General Characteristics of Children with Single- and Co-Infections and Febrile Seizures with a Main Focus on Respiratory Pathogens: Preliminary Results
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General Patient Characteristics
2.2. Distribution of Respiratory Viruses in Patients with Febrile Seizures
2.3. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics in Patients with Viral Single, Co-Infections, and Virus Negative Patients
2.4. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of the Four Most Frequently Detected Pathogens with Febrile Seizures
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population and Data Acquisition
4.2. Analysis of Nasopharyngeal Aspirates
4.3. Statistics
4.4. Ethical Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| All | Male | Female | |
| Total number | 184 | 106 | 78 |
| Disease symptoms before seizure | 119 | 71 (67%) | 48 (62%) |
| Type of seizure | |||
| Simple | 151 | 80 (75%) | 71 (91%) |
| Complex | 33 | 26 (25%) * | 7 (9%) |
| p = 0.0041 |

| HHV6 | Influenza A | AV | RV | HBoV | CoV | RSV | hPIV | S. typhimurium | |
| HHV6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Influenza A | 1 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AV | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| RV | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| HBoV | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| CoV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| RSV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| hPIV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. typhimurium | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
References
- Leung, A.K.; Hon, K.L.; Leung, T.N. Febrile seizures: An overview. Drugs Context 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zeijl, J.H.; Mullaart, R.A.; Galama, J.M.D. The pathogenesis of febrile seizures: Is there a role for specific infections? Rev. Med. Virol. 2002, 12, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baymacova, M.; Plochev, K.; Dikov, I.; Popov, G.T.; Mihaylova-Garnizova, R.; Kovaleva, V.; Kundurdjiev, T. Fever of Unknown Origin in a Bulgarian Hospital: Evaluation of 54 Cases for a Four Year-Period. J. Clin. Anal. Med. 2015, 7, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chien, Y.-L.; Huang, F.-L.; Huang, C.-M.; Chen, P.-Y. Clinical approach to fever of unknown origin in children. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, A.M.; Clifford, H.; Ronnis, T. Fever of unknown origin: A retrospective review of pediatric patients from an urban, tertiary care center in Washington, DC. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijl, J.P.; Kwee, T.C.; Legger, G.E.; Peters, H.J.; Armbrust, W.; Schölvinck, E.H.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M. Role of FDG-PET/CT in children with fever of unknown origin. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantala, H.; Uhari, M.; Tuokko, H. Viral infections and recurrences of febrile convulsions. J. Pediatr. 