Todaka, H.; Uchiyama, J.; Sato, R.; Sogawa, K. A point mutation to the long terminal repeat of bovine leukemia virus related to viral productivity and transmissibility. Virology 2019, 537, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajiki, Y.; Konnai, S.; Nishimori, A.; Okagawa, T.; Maekawa, N.; Goto, S.; Nagano, M.; Kohara, J.; Kitano, N.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Intrauterine infection with bovine leukemia virus in pregnant dam with high viral load. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 2036–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekata, H.; Kusuda, E.; Mori, C. Avoidance of Natural Suckling from Dams with Bovine Leukemia Virus Is a Low Priority Countermeasure against Postnatal Transmission. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Mekata, H.; Sekiguchi, S.; Kirino, Y.; Mitoma, S.; Honkawa, K.; Horii, Y.; Norimine, J. Cattle with the BoLA class II DRB3*0902 allele have significantly lower bovine leukemia proviral loads. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1552–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, Y.; Kabeya, H.; Onuma, M.; Kasai, N.; Okada, K.; Aida, Y. Ovine MHC class II DRB1 alleles associated with resistance or susceptibility to development of bovine leukemia virus-induced ovine lymphoma. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.-W.; Takeshima, S.; Okada, K.; Saitou, E.; Fujita, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Wada, S.; Inoko, H.; Aida, Y. Association of bovine leukemia virus-induced lymphoma with BoLA-DRB3 polymorphisms at DNA, amino acid, and binding pocket property levels. Pathogens 2021, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| BoLA-DRB3 | Holsteins in Egypt n a = 121 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Allele | Frequency | CI b (95%) | |
| * 001:01 | 15.70 c | 11.48 | 21.04 |
| * 002:01 | 2.89 | 1.27 | 6.12 |
| * 005:01 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 2.64 |
| * 006:01 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 3.28 |
| * 007:01 | 1.65 | 0.53 | 4.46 |
| * 007:04 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 3.28 |
| * 008:01 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 3.28 |
| * 009:02 | 7.44 | 4.59 | 11.69 |
| * 010:01 | 7.44 | 4.59 | 11.69 |
| * 011:01 | 16.94 | 12.56 | 22.40 |
| * 012:01 | 6.61 | 3.95 | 10.72 |
| * 013:01 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 2.64 |
| * 014:01:01 | 8.68 | 5.58 | 13.14 |
| * 015:01 | 20.25 | 15.48 | 25.98 |
| * 016:01 | 1.24 | 0.32 | 3.88 |
| * 017:01 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 3.28 |
| * 018:01 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 3.28 |
| * 027:03 | 6.20 | 3.63 | 10.22 |
| BoLA-DRB3 Alleles | Holstein Cattle | Fisher’s Exact Test b | Susceptibility | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLV-Non-Infected Cattle n a = 76 | BLV-Infected Cattle n = 45 | OR c | p-Value | ||||
| Count | (%) | Count | (%) | ||||
| * 001:01 | 23 | (15.13) | 15 | (16.67) | 0.89 | 0.86 | - |
| * 002:01 | 5 | (3.29) | 2 | (2.22) | 1.50 | 1.00 | - |
| * 005:01 | 1 | (0.66) | 0 | (0.00) | - | 1.00 | - |
| * 006:01 | 1 | (0.66) | 1 | (1.11) | 0.59 | 1.00 | - |
| * 007:01 | 4 | (2.63) | 0 | (0.00) | - | 0.30 | - |
| * 007:04 | 0 | (0.00) | 2 | (2.22) | 0.00 | 0.14 | - |
| * 008:01 | 2 | (1.32) | 0 | (0.00) | - | 0.53 | - |
| * 009:02 | 14 | (9.21) | 4 | (4.44) | 2.18 | 0.21 | - |
