Parapoxvirus Interleukin-10 Homologues Vary in Their Receptor Binding, Anti-Inflammatory, and Stimulatory Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
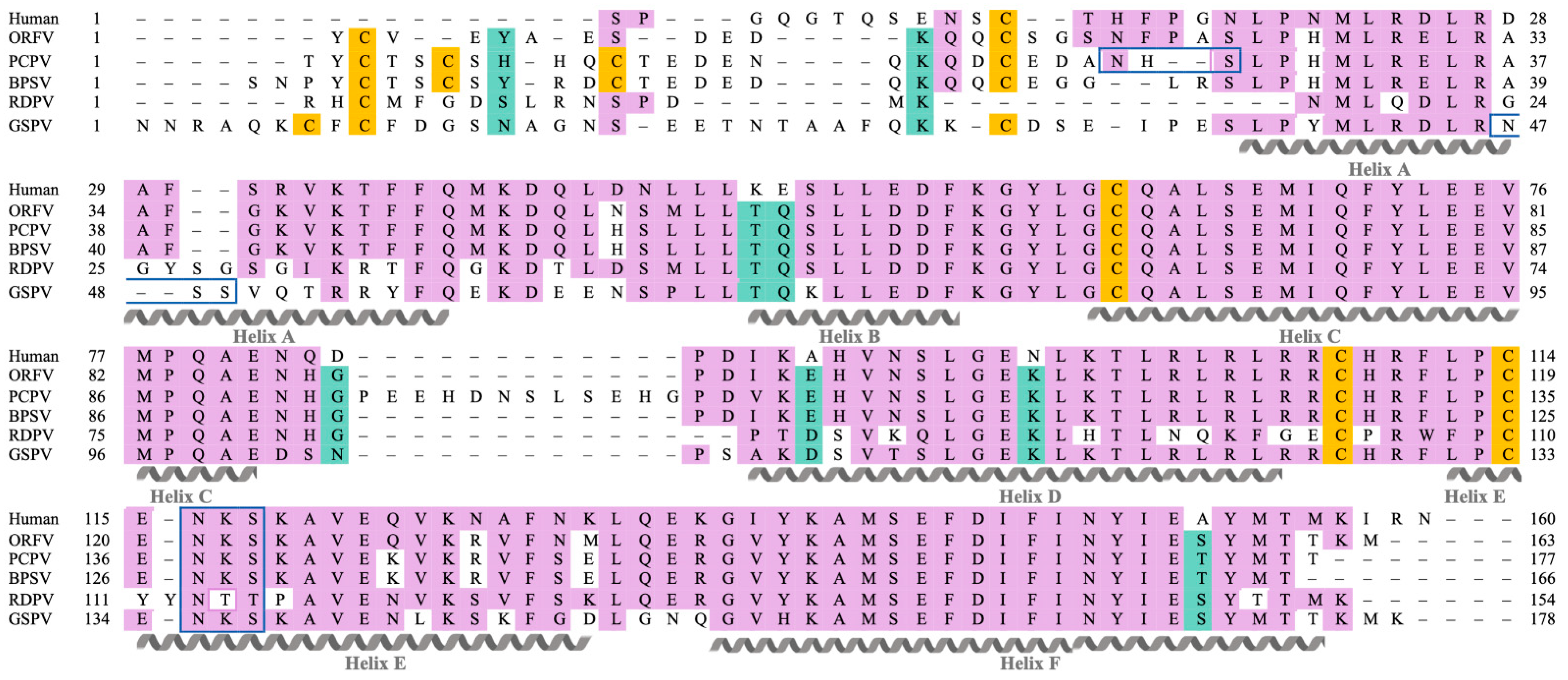
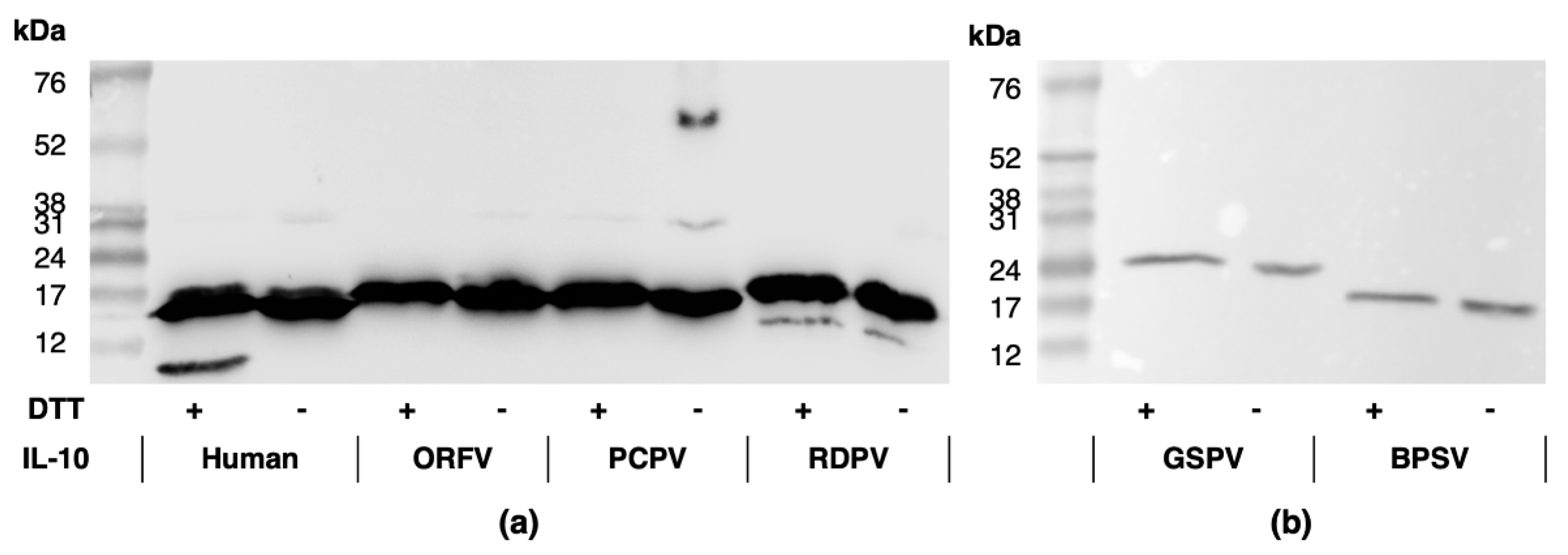
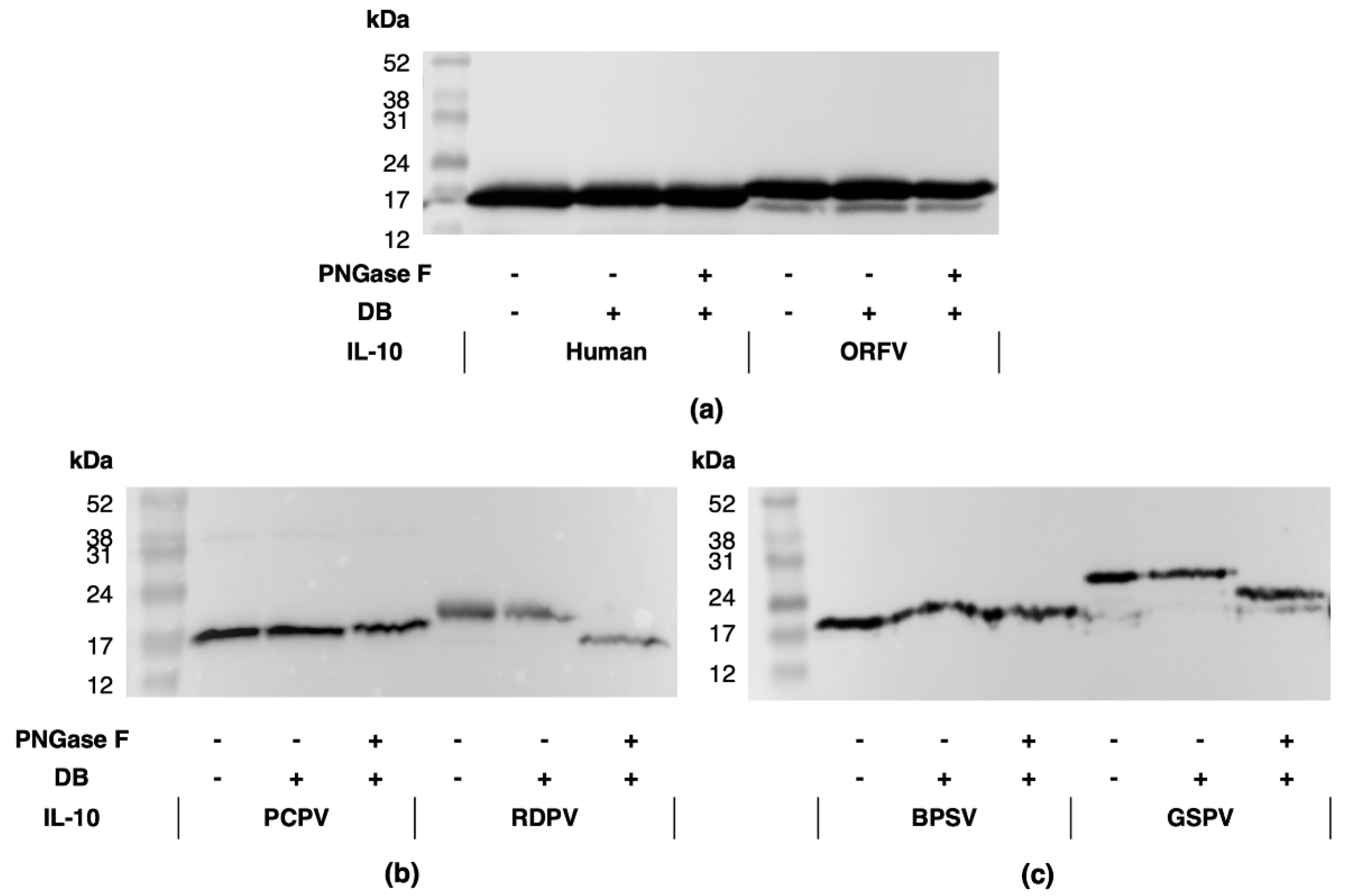
2.1. Parapxvirus IL-10s Differ in Amino Acid Sequence, Molecular Weight and Glycosylation State
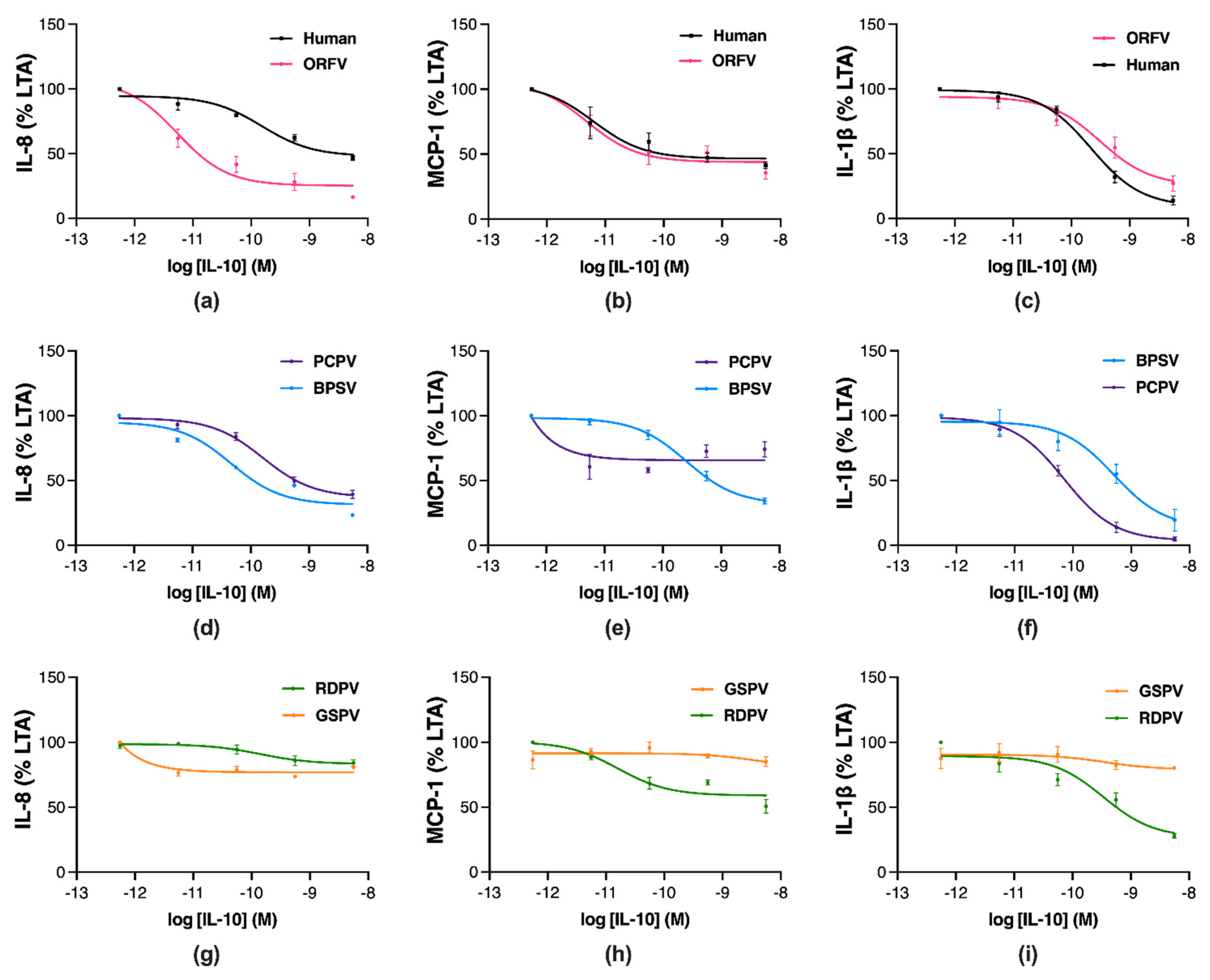
2.2. Parapoxvirus IL-10s Vary in Their Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Production in Stimulated Human Monocytes
2.3. Parapoxvirus IL-10s Vary in Their Stimulation of Murine Mast Cell Proliferation
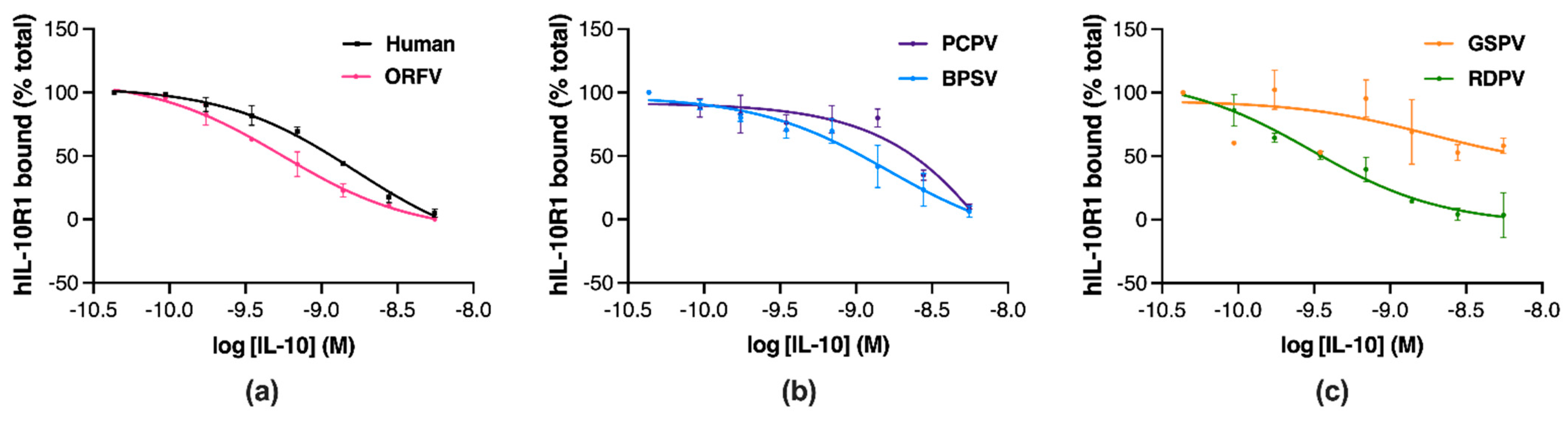
2.4. Parapoxvirus IL-10s Vary in Their Binding to Human IL-10R1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. IL-10 Sequences and Bioinformatic Analyses
4.2. IL-10 Protein Production
4.3. IL-10 Protein Analyses
4.4. Stimulation and Analysis of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Production in Monocytes
4.5. Stimulation and Analysis of Mast Cell Proliferation
4.6. Analysis of hIL-10R1 Binding
4.7. Data and Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosser, D.M.; Zhang, X. Interleukin-10: New perspectives on an old cytokine. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 226, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.; Vieira, P.; O’Garra, A. Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 217, e20190418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asadullah, K.; Döcke, W.-D.; Sabat, R.; Volk, H.-D.; Sterry, W. The treatment of psoriasis with IL-10: Rationale and review of the first clinical trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawiec, P.; Pawłowska-Kamieniak, A.; Pac-Kożuchowska, E. Interleukin 10 and interleukin 10 receptor in paediatric inflammatory bowel disease: From bench to bedside lesson. J. Inflamm. 2021, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, Y.; Duru, E.A.; Ameredes, B.T. Role of IL-10 in the resolution of airway inflammation. Curr. Mol. Med. 2000, 8, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Wang, W.; Zhou, M.; Li, R.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Role of interleukin-10 and interleukin-10 receptor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.W.; De Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.R. The molecular basis of IL-10 function: From receptor structure to the onset of signaling. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 380, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutchins, A.P.; Diezm, D.; Miranda-Saavedra, D. The IL-10/STAT3-mediated anti-inflammatory response: Recent developments and future challenges. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2013, 12, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber-Nordtt, R.M.; Riley, J.K.; Greenlund, A.C.; Moore, K.W.; Darnell, J.E.; Schreiber, R.D. Stat3 recruitment by two distinct ligand-induced, tyrosine- phosphorylated docking sites in the interleukin-10 receptor intracellular domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 27954–27961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wehinger, J.; Gouilleux, F.; Groner, B.; Finke, J.; Mertelsmann, R.; Weber-Nordt, R.M. IL-10 induces DNA binding activity of three STAT proteins (Stat1, Stat3, and Stat5) and their distinct combinatorial assembly in the promoters of selected genes. FEBS Lett. 1996, 394, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoniv, T.T.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Interleukin-10-induced gene expression and suppressive function are selectively modulated by the PI3K-Akt-GSK3 pathway. Immunology 2011, 132, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Brown, J.R.; Sag, D.; Zhang, L.; Suttles, J. Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase regulates IL-10-mediated anti-inflammatory signaling pathways in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleming, S.B.; Wise, L.M.; Mercer, A.A. Molecular genetic analysis of orf virus: A poxvirus that has adapted to skin. Viruses 2015, 7, 1505–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, J.B.; McFaddenm, G. Poxvirus immunomodulatory strategies: Current perspectives. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6093–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schönrich, G.; Abdelazizm, M.O.; Raftery, M.J. Herpesviral capture of immunomodulatory host genes. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, P.; Rakus, K.; van Beurden, S.J.; Westphal, A.H.; Davison, A.J.; Gatherer, D.; Vanderplasschen, A.F. IL-10 encoded by viruses: A remarkable example of independent acquisition of a cellular gene by viruses and its subsequent evolution in the viral genome. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niiro, H.; Otsuka, T.; Abe, M.; Satoh, H.; Ogo, T.; Nakano, T.; Furukawa, Y.; Niho, Y. Epstein-Barr virus BCRF1 gene product (viral interleukin 10) inhibits superoxide anion production by human monocytes. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1992, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, S.B.; McCaughan, C.A.; Andrews, A.E.; Nash, A.D.; Mercer, A.A. A homolog of interleukin-10 is encoded by the poxvirus orf virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7178–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotenko, S.V.; Saccani, S.; Izotova, L.S.; Mirochnitchenko, O.V.; Pestka, S. Human cytomegalovirus harbors its own unique IL-10 homolog (cmvIL-10). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming, S.B.; Mercer, A.A. Genus Parapoxvirus. In Poxviruses; Mercer, A.A., Schmidt, A., Weber, O., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 127–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnelutti, J.F.; Flores, M.M.; Teixeira, F.R.; Weiblen, R.; Flores, E.F. An outbreak of pseudocowpox in fattening calves in southern Brazil. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Sant’Ana, F.J.; Rabelo, R.E.; Vulcani, V.A.; Cargnelutti, J.F.; Flores, E.F. Bovine papular stomatitis affecting dairy cows and milkers in midwestern Brazil. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groves, R.W.; Wilson-Jones, E.; MacDonald, D.M. Human orf and milkers’ nodule: A clinicopathologic study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1991, 25, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, G.W.; Robinson, A.J.; Hunter, R.; Cox, B.T.; Smith, R. Parapoxvirus infections in New Zealand farmed red deer (Cervus elaphus). N. Z. Vet. J. 1987, 35, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.M.; Hutchison, G.; Onwuka, S.K.; Reid, H.W. Changes in the MHC Class II+ Dendritic Cell Population of Ovine Skin In Response to Orf Virus Infection. Vet. Dermatol. 1991, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkinson, D.M.; McEwan, E.P.; Onwuka, S.K.; Moss, V.A.; Elder, H.Y.; Hutchison, G.; Reid, H.W. The Polymorphonuclear and Mast Cell Responses in Ovine Skin Infected with Orf Virus. Vet. Dermatol. 1990, 1, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeever, D.J.; Jenkinson, D.M.; Hutchison, G.; Reid, H.W. Studies of the pathogenesis of orf virus infection in sheep. J. Comp. Pathol. 1988, 99, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.; Gröters, S.; Siebert, U.; Rosenberger, T.; Driver, J.; König, M.; Becher, P.; Hetzel, U.; Baumgärtner, W. Parapoxvirus Infection in Harbor Seals (Phoca vitulina) from the German North Sea. Vet. Pathol. 