Investigation of the Familial Risk of Rheumatic Heart Disease with Systematic Echocardiographic Screening: Data from the PROVAR+ Family Study †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
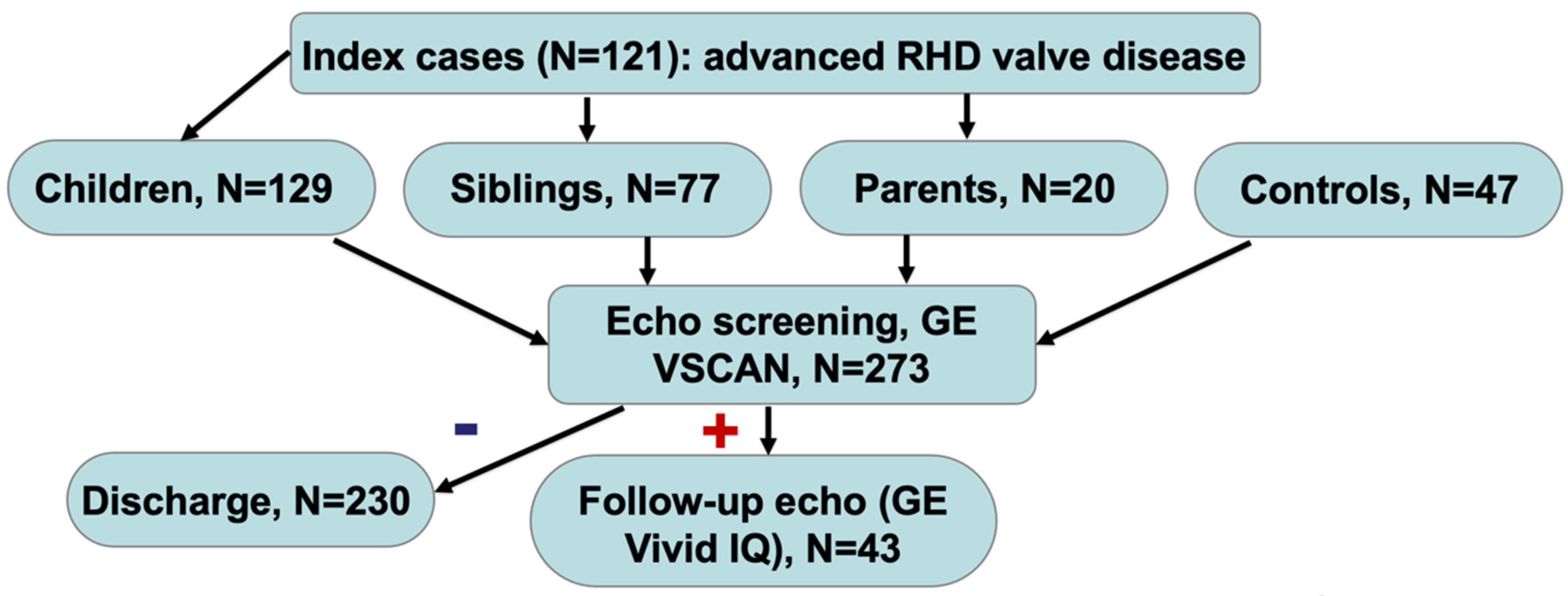
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions:
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, G.S.; Tartof, S.Y.; Oliveira, D.W.; Guedes, A.C.; Reis, M.G.; Riley, L.W.; Ko, A.I. Surgery for valvular heart disease: A population-based study in a Brazilian urban center. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, M.; Haines, A. Brazil’s Family Health Programme. BMJ 2010, 341, c4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, B.R.; Beaton, A.Z.; Nunes, M.C.; Diamantino, A.C.; Carmo, G.A.; Oliveira, K.K.; Oliveira, C.M.; Meira, Z.M.; Castilho, S.R.; Lopes, E.L.; et al. Echocardiographic prevalence of rheumatic heart disease in Brazilian schoolchildren: Data from the PROVAR study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 219, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, B.R.; Sable, C.; Nunes, M.C.P.; Diamantino, A.C.; Oliveira, K.K.B.; Oliveira, C.M.; Meira, Z.M.A.; Castilho, S.R.T.; Santos, J.P.A.; Rabelo, L.M.M.; et al. Comparison Between Different Strategies of Rheumatic Heart Disease Echocardiographic Screening in Brazil: Data From the PROVAR (Rheumatic Valve Disease Screening Program) Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, L.A.; D’Antoine, H.A.; Tong, S.Y.C.; McKinnon, M.; Bessarab, D.; Brown, N.; Remenyi, B.; Steer, A.; Syn, G.; Blackwell, J.M.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Genetic Risk Factors for Rheumatic Heart Disease in Aboriginal Australians Provides Support for Pathogenic Molecular Mimicry. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, T.; Mirabel, M.M.; Kado, J.; Auckland, K.; Nowak, J.; Rautanen, A.; Mentzer, A.J.; Marijon, E.; Jouven, X.; Perman, M.L.; et al. Association between a common immunoglobulin heavy chain allele and rheumatic heart disease risk in Oceania. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machipisa, T.; Chong, M.; Muhamed, B.; Chishala, C.; Shaboodien, G.; Pandie, S.; de Vries, J.; Laing, N.; Joachim, A.; Daniels, R.; et al. Association of Novel Locus With Rheumatic Heart Disease in Black African Individuals: Findings From the RHDGen Study. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliku, T.; Sable, C.; Scheel, A.; Tompsett, A.; Lwabi, P.; Okello, E.; McCarter, R.; Summar, M.; Beaton, A. Targeted Echocardiographic Screening for Latent Rheumatic Heart Disease in Northern Uganda: Evaluating Familial Risk Following Identification of an Index Case. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkmim, M.B.; Figueira, R.M.; Marcolino, M.S.; Cardoso, C.S.; de Abreu, M.P.; Cunha, L.R.; da Cunha, D.F.; Antunes, A.P.; Resende, A.G.; Resende, E.S.; et al. Improving patient access to specialized health care: The Telehealth Network of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Bull. World Health Organ. 