Isolation and Characterization of Chi-like Salmonella Bacteriophages Infecting Two Salmonella enterica Serovars, Typhimurium and Enteritidis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Their Culture Conditions
2.2. Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
2.3. Enrichment and Isolation of Phages
2.4. Phages Purification and Propagation
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Determination of Phages Host Range
2.7. One-Step Growth Curve
2.8. Thermal and pH Stability Assay
2.9. Killing Assay
2.10. Organic and Detergent Solvents
2.11. Genomic Characterization of the Isolated Phages
2.12. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.13. Genome Comparison in a Two-Dimensional Plot
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Sensitivity
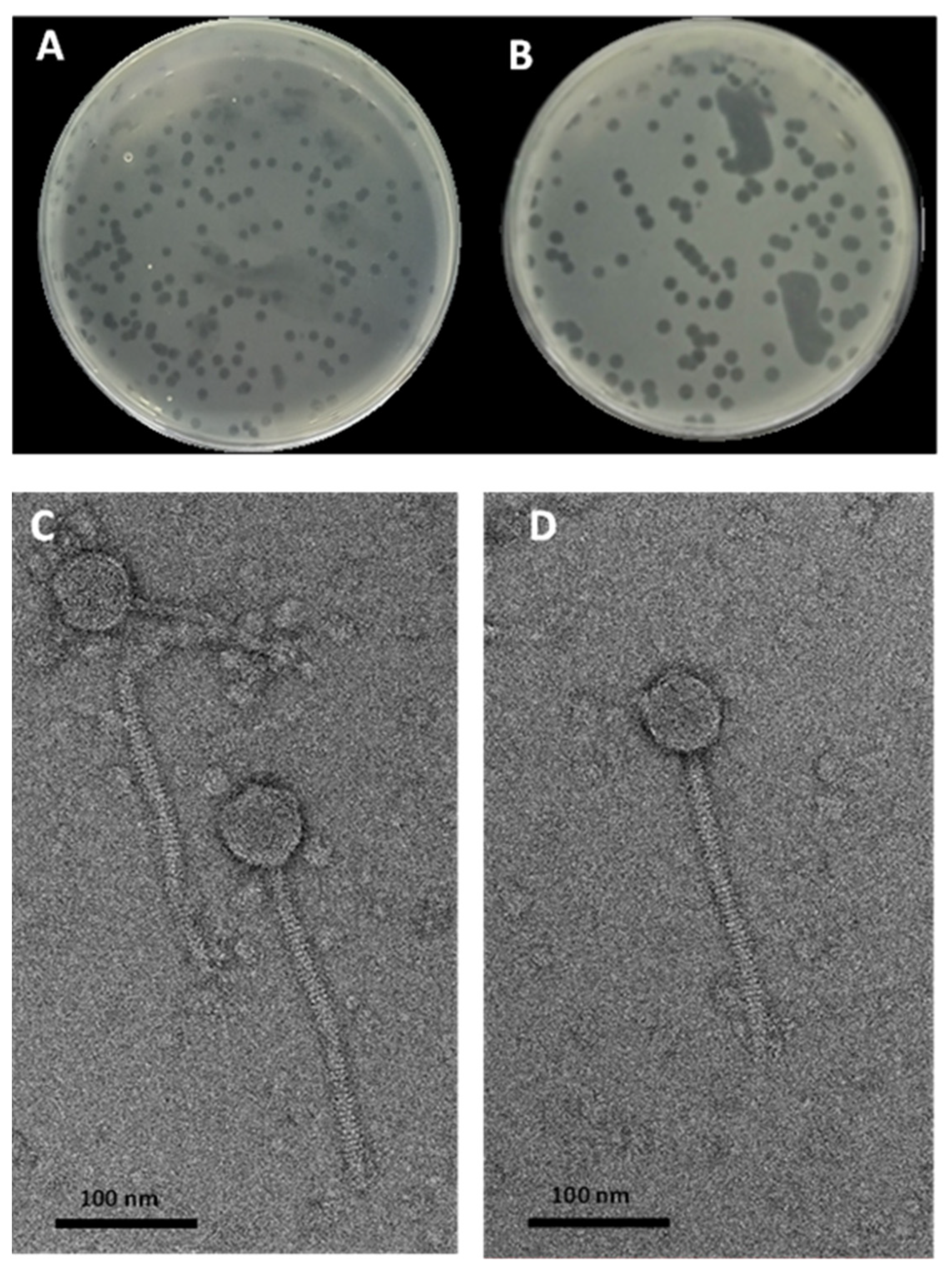
3.2. Bacteriophages Isolation and TEM Characterization
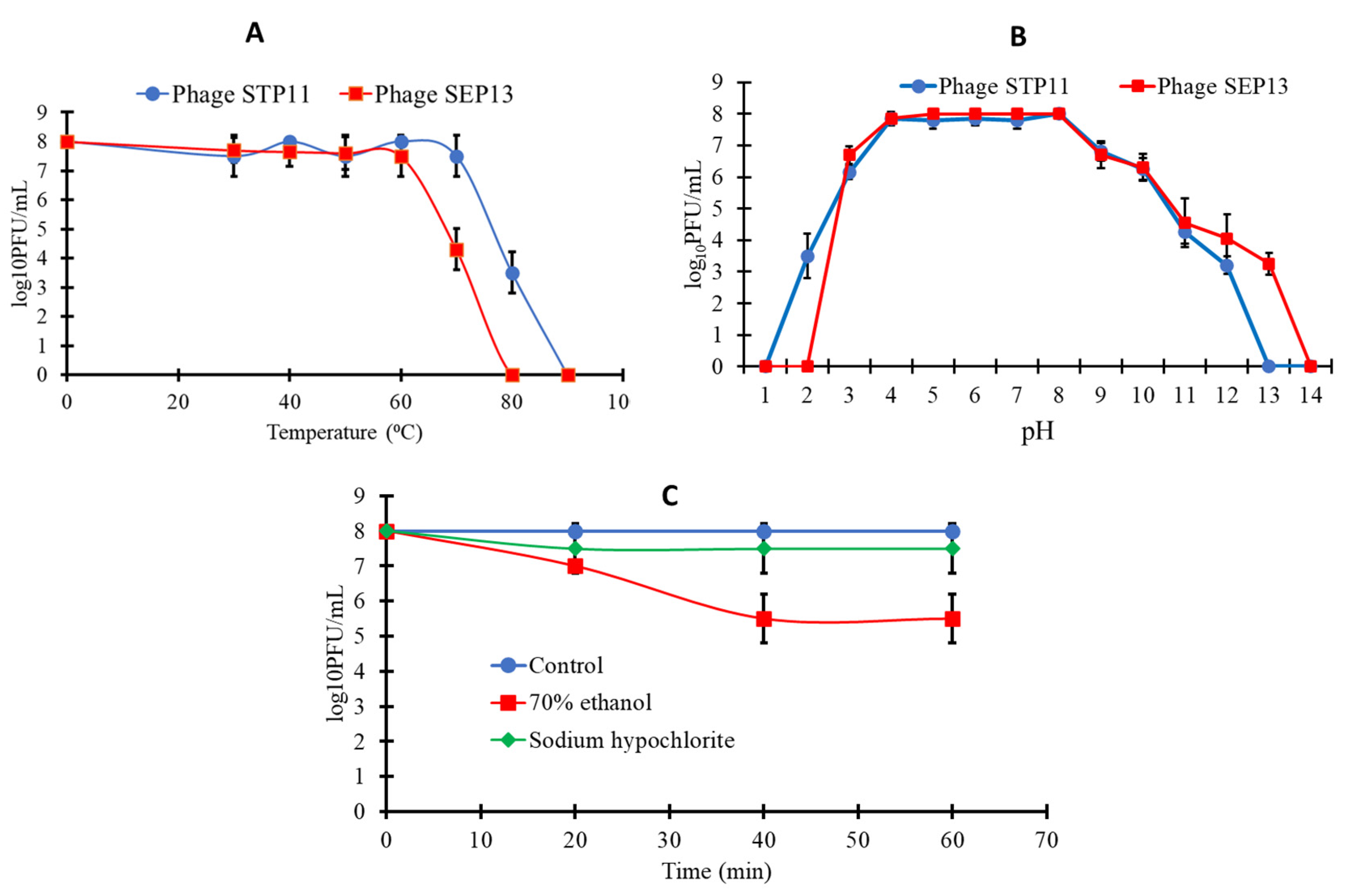
3.3. Sensitivity of the Isolated Phages to Physical and Chemical Agents
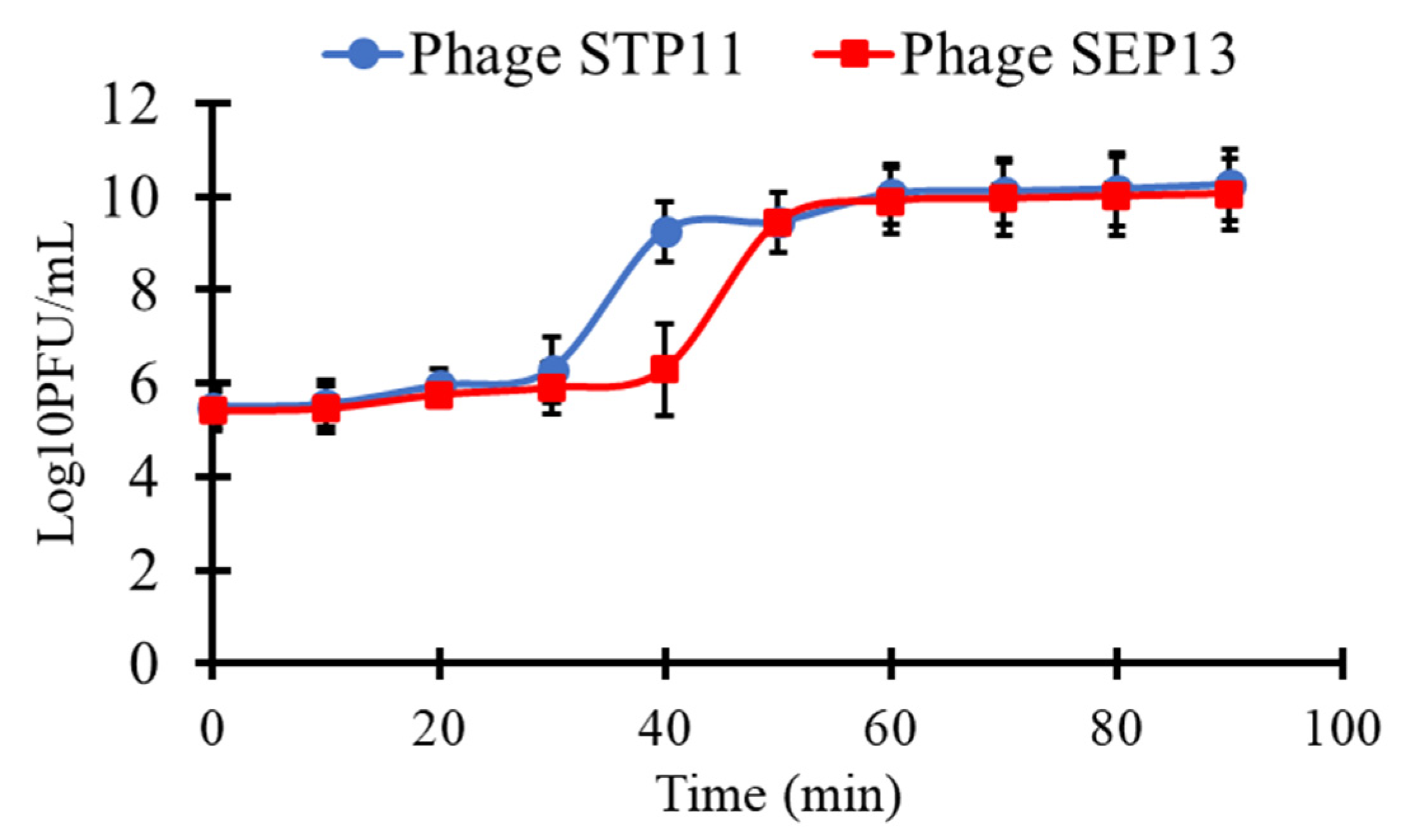
3.4. One-Step Growth Curve
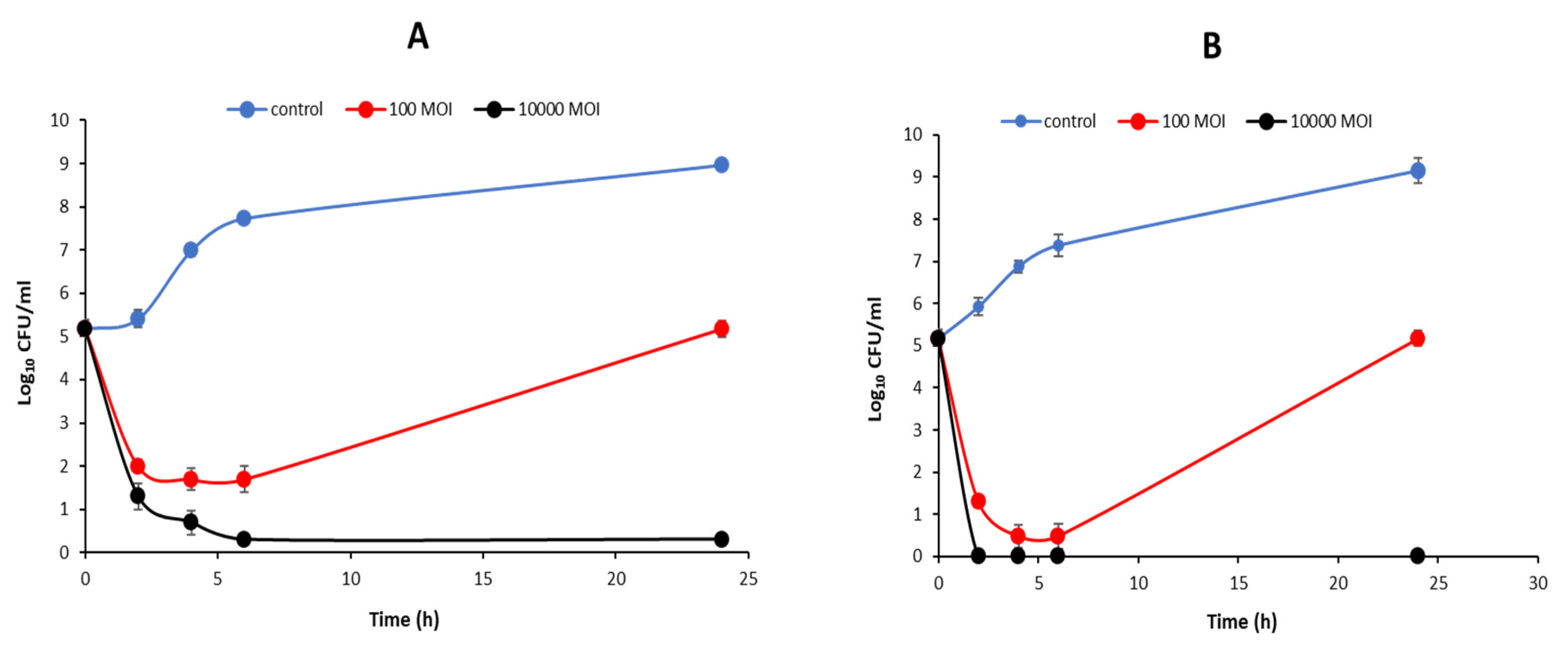
3.5. Bacterial Challenge Test
3.6. Host Range
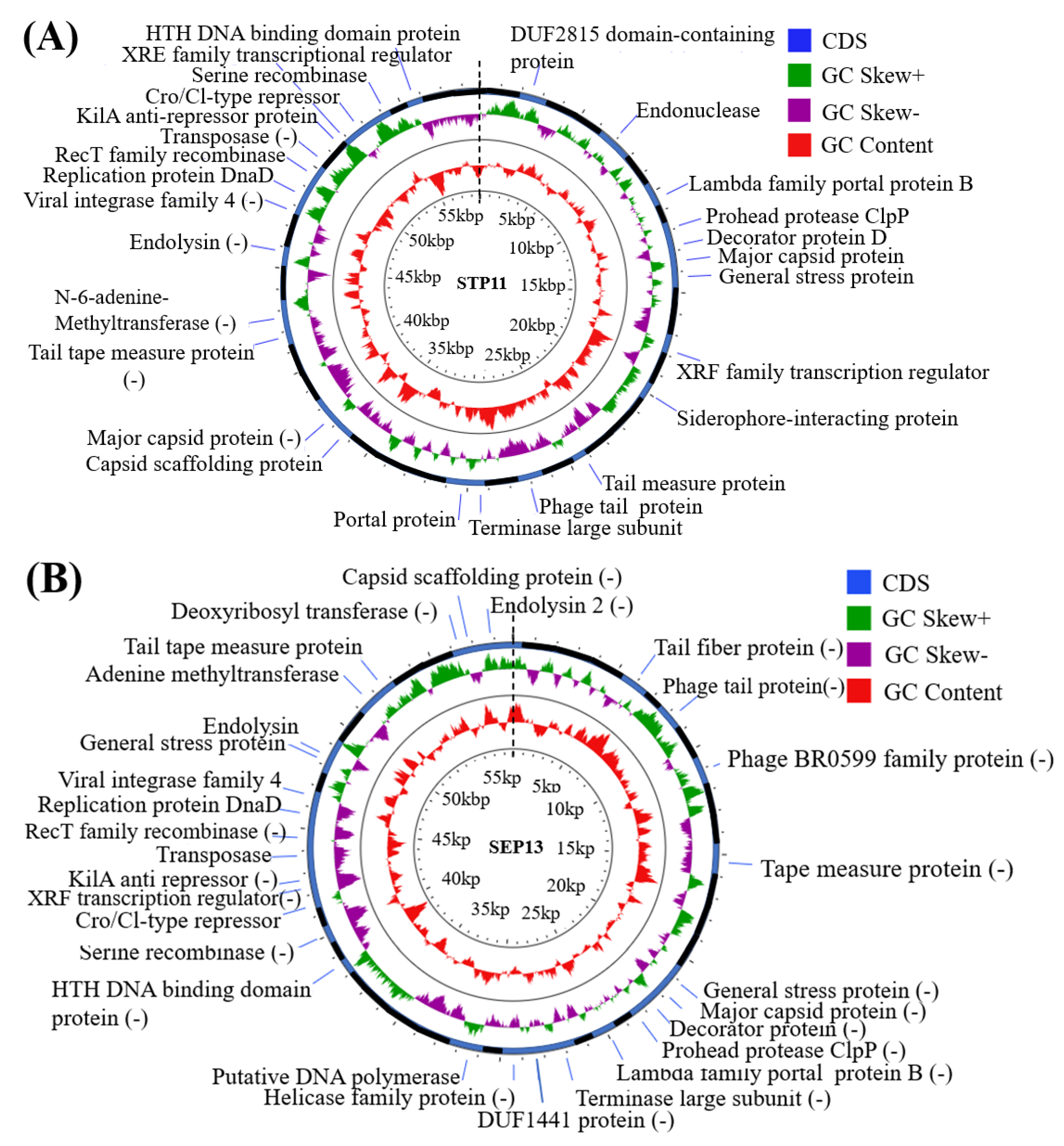
3.7. Genomic Features
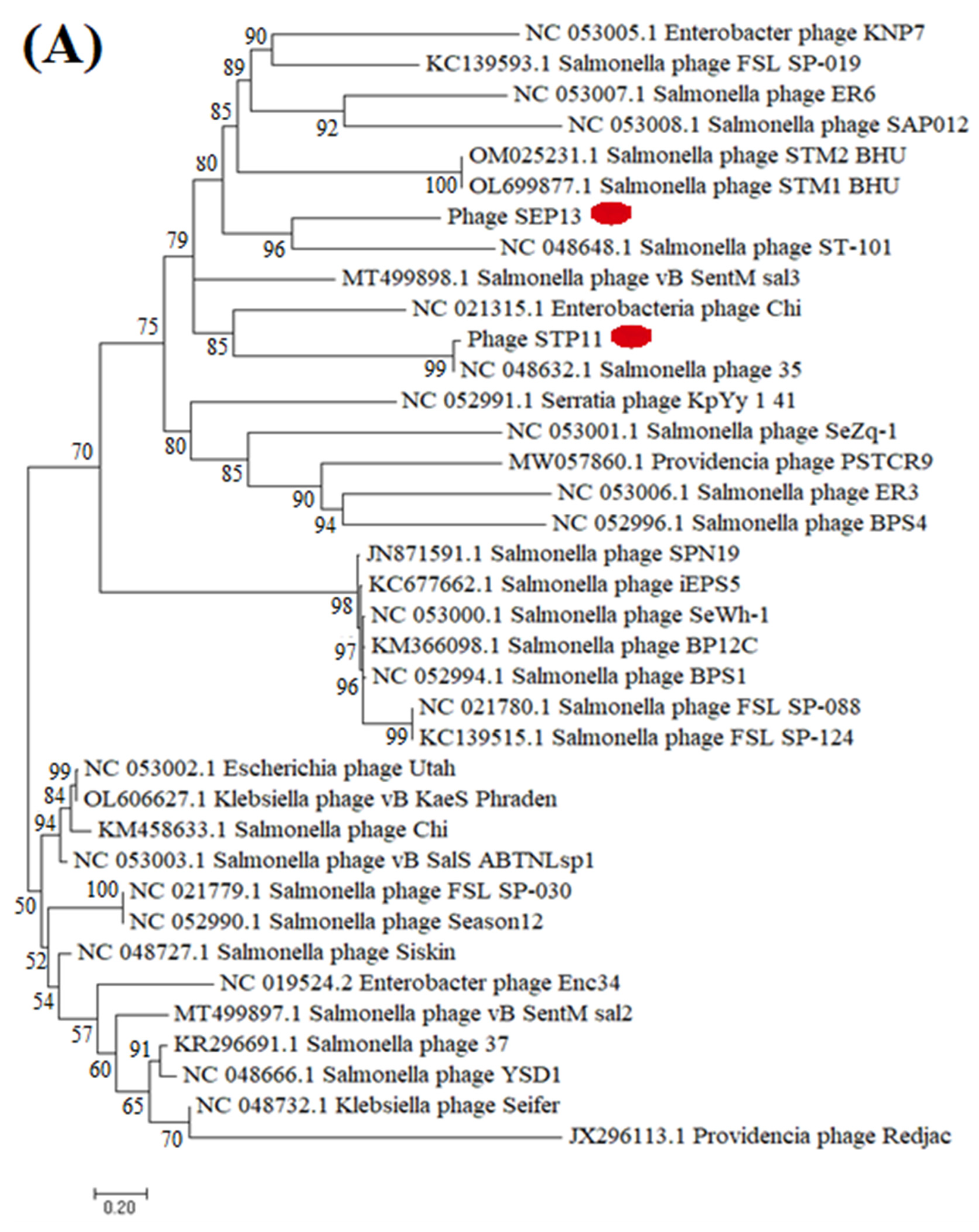
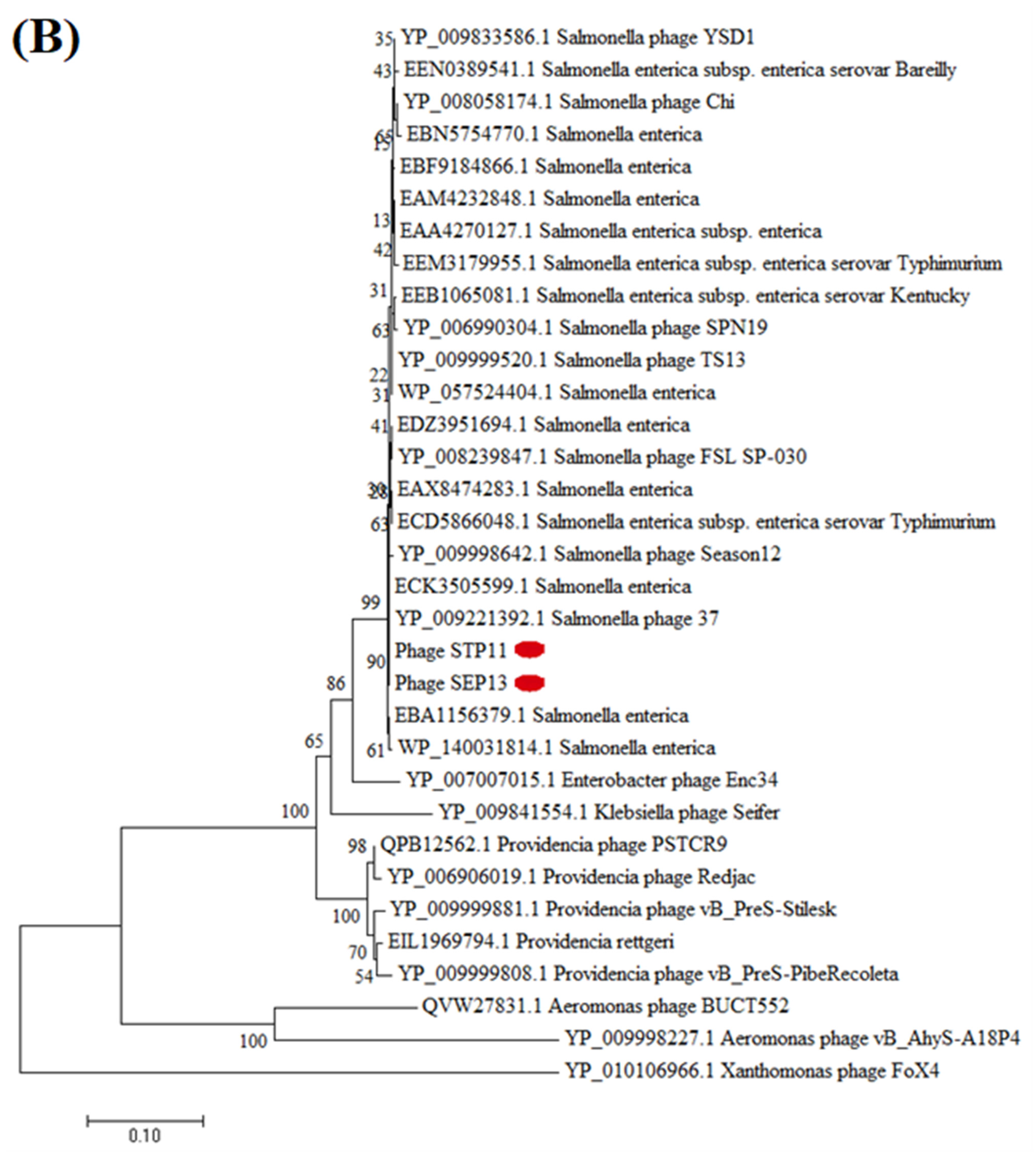
3.8. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; International Collaboration on Enteric Disease “Burden of Illness” Studies. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguale, T.; Gebreyes, W.A.; Asrat, D.; Alemayehu, H.; Gunn, J.S.; Engidawork, E. Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Serotypes, Antimicrobial Resistance and Co-Infection with Parasites among Patients with Diarrhea and Other Gastrointestinal Complaints in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Im, J.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeon, H.J.; Mogeni, O.D.; Kim, J.H.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; Baker, S.; Marks, F. The Global Burden and Epidemiology of Invasive Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Infections. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Roggentin, P.; Mikoleit, M.; Guibourdenche, M.; De Pinna, E.; Nair, S.; Fields, P.I.; Weill, F.-X. Supplement 2008–2010 (No. 48) to the White–Kauffmann–Le Minor Scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.-X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella: Paris, France, 2007; Volume 9, pp. 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-H.; Huang, J.-F.; Sun, Y.-F.; Adams, P.J.; Lin, J.-H.; Robertson, I.D. Detection of Chicken Carcasses Contaminated with Salmonella Enterica Serovar in the Abattoir Environment of Taiwan. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 325, 108640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odoch, T.; Wasteson, Y.; L’Abée-Lund, T.; Muwonge, A.; Kankya, C.; Nyakarahuka, L.; Tegule, S.; Skjerve, E. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Risk Factors Associated with Non-Typhoidal Salmonella on Ugandan Layer Hen Farms. