Towards Accurate Point-of-Care Tests for Tuberculosis in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
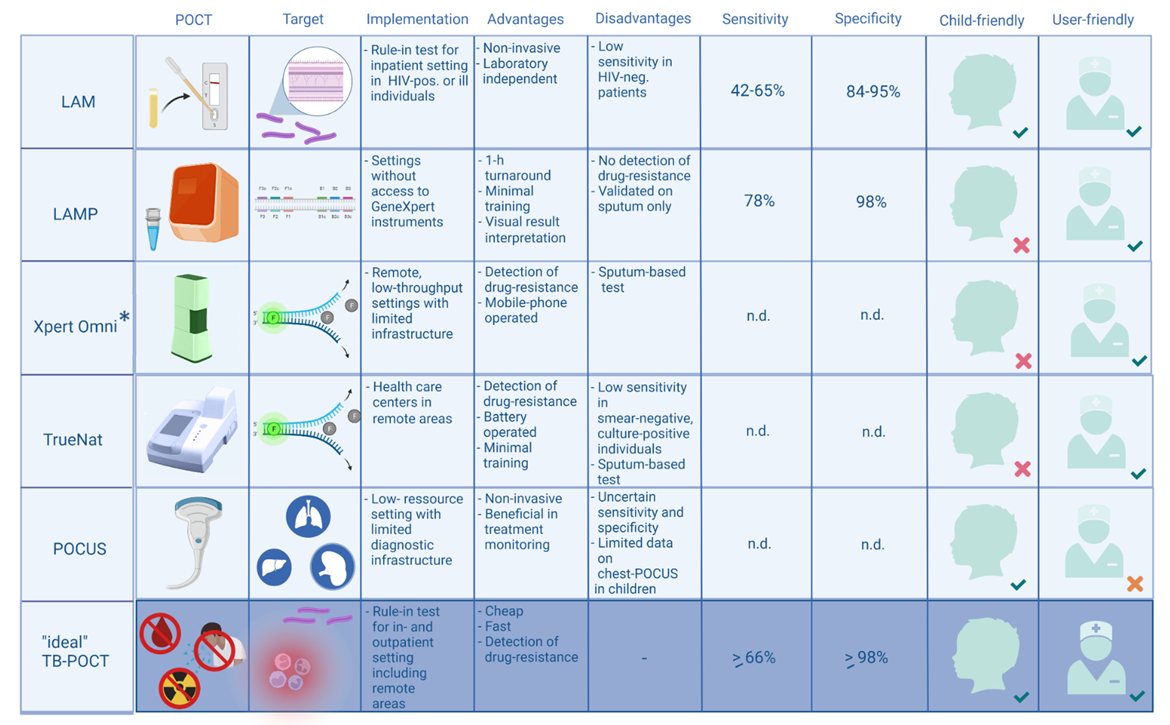
2. Currently Available Point-of-Care Tests (POCT) for Childhood Tuberculosis
2.1. Detection of Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) in Urine Using Lateral Flow Assays
2.2. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
2.3. PCR-Based Point-of-Care Tests
2.4. Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) Imaging for Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
2.5. Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) Imaging for Pulmonary Tuberculosis
2.6. Developments Using Ultrasound Imaging
3. Pipeline and Developments of Point-of-Care Tests for the Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
3.1. Immune Response Biomarkers
3.2. Biomarker Detection in Urine
3.3. Artificial Intelligence-Supported Interpretation Radiography
4. Potentially Available Point-of-Care Tests in the More Distant Future
4.1. Portable Radiography
4.2. Artificial Intelligence and Robotic Supported Ultrasound Imaging
4.3. The “Omics” Approach and Digital Development
5. Challenges for Tuberculosis Point-of-Care Tests
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Roadmap towards Ending in Children and Adolescents; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The END TB Strategy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/the-end-tb-strategy (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Chen, H.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, P. Point of care testing for infectious diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 493, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Berhane, S.; Taylor, M.; Adriano, A.; Davenport, C.; Dittrich, S.; Emperador, D.; Takwoingi, Y.; Cunningham, J.; et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 3, CD013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keitel, K.; Lacroix, L.; Gervaix, A. Point-of-care Testing in Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeling, R.W.; Holmes, K.K.; Mabey, D.; Ronald, A. Rapid tests for sexually transmitted infections (STIs): The way forward. Sexually Transm. Infect. 2006, 82 (Suppl. 5), v1–v6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Lateral Flow Urine Lipoarabinomannan Assay (LF-LAM) for the Diagnosis of Active Tuberculosis in People Living with HIV; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nicol, M.P.; Schumacher, S.G.; Workman, L.; Broger, T.; Baard, C.; Prins, M.; Bateman, L.; du Toit, E.; van Heerden, J.; Szekely, R.; et al. Accuracy of a Novel Urine Test, Fujifilm SILVAMP Tuberculosis Lipoarabinomannan, for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, e280–e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broger, T.; Sossen, B.; du Toit, E.; Kerkhoff, A.D.; Schutz, C.; Ivanova Reipold, E.; Ward, A.; Barr, D.A.; Mace, A.; Trollip, A.; et al. Novel lipoarabinomannan point-of-care tuberculosis test for people with HIV: A diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broger, T.; Nicol, M.P.; Sigal, G.B.; Gotuzzo, E.; Zimmer, A.J.; Surtie, S.; Caceres-Nakiche, T.; Mantsoki, A.; Reipold, E.I.; Szekely, R.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 3 urine lipoarabinomannan tuberculosis assays in HIV-negative outpatients. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5756–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broger, T.; Nicol, M.P.; Szekely, R.; Bjerrum, S.; Sossen, B.; Schutz, C.; Opintan, J.A.; Johansen, I.S.; Mitarai, S.; Chikamatsu, K.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a novel tuberculosis point-of-care urine lipoarabinomannan assay for people living with HIV: A meta-analysis of individual in- and outpatient data. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comella-Del-Barrio, P.; Bimba, J.S.; Adelakun, R.; Kontogianni, K.; Molina-Moya, B.; Osazuwa, O.; Creswell, J.; Cuevas, L.E.; Dominguez, J. Fujifilm SILVAMP TB-LAM for the Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Nigerian Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyoyeta, M.; Kerkhoff, A.D.; Chilukutu, L.; Moreau, E.; Schumacher, S.G.; Ruhwald, M. Diagnostic accuracy of a novel point-of-care urine lipoarabinomannan assay for the detection of tuberculosis among adult outpatients in Zambia: A prospective cross-sectional study. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2003999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, S.D.; Gupta-Wright, A. Detection of lipoarabinomannan (LAM) in urine is indicative of disseminated TB with renal involvement in patients living with HIV and advanced immunodeficiency: Evidence and implications. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkereuwem, E.; Togun, T.; Gomez, M.P.; Szekely, R.; Mace, A.; Jobe, D.; Schumacher, S.G.; Kampmann, B.; Denkinger, C.M.; Reach4KidsAfrica, C. Comparing accuracy of lipoarabinomannan urine tests for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in children from four African countries: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comella-Del-Barrio, P.; Molina-Moya, B.; Gautier, J.; Villar-Hernandez, R.; Doresca, M.J.C.; Salles-Mingels, B.; Canales-Aliaga, L.; Narcisse, M.; Perez-Porcuna, T.M.; Creswell, J.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of the Fujifilm SILVAMP TB-LAM in Children with Presumptive Tuberculosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.A.; Lukande, R.L.; Kalungi, S.; Van Marck, E.; Van de Vijver, K.; Kambugu, A.; Nelson, A.M.; Colebunders, R.; Manabe, Y.C. Is Urinary Lipoarabinomannan the Result of Renal Tuberculosis? Assessment of the Renal Histology in an Autopsy Cohort of Ugandan HIV-Infected Adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganath, D.; Mupere, E. Childhood tuberculosis and malnutrition. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Saravanan, N.; Bethunaickan, R.; Tripathy, S. Malnutrition: Modulator of Immune Responses in Tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The Use of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (TB-LAMP) for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, C.M.; Katamba, A.; Narang, P.; Giraldo, J.; Zamudio, C.; Joloba, M.; Narang, R.; Paramasivan, C.N.; Hillemann, D.; Nabeta, P.; et al. Feasibility and Operational Performance of Tuberculosis Detection by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Platform in Decentralized Settings: Results from a Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1984–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojang, A.L.; Mendy, F.S.; Tientcheu, L.D.; Otu, J.; Antonio, M.; Kampmann, B.; Agbla, S.; Sutherland, J.S. Comparison of TB-LAMP, GeneXpert MTB/RIF and culture for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in The Gambia. J. Infect. 2016, 72, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakiyingi, L.; Nakanwagi, P.; Briggs, J.; Agaba, T.; Mubiru, F.; Mugenyi, M.; Ssengooba, W.; Joloba, M.L.; Manabe, Y.C. Performance of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in a high prevalence TB/HIV rural setting in Uganda. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, R.; Yadav, A.; Agarwal, D.; Kumar, M.; Kamal, R.; Singh, D.; Bhatnagar, S. Comparison of Diagnostic Yield of Tuberculosis Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay With Cartridge-Based Nucleic Acid Amplification Test, Acid-Fast Bacilli Microscopy, and Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube Culture in Children With Pulmonary Tuberculosis. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2021, 10, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Daroch, P.; Gupta, P.; Vaidya, P.; Mathew, J.L.; Singh, M.; Sethi, S. Evaluation of TB-LAMP assay for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in children. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreedeep, K.S.; Sethi, S.; Yadav, R.; Vaidya, P.C.; Angurana, S.K.; Saini, A.; Mehra, N.; Singh, M. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) in the respiratory specimens for the diagnosis of pediatric pulmonary tuberculosis: A pilot study. J. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 26, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, A.W.; Gonzalez Fernandez, L.; Takwoingi, Y.; Eisenhut, M.; Detjen, A.K.; Steingart, K.R.; Mandalakas, A.M. Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assays for active tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 8, CD013359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zar, H.J.; Workman, L.J.; Prins, M.; Bateman, L.J.; Mbhele, S.P.; Whitman, C.B.; Denkinger, C.M.; Nicol, M.P. Tuberculosis Diagnosis in Children Using Xpert Ultra on Different Respiratory Specimens. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssengooba, W.; Iragena, J.D.; Nakiyingi, L.; Mujumbi, S.; Wobudeya, E.; Mboizi, R.; Boulware, D.; Meya, D.B.; Choo, L.; Crook, A.M.; et al. Accuracy of Xpert Ultra in Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis among Children in Uganda: A Substudy from the SHINE Trial. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00410-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, M.; Shi, Y.; Peng, X.; Liao, Q.; Wang, X.; Quan, S.; Wang, Y.; Duan, L.; et al. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Assay for Diagnosis of Childhood Tuberculosis: A Multicenter Accuracy Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00702-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, M.; Cameron, L.H.; Tadesse, G.; Woldeamanuel, Y.; Wassie, L. Variable Diagnostic Performance of Stool Xpert in Pediatric Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MI, USA, 2021; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, E.; Sulis, G.; Denkinger, C.M.; Johnston, J.C.; Pai, M.; Khan, F.A.; Burnham, C.-A.D. Diagnostic Accuracy of Stool Xpert MTB/RIF for Detection of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e02057-02018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simple KNCV Stool Test Breakthrough for Childhood; KNCV Tuberculosis Foundation: Hague, The Netherlands, 2018; Available online: https://www.kncvtbc.org/en/2018/10/25/simple-kncv-stool-test-break-through-for-childhood-tb/ (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Gotham, D.; McKenna, L.; Deborggraeve, S.; Madoori, S.; Branigan, D. Public investments in the development of GeneXpert molecular diagnostic technology. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branigan, D. Tuberculosis Diagnostics Pipeline Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.treatmentactiongroup.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/pipeline_TB_diagnostics_2021_final.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Cordeiro-Santos, M.; Pinheiro, J.D.S.; Spener-Gomes, R.; Souza, A.B.; Rodrigues, M.G.A.; Silva, J.; Jesus, J.S.; Sacramento, D.S.; Brito, A.C.; Bastos, M.L.S.; et al. Feasibility of GeneXpert((R)) Edge for Tuberculosis Diagnosis in Difficult-to-Reach Populations: Preliminary Results of a Proof-of-Concept Study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, N.S.; Singh, M.; Singh, U.B.; Myneedu, V.P.; Chauhan, D.S.; Sarin, R.; Mohan, A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Khangembam, J.S.; Kannan, T.; et al. Multicentric validation of indigenous molecular test Truenat MTB for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum samples from presumptive pulmonary tuberculosis patients in comparison with reference standards. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 152, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn-Nicholson, A.; Gomathi, S.N.; Ugarte-Gil, C.; Meaza, A.; Lavu, E.; Patel, P.; Choudhury, B.; Rodrigues, C.; Chadha, S.; Kazi, M.; et al. A prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study for the Truenat tuberculosis assays. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2100526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, J.R.; Abo, A.M.; Arroyo, A.C.; Doniger, S.J.; Fischer, J.W.; Rempell, R.; Gary, B.; Holmes, J.F.; Kessler, D.O.; Lam, S.H.; et al. Pediatric emergency medicine point-of-care ultrasound: Summary of the evidence. Crit. Ultrasound J. 2016, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, T.; Wallrauch, C.; Goblirsch, S.; Brunetti, E. Focused assessment with sonography for HIV-associated tuberculosis (FASH): A short protocol and a pictorial review. Crit. Ultrasound J. 2012, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, T.; Wallrauch, C.; Lessells, R.J.; Goblirsch, S.; Brunetti, E. Short course for focused assessment with sonography for human immunodeficiency virus/tuberculosis: Preliminary results in a rural setting in South Africa with high prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus and tuberculosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoving, D.J.; Lamprecht, H.H.; Stander, M.; Vallabh, K.; Fredericks, D.; Louw, P.; Muller, M.; Malan, J.J. Adequacy of the emergency point-of-care ultrasound core curriculum for the local burden of disease in South Africa. Emerg. Med. J. 2013, 30, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, T.; Mtemang’ombe, E.A.; Huson, M.A.; Heuvelings, C.C.; Belard, S.; Janssen, S.; Phiri, S.; Grobusch, M.P. Ultrasound for patients in a high HIV/tuberculosis prevalence setting: A needs assessment and review of focused applications for Sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 56, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobbio, F.; Di Gennaro, F.; Marotta, C.; Kok, J.; Akec, G.; Norbis, L.; Monno, L.; Saracino, A.; Mazzucco, W.; Lunardi, M. Focused ultrasound to diagnose HIV-associated tuberculosis (FASH) in the extremely resource-limited setting of South Sudan: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, D.; Pool, K.L.; Phiri, L.; Chibwana, F.; Schwab, K.; Longwe, L.; Banda, B.A.; Gama, K.; Chimombo, M.; Chipungu, C.; et al. Diagnostic Utility and Impact on Clinical Decision Making of Focused Assessment with Sonography for HIV-Associated Tuberculosis in Malawi: A Prospective Cohort Study. Glob. Health Sci. Pract. 