2012, 90, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remenyi, B.; Carapetis, J.; Wyber, R.; Taubert, K.; Mayosi, B.M.; World Heart, F. Position statement of the World Heart Federation on the prevention and control of rheumatic heart disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2013, 10, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, B.R.; Beaton, A.Z.; Nunes, M.C.P.; Tompsett, A.R.; Oliveira, K.K.B.; Diamantino, A.C.; Barbosa, M.M.; Lourenco, T.V.; Teixeira, I.M.; Ruiz, G.Z.L.; et al. Integration of echocardiographic screening by non-physicians with remote reading in primary care. Heart 2019, 105, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nascimento, B.R.; Sable, C.; Nunes, M.C.P.; Oliveira, K.K.B.; Franco, J.; Barbosa, M.M.; Reese, A.T.; Diamantino, A.C.; Ferreira Filho, D.S.G.; Macedo, F.V.B.; et al. Echocardiographic screening of pregnant women by non-physicians with remote interpretation in primary care. Fam. Pract. 2021, 38, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) Guidelines. Available online: http://asecho.org/ase-guidelines-by-publication-date/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Zoghbi, W.A.; Adams, D.; Bonow, R.O.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Foster, E.; Grayburn, P.A.; Hahn, R.T.; Han, Y.; Hung, J.; Lang, R.M.; et al. Recommendations for Noninvasive Evaluation of Native Valvular Regurgitation: A Report from the American Society of Echocardiography Developed in Collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2017, 30, 303–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.; Rahko, P.S.; Blauwet, L.A.; Canaday, B.; Finstuen, J.A.; Foster, M.C.; Horton, K.; Ogunyankin, K.O.; Palma, R.A.; Velazquez, E.J. Guidelines for Performing a Comprehensive Transthoracic Echocardiographic Examination in Adults: Recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Culliford-Semmens, N.; Tilton, E.; Wilson, N.; Stirling, J.; Doughty, R.; Gentles, T.; Peat, B.; Dimalapang, E.; Webb, R. Echocardiography for latent rheumatic heart disease in first degree relatives of children with acute rheumatic fever: Implications for active case finding in family members. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzeni, F.; Corda, M.; Gianturco, L.; Porcu, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Turiel, M. Cardiovascular Imaging Techniques in Systemic Rheumatic Diseases. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2018, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.; Cannon, J.; Atkinson, D.; Brown, A.; Maguire, G.; Remenyi, B.; Wheaton, G.; Geelhoed, E.; Carapetis, J.R. Echocardiographic Screening for Rheumatic Heart Disease in Indigenous Australian Children: A Cost-Utility Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubels, J.; Sable, C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Nunes, M.C.P.; Oliveira, K.K.B.; Rabelo, L.C.; Teixeira, I.M.; Ruiz, G.Z.L.; Rabelo, L.M.M.; Tompsett, A.R.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Rheumatic Heart Disease Echocardiographic Screening in Brazil: Data from the PROVAR+ Study: Cost-effectiveness of RHD screening in Brazil. Global Heart 2020, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karki, P.; Uranw, S.; Bastola, S.; Mahato, R.; Shrestha, N.R.; Sherpa, K.; Dhungana, S.; Odutayo, A.; Gurung, K.; Pandey, N.; et al. Effectiveness of Systematic Echocardiographic Screening for Rheumatic Heart Disease in Nepalese Schoolchildren: A Cluster Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, B.R.; Nunes, M.C.; Lopes, E.L.; Rezende, V.M.; Landay, T.