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouttotou, N.; Ahmad, S.; Kamran, Z.; Koutoulis, K.C. Prevalence, Risks and Antibiotic Resistance of Salmonella in Poultry Production Chain. In Current topics in Salmonella and Salmonellosis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Elkenany, R.M.; Eladl, A.H.; El-Shafei, R.A. Genetic Characterisation of Class 1 Integrons among Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Serotypes in Broiler Chicken Farms. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liljebjelke, K.A.; Hofacre, C.L.; White, D.G.; Ayers, S.; Lee, M.D.; Maurer, J.J. Diversity of Antimicrobial Resistance Phenotypes in Salmonella Isolated from Commercial Poultry Farms. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Reynolds, J.; Karp, B.E.; Tate, H.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Plumblee, J.R.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Whichard, J.M.; Mahon, B.E. Ceftriaxone-Resistant Nontyphoidal Salmonella from Humans, Retail Meats, and Food Animals in the United States, 1996–2013. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoshaba, E.O.; Olufemi, F.O.; Ojo, O.E.; Sonibare, A.O.; Agbaje, M. Multidrug-Resistant Salmonellae Isolated in Japanese Quails Reared in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migura-Garcia, L.; Ramos, R.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M. Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella Serovars and Campylobacter Spp. Isolated from an Opportunistic Gull Species, Yellow-Legged Gull (Larus Michahellis). J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, F.; Saeed, M.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Baker, D.; Khurshid, M.; Ainsworth, E.V.; Turner, A.K.; Imran, A.A.; Rasool, M.H.; Saqalein, M. Emergence of Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Third-Generation Cephalosporins in Salmonella Typhi in Lahore, Pakistan. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argimón, S.; Nagaraj, G.; Shamanna, V.; Sravani, D.; Vasanth, A.K.; Prasanna, A.; Poojary, A.; Bari, A.K.; Underwood, A.; Kekre, M. Circulation of Third-Generation Cephalosporin Resistant Salmonella Typhi in Mumbai, India. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 2234–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngogo, F.A.; Abade, A.M.; Rumisha, S.F.; Mizinduko, M.M.; Majigo, M. V Factors Associated with Salmonella Infection in Patients with Gastrointestinal Complaints Seeking Health Care at Regional Hospital in Southern Highland of Tanzania. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, K.; Molinier, L.; Hallit, S.; Sartelli, M.; Hardcastle, T.C.; Haque, M.; Lugova, H.; Dhingra, S.; Sharma, P.; Islam, S. Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Low-and Middle-Income Countries: A Scattered Picture. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, E.; Morales-Rueda, A.; García-Gimeno, R.M. Cross-Contamination and Recontamination by Salmonella in Foods: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Fernandez, A.; Bernardo, A.; Lopez, M. Efficacy of trisodium phosphate in killing acid-adapted salmonella typhimurium. J. Food Saf. 2011, 31, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Baek, K.