1990, 116, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millichap, J.G.; Millichap, J.J. Role of Viral Infections in the Etiology of Febrile Seizures. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006, 35, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, N.M.; Yi, D.Y.; Yun, S.W.; Lim, I.S.; Chae, S.A. Seasonal distribution of febrile seizure and the relationship with respiratory and enteric viruses in Korean children based on nationwide registry data. Seizure 2019, 73, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyar, A.; Ayazi, P.; Fallahi, M.; Javadi, A. Risk factors of the first febrile seizures in Iranian children. Int. J. Pediatr. 2010, 2010, 862897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpisheh, A.; Veisani, Y.; Sayehmiri, K.; Fayyazi, A. Febrile seizures: Etiology, prevalence, and geographical variation. Iran. J. Child. Neurol. 2014, 8, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, B.; Wong, V. Relationship between five common viruses and febrile seizure in children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.Y.; Han, S.B. Febrile Seizures and Respiratory Viruses Determined by Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Test and Clinical Diagnosis. Children 2020, 7, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agut, H.; Bonnafous, P.; Gautheret-Dejean, A. Laboratory and clinical aspects of human herpesvirus 6 infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, A.; Adams, O.; Willems, R.; Bonzel, L.; Neuhausen, N.; Schweizer-Krantz, S.; Ruggeberg, J.U.; Willers, R.; Henrich, B.; Schroten, H.; et al. Correlation of viral load of respiratory pathogens and co-infections with disease severity in children hospitalized for lower respiratory tract infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.R.; Wieringa, J.; Koekkoek, S.M.; Visser, C.E.; Pajkrt, D.; Molenkamp, R.; de Jong, M.D.; Schinkel, J. Frequent Detection of Respiratory Viruses without Symptoms: Toward Defining Clinically Relevant Cutoff Values. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2631–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerna, G.; Piralla, A.; Rovida, F.; Rognoni, V.; Marchi, A.; Locatelli, F.; Meloni, F. Correlation of rhinovirus load in the respiratory tract and clinical symptoms in hospitalized immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Yu, X.; Wang, C.; Teng, Z.; Wang, C.; Shen, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; et al. High human bocavirus viral load is associated with disease severity in children under five years of age. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosis, S.; Esposito, S.