Abstract
Tospoviruses infect numerous crop species worldwide, causing significant losses throughout the supply chain. As a defence mechanism, plants use RNA interference (RNAi) to generate virus-derived small-interfering RNAs (vsiRNAs), which target viral transcripts for degradation. Small RNA sequencing and in silico analysis of capsicum and N. benthamiana infected by tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) or capsicum chlorosis virus (CaCV) demonstrated the presence of abundant vsiRNAs, with host-specific differences evident for each pathosystem. Despite the biogenesis of vsiRNAs in capsicum and N. benthamiana, TSWV and CaCV viral loads were readily detectable. In response to tospovirus infection, the solanaceous host species also generated highly abundant virus-activated small interfering RNAs (vasiRNAs) against many endogenous transcripts, except for an N. benthamiana accession lacking a functional RDR1 gene. Strong enrichment for ribosomal protein-encoding genes and for many genes involved in protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum suggested co-localisation of viral and endogenous transcripts as a basis for initiating vasiRNA biogenesis. RNA-seq and RT-qPCR-based analyses of target transcript expression revealed an inconsistent role for vasiRNAs in modulating gene expression in N. benthamiana, which may be characteristic of this tospovirus-host pathosystem.
1. Introduction
Tospoviruses are taxonomically classified in the genus Orthotospovirus, family Tospoviridae, order Bunyavirales [1]. In targeting more than 1090 species in 85 families of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants, tospoviruses cause severe production losses in crops worldwide [2]. Capsicum chlorosis virus (CaCV) and tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) are two tospoviruses of significance across Asia and Australia, impacting many horticultural species in warmer climates [3]. Thrips (Frankliniella and Thrips species) are the primary transmission vectors for these tospoviruses and are also replication hosts, though without associated symptoms [4].
Both CaCV and TSWV have single-stranded RNA genomes that comprise five open reading frames across three segments, with one negative-sense and two ambisense. The small (S) RNA encodes a non-structural RNA-silencing suppressor protein (NSs) and the nucleocapsid protein (N). The medium (M) RNA encodes a cell-to-cell movement protein (NSm) and the precursor of the two envelope glycoproteins (GP), with the Large (L) RNA coding for an RNA-directed RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called L protein [5,6].
Viral RNAs act as both a substrate for and target of the host plant’s RNA interference (RNAi) defence pathways, leading to viral lifecycle disruption through specific transcript degradation. Double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) arising from processes such as viral replication are cleaved by Dicer-like enzymes into virus-derived small-interfering RNA (vsiRNA) duplexes of primarily 21 and 22 nucleotides (nt) [7]. VsiRNAs are then bound by AGO proteins as part of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which subsequently degrades complementary transcripts. Once initiated, secondary vsiRNAs can also be generated via the actions of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RDRs), with an associated amplification of silencing through second-strand synthesis from a single-stranded RNA template. Generation of vsiRNAs in response to TSWV infection has previously been demonstrated in multiple plant hosts, including peanut (Arachis hypogaea; Fabaceae), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum; Solanaceae), and Nicotiana benthamiana (Solanaceae) [8,9,10].
As well as targeting viral transcripts, the plant’s RNAi machinery has several roles in endogenous gene regulation, acting both transcriptionally and post-transcriptionally. Recently, multiple studies have revealed that virus infection triggers the biogenesis of siRNAs targeting host transcripts (termed virus-activated small interfering RNAs, vasiRNAs), in addition to vsiRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana [11,12,13]. VasiRNA biogenesis was observed following inoculation with a cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) mutant carrying a non-functional 2b suppressor of RNA silencing gene and additionally with turnip mosaic virus (TuMV), which encodes a weak silencing suppressor. The 2b protein is thought to reduce vsiRNA abundance by direct sequestration of these siRNA species [14]. Though RDR6, along with RDR1, amplify the RNAi response through the generation of dsRNA from a viral RNA template, vasiRNA production appears to be exclusively RDR1-dependent. Gou and collaborators demonstrated that the P-type ATPases ALA1 and ALA2, which transport phospholipids across cellular membranes, are also essential for vasiRNA production [12]. The authors suggested ALA1 and ALA2 have a role in the formation of vesicle-like membrane invaginations around dsRNA precursors. Further work by the same group identified Antiviral RNAi-defective 2 (AVA2), a putative magnesium transporter, as an additional requirement for vasiRNA biogenesis. AVA2 is also localised to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), similar to ALA1 and ALA2 [13]. More recently, vasiRNAs have been detected in TuMV infection sites in Brassica napus leaves, with demonstrated roles in cleavage of host as well as viral transcripts [15]. Interestingly, infection of Arabidopsis, Brassica rapa, and Brassica napus by cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV), a double-stranded DNA virus, also produced vasiRNAs [16]. Target host transcripts identified in that study functionally overlapped with those previously identified by Cao and collaborators for CMV infection, with roles in photosynthesis and stress response [11,16].
Following their identification and characterisation in the Brassicaceae, the search for vasiRNAs was extended to solanaceous species. Initially, a lack of detectable vasiRNAs in TSWV-infected N. benthamiana was reported [17]. The authors noted that the presence or absence of a functional NSs protein did not impact vasiRNA abundance and speculated that either a defective RDR1 in the N. benthamiana accession used or differences between CMV 2b and TSWV NSs vasiRNA sequestration might be responsible. Using a transgenic approach, the addition of a functional RDR1 to the N. benthamiana accession used resulted in the generation of vasiRNAs following tomato leaf curl Gujarat virus infection, and as with the Brassicaceae species, differential regulation of target genes [18].