2020, 8, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.F.; Saravu, K.; Heller, T.; Kadavigere, R.; Vishwanath, S.; Gehring, S.; Belard, S.; POCUS ETI Study Group. Point-of-Care Ultrasound for Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis in India: A Prospective Cohort Study in HIV-Positive and HIV-Negative Presumptive Tuberculosis Patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.; Grobusch, M.P.; Heller, T. ‘Remote FASH’ tele-sonography—A novel tool to assist diagnosing HIV-associated extrapulmonary tuberculosis in remote areas. Acta Trop. 2013, 127, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartoris, G.; Seddon, J.A.; Rabie, H.; Nel, E.D.; Losurdo, G.; Schaaf, H.S. Abdominal Involvement in Children With Bacteriologically Confirmed Tuberculosis: A Five-year Experience From Cape Town, South Africa. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belard, S.; Heller, T.; Orie, V.; Heuvelings, C.C.; Bateman, L.; Workman, L.; Grobusch, M.P.; Zar, H.J. Sonographic Findings of Abdominal Tuberculosis in Children with Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 1224–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belard, S.; Heuvelings, C.C.; Banderker, E.; Bateman, L.; Heller, T.; Andronikou, S.; Workman, L.; Grobusch, M.P.; Zar, H.J. Utility of Point-of-care Ultrasound in Children With Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrazzoli, D.; Lalli, M.; Boccia, D.; Houben, R.; Kranzer, K. Can tuberculosis patients in resource-constrained settings afford chest radiography? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritschi, N.; Wind, A.; Hammer, J.; Ritz, N.; Swiss Pediatric Surveillance Unit. Subclinical tuberculosis in children: Diagnostic strategies for identification reported in a 6-year national prospective surveillance study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwee, A.; Pantazidou, A.; Ritz, N.; Tebruegge, M.; Connell, T.G.; Cain, T.; Curtis, N. To x-ray or not to x-ray? Screening asymptomatic children for pulmonary TB: A retrospective audit. Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritschi, N.; Schmidt, A.J.; Hammer, J.; Ritz, N.; Swiss Pediatric Surveillance Unit. Pediatric Tuberculosis Disease during Years of High Refugee Arrivals: A 6-Year National Prospective Surveillance Study. Respiration 2021, 100, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronikou, S.; Grier, D.; Minhas, K. Reliability of chest radiograph interpretation for pulmonary tuberculosis in the screening of childhood TB contacts and migrant children in the UK. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvelings, C.C.; Belard, S.; Familusi, M.A.; Spijker, R.; Grobusch, M.P.; Zar, H.J. Chest ultrasound for the diagnosis of paediatric pulmonary diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. Br. Med. Bull. 2019, 129, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvelings, C.C.; Belard, S.; Janssen, S.; Wallrauch, C.; Grobusch, M.P.; Brunetti, E.; Giordani, M.T.; Heller, T. Chest ultrasonography in patients with HIV: A case series and review of the literature. Infection 2016, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, P.; Copetti, R.; Lapini, L.; Badona Monteiro, G.; N’Deque, A.; Baritussio, A. Chest ultrasound findings in pulmonary tuberculosis. Trop. Dr. 2017, 47, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, L.; Belard, S.; Janssen, S.; van Hoving, D.J.; Heller, T. Miliary tuberculosis: Sonographic pattern in chest ultrasound. Infection 2016, 44, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fentress, M.; Ugarte-Gil, C.; Cervantes, M.; Rivas, D.; Moore, D.; Caliguiri, P.; Bergman, K.; Noazin, S.; Padovani, A.; Gilman, R.H. Lung Ultrasound Findings Compared with Chest X-Ray Findings in Known Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study in Lima, Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Marcet, J.; Serres-Creixams, X.; Zuasnabar-Cotro, A.; Codina-Puig, X.; Catala-Puigbo, M.; Simon-Riazuelo, J.L. Comparison of ultrasound with plain radiography and CT for the detection of mediastinal lymphadenopathy in children with tuberculosis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2004, 34, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pool, K.L.; Heuvelings, C.C.; Belard, S.; Grobusch, M.P.; Zar, H.J.; Bulas, D.; Garra, B.; Andronikou, S. Technical aspects of mediastinal ultrasound for pediatric pulmonary tuberculosis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2017, 47, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseme, T.; Andronikou, S. Through the eye of the suprasternal notch: Point-of-care sonography for tuberculous mediastinal lymphadenopathy in children. Pediatr. Radiol. 