A Modular Hepatitis E Virus Replicon System for Studies on the Role of ORF1-Encoded Polyprotein Domains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
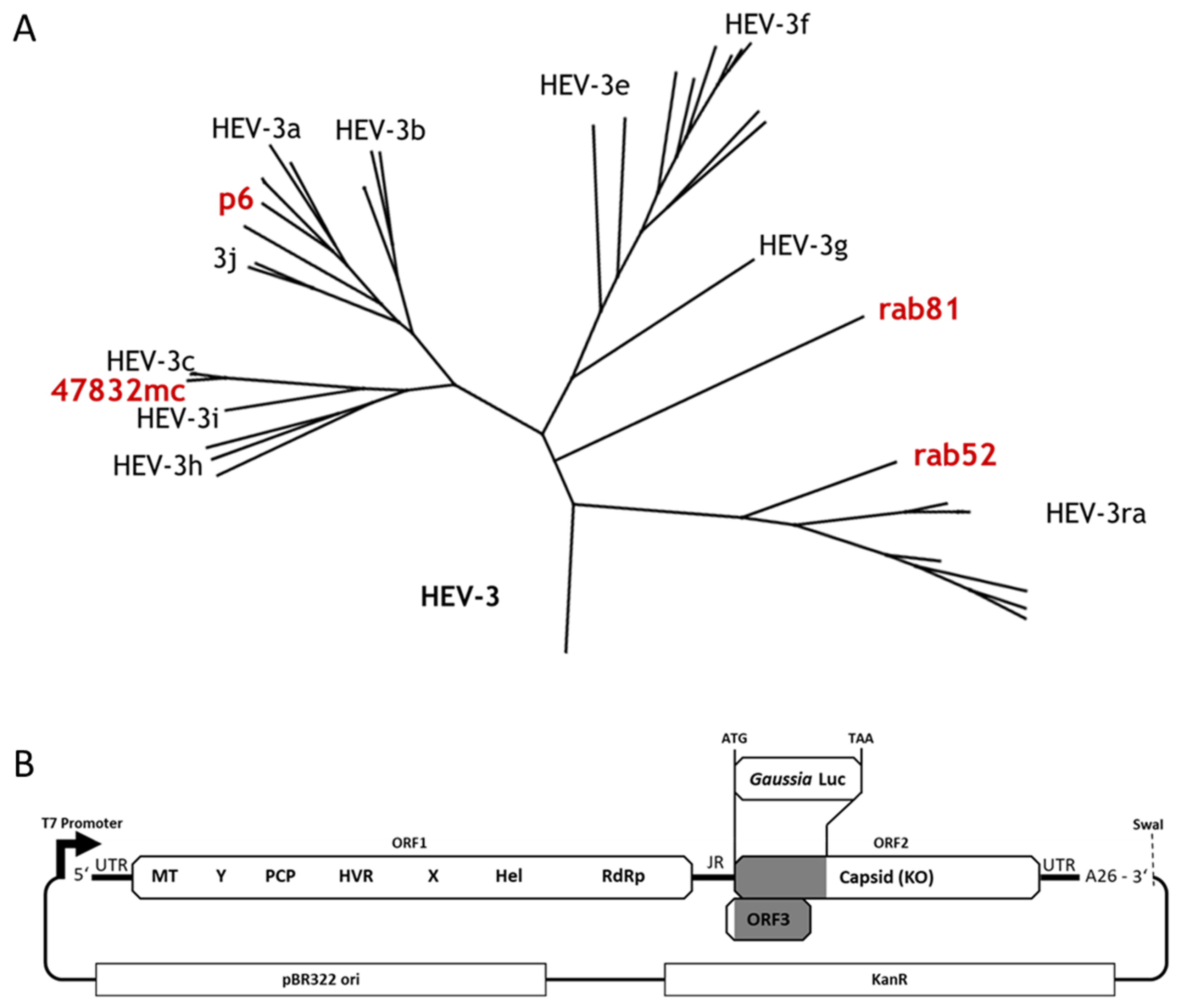
2.1. Construction of Luciferase Reporter Replicons Based on Different HEV-3 Strains
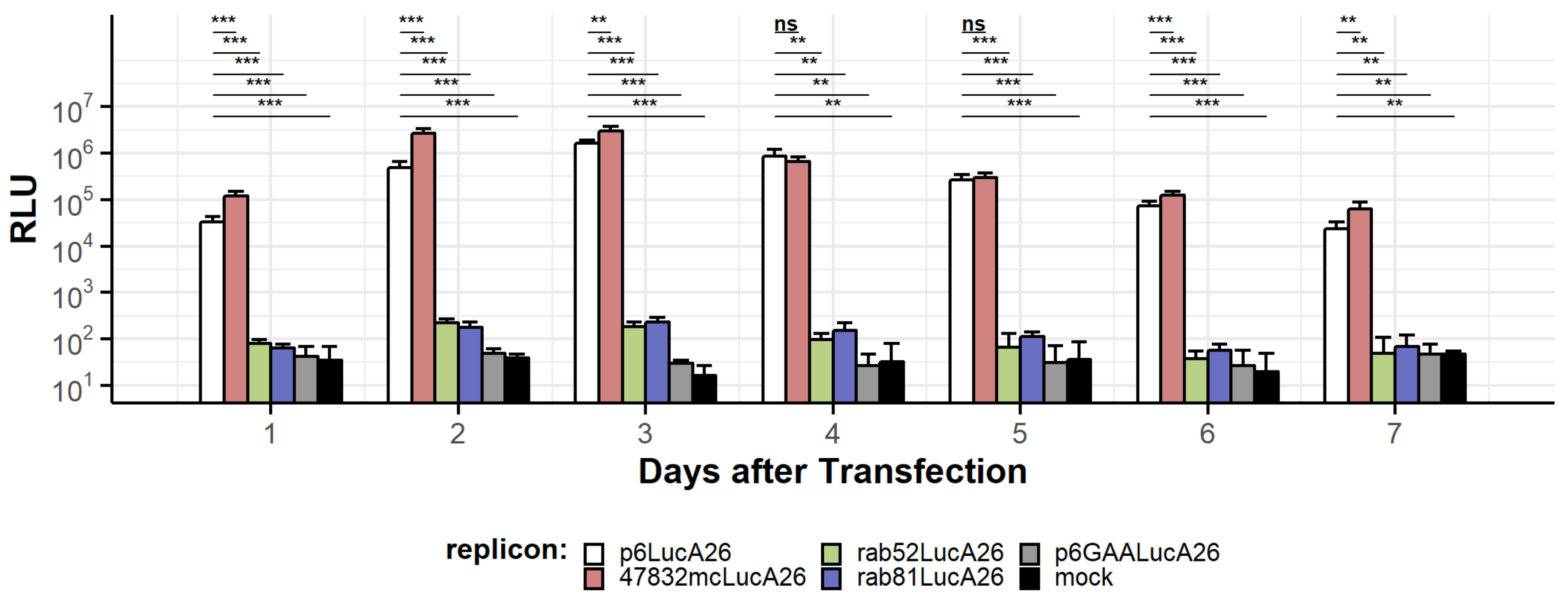
2.2. Rabbit HEV-Based Replicons Generate Low Luciferase Activity
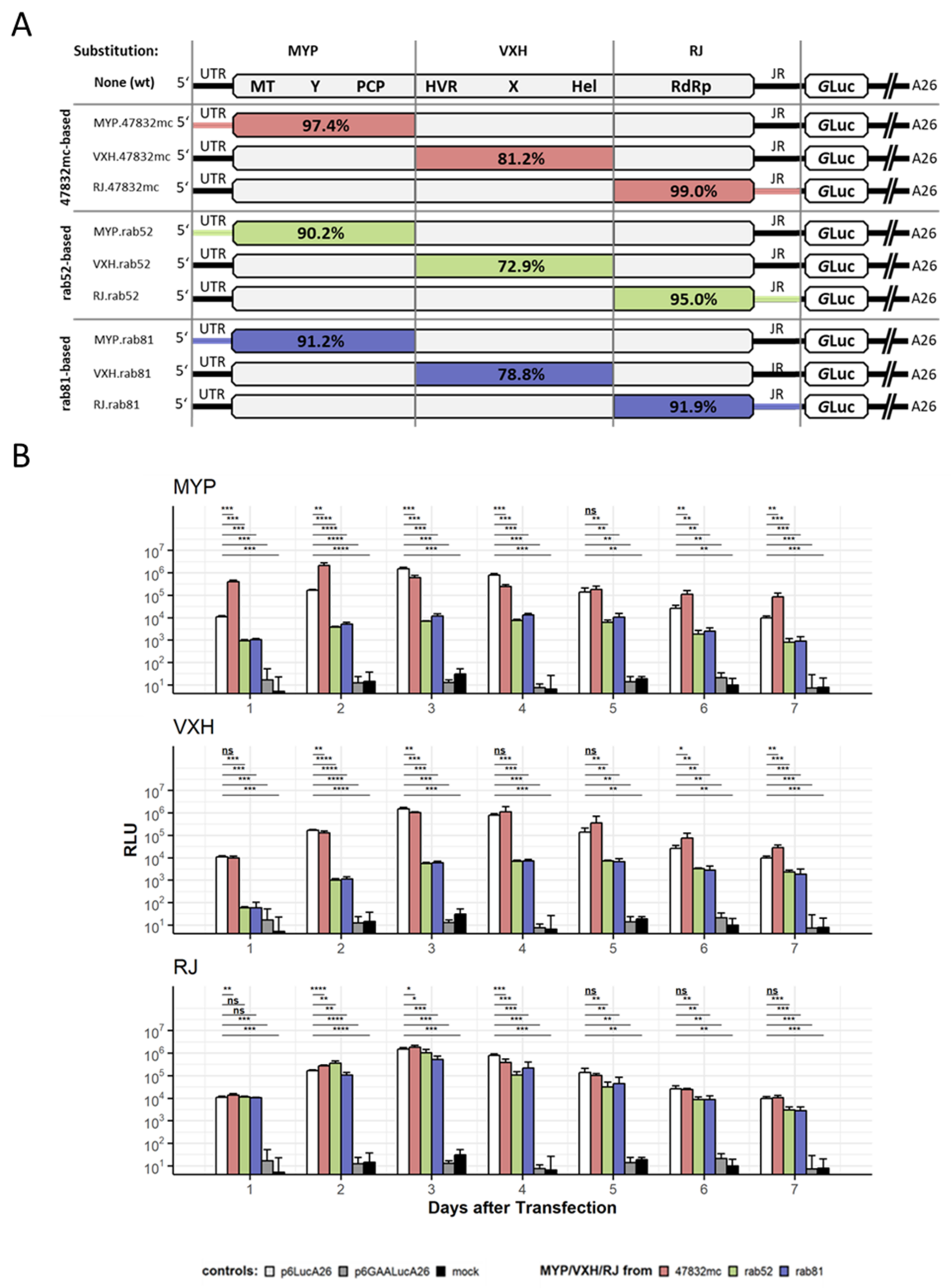
2.3. Construction and Evaluation of Chimeric ORF1 HEV Replicons
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. HEV Strains, Plasmids, and Cell Culture
4.2. PCR and Cloning
4.3. In Vitro Transcription and Transfection
4.4. Luciferase Reporter Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, K.E.; Heaney, C.D.; Kmush, B.L. The Epidemiology and Prevention of Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2017, 4, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Selves, J.; Mansuy, J.-M.; Ouezzani, L.; Péron, J.-M.; Guitard, J.; Cointault, O.; Esposito, L.; Abravanel, F.; Danjoux, M.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus and Chronic Hepatitis in Organ-Transplant Recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Gracia, M.T.; Suay-Garcia, B.; Mateos-Lindemann, M.L. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: Current state. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 27, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, S.P.; Meng, X.-J. Hepatitis E Virus Genome Structure and Replication Strategy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 9, a031724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, H.R.; Izopet, J. Transmission and Epidemiology of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 and 4 Infections. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a032144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dähnert, L.; Eiden, M.; Schlosser, J.; Fast, C.; Schröder, C.; Lange, E.; Gröner, A.; Schäfer, W.; Groschup, M.H. High sensitivity of domestic pigs to intravenous infection with HEV. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlosser, J.; Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Fast, C.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. Chronically infected wild boar can transmit genotype 3 hepatitis E virus to domestic pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasorndorkbua, C.; Thacker, B.J.; Halbur, P.G.; Guenette, D.K.; Buitenwerf, R.M.; Royer, R.L.; Meng, X.-J. Experimental infection of pregnant gilts with swine hepatitis E virus. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2003, 67, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Schlosser, J.; Eiden, M.; Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Fast, C.; Dremsek, P.; Lange, E.; Ulrich, R.G.; Groschup, M.H. Natural and experimental hepatitis E virus genotype 3—Infection in European wild boar is transmissible to domestic pigs. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneillie, L.; Banda, D.H.; Meuleman, P. Animal Models for Hepatitis E Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L. An overview: Rabbit hepatitis E virus (HEV) and rabbit providing an animal model for HEV study. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 28, e1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlosser, J.; Dähnert, L.; Dremsek, P.; Tauscher, K.; Fast, C.; Ziegler, U.; Gröner, A.; Ulrich, R.G.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. Different Outcomes of Experimental Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Diverse Mouse Strains, Wistar Rats, and Rabbits. Viruses 2018, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahli, R.; Fraga, M.; Semela, D.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Rabbit HEV in immunosuppressed patients with hepatitis E acquired in Switzerland. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izopet, J.; Dubois, M.; Bertagnoli, S.; Lhomme, S.; Marchandeau, S.; Boucher, S.; Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Guérin, J.-L. Hepatitis E Virus Strains in Rabbits and Evidence of a Closely Related Strain in Humans, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lei, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, P.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, H. SPF Rabbits Infected with Rabbit Hepatitis E Virus Isolate Experimentally Showing the Chronicity of Hepatitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, P.; Zou, Q.; Zhuang, H. Experimental infection of pregnant rabbits with hepatitis E virus demonstrating high mortality and vertical transmission. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.E.; Faulk, K.; Dalton, H.R.; Bendall, R.P.; Keane, F.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Cross-species infections of cultured cells by hepatitis E virus and discovery of an infectious virus-host recombinant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johne, R.; Reetz, J.; Ulrich, R.G.; Machnowska, P.; Sachsenröder, J.; Nickel, P.; Hofmann, J. An ORF1-rearranged hepatitis E virus derived from a chronically infected patient efficiently replicates in cell culture. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Faulk, K.; Mather, K.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.E.; Emerson, S.U. Adaptation of a Genotype 3 Hepatitis E Virus to Efficient Growth in Cell Culture Depends on an Inserted Human Gene Segment Acquired by Recombination. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholz, J.; Falkenhagen, A.; Johne, R. The Translated Amino Acid Sequence of an Insertion in the Hepatitis E Virus Strain 47832c Genome, But Not the RNA Sequence, Is Essential for Efficient Cell Culture Replication. Viruses 2021, 13, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schemmerer, M.; Johne, R.; Erl, M.; Jilg, W.; Wenzel, J.J. Isolation of Subtype 3c, 3e and 3f-Like Hepatitis E Virus Strains Stably Replicating to High Viral Loads in an Optimized Cell Culture System. Viruses 2019, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Shukla, P.; Torian, U.; Faulk, K.; Emerson, S.U. Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 1 Infection of Swine Kidney Cells In vitro is Inhibited at Multiple Levels. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Córdoba, L.; Feagins, A.R.; Opriessnig, T.; Cossaboom, C.M.; Dryman, B.A.; Huang, Y.; Meng, X.-J. Rescue of a genotype 4 human hepatitis E virus from cloned cDNA and characterization of intergenotypic chimeric viruses in cultured human liver cells and in pigs. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, D.; Yugo, D.M.; Kenney, S.P.; Heffron, C.L.; Opriessnig, T.; Karuppannan, A.K.; Bayne, J.; Halbur, P.G.; Meng, X. Dissecting the potential role of hepatitis E virus ORF1 non-structural gene in cross-species infection by using intergenotypic chimeric viruses. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 3563–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Jirintai, S.; Takahashi, M.; Okamoto, H.; Takeda, N.; Muramatsu, M.; Li, T. Persistent infection with a rabbit hepatitis E virus created by a reverse genetics system. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Bächlein, C.; Gadicherla, A.K.; Falkenhagen, A.; Tausch, S.H.; Johne, R. Establishment of a Plasmid-Based Reverse Genetics System for the Cell Culture-Adapted Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3c Strain 47832c. Pathogens 2020, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, H. Efficient cell culture systems for hepatitis E virus strains in feces and circulating blood. Rev. Med. Virol. 