Getah Virus (Alphavirus): An Emerging, Spreading Zoonotic Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Expansion of GETV in Geographical Region, Vectors and Host Animals
2.1. Literature Collection Method
2.2. GETV Isolated in the 1950s and 1960s
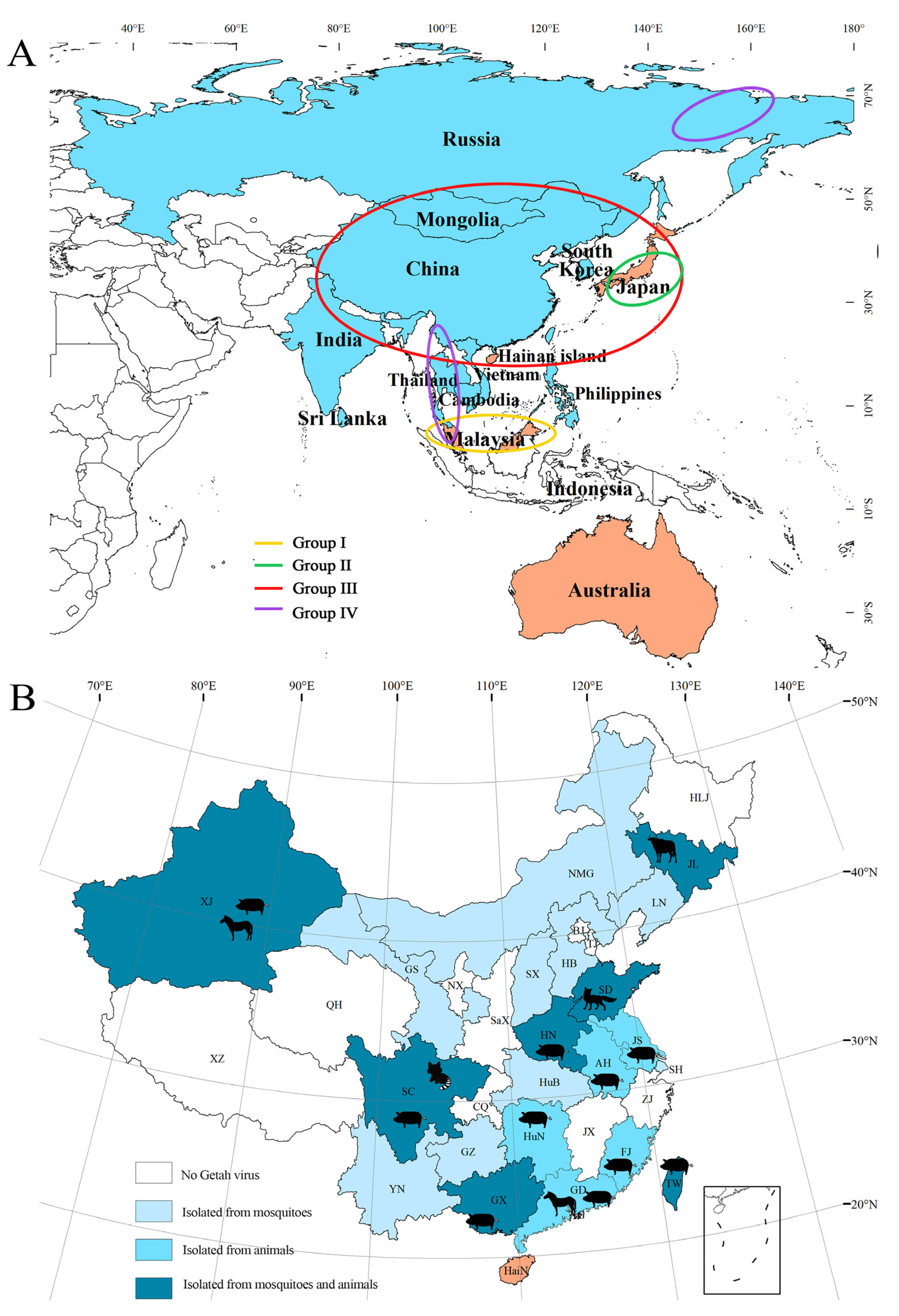
2.3. Geographical Distribution of GETV
2.4. GETV Isolated from Bloodsucking Insects
2.5. GETV Isolated from Host Animals
3. Animal Infection and Disease Outbreaks
3.1. Disease Outbreaks Caused by GETV in Animals
3.1.1. Horses
3.1.2. Pigs
3.1.3. Other Animals
3.2. Seroepidemiological Analysis of GETV Infection in Animals
3.3. GETV Infections in Human
3.4. Methods for the Etiological Detection of GETV
4. Molecular Evolution of GETV
4.1. Group III GETV Is an Emerging, Dominant Virus Group
4.2. Evolutionary Dynamics and Migration of GETV
5. Vaccines
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karabatsos, N. International Catalogue of Arthropod-Borne Viruses, 3rd ed.; American Society for Tropical Medicine and Hygiene: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, S.C.; Frey, T.K.; Huang, H.V.; Kinney, R.M.; Rice, C.M.; Roehrig, J.T.; Shope, R.E.; Strauss, E.G. Togaviridae. In Virus Taxonomy, VIII Report of the ICTV, 1st ed.; Fauquet, C.M., Mayo, M.A., Maniloff, J., Desselberger, U., Ball, L.A., Eds.; Elsevier/Academic Press: London, UK, 2005; pp. 999–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, R.J. Togaviridae: The viruses and their replication. In Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Wolter Kluwer Lippincott Willian & Wikins: Philadephia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 825–841. [Google Scholar]
- Kamada, M.; Ando, Y.; Fukunaga, Y.; Kumanomido, T.; Akiyama, Y. Equine Getah virus infection: Isolation of the virus from racehorses during an enzootic in Japan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1980, 29, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yago, K.; Hagiwara, S.; Kawamura, H.; Narita, M. A fatal case in newborn piglets with Getah virus infection: Isolation of the virus. Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 1987, 49, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.M.; Timoney, P.J. Getah virus infection of Indian horses. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1998, 30, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Li, R.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, D.; Du, L.; Li, J.; Ge, M.; Yu, X. An outbreak of Getah virus infection among pigs in China, 2017. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.G.; Wang, H.Y.; Sun, X.H.; Fu, S.H.; Wang, H.Q.; Attoui, H.; Tang, Q.; Liang, G.D. Complete sequence characterization of isolates of Getah virus (genus Alphavirus, family Togaviridae) from China. J Gen Virol. 2008, 89, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.S.; Zhao, W.Z.; Liu, J.W.; Zhou, H.; Tao, J.P.; Yan, H.J.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, J.J.; Jiang, L.F. Genomic analysis of a Chinese isolate of Getah-like virus and its phylogenetic relationship with other Alphaviruses. Virus Genes. 2007, 35, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Mo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, Z. Emergence and Phylogenetic Analysis of a Getah Virus Isolated in Southern China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 552517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K.; Igarashi, A. Oligonucleotide fingerprint analysis of strains of Getah virus isolated in Japan and Malaysia. J. Gen. Virol. 