-H.; Kang, S.C. Control of Salmonella in Foods by Using Essential Oils: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.; Parveen, S. All Natural and Clean-Label Preservatives and Antimicrobial Agents Used during Poultry Processing and Packaging. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, S.; Ortenzi, R.; Scuota, S.; Mancinelli, A.C.; Dal Bosco, A.; Cotozzolo, E.; Castellini, C. Impact of Ozone and UV Irradiation Sanitation Treatments on the Survival of Salmonella and the Physical–Chemical Characteristics of Hen Eggs. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, A.L.; Maués, D.; Lobato, A.; Franco, E.F.; Pinheiro, K.; Araújo, F.; Pantoja, Y.; Costa da Silva, A.L.D.; Morais, J.; Ramos, R.T.J. PhageWeb–Web Interface for Rapid Identification and Characterization of Prophages in Bacterial Genomes. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHAST, PHASTER and PHASTEST: Tools for Finding Prophage in Bacterial Genomes. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sertic, V.; Boulgakov, N.A. Bacteriophages Specific for Flagellated Forms of Bacteria. Compte Rendu Des Seances De La Soc. De Biol. 1936, 123, 887–888. [Google Scholar]
- Ravid, S.; Eisenbach, M. Correlation between Bacteriophage Chi Adsorption and Mode of Flagellar Rotation of Escherichia Coli Chemotaxis Mutants. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 154, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, S.Z.; Adler, J.; Ris, H. How Bacteriophage χ Attacks Motile Bacteria. J. Virol. 1967, 1, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, A.D.T.; Pitta, T.P.; Ryu, W.S.; Danese, P.N.; Leung, E.C.W.; Berg, H.C. Flagellar Determinants of Bacterial Sensitivity to χ-Phage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9863–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.C.; Viollier, P.H.; Ely, B.; Poindexter, J.S.; Georgieva, M.; Jensen, G.J.; Wright, E.R. Alternative Mechanism for Bacteriophage Adsorption to the Motile Bacterium Caulobacter Crescentus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9963–9968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynell, E.W. A Phage, ?χ, Which Attacks Motile Bacteria. Microbiology 1961, 25, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, R.W.; Ko, C.-C.; Jacobs-Sera, D.; Hatfull, G.F.; Erhardt, M.; Hughes, K.T.; Casjens, S.R. Genome Sequence of Salmonella Phage χ. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01229-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Shin, H.; Choi, Y.; Ryu, S. Complete Genome Sequence Analysis of Bacterial-Flagellum-Targeting Bacteriophage Chi. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2179–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onmus-Leone, F.; Hang, J.; Clifford, R.J.; Yang, Y.; Riley, M.C.; Kuschner, R.A.; Waterman, P.E.; Lesho, E.P. Enhanced de Novo Assembly of High Throughput Pyrosequencing Data Using Whole Genome Mapping. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazaks, A.; Dislers, A.; Lipowsky, G.; Nikolajeva, V.; Tars, K. Complete Genome Sequence of the Enterobacter Cancerogenus Bacteriophage Enc34. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11403–11404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joys, T.M. Correlation between Susceptibility to Bacteriophage PBS1 and Motility in Bacillus Subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 90, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, F.; Helm, R.F.; Broadway, K.M.; Scharf, B.E. More than Rotating Flagella: Lipopolysaccharide as a Secondary Receptor for Flagellotropic Phage 7-7-1. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00363-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Ryu, S. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Flagellum-Dependent Salmonella-Infecting Bacteriophage, IEPS5. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4829–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmael, A.; Hassan, M.G.; Amer, M.M.; Abdelrahman, S.; Hamed, A.M.; Abd-raboh, H.A.; Foda, M.F. Antimicrobial Activity of Certain Natural-Based Plant Oils against the Antibiotic-Resistant Acne Bacteria. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. M100-Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2019, 23, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Twest, R.; Kropinski, A.M. Bacteriophage Enrichment from Water and Soil. In Bacteriophages; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Esmael, A.; Azab, E.; Gobouri, A.A.; Nasr-Eldin, M.A.; Moustafa, M.M.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Badr, O.A.M.; Abdelatty, A.M. Isolation and Characterization of Two Lytic Bacteriophages Infecting a Multi-Drug Resistant Salmonella Typhimurium and Their Efficacy to Combat Salmonellosis in Ready-to-Use Foods. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmael, A.; Abo-Elmaaty, S.A.; Khafaga, E.M.; Abdelrahman, S.; Hassan, M.G. Efficacy of Three Lytic Bacteriophages for Eradicating Biofilms of Multidrug-Resistant Proteus Mirabilis. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 3311–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Shi, J.; Ma, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Isolation, Characterization, and Application of a Novel Specific Salmonella Bacteriophage in Different Food Matrices. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M.; Mazzocco, A.; Waddell, T.E.; Lingohr, E.; Johnson, R.P. Enumeration of Bacteriophages by Double Agar Overlay Plaque Assay. In Bacteriophages; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.H. Bacteriophages; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Amarillas, L.; Rubí-Rangel, L.; Chaidez, C.; González-Robles, A.; Lightbourn-Rojas, L.; León-Félix, J. Isolation and Characterization of PhiLLS, a Novel Phage with Potential Biocontrol Agent against Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia Coli. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.