Abstract
Mites of the family Trombiculidae are known for playing a role in maintaining and spreading the scrub typhus etiologic agent, an intracellular Gram-negative bacterium, Orientia tsutsugamushi. Species of the genus Leptotrombidium are investigated most thoroughly, particularly in SE Asia, and a few are proven vectors for the pathogen. The mentioned association, however, is not the only one among trombiculids. Here, we present a list of chiggers indicated in the literature as positive for bacterial pathogens, tested throughout almost 100 years of research. Taxonomic identities of trombiculids follow recent revisions and checklists. Results point at 100 species, from 28 genera, evidenced for association with 31 bacterial taxa. Pathogen-positive mites constitute around 3.3% of the total number of species comprising the family. Discussed arachnids inhabit six biogeographic realms and represent free-living instars as well as external and internal parasites of rodents, soricomorphs, scadents, lagomorphs, peramelemorphs, bats, passerine birds, reptiles and humans. A variety of so far detected bacteria, including novel species, along with the mites’ vast geographical distribution and parasitism on differentiated hosts, indicate that revealing of more cases of Trombiculidae-pathogens association is highly probable, especially utilizing the newest techniques enabling a large-scale bacterial communities survey.
Keywords:
Anaplasma; Bartonella; Borrelia; Coxiella; Francisella; Leptospira; Mycobacterium; Orientia; Rickettsia 1. Introduction
Trombiculidae, as understood by Kudryashova [1] (Actinotrichida: Parasitengona), comprise 3013 species inhabiting seven zoogeographic regions [2]. These mites are known for the complex life cycle consisting of egg, prelarva, obligatorily parasitic larva, calyptostatic protonymph, predatory deutonymph, calyptostatic tritonymph and predatory adult form [3]. Parasitic instars are especially abundant on small mammals—rodents, insectivores and bats, yet, parasitism of birds, reptiles and amphibians is also reported. Feeding on bigger animals, such as carnivores, ungulates and lagomorphs, occurs considerably less frequently. The rarest cases regard parasitizing invertebrates [4,5,6,7,8,9]. Humans are considered accidental hosts for Trombiculidae, however, locally (especially in SE Asia, often on so-called ‘chigger islands’) parasitism on people is a frequent phenomenon. Recorded duration of larval attachment to a human’s body ranged from one to three days [10,11].
Trombiculid larvae feed basically on dissolved connective tissue similar in composition to a plasma, however, in single cases, ingestion of blood has been also reported [12,13,14]. For the purpose of food intake, after reaching a parasitope, mites pierce the host’s skin with chelicerae and, alternately, secrete enzymes, digesting epithelium and protein substances, solidifying in contact with host tissues. As a result, a stylostome is formed—a canal with a strengthened sidewall, linear or widened distally. This channel is successively extended until the cessation of the parasitic phase [12,15,16]. Such a feeding mechanism implies the group’s medical-veterinary importance, comprising of two issues—inducing, relatively harmless but bothersome (intensive itching), local skin inflammations (called trombiculiasis, trombiculosis or erythema autumnale) being the immunological reaction of the host’s body to larval lytic secretions, and the capability of acquiring and spreading bacterial pathogens, the source of which being the vertebrate organisms [16,17,18].
Among Trombiculidae, representatives of Leptotrombidium spp. are best recognized for maintaining and transmitting (to the hosts, as well as transstadially and transovarially—to the offspring) an etiologic agent of scrub typhus, intracellular bacterium, Orientia tsutsugamushi (Hayashi, 1920) (Pseudomonadota, Rickettsiales, Rickettsiaceae), formerly under the names of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi and R. orientalis [19,20,21]. Due to the significance of the illness, involving lethality without treatment, and its high prevalence in the endemic areas of SE Asia, the relation Leptotrombidium spp.—O. tsutsugamushi is most well explored in literature. Issues raised so far concern scrupulously investigated ecological, epidemiological, molecular and geographical aspects of the chigger-borne rickettsiosis occurrence in general as well as in particular areas of China, South Korea, Japan, Russia, Taiwan, Thailand and Asia–Australia–Pacific region, which together constitute the so called ‘tsutsugamushi triangle’ [10,14,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. Recent studies, however, indicate that scrub typhus is no longer limited to the above-mentioned zone, as cases from Africa, Middle East and South America have been also reported [36,37,38,39].
Despite focusing the research on O. tsutsugamushi, it is not the only pathogenic bacterium associated with trombiculid mites. Records considering other bacterial taxa represent, however, mostly single cases and are rather scattered in the literature. As for the broad scale studies on bacteria and parasitic mites, Chaisiri et al. provided new data on the bacterial flora associated with chiggers in Thailand and summarized the published information on microbiome of representatives of Sarcoptiformes, Trombidiformes and Mesostigmata orders [40,41]. Herrera-Mares et al., in turn, recently reviewed the knowledge on the ecology of infectious and parasitic diseases being shaped by the interactions between parasites representing Trombidiformes and Mesostigmata, their rodent hosts and related etiological agents occurring worldwide [42].
The aim of creating the present review was to provide the most actual list of valid trombiculid taxa, naturally infected with bacterial pathogens, together with information on hosts from which mites were collected (provided it was possible or relevant) and countries of records, reported in the published sources.
2. Results
2.1. Valid Trombiculid Taxa Associated with Bacterial Pathogens
Genus: Acomatacarus Ewing, 1942
Acomatacarus sp.
Mites of this genus are known for the association with O. tsutsugamushi revealed during research in China. Infected larvae were collected from the lesser ricefield rat Rattus losea (Swinhoe, 1871), the brown rat R. norvegicus (Berkenhout, 1769), the black rat R. rattus (Linnaeus, 1758), the house mouse Mus musculus (Linnaeus, 1758), M. bactrianus kakhyenensis (most probably the Ryukyu mouse M. caroli Bonhote, 1902) (Mammalia: Rodentia) and the Asian house shrew Suncus murinus (Linnaeus, 1766) (Mammalia: Soricomorpha) [14,43,44,45].
Genus: Ascoschoengastia Ewing, 1948
Ascoschoengastia spp.
Undetermined to the species level representatives of the genus are known to harbor Bartonella spp. Strong et al., 1915 (Pseudomonadota, Hyphomicrobiales, Bartonellaceae), O. tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia sp. da Rocha-Lima, 1916 (Pseudomonadota, Rickettsiales, Rickettsiaceae). In the case of the latter two, a co-infection was observed in Thailand. Tested chiggers parasitized the Asian house rat R. tanezumi Temminck, 1844, R. rattus, R. norvegicus, R. rattus-complex (i.e., R. tanezumi, R. losea sakeratensis Gyldenstolpe, 1917, Rattus sp.), the Savile’s bandicoot rat Bandicota savilei Thomas, 1916, the greater bandicoot rat B. indica (Bechstein, 1800) (Mammalia: Rodentia), the northern treeshrew Tupaia belangeri (Wagner, 1841) and the common treeshrew T. glis Diard and Duvaucel, 1820 (Mammalia: Scadentia). Reports come from India, Thailand and Vietnam [23,30,46,47,48,49,50].
A. audyi (Womersley, 1952)
Individuals of the species were positive for the presence of O. tsutsugamushi. Collected in the Malayan forest [14].
A. indica (Hirst, 1915)
Species mentioned also as Euschoengastia indica. Associated with O. tsutsugamushi and R. typhi (Wolbach and Todd, 1920). Positive larvae fed on rats, including the ricefield rat R. argentiveter (Robinson and Kloss, 1916) and squirrel. Collected and tested in China, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam [44,51,52,53,54].
Genus: Blankaartia Oudemans, 1911
Blankaartia spp.
In chiggers from this genus, the following pathogens were detected: Bartonella spp., B. tamiae Kosoy et al., 2008 and O. tsutsugamushi. Host animals included rats from R. rattus-complex, R. rattus, R. tanezumi, R. argentiventer, B. indica, B. savilei and the fawn-colored mouse M. cervicolor Hodgson, 1845. Records originate from Thailand and Vietnam [10,48,50,55].
B. acuscutellaris (Walch, 1922)
Known for association with O. tsutsugamushi. Infected larvae were collected from T. glis and rodents including R. rattus in Thailand [46,52].
B. sinnamaryi (Floch and Fauran, 1956)
Pathogen detected in this species was described as Rickettsia felis-like and chiggers were collected from passerine birds: the ruby-crowned tanager Tachyphonus coronatus (Vieillot, 1822) and the pale-breasted thrush Turdus leucomelas Vieillot, 1818 (Aves: Passeriformes) in Brazil [56,57].
Genus: Cheladonta Lipovsky, Crossley and Loomis, 1955
C. costulata (Willmann, 1952)
Species harboring R. helvetica Beati et al., 1993 and R. monacensis Simser et al., 2002 and associated with the following bacteria-positive host rodents: the bank vole Myodes glareolus (Schreber, 1780), the yellow-necked wood mouse Apodemus flavicollis (Melchior, 1834), the common vole Microtus arvalis (Pallas, 1778) and the European wood mouse A. sylvaticus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Mammalia: Rodentia). Mites captured in Slovakia [58].
C. ikaoensis (Sasa, Sawada, Kanoh, Hayashi and Kumada, 1951)
Associated with O. tsutsugamushi and collected from field rodents, mostly the large Japanese field mouse A. speciosus speciosus (Temminck, 1844), the small Japanese field mouse A. argenteus argenteus (Temminck, 1844), Eothenomys kageus Imaizumi, 1957 (Mammalia: Rodentia) and the Japanese grass vole M. montebelli montebelli (Milne-Edwards, 1872) in Japan [59,60].
Genus: Ericotrombidium Vercammen-Grandjean, 1965
E. jayewickremei (Womersley, 1952)
Orientia tsutsugamushi-positive larvae of this species (originally mentioned as Leptotrombidium jayawickremei) were captured in India while feeding on R. rattus [49].
Genus: Euschoengastia Ewing, 1938
Euschoengastia sp.
Individuals of the genus collected from Malayan jungle rats tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi [61].
E. koreaensis Jameson and Toshioka, 1954
Orientia tsutsugamushi-positive larvae were collected from A. agrarius, the Korean red-backed vole M. regulus (Thomas, 1907) and the Ussuri white-toothed shrew Crocidura lasiura Dobson, 1890 (Mammalia: Soricomorpha) in South Korea [34,62,63].
Genus: Eutrombicula Ewing, 1938
Eutrombicula spp.
Individuals of this genus tested positive for sequences of Rickettsia sp., and species very closely related to R. conorii, R. felis and R. typhi. Larvae were collected from birds in Brazil and from the hispid cotton rat Sigmodon hispidus Say and Ord (Mammalia: Rodentia), 1825 in the USA (North Carolina) [57,64].
E. alfreddugesi (Oudemans, 1910)
Rickettsia bellii-like sequence was detected in isolates obtained from larvae of the common Northamerican chigger parasitizning snake Philodryas nattererii Steindachner, 1870 (Reptilia: Squamata) in Brazil [65].
Remarks: According to Sajle [66], R. bellii represent a non-pathogenic ancestral group within Rickettsiaceae, not the typhus or the spotted fever group. On the other hand, the species is evidenced to elicit an immune response in capybaras and horses, therefore, we included this association. Mechanisms of R. bellii possible pathogenicity, however, require more research [67].
E. tinami (Oudemans, 1910)
Species evidenced to harbor a novel bacterium Candidatus Rickettsia colombianensi. Captured parasitizing the Andean sparrow Zonotrichia capensis (Müller, 1776) and T. coronatus in Brazil (Aves: Passeriformes) [57].