In this study, vsiRNA and vasiRNA responses to TSWV and CaCV infection were examined using next-generation sequencing of solanaceous species including N. benthamiana and capsicum (Capsicum annum). N. benthamiana varieties with and without the ability to generate vasiRNAs were used to shed light on the role of vasiRNAs in disease progression as well as endogenous host gene regulation. For each of the species examined, abundant vsiRNA biogenesis against both TSWV and CaCV was evident. In hosts with a functional RDR1, vasiRNA generation was also robust, with localisation of substrate host transcripts proposed as a selective mechanism. Interestingly, the generation of vasiRNAs in N. benthamiana did not result in a general downward trend in target host gene expression attenuation, suggesting many competing factors impact the expression of these genes during infection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Host Plants and Tospovirus Isolates
CaCV isolate QLD-3432, provided by the Queensland Department of Agriculture and Fisheries (DAF), was maintained in capsicum (Capsicum annuum) cv. Yolo Wonder, with the genome of this isolate previously sequenced [19]. TSWV isolate QLD-1 infected capsicum samples were also provided by DAF. This isolate was collected from Bowen, the same region as an Australian isolate that was recently sequenced [20]. C. annuum cv. Yolo Wonder, Nicotiana benthamiana LAB, and N. benthamiana Western Australia (WA; provided by Peter Waterhouse laboratory at the Queensland University of Technology) were used as host plants. All plant material described here was used for TSWV-infection and/or CaCV-infection assays, small RNA sequencing, and RNA-seq.
In this study, small RNA read data from susceptible (Marglobe) and resistant (Red Defender) tomato varieties following TSWV infection were also reanalysed. Red Defender’s resistance is associated with hypersensitivity induced by the Sw-5 gene [21]. The generation of this read data, including plant growth conditions, inoculation methodology, symptoms, and extraction of total RNA, has previously been described [9].
2.2. Virus Inoculations
Capsicum at the four-leaf stage and N. benthamiana at the five-six leaf stage were mechanically inoculated with homogenates from TSWV (QLD-1) or CaCV (QLD-3432) infected plant tissue of the same species. For mechanical inoculation, one or two apical leaves from a systemically infected symptomatic plant were homogenised with chilled mortar and pestle in 10 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) containing 0.4% 2-mercaptoethanol and rub-inoculated to carborundum-dusted leaves of host/test plants.
The youngest two leaves of capsicum plants and leaves two and three of N. benthamiana plants were virus-inoculated. As a negative control, sap from non-infected plants was used for mechanical inoculation (mock treatment). At least three plants were used for each treatment. Virus infection of plants was confirmed by the progression of symptoms, qPCR or DAS-ELISA using TSWV or CaCV kits from Agdia, Inc. (Elkhart, IN, USA) and following the manufacturer’s instructions. Plant images showing symptoms were processed using Adobe Lightroom Classic (v11.4, Adobe, San Jose, CA, USA) to ensure the evenness of exposure and white balance.
2.3. RNA Extraction and Quality Assessment
For all capsicum and N. benthamiana treatments, apical leaf tissue was collected ten days after mechanical inoculation, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C. Tissue was subsequently ground with a chilled mortar and pestle, and total RNA was extracted using TRIsure™ reagent (Bioline, Memphis, TN, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA samples were suspended in nuclease-free water, and the quantity and purity were determined using a NanoDrop™ spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The quality of the RNA was assessed by the Australian Genome Research Facility (AGRF, Brisbane, Australia) using a Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.4. Sequencing Methods
Capsicum and N. benthamiana RNA samples were submitted to AGRF for small RNA sequencing. Small RNA libraries were prepared using the New England Biolabs (Ipswich, UK) kit protocol and selecting for RNA of 18–33 nucleotides (nt). Illumina HiSeq HT Chemistry was used with 50 bp single reads. Samples were distributed across three flow cells. Small RNA sequencing of tomato samples has previously been described [9].
To examine differential expression of vasiRNA targets, RNA-seq was performed on total RNA from apex tissues of N. benthamiana LAB and WA accessions 10 days after TSWV or mock inoculation. RNA-seq of N. benthamiana samples was conducted by Genewiz, with non-strand specific library preparation carried out prior to generation of approximately 20 M paired-end reads per sample on a NovaSeq platform. Raw sequence data is available at the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under BioProject ID PRJNA784690.
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
Small RNA deep sequencing read files were processed with the FASTX-Toolkit (http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit/, accessed on 1 December 2021) to remove 5′ adapters and collapse reads to unique sequence:count couplets. Reads were aligned to TSWV and CaCV genome segments and endogenous transcript sequences using the SCRAM aligner [22]. Profile and comparison plots were generated using the SCRAM pipeline, with differential vasiRNA read abundance calculated using DeSeq2. Boxplots and Venn diagrams were generated using R and Python, respectively. Tomato small RNA sequence data was obtained from the NCBI SRA (BioProject PRJNA606610) and processed using the same bioinformatics pipeline. Large RNA-seq reads were trimmed with Trim Galore (https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore, accessed on 1 December 2021), and then vasiRNA-target transcript abundance was quantified with Kallisto [23]. Plots were generated using Python scripts. Genome alignments of short reads were carried out using Bowtie [24], with no mismatches allowed.
KEGG pathway analysis involved identifying transcripts that had significant differences in complementary vasiRNAs (p < 10−8) for TSWV-infected and mock-inoculated capsicum, tomato (Marglobe), and N. benthamiana (WA genotype) samples. For each differentially expressed (DE) transcript, the longest open reading frame (ORF) was identified and translated to a peptide using a custom Python script. Peptides were assigned KEGG identifiers using BLASTKoala [25]. These identifiers, along with log-fold change values for each species, were analysed using Pathview [26], which classified the ‘protein processing in ER’ and ‘ribosome’ pathways as significantly enriched for vasiRNA DE transcripts. Figures were generated by Pathview with custom colour and limit settings.
2.6. RT-qPCR Analysis
RNA samples were first treated with TURBO DNase I™ (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA) and reactions terminated with 15 mM EDTA. cDNA was synthesised using the sensiFAST™ cDNA synthesis kit with 1.88 mM MgCl2 added to sequester additional EDTA from DNase treatment (Bioline, Memphis, TN, USA). Changes in transcript abundance were calculated for mock vs. infected samples as −ΔΔCt to meet the assumptions of the statistical tests used. As an RT- control to rule out genomic DNA contamination, RNA samples underwent PCR with MyTaq™ DNA polymerase (Bioline, Memphis, TN, USA), with no amplification evident. Primers used for qPCR are shown in Table S2.
3. Results
3.1. Tospovirus Infection of Solanaceous Plants
Responses to CaCV or TSWV infection were investigated in two host plant species of the Solanaceae family: capsicum and N. benthamiana. Of the two N. benthamiana genotypes, N. benthamiana WA had previously unknown TSWV susceptibility, and N. benthamiana LAB with a non-functional RDR1 is considered susceptible to many plant viruses, including TSWV [27,28].