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Tremolati, E.; Begliatti, E.; Tagliabue, C.; Corti, F.; Principi, N.; Niesters, H.G.M. Association between high nasopharyngeal viral load and disease severity in children with human metapneumovirus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.T.; Kuypers, J.; Heugel, J.; Englund, J.A. Clinical disease and viral load in children infected with respiratory syncytial virus or human metapneumovirus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 62, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.T.; Kuypers, J.; Wald, A.; Englund, J.A. Multiple versus single virus respiratory infections: Viral load and clinical disease severity in hospitalized children. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2012, 6, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.R.; Richmond, P.; Robins, C.; Lindsay, K.; Levy, A.; Effler, P.V.; Borland, M.; Blyth, C.C. An observational study of febrile seizures:the importance of viral infection and immunization. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolini, L.; Theodore, W.H.; Jacobson, S.; Gaillard, W.D. Epilepsy Research. Epilepsy Res. 2019, 153, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliassen, E.B.S.; Hemond, C.C.; Santoro, J.D. HHV-6-Associated Neurological Disease in Children: Epidemiologic, Clinical, Diagnostic, and Treatment Considerations. Pediatr. Neurol. 2020, 105, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.B.; Long, C.E.; Schnabel, K.C.; Caserta, M.T.; McIntyre, K.M.; Constanzo, M.A. Human Herpesvirus-6 infection in children A prospective study of complications and reactivation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laina, I.; Syriopoulou, V.P.; Daikos, G.L.; Roma, E.S.; Papageorgiou, F.; Kakourou, T.; Theodoridou, M. Febrile Seizures and Primary Human Herpesvirus 6 Infection. Pediatr. Neurol. 2010, 42, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, L. Detection of HHV-6 and EBV and Cytokine Levels in Saliva from Children with Seizures: Results of a Multi-Center Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Neurol. 2018, 5, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Influenza, A. Bericht zur Epidemiologie der Influenza in Deutschland Saison 2015/16. 2016; pp. 1–109. Available online: https://influenza.rki.de/saisonberichte/2015.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Influenza, A. Bericht zur Epidemiologie der Influenza in Deutschland Saison 2014/15. 2015; pp. 1–116. Available online: https://influenza.rki.de/saisonberichte/2014.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Fraaij, P.L.A.; Heikkinen, T. Seasonal influenza: The burden of disease in children. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7524–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.D.; Campbell, A.P. Pediatric influenza and illness severity: What is known and what questions remain? Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, K.L.; Lam, S.Y.; Que, T.L.; Wong, S.N. Influenza A and Febrile Seizures in Childhood. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006, 35, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Sun, Y. Routine blood parameters are helpful for early identification of influenza infection in children. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Huang, S.-L.; Chen, S.-P.; Huang, Y.-L.; Huang, C.-G.; Tsao, K.-C.; Lin, T.-Y. Journal of Clinical Virology. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, K.L.; Richardson, S.E.; MacGregor, D.; Mahant, S.; Raghuram, K.; MSc, A.B.M. Adenovirus-Associated Central Nervous System Disease in Children. J. Pediatr. 2019, 205, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.R.; Yang, S.L.; Gong, Y.N.; Kuo, C.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Chen, C.J.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Kuo, C.Y.; Fang, C.W.; Tsao, K.C.; et al. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonzel, L.; Tenenbaum, T.; Schroten, H.; Schildgen, O.; Schweitzer-Krantz, S.; Adams, O. Frequent Detection of Viral Coinfection in Children Hospitalized With Acute Respiratory Tract Infection Using a Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.; Adams, O.; Weiss, C.; Merz, U.; Schroten, H.; Tenenbaum, T. Clinical Characteristics of Children with Viral Single- and Co-Infections and a Petechial Rash. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 32, e186–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
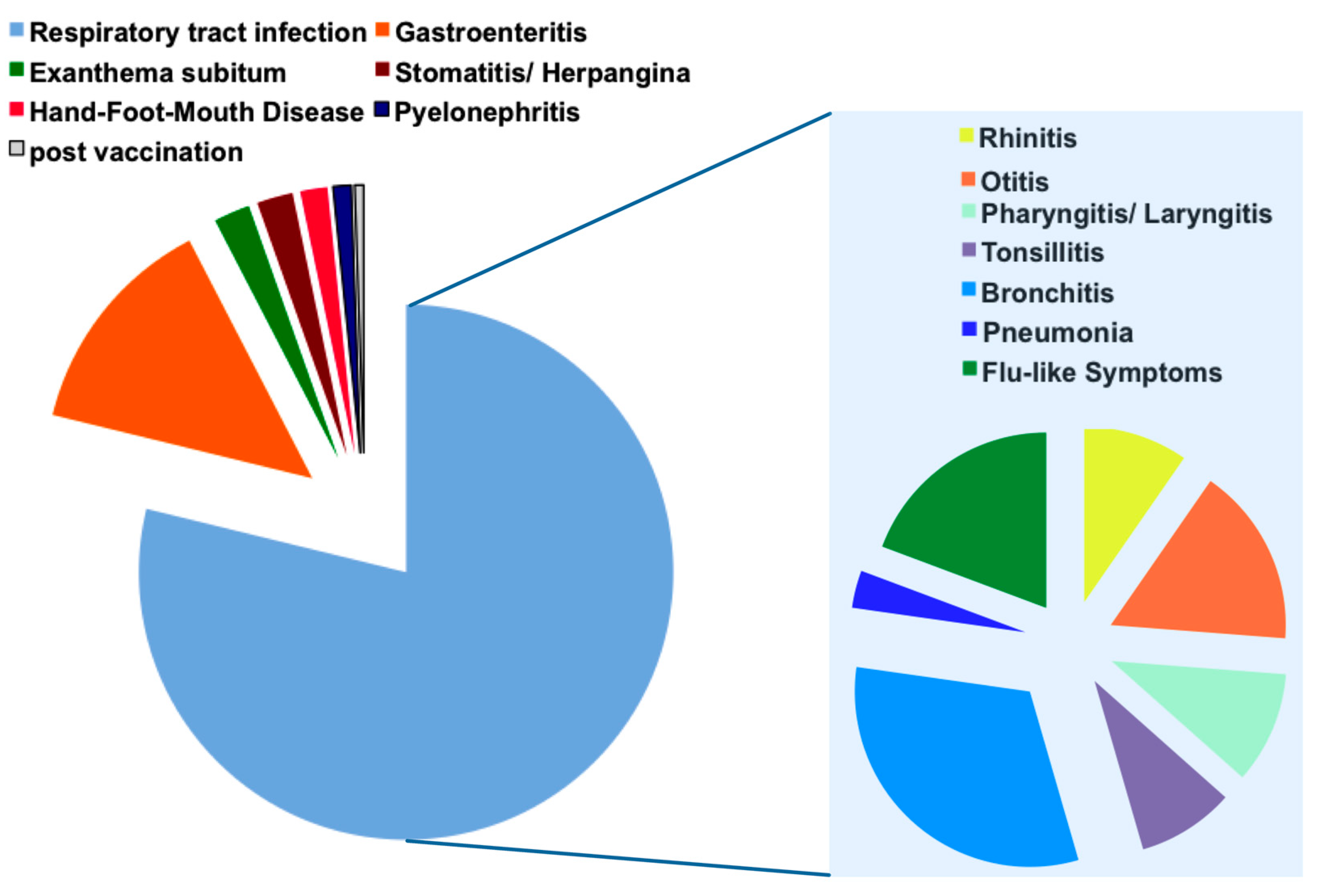
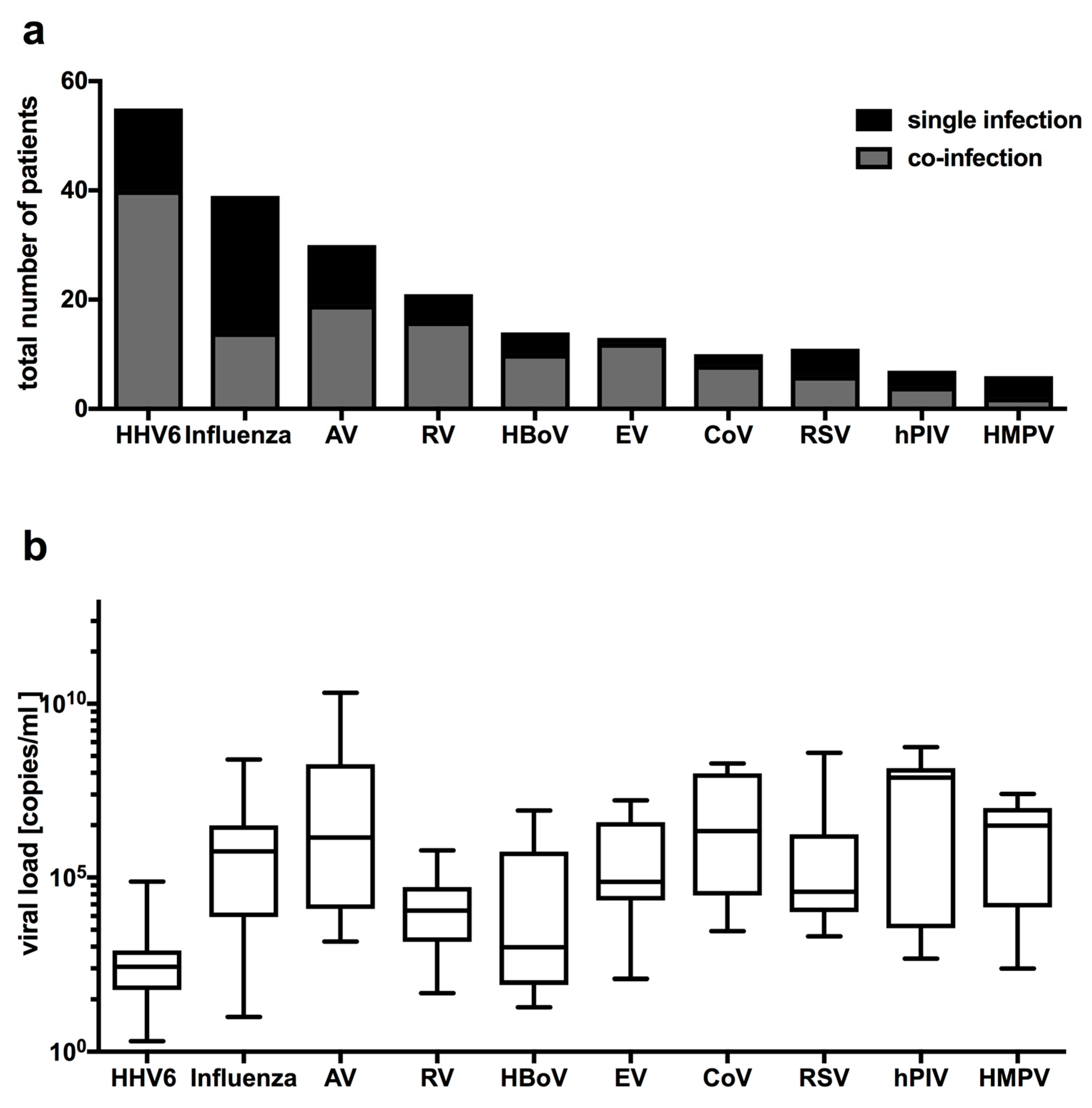
| No Pathogen | Single Infection | Co-Infection | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total number | 46 | 79 | 59 | |
| Age (months) | 30.9 ± 18.4 | 29.3 ± 20.0 | 26.2 ± 15.8 | 0.3150 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 25 (54%) | 48 (61%) | 33 (56%) | 0.5688 |
| Female | 21 (46%) | 31 (39%) | 26 (44%) | |
| Fever before seizure | 41 (89%) | 68 (86%) | 56 (95%) | 0.0889 |
| Temperature during seizure | 39.1 ± 0.9 °C | 38.9 ± 1.1 °C | 39.2 ± 0.9 °C | 0.0734 |
| Type of seizure | ||||
| Focal | 2 (4%) | 2 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 0.5069 |
| Generalized | 44 (96%) | 76 (97%) | 60 (100%) | |
| Simple | 37 (80%) | 65 (82%) | 49 (83%) | 0.9057 |
| Complex | 9 (20%) | 14 (18%) | 10 (17%) | |
| Cyanosis | 14 (30%) | 20 (25%) | 13 (22%) | 0.6547 |
| Hospital admission | 46 (100%) | 75 (95%) | 57 (97%) | 1.0000 |
| Benzo-diazepine use | 7 (15%) | 10 (13%) | 18 (31%) | 0.0099 |
| Family history | ||||
| Febrile seizures | 12 (26%) | 15 (19%) | 18 (31%) | 0.1165 |
| Epilepsy | 4 (9%) | 14 (18%) | 4 (7%) | 0.0590 |
| Personal history | ||||
| Febrile seizures | 4 (9%) | 5 (6%) | 8 (14%) | 0.1503 |
| Epilepsy | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (2%) | 0.4275 |
| No Pathogen | HHV6 Single | HHV6 Co | p-Value | Influenza Single | Influenza Co | p-Value | AV Single | AV Co | p-Value | RV Single | RV co | p-Value | |
| Total patient number | 46 | 15 | 40 | 25 | 14 | 11 | 19 | 5 | 16 | ||||
