Abstract
Aim: Understanding the prevalence of antibiotic resistance can provide reliable information for selecting treatment options. The goal of this meta-analysis was to observe the primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in different regions and time periods of China. Method: We searched PubMed, EMBASE, Chinese Biomedical databases and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure from inception to 20 February 2022. Data on the prevalence of H. pylori primary resistance at various time points were included. A random-effect model was established to calculate the pooled antibiotic resistance. Results: In total, 2150 articles were searched, with 70 meeting the inclusion criteria. The resistance to clarithromycin, metronidazole, levofloxacin amoxicillin, tetracycline and furazolidone in 2016–2020 were 34% (95% CI: 30–39%), 78% (95% CI: 73–84%), 35% (95% CI: 30–40%), 3% (95% CI: 1–5%), 2% (95%CI: 1–4%) and 1% (95% CI: 0–4%), respectively. Clarithromycin showed regional difference, as the resistance was higher in northern (37%, 95% CI: 32–41%) and western China (35%, 95% CI: 17–54%) than that in southern (24%, 95% CI: 17–32%) and eastern China (24%, 95% CI: 20–28%). Conclusion: The resistance of H. pylori to clarithromycin and metronidazole was high and increased over time, whereas resistance to levofloxacin, amoxicillin, tetracycline and furazolidone remained stable.
1. Introduction
Though decreasing in developed countries, the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is still high in China, causing a major health burden due to peptic ulcer disease complications and gastric cancer [1,2]. As an infectious disease, antibiotics-based therapies play a leading role in the treatment [3,4]. However, we face the serious challenge of high antimicrobial resistance because of the previous use of these antibiotics [5]. The primary antibiotic resistance decreases the efficiency of first-line treatment. The overall effect is dependent on both the cure rate with resistant strains and the proportion with resistance, especially clarithromycin and levofloxacin-containing regimen [6,7]. Empirical anti-H. pylori therapy is commonly used in current clinical practice instead of susceptibility-guided therapy which is unavailable in most of China. Therefore, obtaining high-quality local data and the antibiotic resistance pattern is needed to get good clinical outcomes [8]. In this study, we reviewed and analyzed primary antibiotic resistance rates of H. pylori in different regions and time periods in China over two decades to provide some guidance for selecting the first-line antibiotics.
2. Method
2.1. Search Strategy and Select Criteria
A search focused on the primary antibiotic resistance of H. pylori in the Chinese mainland population was done on Pubmed, Embase, the Chinese Biomedical (CBM) and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) from inception to 20 February 2022. The study was performed based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [9]. The search terms included were as follows: “Helicobacter pylori” and “China”, these search terms were combined with “Antibiotic resistance” and each individual antibiotic serially (“clarithromycin”, “metronidazole”, “levofloxacin”, “amoxicillin”, “furazolidone” and “tetracycline”).
In order to minimize selection bias, inclusion and exclusion criteria were established as follows: (1) the diagnosis of H. pylori infection must be based on at least one of the routine diagnostic methods (13C or 14C urea breath test, histology examination, rapid urease test or in vitro culture); (2) the patients had no use of Proton pump inhibitor, antibiotic or herbal medicine within the previous 2 weeks; (3) the patients did not receive H. pylori eradication therapy, which could exclude the influence of secondary drug resistance; (4) drug susceptibility was tested using the Agar dilution method, Epsilometer test (E-test), Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) or Kirby–Bauer (KB) disk diffusion method; (5) the patients were older than 18 years old; (6) the patients were mainland residents; (7) the articles must be original articles, not reviews or letters to editors. The inclusion of the article and data extraction were conducted by two authors. The disagreements were resolved by discussion between the two authors.
2.2. Data Extraction
Two authors (JN Chen and PH Li) extracted relevant information including: publication year, study period, source area, drug susceptibility method, number of patients enrolled and those with resistance of different antibiotics independently according to a standardized data extraction form. Yu Huang was responsible for the discordant results.