-H.; Horikawa, S.; Bryant, K.; Riggs, R.; Chin, B.A.; Barbaree, J.M. Bacterial Assessment of Phage Magnetoelastic Sensors for Salmonella Enterica Typhimurium Detection in Chicken Meat. Food Control 2017, 71, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutter, E. Phage Host Range and Efficiency of Plating. In Bacteriophages; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Bloch, S.; Nejman-Faleńczyk, B.; Łoś, J.M.; Barańska, S.; Łepek, K.; Felczykowska, A.; Łoś, M.; Węgrzyn, G.; Węgrzyn, A. Genes from the Exo–Xis Region of λ and Shiga Toxin-Converting Bacteriophages Influence Lysogenization and Prophage Induction. Arch. Microbiol. 2013, 195, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurczak-Kurek, A.; Gąsior, T.; Nejman-Faleńczyk, B.; Bloch, S.; Dydecka, A.; Topka, G.; Necel, A.; Jakubowska-Deredas, M.; Narajczyk, M.; Richert, M. Biodiversity of Bacteriophages: Morphological and Biological Properties of a Large Group of Phages Isolated from Urban Sewage. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothard, P.; Wishart, D.S. Circular Genome Visualization and Exploration Using CGView. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavigne, R.; Sun, W.D.; Volckaert, G. PHIRE, a Deterministic Approach to Reveal Regulatory Elements in Bacteriophage Genomes. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A Genome Comparison Visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besemer, J.; Borodovsky, M. GeneMark: Web Software for Gene Finding in Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes and Viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W451–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallet, R.; Kannoly, S.; Wang, I.-N. Effects of Bacteriophage Traits on Plaque Formation. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lynch, K.H.; Dennis, J.J.; Wishart, D.S. PHAST: A Fast Phage Search Tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W347–W352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schattner, P.; Brooks, A.N.; Lowe, T.M. The TRNAscan-SE, Snoscan and SnoGPS Web Servers for the Detection of TRNAs and SnoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W686–W689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. GtRNAdb: A Database of Transfer RNA Genes Detected in Genomic Sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D93–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrich, T.N.; Hatfull, G.F. Bacteriophage Evolution Differs by Host, Lifestyle and Genome. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, L.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2012 Update: Toward the Genetic Diversity and Molecular Evolution of Bacterial Virulence Factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D641–D645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinheinz, K.A.; Joensen, K.G.; Larsen, M.V. Applying the ResFinder and VirulenceFinder Web-Services for Easy Identification of Acquired Antibiotic Resistance and E. Coli Virulence Genes in Bacteriophage and Prophage Nucleotide Sequences. Bacteriophage 2014, 4, e27943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT Online Service: Multiple Sequence Alignment, Interactive Sequence Choice and Visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v3: An Online Tool for the Display and Annotation of Phylogenetic and Other Trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.Y.; Dozois, C.M.; Tinge, S.A.; Lee, T.H.; Curtiss III, R. Transduction-Mediated Transfer of Unmarked Deletion and Point Mutations through Use of Counterselectable Suicide Vectors. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.L.; Brown, P.K.; Reeves, P.R. Use of Salmonella Phage P22 for Transduction in Escherichia Coli. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 7115–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rabsch, W. Salmonella Typhimurium Phage Typing for Pathogens. In Salmonella; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 177–211. [Google Scholar]
- Dunne, M.; Loessner, M.J. Modified Bacteriophage Tail Fiber Proteins for Labeling, Immobilization, Capture, and Detection of Bacteria. In Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 67–86. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Poshtiban, S.; Evoy, S. Recent Advances in Bacteriophage Based Biosensors for Food-Borne Pathogen Detection. Sensors 2013, 13, 1763–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hungaro, H.M.; Mendonça, R.C.S.; Gouvêa, D.M.; Vanetti, M.C.D.; de Oliveira Pinto, C.L. Use of Bacteriophages to Reduce Salmonella in Chicken Skin in Comparison with Chemical Agents. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseh, S.; Hanifi-Moghaddam, P.; Coleman, R.; Masotti, M.; Ryan, S.; Foss, M.; MacKenzie, R.; Henry, M.; Szymanski, C.M.; Tanha, J. Orally Administered P22 Phage Tailspike Protein Reduces Salmonella Colonization in Chickens: Prospects of a Novel Therapy against Bacterial Infections. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, A.S. Phage Therapy—Constraints and Possibilities. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilcher, S.; Loessner, M.J. Engineering Bacteriophages as Versatile Biologics. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.P.; Cleto, S.; Sillankorva, S.; Azeredo, J.; Lu, T.K. Genetically Engineered Phages: A Review of Advances over the Last Decade. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedrick, R.M.; Guerrero-Bustamante, C.A.; Garlena, R.A.; Russell, D.A.; Ford, K.; Harris, K.; Gilmour, K.C.; Soothill, J.; Jacobs-Sera, D.; Schooley, R.T. Engineered Bacteriophages for Treatment of a Patient with a Disseminated Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium Abscessus. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phothaworn, P.; Dunne, M.; Supokaivanich, R.; Ong, C.; Lim, J.; Taharnklaew, R.; Vesaratchavest, M.; Khumthong, R.; Pringsulaka, O.; Ajawatanawong, P. Characterization of Flagellotropic, Chi-Like Salmonella Phages Isolated from Thai Poultry Farms. Viruses 2019, 11, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Kuatsjah, E.; Wu, E.; Yuan, S. The Effect of Cell Size on the Burst Size of T4 Bacteriophage Infections of Escherichia Coli B23. J. Exp. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 14, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Hu, Y.; Mizan, M.; Rahaman, F.; Yan, T.; Nime, I.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J. Characterization of Salmonella Phage LPST153 That Effectively Targets Most Prevalent Salmonella Serovars. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wen, H.; Ma, L.; Chen, Z. Isolation, Characterization and Application of Bacteriophage PSDA-2 against Salmonella Typhimurium in Chilled Mutton. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Du, M.; Zha, F.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, J. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Salmonella Phage VB_SalP_TR2. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.C.; Paul, J.H. Gene Transfer by Transduction in the Marine Environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2780–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grose, J.H.; Casjens, S.R. Understanding the Enormous Diversity of Bacteriophages: The Tailed Phages That Infect the Bacterial Family Enterobacteriaceae. Virology 2014, 468, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohwer, F.; Edwards, R. The Phage Proteomic Tree: A Genome-Based Taxonomy for Phage. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibiotic Category | Antibiotics (Conc.) | S. Enteritidis Strain FORC_052 (Inhibition Zone in mm) | S. Typhimurium Strain 85 (Inhibition Zone in mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Amikacin (30 μg) | R (10) | R (10) |
| Gentamicin (10 μg) | R (9) | R (10) | |
| Tobramycin (10 μg) | R (9) | R (10) | |
| Streptomycin (5 μg) | S (20) | R (10) | |
| Neomycin (15 μg) | S (17) | R (12) | |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin (5 μg) | R (15) | R (10) |
| Penicillins | Ampicillin (10 μg) | R (10) | R (10) |
| Tetracyclines | Doxycycline (30 μg) | R (10) | R (10) |
| Phenolics | Chloramphenicol (30 μg) | R (10) | R (10) |
| 2nd generation Cefalosporins | Cefuroxime (30 μg) | S (23) | R (10) |
| 3rd generation Cefalosporins | Cefotaxime (30 μg) | S (20) | S (16) |
| Ceftriaxone (30 μg) | S (22) | S (16) | |
| Ceftazidime (30 μg) | S (23) | S (18) | |
| Carbapenems | Imipenem (10 μg) | S (25) | S (23) |
| Meropenem (10 μg) | S (16) | S (15) | |
| Resistance percentage (%) | 46.6% | 66.6% | |
| Category | Bacterial Species | Host Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| STP11 | SEP13 | ||
| Enterobacteriaceae | Salmonella enterica subsp. Enterica serovar Dublin | + | + |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. Enterica serovar Enteritidis | + | + | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. Enterica serovar Typhimurium | + | + | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. arizonae | + | + | |
| S. Typhimurium (ATCC14028) | + | + | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. Enterica serovar Typhi strain SRDF2 | + | − | |
| Escherichia coli | − | − | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | − | − | |
| Shigella flexneri | − | − | |
| Shigella sonnei | − | − | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | − | − | |
| Non- Enterobacteriaceae | Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus | − | − |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | − | − | |
| Bacillus cereus | − | − | |
| Total n (%) | - | 6 (42.9%) | 5 (35.7%) |
| Category | ORFs (Phage STP11) | ORFs (Phage SEP13) | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Head-tail associated proteins | ORF31 | ORF69 | Capsid scaffolding protein |