E. wichmanni (Oudemans, 1905)
Host-questing larvae of the species, collected with black plates, were reported to test positive for O. tsutsugamushi in Thailand [68].
Genus: Gahrliepia Oudemans, 1912
Gahrliepia sp.
Known for the association with O. tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia sp. Collected from R. rattus-complex, R. tanezumi, B. savilei, B. indica and T. belangeri. Records come fromChina and Thailand [30,45,47,50].
G. saduski Womersley, 1952
Unengorged and parasitic (on A. speciosus) larvae captured in Japan tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi [69,70].
G. xiaowoi Wen and Xiang, 1984
Individuals of the species contained O. tsutsugamushi. Material collected from the Bower’s white-toothed rat Berylmys bowersi (Anderson, 1879) (Mammalia: Rodentia) in Thailand [23].
Genus: Helenicula Audy, 1954
Helenicula sp.
Genus listed among mites positive for O. tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia sp., parasitizing R. tanezumi, B. savilei and B. indica in Thailand [47].
H. miyagawai (Sasa, Kumada and Miura, 1951)
Species individuals (also reported as Euschoengastia miyagawai) captured with chigger traps and collected from rodents (mainly A. agrarius) revealed the presence of O. tsutsugamushi in South Korea and some other Rickettsia species (most probably not O. tsutsugamushi) in Japan [14,34,71,72].
H. naresuani Stekolnikov, 2016
Associated with O. tsutsugamushi. Captured on T. glis in Thailand [24].
Genus: Herpetacarus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
H. antarctica (Stekolnikov and Gonzalez-Acuña, 2015)
The species is a proven vector for Candidatus Orientia chiloensis Abarca et al. 2020, a novel bacterium causing scrub typhus in the area of subantarctic Chile. Parasitic mites were collected from human hosts while unengorged individuals from low vegetation [73].
H. eloisae Stekolnikov and Silva-de la Fuente, 2021
Orientia spp-positive chiggers fed on the olive-colored akodont Abrothrix olivacea (Waterhouse, 1837), the Sanborn’s akodont A. sanborni (Osgood, 1943) and the Valdivian long-clawed akodont Geoxus valdivianus (Philippi, 1858) (Mammalia: Rodentia) in Chile [73,74,75].
H. hertigi (Brennan, 1970)
A species reported to carry a novel bacterium Candidatus Rickettsia colombianensi. Larvae were collected from the colilargo Oligoryzomys sp. Bangs, 1900 (Mammalia: Rodentia) in Brazil [76].
Genus: Hirsutiella Schluger and Vysotzkaja, 1970
H. zachvatkini (Schluger, 1948)
Species tested positive for R. helvetica and R. monacensis. Fed on Rickettsia-positive rodents: M. glareolus, A. flavicollis, M. arvalis and A. sylvaticus, captured in Slovakia [58].
Genus: Intercutestrix Brennan and Yunker, 1966
I. mondolfi Brennan and Yunker, 1969
Species associated with Coxiella burnetii (Derrick, 1939) (Pseudomonadota, Legionellales, Coxiellaceae). Larvae were attached to the nasal cavities of the Central American spiny rat Proechimys semispinosus (Tomes, 1860) (Mammalia: Rodentia) in Panama [77].
Genus: Leptotrombidium Nagayo, Miyagawa, Mitamura and Imamura, 1916
Leptotrombidium spp.
Representatives of Leptotrombidium spp. were reported to carry B. tamiae, O. tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia sp. Infected chiggers parasitized small mammals: R. rattus, R. rattus-complex, R. argentiventer, R. tanezumi, the Polynesian rat R. exulans (Peale, 1848), M. cervicolor, B. indica, B. saliviei, the Royle’s mountain vole Alticola roylei (Gray, 1842) (Mammalia: Rodentia) and T. belangeri as well as swarmed on the ground and plants (unfed parasites). Above observations come from India, Indonesia, Pakistan, Taiwan and Thailand [29,30,47,49,50,55,68,78,79].
L. akamushi (Brumpt, 1910)
Species listed among the most important O. tsutsugamushi vectors. Positive larvae were obtained from Rattus spp., R. exulans, as well as from the vegetation. Records come from Japan, Malaysia, New Guinea, Philippines and Solomon Islands [21,33,54,60,80].
L. arenicola Traub, 1960
Orientia tsutsugamushi-infected larvae were collected from Rattus spp. and from the ground in Indonesia and Malaysia [81,82].
L. arvinum (Schluger, Grokhovskaya, Dang-Van-Ngu, Nguen-Xuan-Hoe and Do-Kinh-Tung, 1960)
Host-seeking larvae collected from the black plates tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi in Thailand [68].
L. bodense (Gunther, 1940)
Unengorged larvae obtained with the above-mentioned technique were positive for O. tsutsugamushi. Malaysia [83].
L. chaigraiensis Tanskul and Linthicum 1997
Species listed among proven vectors of O. tsutsugamushi. Infected larvae were taken from the bodies of R. losea and R. rattus captured in Thailand [84,85].
Remarks: According to revision of Leptotrombidium genus by Stekolnikov [86] and check list of Asian trombiculids by Chaisiri et al. [87], L. chiangraiensis should be considered a synonym of L. imphalum, as metric traits of both taxa overlap. Still, molecular sequences subsequently provided by Kumlert et al. [88] indicated distinctiveness of the two species, therefore, we treat the data for L. chaigraiensis separately.
L. deliense (Walch, 1922)
The species is most frequently listed (also as L. deliensis) as a proven and widespread vector of O. tsutsugamushi, however, it is also reported for the association with Borrelia spp. Swellengrebel, 1907 (Spirochaetota, Spirochaetales, Borreliaceae), Rickettsia sp., species close to R. australis, R. felis Bouyer et al., 2001, R. conorii Brumpt, 1932, R. raoultii Mediannikov et al., 2008, R. rhipicephali Burgdorfer et al., 1978 and R. typhi, as well as a novel species Candidatus Rickettsia jingxinensis. Bacteria-positive larvae were obtained from A. agrarius, the Indian mole-rat B. bengalensis Gray, 1835, B. indica, A. roylei, R. rattus, the buff-breasted rat R. tanezumi flavipectus (Milne-Edwards, 1872), R. tanezumi, the Sikkim rat R. andamanensis (Blyth, 1860), R. exulans, R. norvegicus, R. losea, Rattus spp., the small white-toothed rat B. berdmorei (Blyth, 1851), T. belangeri (mentioned as T. belangeri persurae), T. glis and S. murinus (mentioned as S. murinus fulvo-cinerea) as well as from the moist marshlands (host-questing larvae). The above observations were made in Australia, China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan (including Pescadores), Thailand and Vietnam [10,14,23,40,46,49,51,52,68,78,83,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102].
L. dihumerale Traub and Nadchatram, 1967
Mentioned among O. tsutsugamushi infected mites in India and Pakistan [14,103].
L. fletcheri (Womersley and Heaslip, 1943)
Parasitic larvae feeding on the common echymipera Echymipera kalubu cockerelli (Ramsay, 1877) (Mammalia: Peramelemorphia) as well as questing ones taken from the ground in Papua New Guinea, Philippines and Malaysia tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi [14,83,104].
L. fujii (Kuwata, Berge and Philip, 1950)
Species mentioned as positive for O. tsutsugamushi. Infected larvae parasitized A. speciosus and unengorged chiggers were collected from ground and vegetation in Japan [69,70].
L. gaohuense Wei, Tong and Shi, 1987
Listed (as L. gaohuensis) in Epidemiology and ecology of rickettsial diseases in the People’s Republic of China as a vector of O. tsutsugamushi [44].
L. himizui (Sasa, Kumada, Hayashi, Enomoto, Fukuzumi and Obata, 1951)
Orientia tsutsugamushi-associated species (originally listed as L. himizu). Host-seeking larvae were gathered from the ground and vegetation in Japan [69].
L. imphalum Vercammen-Grandjean and Langston, 1976
Species known to carry O. tsutsugamushi, R. conorii, R. typhi, Rickettsia sp. and a novel bacterium Candidatus Rickettsia jingxinensis. Laboratory reared individuals originating from larvae captured in nature were also positive for Mycobacterium sp. Lehmann and Neumann, 1896 (Actinomycetota, Mycobacteriales, Mycobacteriaceae) Infected larvae were obtained from the bodies of A. agrarius, B. indica, R. exulans, R. losea, R. rattus and R. tanezumi captured in Taiwan and Thailand [23,29,84,85,97,105].
L. insulare Wei, Wang and Tong, 1989
Listed among O. tsutsugamushi vectors in China [106].
L. intermedium (Nagayo, Mitamura and Tamiya, 1920)
Species associated with O. tsutsugamushi. Positive larvae were obtained from A. speciosus, M. musculus and R. norvegicus as well as from the vegetation (prior to parasitic phase). Records come from China and Japan [70,107,108,109].
L. kawamurai (Fukuzumi and Obata, 1953)
Larvae parasitizing the gray red-backed vole M. rufocanus (Sundevall, 1846) (originally mentioned as Clethrionomys rufocanus bedfordiae) and A. speciosus ainu were reported as O. tsutsugamushi-positive in Japan [81,107,110].
L. keukenshrijveri (Walch, 1924)
Unengorged larvae gathered from the ground by the black plates method in Malaysia tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi [83].
L. kitasatoi(Fukuzumi and Obata, 1950)
Species evidenced as positive for O. tsutsugamushi. Parasitic larvae were taken from A. speciosus and unengorged chiggers derived from the ground and vegetation in Japan [69,70,107].
L. linhuaikongense (Wen and Hsu, 1961)
Known for association with O. tsutsugamushi. Positive parasites originated mostly from rodents: A. agrarius, M. musculus, R. norvegicus and the greater long-tailed hamster Tscherskia triton (de Winton, 1899) (Mammalia: Rodentia) captured in China. Scrub typhus agent was also detected in a nymph reared in the laboratory from engorged larva [109,110,111,112,113,114].
L. murotoense (Sasa and Kawashima, 1951)
Listed among O. tsutsugamushi vectors in Japan [60,107].
L. orientale (Schluger, 1948)
Orientia tsutsugamushi-positive parasitic larvae were found in South Korea and Russia (Primorsky Krai). Chiggers were captured on wild animals including A. agrarius, M. regulus and C. lasiura [34,62,63,115,116,117].
L. pallidumNagayo, Miyagawa, Mitamura and Tamiya, 1919
Species reported as positive for O. tsutsugamushi, R. conorii and Rickettsia sp. Infected individuals were collected from the vegetation (unengorged larvae) and the following mammal hosts: A. agrarius, A. speciosus, B. indica, M. fortis, M. montebelli, M. regulus, ‘C. triton’ (most probably T. triton), R. exulans, R. losea, R. tanezumi and C. lasiura. Reports come from Japan, Russia (Primorsky Krai), South Korea and Taiwan. [34,60,62,63,69,70,97,108,115,118,119,120].
L. palpale (Nagayo, Miyagawa, Mitamura and Tamiya, 1919)
Orientia tsutsugamushi-positive species, larvae of which were collected from A. agrarius, A. speciosus, M. regulus, M. musculus, R. norvegicus, T. triton and C. lasiura. Laboratory reared nymph also tested positive for the presence of the pathogen. Records originate from China, Japan, Russia (Primorsky Krai) and South Korea [34,60,62,63,70,109,111,113,114,115,117].
L. pavlovskyi (Schluger, 1948)
Species associated with O. tsutsugamushi, collected and examined in Russia (Primorsky Krai). Pathogen-positive individuals included parasitic larvae feeding on infected rodents and shrews: A. agrarius, ‘C. triton’ (most probably T. triton), the reed vole M. fortis (Büchner, 1889) and C. lasiura, along with nymphs reared in the laboratory [28,115,117,120].