Following TSWV or CaCV inoculation in capsicum, mild leaf mottling and yellowing symptoms were evident compared to mock-inoculated plants at 10 dpi (Figure S1C). CaCV and TSWV RNA accumulation in non-inoculated apical leaf tissue was measured by RT-qPCR and confirmed systemic virus infection of inoculated plants (Figure S5A).
Like tospovirus-challenged capsicum plants, N. benthamiana LAB showed mild symptoms with CaCV or TSWV infection compared to the mock treatment (Figure S1A). Correspondingly, the symptoms of N. benthamiana WA infected with TSWV were also mild compared to mock treatments (Figure S1B). Both the N. benthamiana WA and LAB accessions showed mild leaf curling and mottling (Figure S1A,B). N. benthamiana WA and LAB plants also had similar viral titres as assessed by RT-qPCR of the N gene and ELISA (Figure S5B,C). However, at 23 dpi, N. benthamiana LAB plants appeared yellow and perished with signs of necrosis at the apex, whereas N. benthamiana WA and capsicum plants survived with new green leaf tissue emerging (Figure S2). At 47 dpi, LAB plants had completely perished, while WA plants generally survived.
3.2. Tospovirus Infection Induces a Shift in Small RNA Size Distribution
Small RNA sequencing was conducted on TSWV or CaCV infected capsicum and N. benthamiana samples to help elucidate the molecular response of these solanaceous species to tospovirus infection. In silico analyses of the resulting sequence data revealed dramatic changes in the relative abundance of 20 to 24 nt reads in both N. benthamiana accessions as well as capsicum in response to TSWV (Figure 1) or CaCV (Figure S3A,B) infection. In mock treatments, 24 nt reads were most abundant, whereas 21 to 22 nt reads were dominant in tospovirus-infected samples. An average of 29.4%, 28.4%, and 22.5% of the total small RNA reads from TSWV-inoculated capsicum, N. benthamiana LAB, and WA, respectively, perfectly matched the TSWV genome, and 43.7% and 12.1% of total small RNAs from CaCV-infected capsicum and N. benthamiana LAB, respectively, targeted the CaCV genome (n = 3 biologically independent replicates per treatment; Figure S3A,B). Accompanying the shift towards 21–22 nt reads was a reduction in reads mapping to host repeated elements.
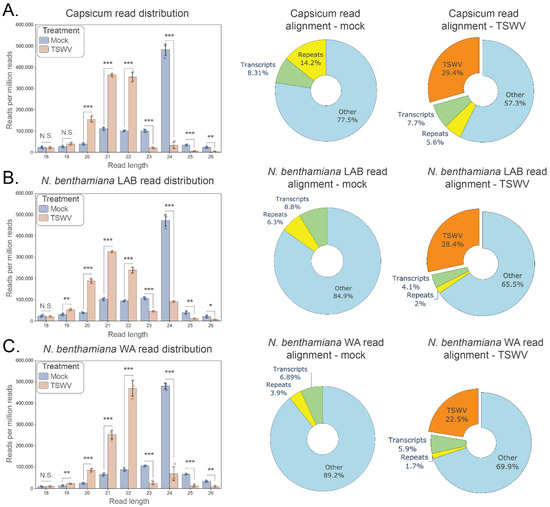
Figure 1.
Changes in small RNA read distribution in solanaceous hosts following inoculation by TSWV. Small RNA read distributions are shown for each host 10 days post tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) and mock inoculation (n = 3 for each treatment). (A). Capsicum, (B). Nicotiana benthamiana LAB, (C). N. benthamiana WA. Left panels: Small RNA read distribution by length (18–26 nt; error bars represent ± 1 SD; individual data points shown); Right panels: host and TSWV functional genomic alignment of reads for mock and TSWV treatments (pie chart percentages are the average of three replicates aligning to host transcripts, host repeat elements, other host genomic locations, and the combined RNA segments of TSWV). For each host, a significant reduction in the relative abundance of 23–24 nt reads and increase in 20–22 nt reads has occurred 10 days post TSWV inoculation (t-test; 2 tailed; FDR-BH multiple correction; N.S. (not significant): p ≥ 0.05, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001). The proportion of reads aligning to TSWV genome segments ranges from an average of 22.5–29.4% (orange; right pie chart) at this timepoint, indicating a sizable small RNA perturbation in response to TSWV infection.
Dicer-like (DCL) enzymes process double-stranded RNA into 21 and 22 nt duplexes [29]. Due to the observed shift in small RNA size classes, expression levels of four DCL homologues in TSWV-and CaCV-infected capsicum and N. benthamiana were first analysed using RT-qPCR (Figure S5D–F). The general response of DCL upregulation was evident in response to TSWV or CaCV in both capsicum and N. benthamiana, though, in one repeated qPCR experiment, DCL2 was downregulated in N. benthamiana WA, which may be a result of experiment-to-experiment variation. Expression of these genes was also examined in N. benthamiana using RNA-seq, which showed upregulation in response to TSWV infection for DCL1, DCL2, and DCL4, and downregulation of DCL3 in N. benthamiana Lab and WA (Figure S6F–I).
3.3. Hotspots of vsiRNA Abundance Are Evident for TSWV and CaCV
Infection of capsicum and N. benthamiana by TSWV (Figure 2) or CaCV (Figure S3C,D) resulted in the biogenesis of vsiRNAs. For TSWV infected samples, in silico small RNA sequence analysis showed ‘hotspots’ of vsiRNA abundance (easily discernible peaks in vsiRNA coverage) that spanned all three genome segments in both the sense and antisense orientations (Figure 2A). A slightly greater total abundance of 22 nt relative to 21 nt siRNAs was apparent for N. benthamiana WA, but in contrast, 21 nt vsiRNAs were more abundant than 22 nt vsiRNAs for capsicum and N. benthamiana LAB. The percentage of vsiRNA reads that aligned to each RNA segment and gene transcript showed significant differences between the two N. benthamiana accessions; the L segment comprising the RdRP gene had a significantly greater percentage of aligning vsiRNAs in the LAB than the WA accession, with a corresponding reduction of vsiRNAs aligning with the S segment and NSs and N genes (Figure 2B). There were no significant differences between alignments to genome segments or genes for the capsicum and N. benthamiana WA hosts. In response to CaCV infection, vsiRNA hotspots were also evident across the three segments, and there were significant differences between capsicum and N. benthamiana LAB for alignments to the M and S segments and the genes present in these segments (Figure S3C,D).