1984, 65, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, S.H.; Li, X.L.; Guo, X.F.; Li, M.H.; Feng, Y.; Chen, W.X.; Wang, L.H.; Lei, W.W.; et al. From discovery to spread: The evolution and phylogeny of Getah virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Qiu, F.X.; Yang, H.; Rao, Y.N.; Calisher, C.H. Isolation of Getah virus from mosquitos collected on Hainan Island, China, and results of a serosurvey. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1992, 23, 730–734. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Jiapaer, H.; Xue, X.M.; Ding, M.Y.; Ma, X.J.; Ye, F.; Ma, J.J.; Yi, X.P.; Gu, W.X.; Zhong, Q. Isolation and Identification of Getah Virus from Culicoides in Xinjiang. Aeta Vet. Zootech. Sin. 2017, 48, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; He, Y.W.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Meng, J.X.; Xu, T.G.; Wang, J.L. Analysis of Molecular Biological Characteristics of Structural Genes of Getah Virus (SZC30) Isolated from Midge. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 48, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Trosper, J.H.; Cross, J.H.; Basaca-Sevilla, V. Isolation of Getah virus from Nueva Ecija Province, Republic of the Philippines. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 312–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, J.S.; Amerasinghe, P.H.; Amerasinghe, F.P.; Calisher, C.H.; Perera, L.P.; Arunagiri, C.K.; Munasingha, N.B.; Karunaratne, S.H. Viruses isolated from mosquitoes collected in Sri Lanka. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1994, 51, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.E.; Crabtree, M.B.; Nam, V.S.; Yen, N.T.; Duc, H.M.; Miller, B.R. Isolation of arboviruses from mosquitoes collected in northern Vietnam. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Vov, S.D.; Gromashevski’I, V.L.; Aristova, V.A.; Morozova, T.N.; Skvortsova, T.M.; Gushchina, E.A.; Petrova, E.S.; L’Vov, D.K. Isolation of Getah virus (Togaviridae, Alfavirus) strains in North–Eastern Asia. Vopr. Virusol. 2000, 45, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sentsui, H.; Kono, Y. An epidemic of Getah virus infection among racehorses: Isolation of the virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 1980, 29, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Ando, Y.; Imagawa, H.; Kumanomido, T.; Fukunaga, Y.; Kamada, M.; Wada, R.; Hirasawa, K.; Akiyama, Y. An Epizootiological Study of Getah Virus among Light Horses in Japan in 1979. Bull. Equine Res. Inst. 1981, 18, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Shi, N.; Sun, X.; Liu, Q.; Jin, N.; Si, X. First isolation and characterization of Getah virus from cattle in northeastern China. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Li, L.X.; Lu, R.G.; Yan, X.J.; Liu, H. Highly Pathogenic Swine Getah Virus in Blue Foxes, Eastern China, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1252–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T. Getah Virus Infection among Racehorses, Japan, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 883–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannai, H.; Ochi, A.; Nemoto, M.