2003, 40, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming, S.B.; Haig, D.M.; Nettleton, P.; Reid, H.W.; McCaughan, C.A.; Wise, L.M.; Mercer, A.A. Sequence and Functional Analysis of a Homolog of Interleukin-10 Encoded by the Parapoxvirus Orf Virus. Virus Genes 2000, 21, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.; Baird, M.; Mercer, A.A.; Fleming, S.B. Maturation and function of human dendritic cells are inhibited by orf virus-encoded interleukin-10. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3177–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlach, W.; McCaughan, C.A.; Mercer, A.A.; Haig, D.; Fleming, S.B. Orf virus-encoded interleukin-10 stimulates the proliferation of murine mast cells and inhibits cytokine synthesis in murine peritoneal macrophages. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, L.; McCaughan, C.; Tan, C.K.; Mercer, A.A.; Fleming, S.B. Orf virus interleukin-10 inhibits cytokine synthesis in activated human THP-1 monocytes, but only partially impairs their proliferation. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.R.; Lateef, Z.; Fleming, S.B.; Mercer, A.A.; Wise, L.M. Orf virus IL-10 reduces monocyte, dendritic cell and mast cell recruitment to inflamed skin. Virus Res. 2016, 213, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, S.B.; Anderson, I.E.; Thomson, J.; Deane, D.L.; McInnes, C.J.; McCaughan, C.A.; Mercer, A.A.; Haig, D.M. Infection with recombinant orf viruses demonstrates that the viral interleukin-10 is a virulence factor. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhon, G.; Tulman, E.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Lu, Z.; de la Concha-Bermejillo, A.; Lehmkuhl, H.D.; Piccone, M.E.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. Genomes of the parapoxviruses ORF virus and bovine papular stomatitis virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friederichs, S.; Krebs, S.; Blum, H.; Lang, H.; Büttner, M. Parapoxvirus (PPV) of red deer reveals subclinical infection and confirms a unique species. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1446–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, T.; Haas, L.; Alawi, M.; Wohlsein, P.; Marks, J.; Grundhoff, A.; Becher, P.; Fischer, N. Recovery of the first full-length genome sequence of a parapoxvirus directly from a clinical sample. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautaniemi, M.; Ueda, N.; Tuimala, J.; Mercer, A.A.; Lahdenperä, J.; McInnes, C.J. The genome of pseudocowpoxvirus: Comparison of a reindeer isolate and a reference strain. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1560–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syto, R.; Murgolo, N.J.; Braswell, E.H.; Mui, P.; Huang, E.; Windsor, W.T. Structural and biological stability of the human interleukin 10 homodimer. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 16943–16951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minshawi, F.; Lanvermann, S.; McKenzie, E.; Jeffery, R.; Couper, K.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Roers, A.; Muller, W. The Generation of an Engineered Interleukin-10 Protein With Improved Stability and Biological Function. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, L.M.; Stuart, G.S.; Sriutaisuk, K.; Adams, B.R.; Riley, C.B.; Theoret, C.L. Anti-fibrotic Actions of Equine Interleukin-10 on Transforming Growth Factor-Beta1-Stimulated Dermal Fibroblasts Isolated From Limbs of Horses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 577835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsen, N.J.; Deininger, S.; Nonstad, U.; Skjeldal, F.; Husebye, H.; Rodionov, D.; von Aulock, S.; Hartung, T.; Lien, E.; Bakke, O.; et al. Cellular trafficking of lipoteichoic acid and Toll-like receptor 2 in relation to signaling: Role of CD14 and CD36. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Qin, L.; Zamarin, D.; Kotenko, S.V.; Pestka, S.; Moore, K.W.; Bromberg, J.S. Differential IL-10R1 expression plays a critical role in IL-10-mediated immune regulation. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 6884–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilbers, R.H.P.; van Raaij, D.R.; Westerhof, L.B.; Bakker, J.; Smant, G.; Schots, A. Re-evaluation of IL-10 signaling reveals novel insights on the contribution of the intracellular domain of the IL-10R2 chain. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagata, K.; Nishiyama, C. IL-10 in Mast Cell-Mediated Immune Responses: Anti-Inflammatory and Proinflammatory Roles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorby, C.; Sotolongo Bellón, J.; Wilmes, S.; Warda, W.; Pohler, E.; Fyfe, P.K.; Cozzani, A.; Ferrand, C.; Walter, M.R.; Mitra, S.; et al. Engineered IL-10 variants elicit potent immunomodulatory effects at low ligand doses. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eabc0653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Tsutsumi, N.; Su, L.L.; Abhiraman, G.C.; Mohan, K.; Henneberg, L.T.; Aduri, N.G.; Gati, C.; Garcia, K.C. Structure-based decoupling of the pro- and anti-inflammatory functions of interleukin-10. Science 2021, 371, eabc8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.I.; Jones, B.C.; Logsdon, N.J.; Harris, B.D.; Deshpande, A.; Radaeva, S.; Halloran, B.A.; Gao, B.; Walter, M.R. Structure and mechanism of receptor sharing by the IL-10R2 common chain. Structure 2010, 18, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.I.; Logsdon, N.J.; Sheikh, F.; Donnelly, R.P.; Walter, M.R. Conformational changes mediate interleukin-10 receptor 2 (IL-10R2) binding to IL-10 and assembly of the signaling complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35088–35096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.I.; Jones, B.C.; Logsdon, N.J.; Walter, M.R. Same structure, different function: Crystal structure of the Epstein-Barr virus IL-10 bound to the soluble IL-10r1 chain. Structure 2005, 13, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Briere, F.; Parham, C.; Bridon, J.M.; Banchereau, J.; Moore, K.W.; Xu, J. The EBV IL-10 homologue is a selective agonist with impaired binding to the IL-10 receptor. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Qin, L.; Kotenko, S.V.; Pestka, S.; Bromberg, J.S. A single amino acid determines the immunostimulatory activity of interleukin 10. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, P.; de Waal-Malefyt, R.; Dang, M.N.; Johnson, K.E.; Kastelein, R.; Fiorentino, D.F.; deVries, J.E.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Mosmann, T.R.; Moore, K.W. Isolation and expression of human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor cDNA clones: Homology to Epstein-Barr virus open reading frame BCRFI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.I.; Jones, B.C.; Logsdon, N.J.; Harris, B.D.; Kuruganti, S.; Walter, M.R. Epstein-barr virus IL-10 engages IL-10R1 by a two-step mechanism leading to altered signaling properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26586–26595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motakis, E.; Guhl, S.; Ishizu, Y.; Itoh, M.; Kawaji, H.; de Hoon, M.; Lassmann, T.; Carninci, P.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Zuberbier, T.; et al. Redefinition of the human mast cell transcriptome by deep-CAGE sequencing. Blood 2014, 123, e58–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephson, K.; Logsdon, N.J.; Walter, M.R. Crystal structure of the IL-10/IL-10R1 complex reveals a shared receptor binding site. Immunity 2001, 15, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pletnev, S.; Magracheva, E.; Wlodawer, A.; Zdanov, A. A model of the ternary complex of