Absence of Coronavirus RNA in Faecal Samples from Wild Primates in Gabon, Central Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
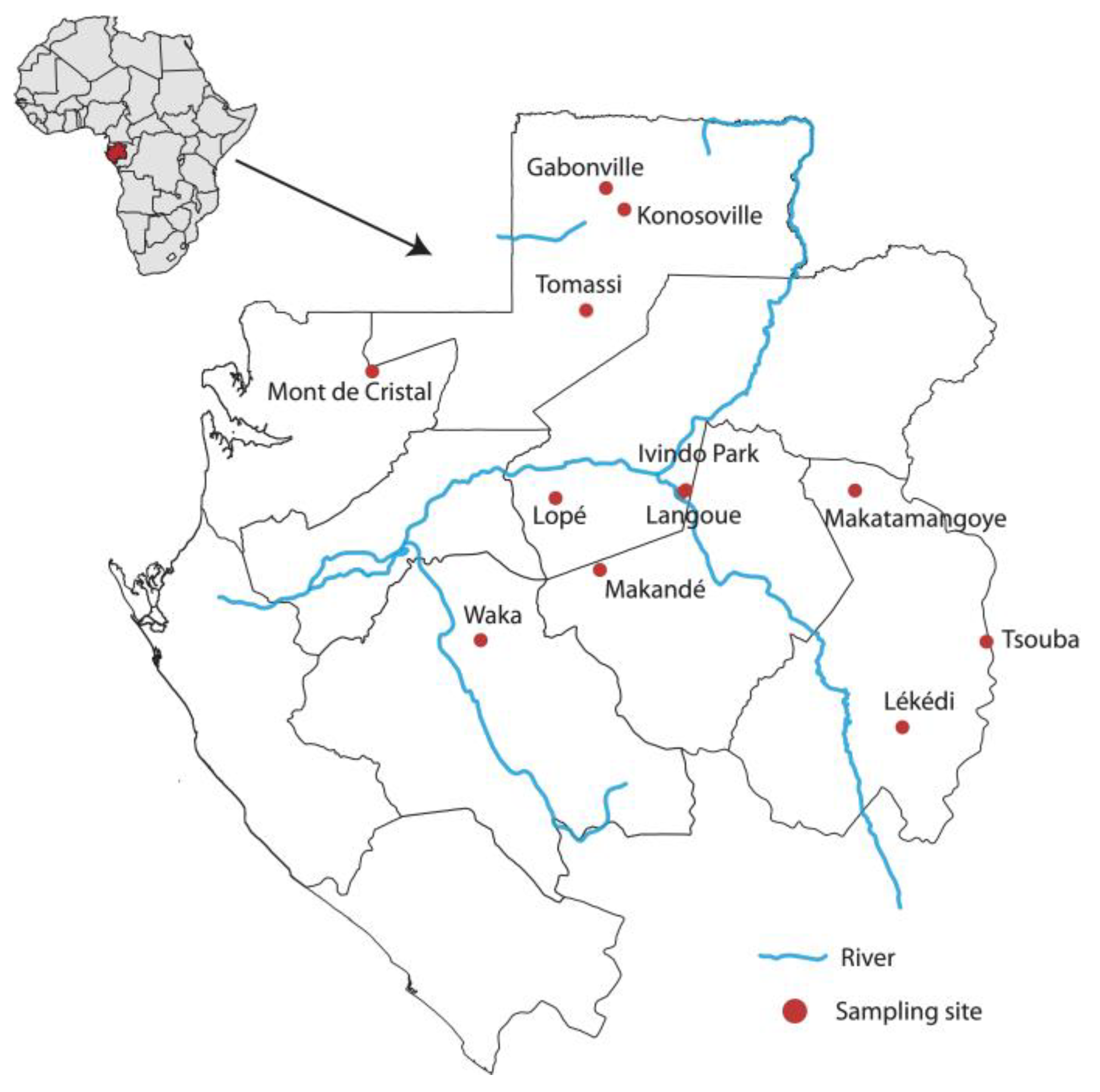
2.1. Sample Collection and RNA Extraction
2.2. Reverse Transcription and Coronavirus Detection
2.3. Ethic Approval
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Lam, C.S.F.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Lau, J.H.N.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.L.; Tsang, C.C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of Seven Novel Mammalian and Avian Coronaviruses in the Genus Deltacoronavirus Supports Bat Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and Avian Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.M.; Cavanagh, D. The Molecular Biology of Coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 1997, 48, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Comparative Analysis of 22 Coronavirus HKU1 Genomes Reveals a Novel Genotype and Evidence of Natural Recombination in Coronavirus HKU1. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7136–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memish, Z.A.; Perlman, S.; Van Kerkhove, M.D.; Zumla, A. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome. Lancet 2020, 395, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-D.; Tu, C.-C.; Zhang, G.-W.; Wang, S.-Y.; Zheng, K.; Lei, L.-C.; Chen, Q.-X.; Gao, Y.-W.; Zhou, H.-Q.; Xiang, H.; et al. Cross-Host Evolution of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus in Palm Civet and Human. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, T.T.-Y.; Jia, N.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Shum, M.H.-H.; Jiang, J.-F.; Zhu, H.-C.; Tong, Y.-G.; Shi, Y.-X.; Ni, X.-B.; Liao, Y.-S.; et al. Identifying SARS-CoV-2-Related Coronaviruses in Malayan Pangolins. Nature 2020, 583, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Shah, T.; Wang, B.; Qu, L.; Wang, R.; Hou, Y.; Baloch, Z.; Xia, X. Cross-Species Transmission, Evolution and Zoonotic Potential of Coronaviruses. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheim, J.O.; Chu, D.K.W.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Poon, L.L.M. A Case for the Ancient Origin of Coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7039–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, A.; Garber, P.A.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Wich, S.; Gouveia, S.; Dobrovolski, R.; Nekaris, K.A.I.; Nijman, V.; Rylands, A.B.; Maisels, F.; et al. Primates in Peril: The Significance of Brazil, Madagascar, Indonesia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo for Global Primate Conservation. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, P.D.; Abernethy, K.A.; Bermejo, M.; Beyers, R.; De Wachter, P.; Akou, M.E.; Huijbregts, B.; Mambounga, D.I.; Toham, A.K.; Kilbourn, A.M.; et al. Catastrophic Ape Decline in Western Equatorial Africa. Nature 2003, 422, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köndgen, S.; Kühl, H.; N’Goran, P.K.; Walsh, P.D.; Schenk, S.; Ernst, N.; Biek, R.; Formenty, P.; Mätz-Rensing, K.; Schweiger, B.; et al. Pandemic Human Viruses Cause Decline of Endangered Great Apes. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.M.; Rouquet, P.; Formenty, P.; Souquière, S.; Kilbourne, A.; Froment, J.-M.; Bermejo, M.; Smit, S.; Karesh, W.; Swanepoel, R.; et al. Multiple Ebola Virus Transmission Events and Rapid Decline of Central African Wildlife. Science 2004, 303, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boundenga, L.; Ollomo, B.; Rougeron, V.; Mouele, L.Y.; Mve-Ondo, B.; Delicat-Loembet, L.M.; Moukodoum, N.D.; Okouga, A.P.; Arnathau, C.; Elguero, E.; et al. Diversity of Malaria Parasites in Great Apes in Gabon. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombo, I.M.; Lukashev, A.N.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Berthet, N.; Maganga, G.D.; Durand, P.; Arnathau, C.; Boundenga, L.; Ngoubangoye, B.; et al. African Non-Human Primates Host Diverse Enteroviruses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidoti, V.; De Nys, H.; Pinarello, V.; Mashura, G.; Missé, D.; Guerrini, L.; Pfukenyi, D.; Cappelle, J.; Chiweshe, N.; Ayouba, A.; et al. Longitudinal Survey of Coronavirus Circulation and Diversity in Insectivorous Bat Colonies in Zimbabwe. Viruses 2022, 14, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.A.; Jordan, K.; Clyne, B.; Rohde, D.; Drummond, L.; Byrne, P.; Ahern, S.; Carty, P.G.; O’Brien, K.K.; O’Murchu, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Detection, Viral Load and Infectivity over the Course of an Infection. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniiappa, L.; Mitov, B.K.; Kharalambiev, K.E. Demonstration of coronavirus infection in buffaloes. Vet. Med. Nauk. 1985, 22, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, H.M. Bovine-like Coronaviruses in Domestic and Wild Ruminants. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2018, 19, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV): An Update on Etiology, Transmission, Pathogenesis, and Prevention and Control. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, E.; Dowlatshahi, S.; Abdekhodaie, M.J. Laboratory Detection Methods for the Human Coronaviruses. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiley Evans, T.; Lowenstine, L.J.; Ssebide, B.; Barry, P.A.; Kinani, J.F.; Nizeyimana, F.; Noheli, J.B.; Okello, R.; Mudakikwa, A.; Cranfield, M.R.; et al. Simian Homologues of Human Herpesviruses and Implications for Novel Viral Introduction to Free-Living Mountain Gorillas. Am. J. Primatol. 2023, 85, e23439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchier, R.A.M.; Kuiken, T.; Schutten, M.; van Amerongen, G.; van Doornum, G.J.J.; van den Hoogen, B.G.; Peiris, M.; Lim, W.; Stöhr, K.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Aetiology: Koch’s Postulates Fulfilled for SARS Virus. Nature 2003, 423, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munster, V.J.; de Wit, E.; Feldmann, H. Pneumonia from Human Coronavirus in a Macaque Model. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1560–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, S.L.; van den Brand, J.M.A.; de Lang, A.; Leijten, L.M.E.; van IJcken, W.F.; van Amerongen, G.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Andeweg, A.C.; Haagmans, B.L. Distinct Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-Induced Acute Lung Injury Pathways in Two Different Nonhuman Primate Species. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4234–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrono, L.V.; Samuni, L.; Corman, V.M.; Nourifar, L.; Röthemeier, C.; Wittig, R.M.; Drosten, C.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Leendertz, F.H. Human Coronavirus OC43 Outbreak in Wild Chimpanzees, Côte D’Ivoire, 2016. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2018, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Year of Collection | Location | Species | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gorilla | Chimpanzee | Mandrill | |||
| 2012 | Gabonville | 13 | _ | 3 | 16 |
| Lyokomillieu | 1 | _ | _ | 1 | |
| Kokossoville | 11 | 7 | _ | 18 | |
| Langoué | 12 | 1 | _ | 13 | |
| Lopé | 7 | 39 | _ | 46 | |
| Makatamangoye | 1 | 4 | _ | 5 | |
| Tomassi | 2 | 3 | 17 | 22 | |
| Waka | 10 | 5 | _ | 15 | |
| 2010 | Lekedi | 3 | _ | _ | 3 |
| Lopé | 28 | 13 | 1 | 42 | |
| Makande | 12 | _ | _ | 12 | |
| Mont de Cristal | 4 | 8 | _ | 12 | |
| Parc-Ivindo | 1 | _ | _ | 1 | |
| Tsouba | _ | 4 | _ | 4 | |
| 2009 | Lekedi | 1 | _ | _ | 1 |
| Lopé | 16 | 2 | _ | 18 | |
| Total | 122 | 86 | 21 | 229 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mombo, I.M.; Rieu, O.; Fritz, M.; Boundenga, L.; Mebaley, T.N.; Mbou-Boutambe, C.; Lenguiya, L.H.; Maganga, G.D.; Rougeron, V.; Prugnolle, F.; et al. Absence of Coronavirus RNA in Faecal Samples from Wild Primates in Gabon, Central Africa. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101272
Mombo IM, Rieu O, Fritz M, Boundenga L, Mebaley TN, Mbou-Boutambe C, Lenguiya LH, Maganga GD, Rougeron V, Prugnolle F, et al. Absence of Coronavirus RNA in Faecal Samples from Wild Primates in Gabon, Central Africa. Pathogens. 2023; 12(10):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101272
Chicago/Turabian StyleMombo, Illich Manfred, Océane Rieu, Matthieu Fritz, Larson Boundenga, Telstar Ndong Mebaley, Clark Mbou-Boutambe, Léadisaelle Hosanna Lenguiya, Gael Darren Maganga, Virginie Rougeron, Franck Prugnolle, and et al. 2023. "Absence of Coronavirus RNA in Faecal Samples from Wild Primates in Gabon, Central Africa" Pathogens 12, no. 10: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101272
APA StyleMombo, I. M., Rieu, O., Fritz, M., Boundenga, L., Mebaley, T. N., Mbou-Boutambe, C., Lenguiya, L. H., Maganga, G. D., Rougeron, V., Prugnolle, F., Thomas, F., & Leroy, E. M. (2023). Absence of Coronavirus RNA in Faecal Samples from Wild Primates in Gabon, Central Africa. Pathogens, 12(10), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101272