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Sable, C.; Beaton, A.Z. Rheumatic heart disease echocardiographic screening: Approaching practical and affordable solutions. Heart 2016, 102, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, E.L.; Beaton, A.Z.; Nascimento, B.R.; Tompsett, A.; Dos Santos, J.P.; Perlman, L.; Diamantino, A.C.; Oliveira, K.K.; Oliveira, C.M.; Nunes, M.; et al. Telehealth solutions to enable global collaboration in rheumatic heart disease screening. J. Telemed. Telecare 2018, 24, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantino Soares, A.C.; Araujo Passos, L.S.; Sable, C.; Beaton, A.; Ribeiro, V.T.; Gollob, K.J.; Dutra, W.O.; Nunes, M.C.P. Circulating cytokines predict severity of rheumatic heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 289, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tormin, J.; Nascimento, B.R.; Sable, C.A.; da Silva, J.L.P.; Brandao-de-Resende, C.; Rocha, L.P.C.; Pinto, C.H.R.; Neves, E.G.A.; Macedo, F.V.B.; Fraga, C.L.; et al. Cytokine gene functional polymorphisms and phenotypic expression as predictors of evolution from latent to clinical rheumatic heart disease. Cytokine 2021, 138, 155370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, M.E.; Stander, R.; Vogel, J.; Adeyemo, A.A.; Mayosi, B.M. Genetic susceptibility to acute rheumatic fever: A systematic review and meta-analysis of twin studies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nascimento, B.R.; Nunes, M.C.P.; Lima, E.M.; Sanyahumbi, A.E.; Wilson, N.; Tilton, E.; Remond, M.G.W.; Maguire, G.P.; Ribeiro, A.L.P.; Kazembe, P.N.; et al. Outcomes of Echocardiography-Detected Rheumatic Heart Disease: Validating a Simplified Score in Cohorts From Different Countries. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE. IBGE-Cidades. Available online: http://cidades.ibge.gov.br (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Nascimento, B.R.; Brant, L.C.C.; Yadgir, S.; Oliveira, G.M.M.; Roth, G.; Glenn, S.D.; Mooney, M.; Naghavi, M.; Passos, V.M.A.; Duncan, B.B.; et al. Trends in prevalence, mortality, and morbidity associated with high systolic blood pressure in Brazil from 1990 to 2017: Estimates from the “Global Burden of Disease 2017” (GBD 2017) study. Popul. Health Metr. 2020, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelini, F.; Blair, N.; Wilson, N.; Farrell, A.; Aitken, A. Family acceptability of school-based echocardiographic screening for rheumatic heart disease in a high-risk population in New Zealand. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2015, 51, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables: | Relatives (N = 226) | Controls (N = 47) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 37.8 ± 16.6 | 52.2 ± 16.3 | <0.001* |
| Sex (female, N (%)) | 153 (67.7) | 14 (29.8) | <0.001* |
| Household (mean ± SD) | 5.5 ± 2.4 | 4.8 ± 3.9 | 0.23 |
| Origin (rural/small town) (N, %) | 106 (46.9) | 28 (59.6) | 0.28 |
| Mother’s education (illiterate/incomplete elementary school) (N, %) † | 166 (73.5) | 42 (89.4) | 0.08 |
| Kinship (N, %): | |||
| • Siblings | • 77 (34.1) | N/A | |
| • Children | • 129 (57.1) | ||
| • Parents | • 20 (8.8) | ||
| • Other (controls) | • 47 (100) | ||
| Living with index case (N, %): | |||
| • Up to 10 years | • 21 (9.3) | • 10 (21.3) | 0.013 * |
| • 10 to 20 years | • 85 (37.6) | • 8 (17) | |
| • Over 20 years | • 118 (52.2) | • 28 (59.6) | |
| Hypertension (N, %) | 42 (18.6) | 15 (31.9) | 0.049 * |
| Diabetes (N, %) | 18 (8.0) | 1 (2.1) | 0.21 |
| Known history of RHD (N, %) | 6 (2.7) | 0 | 0.59 |
| Stroke (N, %) | 4 (1.8) | 1 (2.1) | 1.00 |
| Previous symptoms of heart failure (N, %) | 4 (1.8) | 0 | 1.00 |
| Known history of coronary artery disease (N, %) | 5 (2.2) | 3 (6.4) | 0.14 |
| Recurrent pharyngitis (N, %) ‡ | 65 (28.8) | 8 (17.0) | 0.08 |
| Symptoms and clinical presentation: | |||
| Dyspnea (N, %) | 76 (33.6) | 7 (14.9) | 0.014 * |