| * 010:01 | 18 | (11.84) | 0 | (0.00) | - | 0.00 | R d |
| * 011:01 | 26 | (17.11) | 15 | (16.67) | 1.03 | 1.00 | - |
| * 012:01 | 10 | (6.58) | 6 | (6.67) | 0.99 | 1.00 | - |
| * 013:01 | 1 | (0.66) | 0 | (0.00) | - | 1.00 | - |
| * 014:01:01 | 15 | (9.87) | 6 | (6.67) | 1.53 | 0.48 | - |
| * 015:01 | 18 | (11.84) | 31 | (34.44) | 0.26 | 0.00 | S |
| * 016:01 | 3 | (1.97) | 0 | (0.00) | - | 0.30 | - |
| * 017:01 | 1 | (0.66) | 1 | (1.11) | 0.59 | 1.00 | - |
| * 018:01 | 1 | (0.66) | 1 | (1.11) | 0.59 | 1.00 | - |
| * 027:03 | 9 | (5.92) | 6 | (6.67) | 0.88 | 0.79 | - |
| n a of Tested Animals (Heads) | n of qPCR-Positive Samples (Heads) | Mean PVL b (Copies/105 Cells) | PVL Category | PVL Range (Copies/105 Cells) | n of Cattle (Heads) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | 45 | 20,027 | Low PVL (LPVL) | 34–85 | 14 |
| Moderate | 89–25,858 | 17 | |||
| High PVL (HPVL) | 35,138–98,725 | 14 |
| DRB3 Allele | Holstein Cattle BLV (+) | Chi-Square Test b | Susceptibility | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPVL (n a = 14) | HPVL (n a = 14) | ||||||
| Count | Freq. | Count | Freq. | OR c | p-Value | ||
| * 001:01 | 4 | 14.3 | 6 | 21.4 | 0.6111 | 0.4853 | |
| * 002:01 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.6 | 0 | 0.3130 | |
| * 006:04 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.6 | 0 | 0.3130 | |
| * 007:04 | 1 | 3.6 | 0 | 0 | - | 0.3130 | |
| * 009:02 | 2 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | - | 0.1498 | |
| * 011:01 | 5 | 17.9 | 3 | 10.7 | 1.8116 | 0.4450 | |
| * 012:01 | 4 | 14.3 | 0 | 0 | - | 0.0379 | R d |
| * 014:01:01 | 2 | 7.3 | 1 | 3.6 | 2.0769 | 0.5529 | |
| * 015:01 | 8 | 28.6 | 12 | 42.9 | 0.5333 | 0.2646 | |
| *017:01 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.6 | 0 | 0.3130 | |
| * 018:01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | |
| * 027:03 | 2 | 7.1 | 3 | 10.7 | 0.6410 | 0.6393 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamada, R.; Metwally, S.; Matsuura, R.; Borjigin, L.; Lo, C.-W.; Ali, A.O.; Mohamed, A.E.A.; Wada, S.; Aida, Y. BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphism Associated with Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection and Proviral Load in Holstein Cattle in Egypt. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121451
Hamada R, Metwally S, Matsuura R, Borjigin L, Lo C-W, Ali AO, Mohamed AEA, Wada S, Aida Y. BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphism Associated with Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection and Proviral Load in Holstein Cattle in Egypt. Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121451
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamada, Rania, Samy Metwally, Ryosuke Matsuura, Liushiqi Borjigin, Chieh-Wen Lo, Alsagher O. Ali, Adel E. A. Mohamed, Satoshi Wada, and Yoko Aida. 2023. "BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphism Associated with Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection and Proviral Load in Holstein Cattle in Egypt" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121451
APA StyleHamada, R., Metwally, S., Matsuura, R., Borjigin, L., Lo, C.-W., Ali, A. O., Mohamed, A. E. A., Wada, S., & Aida, Y. (2023). BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphism Associated with Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection and Proviral Load in Holstein Cattle in Egypt. Pathogens, 12(12), 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121451