L. peniculatum Traub and Lakshana, 1966
Unengorged larvae (originally mentioned as L. paniculatum) gathered with use of the black plate method in Thailand tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi [68].
L. peromysci Vercammen-Grandjean and Langston, 1976
Parasitic larvae found on the white footed deer mouse Peromyscus leucopus Rafinesque, 1818 (Mammalia: Rodentia) in the USA (North Carolina) turned out positive for Rickettsia sp. and species very closely related to R. conorii, R. felis and R. typhi [64].
L. rajasthanense Fernandes and Kulkarni, 2003
Orientia tsutsugamushi-positive larvae of this species fed on R. rattus captured in India [49].
L. rubellum Wang and Liao, 1984
Listed among O. tsutsugamushi vectors in China [106].
L. rupestre Traub and Nadchatram, 1967
Species found in mite pools positive for O. tsutsugamushi in Pakistan [14].
L. scutellare Nagayo, Miyagawa, Mitamura, Tamiya and Tenjin, 1921
Species positive for O. tsutsugamushi, R. typhi, R. felis, Rickettsia sp. as well as pathogens most closely related to R. akari Huebner, 1946 and R. australis Philip, 1950 as well as a novel species Candidatus Rickettsia leptotrombidium. Host-searching larvae were gathered from plants and soil while parasites were collected from the bodies of A. agrarius, A. agrarius chejuensis, A. speciosus speciosus, the small Japanese field mouse A. argenteus argenteus (Temminck, 1844), B. indica, Eothenomys kageus Imaizumi, 1957, M. montebelli, M. regulus, M. musculus, R. exulans, R. losea, R. norvegicus, R. tanezumi, T. triton, Urotrichus talpoides hondonis, C. lasiura and S. murinus. Listed records originate from China, Japan, Malaysia, South Korea, Taiwan and Thailand [34,62,63,68,69,83,97,109,111,113,114,118,121,122,123,124,125,126].
L. sialkotense Vercammen-Grandjean and Langston, 1976
Listed among O. tsutsugamushi vectors in China [106].
L. subintermedium (Jameson and Toshioka, 1954)
Mentioned among O. tsutsugamushi vectors in India and Pakistan [14,103].
L. taishanicum Meng, Xue and Wen, 1983
Orientia tsutsugamushi-positive larvae were collected from M. musculus and R. norvegicus in China. Among tested hosts, also A. argarius and T. triton were bacteria-positive [109,111].
L. tosai (Sasa and Kawashima, 1951)
Species (originally mentioned as Trombicula tosa) tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi. Larvae fed on M. montebelli and A. speciosus in Japan [107,123]
L. turdicola Vercammen-Grandjean and Langston, 1976
Associated with O. tsutsugamushi. Parasites collected from T. glis in Thailand [24].
L. umbricola Nadchatram and Dohany, 1980
Host-questing larvae tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi in Malaysia. Collected with the method of black plates [83,127].
Remarks: unengorged larvae of L. vivericola Vercammen-Grandjean and Langston, 1976 found in Malaysia by Dohany et al. [128] were also reported as O. tsutsugamushi-associated, however, the subsequent revision of the material proved the first species determination wrong and larvae were then assigned to L. umbricola [127].
L. wenense Wu, Wen, Yang and Wu, 1982
Listed among O. tsutsugamushi vectors in China [106,129]
L. zetum (Traub, Morrow and Lipovsky, 1958)
O. tsutsugamushi-associated larvae (mentioned as L. zeta) were collected from the mice, including A. agrarius, in South Korea [34,116].
Genus: Lorillatum Nadchatram, 1963
Lorillatum sp.
Genus representatives were reported to harbor O. tsutsugamushi. Larvae parasitized rodents from R. rattus-complex in Thailand [50].
Genus: Microtrombicula Ewing, 1950
Microtrombicula sp.
Reported as positive for Candidatus Orientia chuto Izzard et al., 2010. Parasites collected from ‘Micromys natalensis’, in Kenya [130].
M. chamlongi Nadchatram and Kethley, 1974
Unengorged larvae collected from the black plates spread over the ground tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi. Record from Thailand [68].
Genus: Miyatrombicula Sasa, Kawashima and Egashira, 1952
M. kochiensis Sasa, Kawashima and Egashira, 1952
Orientia tsutsugamushi-associated species. Unengorged larvae were gathered from the ground and vegetation in Japan [69].
Genus: Neoschoengastia Ewing, 1929
Neoschoengastia sp.
Listed in Epidemiology and ecology of rickettsial diseases in the People’s Republic of China as a genus characterized by low rate infection with O. tsutsugamushi [44].
Genus: Neotrombicula Hirst, 1925
Neotrombicula sp.
Evidenced as positive for Candidatus Orientia chuto. Larvae were collected from ‘Micromys natalensis’, in Kenya. Reported also from Spain as associated with R. felis [120,131].
N. autumnalis (Shaw, 1790)
Individuals of the European harvest mite were reported to contain Anaplasma phagocytophilum (Foggie 1949) (Pseudomonadota, Rickettsiales, Anaplasmataceae) (originally mentioned as Ehrlichia phagocytophila), B. burgdorferi s.l. Johnson et al., 1984, B. garinii Baranton et al., 1992, B. valaisiana Wang et al., 1997, R. monacensis, R. helvetica, R. pavlovskyi and Rickettsia sp. Infected larvae were collected from rodents (M. glareolus, A. flavicollis, M. arvalis and A. sylvaticus), birds (the Eurasian blackcap Sylvia atricapilla (Linnaeus, 1758) (Aves: Passeriformes)), soricomorphs (the white-toothed shrew C. russula (Hermann, 1780)), lizards (the common wall lizard Podarcis muralis (Laurenti, 1768), the Italian wall lizard P. siculus (Rafinesque, 1810) and the western green lizard Lacerta bilineata Daudin, 1802 (Reptilia: Squamata)) as well as from the vegetation. One case of infected nymph was reported too. Observations were made in Czech Republic, Germany, Italy, Russia, Slovakia, Spain and Ukraine [58,65,132,133,134,135,136].
Remarks: According to Stekolnikov et al. [18], all records concerning N. autumnalis should be thoroughly verified after proper mounting on microscopic slides, due to considerable resemblance of this species to N. inopinata. Proven misidentification was reported from Turkey.
N. carpathica Stekolnikov, 1996
Reported as carrier of B. garinii and B. valaisiana. Larvae parasitized S. atricapilla in Czech Republic [134].
N. inopinata (Oudemans, 1909)
Associated with B. garinii, B. valaisiana and Rickettsia spp. Parasitic larvae were gathered from S. atricapilla in Czech Republic and unengorged ones from the vegetation in Spain [134,137].
N. japonica(Tanaka, Kaiwa, Teramura and Kagaya, 1930)
Frequently mentioned as O. tsutsugamushi-related species. Collected from wild rodents, mainly A. agrarius, M. fortis, ‘C. triton’ (most probably T. triton) and insectivorous C. laisiura, along with the host-questing larvae from the ground and vegetation. Records come from Japan, South Korea and Russia (Primorsky Krai) [28,34,63,69,115,117,120,138].
N. microti (Ewing, 1928)
Mentioned as O. tsutsugamushi-positive species collected from rodents in Russia (Primorsky Krai) [139].
N. mitamurai (Sasa, Hayashi, Kumada and Teramura, 1950)
Listed among O. tsutsugamushi carrying mites parasitizing rodents and shrews in Russia (Primorsky Krai) [28,116,138].
N. nagayoi (Sasa, Hayashi, Sato, Miura and Asahina, 1950)
Mentioned as O. tsutsugamushi-positive species collected from rodents, including A. agrarius, in Russia (Primorsky Krai) and Korea [126,139].
N. pomeranzevi (Schluger, 1948)
Larvae were reported as O. tsutsugamushi-associated. Parasites captured most probably from M. rufocanus (originally: Clethrionomys rufocanus bedfordiae) and A. speciosus ainu in Japan and Russia (Primorsky Krai) [110,137,139].
N. sadoensis Saito and Otsuru, 1959
Orientia tsutsugamushi-positive representatives of the species were reported and taxonomically described from the Sado Island (Japan) [71].
N. tamiyai (Philip and Fuller, 1950)
Mentioned (originally as Trombicula tamiyai) as O. tsutsugamushi-positive species collected from rodents and shrews in Russia (Primorsky Krai) [28].
N. vulgaris (Schluger, 1959)
Larvae of the species revealed the presence of R. helvetica and R. monacensis. Gathered from Rickettsia-positive rodents: M. glareolus, A. flavicollis, M. arvalis and A. sylvaticus in Slovakia [58].
Genus: Odontocarus Ewing, 1929
Odontocarus sp.
Unengorged larvae captured by the method of black plates tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi. Report from Thailand [68].
Genus: Parasecia Loomis, 1966
Parasecia sp.
Rickettsia sp. was detected in larvae of this genus parasitizing birds in Brazil [57].
Genus: Quadraseta Brennan, 1970
Q. trapezoides (Brennan and Jones, 1964)
Parasite carrying a novel bacterium Candidatus Rickettsia colombianensi. Larvae were collected from the South American water rat Nectomys squamipes (Brants, 1827) (Mammalia: Rodentia) in Brazil [76].
Genus: Sauriscus Lawrence, 1949
S. sandovali (Hoffmann, 1947)
Larvae (originally mentioned as Tecomatlana sandovali) taken from the sac-winged bat Saccopteryx bilineata (Temminck, 1838) (Mammalia: Chiroptera) tested positive for C. burnetii. Record from Panama [77].
Genus: Schoengastia Oudemans, 1910
Schoengastia sp.
Larvae of this genus are known for association with B. tamiae. Tested parasites were obtained from R. rattus, R. argentiventer, B. indica, B. savilei and M. cervicolor in Thailand [55].
Genus: Schoengastiella Hirst, 1915
Schoengastiella spp.
Genus representatives parasitizing R. rattus were evidenced for the presence of O. tsutsugamushi. Observation from India [49].
S. ligula Radford, 1946
Individuals captured on R. rattus and S. murinus tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi in India. The association was mentioned also from Malaya and Pakistan [14,49,140].
Genus: Schoutedenichia Jadin and Vercammen-Grandjean, 1954
Schoutedenichia sp.
Mites of the genus are reported to carry O. tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia sp. Bacteria-positive larvae were obtained from R. tanezumi, B. savilei, and B. indica in Thailand [23,47].
Genus: Trombewingia Fonseca, 1955
T. bakeri (Fonseca, 1955)
Mite associated with a novel bacterium Candidatus Rickettsia colombianensi. Larvae were captured feeding on the montane grass mouse Akodon montensis Thomas, 1913 (Mammalia: Rodentia) in Brazil [76].
Genus: Trombiculindus Radford, 1948
T. variaculum (Traub and Nadchatram, 1967)
Orientia tsutsugamushi-associated species, larvae of which were collected from R. exulans in Thailand [23].
Genus: Walchia Ewing, 1931
Walchia sp.
Orientia tsutsugamushi-positive chiggers of this genus were obtained from B. indica. Thailand [23].
W. chinensis (Chen and Hsu, 1955)
Known for carrying O. tsutsugamushi. Larvae taken mostly from R. tanezumi flavipectus, captured in China [44,141].