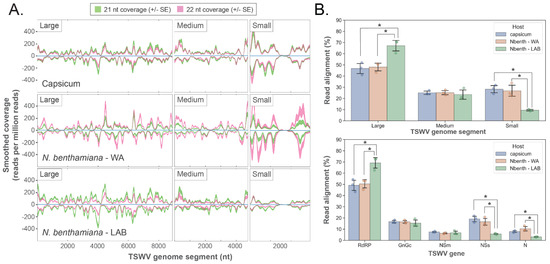
Figure 2.
Mapping of 21 and 22 nt reads to TSWV RNA segments and genes reveals alignment hotspots and host-specific variation. Small RNA reads were generated from samples 10 days post TSWV inoculation (n = 3 for each host; mock data not shown as aligning reads absent). (A). Small RNA coverage profiles for the Large, Medium, and Small TSWV RNA segments. Each plot shows smoothed read coverage in both orientations (shaded regions represent ± 1 SE for each alignment length). Consistently located hotspots of increased coverage (prominent peaks) are evident in each segment and in each orientation for all hosts. (B). Mean alignment proportions to TSWV RNA segments and genes for each host (n = 3; error bars represent ± 1 SD; individual data points shown). Significantly more reads aligned to the large TSWV RNA segment in N. benthamiana LAB compared to WA and capsicum, and fewer reads aligned to the small segment for the same comparison (top). Small RNA alignments to TSWV genes showed a similar pattern, with more reads aligning to RdRP in N. benthamiana LAB compared to the other hosts and fewer reads to the NSs and N genes in the same comparison (bottom). RdRP covers most of the large RNA segment, and only NSs and N are located in the small RNA segment. (t-test; 2-tailed; FDR-BH multiple correction; *: p<0.05).
3.4. Virus-Activated siRNAs Associated with Endogenous Transcripts in Solanaceous Plant Species
In silico analysis of small RNA reads exactly matching host transcripts suggested vasiRNAs were generated in response to TSWV and CaCV infection in hosts with a functional RDR1. Differential analysis of 21 and 22 nt read alignments revealed a subset of capsicum and N. benthamiana WA transcripts in which small RNA coverage increased by orders of magnitude following infection by TSWV (>10-fold increase; p < 10−8; capsicum: 1084 transcripts; N. benthamiana WA: 4093 transcripts; Figure 3A) or CaCV (>10-fold increase; p < 10−8; capsicum: 2307 transcripts; Figure S4A). Importantly, the same global shift in abundance of small RNAs targeting endogenous genes was not apparent in either the TSWV- or CaCV-infected N. benthamiana LAB accession that lacks a functional RDR1.
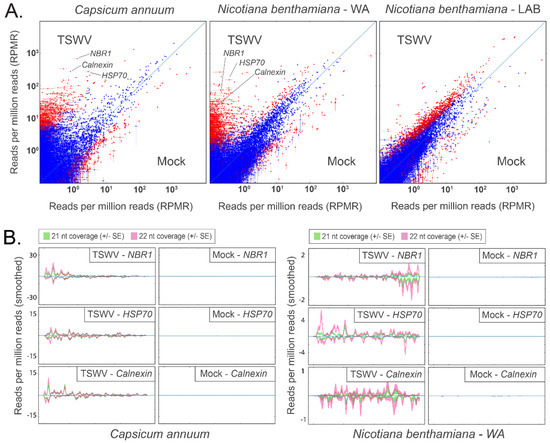
Figure 3.
Host-specific alignment of 21 nt and 22 nt reads to host transcripts 10 days post TSWV inoculation suggests the presence of vasiRNAs in capsicum and N. benthamiana WA, but not in N. benthamiana Lab. These alignments are largely absent in mock-inoculated samples. (A) Comparison plots for transcriptome-wide alignments to capsicum (left), N. benthamiana WA (centre), and N. benthamiana Lab (right) are shown. Each point indicates the normalised alignment abundance in TSWV-inoculated samples (Y-axis) and mock inoculated samples (X-axis) to each transcript (n = 3 for each treatment; vertical and horizontal bars represent ± 1 SE). Red points show a significant difference between the alignment abundance of each treatment (TSWV v. mock), whereas blue points are not significant (calculated using DESeq2; red: padj < 10−8, blue: padj > 10−8). NBR1, HSP70, and Calnexin (individually labelled) are examples of transcripts with abundant 21 nt and 22 nt alignments in TSWV-infected hosts. (B) Profile plots for vasiRNA targets NBR1, HSP70, and Calnexin. Furthermore, 21 nt and 22 nt alignment hotspots are evident in TSWV-inoculated capsicum and N. benthamiana WA samples but absent in mock-inoculated samples. Hotspots occur in both orientations, indicating the originating template was dsRNA. Profile alignments were absent in N. benthamiana Lab (data not shown).
To determine whether the generation of vasiRNAs was prevalent in solanaceous species, we reanalysed small RNA read data from susceptible (Marglobe) and resistant (Red Defender) tomato varieties following TSWV infection. Like capsicum and N. benthamiana WA, abundant vasiRNAs were also observed in TSWV-infected Marglobe tomato (Figure S4B), while these were largely absent in Red Defender. In contrast to Red Defender and its Marglobe counterpart, N. benthamiana LAB did not show a diminished viral load relative to WA (Figure S5B,C), indicating a decoupling of vasiRNA production from viral load in this instance.
A subset of vasiRNA generating host transcripts was selected for further analysis based on abundant 21 and 22 nt read alignments in TSWV inoculated capsicum and N. benthamiana WA samples and very low alignments in their mock-inoculated counterparts (Figure 3A). Alignment profiles to Heat Shock Cognate 70-2 (HSC70-2), Calnexin 1 (CNX1), and Next to BRCA 1 (NBR1) in TSWV- and CaCV-infected capsicum and N. benthamiana WA displayed the distribution of 21 and 22 nt hotspots in both orientations (Figure 3B and Figure S4A). Minimal alignments to the same transcripts in N. benthamiana LAB were evident. In the reanalysed tomato samples, vasiRNA profiles with alignment hotpots were apparent for the HSP70 heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and Calnexin transcripts in Marglobe but not in Red Defender where vasiRNAs were absent (Figure S4B).