2.3. Statistics Analysis
Meta-analysis was performed for the primary antibiotic resistance of H. pylori in Chinese patients. In some studies, the H. pylori resistance rates were close to 0%. Therefore, Freeman–Tukey double arcsine transformation was used to process the data. Heterogeneity was tested by Cochran’s Q test and I² test (I2 < 25%, 25–75%, and I2 > 75% represents low, moderate and high heterogeneity, respectively). The DerSimonian and Laird random effect model was used to calculate the pooled rate and 95% confidence interval (CI). We used Egger’s test and Funnel plot to examine the potential heterogeneity. We calculated the mean annual percentage change and its confidence interval by calculating resistance rates between the earliest and most recent study periods available. For time period analysis, we divided the sample year into 4 groups based on their study period: before 2005, 2006–2010, 2011–2015 and 2016–2020. If the article spanned two time periods, we included it in its closest time periods. If the article included two or more time periods, we classified them separately. If the year of sample collection was not indicated in the study, 2 years before the publication of the article was defined as the study period [8]. For the region analysis, we divided China into four regions based on their geographical characteristics and matched each study, except the multicenter study, according to its urban location. All of the data analyses were performed using R version 4.1.0.
3. Results
We searched 2150 articles, and 70 articles were enrolled in the study (Figure 1). Among the included studies, 21 were from northern China, 27 were from eastern China, 8 were from southern China, 7 from western China and 7 studies were multicenter studies (Table 1).
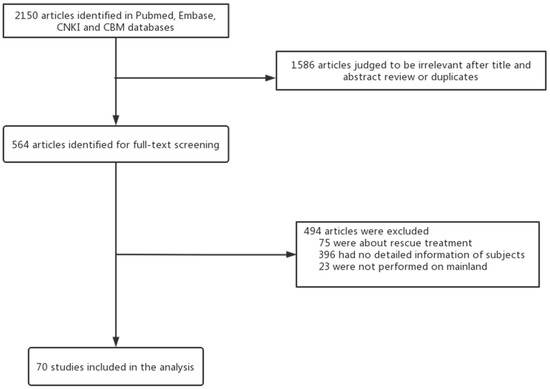
Figure 1.
Study selection.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the enrolled studies on resistance rate of H. pylori to antibiotics.
3.1. Primary Resistance of H. pylori to Clarithromycin
The clarithromycin resistance sharply increased from 15% (95% CI: 9–22%) before 2005 to 34% (95% CI: 22–48%) in 2016–2020 (p < 0.001, Figure 2 and Figure S1). Meanwhile, the prevalence of clarithromycin resistance in different regions was also detected. The clarithromycin resistance in northern (37%, 95% CI: 32–41%) and western China (34%, 95% CI: 17–54%) were higher than that in eastern (24%, 95% CI: 20–28%) and southern China (24%, 95% CI: 17–32%) (p = 0.0004, Figure S2).
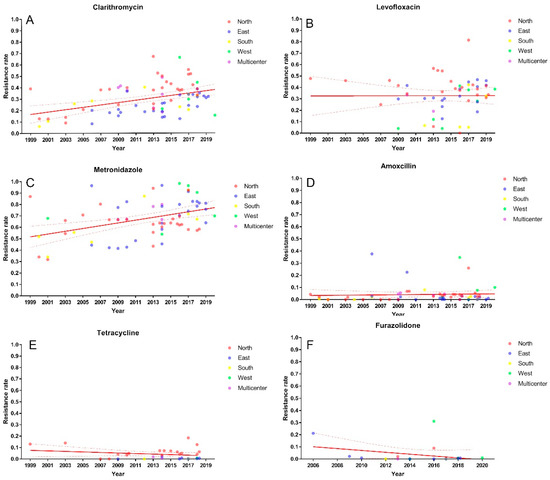
Figure 2.
Primary clarithromycin (A), metronidazole (B), levofloxacin (C), amoxicillin (D), tetracycline (E) and furazolidone (F) resistance of H. pylori in China.
Subsequent time period analysis of northern and eastern China showed an upward trend of clarithromycin resistance in both regions over the past 20 years, from 16% to 42% (p < 0.0001, Figure 3 and Figure S3) and from 20% to 30% (p = 0.008, Figure 3 and Figure S4), respectively.
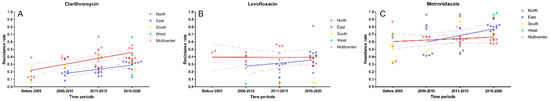
Figure 3.
Time trends of primary clarithromycin (A), metronidazole (B) and levofloxacin (C) resistance in different regions of China.
3.2. Primary Resistance of H. pylori to Metronidazole
The resistance rate of H. pylori to metronidazole steadily increased from 55% (95% CI: 44–65%) before 2005 to 78% (95% CI: 73–84%) in 2016–2020 (p = 0.0003, Figure 2 and Figure S5). Western China had the highest metronidazole resistance (83%, 95% CI: 65–95%), followed by eastern China (72%, 95% CI: 65–78%), southern China (68%, 95% CI: 54–82%) and northern China (64%, 95% CI: 60–68%). However, the difference did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.054, Figure S6).
