Glanders Diagnosis in an Asymptomatic Mare from Brazil: Insights from Serology, Microbiological Culture, Mass Spectrometry, and Genome Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
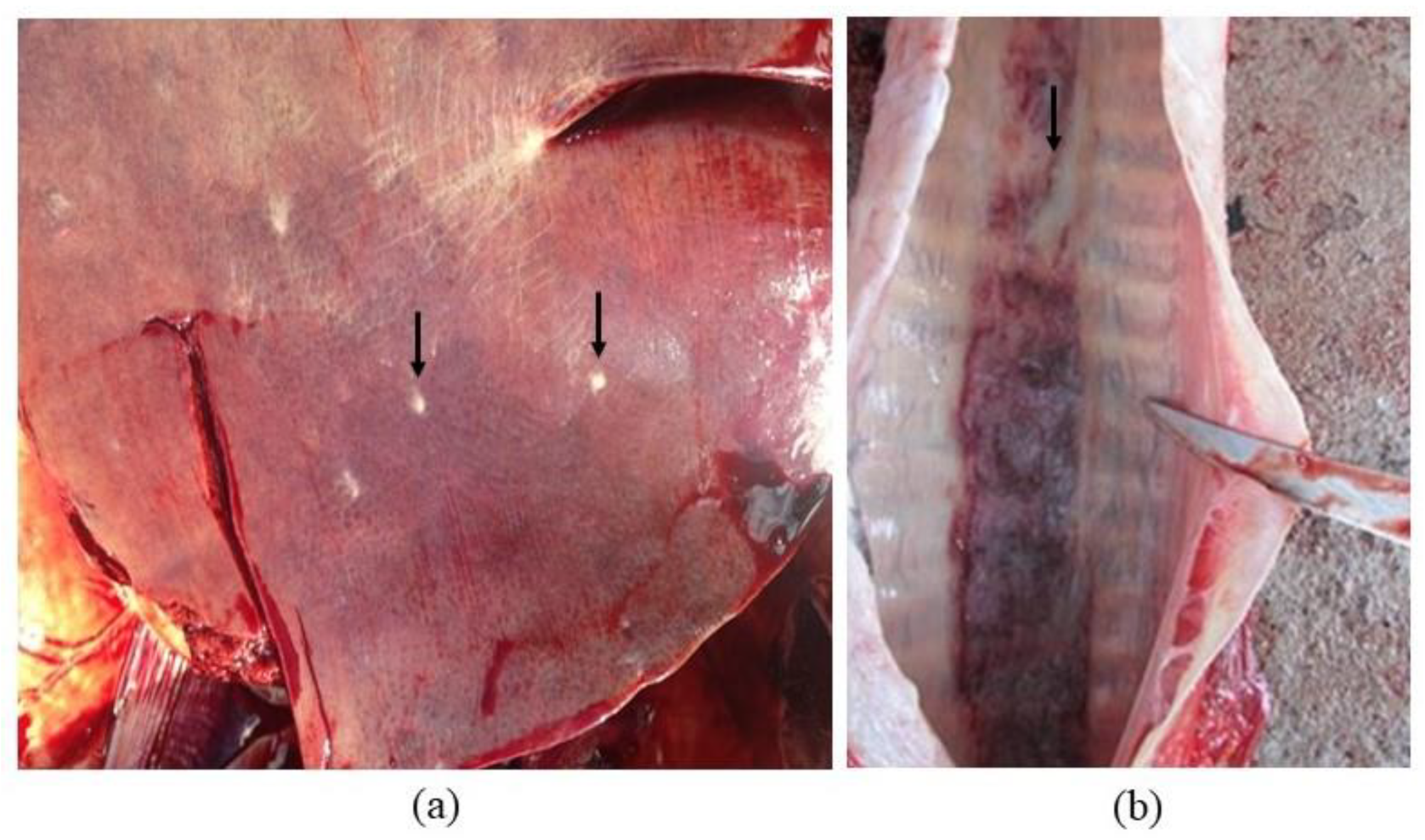
2.1. Clinical Case
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Molecular Detection
2.3. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.5. Quality Assessment, Assembly, and Annotation
2.6. Genetic Markers for Species Confirmation
2.7. Lineage Identification
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Isolation and Molecular Detection
3.2. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
3.3. The Draft Genome of B. mallei BAC 86/19
3.4. Species Confirmation Using Genetic Markers
3.5. Lineage Identification
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, G.; Glaser, L.; Scott, N.E.; Fathy Mohamed, Y.; Ingram, R.; Laroucau, K.; Valvano, M.A. A glycoengineered antigen exploiting a conserved protein O-glycosylation pathway in the Burkholderia genus for detection of glanders infections. Virulence 2021, 12, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waag, D.M.; Chance, T.B.; Trevino, S.R.; Rossi, F.D.; Fetterer, D.P.; Amemiya, K.; Welkos, S.L. Comparison of three nonhuman primate aerosol models for glanders, caused by Burkholderia mallei. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Vaccines for the prevention of melioidosis and glanders. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2017, 4, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Bioterrorism Agents/Diseases. 2018. Available online: https://emergencycdcgov/agent/agentlist-categoryasp (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- OIE. Glanders and Melioidosis. 2018. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.06.11_GLANDERS.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Fonseca-Rodríguez, O.; Júnior, J.W.P.; Mota, R.A. Spatiotemporal analysis of glanders in Brazil. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2019, 78, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, R.A.; Brito, M.F.; Castro, F.J.; Massa, M. Mormo em eqüídeos nos estados de Pernambuco e Alagoas. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2000, 20, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, R.A.; Oliveira, A.A.D.F.; Pinheiro Junior, J.W.; Silva, L.B.G.D.; Brito, M.D.F.; Rabelo, S.S.A. Glanders in donkeys (Equus asinus) in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil: A case report. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, L.O.D.; Lima, L.A.R.D.; Albuquerque, R.M.S.D.; Lages, S.L.S.; Nunes, A.C.B.T.; Castro, R.S.D.; Falcão, M.V.D. Monitoring the outbreak of equine glanders in Alagoas, Brazil: Clinical, immunological, molecular and anatomopathological findings. Ciência Rural 2021, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, D.C.; Gomes, A.S.; Tessler, D.K.; Chiebao, D.P.; Del Fava, C.; Romaldini, A.H.D.C.N.; Nassar, A.F.C. Systematic monitoring of glanders-infected horses by complement fixation test, bacterial isolation, and PCR. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2020, 10, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suniga, P.A.P.; Mantovani, C.; Santos, M.G.; Rieger, J.S.G.; Gaspar, E.B.; Santos, F.L.; Mota, R.A.M.; Chaves, K.P.; Egito, A.A.; Filho, J.C.O.; et al. Molecular detection of Burkholderia mallei in different geographic regions of Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelt, S.; Rohleder, A.M.; Jacob, D.; Von Buttlar, H.; Georgi, E.; Mueller, K.; Scholz, H.C. Genetic diversity and spatial distribution of Burkholderia mallei by core genome-based multilocus sequence typing analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, P.J.; Markey, B.K.; Leonard, F.C.; Hartigan, P.; Fanning, S.; Fitzpatrick, E. Veterinary Microbiology and Microbial Disease; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Winn, W.C., Jr.; Allen, S.D.; Janda, W.M.; Koneman, E.; Procop, G.; Schreckenberger, P.C.; Woods, G. Bacilos gram-negativos não fermentadores. In Koneman Diagnostico Microbiológico; Texto e Atlas Colorido: Guanabara, RJ, Brazil, 2008; Volume 6, pp. 302–386. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, S.; Freiwald, A.; Maier, T.; Kube, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Kostrzewa, M.; Geider, K. Classification and identification of bacteria by mass spectrometry and computational analysis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiwald, A.; Sauer, S. Phylogenetic classification and identification of bacteria by mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacanelli, G.; Olarte, L.C.; Silva, M.R.; Rodrigues, R.A.; Carneiro, P.A.; Kaneene, J.B.; Verbisck, N.V. Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry identification of Mycobacterium bovis in Bovinae. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasch, P.; Stämmler, M.; Schneider, A. A MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry database for identification and classification of highly pathogenic microorganisms from the robert koch-institute (RKI). Zenodo 2016, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbisck, N.; Araujo, F.; Gaspar, E.; Fonseca Júnior, A.; Mota, R.; Silva, K.; Alvarenga, L.; Lima, D. Caracterização e identificação de Burkholderia mallei por espectrometria de massas MALDI-TOF: Resultados de um estudo piloto. Campo Grande; MS: Embrapa Gado de Corte. Bol. Pesqui. E Desenvolv. 2020, 47, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Pevzner, P.A. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonge, M.; Lebeigle, L.; Kirsche, M.; Jenike, K.; Ou, S.; Aganezov, S.; Wang, X.; Lippman, Z.B.; Schatz, M.C.; Soyk, S. Automated assembly scaffolding using RagTag elevates a new tomato system for high-throughput genome editing. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, F.M.; Valade, E.; Vidal, D.R. Identification and discrimination of Burkholderia pseudomallei, B. mallei and B. thailandensis by real-time PCR targeting type III secretion system genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5871–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, C.W.; Satterfield, B.A.; Nelson, D.B.; Thiriot, J.D.; Heder, M.J.; March, J.K.; Robison, R.A. A Quadruplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Rapid Detection and Differentiation of the Most Relevant Members of the B. pseudomallei Complex: B. mallei, B. pseudomallei and B. thailandensis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.A.; Wang, D.; Yap, E.H. Detection and differentiation of Burkholderia pseudomallei, Burkholderia mallei and Burkholderia thailandensis by multiplex PCR FEMS. Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Girault, G.; Wattiau, P.; Saqib, M.; Martin, B.; Vorimore, F.; Singha, H.; Laroucau, K. High-resolution melting PCR analysis for rapid genotyping of Burkholderia mallei infection. Genet. Evol. 2018, 63, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poplin, R.; Ruano-Rubio, V.; DePristo, M.A.; Fennell, T.J.; Carneiro, M.O.; Van der Auwera, G.A.; Banks, E. Scaling accurate genetic variant discovery to tens of thousands of samples. bioRxiv 2017, 201178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; DePristo, M.A. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brangsch, H.; Singha, H.; Laroucau, K.; Elschner, M. Sequence-based detection and typing procedures for Burkholderia mallei: Assessment and prospects. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1056996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, P.; Ng, K.L.; Krogh, A. Fast and sensitive taxonomic classification for metagenomics with Kaiju. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, K.P.; Mota, R.A.; Cunha, A.P.; Silva, L.B.; Leal, N.C.; Cavalcante, Y.V.; Teles, J.A.A.; Pereira, M.C.C. Caracterização fenotípica e molecular de amostras de Burkholderia mallei isoladas na Região Nordeste do Brasil. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2009, 29, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernfeind, A.; Roller, C.; Meyer, D.; Jungwirth, R.; Schneider, I. Molecular procedure for rapid detection of Burkholderia mallei and Burkholderia Pseudomallei. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2737–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, J.R.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Ginther, J.L.; Pearson, T.; Peacock, S.J.; Tuanyok, A.; Keim, P.S. BurkDiff: A real-time PCR allelic discrimination assay for Burkholderia pseudomallei and B. mallei. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcão, M.V.; Laroucau, K.; Vorimore, F.; Deshayes, T.; Santana, V.L.; Silva, K.P.; Mota, R.A. Molecular characterization of Burkholderia mallei strains isolated from horses in Brazil (2014–2017). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 99, 105250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroucau, K.; Santana, V.L.A.; Girault, G.; Martin, B.; Silveira, P.M.; Machado, M.B.; Madani, N. First molecular characterization of a Brazilian Burkholderia mallei strain isolated from a mule in 2016. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 57, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, A.; Stock, R.; Ziller, M.; Elschner, M.C.; Bettin, B.; Melzer, F.; Maier, T.; Kostrzewa, M.; Scholz, H.C.; Neubauer, H.; et al. Rapid identification of Burkholderia mallei and Burkholderia pseudomallei by intact cell Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionisation mass spectrometric typing. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttisunhakul, V.; Pumpuang, A.; Ekchariyawat, P.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Elrod, M.G.; Turner, P.; Currie, B.J.; Phetsouvanh, R.; Dance, D.A.B.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; et al. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the identification of Burkholderia pseudomallei from Asia and Australia and differentiation between Burkholderia species. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lineage | Genomic Position * | Reference Base to Be Called a Lineage ** | Base in B. mallei BAC 86/19 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 330,697 | C | T |
| L2 | 2,621,027 | A | G |
| L2B1 | 354,181 | A | G |
| L2B2 | 1,408,904 | C | T |
| L2B2sB1 | 1,853,849 | T | C |
| L2B2sB1Gp1 | 1,163,826 | T | C |
| L2B2sB1Gp2 | 559,637 | G | A |
| L2B2sB2 | 707,292 | T | C |
| L3 | 2,557,840 | T | T |
| L3B1 | 309,945 | T | C |
| L3B2 *** | 1,767,871 | A | A |
| L3B3 | 135,971 | T | C |
| L3B3sB1 | 155,657 | T | C |
| L3B3sB2 | 1,560,255 | A | G |
| L3B3sB3 | 922,706 | T | C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suniga, P.A.P.; Mantovani, C.; dos Santos, M.G.; do Egito, A.A.; Verbisck, N.V.; dos Santos, L.R.; Dávila, A.M.R.; Zimpel, C.K.; Zerpa, M.C.S.; Chiebao, D.P.; et al. Glanders Diagnosis in an Asymptomatic Mare from Brazil: Insights from Serology, Microbiological Culture, Mass Spectrometry, and Genome Sequencing. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101250
Suniga PAP, Mantovani C, dos Santos MG, do Egito AA, Verbisck NV, dos Santos LR, Dávila AMR, Zimpel CK, Zerpa MCS, Chiebao DP, et al. Glanders Diagnosis in an Asymptomatic Mare from Brazil: Insights from Serology, Microbiological Culture, Mass Spectrometry, and Genome Sequencing. Pathogens. 2023; 12(10):1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101250
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuniga, Paula Adas Pereira, Cynthia Mantovani, Maria Goretti dos Santos, Andréa Alves do Egito, Newton Valério Verbisck, Lenita Ramires dos Santos, Alberto Martín Rivera Dávila, Cristina Kraemer Zimpel, Maria Carolina Sisco Zerpa, Daniela Pontes Chiebao, and et al. 2023. "Glanders Diagnosis in an Asymptomatic Mare from Brazil: Insights from Serology, Microbiological Culture, Mass Spectrometry, and Genome Sequencing" Pathogens 12, no. 10: 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101250
APA StyleSuniga, P. A. P., Mantovani, C., dos Santos, M. G., do Egito, A. A., Verbisck, N. V., dos Santos, L. R., Dávila, A. M. R., Zimpel, C. K., Zerpa, M. C. S., Chiebao, D. P., de Sá Guimarães, A. M., de Castro Nassar, A. F., & de Araújo, F. R. (2023). Glanders Diagnosis in an Asymptomatic Mare from Brazil: Insights from Serology, Microbiological Culture, Mass Spectrometry, and Genome Sequencing. Pathogens, 12(10), 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12101250