3.5. Expression Analysis of Host Transcripts Targeted by vasiRNAs
Using an RNA-seq approach, viral genome segments were identified in the resulting datasets. There were no significant differences in the abundance of the three TSWV genome segments between inoculated N. benthamiana LAB and WA samples, though the WA samples (n = 3) were more variable (Figure 4A). Next, host vasiRNA-targeted transcripts were quantified, and their attenuation status was determined on a transcript-by-transcript basis. An attenuated transcript was identified as showing either greater downregulation or reduced upregulation in vasiRNA-generating WA samples compared to vasiRNA-free LAB samples following TSWV infection. A heatmap of relative host transcript abundance is shown in Figure 4B, with normalised abundances of selected targets shown in Figure S6A–E. In this analysis, the 50 transcripts with the most aligning vasiRNAs were selected, with no duplication of functional annotation. When comparing Log Fold Change (LFC) of these transcripts relative to the mock inoculation mean, no overarching trend of vasiRNA regulation of gene expression was evident. Of the transcripts analysed, the degree of upregulation was significantly reduced for six transcripts in WA compared to LAB, with 44 showing no significant differences (1-tailed t-test; n = 3 for each treatment). Expression levels of individual targets were also analysed via RT-qPCR for N. benthamiana WA and LAB, and additionally, capsicum (Figure S5G,H). Similar results to the RNA-seq analysis were evident for N. benthamiana, with abundant vasiRNAs not significantly resulting in attenuation in the WA genotype compared to vasiRNA-deficient LAB genotype. For capsicum, up- and downregulation of vasiRNA target genes occurred for both TSWV- and CaCV-inoculated treatments relative to mock across two experimental repeats.
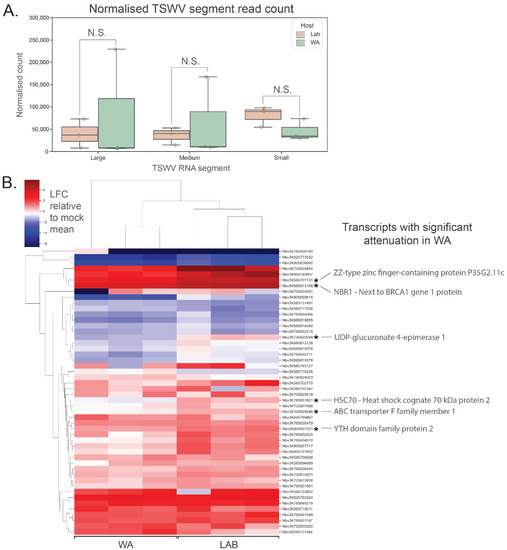
Figure 4.
RNA-seq analysis of putative vasiRNA target transcripts in N. benthamiana shows inconsistent attenuation of vasiRNA-mediated expression. (A) No significant difference in TSWV RNA segment (L, M and S) expression was evident between N. benthamiana WA and LAB 10 days post inoculation (n = 3 for each host; error bars represent ± 1 SD; t-test; 2-tailed; FDR-BH multiple correction, N.S. (not significant): p ≥ 0.05). (B) Heatmap of relative vasiRNA target gene expression in N. benthamiana WA and LAB. Red shading indicates upregulation and blue shading downregulation in TSWV-inoculated samples relative to the mean expression in mock-inoculated samples. VasiRNA targets were selected based on the lowest adjusted p-values from differential vasiRNA expression analysis using DeSeq2, without functional duplication. Of the 50 transcripts shown, six were demonstrated to have significant attenuation (n = 3 for each host; t-test; 1-tailed; FDR-BH multiple correction; LFC = log transformed TSWV/mock proportional expression; alternate hypothesis = mean LFC is lower in WA compared to LAB).
3.6. Functional Examination of Host Transcripts Targeted by vasiRNAs
To understand why certain transcripts were targeted by vasiRNAs, a literature review of selected target genes, along with their roles in responding to pathogens, was performed (Table S1). Functional analyses were expanded to vasiRNA targets more broadly, with KEGG pathway analysis revealing vasiRNA-generating transcripts were involved in a diverse array of pathways, with genes in the cytoplasm-situated ‘ribosome’ and ‘protein processing in ER’ pathways strongly enriched (Figure 5). Both these pathways are expected to be highly active during viral replication when viral messenger RNAs are translated to proteins that are folded and modified into their final state. In order to determine whether vasiRNA biogenesis does indeed take place in the cytoplasm, small RNA reads from TSWV-infected Marglobe tomato were aligned to the well-annotated tomato genome, with no mismatches allowed. No alignments to introns were evident for the vasiRNA-generating transcripts analysed, indicating that vasiRNA generation does not take place in the nucleus, at least prior to splicing (Figure S7).
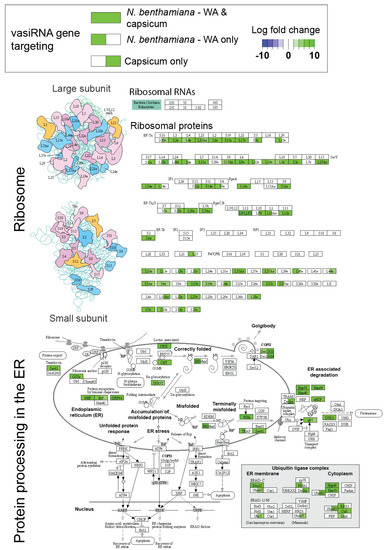
Figure 5.
Capsicum and N. benthamiana WA vasiRNA targets are enriched in the ribosome and protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) KEGG pathways. Log fold changes of significantly differentially regulated vasiRNAs (21 nt and 22 nt combined) are shown for one or both of capsicum and N. benthamiana WA (green shading indicates increased significantly abundance of vasiRNAs targeting associated host transcripts in response to TSWV infection, and blue shading indicates significantly decreased vasiRNA abundance). Enrichment for these pathways suggests that localisation of vasiRNA template to the ER may be the functional basis for vasiRNA target ‘selection’. KEGG pathway analysis and visualisation were carried out using Pathview, v1.36.0 (Charlotte, NC, USA) [26].