Time period analysis was also performed. Despite the fact that no statistical difference was found in northern China (p = 0.279, Figure 3 and Figure S7), the metronidazole resistance showed a decreasing trend in the last 10 years, from 71% (95% CI: 63–78%) in 2006–2010 to 62% (95% CI: 57–67%) in 2016–2020. Similarly, no discrepancy was observed in eastern China within periods. However, the metronidazole resistance had increased from 63% (95% CI: 44–81%) to 79% (95% CI: 76–82%) numerically (p = 0.107, Figure 3 and Figure S8).
3.3. Primary Resistance of H. pylori to Levofloxacin
The levofloxacin resistance in China had decreased from 47% (95% CI: 35–58%) before 2005 to 24% (95% CI: 16%, 33%) in 2011–2015 but increased to 35% in 2016–2020 (95% CI: 30–40%) (p = 0.0186, Figure 2 and Figure S9). Regional variation had not been found with resistance estimates from northern (38%, 95% CI: 31–45%), eastern (32%, 95% CI: 27–37%), southern (21%, 95% CI: 10–36%) and western China (16%, 95% CI: 3–35%) (p = 0.087, Figure S10).
Further subgroup analysis showed there was no statistical difference of the levofloxacin resistance in northern China (p = 0.364, Figure 3 and Figure S11) and eastern China (p = 0.052, Figure 3 and Figure S12) during the same time periods.
3.4. Primary Resistance of H. pylori to Amoxicillin, Tetracycline and Furazolidone
The primary resistance of H. pylori to amoxicillin (3%), tetracycline (2%) and furazolidone (1%) were low (Figures S13–S15) and have remained relatively stable in the past two decades (Figure 3)
3.5. Influence of Gender on the Primary Resistance of H. pylori to Clarithromycin, Levofloxacin and Metronidazole
The level of resistance depending on the gender of patients was shown in Table S1. The results showed no difference in the resistance rates of clarithromycin (p = 0.5459), levofloxacin (p = 0.6522) or metronidazole (p = 0.2311) between male and female (Figures S16–S18).
3.6. Meta-Regression Analysis of Antibiotics Resistance of H. pylori
Meta-regression analysis including regions, time periods and method was performed (Table 2) and indicated that compared with northern China and western China, eastern China (Difference: −0.23; 95% CI: −0.32, −0.14; p < 0.0.0001) and southern China (Difference: −0.17; 95% CI: −0.29, −0.05; p = 0.0066) had a lower risk of clarithromycin resistance. Southern China had the lowest levofloxacin resistance (Difference: −0.22; 95% CI: −0.40, −0.04; p = 0.0174).

Table 2.
Multivariate meta-analysis of antibiotics resistance of H. pylori in China.
A positive correlation could be found between time periods and clarithromycin resistance based on multivariate analysis (p < 0.0001). Metronidazole resistance was higher in 2016–2020 (Difference: 0.22; 95% CI: 0.09, 0.35; p = 0.0009) than that before 2005.
The method of the susceptibility test might also affect the results. Sub-analysis showed (Figures S19–S24) the choice of susceptibility test method might affect the resistance rate of levofloxacin (p = 0.0013), amoxicillin (p < 0.0001), tetracycline (p < 0.0001) and furazolidone (p = 0.0293) rather than that of clarithromycin (p = 0.4019) and metronidazole (p = 0.0565). Further multivariate regression analysis demonstrated that compared with the agar dilution method, the disk diffusion method might overestimate the resistance rate of metronidazole (Difference: 0.13; 95% CI: 0.00, 0.25; p = 0.0417) and amoxicillin (Difference: 0.23, 95% CI: 0.15, 0.30; p < 0.0001) but underestimate that of levofloxacin (Difference: −0.21; 95%CI: −0.36, −0.06; p = 0.007). Meanwhile, E-test might overestimate the resistance rate of amoxicillin (Difference: 0.11; 95% CI: 0.01, 0.20; p = 0.0269) and tetracycline (Difference: 0.07; 95% CI: 0.01, 0.13; p = 0.0264) when compared with the agar dilution method.
4. Discussion
Supervising the prevalence of primary antibiotic resistance in a region can provide reliable information for the choice of treatment options [8].