2011, 21, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschmidt, F.; Schwaiger, K.; Dähnert, L.; Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Höper, D.; Gareis, M.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. Hepatitis E virus in wild rabbits and European brown hares in Germany. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierniak, F.; von Arnim, F.; Heckel, G.; Ulrich, R.; Groschup, M.; Eiden, M. A Putative Novel Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 Subtype Identified in Rabbit, Germany 2016. Viruses 2021, 13, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magden, J.; Takeda, N.; Li, T.; Auvinen, P.; Ahola, T.; Miyamura, T.; Merits, A.; Kaariainen, L. Virus-Specific mRNA Capping Enzyme Encoded by Hepatitis E Virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6249–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emerson, S.U.; Zhang, M.; Meng, X.-J.; Nguyen, H.; Claire, M.S.; Govindarajan, S.; Huang, Y.K.; Purcell, R.H. Recombinant hepatitis E virus genomes infectious for primates: Importance of capping and discovery of a cis-reactive element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15270–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Choi, C.; Choi, I.; Han, G.; Rho, S.W.; Choi, J.; Kwon, J.; Park, M.-K.; Kim, S.-J.; Myoung, J. Hepatitis E Virus Methyltransferase Inhibits Type I Interferon Induction by Targeting RIG-I. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1554–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, D.; Panda, S.K.; Kapur, N.; Varma, S.P.K.; Durgapal, H. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) protease: A chymotrypsin-like enzyme that processes both non-structural (pORF1) and capsid (pORF2) protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Khattar, S.K.; Fredericksen, B.; Zhang, Y.-J. Hepatitis E Virus Inhibits Type I Interferon Induction by ORF1 Products. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11924–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parvez, M.K. Mutational analysis of hepatitis E virus ORF1 "Y-domain": Effects on RNA replication and virion infectivity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahilkar, S.; Paingankar, M.; Lole, K.S. Hepatitis E virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: RNA template specificities, recruitment and synthesis. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2231–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, S.P.; Meng, X.-J. The Lysine Residues within the Human Ribosomal Protein S17 Sequence Naturally Inserted into the Viral Nonstructural Protein of a Unique Strain of Hepatitis E Virus Are Important for Enhanced Virus Replication. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3793–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debing, Y.; Gisa, A.; Dallmeier, K.; Pischke, S.; Bremer, B.; Manns, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Suneetha, P.V.; Neyts, J. A Mutation in the Hepatitis E Virus RNA Polymerase Promotes Its Replication and Associates with Ribavirin Treatment Failure in Organ Transplant Recipients. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1008–1011.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Archer, N.; Bram, Y.; Heller, B.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ploss, A. Identification of the Intragenomic Promoter Controlling Hepatitis E Virus Subgenomic RNA Transcription. mBio 2018, 9, e00769-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schemmerer, M.; Apelt, S.; Trojnar, E.; Ulrich, R.G.; Wenzel, J.J.; Johne, R. Enhanced Replication of Hepatitis E Virus Strain 47832c in an A549-Derived Subclonal Cell Line. Viruses 2016, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potapov, V.; Ong, J.L.; Kucera, R.B.; Langhorst, B.W.; Bilotti, K.; Pryor, J.M.; Cantor, E.J.; Canton, B.; Knight, T.F.; Evans, T.C.; et al. Comprehensive Profiling of Four Base Overhang Ligation Fidelity by T4 DNA Ligase and Application to DNA Assembly. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inoue, H.; Nojima, H.; Okayama, H. High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. Gene 1990, 96, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannous, B.A. Gaussia luciferase reporter assay for monitoring biological processes in culture and in vivo. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Bryan, J. readxl: Read Excel Files; Version 1.3.1; RStudio: Boston, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. tidyr: Tidy Messy Data, Version 1.2.0. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=tidyr (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- Müller, K.; Wickham, H. tibble: Simple Data Frames, Version 3.1.6. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=tibble (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- Kassambara, A. rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests, Version 0.7.0. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rstatix (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K.; RStudio. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation, Version 1.0.8. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr: ‘ggplot2’ Based Publication Ready Plots, Version 0.4.0. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- Brand, T.V.D. ggh4x: Hacks for ‘ggplot2’, Version 0.2.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggh4x (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