2014, 44, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Alvarez, C.; Otero Fernandez, M.; Cabero-Perez, M.J.; Guerra Diez, L.; Galan Cuesta, M.; Aguero Balbin, J. Description of tuberculosis outbreak and usefulness of mediastinal ultrasound. An. Pediatr. 2013, 79, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvelings, C.C.; Belard, S.; Andronikou, S.; Jamieson-Luff, N.; Grobusch, M.P.; Zar, H.J. Chest ultrasound findings in children with suspected pulmonary tuberculosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvelings, C.C.; Belard, S.; Andronikou, S.; Lederman, H.; Moodley, H.; Grobusch, M.P.; Zar, H.J. Chest ultrasound compared to chest X-ray for pediatric pulmonary tuberculosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1914–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, R.; Cattarossi, L. Ultrasound diagnosis of pneumonia in children. Radiol. Med. 2008, 113, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.F.; Weber, M.; Tenbrock, K.; Belard, S. Call for ultrasound in paediatric tuberculosis work-up: A case report from Germany. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2020, 56, 964–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 2: Screening—Systematic Screening for Tuberculosis Disease; Geneva Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; World Health Organization: Geneva, Swizerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chegou, N.N.; Sutherland, J.S.; Malherbe, S.; Crampin, A.C.; Corstjens, P.L.; Geluk, A.; Mayanja-Kizza, H.; Loxton, A.G.; van der Spuy, G.; Stanley, K.; et al. Diagnostic performance of a seven-marker serum protein biosignature for the diagnosis of active TB disease in African primary healthcare clinic attendees with signs and symptoms suggestive of TB. Thorax 2016, 71, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, V.V.S.; Kumar, N.P.; Fukutani, K.F.; Vasconcelos, B.; Arriaga, M.B.; Silveira-Mattos, P.S.; Babu, S.; Andrade, B.B. Plasma levels of C-reactive protein, matrix metalloproteinase-7 and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein distinguish active pulmonary or extrapulmonary tuberculosis from uninfected controls in children. Cytokine 2019, 123, 154773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, E.; Broger, T.; Yerlikaya, S.; Fernandez-Carballo, B.L.; Pai, M.; Denkinger, C.M. A systematic review of biomarkers to detect active tuberculosis. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulenga, H.; Zauchenberger, C.Z.; Bunyasi, E.W.; Mbandi, S.K.; Mendelsohn, S.C.; Kagina, B.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Scriba, T.J.; Hatherill, M. Performance of diagnostic and predictive host blood transcriptomic signatures for Tuberculosis disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekambi, T.; Ibegbu, C.C.; Cagle, S.; Kalokhe, A.S.; Wang, Y.F.; Hu, Y.; Day, C.L.; Ray, S.M.; Rengarajan, J. Biomarkers on patient T cells diagnose active tuberculosis and monitor treatment response. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1827–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musvosvi, M.; Duffy, D.; Filander, E.; Africa, H.; Mabwe, S.; Jaxa, L.; Bilek, N.; Llibre, A.; Rouilly, V.; Hatherill, M.; et al. T-cell biomarkers for diagnosis of tuberculosis: Candidate evaluation by a simple whole blood assay for clinical translation. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1800153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira-Mattos, P.S.; Barreto-Duarte, B.; Vasconcelos, B.; Fukutani, K.F.; Vinhaes, C.L.; Oliveira-De-Souza, D.; Ibegbu, C.C.