In our study, we showed the mean overall resistance of H. pylori in China to clarithromycin, metronidazole and levofloxacin was 30.0%, 70.0% and 31.0% and increased over time, but that of amoxicillin, tetracycline and furazolidone was 3.0%, 3.0% and 1.0%, respectively, and remained low during these years.
H. pylori has similar characteristics of clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance with a clear mechanism by some certain gene mutation (23S rRNA and gyrA, respectively), which has an all-or-none effect on the efficacy. That means that the efficacy of treatment does not improve by increasing dose and duration [80,81,82]. Our study showed that the clarithromycin resistance in China has now reached 34%, while it seemed lower in eastern (24%) and southern China (24%). The levofloxacin resistance rate is currently 31%. Lower resistance could be found in the western China. In contrast, an increasing trend could be observed in eastern China, from 25% in 2011–2015 to 37% in 2016–2020. The resistance of clarithromycin and levofloxacin are both above the threshold of empirical use of these antibiotics.
Metronidazole, a class of nitroimidazole compound, is different from clarithromycin and levofloxacin, and the mechanism of resistance is not completely clarified at present. Meanwhile, different susceptibility methods or culture methods also affected the results as our previous work demonstrated that the resistance might be overestimated by E-test when compared with agar dilution in the area with high-level metronidazole resistance [83]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the resistance can be overcome by a high dose and long duration [80,84]. Our data showed that the resistance of metronidazole was 70%, ranging from 64 to 83% in different regions. It was noticeable that the metronidazole resistance in northern China had decreased from 71% to 62% in these years.
The overall primary resistance rate of H. pylori to amoxicillin, tetracycline and furazolidone remained low, and all of them were lower than 5%, with the exception of a few studies that reported higher rates of resistance.
Other studies from Asia, Europe and Latin America have also reported primary resistance of H. pylori, which was lower than that in China, as these data showed that clarithromycin resistance ranged from 12 to 21.4%, levofloxacin resistance ranged from 15 to 18% and metronidazole resistance ranged from 38.9 to 53% with an increasing trend over time.
The increasing resistance to clarithromycin, levofloxacin and metronidazole might be contributed to by the increasing consumption of these antibiotics and cross resistance to the corresponding antibiotics. Megraud et al. reported that the community consumption of these antibiotics was associated with its corresponding H. pylori resistance in European countries [5]. Similarly, Yang et al. found that the macrolide and quinolones ranked third and fourth in consumption of antibiotics, respectively, in China during 2018–2020 [85]. There are no definitive data on imidazole consumption in China. However, since metronidazole was produced in the 1960s, it had been widely used in the treatment of anaerobic infections in China. Compared with macrolide and quinolone, imidazole has been present in the community for a longer time, which has led to a high metronidazole resistance in China.
The success rate of clarithromycin-containing triple therapy has been reported less than 80% in China [86]. The addition of bismuth to the triple therapy, which has been recommended as a first-line therapy, improves cure rates despite a high prevalence of antimicrobial resistance. The effect of bismuth is to attain an additional 30–40% in the success with resistant infections [87]. The rising resistance to clarithromycin and levofloxacin can severely reduce the efficacy of this modified quadruple therapy failing to reach a 90% success rate. For metronidazole, resistance has no clinical significance since it can be overcome after increasing the dosage and prolonging the duration [80]. At present, amoxicillin is widely used in clinical practice, as long as patients have no allergic reaction. Despite the poor accessibility in China, tetracycline combined with metronidazole is often used as a first-line therapy in areas with high clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance [3]. Furazolidone is a special drug, which is widely used in China due to its low resistance rate. Although it may be accompanied by adverse reactions such as peripheral neuritis, the treatment success rate is high [88].
There are still limitations in our review. Firstly, since it was a single rate meta-analysis, there was obvious heterogeneity among different studies. Second, most of the enrolled studies were from northern and eastern China and data from other regions was lacking, thus causing potential publication bias.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens11070786/s1, Figure S1: Clarithromycin [By period]; Figure S2: Clarithromycin [By region]; Figure S3: Clarithromycin [North China]; Figure S4: Clarithromycin [East China]; Figure S5: Metronidazole [By period]; Figure S6: Metronidazole [By region]; Figure S7: Metronidazole [North China]; Figure S8: Metronidazole [East China]; Figure S9: Levofloxacin [By period]; Figure S10: Levofloxacin [By region]; Figure S11: Levofloxacin [North China]; Figure S12: Levofloxacin [East China]; Figure S13: Amoxicillin [By period]; Figure S14: Tetracycline [By period]; Figure S15: Furazolidone [By period]; Figure S16: Clarithromycin [By gender]; Figure S17: Levofloxacin [By gender]; Figure S18: Metronidazole [By gender]; Figure S19: Clarithromycin [By method]; Figure S20: Levofloxacin [By method]; Figure S21: Metronidazole [by method]; Figure S22: Amoxicillin [by method]; Figure S23: Tetracycline [by method]; Figure S24: Furazolidone [by method]; Table S1: Characteristics of the enrolled studies on resistance rate of H. pylori to antibiotics based on Gender.