| Age (months) | 30.9 ± 18.4 | 18.1 ± 4.8 | 26.7 ± 17.5 | 0.0382 | 42.4 ± 26.1 | 32.0 ± 24.1 | 0.1021 | 27.5 ± 12.5 | 25.5 ± 12.1 | 0.4551 | 19.6 ± 7.6 | 25.9 ± 10.1 | 0.2468 |
| Complex seizure | 9 (20%) | 1 (7%) | 7 (18%) | 0.5052 | 5 (20%) | 2 (14%) | 0.0677 | 4 (36%) | 4 (21%) | 0.4928 | 2 (40%) | 1 (6%) | 0.1578 |
| Benzo-diazepine use | 8 (17%) | 1 (7%) | 11 (28%) | 0.1485 | 1 (4%) | 4 (29%) | 0.0949 | 2 (18%) | 6 (32%) | 0.3503 | 1 (20%) | 6 (37%) | 0.1746 |
| Positive family history FS | 12 (26%) | 1 (7%) | 15 (38%) | 0.0612 | 4 (16%) | 2 (14%) | 0.4809 | 6 (55%) | 3 (16%) | 0.0682 | 0 (0%) | 6 (37%) | 0.3540 |
| Positive personal history FS | 4 (9%) | 1 (7%) | 4 (10%) | 1.0000 | 0 (0%) | 1 (7%) | 0.2979 | 0 (0%) | 5 (26%) | 0.0695 | 0 (0%) | 4 (25%) | 0.2676 |
| Leukocytes (µL) | 10.4 (7.1–12.4) | 11.9 (9.7–13.6) | 10.0 (9.2–14.9) | 0.3821 | 7.7 (4.5–11.0) | 10.0 (8.4–13.7) | 0.0273 | 15.4 (13.8–17.8) | 12.0 (10.0–16.2) | 0.0021 | 11.0 (9.2–15.7) | 9.6 (8.0–12.7) | 0.8101 |
| Monocytes (%) * | 7.8 (4.4–10.0) | 8.0 (5.0–10.0) | 7.0 (4.0–9.7) | 0.9766 | 10.7 (9.1–13.4) | 6.7 (2.5–9.4) | 0.0304 | 5.3 (1.5–9.2) | 12.0 (6.0–12.4) | 0.3547 | - | 9.0 (4.0–12.4) | 0.6202 |
| CrP (at admission) (mg/L) | 10.8 (7.0–17.8) | 15.5 (7.2–22.4) | 12.8 (7.4–23.8) | 0.6350 | 9.6 (5.9–16.5) | 12.8 (4.8–21.3) | 0.7153 | 20.4 (15.9–50.0) | 16.4 (12.1–29.8) | 0.0067 | 11.9 | 15.3 (9.3–45.5) | 0.3719 |
| CrP (max.) (mg/L) | 11.3 (6.8–20.4) | 18.0 (8.2–46.0) | 18.0 (8.2–46.0) | 0.4220 | 9.6 (5.9–16.4) | 12.8 (4.8- 21.3) | 0.7378 | 27.1 (16.8–72.4) | 19.3 (12.1–49.4) | 0.0021 | 11.9 | 19.3 (8.9- 62.3) | 0.5137 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudolph, H.; Gress, K.; Weiss, C.; Schroten, H.; Adams, O.; Tenenbaum, T. General Characteristics of Children with Single- and Co-Infections and Febrile Seizures with a Main Focus on Respiratory Pathogens: Preliminary Results. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081061
Rudolph H, Gress K, Weiss C, Schroten H, Adams O, Tenenbaum T. General Characteristics of Children with Single- and Co-Infections and Febrile Seizures with a Main Focus on Respiratory Pathogens: Preliminary Results. Pathogens. 2021; 10(8):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081061
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudolph, Henriette, Katharina Gress, Christel Weiss, Horst Schroten, Ortwin Adams, and Tobias Tenenbaum. 2021. "General Characteristics of Children with Single- and Co-Infections and Febrile Seizures with a Main Focus on Respiratory Pathogens: Preliminary Results" Pathogens 10, no. 8: 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081061
APA StyleRudolph, H., Gress, K., Weiss, C., Schroten, H., Adams, O., & Tenenbaum, T. (2021). General Characteristics of Children with Single- and Co-Infections and Febrile Seizures with a Main Focus on Respiratory Pathogens: Preliminary Results. Pathogens, 10(8), 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081061