W. kritochaeta (Traub and Evans, 1957)
Species tested positive for the scrub typhus etiologic agent. Parasitic larvae were collected from R. exulans, R. tanezumi, B. indica, B. berdmorei and the red spiny rat Maxomys surifer (Miller, 1900) in Thailand [23].
W. masoni (Asanuma and Saito, 1957)
Larvae captured from wild hares (the Japanese hare Lepus brachyurus Temminck, 1845 (Mammalia: Lagomorpha)) in Japan were positive for bacterium related to O. tsutsugamushi, however, according to authors, the record is not fully confirmed [14,71].
W. micropelta (Traub and Evans, 1957)
Larvae of the species contained genetic material of O. tsutsugamushi. Collected from B. indica and M. surifer in Thailand [23].
W. minuscuta (Chen, 1978)
Parasitic larvae found on M. surifer in Thailand tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi. Species also known to harbor Borrelia sp. [23,40].
W. ogatai Sasa and Teramura, 1951
Host-questing larvae gathered from the vegetation in Japan tested positive for O. tsutsugamushi [69].
W. pacifica (Chen and Hsu, 1955)
O. tsutsugamushi-associated larvae were obtained from rodents, mainly, A. agrarius, R. norvegicus and T. triton in China [111,113,114].
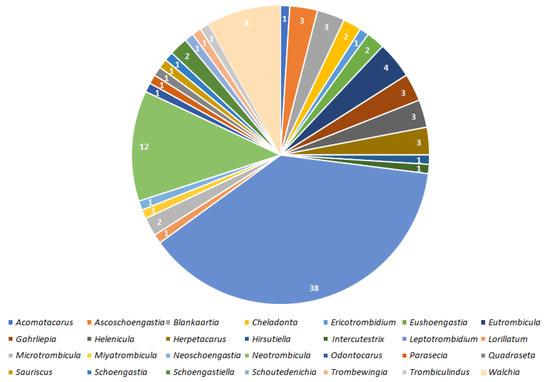
Figure 1.
Numbers of species within 28 mite genera associated with bacterial taxa.
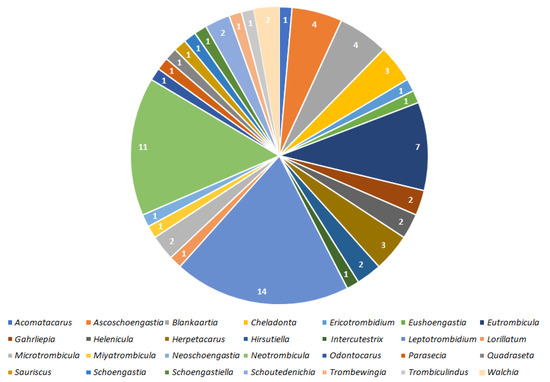
Figure 2.
Numbers of bacterial taxa detected in 28 genera of mites.
Trombiculidae spp.
Metagenomic analysis of rodent-associated chiggers collected in Thailand showed that undetermined chiggers were infected with the following pathogens: Bartonella spp., Borrelia spp., Francisella spp. Dorofe’ev 1947 (Pseudomonadota, Thiotrichales, Francisellaceae), Leptospira spp. Noguchi, 1917 (Spirochaetota, Leptospirales, Leptospiraceae) and O. tsutsugamushi [142]. Additionally, Mycobacterium sp. was detected in trombiculids parasitizing rodents and insectivores from Thai populations [40].
Pioneer survey on ectoparasites of rodents and related pathogens carried out in Saudi Arabia revealed the presence of Borrelia spp., C. burnetii-like bacterium and Candidatus Orientia chuto in trombiculids collected from the Eastern spiny mouse Acomys dimidiatus (Cretzschmar, 1826), the Yemeni mouse Ochromyscus yemeni (Sanborn and Hoogstraal, 1953), the king jird Meriones rex Yerbury and Thomas, 1895 (Mammalia: Rodentia) and R. rattus [143,144].
Research on pathogens associated with trombiculids parasitizing A. agrarius and C. lasiura in South Korea indicated mites’ association with Rickettsia sp., R. akari, R. australis, R. conorii, R. felis, R. japonica Uchida et al., 1992 and R. typhi [145].
Occurrence frequency of particular bacteria (genera and species) as well as bacterial families associated with Trombiculidae are illustrated in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
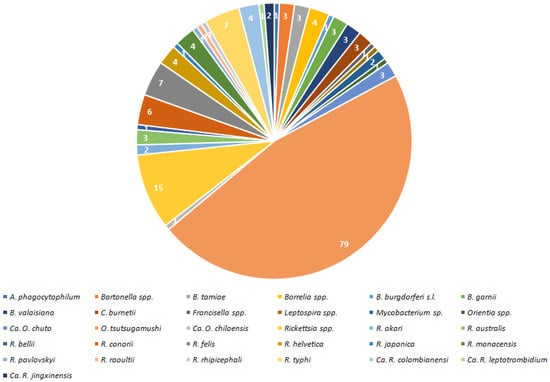
Figure 3.
Incidence of particular bacterial pathogens in hereby listed Trombiculidae.
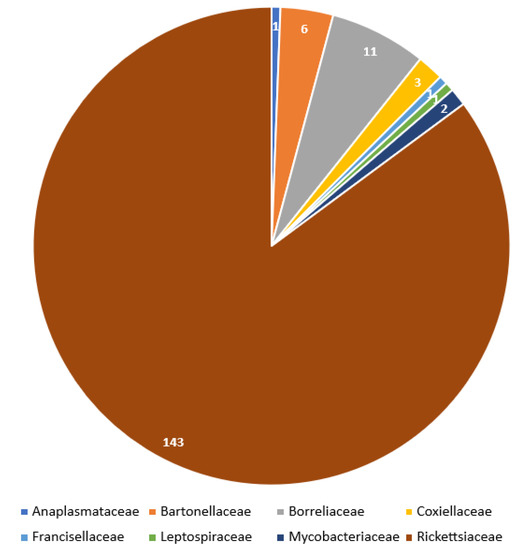
Figure 4.
Incidence of associations between pathogens and listed trombiculids grouped by bacterial families.
2.2. Species Lacking Authorities
Leptotrombidium nangii
L. tachensis
L. waiganmensis
The three taxa were listed in Epidemiology and ecology of rickettsial diseases in the People’s Republic of China and described as infected with O. tsutsugamushi at low rate [44].
Remarks: Species not listed in the reference checklists, even as synonyms.
Neotrombicula shiraii
Listed among O. tsutsugamushi-associated mites in Japan [10,71].
Remarks: This combination has not been found in the current literature, even as a synonym. Reports on ‘Neoschoengastia shiraii’, a parasite of birds occurring in Japan, can be found but without mention of scrub typhus bacterium [146].
3. Discussion
Results indicate that 100 species of Trombiculidae, representing 28 genera, are associated with 31 bacterial taxa from eight families, seven orders and three phyla (Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4). Listed mites constitute around 3.3% of the whole family and occur in Palaearctic, Nearctic, Neotropical, Afrotropical, Oriental and Australian zoogeographic regions [2]. Apart from non-parasitic instars (i.e., host searching larvae swarming on the ground and vegetation and predatory deutonymphs), pathogen-positive individuals include ecto- and endoparasites of rodents (majority of cases), soricomorphs, scadents, lagomorphs, peramelemorphs, bats, passerine birds, reptiles and humans. Among listed genera, Leptotrombidium is characterized by the highest number of bacteria-positive species (38), followed by Neotrombicula (12) and Walchia (8) (Figure 1). This might be reflecting the fact that named genera are considerably numerous in species [2,86]. As for the number of bacteria associated with particular genera, again, Leptotrombidium spp. are positive for the highest quantity of pathogenic taxa (14), next is Neotrombicula (11) and Eutrombicula (7) (Figure 2). Rickettsiaceae is the dominant family detected in Trombiculidae. Orientia tsutsugamushi infection was confirmed in 79 cases, and is followed by R. typhi and R. felis (7 cases, each), to name only the most frequent rickettsial species. Considerable incidence also characterizes Borreliaceae—infection with Borrelia spp. was observed in 11 cases (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Hereby discussed data concern only non-artificial infections of mites originating from the natural environment. We excluded experimentally induced associations, such as acquisition of B. garinii and C. burnetii by larvae of the European harvest mite after parasitizing infected rodents under laboratory conditions, or obtaining O. tsutsugamushi-positive larvae of the common Northamerican chigger resulting from experimental feeding upon host with rickettsaemia [42,54,133]. Associations with viruses, for example, between Hantaan virus and L. scutellare [147,148], however very interesting, were omitted too.
Rickettsiales, the obligate intracellular parasites [66], are especially prevalent within chigger mites. With the highest probability, it is the result of the already described larval feeding mechanism (dissolving and ingesting cell contents from host’s epidermis and dermis) [16], combined with the affinity of rickettsial bacteria to reside in the connective tissue, including its external layers forming the skin [149,150,151,152]. Similar tendency is characteristic for Borrelia spp. spirochetes [153,154,155]. Producing the stylostome during food intake is a common feature of trombiculids, however, its length, width and wall structure is differentiated among genera [16,156]. Hase et al. proposed three types of stylostomes depending on the longitude (epidermal—the shortest, mesenchymal—the longest and a mix of the two) based on observations of Leptotrombidium spp feeding. Authors hypothesized that the canal structure might have been related to the mite’s ability to acquire bacteria, as larvae of L. intermedium (the only species to form epidermal stylostome) turned out to be pathogen-free [157]. This assumption was subsequently refuted as later studies revealed the association between O. tsutsugamushi and L. intermedium. Moreover, Neotrombicula pomeranzevi, Miyatrombicula esoensis (Sasa and Ogata, 1953) and Kepkatrombicula desaleri (Methlagl, 1928) produce the longest feeding canals, thus penetrating host tissues relatively deep, albeit the ability to ingest pathogens by the two latter species still awaits confirmation in laboratory tests. On the other hand, H. zachvatkini and Leptotrombidium spp. Create shorter canals which widen in time and were reported as bacteria-positive quite frequently (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Cheladonta costulata, known for parasitism entailing submergence of almost the entire body into host tissues and producing feeding tubes of very variable length, was capable of acquiring rickettsiae too [16,156]. Considering the fact that the current number of pathogen-associated trombiculids is 100, whereas formation of the stylostome has been examined in a fracture of this group, the relation between the structure of the feeding canal and acquisition of bacteria is still to be verified in the research involving more species. A common feature of the remaining bacterial genera detected in trombiculids (i.e., Bartonella, Coxiella, Francisella, Leptospira, Mycobacterium) is their natural presence in organisms of Rodentia and Soricomorpha [42,158,159,160,161,162], which are not only preferable hosts of chiggers in general but also were sources from which infected parasitic instars were collected. Named microorganisms, however, (unlike Rickettsiaceae and Borreliaceae) do not demonstrate high affinity to external layers of the connective tissue, but are reported to reside mostly in phagocytes, endothelium, erythrocytes and kidney cells as well as in soil and water [163,164,165,166,167,168]. This may potentially explain lower incidence of these genera in mites (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Inasmuch some bacterial species from the above genera can also dwell in the moist microhabitats (also preferred by many trombiculids), it cannot be excluded that their presence in mites might be a result of contamination.