Author Contributions
H.L. conceived the study. J.C. and P.L. wrote the protocol and collected data. J.C. and Y.H. performed the systematic review. P.L., Z.D. and Y.G. did the statistical analysis. J.C. and P.L. wrote the article, which was revised by H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81970497).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; de Martel, C.; Charvat, H.; Clifford, G.M.; Vaccarella, S.; Wang, L. Time trends and other sources of variation in Helicobacter pylori infection in mainland China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, P.; Johansson, S.; Molloy-Bland, M. Systematic review of time trends in the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in China and the USA. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—The Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megraud, F.; Bruyndonckx, R.; Coenen, S.; Wittkop, L.; Huang, T.-D.; Hoebeke, M.; Bénéjat, L.; Lehours, P.; Goossens, H.; Glupczynski, Y. Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics in Europe in 2018 and its relationship to antibiotic consumption in the community. Gut 2021, 70, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y. Hp-normogram (normo-graham) for Assessing the Outcome of H. pylori Therapy: Effect of Resistance, Duration, and CYP2C19 Genotype. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Lee, S.Y. How to Effectively Use Bismuth Quadruple Therapy: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Gastroenterol. Clin. North. Am. 2015, 44, 537–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-T.; Liou, J.-M.; El-Omar, E.M.; Wu, J.-Y.; Leow, A.H.R.; Goh, K.L.; Das, R.; Lu, H.; Lin, J.-T.; Tu, Y.-K.; et al. Primary antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori in the Asia-Pacific region: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Cheng, H.; Hu, F.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.; Zheng, X. The evolution of Helicobacter pylori antibiotics resistance over 10 years in Beijing, China. Helicobacter 2010, 15, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Zhou, L.Y.; Song, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; He, L.H.; Ding, Y. Primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from patients with dyspeptic symptoms in Beijing: A prospective serial study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Qi, D.; Kang, J.; Jin, Y.; Liu, W.; Gao, W.; Hou, P.; Lu, J. Efficacy of real-time PCR-based detection of Helicobacter pylori infection and genotypic resistance-guided quadruple therapy as the first-line treatment for functional dyspepsia with Helicobacter pylori infection. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, P.; Zhou, L.Y.; Xiao, X.M.; Luo, Y.; Ding, Y. Susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori to antibiotics in Chinese patients. J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 16, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Zhou, L.Y.; Song, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; He, L.H.; Ding, Y.; Bai, P. Analysis of Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori Isolates Cultured from Endoscopic Gastric Mucosal Samples. Chin. J. Minim. Invasive Surg. 2015, 15, 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Suo, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L. Rabeprazole, Minocycline, Amoxicillin, and Bismuth as First-Line and Second-Line Regimens for Helicobacter pylori Eradication. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Teng, G.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, H.; Gao, W.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. The effect of previous eradication failure on antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori: A retrospective study over 8 years in Beijing. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; He, L.; Bai, P.; Xue, Y. Hybrid Therapy as First-Line Regimen for Helicobacter pylori Eradication in Populations with High Antibiotic Resistance Rates. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, B.J.; Tian, X.L.; Li, C.L.; Song, Z.Q. Dual therapy with rabeprazole and amoxicillin four times daily for 14 days for the first-line eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Natl. Med. J. China 2019, 99, 3781–3785. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, B.J.; Tian, X.L.; Li, C.L.; Song, Z.Q. Optimized Concomitant Therapy for the First-line Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Chin. Pharm. J. 2020, 55, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Song, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xue, Y.; Ding, Y.; Suo, B.; Tian, X.; Wang, L. Randomized Clinical Trial: Esomeprazole, Bismuth, Levofloxacin, and Amoxicillin or Cefuroxime as First-Line Eradication Regimens for Helicobacter pylori Infection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Gao, H.; Huang, Y.B.; Zhou, J.; Wang, D.X.; Luan, W.H. Clinical efficacy of compound Lactobacillus acidophilus combined with conventional quadruple therapy in treatment of peptic ulcer induced by Helicobacter pylori infection. Chin. J. Nosocomiology 2017, 27, 2932–2934. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Fu, W.; Zhou, L. Cefuroxime, levofloxacin, esomeprazole, and bismuth as first-line therapy for eradicating Helicobacter pylori in patients allergic to penicillin. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Xue, Q.; Xian, H.P.; Sun, Y.J.; Zhao, X.T.; Wang, J.T. Tailored therapy in treatment of Helicobacter pylori infectionbasedon clarithromycinsensitivity. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019, 99, 2826–2830. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xue, Y.; Suo, B.; Tian, X.; Niu, Z. A comparative study of 14-day dual therapy (esomeprazole and amoxicillin four times daily) and triple plus bismuth therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori infection eradication: A randomized trial. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Song, Z.; Suo, B.; Tian, X.; Xue, Y.; Meng, L.; Niu, Z.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L. Correlation Analysis Among Genotype Resistance, Phenotype Resistance and Eradication Effect of Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Du, S.-Y.; Fang, L.; Fan, Y.-H.; Song, A.-P.; Chen, H. Eradication Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection Based on Molecular Pathologic Antibiotic Resistance. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, G.; Wu, J.; Kong, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, X.; Ji, C.; Yang, L. Antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates in Hebei Province. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 96, 270–272. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Dong, Q.; Sun, G. Prevalence and genetic features of multi-drug resistant Helicobacter pylori strains from Qingdao. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2015, 36, 3583–3585. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Guo, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Gong, Y. The antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori to five antibiotics and influencing factors in an area of China with a high risk of gastric cancer. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Guo, R.; Dong, Q.J.; Yu, X.J.; Sun, G.R. Features and influencing factors of rdxA mutation in metronidazole-resistant Helicobacter pylori. Chin. J. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 33, 494–497. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Q.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.P.; He, W.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Y.J.; Gu, E.L.; Gu, L.X. Investigation of Primary Antibiotic-resistance Patterns of Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated from Patients in Shanghai Central City Proper. Chin. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 12, 609. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.H.; Yang, X.T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.R. Clinical analysis of resistance of Hp isolates to five antibiotics. J. Tongji Univ. 2009, 30, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Chen, W.J.; Lu, H.; Sun, Q.J.; Xiao, S.D. Comparison of the efficacy of triple versus quadruple therapy on the eradication of Helicobacter pylori and antibiotic resistance. J. Dig. Dis. 2010, 11, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Liang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, W.; Xiao, S.; Gu, W.; Lu, H. High efficacy of 14-day triple therapy-based, bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for initial Helicobacter pylori eradication. Helicobacter 2010, 15, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y. Study on antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori isolated in Qingpu District, Shanghai. Chin. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 16, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Huo, H.; Wu, M.; Jiang, X. Role of drug sensitivity test in the triple therapy for eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Chin. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 15, 358–360. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Q.; Liao, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W. Evaluation of bismuth-clarithromycin-containing quadruple therapy for initial Helicobacter pylori eradication. Chin. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 17, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Zheng, Q.; Liang, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Q.; Liu, W.; Xiao, S.; Graham, D.Y.; Lu, H. Effect of fluoroquinolone resistance on 14-day levofloxacin triple and triple plus bismuth quadruple therapy. Helicobacter 2013, 18, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhao, F.; Wang, S.; Olszewski, M.A.; Bian, H.; Wu, Y.; Kong, M.; Xu, L.; Miao, Y.; Fang, Y.; et al. A high-throughput multiplex genetic detection system for Helicobacter pylori identification, virulence and resistance analysis. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X.; Liu, W.; Xiao, S.; Graham, D.Y.; Lu, H. Bismuth, lansoprazole, amoxicillin and metronidazole or clarithromycin as first-line Helicobacter pylori therapy. Gut 2015, 64, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, Q.; Long, X.; Liang, X.; Lu, H. Weifuchun Tablet or Bismuth Combined with Standard Triple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Clinical Trial. Chin. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 22, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Chen, Q.; Yu, L.; Liang, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, H. Bismuth improves efficacy of proton-pump inhibitor clarithromycin, metronidazole triple Helicobacter pylori therapy despite a high prevalence of antimicrobial resistance. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Long, X.; Ji, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, D.; Gao, H.; Xu, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Randomised controlled trial: Susceptibility-guided therapy versus empiric bismuth quadruple therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Luo, L.; Long, X.; Liang, X.; Ji, Y.; Graham, D.Y.; Lu, H. High-dose PPI-amoxicillin dual therapy with or without bismuth for first-line Helicobacter pylori therapy: A randomized trial. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Ji, Y.; Yu, L.; Lu, H. Susceptibility-guided therapy for Helicobacter pylori-infected penicillin-allergic patients: A prospective clinical trial of first-line and rescue therapies. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Q.; Zhou, F.; Wu, X.X.; Lu, J.; Cao, Q. Study on the role of Berberine combined with Quadruple therapy in initial Helicobacter pylori eradication. China Med. Her. 2020, 17, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Ji, Y.; Yu, L.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Graham, D.Y.; Lu, H. 14-Day High-Dose Amoxicillin- and Metronidazole-Containing Triple Therapy with or Without Bismuth as First-Line Helicobacter pylori Treatment. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.F.; Ma, H.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Che, H.B. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics in patients with upper gastrointestinal diseases. Mod. Pract. Med. 2007, 19, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Shi, Z.; Lin, D.; Yang, N.; Meng, F.; Lin, L.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Is tailored therapy based on antibiotic susceptibility effective? A multicenter, open-label, randomized trial. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Che, H.B. Analysis on antibiotic resistance and related gene mutations of Helicobacter pylori in Jinhua area, Zhejiang. Int. J. Epidemiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 45, 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Chen, Z.-X.; Li, P.; He, X.-L. Drug resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Zhejiang: Comparison of three methods for detection of drug resistance. World Chin. J. Dig. 2018, 26, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liang, J.C.; Guo, F.; Wu, F.; Jin, J. Clinical value of fecal 23S rRNA gene detection for Helicobacter pylori infection and assessment of its resistance to clarithromycin. Zhejiang Med. J. 2021, 43, 606–610. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Hao, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G. Efficacy of 1st-line bismuth-containing quadruple therapies with levofloxacin or clarithromycin for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection: A 1-week, open-label, randomized trial. Medicine 2017, 96, e5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.-D.; He, B.-S.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wang, S.-K.; Ran, D.; Wang, Z.-B. Analysis of the Primary and Post-Treatment Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori in the Nanjing Area. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.D.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.; Ran, D.; Wang, Z.B.; Xu, X.J.; Wang, W.H.; Lin, H.H.; Xu, X.; Kong, C.M.; et al. Analysis of current status and trend of Helicobacter pylori antibiotics resistance over 5 years in Nanjing area. Chin. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 29, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.-S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhu, Z.-H.; Zhang, S.-H.; Zhu, X.; Wan, J.-H.; Lu, N.-H.; Xie, Y. Characteristics of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance: Data from four different populations. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Shu, X.; Liu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, A.; Xiong, H.; Zeng, H.; et al. Antibiotic resistance and CYP2C19 polymorphisms affect the efficacy of concomitant therapies for Helicobacter pylori infection: An open-label, randomized, single-centre clinical trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.G.; Hu, P.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.X.; Peng, Z.S.; Tan, J.T. Investigation of the resistance of Helicobacter pylori to three antibiotics in Guangdong province. New Chin. Med. 2002, 33, 275–277. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zou, A.; Wu, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, F.; Zou, B.; Wang, J. Application of Visual Gene Clip-Based Tailored Therapy for the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6150628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; He, W.D.; Xu, T.L. Efficacy analysis of drug resistance of Helicobacter pylori and quadruple empirical eradication regimen containing bismuth. China Pract. Med. 2018, 13, 108–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, T.; Ni, L.; Wu, J.; Situ, W.J.; Li, Y.P.; Yang, Q.; Yu, X.Q.; Wu, J.W.; Lv, Z.W.; Liu, J.; et al. A multicentre study of Helicobacter pylori eradication rate change and drug resistance analysis in Shenzhen. Chin. J. Dig. 2020, 40, 557–561. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Z.; Li, X.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Marshall, B.; Tay, A. Analysis of antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Shenzhen area. Electron. J. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, H.L.; Mao, W.H.; Chen, R.L.; Chen, M.H.; Wu, F.; Fu, D.; Pan, X.Z.; Peng, X.W. Comparison of antibiotic resistance of H.pylori between rural island and urban area in Fujian province. Cent. Plains Med. J. 2007, 34, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.-J.; Zeng, X.-P.; Jiang, C.-S.; Liu, G.; Li, D.-Z.; Wang, W. Antofloxacin-based bismuth quadruple therapy is safe and effective in Helicobacter pylori eradication: A prospective, open-label, randomized trial. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 22, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-H.; Liu, D.-H.; Pan, M.-Y.; Lian, H.-Y. Analysis of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance in Liuzhou, China. World Chin. J. Dig. 2013, 21, 3314–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Resistance to Levofloxacin in the Western Area of Chongqing. China Pharm. 