4. Discussion
Confirming previous reports for tospovirus-infected Solanaceae [9,10], our current work demonstrates that TSWV or CaCV infection of susceptible capsicum and N. benthamiana accessions leads to the generation of abundant vsiRNAs and upregulation of the associated RNAi pathway genes. The increase in 21–22 nt small RNA reads derived from infected host plants can be partly attributed to the production of vsiRNAs. Notably, a similar overall change away from 24 nt and towards 21–22 nt small RNAs in response to TSWV infection has previously been reported in peanut [8], indicating a common response across plant families. Though conserved among higher plants, this RNAi response is on its own insufficient to eliminate the virus from the host plant, although it may extend its lifespan. Notably, transgenic approaches to engineer tospovirus resistance that strongly and constitutively express viral dsRNA sequences have proven highly effective [30], indicating that the RNAi pathway induced by TSWV and CaCV does have the capacity to control virus infection effectively if the circumstances permit. Presumably, without transgenic ‘priming’, the tospovirus gains a foothold and eventually overwhelms the plant’s silencing mechanisms, possibly because of the silencing suppressor action of NSs. NSs are considered to be involved in the sequestration of vsiRNAs and preventing them from entering the RNA-induced silencing complex, thus decoupling the presence of vsiRNAs from target transcript degradation [31]. It is apparent that as viral load increases, vsiRNAs similarly proliferate as more viral transcripts become available as templates for RDR-mediated amplification. The susceptible tomato variety Marglobe has previously been shown to accumulate far more vsiRNAs aligning to the TSWV genome upon infection than the resistant Red Defender, supporting the association between vsiRNA response and viral load [9].
Differences in relative TSWV and CaCV vsiRNA abundance for tospovirus RNA segments and genes were evident between hosts. Abundant vsiRNAs were, however, still generated in the functional RDR1 lacking N. benthamiana LAB genotype, suggesting another RdRp, likely RDR6, may be sufficient for secondary vsiRNA production. The length of siRNAs derived from longer dsRNAs is determined by Dicer-like (DCL) enzyme processing, with DCL1 and DCL4 principally generating 21 nt siRNAs, DCL2 generating 22 nt siRNAs, and DCL3 generating 24 nt siRNAs in plants [29]. Though studies in Arabidopsis have shown that DCL4-mediated 21 nt siRNAs generated from dsRNA hairpins are significantly more abundant than their DCL2-mediated 22 nt counterparts [32,33], similar levels of 21 nt and 22 nt vsiRNAs were generated in capsicum and N. benthamiana. If the enhanced potency of systemic silencing induced by 22 nt siRNAs in Arabidopsis also occurs in the Solanaceae, it does not appear to result in reduced viral load, particularly in the N. benthamiana WA/TSWV pathosystem.
Despite similar symptoms, viral loads and accumulation of vsiRNAs in N. benthamiana LAB and WA accessions 10 days post-inoculation, TSWV and CaCV infection subsequently proved lethal to the LAB plants, whereas the WA plants survived, albeit in a weakened state. It has previously been demonstrated that the introduction of transgenic RDR1 into N. benthamiana LAB prevents lethality caused by tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) but does not prevent the systemic spread of the virus [34]. Furthermore, depletion of potato (Solanum tuberosum) RDR1 transcripts does not affect susceptibility to potato virus X or TMV, as measured by the level of viral coat protein [35]. Given that N. benthamiana WA has a functional RDR1, this supports the notion that its presence is the determinant of enhanced survival or at least a significant contributor.
Apart from acting together with RDR6 in the production of vsiRNAs, RDR1’s role in generating vasiRNAs has been proposed to contribute to enhanced plant longevity under viral challenge [11,15,16,18]. Capsicum and N. benthamiana WA generate large numbers of vasiRNAs against a specific subset of endogenous transcripts, while N. benthamiana LAB does not, providing further support for RDR1’s role in vasiRNA biogenesis. Profiles of vasiRNA alignments to target transcripts show the presence of hotspots in both orientations, similar to vsiRNA alignments to viral RNAs. Many endogenous vasiRNA targets identified in earlier reports for Brassicaceae and Solanaceae [11,15,16,18] have functional homologues in the vasiRNA-targeted transcripts we identified in the tospovirus-Solanaceae pathosystem, suggesting a conserved response among higher plants to multiple viruses.
Our findings pose the questions, what impact do vasiRNAs have on transcript expression, and what is the mechanism for the selection of this subset of host transcripts? It has been suggested that vasiRNA-targeted genes are associated with successful virus infection and are thus silenced by the host to resist the virus [11]. Viruses themselves may modulate the expression of host transcripts, with the downregulation of transcripts involved in photosynthesis in response to vasiRNAs identified in Brassicaceae [16]. Our data similarly indicate that these associations are multifaceted; vasiRNA targets such as NBR1 are associated with virus defence, though others act as important components for virus replication or systemic movement through the plant (Table S1).
Importantly, the effect of vasiRNAs on the expression of their target transcripts is nevertheless unclear. Our data do not show a clear and consistent association between vasiRNA abundance and expression of their target transcripts in TSWV-infected N. benthamiana. Examination of fifty representative vasiRNA-targeted transcripts without functional duplication showed that the upregulation or downregulation of these transcripts in response to TSWV infection generally occurred in both the LAB and WA genotypes. If vasiRNAs were leading to attenuation of target transcript expression in the WA genotype where vasiRNAs were present, this attenuation was generally subtle and not easily detected in the transcript expression analyses conducted. There may be several reasons for this outcome, which contrasts with the previous literature for different pathosystems [11,15,16,18]. The TSWV NSs gene, which is a suppressor of silencing, may sequester vasiRNAs, preventing them from silencing target transcripts but not impacting their biogenesis and subsequent detection in small RNA sequencing. The timing of post-inoculation tissue sampling, as well as the selection of sampling tissue type (apex/apical leaf tissue), may mean that vasiRNA-mediated gene expression impacts had occurred but were not detected. Additionally, differences other than a functional RDR1 between the two N. benthamiana genotypes may be confounding, serving to obscure any post-transcriptional downregulation that may be occurring. Translational inhibition is another mechanism by which protein expression could be reduced independent of transcript abundance. Indeed, 22 nt siRNAs have been shown to inhibit the translation of endogenous transcripts in response to environmental stress [36] and could be performing a similar role in virus-impacted plants. The potential disconnect between vasiRNA expression and transcript expression knockdown will be the subject of further work.