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T. A 2015 outbreak of Getah virus infection occurring among Japanese racehorses sequentially to an outbreak in 2014 at the same site. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Ou, J.; Ji, J.; Ren, Z.; Li, S. Emergence of Getah Virus Infection in Horse with Fever in China, 2018. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Rong, X. Isolation and identification of swine Getah virus and study on efficacy of its inactive vaccine. Chin. Vet. Sci. 2020, 50, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Zhou, F.; Chang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Cui, D.; Jimei, D.U.; Liu, H.; Wang, C. Molecular Detection, Isolation and Identification of the Porcine Getah Virus from Pig Herds in Four Provinces, China. Chin. J. Virol. 2018, 34, 522–532. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Yue, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Shen, Q.; Su, X.; Qi, D.; et al. Viral metagenomics unveiled extensive communications of viruses within giant pandas and their associated organisms in the same ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagawa, H.; Ando, Y.; Kamada, M.; Sugiura, T.; Kumanomido, T.; Fukunaga, Y.; Wada, R.; Hirasawa, K.; Akiyama, Y. Sero-epizootiological survey on Getah virus infection in light horses in Japan. Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 1981, 43, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Ide, S.; Yamagishi, H.; Eiguchi, Y.; Nagano, H.; Maehara, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Fujisaki, Y.; Yago, K.; Taguchi, K.; et al. Enzyme–linked immunosorbent assay for the serological survey of Getah virus in pigs. Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 1990, 52, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuwata, R.; Shimoda, H.; Phichitraslip, T.; Prasertsincharoen, N.; Noguchi, K.; Yonemitsu, K.; Minami, S.; Supriyono; Tran, N.T.B.; Takano, A.; et al. Getah virus epizootic among wild boars in Japan around 2012. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2817–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Fu, S.H.; Guo, X.F.; Li, X.L.; Li, M.H.; Wang, L.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Lei, W.W.; Cao, L.; Lv, Z.; et al. Serological Survey of Getah Virus in Domestic Animals in Yunnan Province, China. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Qiu, X.; Cao, X.; Mai, Z.; Zhu, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Shaya, N.; et al. Molecular and serological surveillance of Getah virus in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China, 2017–2020. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, T.; Goto, H.; Shimizu, K.; Ando, Y.; Imagawa, H.; Sugiura, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Taya, Y. Prevalence of antibodies against Getah virus in horses raised in Hokkaido. Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 1981, 43, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, T.; Goto, H.; Shimizu, K.; Sugiura, T.; Ando, Y.; Kumanomido, T.; Hirasawa, K.; Akiyama, Y. Prevalence and distribution of antibodies to Getah and Japanese encephalitis viruses in horses raised in Hokkaido. Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 1982, 44, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sugiyama, I.; Shimizu, E.; Nogami, S.; Suzuki, K.; Miura, Y.; Sentsui, H. Serological survey of arthropod–borne viruses among wild boars in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2009, 71, 1059–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannai, H.; Nemoto, M.; Niwa, H.; Murakami, S.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T. Geospatial and temporal associations of Getah virus circulation among pigs and horses around the perimeter of outbreaks in Japanese racehorses in 2014 and 2015. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, Y.O.; Heo, Y.; Kim, Y.H. Serological survey of horses in Korea for evidence of Getah virus infection. Korean J. Vet. Res. 1986, 26, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Rattanatumhi, K.; Prasertsincharoen, N.; Naimon, N.; Kuwata, R.; Shimoda, H.; Ishijima, K.; Yonemitsu, K.; Minami, S.; Supriyono; Tran, N.; et al. A serological survey and characterization of Getah virus in domestic pigs in Thailand, 2017–2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Yuan, Z.; He, Y.; Ren, Y.; Meng, J.; Wang, S.; Zhong, J.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Sero-epidemiological Investigation on the GTV in Horses in Guangzhou City and Its Surrounding Areas. China Anim. Health Insp. 2021, 38, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; He, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, N.; Zeng, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, J. Establishment and application of an indirect ELISA for detection of swine Getah disease. Chin. Vet. Sci. 2020, 50, 962–968. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Tsuda, T.; Tokuhisa, S.; Sato, K.; Akashi, H.; Matumoto, M. A survey of antibodies to arthropod-borne viruses in Indonesian cattle. Nihon juigaku zasshi. Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 1983, 44, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.I.H.; Smith, C.E.G.; Marshall, T.D.C.; Platt, G.S.; Way, H.J.; Bowen, E.T.W.; Bright, W.F.; Day, J.; McMahon, D.A.; Hill, M.N.; et al. Arbovirus infections in Sarawak: The role of the domestic pig. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1976, 70, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamitsu, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Urasawa, S.; Ogata, T.; Wada, Y.; Wada, Y.; Saroso, J.S. Geographic distribution of arbovirus antibodies in indigenous human populations in the Indo-Australian archipelago. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, S.D.; Gromashevsky, V.L.; Andreev, V.P.; Skvortsova, T.M.; Kondrashina, N.G.; Morozova, T.N.; Avershin, A.D.; Aristova, V.A.; Dmitriev, G.A.; Kandaurov, Y.K.; et al. Natural foci of arboviruses in far northern latitudes of Eurasia. Springer Vienna 1990, 1, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, D.I.; Way, H.J.; Platt, G.S.; Bowen, E.T.; Hill, M.N.; Kamath, S.; Bendell, P.J.; Heathcote, O.H. Arbovirus infections in Sarawak, October 1968–February 1970: GETAH virus isolations from mosquitoes. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1975, 69, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Fu, S.H.; Guo, X.F.; Lei, W.W.; Li, X.L.; Song, J.D.; Cao, L.; Gao, X.Y.; Lv, Z.; He, Y.; et al. Identification of a Newly Isolated Getah Virus in the China-Laos Border, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, X.; Cao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, H.; Jin, N. Origin, genetic diversity, adaptive evolution and transmission dynamics of Getah virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Liu, H.; Li, X.L.; Fu, S.