interleukin-10 with its soluble receptors. BMC Struct. Biol. 2005, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, B.C.; Logsdon, N.J.; Josephson, K.; Cook, J.; Barry, P.A.; Walter, M.R. Crystal structure of human cytomegalovirus IL-10 bound to soluble human IL-10R1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9404–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deane, D.; Ueda, N.; Wise, L.M.; Wood, A.R.; Percival, A.; Jepson, C.; Inglis, N.F.; Fleming, S.B.; Mercer, A.A.; McInnes, C.J. Conservation and variation of the parapoxvirus GM-CSF-inhibitory factor (GIF) proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenburg, S.; Brennan, G. Species-Specific Host-Virus Interactions: Implications for Viral Host Range and Virulence. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahão, J.S.; Silva-Fernandes, A.T.; Assis, F.L.; Guedes, M.I.; Drumond, B.P.; Leite, J.A.; Coelho, L.F.; Turrini, F.; Fonseca, F.G.; Lobato, Z.I.; et al. Human Vaccinia virus and Pseudocowpox virus co-infection: Clinical description and phylogenetic characterization. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassa, T. A Review on Human Orf: A Neglected Viral Zoonosis. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2021, 8, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roess, A.A.; Galan, A.; Kitces, E.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Paddock, C.D.; Adem, P.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Miller, D.; Reynolds, M.G.; et al. Novel Deer-Associated Parapoxvirus Infection in Deer Hunters. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2621–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roess, A.A.; Levine, R.S.; Barth, L.; Monroe, B.P.; Carroll, D.S.; Damon, I.K.; Reynolds, M.G. Sealpox virus in marine mammal rehabilitation facilities, North America, 2007–2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2203–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haig, D.M.; McInnes, C.J. Immunity and counter-immunity during infection with the parapoxvirus orf virus. Virus Res. 2002, 88, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tulman, E.R.; Diel, D.G.; Khatiwada, S.; Sims, W.; Edwards, J.F.; Wen, X.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L.; Delhon, G. Coinfection with multiple strains of bovine papular stomatitis virus. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IL-10 | IL-8 | MCP-1 | IL-1β | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pIC50 (M) ± SEM | Emax (Δ%) ± SEM | pIC50 (M) ± SEM | Emax (Δ%) ± SEM | pIC50 (M) ± SEM | Emax (Δ%) ± SEM | |