| ORF10, ORF32 | ORF18 | Major capsid protein | |
| ORF8 | ORF20 | Prohead protease ClpP | |
| ORF9 | ORF19 | Decorator protein D | |
| ORF19 | ORF11 | Putative tape measure protein | |
| ORF23 | ORF6 | Phage tail protein | |
| - | ORF5 | Putative tail fiber protein | |
| ORF20, ORF44 | ORF57, ORF11 | Tail tape measure protein | |
| Transcription regulator (DNA replication proteins) | ORF63, ORF17 | ORF39 | XRE family transcriptional regulator |
| ORF56 | ORF46 | Replication protein DnaD | |
| ORF46 | ORF56 | Putative N-6-adenine-methyltransferase | |
| - | ORF25 | Helicase family protein | |
| - | ORF27 | Putative DNA polymerase | |
| - | ORF67 | Deoxyribosyl transferase | |
| Packaging proteins | ORF25 | - | Phage portal protein |
| ORF7 | ORF21 | Putative lambda family portal protein B | |
| ORF24 | ORF23 | Terminase large subunit | |
| Cell lysis protein | ORF49 | ORF52 | Endolysin |
| - | ORF71 | Putative endolysin 2 | |
| Lysogenic associated protein | ORF6 | - | Endonuclease |
| ORF53 | ORF48 | Viral integrase family 4 | |
| ORF56 | ORF45 | RecT family recombinase | |
| ORF58 | ORF43 | Transposase | |
| ORF61 | ORF40 | kilA anti-repressor protein | |
| ORF63 | ORF38 | Putative Cro/Cl-type repressor | |
| ORF67 | ORF34 | Serine recombinase | |
| ORF68 | ORF33 | HTH DNA binding domain protein | |
| Other | ORF2 | - | DUF2815 domain-containing protein |
| - | ORF9 | Phage BR0599 family protein | |
| - | ORF24 | DUF1441 family protein | |
| ORF11 | ORF17, ORF51 | General stress protein | |
| ORF18 | - | Siderophore-interacting protein |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teklemariam, A.D.; Alharbi, M.G.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Alotibi, I.; Aljaddawi, A.A.; Azhari, S.A.; Esmael, A. Isolation and Characterization of Chi-like Salmonella Bacteriophages Infecting Two Salmonella enterica Serovars, Typhimurium and Enteritidis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121480
Teklemariam AD, Alharbi MG, Al-Hindi RR, Alotibi I, Aljaddawi AA, Azhari SA, Esmael A. Isolation and Characterization of Chi-like Salmonella Bacteriophages Infecting Two Salmonella enterica Serovars, Typhimurium and Enteritidis. Pathogens. 2022; 11(12):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121480
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeklemariam, Addisu D., Mona G. Alharbi, Rashad R. Al-Hindi, Ibrahim Alotibi, Abdullah A. Aljaddawi, Sheren A. Azhari, and Ahmed Esmael. 2022. "Isolation and Characterization of Chi-like Salmonella Bacteriophages Infecting Two Salmonella enterica Serovars, Typhimurium and Enteritidis" Pathogens 11, no. 12: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121480
APA StyleTeklemariam, A. D., Alharbi, M. G., Al-Hindi, R. R., Alotibi, I., Aljaddawi, A. A., Azhari, S. A., & Esmael, A. (2022). Isolation and Characterization of Chi-like Salmonella Bacteriophages Infecting Two Salmonella enterica Serovars, Typhimurium and Enteritidis. Pathogens, 11(12), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11121480