To shed light on the conserved selection of vasiRNA-target transcripts, we examined the expression of these transcripts as well as their putative functions and cellular localisation. The vast range of expression of these transcripts suggests that high expression itself in response to tospovirus infection is not how this subset of genes is selected. KEGG analysis revealed that many vasiRNA-associated transcripts were either ribosomal protein-encoding transcripts or encoded proteins located in the ER that are involved in protein processing and folding. For instance, both CRT/CNX and BiP, identified in our study as vasiRNA targets, sequester unfolded proteins at the ER and re-direct them for re-folding [37]. It is possible that co-localisation of host mRNAs and viral transcripts could lead to the production of vasiRNAs, with mRNA destined for translation at the ER possibly providing a substrate for an ER-localised RDR1 complex. Supporting this hypothesis, the alignment of small RNA reads to the tomato genome demonstrated that vasiRNAs do not align to intronic sequences, suggesting that biogenesis occurs after splicing and likely after export to the cytoplasm. Although the presence of RDR1 at the ER has not been demonstrated, reports in Arabidopsis show that a membrane-bound complex containing aminophospholipid transporting ATPases (ALAs) with flippase activity is essential for RDR6, RDR1, and vasiRNA production during CMV infection [12,13]. Many viruses target the ER and associated machinery for replication [38]. Indeed, localisation of TSWV to the ER during cell-to-cell movement through the plasmodesmata, along with association with membrane compartments during the virus lifecycle stages, has been demonstrated [39]. Whether co-localisation with viral transcripts acts to initiate vasiRNA priming will also be the subject of further work.
5. Conclusions
When taken together, these findings demonstrate the evolutionary persistence of the host gene targeting vasiRNA biogenesis pathway, though its function in tospovirus-Solanaceae interactions remains unclear. Abundant virus-derived vsiRNAs targeting TSWV and CaCV transcripts are apparent in multiple Solanaceous species, including N. benthamiana LAB, which lacks vasiRNAs and a functional RDR1. The interplay between plant viruses and their hosts remains an active area of investigation, with this work showing that plant responses involving RNAi and the generation of vsiRNAs and vasiRNAs are conserved, with the functional differences apparent between different pathosystems a possible focus for enhancing crop protection.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens11070745/s1, Figure S1: Tospovirus and mock inoculated plants used for small RNA and mRNA sequencing; Figure S2: N. benthamiana LAB and WA plants 23- and 47-days post TSWV and mock inoculation; Figure S3: Small RNA sequencing analysis of CaCV inoculated capsicum and N. bethamiana LAB; Figure S4: Abundant alignment of 21 nt and 22 nt reads to host transcripts 10 days post tospovirus inoculation suggests the presence of vasiRNAs in capsicum and N. benthamiana WA in response to CaCV and tomato (cv. Marglobe) in response to TSWV; Figure S5: Quantitative real-time PCR and ELISA analysis of expression of tospovirus segments, RNAi genes and vasiRNA target transcripts; Figure S6: Analysis of RNAi gene and vasiRNA target transcript expression in TSWV and mock inoculated N. benthamiana Lab and WA hosts (10 DPI) using RNA-seq; Figure S7: Small RNA reads do not map to tomato (Marglobe) introns of vasiRNA target genes (HSC2-like and ZZ type zinc finger domain-containing protein), suggesting the mRNAs act as templates after splicing and outside of the nucleus; Table S1: Literature search for vasiRNA targets and host-pathogen interactions; Table S2: List of qPCR primers used in this study.
Author Contributions
S.J.F., J.R.P., C.O, H.P., R.G.D. and N.M. designed research; S.J.F., J.R.P. and C.O. performed research; S.J.F., J.R.P., R.G.D., D.M.P. and B.J.C. analysed data; J.R.P. and S.J.F. wrote manuscript; all authors edited manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by a Horticulture Innovation Australia grant (VG14063) awarded to N.M. This work was also supported in part by the USDA-NIFA Hatch project Accession #1016563 “Reducing the Impact of Pests and Diseases Affecting Washington Agriculture”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All raw sequence data is available at the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under BioProject ID PRJNA784690.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Peter Waterhouse for providing N. benthamiana WA seeds and Christopher Brosnan for reading and critiquing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
Co-author Ralf Dietzgen is an Editor of Pathogens and was not involved in the review of the manuscript. Otherwise, the authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Kuhn, J.H.; Adkins, S.; Agwanda, B.R.; Al Kubrusli, R.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Oliveira, R.C. 2021 Taxonomic update of phylum Negarnaviricota (Riboviria: Orthornavirae), including the large orders Bunyavirales and Mononegavirales. Arch Virol. 2021, 166, 3513–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.; Jain, R.K.; Krishnareddy, M.; Kumar, N.K.K.; Ravi, K.S.; Pappu, H.R. Emerging Problems of Tospoviruses (Bunyaviridae) and their Management in the Indian Subcontinent. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMichael, L.A.; Persley, D.M.; Thomas, J.E. A new tospovirus serogroup IV species infecting capsicum and tomato in Queensland, Australia. Australas Plant Path. 2002, 31, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.E.; Ullman, D.E.; German, T.L. Tospovirus-thrips interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 459–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumford, R.A.; Barker, I.; Wood, K.R. The biology of the tospoviruses. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1996, 128, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.E.; Whitfield, A.E. The Genus Tospovirus: Emerging Bunyaviruses that Threaten Food Security. Ann. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlotshwa, S.; Pruss, G.J.; Vance, V. Small RNAs in viral infection and host defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S.J.; Shrestha, A.; Peters, J.R.; Carroll, B.