| Human | 9.79 ± 0.15 b | 100 ± 1.94 b–f | 11.22 ± 0.47 c | 100 ± 2.57 d,f | 9.66 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 2.33 e–f |
| ORFV | 11.17 ± 0.29 a,d,e | 156.95 ± 1.60 a,c–f | 11.14 ± 0.39 | 109.89 ± 4.82 d–f | 9.50 ± 0.16 | 84.58 ± 3.85 d,f |
| BPSV | 10.37 ± 0.08 | 143.93 ± 1.15 a–b,d–f | 9.64 ± 0.12 a | 112.28 ± 2.20 d–f | 9.41 ± 0.23 | 96.83 ± 6.69 f |
| PCPV | 9.87 b ± 0.05 | 113.97 ± 3.40 a–c,e,f | ND | 78.09 ± 4.10 a–c,f | 10.22 ± 0.08 | 110.44 ± 1.06b,e,f |
| RDPV | 9.74 b ± 0.29 | 30.54 ± 3.16 a–e | 10.70 ± 0.27 | 84.21 ± 5.14 b,c,f | 9.60 ± 0.34 | 83.57 ± 1.10 a,d,f |
| GSPV | ND | 50.07 ± 0.93 a–e | ND | 31.03 ± 2.78 a–e | 11.03 ± 1.88 | 25.83 ± 1.88 a–e |
| IL-10 | MC-9 Proliferation | |
|---|---|---|
| pEC50 (M) ± SEM | Emax (Δ%) ± SEM | |
| Human | 8.71 ± 0.21 | 100 ± 4.47 b,d–f |
| ORFV | 8.80 ± 0.9 | 123.70 ± 0.86 a,c,d,f |
| BPSV | 8.91 ± 0.18 | 110.37 ± 0.72 b,d–f |
| PCPV | 9.06 ± 0.36 | 54.11 ± 3.49 a–c,e,f |
| RDPV | 8.57 ± 0.04 | 126.99 ± 1.65 a,c,d,f |
| GSPV | 9.30 ± 0.80 | 25.77 ± 0.49 a–e |
| IL-10 | hIL-10R1 Binding | |
|---|---|---|
| pIC50 (M) ± SD | Emax (Δ%) ± SD | |
| Human | 8.79 ± 0.16 | 100 ± 1.6 |
| ORFV | 9.24 ± 0.14 | 104.98 ± 0.27 |
| BPSV | 8.72 ± 0.47 | 98.70 ± 2.17 |
| PCPV | 7.66 ± 0.45 | 94.58 ± 1.08 |
| RDPV | 9.51 ± 0.31 | 107.97 ± 5.71 |
| GSPV | ND | ND |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naqash, A.; Stuart, G.; Kemp, R.; Wise, L. Parapoxvirus Interleukin-10 Homologues Vary in Their Receptor Binding, Anti-Inflammatory, and Stimulatory Activities. Pathogens 2022, 11, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11050507
Naqash A, Stuart G, Kemp R, Wise L. Parapoxvirus Interleukin-10 Homologues Vary in Their Receptor Binding, Anti-Inflammatory, and Stimulatory Activities. Pathogens. 2022; 11(5):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11050507
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaqash, Amreen, Gabriella Stuart, Roslyn Kemp, and Lyn Wise. 2022. "Parapoxvirus Interleukin-10 Homologues Vary in Their Receptor Binding, Anti-Inflammatory, and Stimulatory Activities" Pathogens 11, no. 5: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11050507
APA StyleNaqash, A., Stuart, G., Kemp, R., & Wise, L. (2022). Parapoxvirus Interleukin-10 Homologues Vary in Their Receptor Binding, Anti-Inflammatory, and Stimulatory Activities. Pathogens, 11(5), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11050507