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Sterling, T.R.; Rengarajan, J.; et al. Differential Expression of Activation Markers by Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD4+ T Cell Distinguishes Extrapulmonary From Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Latent Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, M.P.; Pradeep, S.P.; Murthy, V.S.; Chikkannaiah, P.; Kambar, V.; Narayanashetty, S.; Burugina Nagaraja, S.; Gangadhar, N.; Yoganand, R.; Satchidanandam, V. CD38+CD27-TNF-alpha + on Mtb-specific CD4+ T Cells Is a Robust Biomarker for Tuberculosis Diagnosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiza, H.; Hella, J.; Arbues, A.; Magani, B.; Sasamalo, M.; Gagneux, S.; Reither, K.; Portevin, D. Case-control diagnostic accuracy study of a non-sputum CD38-based TAM-TB test from a single milliliter of blood. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steingart, K.R.; Flores, L.L.; Dendukuri, N.; Schiller, I.; Laal, S.; Ramsay, A.; Hopewell, P.C.; Pai, M. Commercial serological tests for the diagnosis of active pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekha, R.S.; Kamal, S.M.; Andersen, P.; Rahim, Z.; Hoq, M.I.; Ara, G.; Andersson, J.; Sack, D.; Raqib, R. Validation of the ALS assay in adult patients with culture confirmed pulmonary tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shete, P.B.; Ravindran, R.; Chang, E.; Worodria, W.; Chaisson, L.H.; Andama, A.; Davis, J.L.; Luciw, P.A.; Huang, L.; Khan, I.H.; et al. Evaluation of antibody responses to panels of M. tuberculosis antigens as a screening tool for active tuberculosis in Uganda. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, P.S.; Dolatshahi, S.; Lu, L.L.; Cain, A.; Palmieri, F.; Petrone, L.; Fortune, S.M.; Ottenhoff, T.H.M.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Goletti, D.; et al. Antibody Subclass and Glycosylation Shift Following Effective TB Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 679973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.H.; Roy, R.; McKay, R.T.; Ryan, D.; Brennan, L.; Tenori, L.; Luchinat, C.; Gao, X.; Zeri, A.C.; Gowda, G.A.; et al. Recommendations and Standardization of Biomarker Quantification Using NMR-Based Metabolomics with Particular Focus on Urinary Analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulterys, M.A.; Wagner, B.; Redard-Jacot, M.; Suresh, A.; Pollock, N.R.; Moreau, E.; Denkinger, C.M.; Drain, P.K.; Broger, T. Point-Of-Care Urine LAM Tests for Tuberculosis Diagnosis: A Status Update. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, J.T.; Andama, A.; Grant, B.D.; Ball, A.; Mwebe, S.; Asege, L.; Nakaye, M.; Lopez, B.B.; Hsieh, H.V.; Katumba, D.; et al. Field evaluation of a prototype tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan lateral flow assay on HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panraksa, Y.; Amin, A.G.; Graham, B.; Henry, C.S.; Chatterjee, D. Immobilization of Proteinase K for urine pretreatment to improve diagnostic accuracy of active tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreskovic, A.; Panpradist, N.; Marangu, D.; Ngwane, M.W.; Magcaba, Z.P.; Ngcobo, S.; Ngcobo, Z.; Horne, D.J.; Wilson, D.P.K.; Shapiro, A.E.; et al. Diagnosing Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Using Sequence-Specific Purification of Urine Cell-Free DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0007421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalekamp, S.; Klein, W.M.; van Leeuwen, K.G. Current and emerging artificial intelligence applications in chest imaging: A pediatric perspective. Pediatr. Radiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, M.; Franckling-Smith, Z.; Pillay, T.; Andronikou, S.; Zar, H.J. Chest Imaging for Pulmonary TB—An Update. Pathogens 2022, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahomed, N.; van Ginneken, B.; Philipsen, R.; Melendez, J.; Moore, D.P.; Moodley, H.; Sewchuran, T.; Mathew, D.; Madhi, S.A. Computer-aided diagnosis for World Health Organization-defined chest radiograph primary-endpoint pneumonia in children. Pediatr. Radiol. 2020, 50, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, A.; Pitcher, R.D.; Douglas, T.S. Computer-aided detection of pulmonary pathology in pediatric chest radiographs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Beijing, China, 20–24 September 2010; Volume 13, pp. 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.C.; Yu, H.R.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, W.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, H.H.; Jiang, J.H.; Su, T.Y.; Tsai, C.K.; Tsai, T.A.; et al. Diagnosis of common pulmonary diseases in children by X-ray images and deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, L.N.Q.; Codlin, A.; Ngo, T.D.; Dao, T.P.; Dong, T.T.T.; Mo, H.T.L.; Forse, R.; Nguyen, T.T.; Cung, C.V.; Nguyen, H.B.; et al. Early Evaluation of an Ultra-Portable X-ray System for Tuberculosis Active Case Finding. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Salvia, M.; Secco, G.; Torti, E.; Florimbi, G.; Guido, L.; Lago, P.; Salinaro, F.; Perlini, S.; Leporati, F. Deep learning and lung ultrasound for Covid-19 pneumonia detection and severity classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaban, G.; Galante, O.; Almog, Y.; Ullman, Y.; Fuchs, L. Feasibility of machine integrated point of care lung ultrasound automatic B-lines tool in the Corona-virus 2019 critical care unit. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, M.; Zimic, M.; Barrientos, F.; Barrientos, R.; Roman-Gonzalez, A.; Pajuelo, M.J.; Anticona, C.; Mayta, H.; Alva, A.; Solis-Vasquez, L.; et al. Automatic classification of pediatric pneumonia based on lung ultrasound pattern recognition. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robots Take Ultrasound to the Fourth Dimension. 2017. Available online: https://researchfeatures.com/robots-ultrasound/ (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Bloom Standard Automated Ultrasound. 2021. Available online: https://www.engineeringforchange.org/solutions/product/bloom-standard-automated-ultrasound/?post_type=solib&p=59013 (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Jakhar, S.; Bitzer, A.A.; Stromberg, L.R.; Mukundan, H. Pediatric Tuberculosis: The Impact of “Omics” on Diagnostics Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo Leonardo, S.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Leal-Calvo, T.; Leung, J.; Durán, V.; Samir, M.; Talbot, S.; Tallam, A.; Mello, F.C.D.Q.; Geffers, R.; et al. Reprogramming of Small Noncoding RNA Populations in Peripheral Blood Reveals Host Biomarkers for Latent and Active Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. MBio 2019, 10, e01037-01019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layre, E.; Al-Mubarak, R.; Belisle John, T.; Branch Moody, D.; Hatfull Graham, F.; William, R.J., Jr. Mycobacterial Lipidomics. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layre, E.; Moody, D.B. Lipidomic profiling of model organisms and the world’s major pathogens. Biochimie 2013, 95, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Adewole, O.O.; Erhabor, G.E.; Adewole, T.O.; Ojo, A.O.; Oshokoya, H.; Wolfe, L.M.; Prenni, J.E. Proteomic profiling of eccrine sweat reveals its potential as a diagnostic biofluid for active tuberculosis. PROTEOMICS—Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comella-Del-Barrio, P.; Izquierdo-Garcia, J.L.; Gautier, J.; Doresca, M.J.C.; Campos-Olivas, R.; Santiveri, C.M.; Muriel-Moreno, B.; Prat-Aymerich, C.; Abellana, R.; Perez-Porcuna, T.M.; et al. Urine NMR-based TB metabolic fingerprinting for the diagnosis of TB in children. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasier, N.; Eckstein, J. Sweat as a Source of Next-Generation Digital Biomarkers. Digit. Biomark. 2019, 3, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firouzi, F.; Rahmani, A.M.; Mankodiya, K.; Badaroglu, M.; Merrett, G.V.; Wong, P.; Farahani, B. Internet-of-Things and big data for smarter healthcare: From device to architecture, applications and analytics. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 78, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, N.; Osthoff, M.; De Ieso, F.; Eckstein, J. Next-Generation Digital Biomarkers for Tuberculosis and Antibiotic Stewardship: Perspective on Novel Molecular Digital Biomarkers in Sweat, Saliva, and Exhaled Breath. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e25907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, N.; Geissmann, L.; Kach, M.; Mutke, M.; Hoelz, B.; De Ieso, F.; Eckstein, J. Device- and Analytics-Agnostic Infrastructure for Continuous Inpatient Monitoring: A Technical Note. Digit. Biomark. 2020, 4, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babrak, L.M.; Menetski, J.; Rebhan, M.; Nisato, G.; Zinggeler, M.; Brasier, N.; Baerenfaller, K.; Brenzikofer, T.; Baltzer, L.; Vogler, C.; et al. Traditional and Digital Biomarkers: Two Worlds Apart? Digi. Biomark. 2019, 3, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, A.; Alavi, A.; Buergel, T.; Upadhyayula, S.; Wang, Q.; Ananthakrishnan, S.K.; Alavi, A.; Celis, D.; Gillespie, D.; Young, G.; et al. A scalable, secure, and interoperable platform for deep data-driven health management. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari, V.K.; Vinnakota, S.; Kakarla, R.K.; Maroju, S.; Ganesh, A.; Pervaram, S. Microwave Assisted Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of (E)-1-{2/3/4-[(1-Aryl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy]phenyl}-3-(2-morpholinoquinolin-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-ones. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2018, 88, 1502–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, A.; de Ferranti, S.D. Wearable Biosensors in Pediatric Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2019, 140, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Garcia, B.; Blazquez-Gamero, D.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; Ruiz-Contreras, J.; Bellon, J.M.; Munoz-Fernandez, M.A.; Mellado-Pena, M.J.; Group, E.S. Pediatric Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis: Clinical Spectrum, Risk Factors and Diagnostic Challenges in a Low Prevalence Region. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thwaites, G.E.; van Toorn, R.; Schoeman, J. Tuberculous meningitis: More questions, still too few answers. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellweger, J.P.; Sotgiu, G.; Corradi, M.; Durando, P. The diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI): Currently available tests, future developments, and perspectives to eliminate tuberculosis (TB). Med. Lav. 2020, 111, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprowicz, V.O.; Churchyard, G.; Lawn, S.D.; Squire, S.B.; Lalvani, A. Diagnosing latent tuberculosis in high-risk individuals: Rising to the challenge in high-burden areas. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204 (Suppl. 4), S1168–S1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.; Taegtmeyer, M.; Aol, G.; Bigogo, G.M.; Phillips-Howard, P.A.; Hill, J.; Laserson, K.F.; Ter Kuile, F.; Desai, M. Integrated point-of-care testing (POCT) of HIV, syphilis, malaria and anaemia in antenatal clinics in western Kenya: A longitudinal implementation study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, L.; George, J.; Broberg, E.K.; Struelens, M.J.; Leitmeyer, K.C.; Deshpande, A.; Parkinson, S.; Francombe, J.; Morley, K.I.; de Carvalho Gomes, H. Point of Care Testing for Infectious Disease in Europe: A Scoping Review and Survey Study. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policy-Cures-Research. COVID-19 R&D TRACKER. 2021. Available online: https://www.policycuresresearch.org/covid-19-r-d-tracker/ (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Treatment-Action-Group. 2020 Report on TB Research Funding Trends. 2021. Available online: https://www.treatmentactiongroup.org/resources/tbrd-report/tbrd-report-2020/ (accessed on 2 February 2022).
| Aspects to Be Considered | WHO ASSURED Criteria [7] | For Pediatric Infectious Diseases [6] | Proposed: for Childhood Tuberculosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Affordable | Cost-effective | Cheap |
| Diagnostic performance | Sensitive | Sufficient diagnostic accuracy and reliability | Sensitive |
| Specific | Impact on patient outcome/clinical benefit | Specific | |
| Usability | User-friendly | User-friendly | User and child-friendly |
| Turnaround time | Robust and rapid | Rapid | Rapid |
| Resources | Equipment-free | Adequate operational technology geared to environment of application | Applicable in low-resource settings |
| Target group | Deliverable to those who need them | Children in high- and low resource settings | |
| Specific requirements | Differentiation between TB infection and disease | ||
| Other | Information on drug resistance |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaezipour, N.; Fritschi, N.; Brasier, N.; Bélard, S.; Domínguez, J.; Tebruegge, M.; Portevin, D.; Ritz, N. Towards Accurate Point-of-Care Tests for Tuberculosis in Children. Pathogens 2022, 11, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030327
Vaezipour N, Fritschi N, Brasier N, Bélard S, Domínguez J, Tebruegge M, Portevin D, Ritz N. Towards Accurate Point-of-Care Tests for Tuberculosis in Children. Pathogens. 2022; 11(3):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030327
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaezipour, Nina, Nora Fritschi, Noé Brasier, Sabine Bélard, José Domínguez, Marc Tebruegge, Damien Portevin, and Nicole Ritz. 2022. "Towards Accurate Point-of-Care Tests for Tuberculosis in Children" Pathogens 11, no. 3: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030327
APA StyleVaezipour, N., Fritschi, N., Brasier, N., Bélard, S., Domínguez, J., Tebruegge, M., Portevin, D., & Ritz, N. (2022). Towards Accurate Point-of-Care Tests for Tuberculosis in Children. Pathogens, 11(3), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030327