| Chest pain (N, %) | 72 (31.9) | 9 (19.1) | 0.11 |
| Palpitations (N, %) | 73 (32.3) | 11 (23.4) | 0.30 |
| Variables: | Relatives (N = 226) | Controls (N = 47) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Screening echocardiography (N = 273) | |||
| LV dysfunction (mild) (N, %) | 1 (0.4) | 0 | 1.00 |
| LV hypertrophy (mild/moderate) (N, %) | 15 (6.6) | 7 (14.9) | 0.08 |
| Mitral valve (N, %): | |||
| • Rheumatic mitral valve | • 15 (6.6) | • 0 | 0.17 |
| • Mitral valve prolapse | • 3 (1.3) | • 0 | |
| • Other | • 4 (1.8) | • 2 (4.3) | |
| Mitral regurgitation (mild/moderate) (N, %) | 52 (23.0) | 9 (19.1) | 0.70 |
| Mitral stenosis (N, %) | 6 (2.7) | 0 | 0.59 |
| Aortic valve (N, %): | |||
| • Rheumatic aortic valve | • 3 (1.3) | • 0 | 0.54 |
| • Calcific aortic valve | • 9 (4.0) | • 2 (4.3) | |
| • Other | • 7 (3.1) | • 0 | |
| Aortic regurgitation (mild/moderate) (N, %) | 26 (11.6) | 5 (10.6) | 1.00 |
| Aortic stenosis (N, %) | 7 (3.1) | 0 | 0.61 |
| Tricuspid regurgitation (N, %) | 37 (16.5) | 6 (12.8) | 0.66 |
| Indication for standard echo (N, %) | 39 (17.4) | 4 (8.7) | 0.19 |
| RHD (suggestive) (N, %) | 17 (7.5) | 0 | 0.05 |
| Standard echocardiography (confirmed RHD cases, N = 14) | |||
| Valve involvement (N, %): | |||
| • Mitral valve (isolated) | • 11 (4.9) | - | N/A |
| • Aortic valve (isolated) | • 0 | - | |
| • Mixed (mitral + aortic) | • 3 (1.3) | - | |
| MV disease (N, %): | |||
| • MR (mild/moderate) | • 11 (4.9) | - | N/A |
| • Morphological/prosthesis + MS | • 4 ((1.8) | - | |
| AV disease (N, %): | |||
| • AR + AS + morphological | • 2 (0.9) | - | N/A |
| • Morphological (prosthesis) | • 1 (0.4) | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, J.; Nascimento, B.R.; Beaton, A.Z.; Oliveira, K.K.B.; Barbosa, M.M.; Faria, S.C.C.; Arantes, N.F.; Mello, L.A.; Nassif, M.C.L.; Oliveira, G.C.; et al. Investigation of the Familial Risk of Rheumatic Heart Disease with Systematic Echocardiographic Screening: Data from the PROVAR+ Family Study. Pathogens 2022, 11, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020139
Franco J, Nascimento BR, Beaton AZ, Oliveira KKB, Barbosa MM, Faria SCC, Arantes NF, Mello LA, Nassif MCL, Oliveira GC, et al. Investigation of the Familial Risk of Rheumatic Heart Disease with Systematic Echocardiographic Screening: Data from the PROVAR+ Family Study. Pathogens. 2022; 11(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, Juliane, Bruno R. Nascimento, Andrea Z. Beaton, Kaciane K. B. Oliveira, Marcia M. Barbosa, Sanny Cristina C. Faria, Nayana F. Arantes, Luana A. Mello, Maria Cecília L. Nassif, Guilherme C. Oliveira, and et al. 2022. "Investigation of the Familial Risk of Rheumatic Heart Disease with Systematic Echocardiographic Screening: Data from the PROVAR+ Family Study" Pathogens 11, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020139
APA StyleFranco, J., Nascimento, B. R., Beaton, A. Z., Oliveira, K. K. B., Barbosa, M. M., Faria, S. C. C., Arantes, N. F., Mello, L. A., Nassif, M. C. L., Oliveira, G. C., Spolaor, B. C., Campos, C. F., Silva, V. R. H., Nogueira, M. A. A., Ribeiro, A. L., Sable, C. A., Nunes, M. C. P., & On behalf of the PROVAR+ (Programa de RastreamentO da VAlvopatia Reumática e outras Doenças Cardiovasculares) investigators. (2022). Investigation of the Familial Risk of Rheumatic Heart Disease with Systematic Echocardiographic Screening: Data from the PROVAR+ Family Study. Pathogens, 11(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020139