A term association between mites and pathogens has been deliberately applied as vectorship, i.e., capability of effectively transmitting bacteria to humans (or other vertebrates) is not proven for all pathogen-positive chigger species and the presence of microorganisms may be resulting from ingesting dissolved host tissues (i.e., pathogen’s reservoir), especially when engorged larvae are preserved and tested shortly after being detached from the host. Confirmed vectors of Orientia spp., e.g., L. deliense, L. akamushi, L. scutellare or H. antarctica, meet the criteria formulated by Traub and Wisseman: natural infection with a pathogen, ability to infect a host (by feeding process, after being crushed on host’s body or with infected feaces), high prevalence in a given area and, tendency for parasitizing humans. The latter point regards of course only diseases plaguing people and it is not essential for the mechanism of vectorship as such. As Trombiculidae, unlike, e.g., Ixodidae or Macronyssidae, are parasitic once in a lifetime, to successfully transmit bacteria larvae have to acquire them via transstadial and transovarial transmission from the parental generation [14,54]. The latter two phenomena also have been analyzed mainly in Leptotrombidium spp. so far e.g., [19,20,21]. At the same time, observations of bacteria-positive, unengorged larvae from Eutrombicula, Herpetacarus, Microtrombicula, Miyatrombicula, Neotrombicula, Odontocarus and Walchia genera along with the infected deutonymphs and successful experimental infections, indicate that the possibility of effective pathogen transmission remains high in a variety of chigger mite species.
One should bear in mind, yet, that detailed research on vector competence of the particular mites species is often hindered by two issues. The first one is extremely varied numbers of mites from particular species in collected samples—ranging from thousands of individuals of the most common taxa, to single ones of the most infrequent (H.M. personal observation). This is illustrated by results of chigger collection in NW Russia wherein thousands of H. zachvatkini larvae were present in contrast to nine of A. latyshevi (Schluger, 1955) and one N. absoluta Schluger, 1966 larva. Significant disproportions in field-collected chiggers were also recorded during a survey performed in India—the most common species L. deliense and L. insigne Fernandes and Kulkarni, 2003 combined totalled 9408 larvae, while the rarest—Walchia sp. and Schoutedenichia sp. were 33 and single larva, respectively. Tamura et al., in turn, observed the following shares of mites collected in Japan: L. pallidum (56.6%), L. scutellare (13.6%), L. fuji (12.7%), G. saduski (10.5%), N. japonica (1.6%), L. kitasatoi (1.6%), L. palpale (1.4%), L. intermedium (1.1%), L. miyazakii Sasa, Sawada, Kano, Hayashi and Kumada, 1951 (0.1%), L. miyajimai (Fukuzumi and Obata, 1951) (0.3%), N. tamiyai (0.02%), Eltonella ichikawai Vercammen-Grandjean, 1965 (0.1%) and C. ikaoensis (0.1%) [92,169,170]. Although single specimens can be easily tested for the presence of bacteria, results based on small samples are not fully representative. Moreover, verification of transstadial and transovarial transmissions would require experimental rearing of a few mite generations based on a considerable number of chiggers, with consideration of their mortality [171]. The second problem is the correct identification of potential vector species. An example of this kind of impediment is already signalized misidentification between closely related N. autumnalis (considered the most common European chigger, however, absent in some countries (H.M. personal observation) and N. inopinata (species often determined after the proper identification of specimens previously assigned to ‘N. autumnalis’) [18]. Furthermore, Ponnusamy et al. have recently reported on problems with matching COI sequences of Rickettsia-positive Eutrombicula sp. and Leptotrombidium sp., previously determined upon morphological criteria, with corresponding data in the GeneBank using the BLAST tool [64]. This problem is not limited to chiggers inhabiting Nearctic, as the deficiency of reference sequences in the GeneBank is still noticeable (such data are available for c. 80 nominal species only). At the same time, obtaining COI sequences of L. imphalum and L. chaigraiensis led to separation of these species, formerly considered as one [86,88].
Identification difficulties should not suppress the research on pathogen transmission by Trombiculidae inasmuch the most accurate species determination can be achieved by simultaneous application of morphological and molecular tools, as it has been already implemented in some studies [88,172,173,174]. Moreover, this issue necessitates further exploration as bacterial diseases potentially transmitted by chiggers are largely negligent in parts of the globe where they are apparently absent, as it was emphasized by Weitzel et al. [39]. For example, not only is the scrub typhus present in the subantarctic Chile, but also its etiological agent turned out to be a novel Orientia species—Candidatus Orientia chiloensis. The pathogen was effectively transmitted to humans by H. antarctica [36,39,73,175]. Analogical instances of bush typhus bacterium, distinct from O. tsutsugamushi (i.e., Candidatus Orientia chuto), detected in Trombiculidae occurring outside the ‘tsutsugamushi triangle’ come from Kenya and Saudi Arabia. From the latter country, O. chuto-positive patient was reported as well [37,38,130,143]. Other proposed bacterial species (i.e., Candidatus rickettsia colombianesi, Ca. rickettsia jinxinensis and Ca. rickettsia leptotrombidium) harbored by Trombiculidae, along with the most recent and the first ever findings of rickettsiae in chiggers from North Carolina (USA) [64] only reaffirm the sense of continual survey on, otherwise unrecognized and hidden, pathogens and their transmission routes. Exploring the issue is also justified by non-decreasing importance of parasitic and bacterial zoonoses in general [42] and can be greatly supported by the highly effective technologies (e.g., RAPD-PCR fingerprinting or high throughput sequencing (HTS) related techniques such as DNA metabarcoding), application of which can result in further contributions to the hereby reviewed matter.
4. Materials and Methods
Google scholar, PubMed and Scopus databases were searched with bacteria, chigger mites, detection, pathogen, spirochaetes, Trombiculidae, trombiculid terms. Collected records cover almost 100 years (from 1924 to 2022) of the research on the association between chiggers and bacterial pathogens, detected by means of microscopic, culturing, serological and molecular examinations performed worldwide (Section 2.1). Testing techniques as well as the very history of studies on Trombiculidae-bacteria relation are summarized and thoroughly described in the literature [10,32].
Taxonomic nomenclature and systematics of Trombiculidae follow elaborations, taking into account morphological and molecular data [2,86,87,88,103]. Species authorities, scientific names as well as common names and systematics of vertebrates are given at first mention, according to Wilson and Reeder and IUCN Red List [176,177].
Species of Trombiculidae lacking authority and not present in the above reference sources are placed in a separate subsection (2.2) but are not included in plots and calculations.
5. Conclusions
The share of pathogen-associated trombiculids is low in comparison with the total number of nominal species comprising the Trombiculidae family. Nonetheless, so far revealed bacteria-positive mites are characterized by harboring differentiated bacterial species, vast geographical distribution and association with a variety of hosts. Moreover, the present summary also points at cases of relatively recently discovered novel bacterial species and localities wherein the discussed microorganisms were apparently absent to date. This knowledge, combined with the unwavering significance of zoonotic bacterioses and the recognized mechanisms of pathogens circulation in chigger populations, are premises that the actual number of Trombiculidae-bacteria associations is not limited to the cases presented. An assumption can be made that the continual microbiological testing of chiggers, especially when supported with the fast and highly effective technologies, will result in further findings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M.; methodology, H.M., K.W. and P.C.; formal analysis, H.M. and K.W.; investigation, H.M. and K.W.; data curation, H.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M.; writing—review and editing, H.M., K.W. and P.C.; visualization, H.M.; supervision, H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to express their gratitude to Kittipong Chaisiri from Mahidol University in Bangkok, Thailand, for his help in accessing full versions of articles.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kudryashova, N.I. Chigger Mites (Acariformes, Trombiculidae) of East Palaearctics; KMK Scientific Press: Moscow, Russia, 1998; pp. 1–342. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, D.H.; Robbins, R.G.; Rueda, L.M. Annotated world checklist of the Trombiculidae and Leeuwenhoekiidae (1758–2021) (Acari: Trombiculoidea), with notes on nomenclature, taxonomy, and distribution. Zootaxa 2021, 4967, 1–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniuszko, H.; Shatrov, A.B.; Mąkol, J. Description of active post-larval forms of Neotrombicula vulgaris (Schluger, 1955) (Prostigmata: Trombiculidae), with notes on biology and ecology of the species. Ann. Zool. 2017, 67, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audy, J.R. Trombiculid mites infesting birds, reptiles, and arthropods in Malaya, with a taxonomic revision, and description of a new genus, two new subgenera, and six new species. Bull. Raffles Mus. 1956, 28, 27–80. [Google Scholar]
- Felska, M.; Wohltmann, A.; Mąkol, J. A synopsis of host-parasite associations between Trombidioidea (Trombidiformes: Prostigmata, Parasitengona) and arthropod hosts. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 1375–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniuszko, H.; Mąkol, J. Chigger mites (Actinotrichida: Parasitengona, Trombiculidae) of Poland. An updated distribution and hosts. Ann. Parasitol. 2014, 60, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Salvadori, C.; Formenti, N.; Trogu, T.; Lanfranchi, P.; Rossi, L.; Citterio, C.; Obber, F.; Poli, A. Pathology and distribution of trombiculosis in Northern Chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra rupicapra) in the Italian Alps. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatrov, A.B.; Kudryashova, N.I. Taxonomic ranking of major trombiculid subtaxa with remarks on the evolution of host-parasite relationships (Acariformes: Parasitengona: Trombiculidae). Ann. Zool. 2008, 58, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, A.C.O.; Bernardi, L.F.D.O.; Ferreira, R.L. Uncommon record of a whip spider (Amblypygi: Charinidae) parasitized by a chigger mite (Parasitengona: Trombiculidae: Leeuwenhoekiinae). Int. J. Acarol. 2017, 43, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, I.; Pearson, I.; Dahal, P.; Thomas, N.V.; Roberts, T.; Newton, P.N. Scrub typhus ecology: A systematic review of Orientia in vectors and hosts. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaoka, M.; Asanuma, K.; Otsuji, J. Transmission of Rickettsia orientalis to man by Leptotrombidium akamushi at a scrub typhus endemic area in Akita Prefecture, Japan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1974, 23, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.Y.; Yoon, S.S.; Lee, W.J.; Sin, H.K.; Lee, W.K. Observation of stylostome formation in the striped-field mouse (Apodemus agrarius Pallas) skin by chigger feeding. Korean J. Soil Zool. 2006, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shatrov, A.B.; Antonovskaia, A.A. Stylostome of the trombiculid mite larvae Neotrombicula talmiensis (Schluger, 1955) (Acariformes, Trombiculidae) feeding on two host species in the Russian Far East. Acarologia 2021, 61, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.L., Jr. The ecology of chigger-borne rickettsiosis (scrub typhus). J. Med. Entomol. 1974, 11, 237–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M. The Penetration of the host tissue by the harvest mite, Trombicula autumnalis Shaw. Parasitology 1950, 40, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatrov, A.B. Stylostome formation in trombiculid mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 49, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibáñez, P.; Palomar, A.M.; Portillo, A.; Santibáñez, S.; Oteo, S.S.A.J.A. The role of chiggers as human pathogens. An overview of tropical diseases. Amidou Samie Intech Open 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekolnikov, A.; Santibáñez, P.; Palomar, A.M.; Oteo, J.A. Neotrombicula inopinata (Acari: Trombiculidae)—A possible causative agent of trombiculiasis in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerdthusnee, K.; Nigro, J.; Monkanna, T.; Leepitakrat, W.; Leepitakrat, S.; Insuan, S.; Charoensongsermkit, W.; Khlaimanee, N.; Akkagraisee, W.; Chayapum, K.; et al. Surveys of rodent-borne disease in Thailand with a focus on scrub typhus assessment. Integr. Zool. 2008, 3, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phasomkusolsil, S.; Tanskul, P.; Ratanatham, S.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Frances, S.P.