| Replicon Nucleic Acid Sequence Identity | ORF1 Nucleic Acid Sequence Identity | ORF1 Amino Acid Sequence Identity | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | |||
| rab52 | 77.7% | rab52 | 74.4% | rab52 | 86.7% | ||||||
| 47832mc | 78.4% | 77.5% | 47832mc | 75.1% | 73.5% | 47832mc | 86.5% | 85.3% | |||
| p6 | 78.5% | 77.1% | 83.5% | p6 | 75.5% | 73.4% | 81.3% | p6 | 87% | 84.9% | 92.2% |
| Nucleotide Sequence Identity | |||||||||||
| MYP | VXH | RJ | |||||||||
| rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | |||
| rab52 | 76.9% | rab52 | 68.6% | rab52 | 79% | ||||||
| 47832mc | 79.1% | 78.4% | 47832mc | 67.7% | 63.7% | 47832mc | 79.9% | 81.4% | |||
| p6 | 80.4% | 78.5% | 84.9% | p6 | 67.7% | 63.7% | 75.3% | p6 | 79.4% | 80.6% | 84.7% |
| Amino Acid Sequence Identity | |||||||||||
| MYP | VXH | RJ | |||||||||
| rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | rab81 | rab52 | 47832mc | |||
| rab52 | 88.5% | rab52 | 81% | rab52 | 91.9% | ||||||
| 47832mc | 90.9% | 91.1% | 47832mc | 77.7% | 72.8% | 47832mc | 92.4% | 95.5% | |||
| p6 | 91.2% | 90.2% | 97.4% | p6 | 79.2% | 72.9% | 82% | p6 | 91.9% | 95% | 99% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cierniak, F.; Ulrich, R.G.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. A Modular Hepatitis E Virus Replicon System for Studies on the Role of ORF1-Encoded Polyprotein Domains. Pathogens 2022, 11, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030355
Cierniak F, Ulrich RG, Groschup MH, Eiden M. A Modular Hepatitis E Virus Replicon System for Studies on the Role of ORF1-Encoded Polyprotein Domains. Pathogens. 2022; 11(3):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030355
Chicago/Turabian StyleCierniak, Filip, Rainer G. Ulrich, Martin H. Groschup, and Martin Eiden. 2022. "A Modular Hepatitis E Virus Replicon System for Studies on the Role of ORF1-Encoded Polyprotein Domains" Pathogens 11, no. 3: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030355
APA StyleCierniak, F., Ulrich, R. G., Groschup, M. H., & Eiden, M. (2022). A Modular Hepatitis E Virus Replicon System for Studies on the Role of ORF1-Encoded Polyprotein Domains. Pathogens, 11(3), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030355