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Pappu, H.R.; Mitter, N. The Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus Genome is Processed Differentially in its Plant Host Arachis hypogaea and its Thrips Vector Frankliniella fusca. Front Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olaya, C.; Fletcher, S.J.; Zhai, Y.; Peters, J.; Margaria, P.; Winter, S.; Pappu, H.R. The Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) Genome is Differentially Targeted in TSWV-Infected Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) with or without Sw-5 Gene. Viruses 2020, 12, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitter, N.; Koundal, V.; Williams, S.; Pappu, H. Differential Expression of Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus-Derived Viral Small RNAs in Infected Commercial and Experimental Host Plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.J.; Du, P.; Wang, X.B.; Yu, Y.Q.; Qiu, Y.H.; Li, W.X.; Ding, S.W. Virus infection triggers widespread silencing of host genes by a distinct class of endogenous siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14613–14618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.X.; Lu, J.F.; Wang, X.B.; Zhan, B.H.; Li, W.X.; Ding, S.W. Lipid flippases promote antiviral silencing and the biogenesis of viral and host siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.X.; Wang, X.B.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.X.; Gal-On, A.; Ding, S.W. Identification of a New Host Factor Required for Antiviral RNAi and Amplification of Viral siRNAs. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Pendon, J.A.; Li, F.; Li, W.X.; Ding, S.W. Suppression of antiviral silencing by cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein in Arabidopsis is associated with drastically reduced accumulation of three classes of viral small interfering RNAs. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pitzalis, N.; Amari, K.; Graindorge, S.; Pflieger, D.; Donaire, L.; Wassenegger, M.; Heinlein, M. Turnip mosaic virus in oilseed rape activates networks of sRNA-mediated interactions between viral and host genomes. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, P.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Consiglio, A.; Gursinsky, T.; Behrens, S.-E.; Pantaleo, V. Endogenous activated small interfering RNAs in virus-infected Brassicaceae crops show a common host gene-silencing pattern affecting photosynthesis and stress response. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 1650–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaria, P.; Miozzi, L.; Rosa, C.; Axtell, M.J.; Pappu, H.R.; Turina, M. Small RNA profiles of wild-type and silencing suppressor-deficient tomato spotted wilt virus infected Nicotiana benthamiana. Virus Res. 2015, 208, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Singh, A.; Singh, A.K.; Dalmay, T.; Chakraborty, S. Tobacco RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 affects the expression of defence-related genes in Nicotiana benthamiana upon Tomato leaf curl Gujarat virus infection. Planta 2020, 252, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widana Gamage, S.; Persley, D.M.; Higgins, C.M.; Dietzgen, R.G. First complete genome sequence of a capsicum chlorosis tospovirus isolate from Australia with an unusually large S RNA intergenic region. Arch Virol. 2015, 160, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, R.L.; Pretorius, L.; Carvalhais, L.C.; Schenk, P.M. Complete Nucleotide Sequence of Australian Tomato spotted wilt virus Isolate TSWV-QLD2. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01267-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riley, D.G.; Joseph, S.V.; Kelley, W.T.; Olson, S.; Scott, J. Host Plant Resistance to Tomato spotted wilt virus (Bunyaviridae: Tospovirus) in Tomato. HortSci. Horts 2011, 46, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fletcher, S.J.; Boden, M.; Mitter, N.; Carroll, B.J. SCRAM: A pipeline for fast index-free small RNA read alignment and visualization. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2670–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, W.; Pant, G.; Bhavnasi, Y.K.; Blanchard, S.G., Jr.; Brouwer, C. Pathview Web: User friendly pathway visualization and data integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W501–W508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bally, J.; Jung, H.; Mortimer, C.; Naim, F.; Philips, J.G.; Hellens, R.; Waterhouse, P.M. The Rise and Rise of Nicotiana benthamiana: A Plant for All Reasons. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Carter, S.A.; Cole, A.B.; Cheng, N.H.; Nelson, R.S. A natural variant of a host RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is associated with increased susceptibility to viruses by Nicotiana benthamiana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6297–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Johansen, L.K.; Gustafson, A.M.; Kasschau, K.D.; Lellis, A.D.; Zilberman, D.; Weigel, D. Genetic and Functional Diversification of Small RNA Pathways in Plants. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bucher, E.; Lohuis, D.; van Poppel, P.M.J.A.; Geerts-Dimitriadou, C.; Goldbach, R.; Prins, M. Multiple virus resistance at a high frequency using a single transgene construct. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3697–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedil, M.; de Ronde, D.; Kormelink, R. Biochemical analysis of NSs from different tospoviruses. Virus Res. 2017, 242, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, A.F.; Matthew, L.; Smith, N.A.; Curtin, S.J.; Dedic-Hagan, J.; Ellacott, G.A.; Waterhouse, P.M. RNA interference-inducing hairpin RNAs in plants act through the viral defence pathway. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taochy, C.; Gursanscky, N.R.; Cao, J.; Fletcher, S.J.; Dressel, U.; Mitter, N.; Carroll, B.J. A Genetic Screen for Impaired Systemic RNAi Highlights the Crucial Role of DICER-LIKE 2. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1424–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-S.; Fu, S.-F.; Li, Z.; Murphy, A.M.; Dobson, E.A.; Garland, L.; Carr, J.P. Salicylic acid treatment and expression of an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 transgene inhibit lethal symptoms and meristem invasion during tobacco mosaic virus infection in Nicotiana benthamiana. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, L.J.R.; Brockington, S.F.; Murphy, A.M.; Pate, A.E.; Gruden, K.; MacFarlane, S.A.; Carr, J.P. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 in potato (Solanum tuberosum) and its relationship to other plant RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Sci Rep.-UK 2016, 6, 23082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Li, B.; Iwakawa, H.-o.; Pan, Y.; Tang, X.; Ling-hu, Q.; Guo, H. Plant 22-nt siRNAs mediate translational repression and stress adaptation. Nature 2020, 581, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verchot, J. Cellular chaperones and folding enzymes are vital contributors to membrane bound replication and movement complexes during plant RNA virus infection. Front Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero-Brey, I.; Bartenschlager, R. Endoplasmic Reticulum: The Favorite Intracellular Niche for Viral Replication and Assembly. Viruses 2016, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z.K.; Xue, F.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.J.; Zhao, W.Y.; Garcia-Murria, M.J.; Tao, X. The ER-Membrane Transport System Is Critical for Intercellular Trafficking of the NSm Movement Protein and Tomato Spotted Wilt Tospovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).