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Linthicum, K.J. Transstadial and transovarial transmission of Orientia tsutsugamusi in Leptotrombidium imphalum and Leptotrombidium chiangraiensis (Acari: Trombiculidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapmund, G.; Upham, R.W., Jr.; Kundin, W.D.; Manikumaran, C.; Chan, T.C. Transovarial development of scrub typhus rickettsiae in a colony of vector mites. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1969, 63, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, H.-A.; Lee, M.-J.; Lee, W.-C. Comparative research on epidemiological aspects of tsutsugamushi disease (scrub typhus) between Korea and Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elliott, I.; Thangnimitchok, N.; Chaisiri, K.; Wangrangsimakul, T.; Jaiboon, P.; Day, N.P.J.; Paris, D.H.; Newton, P.N.; Morand, S. Orientia tsutsugamushi dynamics in vectors and hosts: Ecology and risk factors for foci of scrub typhus transmission in northern Thailand. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, I.; Thangnimitchok, N.; de Cesare, M.; Linsuwanon, P.; Paris, D.H.; Day, N.P.; Batty, E.M. Targeted sequence capture of Orientia tsutsugamushi DNA from chiggers and humans. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, D.; Gupta, S.; Nagraik, R.; Verma, V.; Thakur, A.; Kaushal, A. Diagnosis of scrub typhus: Recent advancements and challenges. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, A., Jr.; Tanaka, H.; Tamura, A. Tsutsugamushi Disease; University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, D.J.; Fuerst, P.A.; Ching, W.; Richards, A.L. Scrub typhus: The geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48 (Suppl. S3), S203–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, N.I.; Tarasevich, I.V. Trombiculids in a natural focus of tsutsugamushi disease in the south of the Maritime Province. Meditsinskaya Parazitol. Parazit. Bolezn. 1964, 33, 718–721. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Wang, H.-C.; Huang, C.-L. The potential effect of exotic Pacific rats Rattus exulans on vectors of scrub typhus. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 48, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsuwanon, P.; Auysawasdi, N.; Wongwairot, S.; Leepitakrat, S.; Rodkhamtook, W.; Wanja, E.; Monkanna, T.; Wegner, M.; Davidson, S.; Poovorawan, Y.; et al. Assessing scrub typhus and rickettsioses transmission risks in the Chiang Rai province of northern Thailand. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 42, 102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, T.H.; Ahmad, T.; Wana, M.N.; Li, W.; Musa, H.H.; Sharun, K.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Chaicumpa, W.; Campbell, M.C.; et al. The epidemiology, diagnosis and management of scrub typhus disease in China. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 3795–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, D.; Kelly, D.; Fuerst, P.; Day, N.; Richards, A. A brief history of the major rickettsioses in the Asia–Australia–Pacific region: A capstone review for the special issue of TMID. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.Y.; Cai, Y.P.; Xu, L.; Zha, Y.J.; Yang, B.S. The epidemiology of scrub typhus all over the world: A systematic literature review. Asian J. Adv. Res. 2021, 6, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, M.-G.; Song, B.-G.; Kim, T.-K.; Noh, B.-E.; Lee, H.; Lee, W.-G.; Lee, H. Nationwide incidence of chigger mite populations and molecular detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi in the Republic of Korea, 2020. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Walker, D.H.; Jupiter, D.; Melby, P.C.; Arcari, C.M. A review of the global epidemiology of scrub typhus. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarca, K.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Angulo, J.; Jiang, J.; Farris, C.M.; Richards, A.L.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Weitzel, T. Molecular description of a novel Orientia species causing scrub typhus in Chile. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzard, L.; Fuller, A.; Blacksell, S.D.; Paris, D.H.; Richards, A.L.; Aukkanit, N.; Stenos, J. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L. Scrub typhus: No longer restricted to the tsutsugamushi triangle. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, T.; Makepeace, B.L.; Elliott, I.; Chaisiri, K.; Richards, A.L.; Newton, P.N. Marginalized mites: Neglected vectors of neglected diseases. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisiri, K. Molecular Ecology of Chigger Mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) and Associated Bacteria in Thailand; The University of Liverpool: Liverpool, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chaisiri, K.; McGarry, J.W.; Morand, S.; Makepeace, B.L. Symbiosis in an overlooked microcosm: A systematic review of the bacterial flora of mites. Parasitology 2015, 142, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Mares, A.; Guzmán-Cornejo, C.; Ulloa-García, A.; Córdoba-Aguilar, A.; la Fuente, M.C.S.-D.; Suzán, G. Mites, rodents, and pathogens: A global review for a multi-species interaction in disease ecology. Acta Trop. 2022, 232, 106509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.T. A synopsis of Asian species of Mus (Rodentia, Muridae). Bull. AMNH 1977, 158, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ming-yuan, F.; Walker, D.H.; Shu-rong, Y.; Qing-huai, L. Epidemiology and ecology of rickettsial diseases in the People’s Republic of China. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1987, 9, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.S.; Lin, S.G. Study on the condition of natural infection with R. tsutsugamushi among mites and domestic animals in Fukien. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 1957, 5, 425–432. [Google Scholar]
- Frances, S.P.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Tanskul, P. Occurrence of Orientia tsutsugamushi in chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) and small animals in an orchard near Bangkok, Thailand. J. Med Èntomol. 1999, 36, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsuwanon, P.; Krairojananan, P.; Rodkvamtook, W.; Leepitakrat, S.; Davidson, S.; Wanja, E. Surveillance for scrub typhus, rickettsial diseases, and leptospirosis in US and multinational military training exercise cobra gold sites in Thailand. U.S. Army Med Dep. J. 2018, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Loan, H.K.; Van Cuong, N.; Takhampunya, R.; Klangthong, K.; Osikowicz, L.; Kiet, B.T.; Campbell, J.; Bryant, J.; Promstaporn, S.; Kosoy, M.; et al. Bartonella species and trombiculid mites of rats from the Mekong delta of Vietnam. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.A.J.; Kamarasu, K.; Samuel, P.P.; Govindarajan, R.; Govindasamy, P.; Johnson, L.A.; Seran, K.C. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi in novel trombiculid mite species in northern Tamil Nadu, India: Use of targeting the multicopy traD gene. J. Med. Entomol. 2022, 59, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhampunya, R.; Korkusol, A.; Promsathaporn, S.; Tippayachai, B.; Leepitakrat, S.; Richards, A.L.; Davidson, S.A. Heterogeneity of Orientia tsutsugamushi genotypes in field-collected trombiculid mites from wild-caught small mammals in Thailand. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, M.D.; Truong, S.C.; Le Thanh, D.; Ba, L.C.; Le Van, N.; Nhu, B.D. Identification of trombiculid chigger mites collected on rodents from southern Vietnam and molecular detection of Rickettsiaceae pathogen. Korean J. Parasitol. 2020, 58, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanskul, P.; Strickman, D.; Eamsila, C.; Kelly, D.J. Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in Chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) associated with rodents in central Thailand. J. Med Èntomol. 1994, 31, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, R.; Frick, L.P.; Diercks, F.H. Observations on the occurrence of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in rats and mites in the Malayan jungle. Am. J. Epidemiology 1950, 51, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.L., Jr. Ecological considerations in scrub typhus: 2. Vector species. Bull. World Health Organ. 1968, 39, 219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kabeya, H.; Colborn, J.M.; Bai, Y.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Richardson, J.H.; Maruyama, S.; Kosoy, M.Y. Detection of Bartonella tamiae DNA in ectoparasites from rodents in Thailand and their sequence similarity with bacterial cultures from Thai patients. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassini-Silva, R.; Jacinavicius, F.; Maturano, R.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Ochoa, R.; Bauchan, G.; Labruna, M.B.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. Blankaartia sinnamaryi (Trombidiformes: Trombiculidae) parasitizing birds in southeastern Brazil, with notes on Rickettsia detection. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinária 2018, 27, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.B. Chigger Mites of Brazilian Birds: Morphological Studies and Investigation of the Presence of Associated Pathogens. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Miťková, K.; Berthová, L.; Kalúz, S.; Kazimírová, M.; Burdová, L.; Kocianová, E. First detections of Rickettsia helvetica and R. monacensis in ectoparasitic mites (Laelapidae and Trombiculidae) infesting rodents in south-western Slovakia. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asanuma, K.; Kitaoka, M.; Shimizu, F.; Kano, R. Leptotrombidium scutellare as a vector of scrub typhus at the endemic area of the foothills of Mt. Fuju, Japan. J. Hyg. epidemiology Microbiol. Immunol. 1974, 18, 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kitaoka, M.; Okubo, K.; Asanuma, K. Epidemiological survey by means of complement fixation test on scrub typhus in Japan. Acta Med. Biol. 1967, 15, 69–85. [Google Scholar]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.L., Jr. Ecological considerations in scrub typhus: 1. Emerging concepts. Bull. World Health Organ. 1968, 39, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, I.Y.; Song, H.J.; Kim, J.; Park, H.J.; Song, D.; Jang, W.J. Geographical distribution of Orientia tsutsugamushi strains in chiggers from three provinces in Korea. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.I.; Shim, S.K.; Song, B.G.; Choi, E.N.; Hwang, K.J.; Park, C.; Shin, E.H. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi, the causative agent of scrub typhus, in a novel mite species, Eushoengastia koreaensis, in Korea. Vector Borne Zoonotic 2011, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, L.; Garshong, R.; McLean, B.S.; Wasserberg, G.; Durden, L.A.; Crossley, D.; Apperson, C.S.; Roe, R.M. Rickettsia felis and Other Rickettsia Species in chigger mites collected from wild rodents in north Carolina, USA. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Ribeiro, S.R.; Castilho-Onofrio, V.; Marcili, A.; Simonato, B.B.; Latrofa, M.S.; Benelli, G.; Otranto, D.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. Molecular detection of vector-borne agents in ectoparasites and reptiles from Brazil. Ticks Tick-borne Dis. 2020, 12, 101585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salje, J. Cells within cells: Rickettsiales and the obligate intracellular bacterial lifestyle. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 19, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez, C.S.E.; Troyo, A. A review of the genus Rickettsia in Central America. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2018, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shirai, A.; Tanskul, P.L.; Andre, R.G.; Dohany, A.L.; Huxsoll, D.L. Rickettsia tsutsugamushi strains found in chiggers collected in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1981, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pham, X.D.; Otsuka, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Takaoka, H. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi (Rickettsiales: Rickettsiaceae) in unengorged chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) from Oita Prefecture, Japan, by nested polymerase chain reaction. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Otani, K.; Qiu, Y.; Nakao, R.; Sugimoto, C.; Abiko, C. Proposed vector candidate: Leptotrombidium palpale for Shimokoshi type Orientia tsutsugamushi. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Otsuru, M. Notes on trombiculid mites collected in Sado Island of Japan and isolation of Rickettsia, with a description of Trombicula (Neotrombicula) sadoensis n. sp. Acta Med. Et Biol. 1959, 7, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.W.; Ha, N.-Y.; Ryu, B.; Bang, J.H.; Song, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, G.; Oh, M.-D.; Cho, N.-H.; Lee, J.-K. Urbanization of scrub typhus disease in South Korea. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, T.; la Fuente, M.C.S.-D.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Pérez, C.; Pérez, R.; Vial, C.; Abarca, K.; Acosta-Jamett, G. Novel vector of scrub typhus in Sub-Antarctic Chile: Evidence from human exposure. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 1862–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Jamett, G.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Beltrami, E.; Silva-de La Fuente, M.C.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L.; Weitzel, T.; Abarca, K. Identification of trombiculid mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) on rodents from Chiloé Island and molecular evidence of infection with Orientia species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-de la Fuente, M.C.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Weitzel, T.; Beltrami, E.