2014, 25, 4589–4591. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Wang, T.-Y.; Wang, X.-W.; Chen, D.-F.; Lan, C.-H. Eradication Efficacy of Modified Dual Therapy Compared with Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy as a First-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G. Epidemiological Investigation and Drug Resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Western Chongqing Region. China Pharm. 2018, 27, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Yang, T.; Hu, R.; Debowski, A.W.; Stubbs, K.A.; Benghezal, M.; Marshall, B.J.; Li, H.; et al. Primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori among a Chinese Tibetan population. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.G.; Guo, B.G. Analysis of regional drug resistance in H. pylori-related atrophic gastritis. Hainan Med. J. 2021, 32, 571–573. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-F.; Nan, Q.; Jiang, H.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.-Y.; Duan, L.-P.; Chen, Y.-R. Study on metronidazole resistance to Helicobacter pylori from three populations with different ethnics in Yunnan. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi 2004, 25, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Liu, K.Q.; Yu, M.; Qiu, J.; Tang, Y. Study on Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Qujing City. China Contin. Med. Educ. 2020, 12, 138–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Hou, X.; Li, Z.; Song, Z.; He, L.; Lin, S. A comparative study of sequential therapy and standard triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: A randomized multicenter trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, E.X.; Zhou, L.Y. Impact of minimal inhibitory concentration breakpoint of amoxicillin and clarithromycin on the efficacy of these containing regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Chin. J. Dig. 2021, 41, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, L.; Chen, M.; Hou, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L. Prospective multi-region study on primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from Chinese patients. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, H.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Lv, N. Ten-Day Quadruple Therapy Comprising Low-Dose Rabeprazole, Bismuth, Amoxicillin, and Tetracycline Is an Effective and Safe First-Line Treatment for Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Population with High Antibiotic Resistance: A Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized, Parallel-Controlled Clinical Trial in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00432-18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; et al. New single capsule of bismuth, metronidazole and tetracycline given with omeprazole versus quadruple therapy consisting of bismuth, omeprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in duodenal ulcer patients: A Chinese prospective, randomized, multicentre trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Z.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, J.; Bai, P.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S. Tailored versus Triple plus Bismuth or Concomitant Therapy as Initial Helicobacter pylori Treatment: A Randomized Trial. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.-S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zeng, Z.-R.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Lu, H.; Xu, J.-M.; Du, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.-B.; Xu, S.-P.; et al. Primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Chinese patients: A multiregion prospective 7-year study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 780.e5–780.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, M.P.; Lu, H.; Graham, D.Y. Role of bismuth in improving Helicobacter pylori eradication with triple therapy. Gut 2016, 65, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Suzuki, H. Update on quinolone-containing rescue therapies for Helicobacter pylori infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.E. Pathophysiology of antibiotic resistance: Clarithromycin. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 14, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Liang, X.; Lu, H. E-Test or Agar Dilution for Metronidazole Susceptibility Testing of Helicobacter pylori: Importance of the Prevalence of Metronidazole Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 801537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, L.; Evans, E.L. Meta-analysis: The effect of antibiotic resistance status on the efficacy of triple and quadruple first-line therapies for Helicobacter pylori. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Geng, X.; Liu, X.; Wen, X.; Wu, R.; Cui, D.; Mao, Z. Antibiotic Use in China’s Public Healthcare Institutions During the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Analysis of Nationwide Procurement Data, 2018–2020. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 813213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Lu, N.H. Review: Clinical management of Helicobacter pylori infection in China. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.Z.; Xie, Y.; Lu, H.; Cheng, H.; Zeng, Z.R.; Zhou, L.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.B.; Du, Y.Q.; Lu, N.H.; et al. Fifth Chinese National Consensus Report on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhao, R.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y. Furazolidone treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).