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Lei, W.W.; Zhi, L.; He, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, G.Q.; et al. Phylogenctics of Getah virus and its migration. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2017, 33, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.Y.; Fu, S.H.; Guo, Z.Y.; Liang, G.D. Southernmost Asia is the source of Japanese encephalitis virus (genotype 1) diversity from which the viruses disperse and evolve throughout Asia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, M.; Kumanomido, T.; Wada, R.; Fukunaga, Y.; Imagawa, H.; Sugiura, T. Intranasal infection of Getah virus in experimental horses. J. Vet. Med. Sci./Jpn. Soc. Vet. Sci. 1991, 53, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanomido, T.; Wada, R.; Kanemaru, T.; Kamada, M.; Hirasawa, K.; Akiyama, Y. Clinical and virological observations on swine experimentally infected with Getah virus. Vet. Microbiol. 1988, 16, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, Y.; Kumanomido, T.; Kamada, M. Getah virus as an equine pathogen. Vet. Clin. North Am. Equine Pract. 2000, 16, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannai, H.; Tominari, M.; Kambayashi, Y.; Nemoto, M.; Tsujimura, K.; Ohta, M. Evaluation of Antibody Response in Horses After Vaccination with an Inactivated Getah Virus Vaccine Using an Accelerated Immunization Schedule. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 99, 103396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Country | Region | Year | Animals | Group † | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse | Pig | Blue Fox | Cattle | |||||
| Japan | Kanto district, Sakai T.C. | 1978 | 0/70/455 * | [20] | ||||
| Ibaraki Prefecture, Miho T.C. | 1978 | 0/722/1903 | III | [4] | ||||
| Tochigi Prefecture, Ritto T.C. | 1979 | 0/136/- | [21] | |||||
| Kanagawa Prefecture, Pig farm | 1985 | 8/12/– | [5] | |||||
| Ibaraki Prefecture, Miho T.C. | 2014 | 0/75/2000 | III | [24] | ||||
| Ibaraki Prefecture, Miho T.C. | 2015 | 0/30/1992 | III | [25] | ||||
| India | Horse farm | 1990 | 0/26/88 | [6] | ||||
| China | Hunan Province, pig farm | 2017 | 200/1333/2915 | III | [7] | |||
| Shandong Province, animal farm | 2017 | 6/25/– | III | [23] | ||||
| Guangxi Province, pig farm | 2018 | 0/54/503 | III | [10] | ||||
| Jilin Province, cattle farm | 2018 | 0/10/48 | III | [22] | ||||
| Guangdong Province, T.C. | 2018 | 0/1/– | III | [26] | ||||
| Country | Region | Year | Method * | Animals | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse | Pig | Wild Boar | Cattle | |||||
| Japan | Hokkaido (Tokachi) | 1973–1976 | SNT | 12.7 (8/127) ** | [35] | |||
| Hokkaido (Hidaka) | 1976 | SNT | 11.4 (8/70) | |||||
| Tokyo | 1977 | SNT | 33.3 (17/51) | |||||
| Hokkaido (Southern) | 1979–1981 | HIT | 35.7 (107/300) | [36] | ||||
| Hokkaido (Central) | 1979–1981 | HIT | 31.7 (57/180) | |||||
| Hokkaido (Eastern) | 1979–1981 | HIT | 7.5 (15/200) | |||||
| Hokkaido (Northern) | 1979–1981 | HIT | 45.7 (105/230) | |||||
| Miho T.C. (Infected horses) | 1978 | SNT | 93 (120/129) | [30] | ||||
| Miho T.C. (Uninfected horses) | 1978 | SNT | 24.9 (52/152) | |||||
| Miho T.C. (Before the GETV outbreak) | 1978 | SNT | 6 (14/232) | |||||