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Abarca, K.; Acosta-Jamett, G. Chigger mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) of Chiloé Island, Chile, with descriptions of two new species and new data on the genus Herpetacarus. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacinavicius, F.D.C.; Bassini-Silva, R.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Welbourn, C.; Ochoa, R.; Labruna, M.B.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. Molecular detection of Rickettsia genus in chigger mites (Trombidiformes: Trombiculidae) collected on small mammals in southeastern brazilian. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinária 2019, 28, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunker, G.E.; Brennan, J.M.; Hughes, L.E.; Philip, G.B.; Clifford, C.M.; Peralta, P.H.; Vogel, J. Isolation of viral and Rickettsial agents from Panamanian Acarina. J. Med Èntomol. 1975, 12, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.L., Jr.; Ahmad, N. The occurrence of scrub typhus infection in unusual habitats in West Pakistan. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1967, 61, 23–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjaja, S.; Williams, M.; Winoto, I.; Farzeli, A.; Stoops, C.A.; Barbara, K.A.; Richards, A.L.; Blair, P.J. Geographical assessment of rickettsioses in Indonesia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, J.A.R.; Austin, F.J.; Jennings, L.C. Scrub typhus in the eastern Solomon islands and Northern Vanuatu (New Hebrides). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, D.T.; Hadi, T.R.; Brown, R.J.; Sukaeri, S.; Leksana, B.; Cholid, R. A survey of scrub and murine typhus in the Ancol section of Jakarta, Indonesia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1981, 12, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Upham, R.W., Jr.; Hubert, A.A.; Phang, O.W.; Mat, Y.B.; Rapmund, G. Distribution of Leptotrombidium (Leptotrombidium) arenicola (Acarina: Trombiculidae) on the ground in West Malaysia. J. Med. Entomol. 1971, 8, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, A.; Dohany, A.; Ram, S.; Chiang, G.; Huxsoll, D. Serological classification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi organisms found in chiggers (Acarina: Trombiculidae) collected in Peninsular Malaysia. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerdthusnee, K.; Khuntirat, B.; Leepitakrat, W.; Tanskul, P.; Monkanna, T.; Khlaimanee, N.; Coleman, R.E. Scrub typhus: Vector competence of Leptotrombidium chiangraiensis chiggers and transmission efficacy and isolation of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 990, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phasomkusolsil, S.; Tanskul, P.; Ratanatham, S.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Frances, S.P.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Linthicum, K.J. Influence of Orientia tsutsugamushi infection on the developmental biology of Leptotrombidium imphalum and Leptotrombidium chiangraiensis (Acari: Trombiculidae). J. Med Èntomol. 2012, 49, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekolnikov, A.A. Leptotrombidium (Acari: Trombiculidae) of the World. Zootaxa 2013, 3728, 1–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisiri, K.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Makepeace, B.L.; Morand, S. A revised checklist of chigger mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) from Thailand, with the description of three new species. J. Med Èntomol. 2016, 53, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumlert, R.; Chaisiri, K.; Anantatat, T.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Morand, S.; Prasartvit, A.; Makepeace, B.L.; Sungvornyothin, S.; Paris, D.H. Autofluorescence microscopy for paired-matched morphological and molecular identification of individual chigger mites (Acari: Trombiculidae), the vectors of scrub typhus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audy, J.R. Scrub typhus investigations in South East Asia. A Report on Investigations by GHQ [India] Field Typhus Research Team, and the Medical Research Council Field Typhus Team, based on the Scrub Typhus Research Laboratory South East Asia Command, Imphal. Part III. Appendices. 1947. Available online: https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/19482902020 (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Campbell, R.; Domrow, R. Rickettsioses in Australia: Isolation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi and R. australis from naturally infected arthropods. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1974, 68, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candasamy, S.; Ayyanar, E.; Paily, K.; Karthikeyan, P.A.; Sundararajan, A.; Purushothaman, J. Abundance & distribution of trombiculid mites & Orientia tsutsugamushi, the vectors & pathogen of scrub typhus in rodents & shrews collected from Puducherry & Tamil Nadu, India. Indian J. Med Res. 2016, 144, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisiri, K.; Gill, A.C.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Hinjoy, S.; McGarry, J.W.; Darby, A.C.; Morand, S.; Makepeace, B.L. Ecological and microbiological diversity of chigger mites, including vectors of scrub typhus, on small mammals across stratified habitats in Thailand. Anim. Microbiome 2019, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.C.; Lien, J.C.; Hsu, S.H.; Chen, W.F. Scrub typhus in the Pescadores Islands: An epidemiologic and clinical study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, L.T.L.; Cuong, V.V.; Van Toan, T.; Nhung, H.T.H.; Thuy, C.T.T.; Giang, P.T.H.; Nga, B.T.T.; Anh, B.T.L.; Van Chau, N. Detection of DNA of Rickettsia and Orientia tsutsugamushi in rodents and ectoparasites in Ha Giang province. Vietnam J. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.E.; Austrian, R.C.; Bell, E.J. Observations on tsutsugamushi disease (scrub typhus) in Assam and Burma: The recovery of strains of Rickettsia orientalis. Am. J. Hyg. 1947, 46, 268–286. [Google Scholar]
- Derne, B.; Weinstein, P.; Musso, D.; Lau, C. Distribution of rickettsioses in Oceania: Past patterns and implications for the future. Acta Trop. 2015, 143, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Lee, P.L.; Wang, H.C. Molecular identification of Rickettsia spp. in chigger mites in Taiwan. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2022, 36, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawley, B.J. The discovery, investigation and control of scrub typhus in Singapore. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1957, 51, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanprick, A.; Yooyen, T.; Rodkvamtook, W. Survey of Rickettsia spp. and Orientia tsutsugamushi pathogens found in animal vectors (Ticks, Fleas, Chiggers) in Bangkaew District, Phatthalung Province, Thailand. Korean J. Parasitol. 2019, 57, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, P.; Tsai, K.; Weng, M.; Hung, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, K.; Lien, J.; Lin, P.; Shaio, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Molecular detection and characterization of spotted fever group Rickettsiae in Taiwan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walch, E.W.; Keukenschrijver, N.C. Einige opmerkingen aangaande de Epidemiologie van de Pseudotyphus. Geneeskd. Tijdschr. Voor Ned. Indië 1924, 64, 247–276. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Peng, G.; Jiang, P.; Zheng, N.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Z. Natural foci of tsutsugamushi disease in the Nan Peng Lie Islands in China. Chin. Med J. 2002, 115, 272–275. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, S.; Kulkarni, S.M. Studies on the trombiculid mite fauna of India. In Records of the Zoological Survey of India; Zoological Survey of India: Kolkata, India, 2003; Paper Number 212; pp. 1–539. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, F.G.; Maxcy, K.F.; Sadusk, J.F., Jr.; Kohls, G.M.; Bell, E.J. Trombicula fletcheri Womersley and Heaslip 1943, a vector of tsutsugamushi disease (scrub typhus) in New Guinea. Science 1945, 102, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, L.; Willcox, A.C.; Roe, R.; Davidson, S.A.; Linsuwanon, P.; Schuster, A.L.; Richards, A.L.; Meshnick, S.R.; Apperson, C.S. Bacterial microbiome of the chigger mite Leptotrombidium imphalum varies by life stage and infection with the scrub typhus pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Guo, X.-G. Research Advances of Leptotrombidium scutellare in China. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, N. Recent findings on vector acari for rickettsia and spirochete in Japan. Med Èntomol. Zool. 1995, 46, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Urakami, H.; Takahashi, M.; Misumi, H.; Okubo, K.; Enatsu, T.; Tamura, A. Detection, isolation and characterization of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Leptotrombidium intermedium. Med. Èntomol. Zool. 2000, 51, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, Z.-T.; Yang, H.-L.; Zhang, A.-H.; Xu, X.-Q.; Meng, X.-P.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Li, Z.; Ding, S.-J.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Orientia tsutsugamushi in chiggers and ticks from domestic rodents in Shandong, northern China. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaoka, M.; Asanuma, K.; Okubo, K.; Tanigughi, H.; Tsuboi, M.; Hattori, K. Seasonal occurrence of trombiculid mites species and Leptotrombidium kawamurai (Acariña, Trombiculidae) as a carrier of Rickettsia orientalis in the Nopporo area, Hokkaido, Japan. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1973, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Sun, H.; Peng, Z.; Miao, Z.; Meng, X. Epidemiological study of autumn-winter type scrub typhus in a new endemic focus of Fei County, Shandong Province, China. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2000, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Q.; Peng, Z.; Miao, Z.; Meng, X. First isolation of Orientia (O.) tsutsugamushi from larvae and reared nymphs of Leptotrombidium (L.) linhuaikongense collected from wild rodents in Fei County, Shandong Province, China. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2002, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun-xi, L.; Zhong-tang, Z.; Yuan, G.; Chong-qi, J.; Jing-lan, Z.; Zhan-qing, Y.; Shu-mei, W.; Bao-fa, J. Characterization of Orientia tsutsugamushi strains isolated in Shandong Province, China by immunofluorescence and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analyses. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2004, 35, 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-X.; Jia, N.; Xing, Y.-B.; Suo, J.-J.; Du, M.-M.; Jia, N.; Gao, Y.; Xie, L.-J.; Liu, B.-W.; Ren, S.-W. Consistency of the key genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi in scrub typhus patients, rodents, and chiggers from a new endemic focus of Northern China. Cell Biophys. 2013, 67, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, N.I.; Mirolvubova, L.V.; Tarasevich, I.V.; Plotnikova, L.F.; Egorova, A.D. Natural infection of Trombiculid mites with the rickettsiae of tsutsugamushi disease in the Maritime Province. Meditsinskaya Parazitol. Parazit. Bolezn. 1968, 37, 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- Ree, H.I.; Chang, W.H.; Kee, S.; Lee, I.Y.; Jeon, S.H. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi DNA in individual trombiculids using polymerase chain reaction in Korea. Med. Èntomol. Zool. 1997, 48, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasevich, I.V.; Kulagin, S.M.; Kudryashova, N.I.; Gopachenko, I.M.; Somov, G.P. A natural focus of tsutsugamushi disease. Zh. Mikrobiol. 1964, 5, 19–23. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kawamori, F.; Akiyama, M.; Sugieda, M.; Kanda, T.; Akahane, S.; Uchikawa, K.; Yamada, Y.; Kumada, N.; Furuya, Y.; Yoshida, Y. Epidemiology of Tsutsugamushi disease in relation to the serotypes of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi isolated from patients, field mice, and unfed chiggers on the eastern slope of Mount Fuji, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2842–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Murata, M.; Machida, K.; Hori, E.; Kawamura, A., Jr.; Tanaka, H. Aggregated distribution of infective spots composed of Leptotrombidium pallidum, highly prevalent with Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, demonstrated by sentinel voles, Microtus montebelli, on the ground. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 60, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tarasevich, I.V.; Kulagin, S.M.; Kudryashova, N.I.; Gopachenko, I.M.; Somov, G.P. Natural focus of tsutsugamushi fever. Army Biol. Labs Frederick Md. 1965. translation no. 1399. [Google Scholar]
- Asanuma, K.; Kitaoka, M.; Okubo, K.; Kumada, N.; Suzuki, M.; Karasawa, T.; Kugoh, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawamura, A.J.; Miyamoto, T.; et al. Evidences for Trombicula scutellaris to be a vector of scrub typhus in Chiba Prefecture, Japan. Med Èntomol. Zool. 1959, 10, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Asanuma, K.; Okubo, K.; Kumada, N.; Kitaoka, M. Determination of the vector mites of scrub typhus in Japan. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1962, 15, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.; Xue, Z.; Ma, D.; Sun, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, C.; Qin, X.; et al. Detection of a novel rickettsia from Leptotrombidium scutellare Mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) from Shandong of China. J. Med Èntomol. 2017, 54, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Lee, P.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, H.-C. Surveillance of potential hosts and vectors of scrub typhus in Taiwan. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ree, H.I.; Lee, I.Y.; Cho, M.K. Study on vector mites of tsutsugamushi disease in Cheju Island, Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 1992, 30, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Hwang, K.K. Distribution of chigger mites and Orientia tsutsugamushi in Seogwipo city at 2017. J. Prevtive Vet. Medicine. 2018, 42, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadchatram, M.; Dohany, A.L. Leptotrombidium (Leptotrombidium) umbricola, new species, a probable vector of scrub typhus in peninsular Malaysia. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1980, 33, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohany, A.L.; Shirai, A.; Lim, B.L.; Huxsoll, D.L. Variation in populations of chigger vectors of scrub typhus in developing oil palm areas of different ages. Jpn. J. Med Sci. Biol. 1980, 33, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Wen, T.; Yang, Z.; Wu, C. Description of Leptotrombidium (Leptotrombidium) wenense sp. n. (Acariformes: Trombiculidae). Entomotaxonomia 1982, 4, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Masakhwe, C.; Linsuwanon, P.; Kimita, G.; Mutai, B.; Leepitakrat, S.; Yalwala, S.; Abuom, D.; Auysawasi, N.; Gilbreath, T.; Wanja, E.; et al. Identification and characterization of Orientia chuto in trombiculid chigger mites collected from wild rodents in Kenya. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01124-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lledó, L.; Giménez-Pardo, C.; Domínguez-Peñafiel, G.; Sousa, R.; Gegúndez, M.I.; Casado, N.; Criado, A. Molecular detection of Hemoprotozoa and Rickettsia species in arthropods collected from wild animals in the Burgos Province, Spain. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Soto, P.; Pérez-Sánchez, R.; Encinas-Grandes, A. Molecular detection of Ehrlichia phagocytophila genogroup organisms in larvae of Neotrombicula autumnalis (Acari: Trombiculidae) captured in Spain. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1482–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Kampen, H.; Schöler, A.; Metzen, M.; Oehme, R.; Hartelt, K.; Kimmig, P.; Maier, W.A. Neotrombicula autumnalis (Acari, Trombiculidae) as a vector for Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato? Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2004, 33, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Literak, I.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Sychra, O.; Dubska, L.; Taragelova, V. Larvae of chigger mites Neotrombicula spp. (Acari: Trombiculidae) exhibited Borrelia but no Anaplasma infections: A field study including birds from the Czech Carpathians as hosts of chiggers. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2008, 44, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vysotskaya, S.O.; Schluger, E.G. Licinki krasnotelok-parazity gryzunov Leningradskoj oblasti. Parazitol. Sb. 1953, 15, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Ravindran Santhakumari Manoj, R.; Latrofa, M.S.; Iatta, R.; Annoscia, G.; Lovreglio, P.; Stufano, A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Davoust, B.; Laidoudi, Y.; et al. Role of reptiles and associated arthropods in the epidemiology of rickettsioses: A one health paradigm. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez, P.; Palomar, A.M.; Santibáñez, S.P.A. Chiggers(Acari: Trombiculidae) infected with Rickettsiae in Spain: Preliminary data. In Proceedings of the 6th International Meeting on Rickettsiae and Rickettsial Diseases, Heraklion, Greece, 5–7 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shubin, F.N.; Natsky, K.V.; Somov, G.P. Concerning the vector of tsutsugamushi fever in the Far East. Zhurnal Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. 1970, 9, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Somov, J.P.; Shubin, F.N.; Gopachenko, I.M. Major result of studying Tsutsugamushi fever in Soviet Far East. Folia Microbiol. 1976, 21, 508. [Google Scholar]
- Tilak, R.; Wankhade, U.B.; Kunwar, R.; Tilak, V. Emergence of Schoengastiella ligula as the vector of scrub typhus outbreak in Darjeeling: Has Leptotrombidium deliense been replaced? Indian J. Public Health 2011, 55, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.C.; Chung, C.L.; Lin, T.H.; Wang, C.H.; Wu, W.J. Studies on the vectors and pathogens of scrub typhus on murine-like animals in Kinmen County, Taiwan. Formosa Entomol. 2004, 24, 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Takhampunya, R.; Korkusol, A.; Pongpichit, C.; Yodin, K.; Rungrojn, A.; Chanarat, N.; Promsathaporn, S.; Monkanna, T.; Thaloengsok, S.; Tippayachai, B.; et al. Metagenomic approach to characterizing disease epidemiology in a disease-endemic environment in Northern Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, S. The Vector Biology and Microbiome of Parasitic Mites and Other Ectoparasites of Rodents; The University of Liverpool: Liverpool, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, S.Q.; Alagaili, A.N.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; McGarry, J.W.; Darby, A.C.; Makepeace, B.L. The vector biology of ectoparasites on rodents from the ‘Asir Region of Saudi Arabia. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 113, S100. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Lee, E.-M.; Park, J.-M.; Lee, K.-M.; Han, S.-H.; Kim, J.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Song, H.-J.; Choi, M.-S.; Kim, I.-S.; et al. Molecular detection of various Rickettsiae in mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) in Southern Jeolla Province, Korea. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 51, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Takahashi, M.; Misumi, H.; Deguchi, T.; Watanuki, Y. Notes on trombiculid mites from Teuri Island in northwestern Hokkaido, Japan. Med. Entomol. Zool. 2012, 63, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Deng, X.-Z.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Yao, P.-P.; Zhu, H.-P.; Xiong, H.-R.; Li, C.-L.; Zhang, Y. Study on the transmission of Hantaan virus and Orientia tsutsugamushi by naturally dual infected Leptotrombidium scutellare through stinging. Chinese J. Prev. Med. 2010, 44, 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tao, K.; Wu, G.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xing, A. Proliferation and location of Hantaan virus in gamasid mites and chigger mites, a molecular biological study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002, 82, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, T.S.; Chu, Y.C.; Kim, Y.B.; Lim, B.U.; Kang, J.S. Pathologic study of mice infected with Rickettsia tsutsugamushi R19 strain. J. Korean Med. Sci. 1993, 8, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundin, W.D.; Liu, C.; Harmon, P.; Rodina, P. Pathogenesis of scrub typhus infection (Rickettsia tsutsugamushi) as studied by immunofluorescence. J. Immunol. 1964, 93, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paddock, C.D.; Finley, R.W.; Wright, C.S.; Robinson, H.N.; Schrodt, B.J.; Lane, C.C.; Ekenna, O.; Blass, M.A.; Tamminga, C.L.; Ohl, C.A.; et al. Rickettsia parkeri Rickettsiosis and its clinical distinction from rocky mountain spotted fever. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szakacs, A.T.; Wood, H.; Russell, C.B.; Nelder, M.P.; Patel, S.N. An apparent, locally acquired case of rickettsial pox (Rickettsia akari) in Ontario, Canada. Off. J. Assoc. Med. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Can. 2020, 5, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Breier, F.; Khanakah, G.; Stanek, G.; Kunz, G.; Aberer, E.; Schmidt, B.; Tappeiner, G. Isolation and polymerase chain reaction typing of Borrelia afzelii from a skin lesion in a seronegative patient with generalized ulcerating bullous lichen sclerosus et atrophicus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2001, 144, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.M.; Houwers, D.J.; Jongejan, F.; Van Der Kolk, J.H. Borrelia burgdorferi infections with special reference to horses. A review. Veter. Q. 2005, 27, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, D.M.; Feng, S.; Hodzic, E.; Barthold, S.W. Dynamics of connective-tissue localization during chronic Borrelia burgdorferi infection. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatrov, A.B.; Takahashi, M.; Noda, S.; Misumi, H. Stylostome organization in feeding Leptotrombidium larvae (Acariformes: Trombiculidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 64, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hase, T.; Roberts, L.W.; Hildebrandt, P.K.; Cavanaugh, D.C. Stylostome formation by Leptotrombidium mites (Acari: Trombiculidae). J. Parasitol. 1978, 64, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christova, I.; Gladnishka, T. Prevalence of infection with Francisella tularensis, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in rodents from an endemic focus of tularemia in Bulgaria. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2005, 12, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Durnez, L.; Eddyani, M.; Mgode, G.F.; Katakweba, A.; Katholi, C.R.; Machang’U, R.R.; Kazwala, R.R.; Portaels, F.; Leirs, H. First detection of mycobacteria in African rodents and insectivores, using stratified pool screening. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjeer, T.; Patyal, A.; Shakya, S.; Parkar, S.S.; Shukla, A.; Chandrakar, C.; Naik, V. Rodent borne zoonoses: A brief review. Pharma Innov. 2021, 10, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, N.; Muto, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Baba, Y.; Kudo, M.; Tamae, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Takatori, I.; Iwakiri, A.; Ishikawa, K.; et al. Investigation of reservoir animals of Leptospira in the northern part of Miyazaki Prefecture. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Putz, E.J.; Nally, J.E. Investigating the immunological and biological equilibrium of reservoir hosts and pathogenic Leptospira: Balancing the solution to an acute problem? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, B. Pathogenesis of leptospirosis: Cellular and molecular aspects. Veter- Microbiol. 2014, 172, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosma, C.L.; Sherman, D.R.; Ramakrishnan, L. The secret lives of the pathogenic mycobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 641–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehio, C. Bartonella interactions with endothelial cells and erythrocytes. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, M.; Mühldorfer, K.; Tortosa, P.; Markotter, W. Leptospira and bats: Story of an emerging friendship. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöstedt, A. Tularemia: History, epidemiology, pathogen physiology, and clinical manifestations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1105, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Luo, Z.-Q. Legionella and Coxiella effectors: Strength in diversity and activity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 15, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekolnikov, A.A.; Tretyakov, K.A. The first record of a chigger mite of the genus Neotrombicula (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) in the Northwest of European Russia. Èntomol. Rev. 2018, 98, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Yamamoto, N.; Koyama, S.; Makisaka, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Urabe, K.I.; Takaoka, M.; Nakazawa, K.; Urakami, H.; Fukuhara, M. Epidemiological survey of Orientia tsutsugamushi distribution in field rodents in Saitama Prefecture, Japan, and discovery of a new type. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 45, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatrov, A.B. Some peculiarities of the life cycle and biology of chiggers in laboratory. Entomol. Rev. 1996, 76, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Jacinavicius, F.C.; Bassini-Silva, R.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Hingst-Zaher, E.; Ochoa, R.; Bauchan, G.R.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. A contribution to the knowledge of Quadraseta brasiliensis Goff and Gettinger, 1989 (Trombidiformes: Trombiculidae), with description of the deutonymph instar. Acarologia 2018, 58, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniuszko, H.; Felska, M.; Mąkol, J. Evidence for co-invasion events: Different chigger species (Actinotrichida, Trombidioidea: Trombiculidae) share a host. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 76, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajkowska, P.; Mąkol, J. Parasitism, seasonality, and diversity of trombiculid mites (Trombidiformes: Parasitengona, Trombiculidae) infesting bats (Chiroptera) in Poland. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 86, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, T.; Aylwin, M.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Abarca, K. Scrub typhus in Tierra del Fuego: A tropical rickettsiosis in a subantarctic region. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 27, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, G.; Carleton, M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference; Wilson, D.E., Reeder, D.M., Eds.; JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2018-2. 2019. Available online: http://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 11 July 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).