| Miho T.C. (After the GETV outbreak) | 1978 | SNT | 61.2 (172/281) | |||||
| Hokkaido | 1978 | SNT | 52.2 (12/23) | |||||
| Tohoku | 1978 | SNT | 6.7 (1/15) | |||||
| Kanto | 1978 | SNT | 18.8 (36/192) | |||||
| Chubu | 1978 | SNT | 54.5 (55/101) | |||||
| Kansai | 1978 | SNT | 3.6 (5/140) | |||||
| Kyushu | 1978 | SNT | 72 (18/25) | |||||
| Nakayama Racecourse | 1972–1977 | SNT | 25.9 (2346/1338) | |||||
| Hokkaido | 1980 | HIT | 2.7 (1/37) | [31] | ||||
| Tohoku | 1980 | HIT | 16.8 (20/119) | |||||
| Kanto | 1980 | HIT | 19.1 (40/209) | |||||
| Chubu | 1980 | HIT | 14.2 (36/254) | |||||
| Chugoko | 1980 | HIT | 11.5 (18/156) | |||||
| Kinki | 1980 | HIT | 7.1 (15/211) | |||||
| Shikoku | 1980 | HIT | 11 (13/118) | |||||
| Kyushu | 1980 | HIT | 14.8 (31/209) | |||||
| Kyushu | 2000–2001 | HIT | 47.8 (43/90) | [37] | ||||
| Shimonoseki | 2013–2014 | PRNT | 54.3 (39/70) | [32] | ||||
| Nationwide | 2007–2011 | ELISA | 3 (3/301) | |||||
| Nationwide | 2012 | ELISA | 15.5 (18/116) | |||||
| Nationwide | 2013 | ELISA | 44.6 (4/192) | |||||
| Nationwide | 2014 | ELISA | 29.1 (46/158) | |||||
| Nationwide | 2015 | ELISA | 18.1 (26/144) | |||||
| Nationwide | 2016 | ELISA | 14.3 (34/237) | |||||
| Nationwide | 2007–2016 | ELISA | 16.0 (168/1048) | |||||
| South Ibaraki | 2012 | VNT | 1 (1/100) | [38] | ||||
| South Ibaraki | 2013 | VNT | 0 (0/97) | |||||
| South Ibaraki | 2014 | VNT | 28.8 (19/66) | |||||
| South Ibaraki | 2015 | VNT | 65 (77/117) | |||||
| North Chiba | 2010 | VNT | 1.6 (2/123) | |||||
| North Chiba | 2011 | VNT | 0 (0/111) | |||||
| North Chiba | 2012 | VNT | 0 (0/74) | |||||
| North Chiba | 2013 | VNT | 14.1 (19/135) | |||||
| North Chiba | 2014 | VNT | 17.8 (8/45) | |||||
| North Chiba | 2015 | VNT | 48 (24/50) | |||||
| South Korea | Nationwide | 1985 | HIT | 37 (212/575) | [39] | |||
| Nationwide | 1985 | HIT | 47 (218/462) | |||||
| India | Nationwide | 1990 | SNT | 17 (26/152) | [6] | |||
| Thailand | Eleven provinces | 2017–2018 | ELISA | 23.1 (275/1188) | [40] | |||
| China | Yunnan † | 2015 | PRNT | 45.88 (39/85) | 71.88 (23/32) | [33] | ||
| Xinjiang † | 2017–2020 | ELISA | 70.2 (1140/1625) | 51.1 (203/397) | 25.1 (100/398) | [34] | ||
| Hainan | 1979 | NT | 25 (4/16) | 17.6 (3/17) | [13] | |||
| Hainan † | 1982 | CFT | 22.7 (5/22) | |||||
| Guangzhou | 2019 | SNT | 26.09 (48/184) | [41] | ||||
| Yunnan | 2019 | ELISA | 47.78 (43/90) | [42] | ||||
| Indonesia | Java and Bali | 1979 | HIT | 1.1 (1/90) | [43] | |||
| Malaysia | Sarawak | 1962–1964 | HIT | 52 (205/395 ) | [44] | |||
| Sarawak | 1962–1964 | NT | 77 (210/272) | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Wang, H.; Liang, G. Getah Virus (Alphavirus): An Emerging, Spreading Zoonotic Virus. Pathogens 2022, 11, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080945
Li B, Wang H, Liang G. Getah Virus (Alphavirus): An Emerging, Spreading Zoonotic Virus. Pathogens. 2022; 11(8):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080945
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bin, Huanyu Wang, and Guodong Liang. 2022. "Getah Virus (Alphavirus): An Emerging, Spreading Zoonotic Virus" Pathogens 11, no. 8: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080945
APA StyleLi, B., Wang, H., & Liang, G. (2022). Getah Virus (Alphavirus): An Emerging, Spreading Zoonotic Virus. Pathogens, 11(8), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11080945






